Java 集合 Collection、List、Set
一. Collection 单列集合
1. Collection代表单列集合,每个元素(数据)只包含一个值

2. Collection集合特点
① List系列集合:添加的元素是有序、可重复、有索引。
ArrayList、LinekdList:有序、可重复,有索引
② Set系列集合:添加的元素是无序、不重复、无索引
HashSet:无序、不重复、无索引
LinkedHashSet:有序、不重复、无索引
TreeSet:按照大小默认升序排序、不重复、无索引
3. Collection 集合的常用方法
Collection 是所有单列集合的父类,他规定的方法是全部单列集合都会继承(包括List<E>集合 和 Set<E> 集合)
| 常用方法 | 说明 |
| boolean add(E e) | 添加元素,成功返回true |
| addAll() | 把集合的全部元素移动到另一个集合中 |
| void clear() | 清空集合中的元素 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 是则返回true |
| int size() | 获取集合的大小 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断集合是否包含某个元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除某个元素,如果有多个默认删除第一个 |
| Object[] toArray() | 将集合转换成数组 |
public static void main(String[] args) {Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();//boolean add(E e) 添加元素,成功返回true 因为可重复 所以一定会返回truec.add("卡莎");c.add("泰坦");c.add("洛");System.out.println(c);//[卡莎, 泰坦, 洛]//void clear() 清空集合中的元素c.clear();System.out.println(c);//[卡莎, 泰坦, 洛]//boolean isEmpty() 判断集合是否为空 是则返回trueSystem.out.println(c.isEmpty());//truec.add("卡莎");c.add("泰坦");c.add("洛");c.add("A");c.add("洛");System.out.println(c.isEmpty());//false//int size() 获取集合的大小System.out.println(c.size());//5//boolean contains(Object o) 判断集合是否包含某个元素System.out.println(c);//[卡莎, 泰坦, 洛, A, 洛]System.out.println(c.contains("a"));//falseSystem.out.println(c.contains("A"));//true//boolean remove(Object o) 删除某个元素,如果有多个默认删除第一个c.remove("洛");System.out.println(c);//[卡莎, 泰坦, A, 洛]//Object[] toArray() 将集合转换成数组Object[] object = c.toArray();System.out.println(Arrays.toString(object));//[卡莎, 泰坦, A, 洛]String[] strings = c.toArray(new String[c.size()]);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings));//[卡莎, 泰坦, A, 洛]//把集合的全部元素移动到另一个集合中Collection<String> c2 = new ArrayList<String>();c2.addAll(c);System.out.println(c2);//[卡莎, 泰坦, A, 洛]}4. Collection 集合的遍历方式
(1) 迭代器:迭代器是用来遍历集合的专用方式(数组没有迭代器),Java中最常用的迭代器是Iterator
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| Iterator<E> iterator() | 返回集合中的迭代器对象,该迭代器对象默认指向当前集合的第一个元素 |
| Boolean hasNext() | 询问当前位置是否有元素存在,存在返回true 不存在返回false |
| E next() | 获取当前位置的元素,并同时将迭代器对象指向下一个元素 |
public static void main(String[] args) {//iteratorCollection<String> c = new ArrayList();c.add("卡莎");c.add("泰坦");c.add("洛");//Iterator<E> iterator()返回集合中的迭代器对象,该迭代器对象默认指向当前集合的第一个元素Iterator<String> iterator = c.iterator();//Boolean hasNext() 询问当前位置是否有元素存在,存在返回true 不存在返回false//E next() 获取当前位置的元素,并同时将迭代器对象指向下一个元素/*System.out.println(iterator.next());//卡莎System.out.println(iterator.next());//泰坦System.out.println(iterator.next());//洛System.out.println(iterator.next());//NoSuchElementException 异常*/while (iterator.hasNext()) {String ele = iterator.next();System.out.println(ele);//卡莎 泰坦 洛}}(2) 增强for:既可以用来遍历集合,也可以用来遍历数组
格式:for(元素的数据类型 变量名 : 数组或集合){ }
本质上就是迭代器遍历集合的简化写法
public static void main(String[] args) {Collection<String> c = new ArrayList();c.add("卡莎");c.add("泰坦");c.add("洛");for (String s : c){System.out.println(s);//卡莎 泰坦 洛}String[] ss = {"飞机","奥恩"};for (String s : ss){System.out.println(s);//飞机 奥恩}
}(3) lambda表达式:JDK8 开始的Lambda表达式,提供了一种更简单、更直接的方式来遍历集合
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) 结合lambda遍历集合
public static void main(String[] args) {Collection<String> c = new ArrayList();c.add("卡莎");c.add("泰坦");c.add("洛");// default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) 结合lambda遍历集合c.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {@Overridepublic void accept(String s) {System.out.println(s);//卡莎 泰坦 洛}});c.forEach((String s) ->{System.out.println(s);//卡莎 泰坦 洛});c.forEach((s) ->System.out.println(s)//卡莎 泰坦 洛);c.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));//卡莎 泰坦 洛c.forEach(System.out::println);}5. List集合
(1) List集合支持索引,除了Collection的方法,多了很多与索引相关的方法。包括ArrayList集合和LinkedList集合
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
| void add(int index, E element) | 在此集合中的指定位置插入指定的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除指定索引处的元素,返回被删除的元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 修改指定索引出的元素,返回被修改的元素 |
| E get(int index) | 返回指定索引出的元素 |
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();list.add("卡莎");list.add("泰坦");list.add("泰坦");list.add("洛");System.out.println(list);//[卡莎, 泰坦, 泰坦, 洛]//void add(int index, E element) 在此集合中的指定位置插入指定的元素list.add(3, "霞");System.out.println(list);//[卡莎, 泰坦, 泰坦, 霞, 洛]//E remove(int index) 删除指定索引处的元素,返回被删除的元素System.out.println(list.remove(2));//泰坦System.out.println(list);//[卡莎, 泰坦, 霞, 洛]//E set(int index, E element) 修改指定索引出的元素,返回被修改的元素System.out.println(list.set(2, "伊泽"));//霞//E get(int index) 返回指定索引出的元素System.out.println(list.get(2));//伊泽
}(2) List集合的遍历方式
① for循环(因为List集合有索引)
② 迭代器
③ 增强for循环
④ Lambda表达式
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();list.add("卡莎");list.add("泰坦");list.add("泰坦");list.add("洛");//① for循环(因为List集合有索引)for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.println(list.get(i));}//② 迭代器Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {System.out.println(iterator.next());}//③ 增强for循环for (String string : list) {System.out.println(string);}//④ Lambda表达式list.forEach(System.out::println);
}6. ArrayList集合的底层原理
(1) ArrayList与LinekdList都是 有序、可重复、 有索引,但底层采用的数据结构不同,应用场景也不同。
(2) ArrayList的底层原理:基于数组实现的。利用无参构造器创建的集合,会在底层创建一个默认长度为0的数组;添加第一个元素时,底层会创建一个新的长度为10的数组;存满时,会扩容1.5倍;如果一次添加多个元素,1.5倍还放不下,则新创建数组的长度以实际为准;
① 查询速度快(根据索引查询数据快):查询数据通过地址值和索引定位,查询任意数据耗时相同
② 删除效率低:可能需要把后面很多的数据进行前移
③ 添加效率低:可能需要把后面很多的数据后移,再添加元素;或者可能需要进行数组的扩容
7. LinekdList集合的底层原理
(1) ArrayList的底层原理:基于双链表实现的;链表中的节点都是独立的对象,在内存中时不连续的,每一个节点包含数据值和下一个节点的地址。

(2) 特点:
① 查询慢,无论查询哪个数据都要从头开始找。
② 增删相对快,对首尾元素进行增删改查的速度是极快的。
(3) LinekdList新增了很多首尾操作的特有方法
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
| public void addFirst(E e) | 将指定的元素追加到列表的开头 |
| public void addLast(E e) | 将指定的元素追加到列表的末尾 |
| public E getFirst() | 返回第一个元素 |
| public E getLast() | 返回最后一个元素 |
| public E removeFirst() | 删除并返回第一个元素 |
| public E removeLast() | 删除并返回最后一个元素 |
public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();list.add("卡莎");list.add("泰坦");list.add("泰坦");list.add("洛");System.out.println(list);//[卡莎, 泰坦, 泰坦, 洛]//public void addFirst(E e) 将指定的元素追加到列表的开头list.addFirst("张飞");System.out.println(list);//[张飞, 卡莎, 泰坦, 泰坦, 洛]//public void addLast(E e) 将指定的元素追加到列表的末尾list.addLast("豆芽");System.out.println(list);//[张飞, 卡莎, 泰坦, 泰坦, 洛, 豆芽]//public E getFirst() 返回第一个元素System.out.println(list.getFirst());//张飞//public E getLast() 返回最后一个元素System.out.println(list.getLast());//豆芽//public E removeFirst() 删除并返回第一个元素System.out.println(list.removeFirst());//张飞//public E removeLast() 删除并返回最后一个元素System.out.println(list.removeLast());//豆芽
}8. Set集合
(1) 特点:添加的元素是无序(添加数据的顺序和获取数据出的数据顺序不一样)、不重复、无索引
(2) Set 要用到的常用方法,基本上就是Collection提供的,自己几乎没有新增的方法
9. HashSet集合
(1) 无序、不重复、无索引
底层原理:
(2) 哈希值:就是一个int类型的数值,Java中每一个对象都有一个哈希值。都可以通过Objectl类提供的hashCode方法获取对象的哈希值。public int hashCode()
① 同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值是相同的
② 不同的对象,他们的哈希值一般不相同,但也有可能会相同(哈希碰撞)
(3) HashSet 是基于哈希表实现的。哈希表是一种增删改查数据性能都较好的数据结构。JDK8之前哈希表=数组+链表;JDK8之后:数组+链表+红黑树
(4) DK8开始,当链表的长度超过8,且数组长度>=64时,自动将链表转成红黑树
(5) 如果希望Set集合认为2个内容一样的对象是重复的,必须重写对象的hashCode()和equals()方法
public class Student {private int id;private String name;private Double[] grades;public Student() {}public Student(int id, String name, Double[] grades) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.grades = grades;}// idea快捷键生成,类中右键选择Generate->equals() and hashCode()@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(id, name, Arrays.hashCode(grades));}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return id == student.id && Objects.equals(name, student.name) && Objects.equals(grades, student.grades);}}
10. LinkedHashSet集合
(1) 有序(添加元素的顺序和获取元素的顺序一样)、不重复、无索引
底层原理:
(2) 基于哈希表(数组、链表、红黑树)实现的;但是,他的每个元素都额外多了一个双链表的机制记录它前后元素的位置(更占内存)
11. TreeSet集合
(1) 按照大小默认升序排序、不重复、无索引
底层原理:
(2) 基于红黑树实现的排序
(3) 注意:
① 对于数值类型:Integer、Double,默认按照数值大小进行排序
② 对于字符串类型:默认按照字符的编号升序排序
③ 对于自定义类型(如Student)对象,TreeSet默认是无法直接排序的
④ 自定义排序规则:TreeSet集合存储自定义类型的对象时,必须指定排序规则(有两种):
规则1:让自定义类实现Comparable接口,重写里面的CompareTo()方法
规则2:通过调用TreeSet集合有参构造器,可以设置Comparator对象(比较器对象)--public TreeSet(Comparator<? Super E> comparator)
如果规则1和规则2同时使用,默认就近原则(规则2)
//方式1. Comparable:让该类对象实现Comparable(比较规则)接口,然后重写compareTo方法,自己制定比较规则
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{private String name;private int age;private double score;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age, double score) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.score = score;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public double getScore() {return score;}public void setScore(double score) {this.score = score;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", score=" + score +'}';}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {//左边对象 大于 右边对象 返回正整数//左边对象 小于 右边对象 返回负整数//左边对象 等于 右边对象 返回0//如按照成绩排序 默认升序/*if (this.score > o.score) {return 1;}else if (this.score < o.score) {return -1;}else {return 0;}*/return Double.compare(this.getScore(), o.getScore());//升序//降序的话://左边对象 大于 右边对象 返回负整数//左边对象 小于 右边对象 返回正整数//左边对象 等于 右边对象 返回0/* if (this.score > o.score) {return -1;}else if (this.score < o.score) {return 0;}else {return 0;}return Double.compare(o.getScore(), this.getScore());//降序*/}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {//HashSetSet<String> set = new HashSet();//无序 不重复 无索引set.add("1");set.add("2");set.add("3");set.add("4");set.add("1");set.add("5");set.add("2");System.out.println(set);////LinkedHashSetSet<String> set1 = new LinkedHashSet();//有序 不重复 无索引set1.add("3");set1.add("2");set1.add("1");set1.add("4");set1.add("5");System.out.println(set1);//TreeSetSet<String> set3 = new TreeSet();set3.add("3");set3.add("1");set3.add("2");set3.add("6");set3.add("5");System.out.println(set3);Set<Integer> set4 = new TreeSet();set4.add(1);set4.add(7);set4.add(5);set4.add(6);set4.add(2);set4.add(5);System.out.println(set4);//自定义对象TreeSetStudent student = new Student("卡莎", 18, 99);Student student1 = new Student("泰坦", 19, 93);Student student2 = new Student("伊泽", 16, 98);Student student3 = new Student("璐璐", 16, 98);Set<Student> set5 = new TreeSet();set5.add(student);set5.add(student1);set5.add(student2);set5.add(student3);//[Student{name='泰坦', age=19, score=93.0}, Student{name='伊泽', age=16, score=98.0}, Student{name='卡莎', age=18, score=99.0}]System.out.println(set5);//由于伊泽和璐璐 分数98相同 后一个不存了Set<Student> set6 = new TreeSet(new Comparator<Student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {return o1.getAge()- o2.getAge();}});set6.add(student);set6.add(student1);set6.add(student2);set6.add(student3);//[Student{name='伊泽', age=16, score=98.0}, Student{name='卡莎', age=18, score=99.0}, Student{name='泰坦', age=19, score=93.0}]System.out.println(set6);}二. 集合的并发修改异常问题
1. 集合的并发修改异常:使用迭代器遍历集合时,又同时在删除集合中的数据,程序就会出现并发修改异常
2. 由于增强for循环遍历集合就是迭代器遍历集合的简化写法,因此,使用增强for循环遍历集合,又在同时删除集合中的数据时,程序也会出现并发修改异常
3. 解决方法:
① 如果使用迭代器遍历集合,用迭代器自己的删除方法删除数据即可
② 如果能用for循环遍历时,可以倒着遍历并删除;或者从前往后遍历,删除元素后进行i--;
public static void main(String[] args) {//集合的并发修改异常问题ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();list.add("泰坦");list.add("卡莎");list.add("王莎");list.add("洛");list.add("伊泽");list.add("赵莎");list.add("璐璐");list.add("孙莎");System.out.println(list);//迭代器 ConcurrentModificationException异常Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();/*while (iterator.hasNext()) {String s = iterator.next();if (s.contains("莎")){list.remove(s);//ConcurrentModificationException}}*///解决方法iterator.remove();while (iterator.hasNext()) {String s = iterator.next();if (s.contains("莎")){iterator.remove();//删除迭代器当前遍历到的数据,每删除一个数据后,相当于i--}}System.out.println(list);ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<String>();list2.add("泰坦");list2.add("卡莎");list2.add("王莎");list2.add("洛");list2.add("伊泽");list2.add("赵莎");list2.add("璐璐");list2.add("孙莎");//for循环for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) {String s = list2.get(i);if (s.contains("莎")){list2.remove(i);}}//出现bug 没有删除完System.out.println(list2);//[泰坦, 王莎, 洛, 伊泽, 璐璐]//解决方法1 i--for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) {String s = list2.get(i);if (s.contains("莎")){list2.remove(i);i--;}}//解决方法2 倒着删for (int i = list2.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {String s = list2.get(i);if (s.contains("莎")){list2.remove(i);}}ArrayList<String> list3 = new ArrayList<String>();list3.add("泰坦");list3.add("卡莎");list3.add("王莎");list3.add("洛");list3.add("伊泽");list3.add("赵莎");list3.add("璐璐");list3.add("孙莎");//使用正确for循环遍历集合并删除数据,没有办法解决ConcurrentModificationException异常//ConcurrentModificationException异常for (String s : list3) {if (s.contains("莎")){list3.remove(s);}}//使用正确forEach循环遍历集合并删除数据 没有办法解决ConcurrentModificationException异常//ConcurrentModificationException异常list.forEach(name -> {if (name.contains("莎")){list3.remove(name);}});}相关文章:

Java 集合 Collection、List、Set
一. Collection 单列集合 1. Collection代表单列集合,每个元素(数据)只包含一个值 2. Collection集合特点 ① List系列集合:添加的元素是有序、可重复、有索引。 ArrayList、LinekdList:有序、可重复,有索引 ② Set系列集合&…...

报错:nginx [emerg] open() etcnginxnginx.conf failed (2 No such file or directory)
报错:nginx: [emerg] open() “/etc/nginx/nginx.conf” failed (2: No such file or directory) 背景:在创建nginx容器时,想把宿主机上的某一目录挂载到容器的/etc/nginx路径,报错"/etc/nginx/nginx.conf" failed (2:…...

基于AI的运维资源调度:效率与智能的双重提升
在现代运维场景中,随着系统复杂性和服务规模的不断增长,传统的资源调度方式已无法满足高效、动态和精准的需求。AI技术的引入为资源调度带来了新的解决方案,通过智能算法和数据驱动,实现了资源分配的自动化与优化。本文将详细探讨…...

自动化办公 | 根据成绩进行自动评级
今天我们将介绍一个常见的自动化办公需求:根据成绩自动评级。通过这篇文章,我们将介绍如何利用Python进行自动化办公,将表格中的成绩根据预定的规则进行评级,并生成一个新的带评级信息的表格。 需求背景 我们有一个表格…...

纯血鸿蒙ArkUI线性布局详解
线性布局说明 线性布局(LinearLayout)是开发中最常用的布局,通过线性容器Row和Column构建。线性布局是其他布局的基础,其子元素在线性方向上(水平方向和垂直方向)依次排列。线性布局的排列方向由所选容器组…...

小程序组件 —— 22 组件案例 - 轮播区域绘制
这一节我们实现轮播图最外层的盒子,也就是把轮播图的最外层搭好,先不给轮播图添加图片,因为图片属于新的组件,组件里面有一些知识点,需要单独分开讲; 回顾一下,在进行传统网页开发时࿰…...

如何判断一个学术论文是否具有真正的科研价值?ChatGPT如何提供帮助?
目录 1.创新性与学术贡献的超级加分✔ 2.科研过程中的各个环节—从0到1✔ 3.创新性与理论深度的完美结合✔ 4.论证与写作的清晰性✔ 5.数据整理和文献回顾——效率与精准并存✔ 6.创新性要求辅助✔ 总结 宝子们,学术论文写作的旅程是不是感觉像是走进了迷雾森…...

【置顶】测试学习笔记整理
一、测试开发体系介绍 1.软件测试概念 (1)【理论】软件测试基础概念:软件测试概念、作用、原则、对象,软件缺陷、测试用例 (2)【理论】软件开发流程扫盲:敏捷开发(XP、SCRUM&#…...

新浪微博Java开发面试题及参考答案
怎么判断两个链表是否相交?怎么优化? 判断两个链表是否相交可以采用多种方法。 一种方法是使用双指针。首先分别遍历两个链表,得到两个链表的长度。然后让长链表的指针先走两个链表长度差的步数。之后,同时移动两个链表的指针,每次比较两个指针是否指向相同的节点。如果指…...

【SQL Server】教材数据库(1)
1 利用sql建立教材数据库,并定义以下基本表: 学生(学号,年龄,性别,系名) 教材(编号,书名,出版社编号,价格) 订购(学号…...
Windows系统下载、部署Node.js与npm环境的方法
本文介绍在Windows电脑中,下载、安装并配置Node.js环境与npm包管理工具的方法。 Node.js是一个基于Chrome V8引擎的JavaScript运行时环境,其允许开发者使用JavaScript编写命令行工具和服务器端脚本。而npm(Node Package Manager)则…...

SQL 总结
SQL 总结 引言 SQL(Structured Query Language,结构化查询语言)是一种用于管理关系数据库管理系统(RDBMS)的标准编程语言。自1974年首次提出以来,SQL已成为数据库领域中不可或缺的一部分。它允许用户执行各种操作,如查询、更新、插入和删除数据库中的数据。本文旨在提…...

设计一个基于Spring Boot开发的电商网站,部署在阿里云上
系统架构设计,包含网络、部署架构等关键信息,要保证系统的高可用。设计中请明确指出使用的产品名称。 为了设计一个基于Spring Boot开发的电商网站系统架构,并确保其高可用性,以下是一个详细的系统架构设计方案,包含网…...

Java jni调用nnom rnn-denoise 降噪
介绍:https://github.com/majianjia/nnom/blob/master/examples/rnn-denoise/README_CN.md 默认提供了一个wav的例子 #include <stdint.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include <string.h>#include …...

C++软件设计模式之状态模式
在C设计模式中,状态模式(State Pattern)是一种行为设计模式,它允许对象在内部状态改变时改变其行为,使对象看起来似乎修改了其类。状态模式的主要动机、意图和适用场合如下: 动机 在面向对象的设计中&…...

Microsoft Visual Studio中的/MT, /MTd,/MD,/MDd分别是什么意思?
1. /MT,/MTd,/MD,/MDd的含义 /MT,/MTd,/MD,/MDd是 Microsoft Visual C 编译器的运行时库链接选项。它们决定了程序如何链接 C 运行时库(CRT)。具体含义如下: /MT&#x…...
谷粒商城项目125-spring整合high-level-client
新年快乐! 致2025年还在努力学习的你! 你已经很努力了,今晚就让自己好好休息一晚吧! 在后端中选用哪种elasticsearch客户端? elasticsearch可以通过9200或者9300端口进行操作 1)9300:TCP spring-data-elasticsearch:transport-…...

日期时间选择(设置禁用状态)
目录 1.element文档需要 2.禁用所有过去的时间 3.设置指定日期的禁用时间 <template><div class"block"><span class"demonstration">起始日期时刻为 12:00:00</span><el-date-pickerv-model"value1"type"dat…...

基于SpringBoot的题库管理系统的设计与实现(源码+SQL+LW+部署讲解)
文章目录 摘 要1. 第1章 选题背景及研究意义1.1 选题背景1.2 研究意义1.3 论文结构安排 2. 第2章 相关开发技术2.1 前端技术2.2 后端技术2.3 数据库技术 3. 第3章 可行性及需求分析3.1 可行性分析3.2 系统需求分析 4. 第4章 系统概要设计4.1 系统功能模块设计4.2 数据库设计 5.…...
)
钉钉h5微应用安卓报错error29 ios报错error3 加上报错52013,签名校验失败 (前端)
这两个都是应为 免登报错52013,签名校验失败 用户后端签名使用的url地址和前端访问地址需要严格一致,包括端口号。前端部分可以用alert显示出当前的location.href,后端部分请在签名的时候打印日志。 访问通过反向代理服务器、各种NAT等场景下…...
Spark 之 入门讲解详细版(1)
1、简介 1.1 Spark简介 Spark是加州大学伯克利分校AMP实验室(Algorithms, Machines, and People Lab)开发通用内存并行计算框架。Spark在2013年6月进入Apache成为孵化项目,8个月后成为Apache顶级项目,速度之快足见过人之处&…...

深入理解JavaScript设计模式之单例模式
目录 什么是单例模式为什么需要单例模式常见应用场景包括 单例模式实现透明单例模式实现不透明单例模式用代理实现单例模式javaScript中的单例模式使用命名空间使用闭包封装私有变量 惰性单例通用的惰性单例 结语 什么是单例模式 单例模式(Singleton Pattern&#…...

django filter 统计数量 按属性去重
在Django中,如果你想要根据某个属性对查询集进行去重并统计数量,你可以使用values()方法配合annotate()方法来实现。这里有两种常见的方法来完成这个需求: 方法1:使用annotate()和Count 假设你有一个模型Item,并且你想…...

反射获取方法和属性
Java反射获取方法 在Java中,反射(Reflection)是一种强大的机制,允许程序在运行时访问和操作类的内部属性和方法。通过反射,可以动态地创建对象、调用方法、改变属性值,这在很多Java框架中如Spring和Hiberna…...
)
是否存在路径(FIFOBB算法)
题目描述 一个具有 n 个顶点e条边的无向图,该图顶点的编号依次为0到n-1且不存在顶点与自身相连的边。请使用FIFOBB算法编写程序,确定是否存在从顶点 source到顶点 destination的路径。 输入 第一行两个整数,分别表示n 和 e 的值(1…...
)
安卓基础(aar)
重新设置java21的环境,临时设置 $env:JAVA_HOME "D:\Android Studio\jbr" 查看当前环境变量 JAVA_HOME 的值 echo $env:JAVA_HOME 构建ARR文件 ./gradlew :private-lib:assembleRelease 目录是这样的: MyApp/ ├── app/ …...
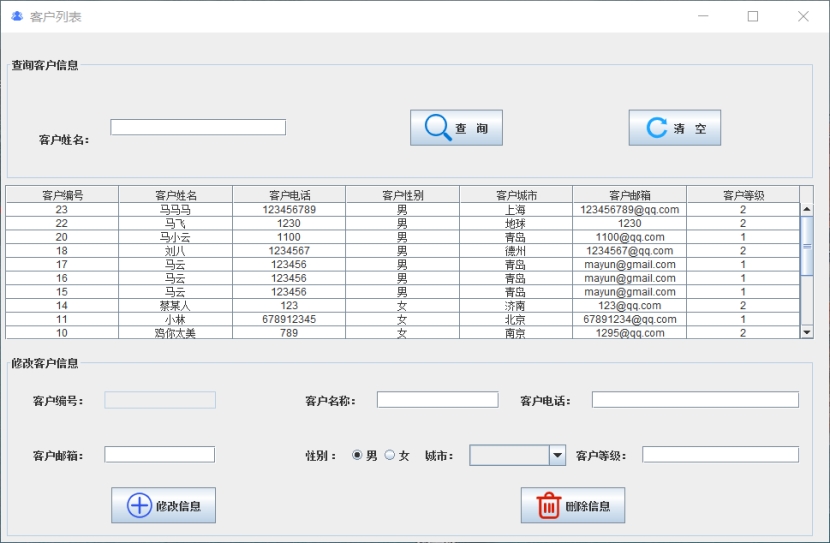
基于Java+MySQL实现(GUI)客户管理系统
客户资料管理系统的设计与实现 第一章 需求分析 1.1 需求总体介绍 本项目为了方便维护客户信息为了方便维护客户信息,对客户进行统一管理,可以把所有客户信息录入系统,进行维护和统计功能。可通过文件的方式保存相关录入数据,对…...
群晖NAS如何在虚拟机创建飞牛NAS
套件中心下载安装Virtual Machine Manager 创建虚拟机 配置虚拟机 飞牛官网下载 https://iso.liveupdate.fnnas.com/x86_64/trim/fnos-0.9.2-863.iso 群晖NAS如何在虚拟机创建飞牛NAS - 个人信息分享...
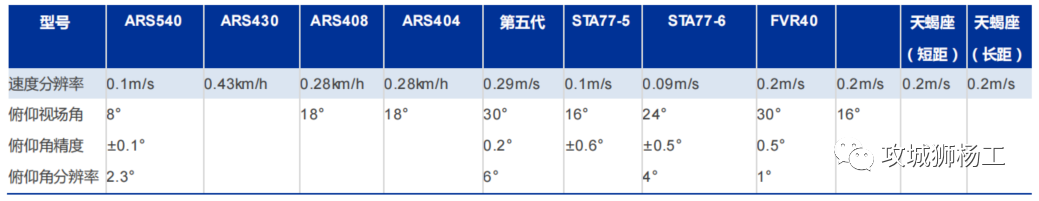
毫米波雷达基础理论(3D+4D)
3D、4D毫米波雷达基础知识及厂商选型 PreView : https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bQkju4r6med7I3TBGJI_bQ 1. FMCW毫米波雷达基础知识 主要参考博文: 一文入门汽车毫米波雷达基本原理 :https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_EN7A5lKcz2Eh8dLnjE19w 毫米波雷达基础…...

MySQL 主从同步异常处理
阅读原文:https://www.xiaozaoshu.top/articles/mysql-m-s-update-pk MySQL 做双主,遇到的这个错误: Could not execute Update_rows event on table ... Error_code: 1032是 MySQL 主从复制时的经典错误之一,通常表示ÿ…...
