【Block总结】动态蛇形卷积,专注于细长和弯曲的局部结构|即插即用
论文信息
标题: Dynamic Snake Convolution based on Topological Geometric Constraints for Tubular Structure Segmentation
作者: 戚耀磊、何宇霆、戚晓明、张媛、杨冠羽
会议: 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)
发表时间: 2023年10月
论文链接: arXiv:2307.08388
关键词: 动态蛇形卷积、拓扑几何约束、管状结构分割

创新点
该论文提出了一种新的动态蛇形卷积(Dynamic Snake Convolution, DSCNet)方法,主要创新点包括:
-
动态蛇形卷积(DSConv): 通过自适应聚焦细长和曲折的局部结构,增强对管状特征的捕捉能力。
-
多视角特征融合策略: 结合来自不同视角的信息,确保在特征融合过程中保留重要的全局形态信息。
-
拓扑连续性约束损失函数(TCLoss): 基于持久同调的方法,增强分割结果的拓扑连续性。
方法
论文的方法主要分为三个阶段:
-
特征提取: 采用动态蛇形卷积,专注于细长和弯曲的局部结构,以准确捕捉管状特征。
-
特征融合: 通过多视角特征融合策略,整合来自不同视角的信息,确保在特征融合过程中保留重要的细节。
-
损失约束: 引入拓扑连续性约束损失函数,以确保分割结果的拓扑结构连续性。

动态蛇形卷积
一、原理
动态蛇形卷积(Dynamic Snake Convolution, DSC)是一种新型的卷积操作,旨在提高对细长和复杂管状结构(如血管和道路)的特征提取能力。其设计灵感来源于生物医学中的“活性轮廓”模型,特别适用于处理具有复杂几何形状和拓扑结构的图像。
-
自适应卷积核: 动态蛇形卷积通过引入变形偏移(deformation offsets),使卷积核能够根据输入数据的特征动态调整其形状和大小。这种灵活性使得卷积核能够更好地聚焦于细长和曲折的局部结构。
-
连续性约束: 为了避免卷积核在处理细长结构时偏离目标,DSC引入了连续性约束。每个卷积位置的选择依赖于前一个位置,确保卷积核的运动是连续的,类似于蛇的移动方式。这种设计可以有效捕捉细小的结构特征,减少分割结果中的断裂现象。
二、结构
动态蛇形卷积的结构主要包括以下几个部分:
-
卷积核设计: DSC的卷积核不是固定的,而是根据输入数据的特征动态调整。以一个标准的3x3卷积核为例,卷积核的每个位置可以通过变形偏移来改变其位置,从而更好地适应目标的几何特征。
- 对于每个卷积核位置 ( K ),其位置可以表示为:
K i ± c = ( x i ± c , y i + Σ i i ± c Δ y ) K_{i \pm c} = (x_i \pm c, y_i + \Sigma_{i}^{i \pm c} \Delta y) Ki±c=(xi±c,yi+Σii±cΔy)
其中,( c ) 表示距离中心网格的水平距离, ( Δ y ) ( \Delta y ) (Δy) 是动态调整的偏移量。
- 对于每个卷积核位置 ( K ),其位置可以表示为:
-
特征提取与融合: DSC在特征提取阶段,通过动态卷积核自适应地聚焦于细长和曲折的局部结构,确保捕捉到管状结构的关键特征。在特征融合阶段,DSC结合来自不同视角的信息,增强对全局形态的理解。
-
损失约束: DSC还引入了基于持久同调的拓扑连续性约束损失函数,以确保分割结果的拓扑结构连续性。这一约束有助于提高分割的准确性和一致性。
动态蛇形卷积通过自适应的卷积核设计和连续性约束,显著提高了对细长和复杂管状结构的特征提取能力。其灵活性和适应性使其在医学图像处理和道路检测等领域具有广泛的应用前景。
效果
实验结果表明,DSCNet在管状结构分割任务上表现出色,尤其是在处理细小脆弱的局部结构和复杂多变的全局形态时,能够提供更好的准确性和连续性。
实验结果
在多个数据集上的实验结果显示,DSCNet相较于多种现有方法,提供了更高的分割准确性和更好的拓扑连续性。具体实验结果包括:
-
DRIVE视网膜数据集:
- Dice: 82.06%
- ACC: 96.87%
-
马萨诸塞州道路数据集(ROADS):
- Dice: 78.21%
-
3D心脏CCTA数据集:
- Dice提升: 1.31%
这些结果表明,DSCNet在捕捉细小管状结构的关键特征方面表现良好,具有重要的临床应用价值。
总结
该论文提出的动态蛇形卷积方法为管状结构的分割提供了一种新的思路,结合了动态卷积和拓扑几何约束,能够有效应对细长和复杂形态的挑战。通过多视角特征融合和拓扑连续性约束,DSCNet在准确性和连续性上均取得了显著的进展,为相关领域的研究提供了重要的参考和启示。
代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import torch
from torch import nn
import einops"""Dynamic Snake Convolution Module"""class DSConv_pro(nn.Module):def __init__(self,in_channels: int = 1,out_channels: int = 1,kernel_size: int = 9,extend_scope: float = 1.0,morph: int = 0,if_offset: bool = True,device: str | torch.device = "cuda",):"""A Dynamic Snake Convolution ImplementationBased on:TODOArgs:in_ch: number of input channels. Defaults to 1.out_ch: number of output channels. Defaults to 1.kernel_size: the size of kernel. Defaults to 9.extend_scope: the range to expand. Defaults to 1 for this method.morph: the morphology of the convolution kernel is mainly divided into two types along the x-axis (0) and the y-axis (1) (see the paper for details).if_offset: whether deformation is required, if it is False, it is the standard convolution kernel. Defaults to True."""super().__init__()if morph not in (0, 1):raise ValueError("morph should be 0 or 1.")self.kernel_size = kernel_sizeself.extend_scope = extend_scopeself.morph = morphself.if_offset = if_offsetself.device = torch.device(device)self.to(device)# self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * kernel_size)self.gn_offset = nn.GroupNorm(kernel_size, 2 * kernel_size)self.gn = nn.GroupNorm(out_channels // 4, out_channels)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.tanh = nn.Tanh()self.offset_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 2 * kernel_size, 3, padding=1)self.dsc_conv_x = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=(kernel_size, 1),stride=(kernel_size, 1),padding=0,)self.dsc_conv_y = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=(1, kernel_size),stride=(1, kernel_size),padding=0,)def forward(self, input: torch.Tensor):# Predict offset map between [-1, 1]offset = self.offset_conv(input)# offset = self.bn(offset)offset = self.gn_offset(offset)offset = self.tanh(offset)# Run deformative convy_coordinate_map, x_coordinate_map = get_coordinate_map_2D(offset=offset,morph=self.morph,extend_scope=self.extend_scope,device=self.device,)deformed_feature = get_interpolated_feature(input,y_coordinate_map,x_coordinate_map,)if self.morph == 0:output = self.dsc_conv_x(deformed_feature)elif self.morph == 1:output = self.dsc_conv_y(deformed_feature)# Groupnorm & ReLUoutput = self.gn(output)output = self.relu(output)return outputdef get_coordinate_map_2D(offset: torch.Tensor,morph: int,extend_scope: float = 1.0,device: str | torch.device = "cuda",
):"""Computing 2D coordinate map of DSCNet based on: TODOArgs:offset: offset predict by network with shape [B, 2*K, W, H]. Here K refers to kernel size.morph: the morphology of the convolution kernel is mainly divided into two types along the x-axis (0) and the y-axis (1) (see the paper for details).extend_scope: the range to expand. Defaults to 1 for this method.device: location of data. Defaults to 'cuda'.Return:y_coordinate_map: coordinate map along y-axis with shape [B, K_H * H, K_W * W]x_coordinate_map: coordinate map along x-axis with shape [B, K_H * H, K_W * W]"""if morph not in (0, 1):raise ValueError("morph should be 0 or 1.")batch_size, _, width, height = offset.shapekernel_size = offset.shape[1] // 2center = kernel_size // 2device = torch.device(device)y_offset_, x_offset_ = torch.split(offset, kernel_size, dim=1)y_center_ = torch.arange(0, width, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)y_center_ = einops.repeat(y_center_, "w -> k w h", k=kernel_size, h=height)x_center_ = torch.arange(0, height, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)x_center_ = einops.repeat(x_center_, "h -> k w h", k=kernel_size, w=width)if morph == 0:"""Initialize the kernel and flatten the kernely: only need 0x: -num_points//2 ~ num_points//2 (Determined by the kernel size)"""y_spread_ = torch.zeros([kernel_size], device=device)x_spread_ = torch.linspace(-center, center, kernel_size, device=device)y_grid_ = einops.repeat(y_spread_, "k -> k w h", w=width, h=height)x_grid_ = einops.repeat(x_spread_, "k -> k w h", w=width, h=height)y_new_ = y_center_ + y_grid_x_new_ = x_center_ + x_grid_y_new_ = einops.repeat(y_new_, "k w h -> b k w h", b=batch_size)x_new_ = einops.repeat(x_new_, "k w h -> b k w h", b=batch_size)y_offset_ = einops.rearrange(y_offset_, "b k w h -> k b w h")y_offset_new_ = y_offset_.detach().clone()# The center position remains unchanged and the rest of the positions begin to swing# This part is quite simple. The main idea is that "offset is an iterative process"y_offset_new_[center] = 0for index in range(1, center + 1):y_offset_new_[center + index] = (y_offset_new_[center + index - 1] + y_offset_[center + index])y_offset_new_[center - index] = (y_offset_new_[center - index + 1] + y_offset_[center - index])y_offset_new_ = einops.rearrange(y_offset_new_, "k b w h -> b k w h")y_new_ = y_new_.add(y_offset_new_.mul(extend_scope))y_coordinate_map = einops.rearrange(y_new_, "b k w h -> b (w k) h")x_coordinate_map = einops.rearrange(x_new_, "b k w h -> b (w k) h")elif morph == 1:"""Initialize the kernel and flatten the kernely: -num_points//2 ~ num_points//2 (Determined by the kernel size)x: only need 0"""y_spread_ = torch.linspace(-center, center, kernel_size, device=device)x_spread_ = torch.zeros([kernel_size], device=device)y_grid_ = einops.repeat(y_spread_, "k -> k w h", w=width, h=height)x_grid_ = einops.repeat(x_spread_, "k -> k w h", w=width, h=height)y_new_ = y_center_ + y_grid_x_new_ = x_center_ + x_grid_y_new_ = einops.repeat(y_new_, "k w h -> b k w h", b=batch_size)x_new_ = einops.repeat(x_new_, "k w h -> b k w h", b=batch_size)x_offset_ = einops.rearrange(x_offset_, "b k w h -> k b w h")x_offset_new_ = x_offset_.detach().clone()# The center position remains unchanged and the rest of the positions begin to swing# This part is quite simple. The main idea is that "offset is an iterative process"x_offset_new_[center] = 0for index in range(1, center + 1):x_offset_new_[center + index] = (x_offset_new_[center + index - 1] + x_offset_[center + index])x_offset_new_[center - index] = (x_offset_new_[center - index + 1] + x_offset_[center - index])x_offset_new_ = einops.rearrange(x_offset_new_, "k b w h -> b k w h")x_new_ = x_new_.add(x_offset_new_.mul(extend_scope))y_coordinate_map = einops.rearrange(y_new_, "b k w h -> b w (h k)")x_coordinate_map = einops.rearrange(x_new_, "b k w h -> b w (h k)")return y_coordinate_map, x_coordinate_mapdef get_interpolated_feature(input_feature: torch.Tensor,y_coordinate_map: torch.Tensor,x_coordinate_map: torch.Tensor,interpolate_mode: str = "bilinear",
):"""From coordinate map interpolate feature of DSCNet based on: TODOArgs:input_feature: feature that to be interpolated with shape [B, C, H, W]y_coordinate_map: coordinate map along y-axis with shape [B, K_H * H, K_W * W]x_coordinate_map: coordinate map along x-axis with shape [B, K_H * H, K_W * W]interpolate_mode: the arg 'mode' of nn.functional.grid_sample, can be 'bilinear' or 'bicubic' . Defaults to 'bilinear'.Return:interpolated_feature: interpolated feature with shape [B, C, K_H * H, K_W * W]"""if interpolate_mode not in ("bilinear", "bicubic"):raise ValueError("interpolate_mode should be 'bilinear' or 'bicubic'.")y_max = input_feature.shape[-2] - 1x_max = input_feature.shape[-1] - 1y_coordinate_map_ = _coordinate_map_scaling(y_coordinate_map, origin=[0, y_max])x_coordinate_map_ = _coordinate_map_scaling(x_coordinate_map, origin=[0, x_max])y_coordinate_map_ = torch.unsqueeze(y_coordinate_map_, dim=-1)x_coordinate_map_ = torch.unsqueeze(x_coordinate_map_, dim=-1)# Note here grid with shape [B, H, W, 2]# Where [:, :, :, 2] refers to [x ,y]grid = torch.cat([x_coordinate_map_, y_coordinate_map_], dim=-1)interpolated_feature = nn.functional.grid_sample(input=input_feature,grid=grid,mode=interpolate_mode,padding_mode="zeros",align_corners=True,)return interpolated_featuredef _coordinate_map_scaling(coordinate_map: torch.Tensor,origin: list,target: list = [-1, 1],
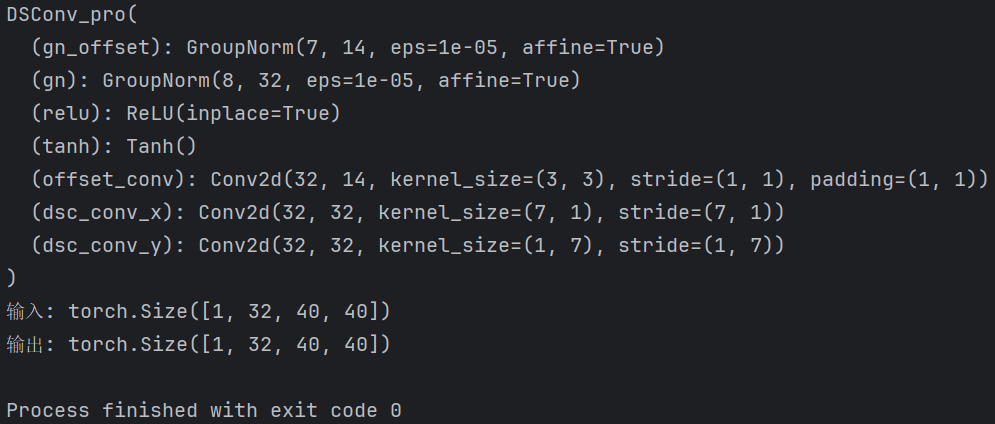
):"""Map the value of coordinate_map from origin=[min, max] to target=[a,b] for DSCNet based on: TODOArgs:coordinate_map: the coordinate map to be scaledorigin: original value range of coordinate map, e.g. [coordinate_map.min(), coordinate_map.max()]target: target value range of coordinate map,Defaults to [-1, 1]Return:coordinate_map_scaled: the coordinate map after scaling"""min, max = origina, b = targetcoordinate_map_scaled = torch.clamp(coordinate_map, min, max)scale_factor = (b - a) / (max - min)coordinate_map_scaled = a + scale_factor * (coordinate_map_scaled - min)return coordinate_map_scaledif __name__ == "__main__":# 如果GPU可用,将模块移动到 GPUdevice = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")# 输入张量 (batch_size, height, width,channels)x = torch.randn(1,32,40,40).to(device)# 初始化 HWD 模块dim=32block = DSConv_pro(32,32,7)print(block)block = block.to(device)# 前向传播output = block(x)print("输入:", x.shape)print("输出:", output.shape)
输出结果:
相关文章:

【Block总结】动态蛇形卷积,专注于细长和弯曲的局部结构|即插即用
论文信息 标题: Dynamic Snake Convolution based on Topological Geometric Constraints for Tubular Structure Segmentation 作者: 戚耀磊、何宇霆、戚晓明、张媛、杨冠羽 会议: 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 发表时间: 2023年10月…...

Spring MVC 框架:构建高效 Java Web 应用的利器
Java学习资料 Java学习资料 Java学习资料 一、引言 在 Java Web 开发领域,Spring MVC 框架是一颗耀眼的明星。它作为 Spring 框架家族的重要成员,为开发者提供了一套强大而灵活的解决方案,用于构建 Web 应用程序。Spring MVC 遵循模型 - 视…...
新鲜速递:DeepSeek-R1开源大模型本地部署实战—Ollama + MaxKB 搭建RAG检索增强生成应用
在AI技术快速发展的今天,开源大模型的本地化部署正在成为开发者们的热门实践方向。最火的莫过于吊打OpenAI过亿成本的纯国产DeepSeek开源大模型,就在刚刚,凭一己之力让英伟达大跌18%,纳斯达克大跌3.7%,足足是给中国AI产…...
Linux_线程同步生产者消费者模型
同步的相关概念 同步:在保证数据安全的前提下,让线程能够按照某种特定的顺序访问临界资源,从而有效避免饥饿问题,叫做同步竞态条件:因为时序问题,而导致程序异常,我们称之为竞态条件。 同步的…...
Origami Agents:通过AI驱动的研究工具提升B2B销售效率
在当今竞争激烈的商业环境中,B2B销售团队面临着巨大的挑战,如何高效地发现潜在客户并进行精准的外展活动成为关键。Origami Agents通过其创新的AI驱动研究工具,正在彻底改变这一过程。本文将深入探讨Origami Agents的产品特性、技术架构以及其快速增长背后的成功因素。 一、…...

linux的/proc 和 /sys目录差异
/proc 和 /sys 都是Linux系统中用于提供系统信息和进行系统配置的虚拟文件系统,但它们的原理并不完全一样,以下是具体分析: 目的与功能 /proc :主要用于提供系统进程相关信息以及内核运行时的一些参数等,可让用户和程…...

AIGC时代的Vue或React前端开发
在AIGC(人工智能生成内容)时代,Vue开发正经历着深刻的变革。以下是对AIGC时代Vue开发的详细分析: 一、AIGC技术对Vue开发的影响 代码生成与自动化 AIGC技术使得开发者能够借助智能工具快速生成和优化Vue代码。例如,通…...

代码随想录算法训练营第三十九天-动态规划-337. 打家劫舍 III
老师讲这是树形dp的入门题目解题思路是以二叉树的遍历(递归三部曲)再结合动规五部曲dp数组如何定义:只需要定义一个二个元素的数组,dp[0]与dp[1] dp[0]表示不偷当前节点的最大价值dp[1]表示偷当前节点后的最大价值这样可以把每个节…...
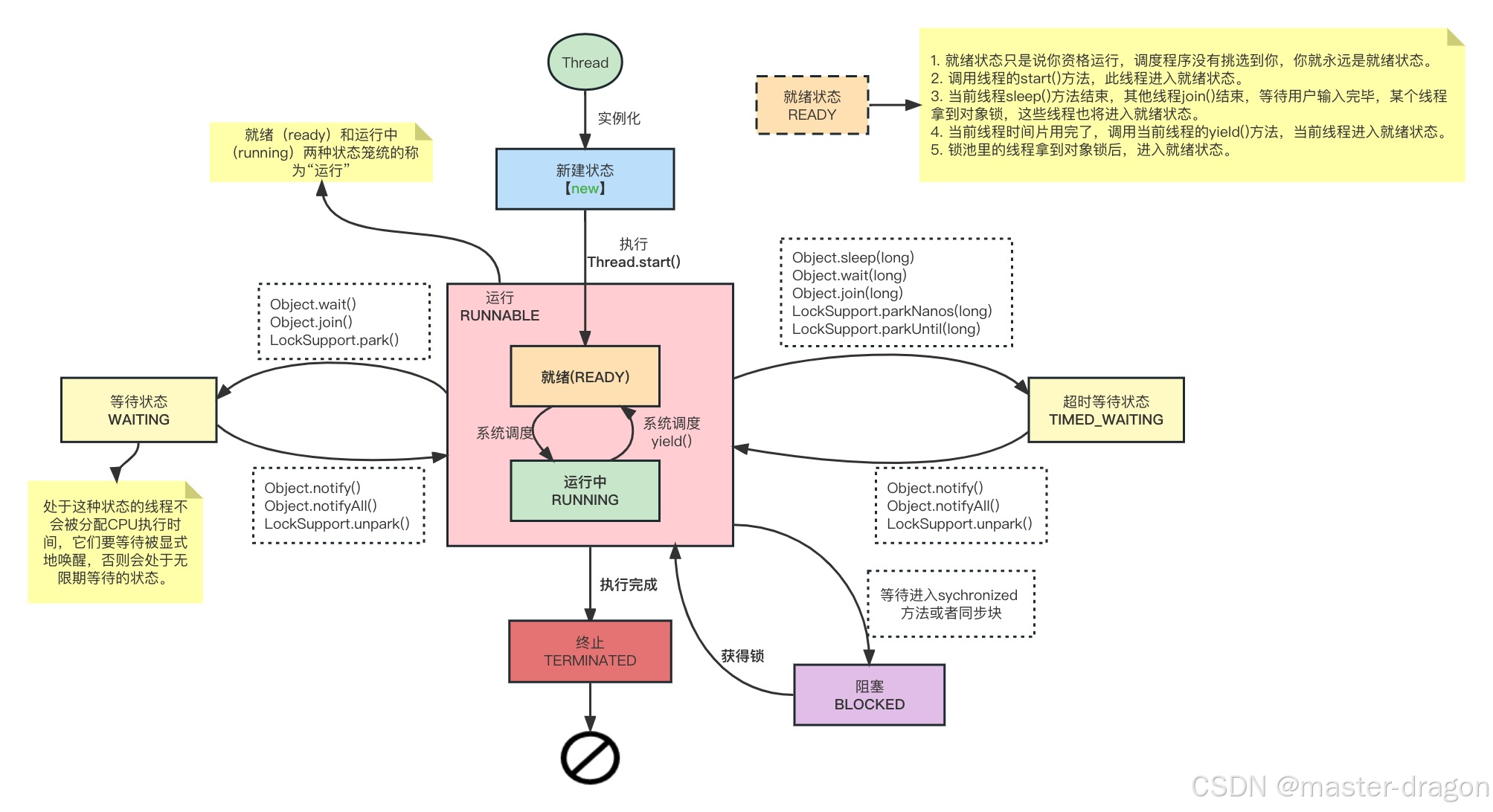
Java线程认识和Object的一些方法
专栏系列文章地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26437925/article/details/145290162 本文目标: 要对Java线程有整体了解,深入认识到里面的一些方法和Object对象方法的区别。认识到Java对象的ObjectMonitor,这有助于后面的Synchron…...
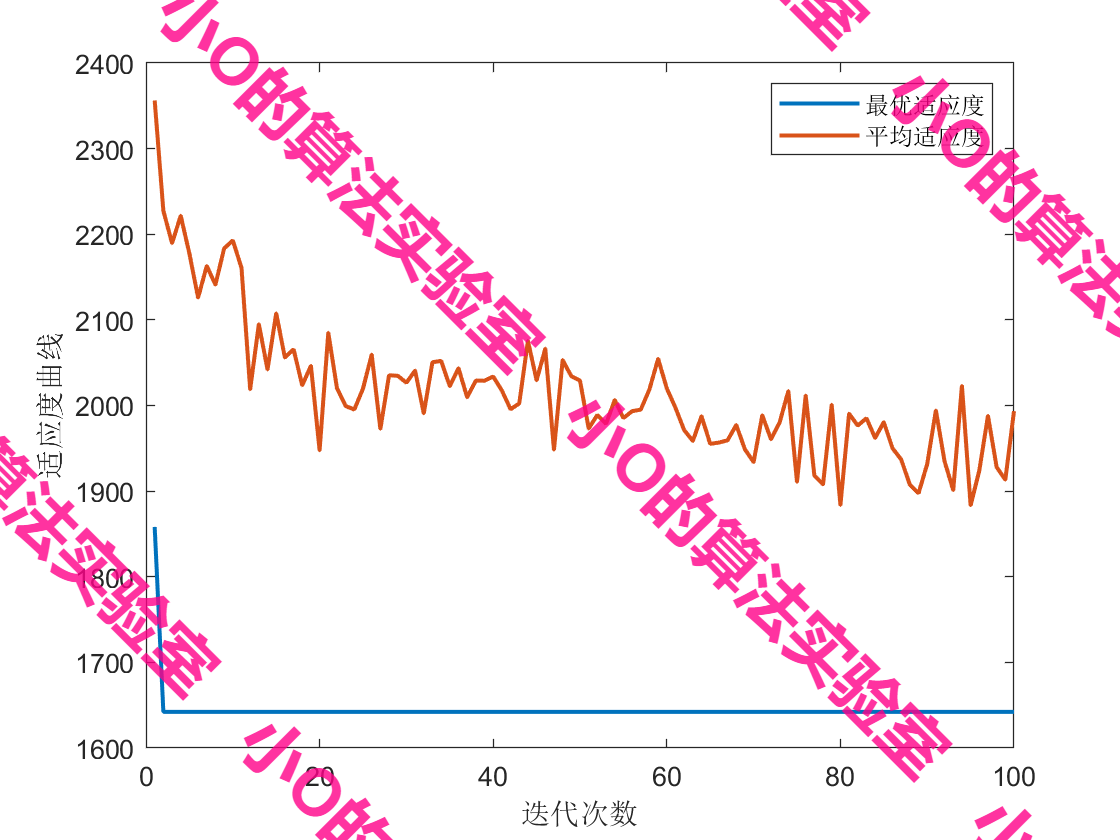
【算法应用】基于A*-蚁群算法求解无人机城市多任务点配送路径问题
目录 1.A星算法原理2.蚁群算法原理3.结果展示4.代码获取 1.A星算法原理 A*算法是一种基于图搜索的智能启发式算法,它具有高稳定性和高节点搜索效率。主要原理为:以起点作为初始节点,将其加入开放列表。从开放列表中选择具有最小总代价值 f (…...

电梯系统的UML文档14
对于 HallButtonControl,我们有二个状态: "门厅灯开 " 和 " 门厅灯关"。 从给出的初始信息,初始的状态应该是"门厅灯关"。行为定义: " 当 HallCall[f,d]是真,则指令 HallLight[f&…...
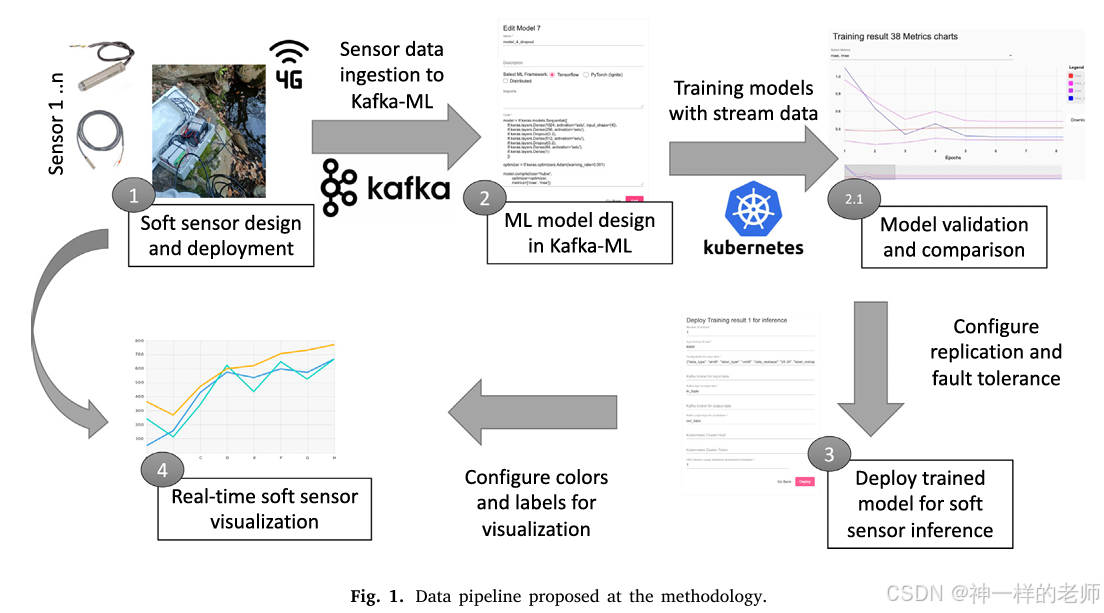
一种用于低成本水质监测的软传感器开源方法:以硝酸盐(NO3⁻)浓度为例
论文标题 A Soft Sensor Open-Source Methodology for Inexpensive Monitoring of Water Quality: A Case Study of NO3− Concentrations 作者信息 Antonio Jess Chaves, ITIS Software, University of Mlaga, 29071 Mlaga, Spain Cristian Martn, ITIS Software, Universi…...

[250130] VirtualBox 7.1.6 维护版本发布 | Anthropic API 推出全新引用功能
目录 VirtualBox 7.1.6 维护版本发布⚙️ 功能改进🛠️ Bug 修复 Anthropic API 推出全新引用功能,让 Claude 的回答更可信 VirtualBox 7.1.6 维护版本发布 VirtualBox 7.1.6 现已发布,这是一个维护版本,主要修复了一些错误并进行…...

JVM_类的加载、链接、初始化、卸载、主动使用、被动使用
①. 说说类加载分几步? ①. 按照Java虚拟机规范,从class文件到加载到内存中的类,到类卸载出内存为止,它的整个生命周期包括如下7个阶段: 第一过程的加载(loading)也称为装载验证、准备、解析3个部分统称为链接(Linking)在Java中数据类型分为基本数据类型和引用数据…...

2025最新版MySQL安装使用指南
2025最新版MySQL安装使用指南 The Installation and Usage Guide of the Latest Version of Oracle MySQL in 2025 By JacksonML 1. 获取MySQL 打开Chrome浏览器,访问官网链接:https://www.mysql.com/ ,随即打开MySQL官网主页面ÿ…...

MIMIC IV数据库中mimiciv_hosp的transfers表的careunit分析
以下是MIMIC IV数据库中mimiciv_hosp的transfers表的careunit的所有值,从医学专业角度分析,下面哪些科室会有实施心脏或神经手术? Cardiac Surgery Cardiac Vascular Intensive Care Unit (CVICU) Cardiology Cardiology Surgery Intermediat…...

AI学习指南HuggingFace篇-Hugging Face 的环境搭建
一、引言 Hugging Face作为自然语言处理(NLP)领域的强大工具,提供了丰富的预训练模型和数据集,极大地简化了开发流程。本文将详细介绍如何搭建适合Hugging Face开发的环境,包括Python环境配置、依赖安装以及推荐的开发工具,帮助读者准备好开发环境。 二、Python环境配置…...
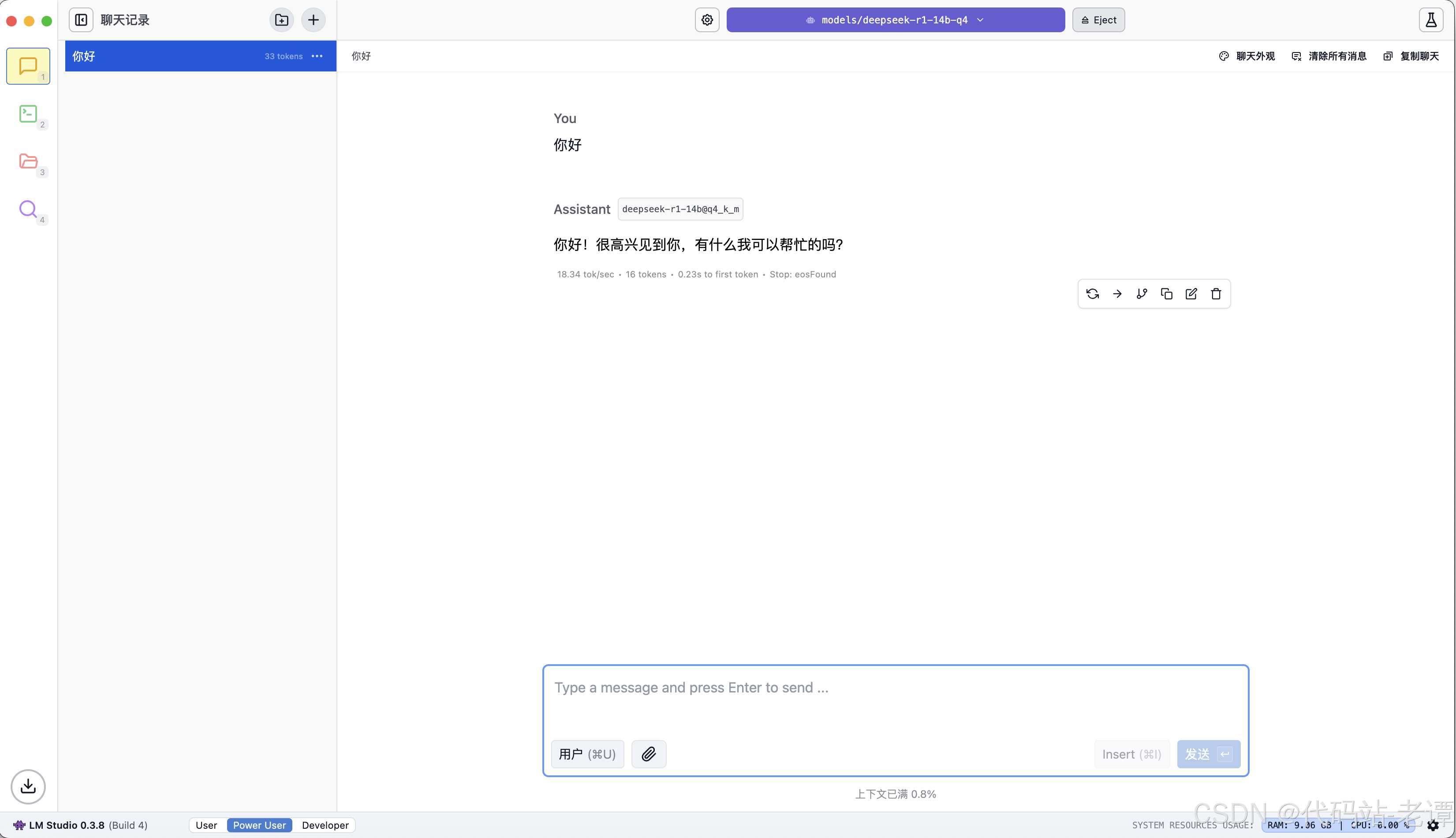
白嫖DeepSeek:一分钟完成本地部署AI
1. 必备软件 LM-Studio 大模型客户端DeepSeek-R1 模型文件 LM-Studio 是一个支持众多流行模型的AI客户端,DeepSeek是最新流行的堪比GPT-o1的开源AI大模型。 2. 下载软件和模型文件 2.1 下载LM-Studio 官方网址:https://lmstudio.ai 打开官网&#x…...
C# dataGridView1获取选中行的名字
在视觉项目中编写的框架需要能够选择产品或复制产品等方便后续换型,视觉调试仅需调试相机图像、调试视觉相关参数、标定,再试跑调试优化参数。 C# dataGridView1 鼠标点击某一行能够计算出是那一行 使用CellMouseClick事件 首先,在Form的构造…...
-【AI思考】-AI会不会考虑自己的需求?)
Day28(补)-【AI思考】-AI会不会考虑自己的需求?
文章目录 AI会不会考虑自己的需求?一、**技术本质:深度≠理解**二、**传播机制:热搜如何制造幻觉**三、**伦理考量:为何必须"撇清"**关键结论 AI会不会考虑自己的需求? 让思想碎片重焕生机的灵魂:…...

从零到一:实战华为OceanStor SAN存储与Linux服务器的iSCSI对接
1. 环境准备:理解iSCSI与SAN存储的“桥梁”作用 大家好,我是老张,一个在运维圈子里摸爬滚打了十多年的老家伙。今天咱们不聊虚的,就来手把手干一件在数据中心里特别常见,但对新手又有点“发怵”的活儿:把一…...
)
WORD自动编号全攻略:从基础到高级定制(图文并茂)
1. 自动编号:不只是“1、2、3”那么简单 很多朋友一听到WORD的“自动编号”,脑子里蹦出来的就是“1、2、3”或者“A、B、C”。我以前也是这么想的,觉得这功能不就是给段落前面加个顺序嘛,能有多复杂?直到有一次&#x…...
)
eVTOL/无人机动力测试:是该选用六分量天平还是普通力传感器?(从原理、优劣势、应用场景一文讲清楚)
随着低空经济加速落地,eVTOL(电动垂直起降飞行器)作为核心载体,正从实验室走向商业化落地。而动力系统作为eVTOL的“心脏”,其性能直接决定飞行器的续航、载荷、安全性与适航合规性——从旋翼拉力的动态波动到机身姿态…...

Databricks收购Quotient AI:AI智能体领域的战略布局
Databricks收购Quotient AI,剑指AI智能体可靠性难题Databricks收购了AI智能体评估与训练软件提供商Quotient AI,虽未公布具体交易金额,但此次收购旨在帮助企业更可靠地在生产环境中扩展AI智能体。Databricks在声明中表示,Quotient…...

百度网盘秒传脚本:文件传输效率工具的深度解析与应用指南
百度网盘秒传脚本:文件传输效率工具的深度解析与应用指南 【免费下载链接】rapid-upload-userscript-doc 秒传链接提取脚本 - 文档&教程 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/ra/rapid-upload-userscript-doc 1.溯源文件分享痛点:传统模…...

MATLAB环境下基于傅里叶分析的3级自适应信号分解方法
MATLAB环境下一种基于傅里叶分析的自适应信号分解方法。 该方法为数据驱动的傅里叶分解方法,分解的前3级的能量分布,分解的前3级基函数,分解的前3级模态分量如下。 算法可迁移至金融时间序列,地震信号,语音信号&#x…...

学术排版新选择:ElegantBook LaTeX模板助力论文写作全流程指南
学术排版新选择:ElegantBook LaTeX模板助力论文写作全流程指南 【免费下载链接】ElegantBook Elegant LaTeX Template for Books 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/el/ElegantBook ElegantBook是一款专为学术书籍和长篇论文设计的LaTeX模板…...

重庆大学LaTeX论文模板:学术排版规范与高效应用指南
重庆大学LaTeX论文模板:学术排版规范与高效应用指南 【免费下载链接】CQUThesis :pencil: 重庆大学毕业论文LaTeX模板---LaTeX Thesis Template for Chongqing University 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/cq/CQUThesis 作为重庆大学的毕业生&…...

使用slack-cleaner,打造清爽的Slack工作环境
使用slack-cleaner,打造清爽的Slack工作环境 【免费下载链接】slack-cleaner :speech_balloon: Bulk delete messages and files on Slack 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/sl/slack-cleaner 在现代企业中,Slack是团队协作的重要工具。…...

Godepgraph核心功能解析:从安装到高级用法的完整指南
Godepgraph核心功能解析:从安装到高级用法的完整指南 【免费下载链接】godepgraph A Go dependency graph visualization tool 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/go/godepgraph Godepgraph是一款功能强大的Go依赖关系可视化工具,能够帮助…...
