llama.cpp GGML Quantization Type
llama.cpp GGML Quantization Type
- 1. GGML Quantization Type
- 2. `static const struct ggml_type_traits type_traits[GGML_TYPE_COUNT]`
- 3. `Q#_K_M` and `Q#_K`
- References
什么神仙妖魔,不过是他们禁锢异族命运的枷锁!
GGUF
https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/gguf
docs/hub/gguf.md
https://github.com/huggingface/hub-docs/blob/main/docs/hub/gguf.md
1. GGML Quantization Type
packages/gguf/src/quant-descriptions.ts
https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface.js/blob/main/packages/gguf/src/quant-descriptions.ts
import { GGMLQuantizationType } from "./types";export const GGUF_QUANT_DESCRIPTIONS: Record<GGMLQuantizationType, { txt: string; src_url?: string }> = {[GGMLQuantizationType.F32]: {txt: "32-bit standard IEEE 754 single-precision floating-point number.",src_url: "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single-precision_floating-point_format",},[GGMLQuantizationType.F16]: {txt: "16-bit standard IEEE 754 half-precision floating-point number.",src_url: "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Half-precision_floating-point_format",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q8_0]: {txt: "8-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today).",src_url: "https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface.js/pull/615#discussion_r1557654249",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q8_1]: {txt: "8-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale + block_minimum. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today).",src_url: "https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface.js/pull/615#discussion_r1557682290",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q8_K]: {txt: `8-bit quantization (q). Each block has 256 weights. Only used for quantizing intermediate results. All 2-6 bit dot products are implemented for this quantization type. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale.`,src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/1684#issue-1739619305",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q6_K]: {txt: `6-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 16 blocks, each block has 16 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(8-bit), resulting in 6.5625 bits-per-weight.`,src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/1684#issue-1739619305",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q5_0]: {txt: "5-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today).",src_url: "https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface.js/pull/615#discussion_r1557654249",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q5_1]: {txt: "5-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale + block_minimum. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today).",src_url: "https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface.js/pull/615#discussion_r1557682290",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q5_K]: {txt: `5-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 8 blocks, each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(6-bit) + block_min(6-bit), resulting in 5.5 bits-per-weight.`,src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/1684#issue-1739619305",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q4_0]: {txt: "4-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today).",src_url: "https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface.js/pull/615#discussion_r1557654249",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q4_1]: {txt: "4-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale + block_minimum. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today).",src_url: "https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface.js/pull/615#discussion_r1557682290",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q4_K]: {txt: `4-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 8 blocks, each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(6-bit) + block_min(6-bit), resulting in 4.5 bits-per-weight.`,src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/1684#issue-1739619305",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q3_K]: {txt: `3-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 16 blocks, each block has 16 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(6-bit), resulting. 3.4375 bits-per-weight.`,src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/1684#issue-1739619305",},[GGMLQuantizationType.Q2_K]: {txt: `2-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 16 blocks, each block has 16 weight. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(4-bit) + block_min(4-bit), resulting in 2.5625 bits-per-weight.`,src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/1684#issue-1739619305",},[GGMLQuantizationType.IQ4_XS]: {txt: "4-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 4.25 bits-per-weight.",src_url:"https://huggingface.co/CISCai/OpenCodeInterpreter-DS-6.7B-SOTA-GGUF/blob/main/README.md?code=true#L59-L70",},[GGMLQuantizationType.IQ3_S]: {txt: "3-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 3.44 bits-per-weight.",src_url:"https://huggingface.co/CISCai/OpenCodeInterpreter-DS-6.7B-SOTA-GGUF/blob/main/README.md?code=true#L59-L70",},[GGMLQuantizationType.IQ3_XXS]: {txt: "3-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 3.06 bits-per-weight.",src_url:"https://huggingface.co/CISCai/OpenCodeInterpreter-DS-6.7B-SOTA-GGUF/blob/main/README.md?code=true#L59-L70",},[GGMLQuantizationType.IQ2_S]: {txt: "2-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 2.5 bits-per-weight.",src_url:"https://huggingface.co/CISCai/OpenCodeInterpreter-DS-6.7B-SOTA-GGUF/blob/main/README.md?code=true#L59-L70",},[GGMLQuantizationType.IQ2_XS]: {txt: "2-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 2.31 bits-per-weight.",src_url:"https://huggingface.co/CISCai/OpenCodeInterpreter-DS-6.7B-SOTA-GGUF/blob/main/README.md?code=true#L59-L70",},[GGMLQuantizationType.IQ2_XXS]: {txt: "2-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 2.06 bits-per-weight.",src_url:"https://huggingface.co/CISCai/OpenCodeInterpreter-DS-6.7B-SOTA-GGUF/blob/main/README.md?code=true#L59-L70",},[GGMLQuantizationType.IQ1_S]: {txt: "1-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 1.56 bits-per-weight.",src_url:"https://huggingface.co/CISCai/OpenCodeInterpreter-DS-6.7B-SOTA-GGUF/blob/main/README.md?code=true#L59-L70",},[GGMLQuantizationType.IQ4_NL]: {txt: "4-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix.",src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/5590",},[GGMLQuantizationType.I8]: {txt: "8-bit fixed-width integer number.",src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/6045",},[GGMLQuantizationType.I16]: {txt: "16-bit fixed-width integer number.",src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/6045",},[GGMLQuantizationType.I32]: {txt: "32-bit fixed-width integer number.",src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/6045",},[GGMLQuantizationType.I64]: {txt: "64-bit fixed-width integer number.",src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/6062",},[GGMLQuantizationType.F64]: {txt: "64-bit standard IEEE 754 double-precision floating-point number.",src_url: "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double-precision_floating-point_format",},[GGMLQuantizationType.IQ1_M]: {txt: "1-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 1.75 bits-per-weight.",src_url: "https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/6302",},[GGMLQuantizationType.BF16]: {txt: "16-bit shortened version of the 32-bit IEEE 754 single-precision floating-point number.",src_url: "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bfloat16_floating-point_format",},
};
| type | source | description |
|---|---|---|
| F64 | Wikipedia | 64-bit standard IEEE 754 double-precision floating-point number. |
| I64 | GH | 64-bit fixed-width integer number. |
| F32 | Wikipedia | 32-bit standard IEEE 754 single-precision floating-point number. |
| I32 | GH | 32-bit fixed-width integer number. |
| F16 | Wikipedia | 16-bit standard IEEE 754 half-precision floating-point number. |
| BF16 | Wikipedia | 16-bit shortened version of the 32-bit IEEE 754 single-precision floating-point number. |
| I16 | GH | 16-bit fixed-width integer number. |
| Q8_0 | GH | 8-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today). |
| Q8_1 | GH | 8-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale + block_minimum. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today) |
| Q8_K | GH | 8-bit quantization (q). Each block has 256 weights. Only used for quantizing intermediate results. All 2-6 bit dot products are implemented for this quantization type. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale. |
| I8 | GH | 8-bit fixed-width integer number. |
| Q6_K | GH | 6-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 16 blocks, each block has 16 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(8-bit), resulting in 6.5625 bits-per-weight. |
| Q5_0 | GH | 5-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today). |
| Q5_1 | GH | 5-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale + block_minimum. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today). |
| Q5_K | GH | 5-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 8 blocks, each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(6-bit) + block_min(6-bit), resulting in 5.5 bits-per-weight. |
| Q4_0 | GH | 4-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today). |
| Q4_1 | GH | 4-bit round-to-nearest quantization (q). Each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale + block_minimum. Legacy quantization method (not used widely as of today). |
| Q4_K | GH | 4-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 8 blocks, each block has 32 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(6-bit) + block_min(6-bit), resulting in 4.5 bits-per-weight. |
| Q3_K | GH | 3-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 16 blocks, each block has 16 weights. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(6-bit), resulting. 3.4375 bits-per-weight. |
| Q2_K | GH | 2-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 16 blocks, each block has 16 weight. Weight formula: w = q * block_scale(4-bit) + block_min(4-bit), resulting in 2.5625 bits-per-weight. |
| IQ4_NL | GH | 4-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix. |
| IQ4_XS | HF | 4-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 4.25 bits-per-weight. |
| IQ3_S | HF | 3-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 3.44 bits-per-weight. |
| IQ3_XXS | HF | 3-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 3.06 bits-per-weight. |
| IQ2_XXS | HF | 2-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 2.06 bits-per-weight. |
| IQ2_S | HF | 2-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 2.5 bits-per-weight. |
| IQ2_XS | HF | 2-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 2.31 bits-per-weight. |
| IQ1_S | HF | 1-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 1.56 bits-per-weight. |
| IQ1_M | GH | 1-bit quantization (q). Super-blocks with 256 weights. Weight w is obtained using super_block_scale & importance matrix, resulting in 1.75 bits-per-weight. |
GitHub, GH
Hugging Face, HF
2. static const struct ggml_type_traits type_traits[GGML_TYPE_COUNT]
https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/blob/master/ggml/src/ggml-quants.h
https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/blob/master/ggml/src/ggml-quants.c
https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/blob/master/ggml/src/ggml.c
static const struct ggml_type_traits type_traits[GGML_TYPE_COUNT] = {[GGML_TYPE_I8] = {.type_name = "i8",.blck_size = 1,.type_size = sizeof(int8_t),.is_quantized = false,},[GGML_TYPE_I16] = {.type_name = "i16",.blck_size = 1,.type_size = sizeof(int16_t),.is_quantized = false,},[GGML_TYPE_I32] = {.type_name = "i32",.blck_size = 1,.type_size = sizeof(int32_t),.is_quantized = false,},[GGML_TYPE_I64] = {.type_name = "i64",.blck_size = 1,.type_size = sizeof(int64_t),.is_quantized = false,},[GGML_TYPE_F64] = {.type_name = "f64",.blck_size = 1,.type_size = sizeof(double),.is_quantized = false,},[GGML_TYPE_F32] = {.type_name = "f32",.blck_size = 1,.type_size = sizeof(float),.is_quantized = false,},[GGML_TYPE_F16] = {.type_name = "f16",.blck_size = 1,.type_size = sizeof(ggml_fp16_t),.is_quantized = false,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) ggml_fp16_to_fp32_row,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) ggml_fp32_to_fp16_row,},[GGML_TYPE_Q4_0] = {.type_name = "q4_0",.blck_size = QK4_0,.type_size = sizeof(block_q4_0),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q4_0,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q4_0_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q4_1] = {.type_name = "q4_1",.blck_size = QK4_1,.type_size = sizeof(block_q4_1),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q4_1,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q4_1_ref,},[4] = { // GGML_TYPE_Q4_2.type_name = "DEPRECATED",.blck_size = 0,.type_size = 0,.is_quantized = false,},[5] = { // GGML_TYPE_Q4_3.type_name = "DEPRECATED",.blck_size = 0,.type_size = 0,.is_quantized = false,},[GGML_TYPE_Q5_0] = {.type_name = "q5_0",.blck_size = QK5_0,.type_size = sizeof(block_q5_0),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q5_0,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q5_0_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q5_1] = {.type_name = "q5_1",.blck_size = QK5_1,.type_size = sizeof(block_q5_1),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q5_1,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q5_1_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q8_0] = {.type_name = "q8_0",.blck_size = QK8_0,.type_size = sizeof(block_q8_0),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q8_0,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q8_0_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q8_1] = {.type_name = "q8_1",.blck_size = QK8_1,.type_size = sizeof(block_q8_1),.is_quantized = true,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q8_1_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q2_K] = {.type_name = "q2_K",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_q2_K),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q2_K,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q2_K_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q3_K] = {.type_name = "q3_K",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_q3_K),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q3_K,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q3_K_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q4_K] = {.type_name = "q4_K",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_q4_K),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q4_K,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q4_K_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q5_K] = {.type_name = "q5_K",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_q5_K),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q5_K,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q5_K_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q6_K] = {.type_name = "q6_K",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_q6_K),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_q6_K,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_q6_K_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_IQ2_XXS] = {.type_name = "iq2_xxs",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_iq2_xxs),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_iq2_xxs,.from_float_ref = NULL,},[GGML_TYPE_IQ2_XS] = {.type_name = "iq2_xs",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_iq2_xs),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_iq2_xs,.from_float_ref = NULL,},[GGML_TYPE_IQ3_XXS] = {.type_name = "iq3_xxs",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_iq3_xxs),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_iq3_xxs,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t)quantize_row_iq3_xxs_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_IQ3_S] = {.type_name = "iq3_s",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_iq3_s),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_iq3_s,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t)quantize_row_iq3_s_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_IQ2_S] = {.type_name = "iq2_s",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_iq2_s),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_iq2_s,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t)quantize_row_iq2_s_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_IQ1_S] = {.type_name = "iq1_s",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_iq1_s),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_iq1_s,.from_float_ref = NULL,},[GGML_TYPE_IQ1_M] = {.type_name = "iq1_m",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_iq1_m),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_iq1_m,.from_float_ref = NULL,},[GGML_TYPE_IQ4_NL] = {.type_name = "iq4_nl",.blck_size = QK4_NL,.type_size = sizeof(block_iq4_nl),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_iq4_nl,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t)quantize_row_iq4_nl_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_IQ4_XS] = {.type_name = "iq4_xs",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_iq4_xs),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_iq4_xs,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t)quantize_row_iq4_xs_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_Q8_K] = {.type_name = "q8_K",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_q8_K),.is_quantized = true,},[GGML_TYPE_BF16] = {.type_name = "bf16",.blck_size = 1,.type_size = sizeof(ggml_bf16_t),.is_quantized = false,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) ggml_bf16_to_fp32_row,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) ggml_fp32_to_bf16_row_ref,},[31] = { // GGML_TYPE_Q4_0_4_4.type_name = "TYPE_Q4_0_4_4 REMOVED, use Q4_0 with runtime repacking",.blck_size = 0,.type_size = 0,.is_quantized = false,},[32] = { // GGML_TYPE_Q4_0_4_8.type_name = "TYPE_Q4_0_4_8 REMOVED, use Q4_0 with runtime repacking",.blck_size = 0,.type_size = 0,.is_quantized = false,},[33] = { // GGML_TYPE_Q4_0_8_8.type_name = "TYPE_Q4_0_8_8 REMOVED, use Q4_0 with runtime repacking",.blck_size = 0,.type_size = 0,.is_quantized = false,},[GGML_TYPE_TQ1_0] = {.type_name = "tq1_0",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_tq1_0),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_tq1_0,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_tq1_0_ref,},[GGML_TYPE_TQ2_0] = {.type_name = "tq2_0",.blck_size = QK_K,.type_size = sizeof(block_tq2_0),.is_quantized = true,.to_float = (ggml_to_float_t) dequantize_row_tq2_0,.from_float_ref = (ggml_from_float_t) quantize_row_tq2_0_ref,},[36] = { // GGML_TYPE_IQ4_NL_4_4.type_name = "TYPE_IQ4_NL_4_4 REMOVED, use IQ4_NL with runtime repacking",.blck_size = 0,.type_size = 0,.is_quantized = false,},[37] = { // GGML_TYPE_IQ4_NL_4_8.type_name = "TYPE_IQ4_NL_4_8 REMOVED, use IQ4_NL with runtime repacking",.blck_size = 0,.type_size = 0,.is_quantized = false,},[38] = { // GGML_TYPE_IQ4_NL_8_8.type_name = "TYPE_IQ4_NL_8_8 REMOVED, use IQ4_NL with runtime repacking",.blck_size = 0,.type_size = 0,.is_quantized = false,},
};
/home/yongqiang/llm_work/llama_cpp_25_01_05/llama.cpp/ggml/include/ggml.h
// NOTE: always add types at the end of the enum to keep backward compatibilityenum ggml_type {GGML_TYPE_F32 = 0,GGML_TYPE_F16 = 1,GGML_TYPE_Q4_0 = 2,GGML_TYPE_Q4_1 = 3,// GGML_TYPE_Q4_2 = 4, support has been removed// GGML_TYPE_Q4_3 = 5, support has been removedGGML_TYPE_Q5_0 = 6,GGML_TYPE_Q5_1 = 7,GGML_TYPE_Q8_0 = 8,GGML_TYPE_Q8_1 = 9,GGML_TYPE_Q2_K = 10,GGML_TYPE_Q3_K = 11,GGML_TYPE_Q4_K = 12,GGML_TYPE_Q5_K = 13,GGML_TYPE_Q6_K = 14,GGML_TYPE_Q8_K = 15,GGML_TYPE_IQ2_XXS = 16,GGML_TYPE_IQ2_XS = 17,GGML_TYPE_IQ3_XXS = 18,GGML_TYPE_IQ1_S = 19,GGML_TYPE_IQ4_NL = 20,GGML_TYPE_IQ3_S = 21,GGML_TYPE_IQ2_S = 22,GGML_TYPE_IQ4_XS = 23,GGML_TYPE_I8 = 24,GGML_TYPE_I16 = 25,GGML_TYPE_I32 = 26,GGML_TYPE_I64 = 27,GGML_TYPE_F64 = 28,GGML_TYPE_IQ1_M = 29,GGML_TYPE_BF16 = 30,// GGML_TYPE_Q4_0_4_4 = 31, support has been removed from gguf files// GGML_TYPE_Q4_0_4_8 = 32,// GGML_TYPE_Q4_0_8_8 = 33,GGML_TYPE_TQ1_0 = 34,GGML_TYPE_TQ2_0 = 35,// GGML_TYPE_IQ4_NL_4_4 = 36,// GGML_TYPE_IQ4_NL_4_8 = 37,// GGML_TYPE_IQ4_NL_8_8 = 38,GGML_TYPE_COUNT = 39,};// precisionenum ggml_prec {GGML_PREC_DEFAULT,GGML_PREC_F32,};// model file typesenum ggml_ftype {GGML_FTYPE_UNKNOWN = -1,GGML_FTYPE_ALL_F32 = 0,GGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_F16 = 1, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_0 = 2, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_1 = 3, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_1_SOME_F16 = 4, // tok_embeddings.weight and output.weight are F16GGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q8_0 = 7, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q5_0 = 8, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q5_1 = 9, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q2_K = 10, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q3_K = 11, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q4_K = 12, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q5_K = 13, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_Q6_K = 14, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_IQ2_XXS = 15, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_IQ2_XS = 16, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_IQ3_XXS = 17, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_IQ1_S = 18, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_IQ4_NL = 19, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_IQ3_S = 20, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_IQ2_S = 21, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_IQ4_XS = 22, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_IQ1_M = 23, // except 1d tensorsGGML_FTYPE_MOSTLY_BF16 = 24, // except 1d tensors};
3. Q#_K_M and Q#_K
https://netraneupane.medium.com/hands-on-llms-quantization-a4c7ab1421c2
In the context of llama.cpp, Q4_K_M refers to a specific type of k-means quantization method. The naming convention is as follows:
Qstands for Quantization.4indicates the number of bits used in the quantization process.Krefers to the use of k-means clustering in the quantization.Mrepresents the size of the model after quantization. (S = Small, M = Medium, L = Large).
Similarly, Q2_K refers to specific type of k-means quantization too. The naming convention is as follow:
Qstands for Quantization.2indicates the number of bits used in the quantization process.Krefers to the use of k-means clustering in the quantization.
References
[1] Yongqiang Cheng, https://yongqiang.blog.csdn.net/
[2] huggingface/gguf, https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface.js/tree/main/packages/gguf
[3] llama.cpp, https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp
[4] k-quants, https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/1684
相关文章:

llama.cpp GGML Quantization Type
llama.cpp GGML Quantization Type 1. GGML Quantization Type2. static const struct ggml_type_traits type_traits[GGML_TYPE_COUNT]3. Q#_K_M and Q#_KReferences 什么神仙妖魔,不过是他们禁锢异族命运的枷锁! GGUF https://huggingface.co/docs/hu…...
k8s部署go-fastdfs
前置环境:已部署k8s集群,ip地址为 192.168.10.1~192.168.10.5,总共5台机器。 1. 创建provisioner制备器(如果已存在,则不需要) 制备器的具体部署方式可参考我的上一篇文章: k8s部署rabbitmq-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读254次,点赞3次,收藏5次。k8s部署rabbitmqhttps://blo…...

Python----Python高级(并发编程:协程Coroutines,事件循环,Task对象,协程间通信,协程同步,将协程分布到线程池/进程池中)
一、协程 1.1、协程 协程,Coroutines,也叫作纤程(Fiber) 协程,全称是“协同程序”,用来实现任务协作。是一种在线程中,比线程更加轻量级的存在,由程序员自己写程序来管理。 当出现IO阻塞时,…...

什么是可观测性?
现代服务架构常常谈及三个性: 弹性,韧性,可观测性。今天且按下其他两性不表,着重聊一聊可观测性。本文就几个主题对可观测性展开讨论: 可观测性是什么可观测性是必须的吗企业的可观测性落地 可观测性理念 可观测性是…...

3. 【.NET Aspire 从入门到实战】--理论入门与环境搭建--环境搭建
构建现代云原生应用程序时,开发环境的搭建至关重要。NET Aspire 作为一款专为云原生应用设计的开发框架,提供了一整套工具、模板和集成包,旨在简化分布式系统的构建和管理。开始项目初始化之前,确保开发环境的正确配置是成功的第一…...

kubeadm构建k8s源码阅读环境
目标 前面看了minikube的源码了解到其本质是调用了kubeadm来启动k8s集群,并没有达到最初看代码的目的。 所以继续看看kubeadm的代码,看看能否用来方便地构建源码调试环境。 k8s源码编译 kubeadm源码在k8s源码库中,所以要先克隆k8s源码。之…...

【Flink快速入门-1.Flink 简介与环境配置】
Flink 简介与环境配置 实验介绍 在学习一门新的技术之前,我们首先要了解它的历史渊源,也就是说它为什么会出现,它能够解决什么业务痛点。所以本节我们的学习目的是了解 Flink 的背景,并运行第一个 Flink 程序,对它有…...

硬盘修复后,文件隐身之谜
在数字时代,硬盘作为数据存储的重要载体,承载着无数珍贵的信息与回忆。然而,当硬盘遭遇故障并经过修复后,有时我们会遇到这样一个棘手问题:硬盘修复后,文件却神秘地“隐身”,无法正常显示。这一…...

如何处理网络连接错误导致的fetch失败?
处理由于网络连接错误导致的 fetch 失败通常涉及捕获网络错误并提供适当的用户反馈。以下是如何在 Vue 3 中实现这一点的步骤和示例。 一、更新 useFetch 函数 在 useFetch 函数中,需要捕获网络错误,并设置相应的错误信息。网络错误通常会抛出一个 TypeError,可以根据这个…...

Qt之设置QToolBar上的按钮样式
通常给QAction设置icon后,菜单栏的菜单项和工具栏(QToolBar)上对应的按钮会同时显示该icon。工具栏还可以使用setToolButtonStyle函数设置按钮样式,其参数为枚举值: enum ToolButtonStyle {ToolButtonIconOnly,ToolButtonTextOnly,ToolButtonTextBesideIcon,ToolButtonTe…...
)
责任链模式(Chain Responsibility)
一、定义:属于行为型设计模式,包含传递的数据、创建处理的抽象和实现、创建链条、将数据传递给顶端节点; 二、UML图 三、实现 1、需要传递处理的数据类 import java.util.Date;/*** 需要处理的数据信息*/ public class RequestData {priva…...

docker安装 mongodb
1、拉取镜像 docker run -dit --name mongo \ -p 17017:27017 \ -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAMEadmin \ -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD2018 \ --restartalways \ mongo2、进入容器 docker exec -it mongo bash 3、进入mongo ./bin/mongosh -u admin -p 2018 --authenticat…...

RabbitMQ 从入门到精通:从工作模式到集群部署实战(五)
#作者:闫乾苓 系列前几篇: 《RabbitMQ 从入门到精通:从工作模式到集群部署实战(一)》:link 《RabbitMQ 从入门到精通:从工作模式到集群部署实战(二)》: lin…...

salesforce SF CLI 数据运维经验分享
SF CLI data默认使用bulk api v2, 数据操作效率有了极大的提高。 Bulk api v2的优点: 执行结果可以很直观的从Bulk Data Load Jobs中看到。相较于bulk api v1,只能看到job执行in progress,或者closed的状态,有了很大的改善。执行…...

5.2Internet及其作用
5.2.1Internet概述 Internet称为互联网,又称英特网,始于1969年的美国ARPANET(阿帕网),是全球性的网络。 互连网指的是两个或多个不同类型的网络通过路由器等网络设备连接起来,形成一个更大的网络结构。互连…...

【蓝桥杯—单片机】第十一届省赛真题代码题解题笔记 | 省赛 | 真题 | 代码题 | 刷题 | 笔记
第十一届省赛真题代码部分 前言赛题代码思路笔记竞赛板配置内部振荡器频率设定键盘工作模式跳线扩展方式跳线 建立模板明确设计要求和初始状态显示功能部分数据界面第一部分第二部分第三部分调试时发现的问题 参数设置界面第一部分第二部分和第四部分第三部分和第五部分 按键功…...

数据分析:企业数字化转型的金钥匙
引言:数字化浪潮下的数据金矿 在数字化浪潮席卷全球的背景下,有研究表明,只有不到30%的企业能够充分利用手中掌握的数据,这是否让人深思?数据已然成为企业最为宝贵的资产之一。然而,企业是否真正准备好从数…...

网络工程师 (23)OSI模型层次结构
前言 OSI(Open System Interconnect)模型,即开放式系统互联模型,是一个完整的、完善的宏观模型,它将计算机网络体系结构划分为7层。 OSI七层模型 1. 物理层(Physical Layer) 功能:负…...

DeepSeek添加知识库
1、下载dify 项目地址:https://github.com/langgenius/dify 2、通过docker安装 端口报错 修改端口 .env文件下所有80端口替换成了其它端口 执行正常了 查看 docker容器 <...

2、k8s的cni网络插件和基本操作命令
kube-prxoy属于节点组件,网络代理,实现服务的自动发现和负载均衡。 k8s的内部网络模式 1、pod内的容器于容器之间的通信。 2、一个节点上的pod之间的通信,docker0网桥直接通信。 3、不同节点上的pod之间的通信: 通过物理网卡的…...
结构体的进阶应用)
基于算法竞赛的c++编程(28)结构体的进阶应用
结构体的嵌套与复杂数据组织 在C中,结构体可以嵌套使用,形成更复杂的数据结构。例如,可以通过嵌套结构体描述多层级数据关系: struct Address {string city;string street;int zipCode; };struct Employee {string name;int id;…...
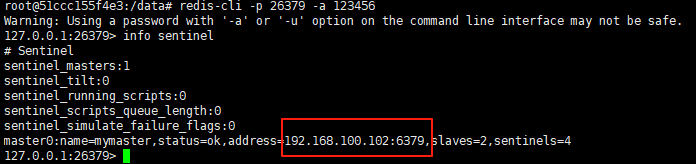
使用docker在3台服务器上搭建基于redis 6.x的一主两从三台均是哨兵模式
一、环境及版本说明 如果服务器已经安装了docker,则忽略此步骤,如果没有安装,则可以按照一下方式安装: 1. 在线安装(有互联网环境): 请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 2. 离线安装(内网环境):请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 说明:假设每台服务器已…...

AI-调查研究-01-正念冥想有用吗?对健康的影响及科学指南
点一下关注吧!!!非常感谢!!持续更新!!! 🚀 AI篇持续更新中!(长期更新) 目前2025年06月05日更新到: AI炼丹日志-28 - Aud…...
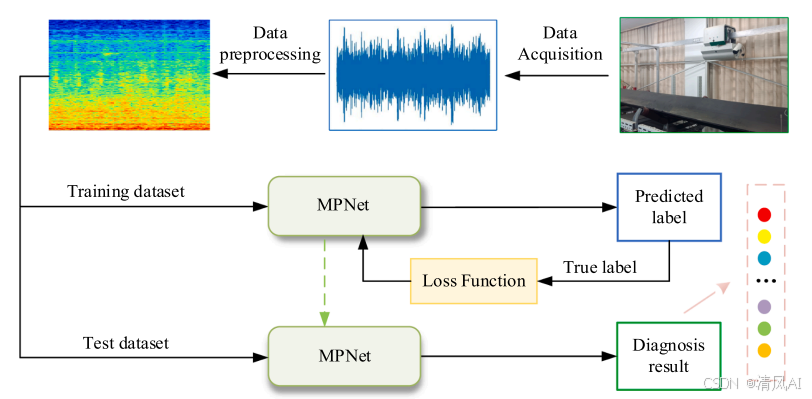
MPNet:旋转机械轻量化故障诊断模型详解python代码复现
目录 一、问题背景与挑战 二、MPNet核心架构 2.1 多分支特征融合模块(MBFM) 2.2 残差注意力金字塔模块(RAPM) 2.2.1 空间金字塔注意力(SPA) 2.2.2 金字塔残差块(PRBlock) 2.3 分类器设计 三、关键技术突破 3.1 多尺度特征融合 3.2 轻量化设计策略 3.3 抗噪声…...
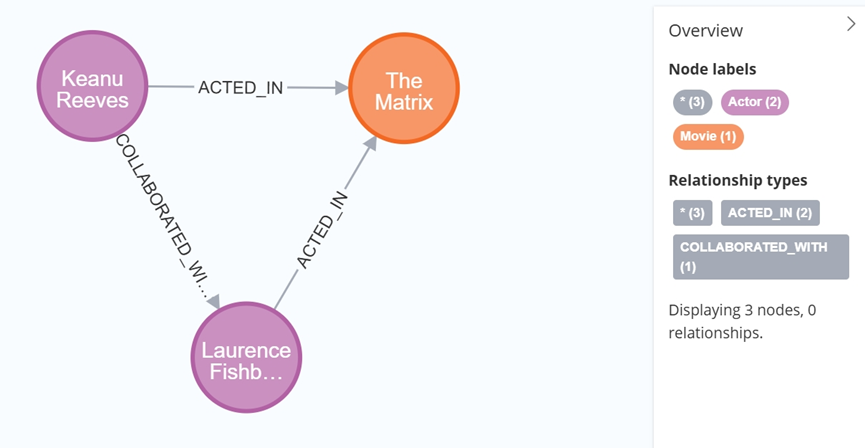
大数据学习栈记——Neo4j的安装与使用
本文介绍图数据库Neofj的安装与使用,操作系统:Ubuntu24.04,Neofj版本:2025.04.0。 Apt安装 Neofj可以进行官网安装:Neo4j Deployment Center - Graph Database & Analytics 我这里安装是添加软件源的方法 最新版…...

Linux链表操作全解析
Linux C语言链表深度解析与实战技巧 一、链表基础概念与内核链表优势1.1 为什么使用链表?1.2 Linux 内核链表与用户态链表的区别 二、内核链表结构与宏解析常用宏/函数 三、内核链表的优点四、用户态链表示例五、双向循环链表在内核中的实现优势5.1 插入效率5.2 安全…...
2.Vue编写一个app
1.src中重要的组成 1.1main.ts // 引入createApp用于创建应用 import { createApp } from "vue"; // 引用App根组件 import App from ./App.vue;createApp(App).mount(#app)1.2 App.vue 其中要写三种标签 <template> <!--html--> </template>…...
基于当前项目通过npm包形式暴露公共组件
1.package.sjon文件配置 其中xh-flowable就是暴露出去的npm包名 2.创建tpyes文件夹,并新增内容 3.创建package文件夹...
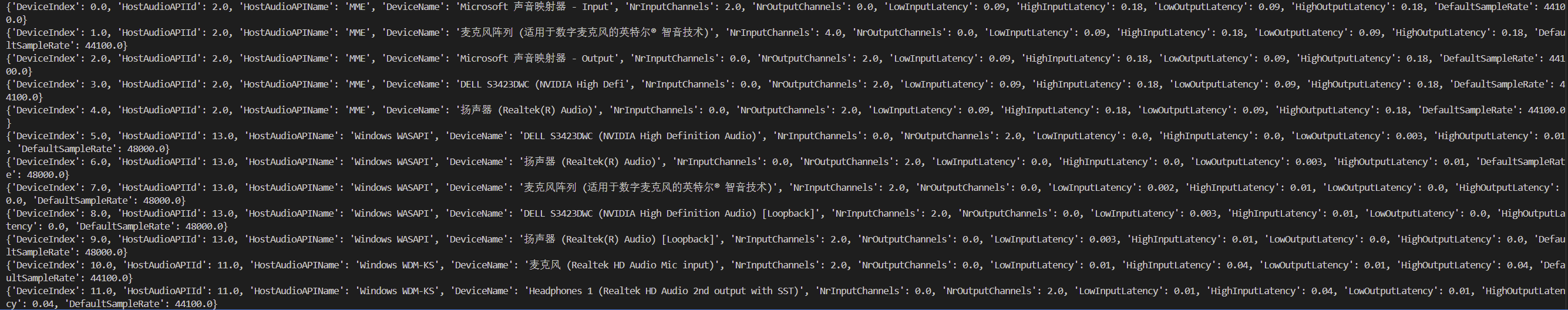
Psychopy音频的使用
Psychopy音频的使用 本文主要解决以下问题: 指定音频引擎与设备;播放音频文件 本文所使用的环境: Python3.10 numpy2.2.6 psychopy2025.1.1 psychtoolbox3.0.19.14 一、音频配置 Psychopy文档链接为Sound - for audio playback — Psy…...

Web 架构之 CDN 加速原理与落地实践
文章目录 一、思维导图二、正文内容(一)CDN 基础概念1. 定义2. 组成部分 (二)CDN 加速原理1. 请求路由2. 内容缓存3. 内容更新 (三)CDN 落地实践1. 选择 CDN 服务商2. 配置 CDN3. 集成到 Web 架构 …...
