2025.2.14——1400
2025.2.14——1400
A 1400
B 1400
C 1400
D 1400
E 1400
F 1400
G 1400
H 1400
------------------------------------------------
A
- 一眼想到的是维护信息计数。
- 维护两个信息同时用长的一半去找短的一半。
- 较好的思维题。
B
- 贪心匹配:优先使用最小的匹配合法最小的。
- 排序+双指针/二分/队列匹配。
C
- 出现一次,子数组也是子序列,所以不能再出现了。
- 发现边界是控制出现与否的充要条件。
D
- 从每一位考虑,最初以为 k k k 每一位都需要出现,其实不是,但可以凭借这个思路计算出区间按位与具体数的。
- 另解:今天才知道 s t st st 表可以维护区间按位与、按位或值。
E
- 逆向思维+优化模拟:指针移动+找循环。
- 思维量挺多。
F
- 数学题。证明无解不太懂,限制次数过了。 洛谷题解。
G
- LCM与GCD问题,数学一下分析因子。
H
- 横向纵向分别考虑。横向可转化为纵向。
- 考虑纵向:交替发现对纵向平衡性无影响。同时对两行平衡性无影响且无后效性。
------------------------代码------------------------
A
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC) \{ \for (auto Vec : VEC) \cout << Vec << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;// cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}int has[6][46];
auto sum(string s, int l, int r)
{int ans = 0;for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)ans += s[i] - '0';return ans;
}
auto sum(string s)
{int ans = 0;for (auto v : s)ans += v - '0';return ans;
}
auto tar_sum(string s, int l, int r)
{return 2 * sum(s, l, r) - sum(s);
}
void _()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<string> s(n);for (auto &v : s){cin >> v;has[v.size()][sum(v)]++;}int res = 0;for (auto l : s){int ln = l.size();for (int i = 2; i <= 10; i += 2){int rn = i - ln;if (rn <= 0 || rn > ln)continue;int tar_r = tar_sum(l, 0, i / 2 - 1);if (tar_r < 0)continue;res += has[rn][tar_r];}}for (auto r : s){int rn = r.size();for (int i = 2; i <= 10; i += 2){int ln = i - rn;if (ln <= 0 || ln >= rn)continue;int tar_l = tar_sum(r, rn - i / 2, rn - 1);if (tar_l < 0)continue;res += has[ln][tar_l];}}cout << res;
}
// int has[6][46][6][46];
// void _()
// {
// memset(has, 0x3f, sizeof has);
// int n;
// cin >> n;
// // struct Node
// // {
// // /* data */
// // int len, sum, prelen, presum;
// // };
// // map<Node, int> has;
// auto get_suf = [&](string s, int suf)
// {
// int sum = 0, m = s.size();
// for (int i = m - 1; i >= m - suf; i--)
// sum += s[i] - '0';
// return sum;
// };
// auto get_pre = [&](string s, int pre)
// {
// int sum = 0, m = s.size();
// for (int i = 0; i < pre; i++)
// sum += s[i] - '0';
// return sum;
// };
// int res = 0;
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// {
// string s;
// cin >> s;
// res++;
// int m = s.size();// for (int sum = 0; sum <= 90; sum += 2)
// for (int len = 2; len <= 10; len += 2)
// {
// int tar_sum = sum - get_pre(s, m);
// int tar_len = len - m;
// // bug3(len, m, tar_len);
// if (tar_sum < 0 || tar_len < 0 || tar_len > 5 || tar_sum > 45)
// continue;
// int half = len >> 1;
// if (m >= tar_len)
// {
// if (get_suf(s, half) << 1 == len)
// {
// for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
// for (int j = 0; j <= 45; j++)
// res += has[tar_len][tar_sum][i][j];
// }
// }
// else
// {
// // bug2(tar_len, tar_sum);
// // bug2(half, tar_sum >> 1);
// res += has[tar_len][tar_sum][half][tar_sum >> 1];
// }
// }
// int sum = get_pre(s, m);
// for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
// has[m][sum][i + 1][get_pre(s, i + 1)]++, bug(has[m + 1][sum][i][get_pre(s, i + 1)]);
// }
// cout << res;
// el;
// }
B
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC) \{ \for (auto Vec : VEC) \cout << Vec << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<pair<int, int>> a;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int x;cin >> x;a.push_back({x, -1});}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int x;cin >> x;a.push_back({x, 1});}sort(begin(a), end(a));int res = n;queue<int> q;for (auto [x, y] : a){if (y == -1)q.push(x);else{if (q.size() && x > q.front())res--, q.pop();}}cout << res << '\n';
}
// void _()
// {
// int n;
// cin >> n;
// vector<int> a(n), b(n);
// for (int &x : a)
// cin >> x;
// for (int &x : b)
// cin >> x;
// sort(begin(a), end(a));
// sort(begin(b), end(b));
// int l = 0, r = 0, res = n;
// for (; r < n; r++)
// if (a[l] < b[r])
// l++, res--;
// cout << res;
// el;
// }
C
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC) \{ \for (auto Vec : VEC) \cout << Vec << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<int> a(n + 1), f(n + 1), g(n + 1);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];map<int, bool> has;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (!has[a[i]])f[i] = 1, has[a[i]] = 1;has.clear();for (int i = n; i; i--)if (!has[a[i]])g[i] = 1, has[a[i]] = 1;int pre = 0, res = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){pre += f[i];res += pre * g[i];}cout << res;el;
}
D
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC) \{ \for (auto Vec : VEC) \cout << Vec << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<int> a(n + 1);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];vector<vector<int>> pre(30, vector<int>(n + 1));for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++)for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)pre[i][j] = pre[i][j - 1] + (a[j] >> i & 1);// ST表 RMQ 倍增// dp[i][j] 以i为起点 长度为1<<j的区间的最大值vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(32));// initfor (int j = 0; j < 30; j++) // j 是每一层状态for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){if (i + (1 << j) - 1 > n)continue;if (!j)dp[i][j] = a[i];elsedp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] & dp[i + (1 << j - 1)][j - 1];}// queryauto ask = [&](int l, int r){int k = __lg(r - l + 1);return dp[l][k] & dp[r + 1 - (1 << k)][k];};auto ok = [&](int l, int r, int k){// int ans = 0;// for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++)// {// if (pre[i][r] - pre[i][l - 1] == (r - l + 1))// ans += 1ll << i;// }// return ans >= k;return ask(l, r) >= k; // ST表只需这一句};// bug(ok(1, 1, 7));// bug(ok(1, 2, 7));int q;cin >> q;while (q--){int L, k;cin >> L >> k;int l = L - 1, r = n + 1;while (r - l - 1){int R = l + r >> 1;if (ok(L, R, k))l = R;elser = R;}// bug2(l, r);cout << (l < L ? -1 : l) << ' ';}el;
}
E
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC) \{ \for (auto Vec : VEC) \cout << Vec << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n, k;cin >> n >> k;vector<int> a(n + 1);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];int f = n;vector<int> vis(n + 1);while (k--){if (a[f] > n){cout << "No";el;return;}vis[f] = 1;f = (f - a[f] + n) % n;if (vis[f])break;}// k %= cnt;// while (k--)// f = a[f];// for (int i = f + 1; i <= n; i++)// cout << a[i] << ' ';// for (int i = 1; i <= f; i++)// cout << a[i] << ' ';cout << "Yes";el;
}
F
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC) \{ \for (auto Vec : VEC) \cout << Vec << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n, m;cin >> n >> m;n % m;int cnt = 100, res = 0;while (cnt--){if (n % m == 0){cout << res;el;return;}while (n < m){res += n;n <<= 1;}n %= m;}cout << -1;el;
}
G
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC) \{ \for (auto Vec : VEC) \cout << Vec << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;// cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n, m;cin >> n;vector<int> t(n);map<int, int> a, b;for (int &x : t)cin >> x;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int x;cin >> x;a[t[i]] = x;}cin >> m;t.assign(m, 0);for (int &x : t)cin >> x;for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){int x;cin >> x;b[t[i]] = x;}constexpr int mod = 998244353;int res = 1;for (auto [x, y] : b)if (a[x] < y)res = 0;for (auto [x, y] : a)res *= y > b[x] ? 2 : 1, res %= mod;cout << res;el;
}
H
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long //
#define endl '\n' // attention: interactive/debug
#define el cout << endl
using namespace std;
#define bug(BUG) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG) << endl
#define bug2(BUG1, BUG2) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << " " << (BUG2) << endl
#define bug3(BUG1, BUG2, BUG3) cout << "bug:# " << (BUG1) << ' ' << (BUG2) << ' ' << (BUG3) << endl
#define bugv(VEC) \{ \for (auto Vec : VEC) \cout << Vec << ' '; \el; \}void _();
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);cout << fixed << setprecision(10);int T = 1;cin >> T;while (T--)_();return 0;
}void _()
{int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector<string> s(n + 1);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> s[i], s[i] = ' ' + s[i];vector<vector<int>> f(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));bool fail = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int ans = 1;for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)if (s[i][j] == 'U')f[i][j] = ans, ans = -ans, f[i + 1][j] = ans;}for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++){int ans = 1;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (s[i][j] == 'L')f[i][j] = ans, ans = -ans, f[i][j + 1] = ans;}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int sum_row = 0;for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)sum_row += f[i][j];if (sum_row)fail = 1;}for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++){int sum_col = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)sum_col += f[i][j];if (sum_col)fail = 1;}if (fail){cout << -1 << '\n';return;}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++){if (f[i][j])cout << (f[i][j] == 1 ? 'W' : 'B');elsecout << '.';}cout << '\n';}
}
// void _()
// {
// int n, m;
// cin >> n >> m;
// vector<string> s(n + 1);
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// cin >> s[i], s[i] = ' ' + s[i];
// vector<vector<int>> f(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));
// bool fail = 0;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// int sum_row = 0;
// for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
// {
// if (s[i][j] - '.')
// f[i][j] = i + j & 1 ? 1 : -1;
// sum_row += f[i][j];
// }
// if (sum_row)
// fail = 1;
// }
// for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
// {
// int sum_col = 0;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// sum_col += f[i][j];
// if (sum_col)
// fail = 1;
// }
// if (fail)
// {
// cout << -1 << '\n';
// return;
// }
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
// {
// if (f[i][j])
// cout << (f[i][j] == 1 ? 'W' : 'B');
// else
// cout << '.';
// }
// cout << '\n';
// }
// }
相关文章:

2025.2.14——1400
2025.2.14——1400 A 1400 B 1400 C 1400 D 1400 E 1400 F 1400 G 1400 H 1400 ------------------------------------------------ 思维排序/双指针/二分/队列匹配思维二分/位运算思维数学思维 A 一眼想到的是维护信息计数。维护两个信息同时用长的一半去找短的一半…...

DeepSeek教unity------MessagePack-04
Union 联合 MessagePack for C# 支持序列化接口类型和抽象类类型的对象。它的行为类似于 XmlInclude 或 ProtoInclude。在 MessagePack for C# 中,这些被称为Union。只有接口和抽象类可以被 Union 属性注解。需要唯一的联合键。 /******************************…...

Java异常体系深度解析:从Exception到Error
文章目录 前言一、Java异常体系概览ExceptionError 二、受检异常与非受检异常受检异常(Checked Exception)非受检异常(Unchecked Exception) 三、常见的Error类型四、异常处理机制try-catch-finally结构Throws关键字 五、自定义异…...

【linux】文件与目录命令 - ln
文章目录 1. 基本用法2. 常用参数3. 用法举例4. 注意事项 ln 命令用于在文件系统中创建硬链接或符号链接(软链接),是文件共享和路径引用的常用工具。 1. 基本用法 语法: ln [选项] 源文件 [目标文件/目标目录]功能: 创…...

Xilinx kintex-7系列 FPGA支持PCIe 3.0 吗?
Xilinx kintex-7系列资源如下图 Xilinx各系列的GT资源类型和性能 PCIe Gen1/2/3的传输速率对比 K7上面使用的高速收发器GTX最高速率为12.5GT/s, PCIe Gen2 每个通道的传输速率为 5 GT/s。 PCIe Gen3 每个通道的传输速率为 8 GT/s。 所以理论上硬件支持PCIe3.0&#…...

无人机遥感技术在农业中的具体应用:株数和株高、冠层覆盖度、作物倒伏检测、叶面积指数、病虫害监测、产量估算、空间数据综合制图
近年来,随着无人机技术的飞速发展,其在智慧农业领域的应用越来越广泛。无人机遥感作为一种高效的空间大数据获取手段,能够为农业生产提供多时相、多维度、大面积的农情信息,为实现精准农业和智慧农业提供了有力支持。今天…...

前端框架React知识回顾
首先,得确定用户的需求,可能是一个准备面试的前端开发者,想要系统复习React相关知识点。接下来要考虑React的核心概念,比如组件、生命周期、Hooks这些肯定是必须的。然后,面试中常问的问题,比如虚拟DOM、状…...

坑多多之ac8257 i2c1 rtc-pcf8563
pcf85163 ordering information Ordering information Package Description Version Marking code PCF85163T/1 SO8 ① SOT96-1 PF85163 PCF85163TS/1 TSSOP8 ② SOT505-1 85163 ①plastic small outline package; 8 leads;body width 3.9 mm ②plastic thin…...

webpack构建流程
文章目录 [TOC](文章目录) 运行流程初始化流程编译构建流程compile编译make 编译模块build module 完成模块编译 输出流程seal输出资源emit输出完成 小结 运行流程 是一个串行的过程,它的工作流程就是将各个插件串联起来 在运行过程中会广播事件,插件只…...

React - 组件之props属性
在 React 中,props(即属性)是组件之间传递数据的一种方式。它是 React 组件的基础,用于将数据从父组件传递到子组件。 一、类组件中 1. props 的作用 数据传递: props 允许父组件向子组件传递数据。子组件可以使用这些数据来渲…...

PMTUD By UDP
通过UDP探测MTU,并实现udp echo server // Description: UDP echo server. // g udp_echo_server.cc -o udp_echo_server #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <unistd.h>#define PORT …...

Hutool - BloomFilter:便捷的布隆过滤器实现
1. 布隆过滤器简介 布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)是一种空间效率极高的概率型数据结构,用于判断一个元素是否存在于一个集合中。它的优点是空间效率和查询时间都远远超过一般的算法,但缺点是有一定的误判率,即判断元素存在…...

【学习资源】时间序列数据分析方法(1)
时间序列数据分析是一个有趣的话题,让我们多花一些时间来研究。此篇为第一篇文章。主要介绍特征提取方法、深度学习时序数据分析模型、参考资源。期望能帮助大家解决工业领域的相关问题。 1 特征提取方法:信号处理 (来源:INTELLIGENT FAULT DIAGNOSIS A…...
盛铂科技SWFA100捷变频频率综合器:高性能国产射频系统的关键选择
在现代射频系统中,频率综合器是实现精确频率控制和快速跳频的核心组件。盛铂科技推出的SWFA100捷变频频率综合器凭借其卓越的性能和小型化设计,成为高性能射频系统中的理想选择。 SWFA100捷变频频率综合器 高速跳频与宽频覆盖 SWFA100捷变频频率综合器能…...

释放你的元数据:使用 Elasticsearch 的自查询检索器
作者:来自 Elastic Josh Asres 了解如何使用 Elasticsearch 的 “self-quering” 检索器来通过结构化过滤器提高语义搜索的相关性。 在人工智能搜索的世界中,在海量的数据集中高效地找到正确的数据至关重要。传统的基于关键词的搜索在处理涉及自然语言的…...

【快速幂算法】快速幂算法讲解及C语言实现(递归实现和非递归实现,附代码)
快速幂算法 快速幂算法可用分治法实现 不难看出,对任意实数a和非负整数n,有: a n { 1 , n 0 , a ≠ 0 0 , a 0 ( a n 2 ) 2 , n > 0 , n 为偶数 ( a n 2 ) 2 ∗ a , n > 0 , n 为奇数 a^n \begin{cases} 1, & n 0, a\neq 0…...

3. 导入官方dashboard
官方dashboard:https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards 1. 点击仪表板 - 新建 - 导入 注:有网络的情况想可以使用ID,无网络情况下使用仪表板josn文件 2. 在官方dashboard网页上选择符合你现在数据源的dashboard - 点击进入 3. 下拉网页选…...

怎么理解 Spring Boot 的约定优于配置 ?
在传统的 Spring 开发中,大家可能都有过这样的经历:项目还没开始写几行核心业务代码,就已经在各种配置文件中耗费了大量时间。比如,要配置数据库连接,不仅要在 XML 文件里编写冗长的数据源配置,还要处理事务…...

Dify 是什么?Dify是一个开源的LLM应用开发平台,支持快速搭建生成式AI应用,具有RAG管道、Agent功能、模型集成等特点
首先,Dify是一个开源的LLM应用开发平台,支持快速搭建生成式AI应用,具有RAG管道、Agent功能、模型集成等特点75。根据搜索结果,网页6详细对比了多个RAG和AI开发框架,包括MaxKB、FastGPT、RagFlow、Anything-LLM等。其中…...

数据预处理都做什么,用什么工具
数据预处理是数据分析、数据挖掘和机器学习中的关键步骤,其目的是将原始数据转换为适合后续分析或建模的格式。以下是关于数据预处理的主要内容及常用工具的详细介绍: 一、数据预处理的主要任务 数据预处理的主要任务包括以下几个方面: 数据…...
: K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?)
云原生核心技术 (7/12): K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?
大家好,欢迎来到《云原生核心技术》系列的第七篇! 在上一篇,我们成功地使用 Minikube 或 kind 在自己的电脑上搭建起了一个迷你但功能完备的 Kubernetes 集群。现在,我们就像一个拥有了一块崭新数字土地的农场主,是时…...
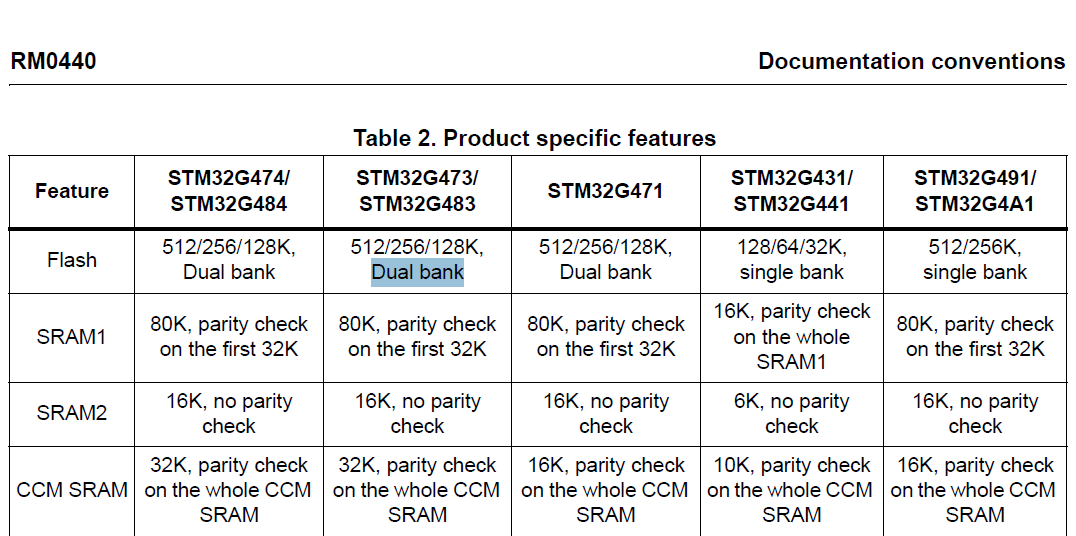
stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?
今天突然有人stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?由于时间太久,我真忘记了。搜搜发现,还真有人和我一样。见下面的链接:https://shequ.stmicroelectronics.cn/forum.php?modviewthread&tid644563 根据STM32G4系列参考手…...
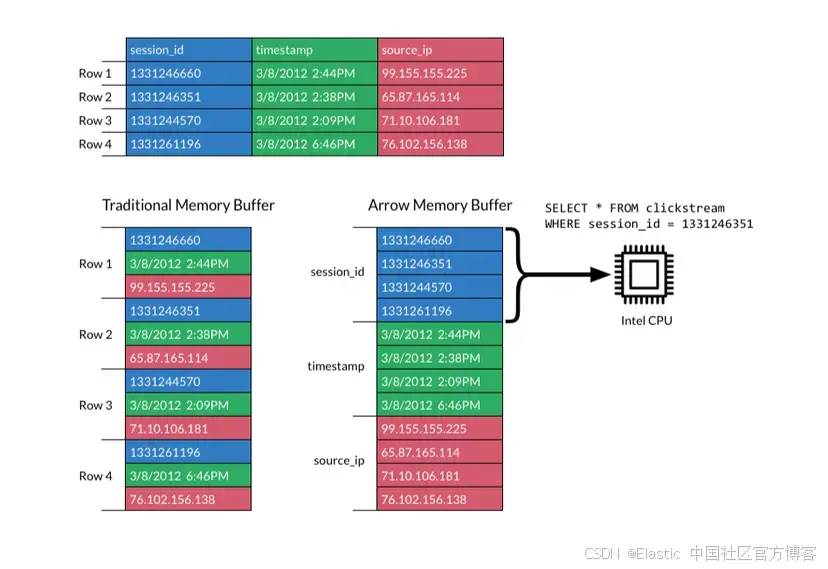
JavaScript 中的 ES|QL:利用 Apache Arrow 工具
作者:来自 Elastic Jeffrey Rengifo 学习如何将 ES|QL 与 JavaScript 的 Apache Arrow 客户端工具一起使用。 想获得 Elastic 认证吗?了解下一期 Elasticsearch Engineer 培训的时间吧! Elasticsearch 拥有众多新功能,助你为自己…...

Python爬虫实战:研究feedparser库相关技术
1. 引言 1.1 研究背景与意义 在当今信息爆炸的时代,互联网上存在着海量的信息资源。RSS(Really Simple Syndication)作为一种标准化的信息聚合技术,被广泛用于网站内容的发布和订阅。通过 RSS,用户可以方便地获取网站更新的内容,而无需频繁访问各个网站。 然而,互联网…...

如何为服务器生成TLS证书
TLS(Transport Layer Security)证书是确保网络通信安全的重要手段,它通过加密技术保护传输的数据不被窃听和篡改。在服务器上配置TLS证书,可以使用户通过HTTPS协议安全地访问您的网站。本文将详细介绍如何在服务器上生成一个TLS证…...

Matlab | matlab常用命令总结
常用命令 一、 基础操作与环境二、 矩阵与数组操作(核心)三、 绘图与可视化四、 编程与控制流五、 符号计算 (Symbolic Math Toolbox)六、 文件与数据 I/O七、 常用函数类别重要提示这是一份 MATLAB 常用命令和功能的总结,涵盖了基础操作、矩阵运算、绘图、编程和文件处理等…...
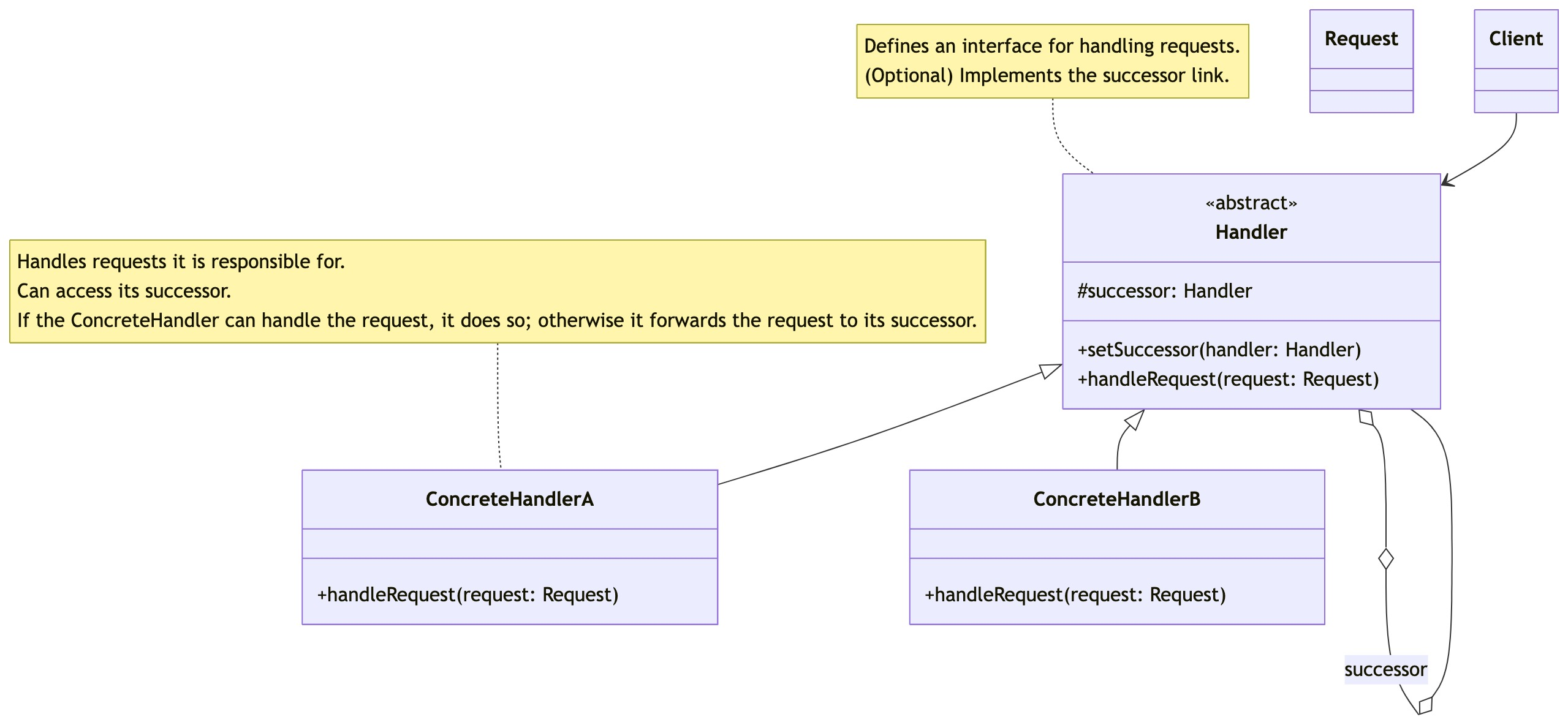
零基础设计模式——行为型模式 - 责任链模式
第四部分:行为型模式 - 责任链模式 (Chain of Responsibility Pattern) 欢迎来到行为型模式的学习!行为型模式关注对象之间的职责分配、算法封装和对象间的交互。我们将学习的第一个行为型模式是责任链模式。 核心思想:使多个对象都有机会处…...

06 Deep learning神经网络编程基础 激活函数 --吴恩达
深度学习激活函数详解 一、核心作用 引入非线性:使神经网络可学习复杂模式控制输出范围:如Sigmoid将输出限制在(0,1)梯度传递:影响反向传播的稳定性二、常见类型及数学表达 Sigmoid σ ( x ) = 1 1 +...

多模态大语言模型arxiv论文略读(108)
CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文标题:CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文作者:Sayna Ebrahimi, Sercan O. Arik, Tejas Nama, Tomas Pfister ➡️ 研究机构: Google Cloud AI Re…...

力扣-35.搜索插入位置
题目描述 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。 请必须使用时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法。 class Solution {public int searchInsert(int[] nums, …...
