机器学习模型评估指标
-
准确率(Accuracy): 正确预测的样本数占总样本数的比例。适用于类别分布均衡的数据集。
-
精确率(Precision): 在所有被预测为正类的样本中,实际为正类的比例。高精确率意味着较少的假正例。
-
召回率(Recall): 在所有实际为正类的样本中,被正确预测为正类的比例。高召回率意味着较少的假负例。
-
F1分数(F1 Score): 精确率和召回率的调和平均,是两者之间的平衡指标。F1分数在类别不平衡时特别有用。
-
AUC-ROC曲线下面积(AUC): ROC曲线下的面积,衡量模型对正负样本的区分能力。AUC值越高,模型性能越好。
-
平均精度(Average Precision): 每个类别的精确率的平均值,特别用于多标签分类问题。
-
平均召回率(Average Recall): 每个类别的召回率的平均值,同样适用于多标签分类。
-
混淆矩阵(Confusion Matrix): 一个表格,显示了实际类别与预测类别之间的关系,可以用来计算上述指标。
-
平均F1分数(Average F1 Score): 对每个类别计算F1分数后取平均值。
-
马修距离(Mean Absolute Error, MAE): 预测值与真实值之间差的绝对值的平均。
-
均方误差(Mean Square Error, MSE): 预测值与真实值之间差的平方的平均值。
-
均方根误差(Root Mean Square Error, RMSE): MSE的平方根,提供了误差的尺度化度量。
-
对数平均绝对误差(Mean Absolute Percentage Error, MAPE): 预测值与真实值之间差的绝对值的百分比的平均值。
-
洛斯损失(Log Loss): 常用于逻辑回归模型,衡量预测概率与实际标签之间的差异。
-
杰卡指数(Jaccard Index): 1减去预测类别与真实类别的交集与并集的比例,用于衡量两个集合的相似度。
结合场景来看待这些指标:
-
分类问题(Classification):
- 类别不平衡(Class Imbalance): 在这种情况下,召回率(Recall)和F1分数(F1 Score)通常比准确率(Accuracy)更能反映模型性能,因为准确率可能会因为多数类而产生误导。
- 多类别分类(Multi-class Classification): 精确率(Precision)、召回率(Recall)和F1分数(F1 Score)可以为每个类别单独计算,然后平均得到宏平均(Macro-average)或微平均(Micro-average)指标。
-
回归问题(Regression):
- 均方误差(Mean Squared Error, MSE)和均方根误差(Root Mean Squared Error, RMSE)是衡量预测值与实际值之间差异的常用指标。
- 平均绝对误差(Mean Absolute Error, MAE)提供了预测误差的平均绝对值,对异常值不敏感。
-
异常检测:
- 查准率(Precision)和召回率(Recall)在这里同样重要,尤其是在异常类别较少的情况下。
-
排名问题:
- 平均精度(Mean Average Precision, MAP)是一个关键指标,它衡量的是模型在整个排名列表中保持高精确度的能力。
-
多标签分类:
- 每个标签的精确率和召回率可以单独计算,然后根据标签的分布进行加权平均。
-
多输出问题:
- 对于每个输出变量,可以单独计算MSE、RMSE或准确率等指标。
1.准确率

即希望11(模型正确预测正例)、10(模型正确预测负例)的占比更高
基本原理
准确率是将预测正确的样本数量与总样本数量之比,它衡量的是模型在整个数据集上的表现。然而,当数据集不平衡(即某一类样本数量明显多于其他类别)时,准确率可能不是一个很好的评估指标,因为即使模型预测所有样本都属于多数类别,也能获得相对较高的准确率。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_classes=2, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练逻辑回归模型
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)# 计算准确率
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)# 绘制混淆矩阵
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print("Confusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)# 绘制评估指标
plt.imshow(conf_matrix, cmap='binary', interpolation='None')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xticks([0, 1])
plt.yticks([0, 1])
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.ylabel('True Label')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.show()

2.精确率

基本原理
精确率的核心思想是衡量模型在所有预测为正类别的样本中,真正为正类别的样本所占的比例。这个指标对于那些需要准确识别正例的任务尤为重要,比如医学诊断中的疾病检测。高精确率表示模型在识别正例方面有很好的表现。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score, confusion_matrix# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_classes=2, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练逻辑回归模型
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)# 计算精确率
precision = precision_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("Precision:", precision)# 绘制混淆矩阵
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print("Confusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)# 绘制评估指标
plt.imshow(conf_matrix, cmap='binary', interpolation='None')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xticks([0, 1])
plt.yticks([0, 1])
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.ylabel('True Label')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.show()
3.召回率

基本原理
召回率的核心思想是衡量模型在识别正例方面的表现。它强调了模型对于实际为正类别的样本的识别能力,对于那些需要尽量避免漏诊的任务,比如疾病检测,召回率是一个非常重要的评估指标。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score, confusion_matrix# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_classes=2, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练逻辑回归模型
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)# 计算召回率
recall = recall_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("Recall:", recall)# 绘制混淆矩阵
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print("Confusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)# 绘制评估指标
plt.imshow(conf_matrix, cmap='binary', interpolation='None')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xticks([0, 1])
plt.yticks([0, 1])
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.ylabel('True Label')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.show()
4.F1分数

基本原理
F1分数综合考虑了模型的精确率和召回率,因此可以在一定程度上弥补精确率和召回率单独使用时的不足。F1分数越高,表示模型在识别和预测正类别方面的综合表现越好。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, confusion_matrix# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_classes=2, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练逻辑回归模型
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)# 计算F1分数
f1 = f1_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("F1 Score:", f1)# 绘制混淆矩阵
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print("Confusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)# 绘制评估指标
plt.imshow(conf_matrix, cmap='binary', interpolation='None')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xticks([0, 1])
plt.yticks([0, 1])
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.ylabel('True Label')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')plt.show()
5.ROC曲线和AUC

基本原理
ROC曲线基于真正例率和假正例率,它展示了在不同分类阈值下,模型在识别正例和负例方面的性能。ROC曲线上的点越靠近左上角,表示模型性能越好。AUC是ROC曲线下的面积,它等于ROC曲线与横轴之间的面积,可以用来比较不同模型的性能,AUC越大表示模型性能越好。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_classes=2, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练逻辑回归模型
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred_proba = model.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]# 计算ROC曲线和AUC
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, y_pred_proba)
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
print("AUC:", roc_auc)# 绘制ROC曲线
plt.figure()
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange', lw=2, label='ROC curve (area = %0.2f)' % roc_auc)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=2, linestyle='--')
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()

6.混淆矩阵

基本原理
混淆矩阵用于描述模型在不同类别上的预测结果,帮助评估模型的分类准确性和错误情况。通过混淆矩阵,可以计算出模型的精确率、召回率、F1分数等评估指标,从而更全面地评估模型的性能。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_classes=2, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练逻辑回归模型
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)# 计算混淆矩阵
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print("Confusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)# 绘制混淆矩阵
plt.imshow(conf_matrix, cmap='binary', interpolation='None')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xticks([0, 1])
plt.yticks([0, 1])
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.ylabel('True Label')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.show()
7.均方误差


基本原理
均方误差衡量了模型的预测值与真实值之间的平均偏差的平方。当模型的预测值与真实值之间的偏差较大时,MSE会增大;而当偏差较小时,MSE会减小。因此,MSE越小表示模型对数据的拟合程度越好。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1, noise=0.1, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)# 计算均方误差
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print("Mean Squared Error:", mse)# 绘制评估指标
plt.scatter(X_test, y_test, color='black', label='Actual')
plt.plot(X_test, y_pred, color='blue', linewidth=3, label='Predicted')
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.show()

8.平均绝对误差

基本原理
平均绝对误差衡量了模型的预测值与真实值之间的平均绝对偏差。当模型的预测值与真实值之间的偏差较大时,MAE会增大;而当偏差较小时,MAE会减小。因此,MAE越小表示模型对数据的拟合程度越好。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1, noise=0.1, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)# 计算平均绝对误差
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)
print("Mean Absolute Error:", mae)# 绘制评估指标
plt.scatter(X_test, y_test, color='black', label='Actual')
plt.plot(X_test, y_pred, color='blue', linewidth=3, label='Predicted')
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
9.对数损失

基本原理
对数损失衡量了模型的预测概率分布与真实标签之间的差异。当模型的预测概率分布与真实标签完全一致时,对数损失为0;当二者差异较大时,对数损失增大。因此,对数损失越小表示模型性能越好。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import log_loss# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_classes=2, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练逻辑回归模型
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred_proba = model.predict_proba(X_test)# 计算对数损失
logloss = log_loss(y_test, y_pred_proba)
print("Log Loss:", logloss)# 绘制评估指标
thresholds = np.linspace(0.01, 0.99, 100)
logloss_values = []
for threshold in thresholds:
y_pred_threshold = (y_pred_proba[:, 1] > threshold).astype(int)
logloss_values.append(log_loss(y_test, y_pred_threshold))plt.plot(thresholds, logloss_values)
plt.xlabel('Threshold')
plt.ylabel('Log Loss')
plt.title('Log Loss vs Threshold')
plt.show()

10.R平方


基本原理
R平方衡量了模型对数据的拟合程度,其取值范围在0到1之间。当模型对数据的拟合程度越好时,R平方越接近1;当模型对数据的拟合程度较差时,R平方越接近0。当模型的拟合程度与随机平均水平相当时,R平方可能为负。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score# 生成模拟数据集
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1, noise=0.1, random_state=42)# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 训练线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)# 在测试集上做预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)# 计算R平方
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("R-squared:", r2)# 绘制评估指标
plt.scatter(X_test, y_test, color='black', label='Actual')
plt.plot(X_test, y_pred, color='blue', linewidth=3, label='Predicted')
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
11.交叉验证分数

基本原理
交叉验证分数的原理是通过多次训练和测试模型,利用每次测试集上的性能指标来评估模型的泛化能力。通过多次重复这个过程并计算平均值,可以得到更可靠的性能评估结果。
核心点

代码例子
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression# 加载数据集
iris = load_iris()
X, y = iris.data, iris.target# 初始化逻辑回归模型
model = LogisticRegression()# 计算交叉验证分数
cv_scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, cv=5, scoring='accuracy')# 打印交叉验证分数
print("Cross-Validation Scores:", cv_scores)
print("Mean Cross-Validation Score:", np.mean(cv_scores))# 绘制评估指标
plt.plot(range(1, 6), cv_scores, marker='o')
plt.xlabel('Fold')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.title('Cross-Validation Scores')
plt.show()

相关文章:

机器学习模型评估指标
模型的评估指标是衡量一个模型应用于对应任务的契合程度,常见的指标有: 准确率(Accuracy): 正确预测的样本数占总样本数的比例。适用于类别分布均衡的数据集。 精确率(Precision): 在所有被预测为正类的样…...

C# 特性
总目录 C# 语法总目录 C# 特性 特性1. 特性类自定义格式2. 特性的位置参数和命名参数3. 特性的目标4. 指定多个特性5. 调用者信息特性 特性 1. 特性类自定义格式 自定义特性类需要继承自Attribute类,特性使用通常都会省略名字后面的Attribute,会自动识…...

Reactor测试框架之StepVerifier
Reactor测试框架之StepVerifier 测试步骤1、创建StepVerifier实例2、添加断言3、执行验证 代码实例 在响应式编程中,Reactor框架提供了StepVerifier测试类,用于对响应式序列进行断言和验证。StepVerifier主要用于对Publisher发出的元素序列进行逐步的、精…...
——筑梦之路)
k8s helm部署kafka集群(KRaft模式)——筑梦之路
添加helm仓库 helm repo add bitnami "https://helm-charts.itboon.top/bitnami" --force-update helm repo add grafana "https://helm-charts.itboon.top/grafana" --force-update helm repo add prometheus-community "https://helm-charts.itboo…...

unity action委托举例
using System; using UnityEngine; public class DelegateExample : MonoBehaviour { void Start() { // 创建委托实例并添加方法 Action myAction Method1; myAction Method2; myAction Method3; // 调用委托,会依次执…...

conda 批量安装requirements.txt文件
conda 批量安装requirements.txt文件中包含的组件依赖 conda install --yes --file requirements.txt #这种执行方式,一遇到安装不上就整体停止不会继续下面的包安装。 下面这条命令能解决上面出现的不执行后续包的问题,需要在CMD窗口执行: 点…...

Flutter:封装一个自用的bottom_picker选择器
效果图:单列选择器 使用bottom_picker: ^2.9.0实现,单列选择器,官方文档 pubspec.yaml # 底部选择 bottom_picker: ^2.9.0picker_utils.dart AppTheme:自定义的颜色 TextWidget.body Text() <Widget>[].toRow Row()下边代…...

Group3r:一款针对活动目录组策略安全的漏洞检测工具
关于Group3r Group3r是一款针对活动目录组策略安全的漏洞检测工具,可以帮助广大安全研究人员迅速枚举目标AD组策略中的相关配置,并识别其中的潜在安全威胁。 Group3r专为红蓝队研究人员和渗透测试人员设计,该工具可以通过将 LDAP 与域控制器…...

支持向量机算法(一):像讲故事一样讲明白它的原理及实现奥秘
1、支持向量机算法介绍 支持向量机(Support Vector Machine,SVM)是一种基于统计学习理论的模式识别方法, 属于有监督学习模型,主要用于解决数据分类问题。SVM将每个样本数据表示为空间中的点,使不同类别的…...

力扣-数组-35 搜索插入位置
解析 时间复杂度要求,所以使用二分的思想,漏掉了很多问题,这里记录 在left-right1时,已经找到了插入位置,但是没有赋值,然后break,所以导致一直死循环。 if(right - left 1){result right;b…...

List ---- 模拟实现LIST功能的发现
目录 listlist概念 list 中的迭代器list迭代器知识const迭代器写法list访问自定义类型 附录代码 list list概念 list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素…...

HashMap和HashTable区别问题
并发:hashMap线程不安全,hashTable线程安全,底层在put操作的方法上加了synchronized 初始化:hashTable初始容量为11,hashmap初始容量为16 阔容因子:阔容因子都是0.75 扩容比例: 补充 hashMap…...

mysql -> 达梦数据迁移(mbp大小写问题兼容)
安装 注意后面初始化需要忽略大小写 初始化程序启动路径 F:\dmdbms\tool dbca.exe 创建表空间,用户,模式 管理工具启动路径 F:\dmdbms\tool manager.exe 创建表空间 创建用户 创建同名模式,指定模式拥有者TEST dts 工具数据迁移 mysql -&g…...

leetcode热门100题1-4
第一天 两数之和 //暴力枚举 class Solution { public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int n nums.size();for (int i 0; i < n; i) {for (int j i 1; j < n; j) {if (nums[i] nums[j] target) {return {i, j};}}}return {…...

作业:IO:day2
题目一 第一步:创建一个 struct Student 类型的数组 arr[3],初始化该数组中3个学生的属性 第二步:编写一个叫做save的函数,功能为 将数组arr中的3个学生的所有信息,保存到文件中去,使用fread实现fwrite 第三步…...

UVM: TLM机制
topic overview 不建议的方法:假如没有TLM TLM TLM 1.0 整个TLM机制下,底层逻辑离不开动作发起者和被动接受者这个底层的模型基础,但实际上,在验证环境中,任何一个组件,都有可能成为动作的发起者࿰…...

flink的EventTime和Watermark
时间机制 Flink中的时间机制主要用在判断是否触发时间窗口window的计算。 在Flink中有三种时间概念:ProcessTime、IngestionTime、EventTime。 ProcessTime:是在数据抵达算子产生的时间(Flink默认使用ProcessTime) IngestionT…...

arcgis的合并、相交、融合、裁剪、联合、标识操作的区别和使用
1、相交 需要输入两个面要素,最终得到的是两个输入面要素相交部分的结果面要素。 2、合并 合并能将两个单独存放的两个要素类的内容,汇集到一个要素类里面。 3、融合 融合能将一个要素类内的所有元素融合成一个整体。 4、裁剪 裁剪需要输入两个面要…...

【Leetcode 热题 100】20. 有效的括号
问题背景 给定一个只包括 ‘(’,‘)’,‘{’,‘}’,‘[’,‘]’ 的字符串 s s s,判断字符串是否有效。 有效字符串需满足: 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。每…...

比较procfs 、 sysctl和Netlink
procfs 文件系统和 sysctl 的使用: procfs 文件系统(/proc) procfs 文件系统是 Linux 内核向用户空间暴露内核数据结构以及配置信息的一种方式。`procfs` 的挂载点是 /proc 目录,这个目录中的文件和目录呈现内核的运行状况和配置信息。通过读写这些文件,可以查看和控制内…...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...

在软件开发中正确使用MySQL日期时间类型的深度解析
在日常软件开发场景中,时间信息的存储是底层且核心的需求。从金融交易的精确记账时间、用户操作的行为日志,到供应链系统的物流节点时间戳,时间数据的准确性直接决定业务逻辑的可靠性。MySQL作为主流关系型数据库,其日期时间类型的…...

【杂谈】-递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战
递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战 文章目录 递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战1、自我改进型人工智能的崛起2、人工智能如何挑战人类监管?3、确保人工智能受控的策略4、人类在人工智能发展中的角色5、平衡自主性与控制力6、总结与…...
指令的指南)
在Ubuntu中设置开机自动运行(sudo)指令的指南
在Ubuntu系统中,有时需要在系统启动时自动执行某些命令,特别是需要 sudo权限的指令。为了实现这一功能,可以使用多种方法,包括编写Systemd服务、配置 rc.local文件或使用 cron任务计划。本文将详细介绍这些方法,并提供…...

【决胜公务员考试】求职OMG——见面课测验1
2025最新版!!!6.8截至答题,大家注意呀! 博主码字不易点个关注吧,祝期末顺利~~ 1.单选题(2分) 下列说法错误的是:( B ) A.选调生属于公务员系统 B.公务员属于事业编 C.选调生有基层锻炼的要求 D…...
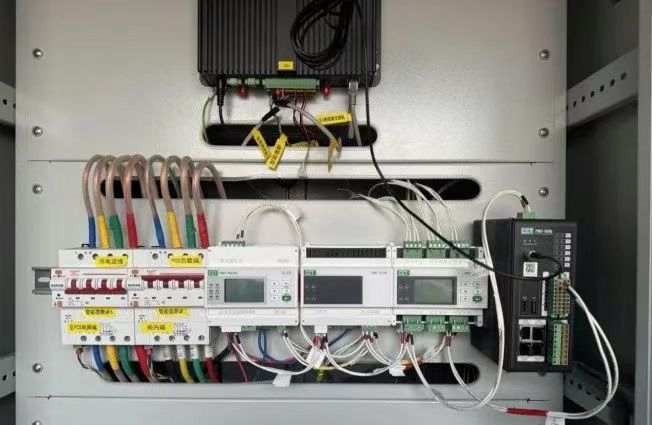
IT供电系统绝缘监测及故障定位解决方案
随着新能源的快速发展,光伏电站、储能系统及充电设备已广泛应用于现代能源网络。在光伏领域,IT供电系统凭借其持续供电性好、安全性高等优势成为光伏首选,但在长期运行中,例如老化、潮湿、隐裂、机械损伤等问题会影响光伏板绝缘层…...

聊一聊接口测试的意义有哪些?
目录 一、隔离性 & 早期测试 二、保障系统集成质量 三、验证业务逻辑的核心层 四、提升测试效率与覆盖度 五、系统稳定性的守护者 六、驱动团队协作与契约管理 七、性能与扩展性的前置评估 八、持续交付的核心支撑 接口测试的意义可以从四个维度展开,首…...

android13 app的触摸问题定位分析流程
一、知识点 一般来说,触摸问题都是app层面出问题,我们可以在ViewRootImpl.java添加log的方式定位;如果是touchableRegion的计算问题,就会相对比较麻烦了,需要通过adb shell dumpsys input > input.log指令,且通过打印堆栈的方式,逐步定位问题,并找到修改方案。 问题…...

python爬虫——气象数据爬取
一、导入库与全局配置 python 运行 import json import datetime import time import requests from sqlalchemy import create_engine import csv import pandas as pd作用: 引入数据解析、网络请求、时间处理、数据库操作等所需库。requests:发送 …...

【Elasticsearch】Elasticsearch 在大数据生态圈的地位 实践经验
Elasticsearch 在大数据生态圈的地位 & 实践经验 1.Elasticsearch 的优势1.1 Elasticsearch 解决的核心问题1.1.1 传统方案的短板1.1.2 Elasticsearch 的解决方案 1.2 与大数据组件的对比优势1.3 关键优势技术支撑1.4 Elasticsearch 的竞品1.4.1 全文搜索领域1.4.2 日志分析…...
