Java注解的原理
目录
问题:
作用:
原理:
注解的限制
拓展:
问题:
今天刷面经,发现自己不懂注解的原理,特此记录。
作用:
注解的作用主要是给编译器看的,让它帮忙生成一些代码,或者是帮忙检查、判断和校验数据。
1.给编译器看:
- 帮助编译器进行语法检查(如 @Override、@Deprecated)。
- 通过注解处处理器生成代(如Lombok的@Getter,@Setter)。
2.给运行时框架看
- 通过反射机制动态读取注解信息,实现功能增强(如依赖注入、AOP、配置管理、数据验证)等。
原理:
注解的本质一个特殊的接口,继承了java.lang.annotation.Annotation 接口。当定义一个注解时,Java 编译器会将其转换为一个实现了 Annotation 接口的代理类。
import java.lang.annotation.*;@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface MyAnnotation {String value() default "defaultValue";int priority() default 1;
}//伪代码
public interface MyAnnotation extends Annotation {String value(); // 对应注解中的 value 属性int priority(); // 对应注解中的 priority 属性
}//验证
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 可以通过反射机制拿去值public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, UnknownHostException {//获取目标类Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class;//判断类有没有注解if(studentClass.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)){//拿到代理对象MyAnnotation annotation = studentClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);System.out.println("value:"+annotation.value());System.out.println("priotity:"+annotation.priority());}}注解的限制
虽然注解看起来像普通的接口,但它们有一些特殊的限制:
- 不能继承其他接口 :注解不能继承其他接口(除了隐式的
Annotation接口)。public @interface MyAnnotation extends SomeOtherInterface {} // 错误!
- 不能包含方法体 :注解中的方法只能声明,不能有实现。
public @interface MyAnnotation { String value() { return "defaultValue"; } // 错误! }
- 不支持泛型 :注解中的方法不能使用泛型。
public @interface MyAnnotation { List<String> values(); // 正确 List<T> values(); // 错误! }

拓展:
java.lang.annotation.Annotation 是所有注解的父接口。它定义了一些通用的方法,用于处理注解的元数据。
package java.lang.annotation;/*** The common interface extended by all annotation interfaces. Note that an* interface that manually extends this one does <i>not</i> define* an annotation interface. Also note that this interface does not itself* define an annotation interface.** More information about annotation interfaces can be found in section* {@jls 9.6} of <cite>The Java Language Specification</cite>.** The {@link java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement} interface discusses* compatibility concerns when evolving an annotation interface from being* non-repeatable to being repeatable.** @author Josh Bloch* @since 1.5*/
/*** 所有注解接口继承的公共接口。注意:手动扩展此接口的接口<i>不会</i>成为注解接口。* 此接口自身也不作为注解接口。* * 更多注解接口的详细信息,请参阅《Java语言规范》第{@jls 9.6}节。* * 当注解接口从不可重复变为可重复时,{@link java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement}* 接口讨论了相关的兼容性问题。* * 作者:Josh Bloch* 自版本:1.5*/
public interface Annotation {
public interface Annotation {/*** Returns true if the specified object represents an annotation* that is logically equivalent to this one. In other words,* returns true if the specified object is an instance of the same* annotation interface as this instance, all of whose members are equal* to the corresponding member of this annotation, as defined below:* <ul>* <li>Two corresponding primitive typed members whose values are* {@code x} and {@code y} are considered equal if {@code x == y},* unless their type is {@code float} or {@code double}.** <li>Two corresponding {@code float} members whose values* are {@code x} and {@code y} are considered equal if* {@code Float.valueOf(x).equals(Float.valueOf(y))}.* (Unlike the {@code ==} operator, NaN is considered equal* to itself, and {@code 0.0f} unequal to {@code -0.0f}.)** <li>Two corresponding {@code double} members whose values* are {@code x} and {@code y} are considered equal if* {@code Double.valueOf(x).equals(Double.valueOf(y))}.* (Unlike the {@code ==} operator, NaN is considered equal* to itself, and {@code 0.0} unequal to {@code -0.0}.)** <li>Two corresponding {@code String}, {@code Class}, enum, or* annotation typed members whose values are {@code x} and {@code y}* are considered equal if {@code x.equals(y)}. (Note that this* definition is recursive for annotation typed members.)** <li>Two corresponding array typed members {@code x} and {@code y}* are considered equal if {@code Arrays.equals(x, y)}, for the* appropriate overloading of {@link java.util.Arrays#equals Arrays.equals}.* </ul>** @return true if the specified object represents an annotation* that is logically equivalent to this one, otherwise false*/boolean equals(Object obj);/*** Returns the hash code of this annotation.** <p>The hash code of an annotation is the sum of the hash codes* of its members (including those with default values).** The hash code of an annotation member is (127 times the hash code* of the member-name as computed by {@link String#hashCode()}) XOR* the hash code of the member-value.* The hash code of a member-value depends on its type as defined below:* <ul>* <li>The hash code of a primitive value <i>{@code v}</i> is equal to* <code><i>WrapperType</i>.valueOf(<i>v</i>).hashCode()</code>, where* <i>{@code WrapperType}</i> is the wrapper type corresponding* to the primitive type of <i>{@code v}</i> ({@link Byte},* {@link Character}, {@link Double}, {@link Float}, {@link Integer},* {@link Long}, {@link Short}, or {@link Boolean}).** <li>The hash code of a string, enum, class, or annotation member-value* <i>{@code v}</i> is computed as by calling* <code><i>v</i>.hashCode()</code>. (In the case of annotation* member values, this is a recursive definition.)** <li>The hash code of an array member-value is computed by calling* the appropriate overloading of* {@link java.util.Arrays#hashCode(long[]) Arrays.hashCode}* on the value. (There is one overloading for each primitive* type, and one for object reference types.)* </ul>** @return the hash code of this annotation*/int hashCode();/*** Returns a string representation of this annotation. The details* of the representation are implementation-dependent, but the following* may be regarded as typical:* <pre>* @com.example.Name(first="Duke", middle="of", last="Java")* </pre>** @return a string representation of this annotation*/String toString();/*** Returns the annotation interface of this annotation.** @apiNote Implementation-dependent classes are used to provide* the implementations of annotations. Therefore, calling {@link* Object#getClass getClass} on an annotation will return an* implementation-dependent class. In contrast, this method will* reliably return the annotation interface of the annotation.** @return the annotation interface of this annotation* @see Enum#getDeclaringClass*/Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType();
}
相关文章:

Java注解的原理
目录 问题: 作用: 原理: 注解的限制 拓展: 问题: 今天刷面经,发现自己不懂注解的原理,特此记录。 作用: 注解的作用主要是给编译器看的,让它帮忙生成一些代码,或者是帮忙检查…...

AI知识架构之神经网络
神经网络:这是整个内容的主题,是一种模拟人类大脑神经元结构和功能的计算模型,在人工智能领域广泛应用。基本概念:介绍神经网络相关的基础概念,为后续深入理解神经网络做铺垫。定义与起源: 神经网络是模拟人类大脑神经元结构和功能的计算模型,其起源于对生物神经系统的研…...

OpenGL 04--GLSL、数据类型、Uniform、着色器类
一、着色器 在 OpenGL 中,着色器(Shader)是运行在 GPU 上的程序,用于处理图形渲染管线中的不同阶段。 这些小程序为图形渲染管线的某个特定部分而运行。从基本意义上来说,着色器只是一种把输入转化为输出的程序。着色器…...

学习笔记06——JVM调优
JVM 调优实战:性能优化的技巧与实战 在 Java 开发中,JVM(Java Virtual Machine)作为 Java 程序的运行环境,其性能直接影响到应用程序的响应速度和吞吐量。合理的 JVM 调优可以显著提升应用性能,降低延迟&a…...
-TensorFlow入门(常数张量和变量))
深度学习(3)-TensorFlow入门(常数张量和变量)
低阶张量操作是所有现代机器学习的底层架构,可以转化为TensorFlow API。 张量,包括存储神经网络状态的特殊张量(变量)。 张量运算,比如加法、relu、matmul。 反向传播,一种计算数学表达式梯度的方法&…...
学习笔记)
3-2 WPS JS宏 工作簿的打开与保存(模板批量另存为工作)学习笔记
************************************************************************************************************** 点击进入 -我要自学网-国内领先的专业视频教程学习网站 *******************************************************************************************…...

【GO】学习笔记
目录 学习链接 开发环境 开发工具 GVM - GO多版本部署 GOPATH 与 go.mod go常用命令 环境初始化 编译与运行 GDB -- GNU 调试器 基本语法与字符类型 关键字与标识符 格式化占位符 基本语法 初始值&零值&默认值 变量声明与赋值 _ 下划线的用法 字…...

【TypeScript】ts在vue中的使用
目录 一、Vue 3 TypeScript 1. 项目创建与配置 项目创建 关键配置文件 2.完整项目结构示例 3. 组件 Props 类型定义 4. 响应式数据与 Ref 5. Composition 函数复用 二、组件开发 1.组合式API(Composition API) 2.选项式API(Options…...

2025前端框架最新组件解析与实战技巧:Vue与React的革新之路
作者:飞天大河豚 引言 2025年的前端开发领域,Vue与React依然是开发者最青睐的框架。随着Vue 3的全面普及和React 18的持续优化,两大框架在组件化开发、性能优化、工程化支持等方面均有显著突破。本文将从最新组件特性、使用场景和编码技巧三…...

Elasticsearch 的分布式架构原理:通俗易懂版
Elasticsearch 的分布式架构原理:通俗易懂版 Lucene 和 Elasticsearch 的前世今生 Lucene 是一个功能强大的搜索库,提供了高效的全文检索能力。然而,直接基于 Lucene 开发非常复杂,即使是简单的功能也需要编写大量的 Java 代码&…...

【DeepSeek】【GPT-Academic】:DeepSeek集成到GPT-Academic(官方+第三方)
目录 1 官方deepseek 1.1 拉取学术GPT项目 1.2 安装依赖 1.3 修改配置文件中的DEEPSEEK_API_KEY 2 第三方API 2.1 修改DEEPSEEK_API_KEY 2.2 修改CUSTOM_API_KEY_PATTERM 2.3 地址重定向 2.4 修改模型参数 2.5 成功调用 2.6 尝试添加一个deepseek-r1参数 3 使用千帆…...

2.部署kafka:9092
官方文档:http://kafka.apache.org/documentation.html (虽然kafka中集成了zookeeper,但还是建议使用独立的zk集群) Kafka3台集群搭建环境: 操作系统: centos7 防火墙:全关 3台zookeeper集群内的机器,1台logstash 软件版本: …...

学习路之PHP --TP6异步执行功能 (无需安装任何框架)
学习路之PHP --异步执行功能 (无需安装任何框架) 简介一、工具类二、调用三、异步任务的操作四、效果: 简介 执行异步任务是一种很常见的需求,如批量发邮箱,短信等等执行耗时任务时,需要程序异步执行&…...

Uniapp 小程序复制、粘贴功能实现
在开发 Uniapp 小程序的过程中,复制和粘贴功能是非常实用且常见的交互需求。今天,我就来和大家详细分享如何在 Uniapp 中实现这两个功能。 复制功能:uni.setClipboardData方法 goResult() {uni.setClipboardData({data: this.copyContent, /…...

seacmsv9注入管理员账号密码+orderby+limit
一、seacmsv9 SQL注入漏洞 查看源码 <?php session_start(); require_once("include/common.php"); //前置跳转start $cs$_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"]; if($GLOBALS[cfg_mskin]3 AND $GLOBALS[isMobile]1){header("location:$cfg_mhost$cs");}…...

多通道数据采集和信号生成的模块化仪器如何重构飞机电子可靠性测试体系?
飞机的核心电子系统包括发电与配电系统,飞机内部所有设备和系统之间的内部数据通信系统,以及用于外部通信的射频设备。其他所有航空电子元件都依赖这些关键总线进行电力传输或数据通信。在本文中,我们将了解模块化仪器(无论是PCIe…...
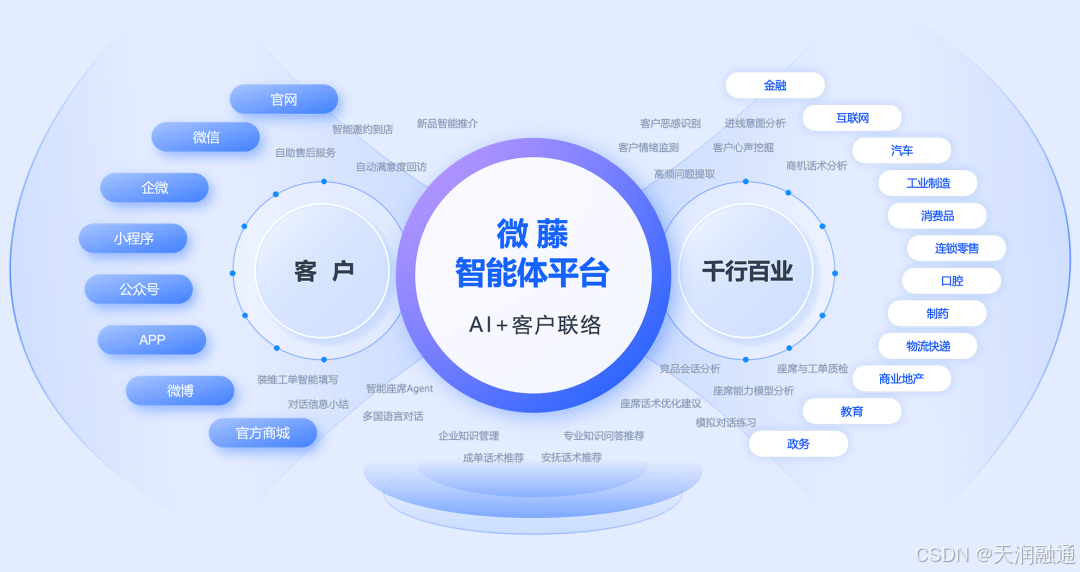
天润融通分析DeepSeek如何一键完成从PR接入,到真正的业务接入
DeepSeek出圈之后,市场上很快掀起了一波DeepSeek接入潮。 在客户服务领域,许多企业见识到DeepSeek的超强能力后,也迅速接入DeepSeek并获得了不错的效果。 比如在客户接待服务场景,有企业将DeepSeek应用到智能问答助手࿰…...

免费PDF工具
Smallpdf.com - A Free Solution to all your PDF Problems Smallpdf - the platform that makes it super easy to convert and edit all your PDF files. Solving all your PDF problems in one place - and yes, free. https://smallpdf.com/#rappSmallpdf.com-解决您所有PD…...

PyTorch 源码学习:GPU 内存管理之它山之石——TensorFlow BFC 算法
TensorFlow 和 PyTorch 都是常用的深度学习框架,各自有一套独特但又相似的 GPU 内存管理机制(BFC 算法)。它山之石可以攻玉。了解 TensorFlow 的 BFC 算法有助于学习 PyTorch 管理 GPU 内存的精妙之处。本文重点关注 TensorFlow BFC 算法的核…...

【学写LibreCAD】1 LibreCAD主程序
一、源码 头文件: #ifndef MAIN_H #define MAIN_H#include<QStringList>#define STR(x) #x #define XSTR(x) STR(x)/*** brief handleArgs* param argc cli argument counter from main()* param argv cli arguments from main()* param argClean a list…...
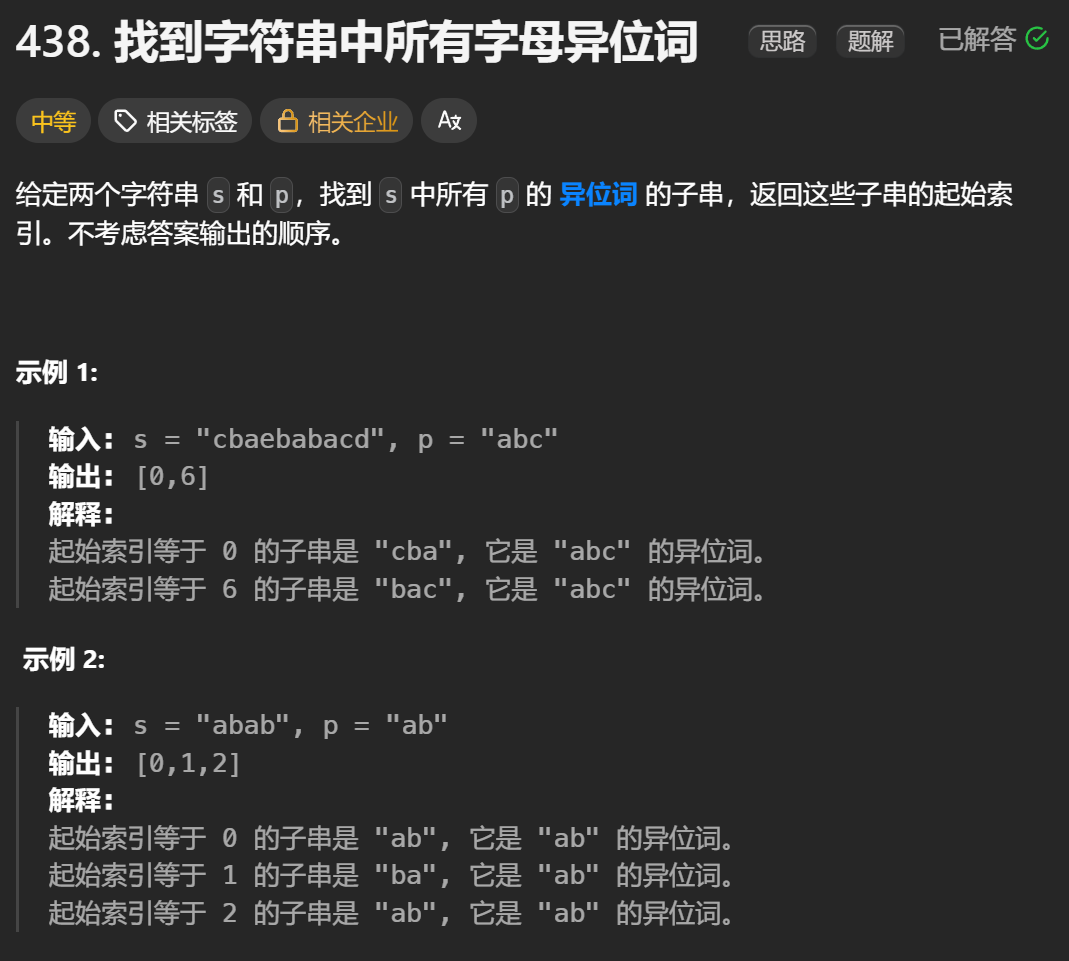
12.找到字符串中所有字母异位词
🧠 题目解析 题目描述: 给定两个字符串 s 和 p,找出 s 中所有 p 的字母异位词的起始索引。 返回的答案以数组形式表示。 字母异位词定义: 若两个字符串包含的字符种类和出现次数完全相同,顺序无所谓,则互为…...

全面解析各类VPN技术:GRE、IPsec、L2TP、SSL与MPLS VPN对比
目录 引言 VPN技术概述 GRE VPN 3.1 GRE封装结构 3.2 GRE的应用场景 GRE over IPsec 4.1 GRE over IPsec封装结构 4.2 为什么使用GRE over IPsec? IPsec VPN 5.1 IPsec传输模式(Transport Mode) 5.2 IPsec隧道模式(Tunne…...

零基础在实践中学习网络安全-皮卡丘靶场(第九期-Unsafe Fileupload模块)(yakit方式)
本期内容并不是很难,相信大家会学的很愉快,当然对于有后端基础的朋友来说,本期内容更加容易了解,当然没有基础的也别担心,本期内容会详细解释有关内容 本期用到的软件:yakit(因为经过之前好多期…...
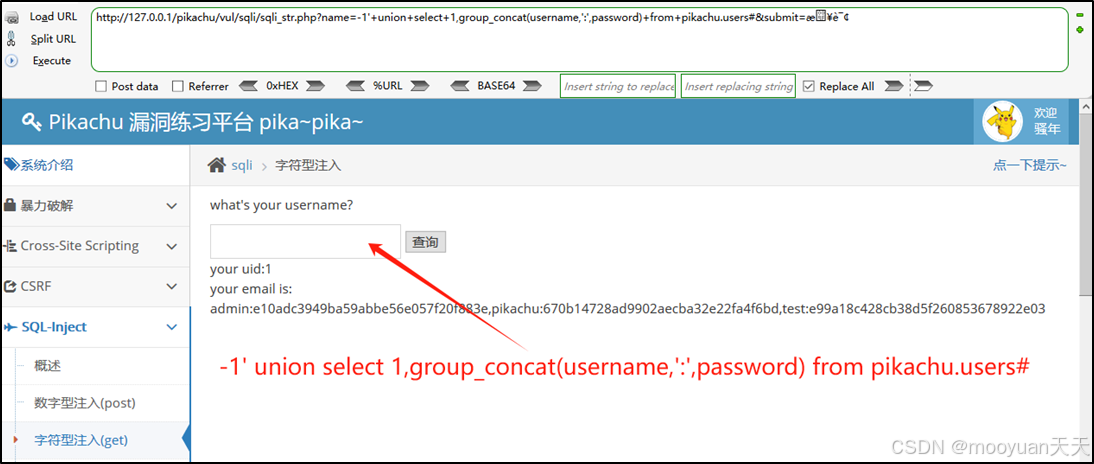
pikachu靶场通关笔记19 SQL注入02-字符型注入(GET)
目录 一、SQL注入 二、字符型SQL注入 三、字符型注入与数字型注入 四、源码分析 五、渗透实战 1、渗透准备 2、SQL注入探测 (1)输入单引号 (2)万能注入语句 3、获取回显列orderby 4、获取数据库名database 5、获取表名…...

6️⃣Go 语言中的哈希、加密与序列化:通往区块链世界的钥匙
Go 语言中的哈希、加密与序列化:通往区块链世界的钥匙 一、前言:离区块链还有多远? 区块链听起来可能遥不可及,似乎是只有密码学专家和资深工程师才能涉足的领域。但事实上,构建一个区块链的核心并不复杂,尤其当你已经掌握了一门系统编程语言,比如 Go。 要真正理解区…...

32位寻址与64位寻址
32位寻址与64位寻址 32位寻址是什么? 32位寻址是指计算机的CPU、内存或总线系统使用32位二进制数来标识和访问内存中的存储单元(地址),其核心含义与能力如下: 1. 核心定义 地址位宽:CPU或内存控制器用32位…...

MeshGPT 笔记
[2311.15475] MeshGPT: Generating Triangle Meshes with Decoder-Only Transformers https://library.scholarcy.com/try 真正意义上的AI生成三维模型MESHGPT来袭!_哔哩哔哩_bilibili GitHub - lucidrains/meshgpt-pytorch: Implementation of MeshGPT, SOTA Me…...

python打卡第47天
昨天代码中注意力热图的部分顺移至今天 知识点回顾: 热力图 作业:对比不同卷积层热图可视化的结果 def visualize_attention_map(model, test_loader, device, class_names, num_samples3):"""可视化模型的注意力热力图,展示模…...

虚幻基础:角色旋转
能帮到你的话,就给个赞吧 😘 文章目录 移动组件使用控制器所需旋转:组件 使用 控制器旋转将旋转朝向运动:组件 使用 移动方向旋转 控制器旋转和移动旋转 缺点移动旋转:必须移动才能旋转,不移动不旋转控制器…...

Qt Quick Controls模块功能及架构
Qt Quick Controls是Qt Quick的一个附加模块,提供了一套用于构建完整用户界面的UI控件。在Qt 6.0中,这个模块经历了重大重构和改进。 一、主要功能和特点 1. 架构重构 完全重写了底层架构,与Qt Quick更紧密集成 移除了对Qt Widgets的依赖&…...
