SpringSpringBoot常用注解总结
目录
1. @SpringBootApplication
2. Spring Bean 相关
2.1. @Autowired
2.2. @Component,@Repository,@Service, @Controller
2.3. @RestController
2.4. @Scope
2.5. @Configuration
3. 处理常见的 HTTP 请求类型
3.1. GET 请求
3.2. POST 请求
3.3. PUT 请求
3.4. DELETE 请求
3.5. PATCH 请求
4. 前后端传值
4.1. @PathVariable 和 @RequestParam
4.2. @RequestBody
5. 读取配置信息
5.1. @Value(常用)
5.2. @ConfigurationProperties(常用)
5.3. @PropertySource(不常用)
6. 参数校验
6.1. 一些常用的字段验证的注解
6.2. 验证请求体(RequestBody)
6.3. 验证请求参数(Path Variables 和 Request Parameters)
7. 全局处理 Controller 层异常
8. JPA 相关
8.1. 创建表
8.2. 创建主键
8.3. 设置字段类型
8.4. 指定不持久化特定字段
8.5. 声明大字段
8.6. 创建枚举类型的字段
8.7. 增加审计功能
8.8. 删除/修改数据
8.9. 关联关系
9. 事务 @Transactional
10. json 数据处理
10.1. 过滤 json 数据
10.2. 格式化 json 数据
10.3. 扁平化对象
11. 测试相关
1. @SpringBootApplication
这里先单独拎出@SpringBootApplication 注解说一下,虽然我们一般不会主动去使用它。
Guide:这个注解是 Spring Boot 项目的基石,创建 SpringBoot 项目之后会默认在主类加上。
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringSecurityJwtGuideApplication {public static void main(java.lang.String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringSecurityJwtGuideApplication.class, args);}
}我们可以把 @SpringBootApplication看作是 @Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan 注解的集合。
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {......
}package org.springframework.boot;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {}根据 SpringBoot 官网,这三个注解的作用分别是:
@EnableAutoConfiguration:启用 SpringBoot 的自动配置机制@ComponentScan:扫描被@Component(@Repository,@Service,@Controller)注解的 bean,注解默认会扫描该类所在的包下所有的类。@Configuration:允许在 Spring 上下文中注册额外的 bean 或导入其他配置类
2. Spring Bean 相关
2.1. @Autowired
自动导入对象到类中,被注入进的类同样要被 Spring 容器管理比如:Service 类注入到 Controller 类中。
@Service
public class UserService {......
}@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;......
}2.2. @Component,@Repository,@Service, @Controller
我们一般使用 @Autowired 注解让 Spring 容器帮我们自动装配 bean。要想把类标识成可用于 @Autowired 注解自动装配的 bean 的类,可以采用以下注解实现:
@Component:通用的注解,可标注任意类为Spring组件。如果一个 Bean 不知道属于哪个层,可以使用@Component注解标注。@Repository: 对应持久层即 Dao 层,主要用于数据库相关操作。@Service: 对应服务层,主要涉及一些复杂的逻辑,需要用到 Dao 层。@Controller: 对应 Spring MVC 控制层,主要用于接受用户请求并调用 Service 层返回数据给前端页面。
2.3. @RestController
@RestController注解是@Controller和@ResponseBody的合集,表示这是个控制器 bean,并且是将函数的返回值直接填入 HTTP 响应体中,是 REST 风格的控制器。
Guide:现在都是前后端分离,说实话我已经很久没有用过@Controller。如果你的项目太老了的话,就当我没说。
单独使用 @Controller 不加 @ResponseBody的话一般是用在要返回一个视图的情况,这种情况属于比较传统的 Spring MVC 的应用,对应于前后端不分离的情况。@Controller +@ResponseBody 返回 JSON 或 XML 形式数据
关于@RestController 和 @Controller的对比,请看这篇文章:@RestController vs @Controller。
2.4. @Scope
声明 Spring Bean 的作用域,使用方法:
@Bean
@Scope("singleton")
public Person personSingleton() {return new Person();
}四种常见的 Spring Bean 的作用域:
- singleton : 唯一 bean 实例,Spring 中的 bean 默认都是单例的。
- prototype : 每次请求都会创建一个新的 bean 实例。
- request : 每一次 HTTP 请求都会产生一个新的 bean,该 bean 仅在当前 HTTP request 内有效。
- session : 每一个 HTTP Session 会产生一个新的 bean,该 bean 仅在当前 HTTP session 内有效。
2.5. @Configuration
一般用来声明配置类,可以使用 @Component注解替代,不过使用@Configuration注解声明配置类更加语义化。
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {@Beanpublic TransferService transferService() {return new TransferServiceImpl();}}3. 处理常见的 HTTP 请求类型
5 种常见的请求类型:
- GET:请求从服务器获取特定资源。举个例子:
GET /users(获取所有学生) - POST:在服务器上创建一个新的资源。举个例子:
POST /users(创建学生) - PUT:更新服务器上的资源(客户端提供更新后的整个资源)。举个例子:
PUT /users/12(更新编号为 12 的学生) - DELETE:从服务器删除特定的资源。举个例子:
DELETE /users/12(删除编号为 12 的学生) - PATCH:更新服务器上的资源(客户端提供更改的属性,可以看做作是部分更新),使用的比较少,这里就不举例子了。
3.1. GET 请求
@GetMapping("users") 等价于@RequestMapping(value="/users",method=RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity<List<User>> getAllUsers() {return userRepository.findAll();
}3.2. POST 请求
@PostMapping("users") 等价于@RequestMapping(value="/users",method=RequestMethod.POST)
关于@RequestBody注解的使用,在下面的“前后端传值”这块会讲到。
@PostMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity<User> createUser(@Valid @RequestBody UserCreateRequest userCreateRequest) {return userRepository.save(userCreateRequest);
}3.3. PUT 请求
@PutMapping("/users/{userId}") 等价于@RequestMapping(value="/users/{userId}",method=RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping("/users/{userId}")
public ResponseEntity<User> updateUser(@PathVariable(value = "userId") Long userId,@Valid @RequestBody UserUpdateRequest userUpdateRequest) {......
}3.4. DELETE 请求
@DeleteMapping("/users/{userId}")等价于@RequestMapping(value="/users/{userId}",method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/users/{userId}")
public ResponseEntity deleteUser(@PathVariable(value = "userId") Long userId){......
}3.5. PATCH 请求
一般实际项目中,我们都是 PUT 不够用了之后才用 PATCH 请求去更新数据。
@PatchMapping("/profile")public ResponseEntity updateStudent(@RequestBody StudentUpdateRequest studentUpdateRequest) {studentRepository.updateDetail(studentUpdateRequest);return ResponseEntity.ok().build();}4. 前后端传值
掌握前后端传值的正确姿势,是你开始 CRUD 的第一步!
4.1. @PathVariable 和 @RequestParam
@PathVariable用于获取路径参数,@RequestParam用于获取查询参数。
举个简单的例子:
@GetMapping("/klasses/{klassId}/teachers")
public List<Teacher> getKlassRelatedTeachers(@PathVariable("klassId") Long klassId,@RequestParam(value = "type", required = false) String type ) {
...
}如果我们请求的 url 是:/klasses/123456/teachers?type=web
那么我们服务获取到的数据就是:klassId=123456,type=web。
4.2. @RequestBody
用于读取 Request 请求(可能是 POST,PUT,DELETE,GET 请求)的 body 部分并且Content-Type 为 application/json 格式的数据,接收到数据之后会自动将数据绑定到 Java 对象上去。系统会使用HttpMessageConverter或者自定义的HttpMessageConverter将请求的 body 中的 json 字符串转换为 java 对象。
我用一个简单的例子来给演示一下基本使用!
我们有一个注册的接口:
@PostMapping("/sign-up")
public ResponseEntity signUp(@RequestBody @Valid UserRegisterRequest userRegisterRequest) {userService.save(userRegisterRequest);return ResponseEntity.ok().build();
}UserRegisterRequest对象:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserRegisterRequest {@NotBlankprivate String userName;@NotBlankprivate String password;@NotBlankprivate String fullName;
}我们发送 post 请求到这个接口,并且 body 携带 JSON 数据:
{ "userName": "coder", "fullName": "shuangkou", "password": "123456" }这样我们的后端就可以直接把 json 格式的数据映射到我们的 UserRegisterRequest 类上。
👉 需要注意的是:一个请求方法只可以有一个@RequestBody,但是可以有多个@RequestParam和@PathVariable。 如果你的方法必须要用两个 @RequestBody来接受数据的话,大概率是你的数据库设计或者系统设计出问题了!
5. 读取配置信息
很多时候我们需要将一些常用的配置信息比如阿里云 oss、发送短信、微信认证的相关配置信息等等放到配置文件中。
下面我们来看一下 Spring 为我们提供了哪些方式帮助我们从配置文件中读取这些配置信息。
我们的数据源application.yml内容如下:
wuhan2020: 2020年初武汉爆发了新型冠状病毒,疫情严重,但是,我相信一切都会过去!武汉加油!中国加油!my-profile:name: Guide哥email: koushuangbwcx@163.comlibrary:location: 湖北武汉加油中国加油books:- name: 天才基本法description: 二十二岁的林朝夕在父亲确诊阿尔茨海默病这天,得知自己暗恋多年的校园男神裴之即将出国深造的消息——对方考取的学校,恰是父亲当年为她放弃的那所。- name: 时间的秩序description: 为什么我们记得过去,而非未来?时间“流逝”意味着什么?是我们存在于时间之内,还是时间存在于我们之中?卡洛·罗韦利用诗意的文字,邀请我们思考这一亘古难题——时间的本质。- name: 了不起的我description: 如何养成一个新习惯?如何让心智变得更成熟?如何拥有高质量的关系? 如何走出人生的艰难时刻?5.1. @Value(常用)
使用 @Value("${property}") 读取比较简单的配置信息:
@Value("${wuhan2020}")
String wuhan2020;5.2. @ConfigurationProperties(常用)
通过@ConfigurationProperties读取配置信息并与 bean 绑定。
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "library")
class LibraryProperties {@NotEmptyprivate String location;private List<Book> books;@Setter@Getter@ToStringstatic class Book {String name;String description;}省略getter/setter......
}你可以像使用普通的 Spring bean 一样,将其注入到类中使用。
5.3. @PropertySource(不常用)
@PropertySource读取指定 properties 文件
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:website.properties")class WebSite {@Value("${url}")private String url;省略getter/setter......
}更多内容请查看我的这篇文章:《10 分钟搞定 SpringBoot 如何优雅读取配置文件?》 。
6. 参数校验
数据的校验的重要性就不用说了,即使在前端对数据进行校验的情况下,我们还是要对传入后端的数据再进行一遍校验,避免用户绕过浏览器直接通过一些 HTTP 工具直接向后端请求一些违法数据。
Bean Validation 是一套定义 JavaBean 参数校验标准的规范 (JSR 303, 349, 380),它提供了一系列注解,可以直接用于 JavaBean 的属性上,从而实现便捷的参数校验。
- JSR 303 (Bean Validation 1.0): 奠定了基础,引入了核心校验注解(如
@NotNull、@Size、@Min、@Max等),定义了如何通过注解的方式对 JavaBean 的属性进行校验,并支持嵌套对象校验和自定义校验器。 - JSR 349 (Bean Validation 1.1): 在 1.0 基础上进行扩展,例如引入了对方法参数和返回值校验的支持、增强了对分组校验(Group Validation)的处理。
- JSR 380 (Bean Validation 2.0): 拥抱 Java 8 的新特性,并进行了一些改进,例如支持
java.time包中的日期和时间类型、引入了一些新的校验注解(如@NotEmpty,@NotBlank等)。
校验的时候我们实际用的是 Hibernate Validator 框架。Hibernate Validator 是 Hibernate 团队最初的数据校验框架,Hibernate Validator 4.x 是 Bean Validation 1.0(JSR 303)的参考实现,Hibernate Validator 5.x 是 Bean Validation 1.1(JSR 349)的参考实现,目前最新版的 Hibernate Validator 6.x 是 Bean Validation 2.0(JSR 380)的参考实现。
SpringBoot 项目的 spring-boot-starter-web 依赖中已经有 hibernate-validator 包,不需要引用相关依赖。如下图所示(通过 idea 插件—Maven Helper 生成):
注:更新版本的 spring-boot-starter-web 依赖中不再有 hibernate-validator 包(如 2.3.11.RELEASE),需要自己引入 spring-boot-starter-validation 依赖。

非 SpringBoot 项目需要自行引入相关依赖包,这里不多做讲解,具体可以查看我的这篇文章:《如何在 Spring/Spring Boot 中做参数校验?你需要了解的都在这里!》。
👉 需要注意的是:所有的注解,推荐使用 JSR 注解,即javax.validation.constraints,而不是org.hibernate.validator.constraints
6.1. 一些常用的字段验证的注解
@NotEmpty被注释的字符串的不能为 null 也不能为空@NotBlank被注释的字符串非 null,并且必须包含一个非空白字符@Null被注释的元素必须为 null@NotNull被注释的元素必须不为 null@AssertTrue被注释的元素必须为 true@AssertFalse被注释的元素必须为 false@Pattern(regex=,flag=)被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式@Email被注释的元素必须是 Email 格式。@Min(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值@Max(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值@DecimalMin(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值@DecimalMax(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值@Size(max=, min=)被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内@Digits(integer, fraction)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内@Past被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期@Future被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期- ……
6.2. 验证请求体(RequestBody)
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Person {@NotNull(message = "classId 不能为空")private String classId;@Size(max = 33)@NotNull(message = "name 不能为空")private String name;@Pattern(regexp = "((^Man$|^Woman$|^UGM$))", message = "sex 值不在可选范围")@NotNull(message = "sex 不能为空")private String sex;@Email(message = "email 格式不正确")@NotNull(message = "email 不能为空")private String email;}我们在需要验证的参数上加上了@Valid注解,如果验证失败,它将抛出MethodArgumentNotValidException。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PersonController {@PostMapping("/person")public ResponseEntity<Person> getPerson(@RequestBody @Valid Person person) {return ResponseEntity.ok().body(person);}
}6.3. 验证请求参数(Path Variables 和 Request Parameters)
一定一定不要忘记在类上加上 @Validated 注解了,这个参数可以告诉 Spring 去校验方法参数。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
@Validated
public class PersonController {@GetMapping("/person/{id}")public ResponseEntity<Integer> getPersonByID(@Valid @PathVariable("id") @Max(value = 5,message = "超过 id 的范围了") Integer id) {return ResponseEntity.ok().body(id);}
}7. 全局处理 Controller 层异常
介绍一下我们 Spring 项目必备的全局处理 Controller 层异常。
相关注解:
@ControllerAdvice:注解定义全局异常处理类@ExceptionHandler:注解声明异常处理方法
如何使用呢?拿我们在第 5 节参数校验这块来举例子。如果方法参数不对的话就会抛出MethodArgumentNotValidException,我们来处理这个异常。
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {/*** 请求参数异常处理*/@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)public ResponseEntity<?> handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpServletRequest request) {......}
}8. JPA 相关
8.1. 创建表
@Entity声明一个类对应一个数据库实体。
@Table 设置表名
@Entity
@Table(name = "role")
public class Role {@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)private Long id;private String name;private String description;省略getter/setter......
}8.2. 创建主键
@Id:声明一个字段为主键。
使用@Id声明之后,我们还需要定义主键的生成策略。我们可以使用 @GeneratedValue 指定主键生成策略。
1.通过 @GeneratedValue直接使用 JPA 内置提供的四种主键生成策略来指定主键生成策略。
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;JPA 使用枚举定义了 4 种常见的主键生成策略,如下:
Guide:枚举替代常量的一种用法
public enum GenerationType {/*** 使用一个特定的数据库表格来保存主键* 持久化引擎通过关系数据库的一张特定的表格来生成主键,*/TABLE,/***在某些数据库中,不支持主键自增长,比如Oracle、PostgreSQL其提供了一种叫做"序列(sequence)"的机制生成主键*/SEQUENCE,/*** 主键自增长*/IDENTITY,/***把主键生成策略交给持久化引擎(persistence engine),*持久化引擎会根据数据库在以上三种主键生成 策略中选择其中一种*/AUTO
}@GeneratedValue注解默认使用的策略是GenerationType.AUTO
public @interface GeneratedValue {GenerationType strategy() default AUTO;String generator() default "";
}一般使用 MySQL 数据库的话,使用GenerationType.IDENTITY策略比较普遍一点(分布式系统的话需要另外考虑使用分布式 ID)。
2.通过 @GenericGenerator声明一个主键策略,然后 @GeneratedValue使用这个策略
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "IdentityIdGenerator")
@GenericGenerator(name = "IdentityIdGenerator", strategy = "identity")
private Long id;等价于:
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;jpa 提供的主键生成策略有如下几种:
public class DefaultIdentifierGeneratorFactoryimplements MutableIdentifierGeneratorFactory, Serializable, ServiceRegistryAwareService {@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")public DefaultIdentifierGeneratorFactory() {register( "uuid2", UUIDGenerator.class );register( "guid", GUIDGenerator.class ); // can be done with UUIDGenerator + strategyregister( "uuid", UUIDHexGenerator.class ); // "deprecated" for new useregister( "uuid.hex", UUIDHexGenerator.class ); // uuid.hex is deprecatedregister( "assigned", Assigned.class );register( "identity", IdentityGenerator.class );register( "select", SelectGenerator.class );register( "sequence", SequenceStyleGenerator.class );register( "seqhilo", SequenceHiLoGenerator.class );register( "increment", IncrementGenerator.class );register( "foreign", ForeignGenerator.class );register( "sequence-identity", SequenceIdentityGenerator.class );register( "enhanced-sequence", SequenceStyleGenerator.class );register( "enhanced-table", TableGenerator.class );}public void register(String strategy, Class generatorClass) {LOG.debugf( "Registering IdentifierGenerator strategy [%s] -> [%s]", strategy, generatorClass.getName() );final Class previous = generatorStrategyToClassNameMap.put( strategy, generatorClass );if ( previous != null ) {LOG.debugf( " - overriding [%s]", previous.getName() );}}}
8.3. 设置字段类型
@Column 声明字段。
示例:
设置属性 userName 对应的数据库字段名为 user_name,长度为 32,非空
@Column(name = "user_name", nullable = false, length=32)
private String userName;设置字段类型并且加默认值,这个还是挺常用的。
@Column(columnDefinition = "tinyint(1) default 1")
private Boolean enabled;8.4. 指定不持久化特定字段
@Transient:声明不需要与数据库映射的字段,在保存的时候不需要保存进数据库 。
如果我们想让secrect 这个字段不被持久化,可以使用 @Transient关键字声明。
@Entity(name="USER")
public class User {......@Transientprivate String secrect; // not persistent because of @Transient}除了 @Transient关键字声明, 还可以采用下面几种方法:
static String secrect; // not persistent because of static
final String secrect = "Satish"; // not persistent because of final
transient String secrect; // not persistent because of transient一般使用注解的方式比较多。
8.5. 声明大字段
@Lob:声明某个字段为大字段。
更详细的声明:
@Lob
//指定 Lob 类型数据的获取策略, FetchType.EAGER 表示非延迟加载,而 FetchType.LAZY 表示延迟加载 ;
@Basic(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
//columnDefinition 属性指定数据表对应的 Lob 字段类型
@Column(name = "content", columnDefinition = "LONGTEXT NOT NULL")
private String content;8.6. 创建枚举类型的字段
可以使用枚举类型的字段,不过枚举字段要用@Enumerated注解修饰。
public enum Gender {MALE("男性"),FEMALE("女性");private String value;Gender(String str){value=str;}
}@Entity
@Table(name = "role")
public class Role {@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)private Long id;private String name;private String description;@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)private Gender gender;省略getter/setter......
}数据库里面对应存储的是 MALE/FEMALE。
8.7. 增加审计功能
只要继承了 AbstractAuditBase的类都会默认加上下面四个字段。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@MappedSuperclass
@EntityListeners(value = AuditingEntityListener.class)
public abstract class AbstractAuditBase {@CreatedDate@Column(updatable = false)@JsonIgnoreprivate Instant createdAt;@LastModifiedDate@JsonIgnoreprivate Instant updatedAt;@CreatedBy@Column(updatable = false)@JsonIgnoreprivate String createdBy;@LastModifiedBy@JsonIgnoreprivate String updatedBy;
}我们对应的审计功能对应地配置类可能是下面这样的(Spring Security 项目):
@Configuration
@EnableJpaAuditing
public class AuditSecurityConfiguration {@BeanAuditorAware<String> auditorAware() {return () -> Optional.ofNullable(SecurityContextHolder.getContext()).map(SecurityContext::getAuthentication).filter(Authentication::isAuthenticated).map(Authentication::getName);}
}简单介绍一下上面涉及到的一些注解:
-
@CreatedDate: 表示该字段为创建时间字段,在这个实体被 insert 的时候,会设置值 -
@CreatedBy:表示该字段为创建人,在这个实体被 insert 的时候,会设置值@LastModifiedDate、@LastModifiedBy同理。
@EnableJpaAuditing:开启 JPA 审计功能。
8.8. 删除/修改数据
@Modifying 注解提示 JPA 该操作是修改操作,注意还要配合@Transactional注解使用。
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> {@Modifying@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)void deleteByUserName(String userName);
}8.9. 关联关系
@OneToOne声明一对一关系@OneToMany声明一对多关系@ManyToOne声明多对一关系@ManyToMany声明多对多关系
更多关于 Spring Boot JPA 的文章请看我的这篇文章:一文搞懂如何在 Spring Boot 正确中使用 JPA 。
9. 事务 @Transactional
在要开启事务的方法上使用@Transactional注解即可!
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void save() {......
}我们知道 Exception 分为运行时异常 RuntimeException 和非运行时异常。在@Transactional注解中如果不配置rollbackFor属性,那么事务只会在遇到RuntimeException的时候才会回滚,加上rollbackFor=Exception.class,可以让事务在遇到非运行时异常时也回滚。
@Transactional 注解一般可以作用在类或者方法上。
- 作用于类:当把
@Transactional注解放在类上时,表示所有该类的 public 方法都配置相同的事务属性信息。 - 作用于方法:当类配置了
@Transactional,方法也配置了@Transactional,方法的事务会覆盖类的事务配置信息。
10. json 数据处理
10.1. 过滤 json 数据
@JsonIgnoreProperties 作用在类上用于过滤掉特定字段不返回或者不解析。
//生成json时将userRoles属性过滤
@JsonIgnoreProperties({"userRoles"})
public class User {private String userName;private String fullName;private String password;private List<UserRole> userRoles = new ArrayList<>();
}@JsonIgnore一般用于类的属性上,作用和上面的@JsonIgnoreProperties 一样。
public class User {private String userName;private String fullName;private String password;//生成json时将userRoles属性过滤@JsonIgnoreprivate List<UserRole> userRoles = new ArrayList<>();
}10.2. 格式化 json 数据
@JsonFormat一般用来格式化 json 数据。
比如:
@JsonFormat(shape=JsonFormat.Shape.STRING, pattern="yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS'Z'", timezone="GMT")
private Date date;10.3. 扁平化对象
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class Account {private Location location;private PersonInfo personInfo;@Getter@Setter@ToStringpublic static class Location {private String provinceName;private String countyName;}@Getter@Setter@ToStringpublic static class PersonInfo {private String userName;private String fullName;}
}未扁平化之前:
{"location": {"provinceName": "湖北","countyName": "武汉"},"personInfo": {"userName": "coder1234","fullName": "shaungkou"}
}使用@JsonUnwrapped 扁平对象之后:
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class Account {@JsonUnwrappedprivate Location location;@JsonUnwrappedprivate PersonInfo personInfo;......
}{"provinceName": "湖北","countyName": "武汉","userName": "coder1234","fullName": "shaungkou"
}11. 测试相关
@ActiveProfiles一般作用于测试类上, 用于声明生效的 Spring 配置文件。
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = RANDOM_PORT)
@ActiveProfiles("test")
@Slf4j
public abstract class TestBase {......
}@Test声明一个方法为测试方法
@Transactional被声明的测试方法的数据会回滚,避免污染测试数据。
@WithMockUser Spring Security 提供的,用来模拟一个真实用户,并且可以赋予权限。
@Test@Transactional@WithMockUser(username = "user-id-18163138155", authorities = "ROLE_TEACHER")void should_import_student_success() throws Exception {......}相关文章:

SpringSpringBoot常用注解总结
目录 1. SpringBootApplication 2. Spring Bean 相关 2.1. Autowired 2.2. Component,Repository,Service, Controller 2.3. RestController 2.4. Scope 2.5. Configuration 3. 处理常见的 HTTP 请求类型 3.1. GET 请求 3.2. POST 请求 3.3. PUT 请求 3.4. DELETE 请…...

24.小R的随机播放顺序<字节青训营-中等题>
1.题目 问题描述 小R有一个特殊的随机播放规则。他首先播放歌单中的第一首歌,播放后将其从歌单中移除。如果歌单中还有歌曲,则会将当前第一首歌移到最后一首。这个过程会一直重复,直到歌单中没有任何歌曲。 例如,给定歌单 [5, …...

【QT】增删改查 XML 文件的类
使用单例类模板实现的对XML文件的节点、属性、文本进行增删改查,可以直接用! 直接POST代码,比较简单好用。 针对以下格式的xml文件比较适用 每个节点的名称都不一样,节点包含了各种属性。 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <config…...

Linux-掉电保护方案
参考链接 https://blog.csdn.net/pwl999/article/details/109411919硬件设计 设备树 驱动程序 #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/interrupt.h> #include <linux/gpio.h>int irq;//中断服务函数 irqreturn_t tes…...

php获取字符串中的汉字
在PHP中,可以使用正则表达式来提取字符串中的汉字。汉字通常位于Unicode范围\u4e00-\u9fa5之内,因此可以使用preg_match_all函数配合适当的正则表达式来实现。 以下是一个PHP代码示例,它会从给定的字符串中提取出所有的汉字: fu…...

java: JDK isn‘t specified for module ‘product-service‘问题解决
目录 问题 解决方法 1.打开File->Project Structure... 2.将Project SDK修改为17 Oracle OpenJDK 17.0.12,并Apply,OK 问题 添加module后报错:java: JDK isnt specified for module product-service 查看pom.xml文件也添加了对应的JDK…...

使用工厂+策略模式实现去除繁琐的if else
使用工厂策略模式实现去除繁琐的if else 在中间有一个mapstruct的bug,即在修改实体类中的类型时,或者修改属性名字,mapstruct都无法进行转换,会报错,此时需要maven cleanmaven compile即可 前言 在这次的开发中&#…...

Dubbo3入门项目搭建
开发环境:jdk8、dubbo3.2.9、nacos2.3.0、springboot2.7.17、dubbo-admin0.6.0。 Dubbo 是一个高性能的 Java RPC(远程调用)框架,最初由阿里巴巴开发并开源,主要用于构建 SOA 架构下的分布式应用系统( soa简单理解就是…...

形象地理解UE4中的数据结构 TLinkedListBase
大家都熟知链表,但不一定能快速看懂UE4中的数据结构。 TLinkedListBase表示“链接”中的一个结点,有三个成员: 一、ElementType Element; 表示具体的业务,例如int链条中的一个整数。 二、NextLink 表示 “下一个Node”&#…...

Python自然语言处理利器:SnowNLP模块深度解析、安装指南与实战案例
Python自然语言处理之SnowNLP模块介绍、安装与常见操作案例 一、SnowNLP模块介绍 SnowNLP是一个专为中文文本设计的Python库,它基于自然语言处理技术,提供了多种功能,包括分词、词性标注、情感分析、文本转换(简繁转换ÿ…...

Llama系列关键知识总结
系列文章目录 第一章:LoRA微调系列笔记 第二章:Llama系列关键知识总结 第三章:LLaVA模型讲解与总结 文章目录 系列文章目录Llama: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models关键要点LLaMa模型架构:Llama2分组查询注意力 (G…...

【开源】创建自动签到系统—QD框架
1. 介绍 QD是一个 基于 HAR 编辑器和 Tornado 服务端的 HTTP 定时任务自动执行 Web 框架。 主要通过抓包获取到HAR来制作任务模板,从而实现异步响应和发起HTTP请求 2. 需要环境 2.1 硬件需求 CPU:至少1核 内存:推荐 ≥ 1G 硬盘:推…...

CDP集群安全指南系列文章导读
[一]大数据安全综述 1-认证 身份验证是任何计算环境的基本安全要求。简单来说,用户和服务必须在使用系统功能并获得授权之前,向系统证明其身份(进行身份验证)。身份验证与授权紧密配合,共同保护系统资源。大多数 CDH …...

MT8788安卓核心板_MTK8788核心板参数_联发科模块定制开发
MT8788安卓核心板是一款尺寸为52.5mm x 38.5mm x 2.95mm的高集成度电路板,专为各种智能设备应用而设计。该板卡整合了处理器、图形处理单元(GPU)、LPDDR3内存、eMMC存储及电源管理模块,具备出色的性能与低功耗特性。 这款核心板搭载了联发科的MT8788处理…...

【微软,模型规模】模型参数规模泄露:理解大型语言模型的参数量级
模型参数规模泄露:理解大型语言模型的参数量级 关键词: #大型语言模型 Large Language Model #参数规模 Parameter Scale #GPT-4o #GPT-4o-mini #Claude 3.5 Sonnet 具体实例与推演 近日,微软在一篇医学相关论文中意外泄露了OpenAI及Claud…...

深入理解并发原子性、可见性、有序性与JMM内存模型
1. 并发三大特性 并发编程Bug的源头:原子性、可见性和有序性问题 1.1 原子性 一个或多个操作,要么全部执行且在执行过程中不被任何因素打断,要么全部不执行。在 Java 中,对基本数据类型的变量的读取和赋值操作是原子性操作&…...

电商项目-数据同步解决方案(四)商品下架同步更新ES索引库数据
商品下架索引库删除数据 一、 需求分析和业务逻辑 商品下架后将商品从索引库中移除。 主要应用技术有: 消息队列-RabbitMQ ,分布式搜索引擎-ElasticSearch,Eureka,Canal,Feign远程调用 (1)在…...

vue学习第一阶段
vue 什么是Vue? 概念:Vue是一个构建用户页面的渐进式框架 Vue的两种使用方式 Vue的核心开发 场景: 局部 {\color{red}局部} 局部模块改造Vue核心包& Vue插件 工程化开发场景: 整站 {\color{red}整站} 整站开发Vue2官网 https://v2.cn.vuejs.org/ 资料存放地址 D:\Baidu…...

React虚拟DOM:理解和应用
写在前面 在现代前端开发中,React 是一个非常流行的 JavaScript 库,用于构建用户界面。它引入了一个名为“虚拟 DOM”(Virtual DOM)的概念,这个概念对于 React 的高效性能和易用性至关重要。本文将深入探讨 React Vir…...

用python编写一个放烟花的小程序
import pygame import random # 代码解释及使用说明: # 首先,导入 pygame 和 random 库。pygame 用于创建游戏窗口和图形绘制,random 用于生成随机数。 # 初始化 pygame,并设置屏幕尺寸为 800x600 像素,设置窗口标题为…...

React hook之useRef
React useRef 详解 useRef 是 React 提供的一个 Hook,用于在函数组件中创建可变的引用对象。它在 React 开发中有多种重要用途,下面我将全面详细地介绍它的特性和用法。 基本概念 1. 创建 ref const refContainer useRef(initialValue);initialValu…...
)
React Native 导航系统实战(React Navigation)
导航系统实战(React Navigation) React Navigation 是 React Native 应用中最常用的导航库之一,它提供了多种导航模式,如堆栈导航(Stack Navigator)、标签导航(Tab Navigator)和抽屉…...
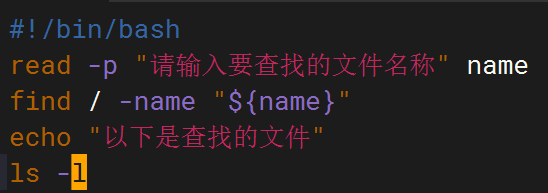
shell脚本--常见案例
1、自动备份文件或目录 2、批量重命名文件 3、查找并删除指定名称的文件: 4、批量删除文件 5、查找并替换文件内容 6、批量创建文件 7、创建文件夹并移动文件 8、在文件夹中查找文件...

边缘计算医疗风险自查APP开发方案
核心目标:在便携设备(智能手表/家用检测仪)部署轻量化疾病预测模型,实现低延迟、隐私安全的实时健康风险评估。 一、技术架构设计 #mermaid-svg-iuNaeeLK2YoFKfao {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg…...

【Java学习笔记】Arrays类
Arrays 类 1. 导入包:import java.util.Arrays 2. 常用方法一览表 方法描述Arrays.toString()返回数组的字符串形式Arrays.sort()排序(自然排序和定制排序)Arrays.binarySearch()通过二分搜索法进行查找(前提:数组是…...
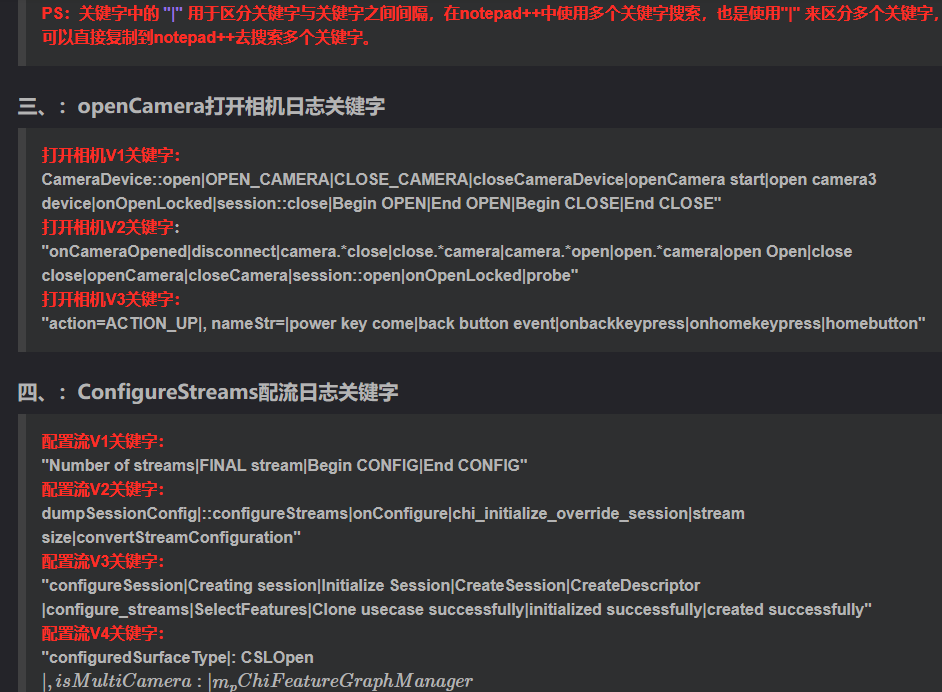
相机Camera日志实例分析之二:相机Camx【专业模式开启直方图拍照】单帧流程日志详解
【关注我,后续持续新增专题博文,谢谢!!!】 上一篇我们讲了: 这一篇我们开始讲: 目录 一、场景操作步骤 二、日志基础关键字分级如下 三、场景日志如下: 一、场景操作步骤 操作步…...

Nuxt.js 中的路由配置详解
Nuxt.js 通过其内置的路由系统简化了应用的路由配置,使得开发者可以轻松地管理页面导航和 URL 结构。路由配置主要涉及页面组件的组织、动态路由的设置以及路由元信息的配置。 自动路由生成 Nuxt.js 会根据 pages 目录下的文件结构自动生成路由配置。每个文件都会对…...

生成 Git SSH 证书
🔑 1. 生成 SSH 密钥对 在终端(Windows 使用 Git Bash,Mac/Linux 使用 Terminal)执行命令: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_emailexample.com" 参数说明: -t rsa&#x…...
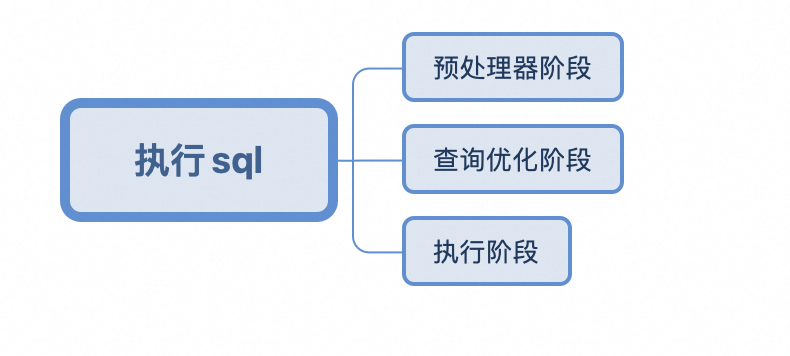
Mysql中select查询语句的执行过程
目录 1、介绍 1.1、组件介绍 1.2、Sql执行顺序 2、执行流程 2.1. 连接与认证 2.2. 查询缓存 2.3. 语法解析(Parser) 2.4、执行sql 1. 预处理(Preprocessor) 2. 查询优化器(Optimizer) 3. 执行器…...
Razor编程中@Html的方法使用大全
文章目录 1. 基础HTML辅助方法1.1 Html.ActionLink()1.2 Html.RouteLink()1.3 Html.Display() / Html.DisplayFor()1.4 Html.Editor() / Html.EditorFor()1.5 Html.Label() / Html.LabelFor()1.6 Html.TextBox() / Html.TextBoxFor() 2. 表单相关辅助方法2.1 Html.BeginForm() …...
