async++源码阅读——task模块
1、task_base.h
本人将自己的理解以注释的形式添加的代码中,方便需要的时候重新复习。该文件中用到的一些技术:
- 该文件中的类并没有使用virtual,而是自定义了需函数表,但是并没有放到每个对象的开始位置,而是通过指针进行存取。
- EBO技术,空类对象本来就占用一个字节的空间,为了节省空间,EBO就是利用这一个字节的空间存储信息
- 对类成员指定内存对齐方式
- 该框架中将一个任务设计成了func和result的组合,task_result用于保存任务的结果而func_holder保存真正执行的函数,而task_func是两者的组合
- template<typename Func, typename = void>,用法在博客中进行了详细介绍
- 这个框架中用到了大量的元编程,感觉很牛逼,本人借助大模型勉强看懂,不知道什么时候能像作者一样,可以熟练的设计一套这样的框架。
// 该枚举是任务的状态,其中比较难理解的是unwrapped
// unwrapped 表示任务处于分解的状态,该任务被分解成了子任务
// completed 和 canceled都表示任务结束状态,一个是正常完成状态,一个是异常取消状态
enum class task_state: unsigned char {pending, // Task has not completed yetlocked, // Task is locked (used by event_task to prevent double set)unwrapped, // Task is waiting for an unwrapped task to finishcompleted, // Task has finished execution and a result is availablecanceled // Task has been canceled and an exception is available
};// Determine whether a task is in a final state
// 判断任务是不是执行完毕
inline bool is_finished(task_state s)
{return s == task_state::completed || s == task_state::canceled;
}// Virtual function table used to allow dynamic dispatch for task objects.
// While this is very similar to what a compiler would generate with virtual
// functions, this scheme was found to result in significantly smaller
// generated code size.
// 自定义的虚函数表
struct task_base_vtable {// Destroy the function and resultvoid (*destroy)(task_base*) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT;// Run the associated functionvoid (*run)(task_base*) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT;// Cancel the task with an exceptionvoid (*cancel)(task_base*, std::exception_ptr&&) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT;// Schedule the task using its schedulervoid (*schedule)(task_base* parent, task_ptr t);
};// Type-generic base task object
// 任务基类
struct task_base_deleter;
struct LIBASYNC_CACHELINE_ALIGN task_base: public ref_count_base<task_base, task_base_deleter> {// Task statestd::atomic<task_state> state;// Whether get_task() was already called on an event_task// 在event类型的任务中使用bool event_task_got_task;// Vector of continuations// 这个任务的后续任务continuation_vector continuations;// Virtual function table used for dynamic dispatchconst task_base_vtable* vtable;// Use aligned memory allocationstatic void* operator new(std::size_t size){return aligned_alloc(size, LIBASYNC_CACHELINE_SIZE);}static void operator delete(void* ptr){aligned_free(ptr);}// Initialize task statetask_base(): state(task_state::pending) {}// Check whether the task is ready and include an acquire barrier if it is// 检查任务是否完成,完成返回true,否则返回falsebool ready() const{return is_finished(state.load(std::memory_order_acquire));}// Run a single continuationtemplate<typename Sched>void run_continuation(Sched& sched, task_ptr&& cont){LIBASYNC_TRY {detail::schedule_task(sched, cont);} LIBASYNC_CATCH(...) {// This is suboptimal, but better than letting the exception leakcont->vtable->cancel(cont.get(), std::current_exception());}}// Run all of the task's continuations after it has completed or canceled.// The list of continuations is emptied and locked to prevent any further// continuations from being added.// 任务执行完后,执行延续任务,执行的时候会锁定队列void run_continuations(){continuations.flush_and_lock([this](task_ptr t) {const task_base_vtable* vtable_ptr = t->vtable;vtable_ptr->schedule(this, std::move(t));});}// Add a continuation to this task// 这个调度器参数只有在当前的任务完成时才有作用template<typename Sched>void add_continuation(Sched& sched, task_ptr cont){// Check for task completion// 当前任务还没有执行完,将延续任务添加到容器// 否则,立马执行延续任务task_state current_state = state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);if (!is_finished(current_state)) {// Try to add the task to the continuation list. This can fail only// if the task has just finished, in which case we run it directly.if (continuations.try_add(std::move(cont)))return;}// Otherwise run the continuation directlystd::atomic_thread_fence(std::memory_order_acquire);run_continuation(sched, std::move(cont));}// Finish the task after it has been executed and the result set// 当前任务结束时需要调用的函数,当前任务结束后,执行后续任务void finish(){state.store(task_state::completed, std::memory_order_release);run_continuations();}// Wait for the task to finish executing// 等待当前任务执行结束task_state wait(){task_state s = state.load(std::memory_order_acquire);if (!is_finished(s)) {wait_for_task(this);s = state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);}return s;}
};// Deleter for task_ptr
struct task_base_deleter {static void do_delete(task_base* p){// Go through the vtable to delete p with its proper typep->vtable->destroy(p);}
};// Result type-specific task object
// 定义了一个可以持有任务结果的任务
template<typename Result>
struct task_result_holder: public task_base {union {alignas(Result) std::uint8_t result[sizeof(Result)];alignas(std::exception_ptr) std::uint8_t except[sizeof(std::exception_ptr)];// Scheduler that should be used to schedule this task. The scheduler// type has been erased and is held by vtable->schedule.void* sched;};template<typename T>void set_result(T&& t){new(&result) Result(std::forward<T>(t));}// Return a result using an lvalue or rvalue reference depending on the task// type. The task parameter is not used, it is just there for overload resolution.// 这里的参数没有使用,作用就是用来指明重载版本template<typename T>Result&& get_result(const task<T>&){return std::move(*reinterpret_cast<Result*>(&result));}template<typename T>const Result& get_result(const shared_task<T>&){return *reinterpret_cast<Result*>(&result);}// Destroy the result~task_result_holder(){// Result is only present if the task completed successfullyif (state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == task_state::completed)reinterpret_cast<Result*>(&result)->~Result();}
};// Specialization for references
// 特化版本
template<typename Result>
struct task_result_holder<Result&>: public task_base {union {// Store as pointer internallyResult* result;alignas(std::exception_ptr) std::uint8_t except[sizeof(std::exception_ptr)];void* sched;};void set_result(Result& obj){result = std::addressof(obj);}template<typename T>Result& get_result(const task<T>&){return *result;}template<typename T>Result& get_result(const shared_task<T>&){return *result;}
};// Specialization for void
template<>
struct task_result_holder<fake_void>: public task_base {union {alignas(std::exception_ptr) std::uint8_t except[sizeof(std::exception_ptr)];void* sched;};void set_result(fake_void) {}// Get the result as fake_void so that it can be passed to set_result and// continuationstemplate<typename T>fake_void get_result(const task<T>&){return fake_void();}template<typename T>fake_void get_result(const shared_task<T>&){return fake_void();}
};
// 外层类,持有结果的任务类
template<typename Result>
struct task_result: public task_result_holder<Result> {// Virtual function table for task_resultstatic const task_base_vtable vtable_impl;task_result(){this->vtable = &vtable_impl;}// Destroy the exception~task_result(){// Exception is only present if the task was canceledif (this->state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == task_state::canceled)reinterpret_cast<std::exception_ptr*>(&this->except)->~exception_ptr();}// Cancel a task with the given exception// 取消任务,并且设置指定异常void cancel_base(std::exception_ptr&& except_){set_exception(std::move(except_));this->state.store(task_state::canceled, std::memory_order_release);this->run_continuations();}// Set the exception value of the taskvoid set_exception(std::exception_ptr&& except_){new(&this->except) std::exception_ptr(std::move(except_));}// Get the exception a task was canceled withstd::exception_ptr& get_exception(){return *reinterpret_cast<std::exception_ptr*>(&this->except);}// Wait and throw the exception if the task was canceled// 该框架中任务的取消都是因为设置了异常void wait_and_throw(){if (this->wait() == task_state::canceled)LIBASYNC_RETHROW_EXCEPTION(get_exception());}// Delete the task using its proper type// 因为是union,因此只需要销毁Result即可static void destroy(task_base* t) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT{delete static_cast<task_result<Result>*>(t);}
};
template<typename Result>
const task_base_vtable task_result<Result>::vtable_impl = {task_result<Result>::destroy, // destroynullptr, // runnullptr, // cancelnullptr // schedule
};// Class to hold a function object, with empty base class optimization
// 这是一个具有默认类型 void 的模板参数,通常用来配合 SFINAE 来决定是否启用某个特定的模板实例化
template<typename Func, typename = void>
struct func_base {Func func;template<typename F>explicit func_base(F&& f): func(std::forward<F>(f)) {}Func& get_func(){return func;}
};
// 特化版本
// 这种特化通过 空基类优化(EBO)减少了内存开销。
// 对于没有成员变量的类型(如空结构体),通过将 Func 对象直接存储在func_base 的内部内存中,可以避免额外的内存分配。
template<typename Func>
struct func_base<Func, typename std::enable_if<std::is_empty<Func>::value>::type> {template<typename F>explicit func_base(F&& f){new(this) Func(std::forward<F>(f));}~func_base(){get_func().~Func();}Func& get_func(){return *reinterpret_cast<Func*>(this);}
};// Class to hold a function object and initialize/destroy it at any time
template<typename Func, typename = void>
struct func_holder {alignas(Func) std::uint8_t func[sizeof(Func)];Func& get_func(){return *reinterpret_cast<Func*>(&func);}template<typename... Args>void init_func(Args&&... args){new(&func) Func(std::forward<Args>(args)...);}void destroy_func(){get_func().~Func();}
};
template<typename Func>
struct func_holder<Func, typename std::enable_if<std::is_empty<Func>::value>::type> {Func& get_func(){return *reinterpret_cast<Func*>(this);}template<typename... Args>void init_func(Args&&... args){new(this) Func(std::forward<Args>(args)...);}void destroy_func(){get_func().~Func();}
};// Task object with an associated function object
// Using private inheritance so empty Func doesn't take up space
// 这个结构体才是拥有func、任务状态、任务结果的结构体
template<typename Sched, typename Func, typename Result>
struct task_func: public task_result<Result>, func_holder<Func> {// Virtual function table for task_funcstatic const task_base_vtable vtable_impl;template<typename... Args>explicit task_func(Args&&... args){this->vtable = &vtable_impl;this->init_func(std::forward<Args>(args)...);}// Run the stored function// 执行对应的任务,其实t指向的是task_func<Sched, Func, Result>类型// Func在编译的时候也已经确定,执行任务t,并将结果放到t中(只不过这部分由上层实现,模板使用方)static void run(task_base* t) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT{LIBASYNC_TRY {// Dispatch to execution functionstatic_cast<task_func<Sched, Func, Result>*>(t)->get_func()(t);} LIBASYNC_CATCH(...) {cancel(t, std::current_exception());}}// Cancel the taskstatic void cancel(task_base* t, std::exception_ptr&& except) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT{// Destroy the function object when canceling since it won't be// used anymore.static_cast<task_func<Sched, Func, Result>*>(t)->destroy_func();static_cast<task_func<Sched, Func, Result>*>(t)->cancel_base(std::move(except));}// Schedule a continuation task using its scheduler// 当当前任务执行完后,执行任务tstatic void schedule(task_base* parent, task_ptr t){void* sched = static_cast<task_func<Sched, Func, Result>*>(t.get())->sched;parent->run_continuation(*static_cast<Sched*>(sched), std::move(t));}// Free the function~task_func(){// If the task hasn't completed yet, destroy the function object. Note// that an unwrapped task has already destroyed its function object.if (this->state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == task_state::pending)this->destroy_func();}// Delete the task using its proper typestatic void destroy(task_base* t) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT{delete static_cast<task_func<Sched, Func, Result>*>(t);}
};
template<typename Sched, typename Func, typename Result>
const task_base_vtable task_func<Sched, Func, Result>::vtable_impl = {task_func<Sched, Func, Result>::destroy, // destroytask_func<Sched, Func, Result>::run, // runtask_func<Sched, Func, Result>::cancel, // canceltask_func<Sched, Func, Result>::schedule // schedule
};// Helper functions to access the internal_task member of a task object, which
// avoids us having to specify half of the functions in the detail namespace
// as friend. Also, internal_task is downcast to the appropriate task_result<>.
template<typename Task>
typename Task::internal_task_type* get_internal_task(const Task& t)
{return static_cast<typename Task::internal_task_type*>(t.internal_task.get());
}
template<typename Task>
void set_internal_task(Task& t, task_ptr p)
{t.internal_task = std::move(p);
}// Common code for task unwrapping
template<typename Result, typename Child>
struct unwrapped_func {explicit unwrapped_func(task_ptr t): parent_task(std::move(t)) {}// 这个函数在子任务执行完成的时候执行,主要的作用是将子任务的执行结果和父任务关联,设置到父任务中去。void operator()(Child child_task) const{// Forward completion state and result to parent tasktask_result<Result>* parent = static_cast<task_result<Result>*>(parent_task.get());LIBASYNC_TRY {if (get_internal_task(child_task)->state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == task_state::completed) {parent->set_result(get_internal_task(child_task)->get_result(child_task));parent->finish();} else {// We don't call the generic cancel function here because// the function of the parent task has already been destroyed.parent->cancel_base(std::exception_ptr(get_internal_task(child_task)->get_exception()));}} LIBASYNC_CATCH(...) {// If the copy/move constructor of the result threw, propagate the exceptionparent->cancel_base(std::current_exception());}}task_ptr parent_task;
};
// Sched:调度器类型
// Result:父任务的结果类型
// Func:父任务执行的函数类型
// Child:子任务类型
// 该函数的主要作用是将设置父任务的状态,并将父任务和子任务结果
template<typename Sched, typename Result, typename Func, typename Child>
void unwrapped_finish(task_base* parent_base, Child child_task)
{// Destroy the parent task's function since it has been executed// 执行到这里父任务已经执行完毕,只需要让其等待子任务执行的结果parent_base->state.store(task_state::unwrapped, std::memory_order_relaxed);static_cast<task_func<Sched, Func, Result>*>(parent_base)->destroy_func();// Set up a continuation on the child to set the result of the parentLIBASYNC_TRY {parent_base->add_ref();// 设置子任务的延续,使得子任务完成后能够通过 unwrapped_func传递结果给父任务。then 是一个常见的延续函数,它会在子任务完成时触发child_task.then(inline_scheduler(), unwrapped_func<Result, Child>(task_ptr(parent_base)));} LIBASYNC_CATCH(...) {// Use cancel_base here because the function object is already destroyed.static_cast<task_result<Result>*>(parent_base)->cancel_base(std::current_exception());}
}// Execution functions for root tasks:
// - With and without task unwraping
// Sched:调度器类型,定义任务调度的策略。
// Result:任务的返回类型,即执行该任务后得到的结果类型。
// Func:任务执行的函数类型或可调用对象类型。
// Unwrap:布尔类型参数,决定任务是否会进行解包(unwrap)
// 我理解poerator()参数中task_base中static_cast<task_func<Sched, root_exec_func, Result>*>(t)指向的
// Func对象,就是的当前this的this->get_func()
template<typename Sched, typename Result, typename Func, bool Unwrap>
struct root_exec_func: private func_base<Func> {template<typename F>explicit root_exec_func(F&& f): func_base<Func>(std::forward<F>(f)) {}void operator()(task_base* t){static_cast<task_result<Result>*>(t)->set_result(detail::invoke_fake_void(std::move(this->get_func())));static_cast<task_func<Sched, root_exec_func, Result>*>(t)->destroy_func();t->finish();}
};
// 特化版本,需要任务分包,其中构造函数中的任务是子任务,operator中的参数是父任务
// 会将子任务的结果设置给父任务
// 我理解poerator()参数中task_base中static_cast<task_func<Sched, root_exec_func, Result>*>(t)指向的
// Func对象是父任务,而this->get_func()是分解出来的任务
template<typename Sched, typename Result, typename Func>
struct root_exec_func<Sched, Result, Func, true>: private func_base<Func> {template<typename F>explicit root_exec_func(F&& f): func_base<Func>(std::forward<F>(f)) {}void operator()(task_base* t){unwrapped_finish<Sched, Result, root_exec_func>(t, std::move(this->get_func())());}
};// Execution functions for continuation tasks:
// - With and without task unwraping
// - For void, value-based and task-based continuations
// Sched:调度器类型,决定任务如何调度。
// Parent:父任务类型,即当前任务的前驱任务。
// Result:父任务的结果类型,后续任务会使用该结果。
// Func:后续任务执行的函数类型(即任务的函数体)。
// ValueCont 表示后续任务是否需要父任务的返回值做参数
// Unwrap:用于指示是否需要解包父任务的结果。true 表示需要解包,false 表示不需要解包。
template<typename Sched, typename Parent, typename Result, typename Func, typename ValueCont, bool Unwrap>
struct continuation_exec_func: private func_base<Func> {template<typename F, typename P>continuation_exec_func(F&& f, P&& p): func_base<Func>(std::forward<F>(f)), parent(std::forward<P>(p)) {}void operator()(task_base* t){static_cast<task_result<Result>*>(t)->set_result(detail::invoke_fake_void(std::move(this->get_func()), std::move(parent)));static_cast<task_func<Sched, continuation_exec_func, Result>*>(t)->destroy_func();t->finish();}Parent parent;
};
// 当任务有值返回,并且不需要解包时,执行函数根据父任务的结果设置当前任务的结果。如果父任务已被取消,则取消当前任务。
template<typename Sched, typename Parent, typename Result, typename Func>
struct continuation_exec_func<Sched, Parent, Result, Func, std::true_type, false>: private func_base<Func> {template<typename F, typename P>continuation_exec_func(F&& f, P&& p): func_base<Func>(std::forward<F>(f)), parent(std::forward<P>(p)) {}void operator()(task_base* t){if (get_internal_task(parent)->state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == task_state::canceled)task_func<Sched, continuation_exec_func, Result>::cancel(t, std::exception_ptr(get_internal_task(parent)->get_exception()));else {static_cast<task_result<Result>*>(t)->set_result(detail::invoke_fake_void(std::move(this->get_func()), get_internal_task(parent)->get_result(parent)));static_cast<task_func<Sched, continuation_exec_func, Result>*>(t)->destroy_func();t->finish();}}Parent parent;
};template<typename Sched, typename Parent, typename Result, typename Func>
struct continuation_exec_func<Sched, Parent, Result, Func, fake_void, false>: private func_base<Func> {template<typename F, typename P>continuation_exec_func(F&& f, P&& p): func_base<Func>(std::forward<F>(f)), parent(std::forward<P>(p)) {}void operator()(task_base* t){if (get_internal_task(parent)->state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == task_state::canceled)task_func<Sched, continuation_exec_func, Result>::cancel(t, std::exception_ptr(get_internal_task(parent)->get_exception()));else {static_cast<task_result<Result>*>(t)->set_result(detail::invoke_fake_void(std::move(this->get_func()), fake_void()));static_cast<task_func<Sched, continuation_exec_func, Result>*>(t)->destroy_func();t->finish();}}Parent parent;
};
// 当需要解包父任务的结果时,且父任务没有值返回时,执行函数将父任务的结果传递给后续任务。
template<typename Sched, typename Parent, typename Result, typename Func>
struct continuation_exec_func<Sched, Parent, Result, Func, std::false_type, true>: private func_base<Func> {template<typename F, typename P>continuation_exec_func(F&& f, P&& p): func_base<Func>(std::forward<F>(f)), parent(std::forward<P>(p)) {}void operator()(task_base* t){unwrapped_finish<Sched, Result, continuation_exec_func>(t, detail::invoke_fake_void(std::move(this->get_func()), std::move(parent)));}Parent parent;
};
// 需要解包且有返回值的情况。它会解包父任务的结果,并使用该结果来设置当前任务的结果。
template<typename Sched, typename Parent, typename Result, typename Func>
struct continuation_exec_func<Sched, Parent, Result, Func, std::true_type, true>: private func_base<Func> {template<typename F, typename P>continuation_exec_func(F&& f, P&& p): func_base<Func>(std::forward<F>(f)), parent(std::forward<P>(p)) {}void operator()(task_base* t){if (get_internal_task(parent)->state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == task_state::canceled)task_func<Sched, continuation_exec_func, Result>::cancel(t, std::exception_ptr(get_internal_task(parent)->get_exception()));elseunwrapped_finish<Sched, Result, continuation_exec_func>(t, detail::invoke_fake_void(std::move(this->get_func()), get_internal_task(parent)->get_result(parent)));}Parent parent;
};
template<typename Sched, typename Parent, typename Result, typename Func>
struct continuation_exec_func<Sched, Parent, Result, Func, fake_void, true>: private func_base<Func> {template<typename F, typename P>continuation_exec_func(F&& f, P&& p): func_base<Func>(std::forward<F>(f)), parent(std::forward<P>(p)) {}void operator()(task_base* t){if (get_internal_task(parent)->state.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == task_state::canceled)task_func<Sched, continuation_exec_func, Result>::cancel(t, std::exception_ptr(get_internal_task(parent)->get_exception()));elseunwrapped_finish<Sched, Result, continuation_exec_func>(t, detail::invoke_fake_void(std::move(this->get_func()), fake_void()));}Parent parent;
};
2、task.h
废话不多说,直接看注释:
namespace detail {// Common code for task and shared_task
// basic_task 主要对task_base进行了封装,
template<typename Result>
class basic_task {// Reference counted internal task objectdetail::task_ptr internal_task;// Real result type, with void turned into fake_voidtypedef typename void_to_fake_void<Result>::type internal_result;// Type-specific task objecttypedef task_result<internal_result> internal_task_type;// Friend accessfriend async::task<Result>;friend async::shared_task<Result>;template<typename T>friend typename T::internal_task_type* get_internal_task(const T& t);template<typename T>friend void set_internal_task(T& t, task_ptr p);// Common code for get()// 这里也会等待任务结束void get_internal() const{LIBASYNC_ASSERT(internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty task object");// If the task was canceled, throw the associated exceptionget_internal_task(*this)->wait_and_throw();}// Common code for then()template<typename Sched, typename Func, typename Parent>// 返回的仍然是一个任务,可以继续使用thentypename continuation_traits<Parent, Func>::task_type then_internal(Sched& sched, Func&& f, Parent&& parent) const{LIBASYNC_ASSERT(internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty task object");// Save a copy of internal_task because it might get moved into exec_functask_base* my_internal = internal_task.get();// Create continuationtypedef continuation_traits<Parent, Func> traits;typedef typename void_to_fake_void<typename traits::task_type::result_type>::type cont_internal_result;typedef continuation_exec_func<Sched, typename std::decay<Parent>::type, cont_internal_result, typename traits::decay_func, typename traits::is_value_cont, is_task<typename traits::result_type>::value> exec_func;typename traits::task_type cont;// 创建一个新的task,并将新创建的任务放到当前任务的后续任务队列set_internal_task(cont, task_ptr(new task_func<Sched, exec_func, cont_internal_result>(std::forward<Func>(f), std::forward<Parent>(parent))));// Add the continuation to this task// Avoid an expensive ref-count modification since the task isn't shared yetget_internal_task(cont)->add_ref_unlocked();get_internal_task(cont)->sched = std::addressof(sched);my_internal->add_continuation(sched, task_ptr(get_internal_task(cont)));return cont;}public:// Task result typetypedef Result result_type;// Check if this task is not emptybool valid() const{return internal_task != nullptr;}// Query whether the task has finished executingbool ready() const{LIBASYNC_ASSERT(internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty task object");return internal_task->ready();}// Query whether the task has been canceled with an exceptionbool canceled() const{LIBASYNC_ASSERT(internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty task object");return internal_task->state.load(std::memory_order_acquire) == task_state::canceled;}// Wait for the task to completevoid wait() const{LIBASYNC_ASSERT(internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty task object");internal_task->wait();}// Get the exception associated with a canceled task// 这里会等待任务执行std::exception_ptr get_exception() const{LIBASYNC_ASSERT(internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty task object");if (internal_task->wait() == task_state::canceled)return get_internal_task(*this)->get_exception();elsereturn std::exception_ptr();}
};// Common code for event_task specializations
// 定义事件,用户可以使用接口从事件获得task<Result>,可以用于存储任务结果
template<typename Result>
class basic_event {// Reference counted internal task objectdetail::task_ptr internal_task;// Real result type, with void turned into fake_voidtypedef typename detail::void_to_fake_void<Result>::type internal_result;// Type-specific task objecttypedef detail::task_result<internal_result> internal_task_type;// Friend accessfriend async::event_task<Result>;template<typename T>friend typename T::internal_task_type* get_internal_task(const T& t);// Common code for set()template<typename T>// 将事件的结果关联到成员对象对应的位置bool set_internal(T&& result) const{LIBASYNC_ASSERT(internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty event_task object");// Only allow setting the value oncedetail::task_state expected = detail::task_state::pending;if (!internal_task->state.compare_exchange_strong(expected, detail::task_state::locked, std::memory_order_acquire, std::memory_order_relaxed))return false;LIBASYNC_TRY {// Store the result and finishget_internal_task(*this)->set_result(std::forward<T>(result));internal_task->finish();} LIBASYNC_CATCH(...) {// At this point we have already committed to setting a value, so// we can't return the exception to the caller. If we did then it// could cause concurrent set() calls to fail, thinking a value has// already been set. Instead, we simply cancel the task with the// exception we just got.get_internal_task(*this)->cancel_base(std::current_exception());}return true;}public:// Movable but not copyablebasic_event(basic_event&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT: internal_task(std::move(other.internal_task)) {}basic_event& operator=(basic_event&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT{internal_task = std::move(other.internal_task);return *this;}// Main constructorbasic_event(): internal_task(new internal_task_type){internal_task->event_task_got_task = false;}// Cancel events if they are destroyed before they are set~basic_event(){// This check isn't thread-safe but set_exception does a proper checkif (internal_task && !internal_task->ready() && !internal_task->is_unique_ref(std::memory_order_relaxed)) {
#ifdef LIBASYNC_NO_EXCEPTIONS// This will result in an abort if the task result is readset_exception(std::exception_ptr());
#elseset_exception(std::make_exception_ptr(abandoned_event_task()));
#endif}}// Get the task linked to this event. This can only be called once.// 事件只能被取走一次task<Result> get_task(){LIBASYNC_ASSERT(internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty event_task object");LIBASYNC_ASSERT(!internal_task->event_task_got_task, std::logic_error, "get_task() called twice on event_task");// Even if we didn't trigger an assert, don't return a task if one has// already been returned.task<Result> out;if (!internal_task->event_task_got_task)set_internal_task(out, internal_task);internal_task->event_task_got_task = true;return out;}// Cancel the event with an exception and cancel continuations// 将异常结果关联到成员对象对应的位置bool set_exception(std::exception_ptr except) const{LIBASYNC_ASSERT(internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty event_task object");// Only allow setting the value oncedetail::task_state expected = detail::task_state::pending;if (!internal_task->state.compare_exchange_strong(expected, detail::task_state::locked, std::memory_order_acquire, std::memory_order_relaxed))return false;// Cancel the taskget_internal_task(*this)->cancel_base(std::move(except));return true;}
};} // namespace detailtemplate<typename Result>
class task: public detail::basic_task<Result> {
public:// Movable but not copyabletask() = default;task(task&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT: detail::basic_task<Result>(std::move(other)) {}task& operator=(task&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT{detail::basic_task<Result>::operator=(std::move(other));return *this;}// Get the result of the task// 等待任务执行完,并获取结果,我理解这是使用了移动语义,取一次后,任务结果就被释放了Result get(){this->get_internal();// Move the internal state pointer so that the task becomes invalid,// even if an exception is thrown.detail::task_ptr my_internal = std::move(this->internal_task);return detail::fake_void_to_void(static_cast<typename task::internal_task_type*>(my_internal.get())->get_result(*this));}// Add a continuation to the task// 为当前任务添加一个子任务template<typename Sched, typename Func>typename detail::continuation_traits<task, Func>::task_type then(Sched& sched, Func&& f){return this->then_internal(sched, std::forward<Func>(f), std::move(*this));}// 为当前任务添加一个子任务,使用默认调度器,调度任务template<typename Func>typename detail::continuation_traits<task, Func>::task_type then(Func&& f){return then(::async::default_scheduler(), std::forward<Func>(f));}// Create a shared_task from this taskshared_task<Result> share(){LIBASYNC_ASSERT(this->internal_task, std::invalid_argument, "Use of empty task object");shared_task<Result> out;detail::set_internal_task(out, std::move(this->internal_task));return out;}
};template<typename Result>
class shared_task: public detail::basic_task<Result> {// get() return value: const Result& -or- voidtypedef typename std::conditional<std::is_void<Result>::value,void,typename std::add_lvalue_reference<typename std::add_const<Result>::type>::type>::type get_result;public:// Movable and copyableshared_task() = default;// Get the result of the task// 这里的任务结果可以多次获取get_result get() const{this->get_internal();return detail::fake_void_to_void(detail::get_internal_task(*this)->get_result(*this));}// Add a continuation to the task// 为当前任务添加一个子任务template<typename Sched, typename Func>typename detail::continuation_traits<shared_task, Func>::task_type then(Sched& sched, Func&& f) const{return this->then_internal(sched, std::forward<Func>(f), *this);}// 为当前任务添加一个子任务,使用默认调度器,调度任务template<typename Func>typename detail::continuation_traits<shared_task, Func>::task_type then(Func&& f) const{return then(::async::default_scheduler(), std::forward<Func>(f));}
};// Special task type which can be triggered manually rather than when a function executes.
// 手动触发的事件任务
template<typename Result>
class event_task: public detail::basic_event<Result> {
public:// Movable but not copyableevent_task() = default;event_task(event_task&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT: detail::basic_event<Result>(std::move(other)) {}event_task& operator=(event_task&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT{detail::basic_event<Result>::operator=(std::move(other));return *this;}// Set the result of the task, mark it as completed and run its continuationsbool set(const Result& result) const{return this->set_internal(result);}bool set(Result&& result) const{return this->set_internal(std::move(result));}
};// Specialization for references
template<typename Result>
class event_task<Result&>: public detail::basic_event<Result&> {
public:// Movable but not copyableevent_task() = default;event_task(event_task&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT: detail::basic_event<Result&>(std::move(other)) {}event_task& operator=(event_task&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT{detail::basic_event<Result&>::operator=(std::move(other));return *this;}// Set the result of the task, mark it as completed and run its continuationsbool set(Result& result) const{return this->set_internal(result);}
};// Specialization for void
template<>
class event_task<void>: public detail::basic_event<void> {
public:// Movable but not copyableevent_task() = default;event_task(event_task&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT: detail::basic_event<void>(std::move(other)) {}event_task& operator=(event_task&& other) LIBASYNC_NOEXCEPT{detail::basic_event<void>::operator=(std::move(other));return *this;}// Set the result of the task, mark it as completed and run its continuationsbool set(){return this->set_internal(detail::fake_void());}
};// Task type returned by local_spawn()
template<typename Sched, typename Func>
class local_task {// Make sure the function type is callabletypedef typename std::decay<Func>::type decay_func;static_assert(detail::is_callable<decay_func()>::value, "Invalid function type passed to local_spawn()");// Task result typetypedef typename detail::remove_task<decltype(std::declval<decay_func>()())>::type result_type;typedef typename detail::void_to_fake_void<result_type>::type internal_result;// Task execution function typetypedef detail::root_exec_func<Sched, internal_result, decay_func, detail::is_task<decltype(std::declval<decay_func>()())>::value> exec_func;// Task object embedded directly. The ref-count is initialized to 1 so it// will never be freed using delete, only when the local_task is destroyed.detail::task_func<Sched, exec_func, internal_result> internal_task;// Friend access for local_spawntemplate<typename S, typename F>friend local_task<S, F> local_spawn(S& sched, F&& f);template<typename F>friend local_task<detail::default_scheduler_type, F> local_spawn(F&& f);// Constructor, used by local_spawnlocal_task(Sched& sched, Func&& f): internal_task(std::forward<Func>(f)){// Avoid an expensive ref-count modification since the task isn't shared yetinternal_task.add_ref_unlocked();detail::schedule_task(sched, detail::task_ptr(&internal_task));}public:// Non-movable and non-copyablelocal_task(const local_task&) = delete;local_task& operator=(const local_task&) = delete;// Wait for the task to complete when destroying~local_task(){wait();// Now spin until the reference count drops to 1, since the scheduler// may still have a reference to the task.while (!internal_task.is_unique_ref(std::memory_order_acquire)) {
#if defined(__GLIBCXX__) && __GLIBCXX__ <= 20140612// Some versions of libstdc++ (4.7 and below) don't include a// definition of std::this_thread::yield().sched_yield();
#elsestd::this_thread::yield();
#endif}}// Query whether the task has finished executingbool ready() const{return internal_task.ready();}// Query whether the task has been canceled with an exceptionbool canceled() const{return internal_task.state.load(std::memory_order_acquire) == detail::task_state::canceled;}// Wait for the task to completevoid wait(){internal_task.wait();}// Get the result of the taskresult_type get(){internal_task.wait_and_throw();return detail::fake_void_to_void(internal_task.get_result(task<result_type>()));}// Get the exception associated with a canceled taskstd::exception_ptr get_exception() const{if (internal_task.wait() == detail::task_state::canceled)return internal_task.get_exception();elsereturn std::exception_ptr();}
};// Spawn a function asynchronously
#if (__cplusplus >= 201703L)
// Use std::invoke_result instead of std::result_of for C++17 or greater because std::result_of was deprecated in C++17 and removed in C++20
template<typename Sched, typename Func>
task<typename detail::remove_task<std::invoke_result_t<std::decay_t<Func>>>::type> spawn(Sched& sched, Func&& f)
#else
// 如果 Func 是一个函数类型(比如 void(int)),则 std::decay<Func>::type 会变成一个对应的函数指针类型(比如 void (*)(int))
// 这个返回其实是一个task<Result> 这样一个对象,这其中包含了任务,执行结果等信息
// 这个模板的函数的作用是用于创建并调度一个异步任务。
template<typename Sched, typename Func>
task<typename detail::remove_task<typename std::result_of<typename std::decay<Func>::type()>::type>::type> spawn(Sched& sched, Func&& f)
#endif
{// Using result_of in the function return type to work around bugs in the Intel// C++ compiler.// Make sure the function type is callabletypedef typename std::decay<Func>::type decay_func;static_assert(detail::is_callable<decay_func()>::value, "Invalid function type passed to spawn()");// Create tasktypedef typename detail::void_to_fake_void<typename detail::remove_task<decltype(std::declval<decay_func>()())>::type>::type internal_result;typedef detail::root_exec_func<Sched, internal_result, decay_func, detail::is_task<decltype(std::declval<decay_func>()())>::value> exec_func;task<typename detail::remove_task<decltype(std::declval<decay_func>()())>::type> out;detail::set_internal_task(out, detail::task_ptr(new detail::task_func<Sched, exec_func, internal_result>(std::forward<Func>(f))));// Avoid an expensive ref-count modification since the task isn't shared yetdetail::get_internal_task(out)->add_ref_unlocked();detail::schedule_task(sched, detail::task_ptr(detail::get_internal_task(out)));return out;
}
// 使用默认的调度器,返回值类型是使用decltype进行推导的
template<typename Func>
decltype(async::spawn(::async::default_scheduler(), std::declval<Func>())) spawn(Func&& f)
{return async::spawn(::async::default_scheduler(), std::forward<Func>(f));
}// Create a completed task containing a value
// make_task 这些函数用于创建已经完成的任务,并将结果或异常存储在任务对象中。
// 我认为目的是为了创建一个统一的对象,将结果放到对应位置,然后返回
template<typename T>
task<typename std::decay<T>::type> make_task(T&& value)
{task<typename std::decay<T>::type> out;detail::set_internal_task(out, detail::task_ptr(new detail::task_result<typename std::decay<T>::type>));detail::get_internal_task(out)->set_result(std::forward<T>(value));detail::get_internal_task(out)->state.store(detail::task_state::completed, std::memory_order_relaxed);return out;
}
template<typename T>
task<T&> make_task(std::reference_wrapper<T> value)
{task<T&> out;detail::set_internal_task(out, detail::task_ptr(new detail::task_result<T&>));detail::get_internal_task(out)->set_result(value.get());detail::get_internal_task(out)->state.store(detail::task_state::completed, std::memory_order_relaxed);return out;
}
inline task<void> make_task()
{task<void> out;detail::set_internal_task(out, detail::task_ptr(new detail::task_result<detail::fake_void>));detail::get_internal_task(out)->state.store(detail::task_state::completed, std::memory_order_relaxed);return out;
}// Create a canceled task containing an exception
template<typename T>
task<T> make_exception_task(std::exception_ptr except)
{task<T> out;detail::set_internal_task(out, detail::task_ptr(new detail::task_result<typename detail::void_to_fake_void<T>::type>));detail::get_internal_task(out)->set_exception(std::move(except));detail::get_internal_task(out)->state.store(detail::task_state::canceled, std::memory_order_relaxed);return out;
}// Spawn a very limited task which is restricted to the current function and
// joins on destruction. Because local_task is not movable, the result must
// be captured in a reference, like this:
// auto&& x = local_spawn(...);
template<typename Sched, typename Func>
#ifdef __GNUC__
__attribute__((warn_unused_result))
#endif
// 局部任务与普通任务不同,局部任务的生命周期受限于当前函数,任务对象在创建后不能移动。
// 局部任务通常用于在当前函数范围内执行一个任务,且确保任务在函数退出时完成。
local_task<Sched, Func> local_spawn(Sched& sched, Func&& f)
{// Since local_task is not movable, we construct it in-place and let the// caller extend the lifetime of the returned object using a reference.return {sched, std::forward<Func>(f)};
}
template<typename Func>
#ifdef __GNUC__
__attribute__((warn_unused_result))
#endif
local_task<detail::default_scheduler_type, Func> local_spawn(Func&& f)
{return {::async::default_scheduler(), std::forward<Func>(f)};
}
相关文章:

async++源码阅读——task模块
1、task_base.h 本人将自己的理解以注释的形式添加的代码中,方便需要的时候重新复习。该文件中用到的一些技术: 该文件中的类并没有使用virtual,而是自定义了需函数表,但是并没有放到每个对象的开始位置,而是通过指针…...

项目开发实践——基于SpringBoot+Vue3实现的在线考试系统(五)
文章目录 一、学生管理模块功能实现1、添加学生功能实现1.1 页面设计1.2 前端功能实现1.3 后端功能实现1.4 效果展示2、学生管理功能实现2.1 页面设计2.2 前端功能实现2.3 后端功能实现2.3.1 后端查询接口实现2.3.2 后端编辑接口实现2.3.3 后端删除接口实现2.4 效果展示二、代码…...

EF Core一对一和多对多
目录 EF Core一对一 关系属性 关系配置 使用 EF Core多对多 关系属性 关系配置 使用 EF Core一对一 关系属性 必须显式的在其中一个实体类中声明一个外键属性,可以在Order建立Delivery,也可以在Delivery建立OrderId class Order {public long…...

记一次sealos部署k8s集群之delete了第一台master如何恢复
记一次sealos部署k8s集群之delete了第一台master如何恢复 一、背景描述 使用sealos部署了一套K8S集群 master信息:172.27.100.1、172.27.100.2、172.27.100.3 node信息:172.27.100.4、172.27.100.5 sealos安装在172.27.100.1节点,根目录下/root/.sealos/文件还在! [root…...

vue3+vite+ts集成第三方js
npm run dev可以正常运行和测试。但是npm run build会报错。 要实现引入静态js,避免使用全局变量报错。 1. HTML 引入第三方 JS 在你的 HTML 文件中,通过 <script> 标签引入一个本地第三方 JS 文件,例如: <script sr…...

android framework.jar 在应用中使用
在开发APP中,有时会使用系统提供的framework.jar 来替代 android.jar, 在gradle中配置如下: 放置framework.jar 依赖配置 3 优先级配置 gradle.projectsEvaluated {tasks.withType(JavaCompile) {Set<File> fileSet options.bootstrapClasspat…...

FFmpeg入门
在音视频处理领域,有一款神器级的工具横扫开发者圈,那就是 FFmpeg。它被誉为“音视频处理的瑞士军刀”,凭借强大的功能和开源的特性成为众多开发者和媒体从业者的首选。今天,我们就来聊聊 FFmpeg 的入门使用,带你轻松开…...

云平台一键部署【Video-Background-Removal】视频换背景,无任何限制,随意换
Video-Background-Removal 是一款革命性的视频背景替换工具,旨在让用户轻松实现视频背景的快速更换。无论你是专业创作者还是普通用户,这款软件都能让你在几秒钟内改变背景,完全消除限制,随心所欲,随时随地想换就换&am…...

量子计算:从薛定谔的猫到你的生活
文章背景 说到量子计算,不少人觉得它神秘又遥不可及。其实,它只是量子物理学的一个“应用小分支”。它的核心在于量子比特的“叠加”和“纠缠”,这些听上去像科幻小说的概念,却为计算世界开辟了一片全新的天地。如果经典计算是“…...

51单片机——I2C-EEPROM
I2C:总线标准或通信协议 EEPROM:AT24C02芯片 开发板板载了1个EEPROM模块,可实现IIC通信 1、EEPROM模块电路(AT24C02) 芯片的SCL和SDA管脚是连接在单片机的P2.1和P2.0上 2、I2C介绍 I2C(Interÿ…...

R语言的语法糖
R语言的语法糖 引言 在编程语言中,所谓的“语法糖”是指那些使得程序员能够以更简洁、直观的方式书写代码的语法形式。R语言作为一种用于统计分析和数据可视化的编程语言,具有丰富的功能和灵活的语法。本文将深入探讨R语言中的语法糖,帮助读…...
和线性筛(Linear Sieve))
【算法学习笔记】30:埃氏筛(Sieve of Eratosthenes)和线性筛(Linear Sieve)
测试题目:AcWing 868. 筛质数 埃氏筛(Sieve of Eratosthenes) 如果 i i i是素数,每次把 i i i的倍数都筛掉,存在重复筛选,时间复杂度 n ⋅ l o g ( l o g n ) n \cdot log(logn) n⋅log(logn)。 #includ…...

【AscendC】tiling方案设计不当引起的一个时隐时现的bug
在设计tiling方案时,通常会考虑到非对齐的场景,对输入数据进行补全操作从而使得非对齐场景也能正确的完成计算。但在某些算子的实现过程中,沿用上述操作却会造成数据的错误计算,且这种错误出现与否取决于随机生成的测试数据质量。…...

视频转码对画质有影响吗?视频融合平台EasyCVR支持哪些转码格式?
视频转码过程是将视频文件从一种编码格式转换为另一种格式的过程,这一过程在现代数字媒体中扮演着至关重要的角色。众所周知,视频转码不仅仅是简单的格式转换,它涉及多个关键参数的改变,例如视频编码格式、比特率、分辨率以及帧率…...

工业视觉2-相机选型
工业视觉2-相机选型 一、按芯片类型二、按传感器结构特征三、按扫描方式四、按分辨率大小五、按输出信号六、按输出色彩接口类型 这张图片对工业相机的分类方式进行了总结,具体如下: 一、按芯片类型 CCD相机:采用电荷耦合器件(CC…...

基于SpringBoot+Vue的健身房管理系统
系统展示 用户前台界面 管理员后台界面 系统背景 随着现代生活节奏的加快,人们对健康的需求日益增强,健身房行业因此迎来了蓬勃的发展。然而,传统的健身房管理方式逐渐暴露出效率低下、会员信息管理混乱、课程安排不灵活等问题。为了解决这些…...

leetcode 面试经典 150 题:快乐数
链接快乐数题序号202题型数组解题方法哈希表难度简单熟练度✅✅✅✅ 题目 编写一个算法来判断一个数 n 是不是快乐数。 [快乐数] 定义为: 对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和。 然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 1࿰…...

Leetcode 279. 完全平方数 动态规划 完全背包问题
原题链接:Leetcode 279. 完全平方数 class Solution { public:int numSquares(int n) {vector<int> dp(n 1, 0);for (int i 1; i < n; i) {int tmp INT_MAX;for (int j 1; j * j < i; j) {tmp min(tmp, dp[i - j * j]);}dp[i] tmp 1;}return dp[…...

python学opencv|读取图像(三十三)阈值处理图像-限定像素
【1】引言 前序我们已经掌握分解图像的通道,设置各个通道的RGB值,相关文章包括且不限于: python学opencv|读取图像(十四)BGR图像和HSV图像通道拆分-CSDN博客 python学opencv|读取图像(十五)B…...

QT Quick QML 实例之椭圆投影,旋转
文章目录 一、前言二、演示三、部分代码与分析 QML 其它文章请点击这里: QT QUICK QML 学习笔记 国际站点 GitHub: https://github.com/chenchuhan 国内站点 Gitee : https://gitee.com/chuck_chee 一、前言 此 Demo 主要用于无人机吊舱视角的模拟…...
)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解) 在开始使用 React Native 开发移动应用之前,正确设置开发环境是至关重要的一步。本文将为你提供一份全面的指南,涵盖 macOS 和 Windows 平台的配置步骤,如何在 Android 和 iOS…...

MySQL中【正则表达式】用法
MySQL 中正则表达式通过 REGEXP 或 RLIKE 操作符实现(两者等价),用于在 WHERE 子句中进行复杂的字符串模式匹配。以下是核心用法和示例: 一、基础语法 SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name REGEXP pattern; …...
的使用)
Go 并发编程基础:通道(Channel)的使用
在 Go 中,Channel 是 Goroutine 之间通信的核心机制。它提供了一个线程安全的通信方式,用于在多个 Goroutine 之间传递数据,从而实现高效的并发编程。 本章将介绍 Channel 的基本概念、用法、缓冲、关闭机制以及 select 的使用。 一、Channel…...
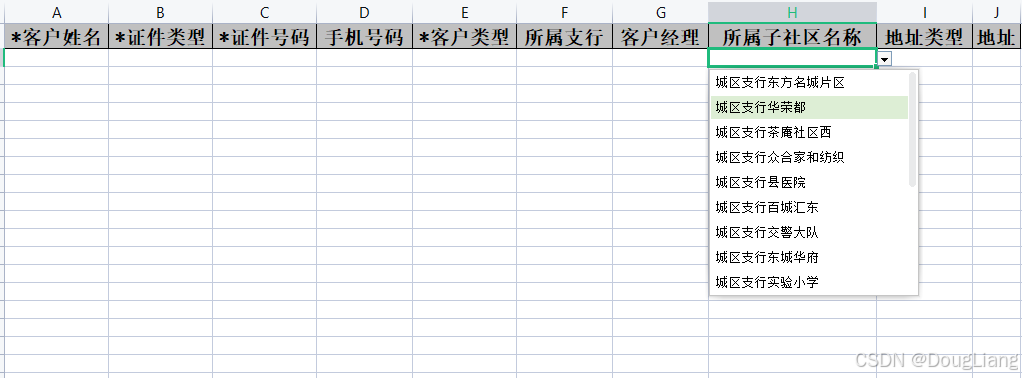
关于easyexcel动态下拉选问题处理
前些日子突然碰到一个问题,说是客户的导入文件模版想支持部分导入内容的下拉选,于是我就找了easyexcel官网寻找解决方案,并没有找到合适的方案,没办法只能自己动手并分享出来,针对Java生成Excel下拉菜单时因选项过多导…...

在树莓派上添加音频输入设备的几种方法
在树莓派上添加音频输入设备可以通过以下步骤完成,具体方法取决于设备类型(如USB麦克风、3.5mm接口麦克风或HDMI音频输入)。以下是详细指南: 1. 连接音频输入设备 USB麦克风/声卡:直接插入树莓派的USB接口。3.5mm麦克…...

智能职业发展系统:AI驱动的职业规划平台技术解析
智能职业发展系统:AI驱动的职业规划平台技术解析 引言:数字时代的职业革命 在当今瞬息万变的就业市场中,传统的职业规划方法已无法满足个人和企业的需求。据统计,全球每年有超过2亿人面临职业转型困境,而企业也因此遭…...
JDK 17 序列化是怎么回事
如何序列化?其实很简单,就是根据每个类型,用工厂类调用。逐个完成。 没什么漂亮的代码,只有有效、稳定的代码。 代码中调用toJson toJson 代码 mapper.writeValueAsString ObjectMapper DefaultSerializerProvider 一堆实…...

云原生安全实战:API网关Envoy的鉴权与限流详解
🔥「炎码工坊」技术弹药已装填! 点击关注 → 解锁工业级干货【工具实测|项目避坑|源码燃烧指南】 一、基础概念 1. API网关 作为微服务架构的统一入口,负责路由转发、安全控制、流量管理等核心功能。 2. Envoy 由Lyft开源的高性能云原生…...

五、jmeter脚本参数化
目录 1、脚本参数化 1.1 用户定义的变量 1.1.1 添加及引用方式 1.1.2 测试得出用户定义变量的特点 1.2 用户参数 1.2.1 概念 1.2.2 位置不同效果不同 1.2.3、用户参数的勾选框 - 每次迭代更新一次 总结用户定义的变量、用户参数 1.3 csv数据文件参数化 1、脚本参数化 …...

EEG-fNIRS联合成像在跨频率耦合研究中的创新应用
摘要 神经影像技术对医学科学产生了深远的影响,推动了许多神经系统疾病研究的进展并改善了其诊断方法。在此背景下,基于神经血管耦合现象的多模态神经影像方法,通过融合各自优势来提供有关大脑皮层神经活动的互补信息。在这里,本研…...
