分布式锁—7.Curator的分布式锁
大纲
1.Curator的可重入锁的源码
2.Curator的非可重入锁的源码
3.Curator的可重入读写锁的源码
4.Curator的MultiLock源码
5.Curator的Semaphore源码
1.Curator的可重入锁的源码
(1)InterProcessMutex获取分布式锁
(2)InterProcessMutex的初始化
(3)InterProcessMutex.acquire()尝试获取锁
(4)LockInternals.attemptLock()尝试获取锁
(5)不同客户端线程获取锁时的互斥实现
(6)同一客户端线程可重入加锁的实现
(7)客户端线程释放锁的实现
(8)客户端线程释放锁后其他线程获取锁的实现
(9)InterProcessMutex就是一个公平锁
(1)InterProcessMutex获取分布式锁
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 3);CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("127.0.0.1:2181", 5000, 3000, retryPolicy);client.start();System.out.println("已经启动Curator客户端");//获取分布式锁InterProcessMutex lock = new InterProcessMutex(client, "/locks/myLock");lock.acquire();Thread.sleep(1000);lock.release();}
}(2)InterProcessMutex的初始化
设置锁的节点路径basePath + 初始化一个LockInternals对象实例。
public class InterProcessMutex implements InterProcessLock, Revocable<InterProcessMutex> {private final LockInternals internals;private final String basePath;private static final String LOCK_NAME = "lock-";...public InterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path) {this(client, path, new StandardLockInternalsDriver());}public InterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, LockInternalsDriver driver) {this(client, path, LOCK_NAME, 1, driver);}//初始化InterProcessMutexInterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases, LockInternalsDriver driver) {//1.设置锁的节点路径basePath = PathUtils.validatePath(path);//2.初始化一个LockInternals对象实例internals = new LockInternals(client, driver, path, lockName, maxLeases);}
}public class LockInternals {private final LockInternalsDriver driver;private final String lockName;private volatile int maxLeases;private final WatcherRemoveCuratorFramework client;private final String basePath;private final String path;...LockInternals(CuratorFramework client, LockInternalsDriver driver, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases) {this.driver = driver;this.lockName = lockName;this.maxLeases = maxLeases;this.client = client.newWatcherRemoveCuratorFramework();this.basePath = PathUtils.validatePath(path);this.path = ZKPaths.makePath(path, lockName);}...
}(3)InterProcessMutex.acquire()尝试获取锁
LockData是InterProcessMutex的一个静态内部类。一个线程对应一个LockData实例对象,用来描述线程持有的锁的具体情况。多个线程对应的LockData存放在一个叫threadData的ConcurrentMap中。LockData中有一个原子变量lockCount,用于锁的重入次数计数。
在执行InterProcessMutex的acquire()方法尝试获取锁时:首先会尝试取出当前线程对应的LockData数据,判断是否存在。如果存在,则说明锁正在被当前线程重入,重入次数自增后直接返回。如果不存在,则调用LockInternals的attemptLock()方法尝试获取锁。默认情况下,attemptLock()方法传入的等待获取锁的时间time = -1。
public class InterProcessMutex implements InterProcessLock, Revocable<InterProcessMutex> {private final LockInternals internals;private final String basePath;private static final String LOCK_NAME = "lock-";//一个线程对应一个LockData数据对象private final ConcurrentMap<Thread, LockData> threadData = Maps.newConcurrentMap();...//初始化InterProcessMutexInterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases, LockInternalsDriver driver) {//设置锁的路径basePath = PathUtils.validatePath(path);//初始化LockInternalsinternals = new LockInternals(client, driver, path, lockName, maxLeases);}@Overridepublic void acquire() throws Exception {//获取分布式锁,会一直阻塞等待直到获取成功//相同的线程可以重入锁,每一次调用acquire()方法都要匹配一个release()方法的调用if (!internalLock(-1, null)) {throw new IOException("Lost connection while trying to acquire lock: " + basePath);}}private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {//获取当前线程Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前线程对应的LockData数据LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);if (lockData != null) {//可重入计算lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();return true;}//调用LockInternals.attemptLock()方法尝试获取锁,默认情况下,传入的time=-1,表示等待获取锁的时间String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());if (lockPath != null) {//获取锁成功,将当前线程 + 其创建的临时顺序节点路径,封装成一个LockData对象LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath);//然后把该LockData对象存放到InterProcessMutex.threadData这个Map中threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);return true;}return false;}//LockData是InterProcessMutex的一个静态内部类private static class LockData {final Thread owningThread;final String lockPath;final AtomicInteger lockCount = new AtomicInteger(1);//用于锁的重入次数计数private LockData(Thread owningThread, String lockPath) {this.owningThread = owningThread;this.lockPath = lockPath;}}protected byte[] getLockNodeBytes() {return null;}...
}(4)LockInternals.attemptLock()尝试获取锁
先创建临时节点,再判断是否满足获取锁的条件。
步骤一:首先调用LockInternalsDriver的createsTheLock()方法创建一个临时顺序节点。其中creatingParentContainersIfNeeded()表示级联创建,forPath(path)表示创建的节点路径名称,withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)表示临时顺序节点。
步骤二:然后调用LockInternals的internalLockLoop()方法检查是否获取到了锁。在LockInternals的internalLockLoop()方法的while循环中,会先获取排好序的客户端线程尝试获取锁时创建的临时顺序节点名称列表。然后获取当前客户端线程尝试获取锁时创建的临时顺序节点的名称,再根据名称获取在节点列表中的位置 + 是否可以获取锁 + 前一个节点的路径,也就是获取一个封装好这些信息的PredicateResults对象。
具体会根据节点名称获取当前线程创建的临时顺序节点在节点列表的位置,然后会比较当前线程创建的节点的位置和maxLeases的大小。其中maxLeases代表了同时允许多少个客户端可以获取到锁,默认是1。如果当前线程创建的节点的位置小,则表示可以获取锁。如果当前线程创建的节点的位置大,则表示获取锁失败。
获取锁成功,则会中断LockInternals的internalLockLoop()方法的while循环,然后向外返回当前客户端线程创建的临时顺序节点路径。接着在InterProcessMutex的internalLock()方法中,会将当前线程 + 其创建的临时顺序节点路径,封装成一个LockData对象,然后把该LockData对象存放到InterProcessMutex.threadData这个Map中。
获取锁失败,则通过PredicateResults对象先获取前一个节点路径名称。然后通过getData()方法获取前一个节点路径在zk的信息,并添加Watcher监听。该Watcher监听主要是用来唤醒在LockInternals中被wait()阻塞的线程。添加完Watcher监听后,便会调用wait()方法将当前线程挂起。
所以前一个节点发生变化时,便会通知添加的Watcher监听。然后便会唤醒阻塞的线程,继续执行internalLockLoop()方法的while循环。while循环又会继续获取排序的节点列表 + 判断当前线程是否已获取锁。
public class LockInternals {private final LockInternalsDriver driver;LockInternals(CuratorFramework client, LockInternalsDriver driver, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases) {this.driver = driver;this.path = ZKPaths.makePath(path, lockName);//生成要创建的临时节点路径名称...}...String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception {//获取当前时间final long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();//默认情况下millisToWait=nullfinal Long millisToWait = (unit != null) ? unit.toMillis(time) : null;//默认情况下localLockNodeBytes也是nullfinal byte[] localLockNodeBytes = (revocable.get() != null) ? new byte[0] : lockNodeBytes;int retryCount = 0;String ourPath = null;boolean hasTheLock = false;//是否已经获取到锁boolean isDone = false;//是否正在获取锁while (!isDone) {isDone = true;//1.这里是关键性的加锁代码,会去级联创建一个临时顺序节点ourPath = driver.createsTheLock(client, path, localLockNodeBytes);//2.检查是否获取到了锁hasTheLock = internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);}if (hasTheLock) {return ourPath;}return null;}private final Watcher watcher = new Watcher() {@Overridepublic void process(WatchedEvent event) {//唤醒LockInternals中被wait()阻塞的线程client.postSafeNotify(LockInternals.this);}};//检查是否获取到了锁private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception {boolean haveTheLock = false;boolean doDelete = false;...while ((client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock) {//3.获取排好序的各个客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点名称列表List<String> children = getSortedChildren();//4.获取当前客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点的名称String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1); // +1 to include the slash//5.获取当前线程创建的节点在节点列表中的位置 + 是否可以获取锁 + 前一个节点的路径名称PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);if (predicateResults.getsTheLock()) {//获取锁成功//返回truehaveTheLock = true;} else {//获取锁失败//获取前一个节点路径名称String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch();synchronized(this) {//use getData() instead of exists() to avoid leaving unneeded watchers which is a type of resource leak//通过getData()获取前一个节点路径在zk的信息,并添加watch监听client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath);//默认情况下,millisToWait = nullif (millisToWait != null) {millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();if (millisToWait <= 0) {doDelete = true;//timed out - delete our nodebreak;}wait(millisToWait);//阻塞} else {wait();//阻塞}}}}...return haveTheLock;}List<String> getSortedChildren() throws Exception {//获取排好序的各个客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点名称列表return getSortedChildren(client, basePath, lockName, driver);}public static List<String> getSortedChildren(CuratorFramework client, String basePath, final String lockName, final LockInternalsSorter sorter) throws Exception {//获取各个客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点名称列表List<String> children = client.getChildren().forPath(basePath);//对节点名称进行排序List<String> sortedList = Lists.newArrayList(children);Collections.sort(sortedList,new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String lhs, String rhs) {return sorter.fixForSorting(lhs, lockName).compareTo(sorter.fixForSorting(rhs, lockName));}});return sortedList;}...
}public class StandardLockInternalsDriver implements LockInternalsDriver {...//级联创建一个临时顺序节点@Overridepublic String createsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, String path, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception {String ourPath;//默认情况下传入的lockNodeBytes=nullif (lockNodeBytes != null) {ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path, lockNodeBytes);} else {//创建临时顺序节点ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path);}return ourPath;}//获取当前线程创建的节点在节点列表中的位置以及是否可以获取锁@Overridepublic PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception {//根据节点名称获取当前线程创建的临时顺序节点在节点列表中的位置int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);//maxLeases代表的是同时允许多少个客户端可以获取到锁//getsTheLock为true表示可以获取锁,getsTheLock为false表示获取锁失败boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases;//获取当前节点需要watch的前一个节点路径String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases);return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);}...
}(5)不同客户端线程获取锁时的互斥实现
maxLeases代表了同时允许多少个客户端可以获取到锁,默认值是1。能否获取锁的判断就是:线程创建的节点的位置outIndex < maxLeases。当线程1创建的节点在节点列表中排第一时,满足outIndex = 0 < maxLeases = 1,可以获取锁。当线程2创建的节点再节点列表中排第二时,不满足outIndex = 1 < maxLeases = 1,所以不能获取锁。从而实现线程1和线程2获取锁时的互斥。
(6)同一客户端线程可重入加锁的实现
客户端线程重复获取锁时,会重复调用InterProcessMutex的internalLock()方法。在InterProcessMutex的internalLock()方法中:线程第一次获取锁成功会创建一个LockData对象,并存放在一个Map中。线程第二次获取锁时,便会从这个Map中取出这个LockData对象,并对LockData对象中的重入计数器lockCount进行递增,接着就返回true。以此实现可重入加锁。
(7)客户端线程释放锁的实现
客户端线程释放锁时会调用InterProcessMutex的release()方法。
首先对LockData里的重入计数器进行递减。当重入计数器大于0时,直接返回。当重入计数器为0时才执行下一步删除节点的操作。
然后删除客户端线程创建的临时顺序节点,client.delete().guaranteed().forPath(ourPath)。
public class InterProcessMutex implements InterProcessLock, Revocable<InterProcessMutex> {private final LockInternals internals;private final ConcurrentMap<Thread, LockData> threadData = Maps.newConcurrentMap();...@Overridepublic void release() throws Exception {//获取当前线程Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前线程对应的LockData对象LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);if (lockData == null) {throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("You do not own the lock: " + basePath);}//1.首先对LockData里的重入计数器lockCount进行递减int newLockCount = lockData.lockCount.decrementAndGet();if (newLockCount > 0) {//当重入计数器大于0时,直接返回return;}if (newLockCount < 0) {throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("Lock count has gone negative for lock: " + basePath);}try {//2.当重入计数器为0时执行删除节点的操作internals.releaseLock(lockData.lockPath);} finally {threadData.remove(currentThread);}}...
}public class LockInternals {...final void releaseLock(String lockPath) throws Exception {client.removeWatchers();revocable.set(null);deleteOurPath(lockPath);}private void deleteOurPath(String ourPath) throws Exception {//删除节点client.delete().guaranteed().forPath(ourPath);}...
}(8)客户端线程释放锁后其他线程获取锁的实现
由于在节点列表里排第二的节点对应的线程会监听排第一的节点,而当持有锁的客户端线程释放锁后,排第一的节点会被删除掉。所以在节点列表里排第二的节点对应的客户端,便会收到zk的通知。于是会回调执行该线程添加的Watcher的process()方法,也就是唤醒该线程,让其继续执行while循环获取锁。
public class LockInternals {...private final Watcher watcher = new Watcher() {@Overridepublic void process(WatchedEvent event) {//唤醒LockInternals中被wait()阻塞的线程client.postSafeNotify(LockInternals.this);}};//检查是否获取到了锁private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception {boolean haveTheLock = false;boolean doDelete = false;...while ((client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock) {//3.获取排好序的各个客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点名称列表List<String> children = getSortedChildren();//4.获取当前客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点的名称String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1); // +1 to include the slash//5.获取当前线程创建的节点在节点列表中的位置+是否可以获取锁+前一个节点的路径名称PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);if (predicateResults.getsTheLock()) {//获取锁成功//返回truehaveTheLock = true;} else {//获取锁失败//获取前一个节点路径名称String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch();synchronized(this) {//use getData() instead of exists() to avoid leaving unneeded watchers which is a type of resource leak//通过getData()获取前一个节点路径在zk的信息,并添加watch监听client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath);//默认情况下,millisToWait = nullif (millisToWait != null) {millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();if (millisToWait <= 0) {doDelete = true;//timed out - delete our nodebreak;}wait(millisToWait);//阻塞} else {wait();//阻塞}}}}...return haveTheLock;}...
}(9)InterProcessMutex就是一个公平锁
因为所有客户端线程都会创建一个顺序节点,然后按申请锁的顺序进行排序。最后会依次按自己所在的排序来尝试获取锁,实现了所有客户端排队获取锁。

2.Curator的非可重入锁的源码
(1)Curator的非可重入锁InterProcessSemaphoreMutex的使用
(2)Curator的非可重入锁InterProcessSemaphoreMutex的源码
(1)Curator的非可重入锁InterProcessSemaphoreMutex的使用
非可重入锁:同一个时间只能有一个客户端线程获取到锁,其他线程都要排队,而且同一个客户端线程是不可重入加锁的。
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 3);final CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("127.0.0.1:2181",//zk的地址5000,//客户端和zk的心跳超时时间,超过该时间没心跳,Session就会被断开3000,//连接zk时的超时时间retryPolicy);client.start();System.out.println("已经启动Curator客户端,完成zk的连接");//非可重入锁InterProcessSemaphoreMutex lock = new InterProcessSemaphoreMutex(client, "/locks");lock.acquire();Thread.sleep(3000);lock.release();}
}(2)Curator的非可重入锁InterProcessSemaphoreMutex的源码
Curator的非可重入锁是基于Semaphore来实现的,也就是将Semaphore允许获取Lease的客户端线程数设置为1,从而实现同一时间只能有一个客户端线程获取到Lease。
public class InterProcessSemaphoreMutex implements InterProcessLock {private final InterProcessSemaphoreV2 semaphore;private final WatcherRemoveCuratorFramework watcherRemoveClient;private volatile Lease lease;public InterProcessSemaphoreMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path) {watcherRemoveClient = client.newWatcherRemoveCuratorFramework();this.semaphore = new InterProcessSemaphoreV2(watcherRemoveClient, path, 1);}@Overridepublic void acquire() throws Exception {//获取非可重入锁就是获取Semaphore的Leaselease = semaphore.acquire();}@Overridepublic boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {Lease acquiredLease = semaphore.acquire(time, unit);if (acquiredLease == null) {return false;}lease = acquiredLease;return true;}@Overridepublic void release() throws Exception {//释放非可重入锁就是释放Semaphore的LeaseLease lease = this.lease;Preconditions.checkState(lease != null, "Not acquired");this.lease = null;lease.close();watcherRemoveClient.removeWatchers();}
}3.Curator的可重入读写锁的源码
(1)Curator的可重入读写锁InterProcessReadWriteLock的使用
(2)Curator的可重入读写锁InterProcessReadWriteLock的初始化
(3)InterProcessMutex获取锁的源码
(4)先获取读锁 + 后获取读锁的情形分析
(5)先获取读锁 + 后获取写锁的情形分析
(6)先获取写锁 + 后获取读锁的情形分析
(7)先获取写锁 + 再获取写锁的情形分析
(1)Curator的可重入读写锁InterProcessReadWriteLock的使用
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 3);final CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("127.0.0.1:2181",//zk的地址5000,//客户端和zk的心跳超时时间,超过该时间没心跳,Session就会被断开3000,//连接zk时的超时时间retryPolicy);client.start();System.out.println("已经启动Curator客户端,完成zk的连接");//读写锁InterProcessReadWriteLock lock = new InterProcessReadWriteLock(client, "/locks");lock.readLock().acquire();lock.readLock().release();lock.writeLock().acquire();lock.writeLock().release();}
}(2)Curator的可重入读写锁InterProcessReadWriteLock的初始化
读锁和写锁都是基于可重入锁InterProcessMutex的子类来实现的。读锁和写锁的获取锁和释放锁逻辑,就是使用InterProcessMutex的逻辑。
public class InterProcessReadWriteLock {private final InterProcessMutex readMutex;//读锁private final InterProcessMutex writeMutex;//写锁//must be the same length. LockInternals depends on itprivate static final String READ_LOCK_NAME = "__READ__";private static final String WRITE_LOCK_NAME = "__WRIT__";...//InterProcessReadWriteLock的初始化public InterProcessReadWriteLock(CuratorFramework client, String basePath, byte[] lockData) {lockData = (lockData == null) ? null : Arrays.copyOf(lockData, lockData.length);//写锁的初始化writeMutex = new InternalInterProcessMutex(client,basePath,WRITE_LOCK_NAME,//写锁的lockName='__WRIT__'lockData,1,//写锁的maxLeasesnew SortingLockInternalsDriver() {@Overridepublic PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception {return super.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);}});//读锁的初始化readMutex = new InternalInterProcessMutex(client,basePath,READ_LOCK_NAME,//读锁的lockName='__READ__'lockData,Integer.MAX_VALUE,//读锁的maxLeasesnew SortingLockInternalsDriver() {@Overridepublic PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception {return readLockPredicate(children, sequenceNodeName);}});}private static class InternalInterProcessMutex extends InterProcessMutex {private final String lockName;private final byte[] lockData;InternalInterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, String lockName, byte[] lockData, int maxLeases, LockInternalsDriver driver) {super(client, path, lockName, maxLeases, driver);this.lockName = lockName;this.lockData = lockData;}...}public InterProcessMutex readLock() {return readMutex;}public InterProcessMutex writeLock() {return writeMutex;}...
}(3)InterProcessMutex获取锁的源码
public class InterProcessMutex implements InterProcessLock, Revocable<InterProcessMutex> {private final LockInternals internals;private final String basePath;private static final String LOCK_NAME = "lock-";//一个线程对应一个LockData数据对象private final ConcurrentMap<Thread, LockData> threadData = Maps.newConcurrentMap();...//初始化InterProcessMutexInterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases, LockInternalsDriver driver) {//设置锁的路径basePath = PathUtils.validatePath(path);//初始化LockInternalsinternals = new LockInternals(client, driver, path, lockName, maxLeases);}@Overridepublic void acquire() throws Exception {//获取分布式锁,会一直阻塞等待直到获取成功//相同的线程可以重入锁,每一次调用acquire()方法都要匹配一个release()方法的调用if (!internalLock(-1, null)) {throw new IOException("Lost connection while trying to acquire lock: " + basePath);}}private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {//获取当前线程Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前线程对应的LockData数据LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);if (lockData != null) {//可重入计算lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();return true;}//调用LockInternals.attemptLock()方法尝试获取锁,默认情况下,传入的time=-1,表示等待获取锁的时间String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());if (lockPath != null) {//获取锁成功,将当前线程 + 其创建的临时顺序节点路径,封装成一个LockData对象LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath);//然后把该LockData对象存放到InterProcessMutex.threadData这个Map中threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);return true;}return false;}//LockData是InterProcessMutex的一个静态内部类private static class LockData {final Thread owningThread;final String lockPath;final AtomicInteger lockCount = new AtomicInteger(1);//用于锁的重入次数计数private LockData(Thread owningThread, String lockPath) {this.owningThread = owningThread;this.lockPath = lockPath;}}protected byte[] getLockNodeBytes() {return null;}...
}public class LockInternals {private final LockInternalsDriver driver;LockInternals(CuratorFramework client, LockInternalsDriver driver, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases) {this.driver = driver;this.path = ZKPaths.makePath(path, lockName);//生成要创建的临时节点路径名称...}...String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception {//获取当前时间final long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();//默认情况下millisToWait=nullfinal Long millisToWait = (unit != null) ? unit.toMillis(time) : null;//默认情况下localLockNodeBytes也是nullfinal byte[] localLockNodeBytes = (revocable.get() != null) ? new byte[0] : lockNodeBytes;int retryCount = 0;String ourPath = null;boolean hasTheLock = false;//是否已经获取到锁boolean isDone = false;//是否正在获取锁while (!isDone) {isDone = true;//1.这里是关键性的加锁代码,会去级联创建一个临时顺序节点ourPath = driver.createsTheLock(client, path, localLockNodeBytes);//2.检查是否获取到了锁hasTheLock = internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);}if (hasTheLock) {return ourPath;}return null;}private final Watcher watcher = new Watcher() {@Overridepublic void process(WatchedEvent event) {//唤醒LockInternals中被wait()阻塞的线程client.postSafeNotify(LockInternals.this);}};//检查是否获取到了锁private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception {boolean haveTheLock = false;boolean doDelete = false;...while ((client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock) {//3.获取排好序的各个客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点名称列表List<String> children = getSortedChildren();//4.获取当前客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点的名称String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1); // +1 to include the slash//5.获取当前线程创建的节点在节点列表中的位置 + 是否可以获取锁 + 前一个节点的路径名称PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);if (predicateResults.getsTheLock()) {//获取锁成功//返回truehaveTheLock = true;} else {//获取锁失败//获取前一个节点路径名称String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch();synchronized(this) {//use getData() instead of exists() to avoid leaving unneeded watchers which is a type of resource leak//通过getData()获取前一个节点路径在zk的信息,并添加watch监听client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath);//默认情况下,millisToWait = nullif (millisToWait != null) {millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();if (millisToWait <= 0) {doDelete = true;//timed out - delete our nodebreak;}wait(millisToWait);//阻塞} else {wait();//阻塞}}}}...return haveTheLock;}List<String> getSortedChildren() throws Exception {//获取排好序的各个客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点名称列表return getSortedChildren(client, basePath, lockName, driver);}public static List<String> getSortedChildren(CuratorFramework client, String basePath, final String lockName, final LockInternalsSorter sorter) throws Exception {//获取各个客户端线程尝试获取分布式锁时创建的临时顺序节点名称列表List<String> children = client.getChildren().forPath(basePath);//对节点名称进行排序List<String> sortedList = Lists.newArrayList(children);Collections.sort(sortedList,new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String lhs, String rhs) {return sorter.fixForSorting(lhs, lockName).compareTo(sorter.fixForSorting(rhs, lockName));}});return sortedList;}...
}public class StandardLockInternalsDriver implements LockInternalsDriver {...//级联创建一个临时顺序节点@Overridepublic String createsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, String path, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception {String ourPath;//默认情况下传入的lockNodeBytes=nullif (lockNodeBytes != null) {ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path, lockNodeBytes);} else {//创建临时顺序节点ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path);}return ourPath;}//获取当前线程创建的节点在节点列表中的位置以及是否可以获取锁@Overridepublic PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception {//根据节点名称获取当前线程创建的临时顺序节点在节点列表中的位置int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);//maxLeases代表的是同时允许多少个客户端可以获取到锁//getsTheLock为true表示可以获取锁,getsTheLock为false表示获取锁失败boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases;//获取当前节点需要watch的前一个节点路径String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases);return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);}...
}(4)先获取读锁 + 后获取读锁的情形分析
当线程创建完临时顺序节点,并获取到排好序的节点列表children后,执行LockInternalsDriver的getsTheLock()方法获取能否成功加锁的信息时,会执行到InterProcessReadWriteLock的readLockPredicate()方法。
由于此时firstWriteIndex = Integer.MAX_VALUE,所以无论多少线程尝试获取读锁,都能满足ourIndex < firstWriteIndex,也就是getsTheLock的值会为true,即表示可以获取读锁。
所以读读不互斥。
public class InterProcessReadWriteLock {...//sequenceNodeName是当前线程创建的临时顺序节点的路径名称private PredicateResults readLockPredicate(List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName) throws Exception {if (writeMutex.isOwnedByCurrentThread()) {return new PredicateResults(null, true);}int index = 0;int firstWriteIndex = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int ourIndex = -1;for (String node : children) {if (node.contains(WRITE_LOCK_NAME)) {firstWriteIndex = Math.min(index, firstWriteIndex);} else if (node.startsWith(sequenceNodeName)) {//找出当前线程创建的临时顺序节点在节点列表中的位置,用ourIndex表示ourIndex = index;break;}++index;}StandardLockInternalsDriver.validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);boolean getsTheLock = (ourIndex < firstWriteIndex);String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(firstWriteIndex);return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);}...
}(5)先获取读锁 + 后获取写锁的情形分析
一.假设客户端线程1首先成功获取了读锁
那么在/locks目录下,此时已经有了如下这个读锁的临时顺序节点。
/locks/43f3-4c2f-ba98-07a641d351f2-__READ__0000000004二.然后另一个客户端线程2过来尝试获取写锁
于是该线程2会也会先在/locks目录下创建出如下写锁的临时顺序节点:
/locks/9361-4fb7-8420-a8d4911d2c99-__WRIT__0000000005接着该线程会获取/locks目录的当前子节点列表并进行排序,结果如下:
[43f3-4c2f-ba98-07a641d351f2-__READ__0000000004,
9361-4fb7-8420-a8d4911d2c99-__WRIT__0000000005]然后会执行StandardLockInternalsDriver的getsTheLock()方法。由于初始化写锁时,设置了其maxLeases是1,而在StandardLockInternalsDriver的getsTheLock()方法中,判断线程能成功获取写锁的依据是:ourIndex < maxLeases。即如果要成功获取写锁,那么线程创建的节点在子节点列表里必须排第一。
而此时,由于之前已有线程获取过一个读锁,而后来又有其他线程往里面创建一个写锁的临时顺序节点。所以写锁的临时顺序节点在子节点列表children里排第二,ourIndex是1。所以index = 1 < maxLeases = 1,条件不成立。
因此,此时客户端线程2获取写锁失败。于是该线程便会给前一个节点添加一个监听器,并调用wait()方法把自己挂起。如果前面一个节点被删除释放了锁,那么该线程就会被唤醒,从而再次尝试判断自己创建的节点是否在当前子节点列表中排第一。如果是,那么就表示获取写锁成功。
public class StandardLockInternalsDriver implements LockInternalsDriver {...//获取当前线程创建的节点在节点列表中的位置以及是否可以获取锁@Overridepublic PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception {//根据节点名称获取当前线程创建的临时顺序节点在节点列表中的位置int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);//maxLeases代表的是同时允许多少个客户端可以获取到锁//getsTheLock为true表示可以获取锁,getsTheLock为false表示获取锁失败boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases;//获取当前节点需要watch的前一个节点路径String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases);return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);}...
}(6)先获取写锁 + 后获取读锁的情形分析
一.假设客户端线程1先获取了写锁
那么在/locks目录下,此时已经有了如下这个写锁的临时顺序节点。
/locks/4383-466e-9b86-fda522ea061a-__WRIT__0000000006二.然后另一个客户端线程2过来尝试获取读锁
于是该线程2会也会先在/locks目录下创建出如下读锁的临时顺序节点:
/locks/5ba2-488f-93a4-f85fafd5cc32-__READ__0000000007接着该线程会获取/locks目录的当前子节点列表并进行排序,结果如下:
[4383-466e-9b86-fda522ea061a-__WRIT__0000000006,
5ba2-488f-93a4-f85fafd5cc32-__READ__0000000007]然后会执行LockInternalsDriver的getsTheLock()方法获取能否加锁的信息,也就是会执行InterProcessReadWriteLock的readLockPredicate()方法。
public class InterProcessReadWriteLock {...//sequenceNodeName是当前线程创建的临时顺序节点的路径名称private PredicateResults readLockPredicate(List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName) throws Exception {//如果是同一个客户端线程,先加写锁,再加读锁,是可以成功的,不会互斥if (writeMutex.isOwnedByCurrentThread()) {return new PredicateResults(null, true);}int index = 0;int firstWriteIndex = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int ourIndex = -1;for (String node : children) {if (node.contains(WRITE_LOCK_NAME)) {firstWriteIndex = Math.min(index, firstWriteIndex);} else if (node.startsWith(sequenceNodeName)) {//找出当前线程创建的临时顺序节点在节点列表中的位置,用ourIndex表示ourIndex = index;break;}++index;}StandardLockInternalsDriver.validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);boolean getsTheLock = (ourIndex < firstWriteIndex);String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(firstWriteIndex);return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);}...
}在InterProcessReadWriteLock的readLockPredicate()方法中,如果是同一个客户端线程,先获取写锁,再获取读锁,是不会互斥的。如果是不同的客户端线程,线程1先获取写锁,线程2再获取读锁,则互斥。因为线程2执行readLockPredicate()方法在遍历子节点列表(children)时,如果在子节点列表(children)中发现了一个写锁,会设置firstWriteIndex=0。而此时线程2创建的临时顺序节点的ourIndex=1,所以不满足ourIndex(1) < firstWriteIndex(0),于是线程2获取读锁失败。
总结,获取读锁时,在当前线程创建的节点前面:如果还有写锁对应的节点,那么firstWriteIndex就会被重置为具体位置。如果没有写锁对应的节点,那么firstWriteIndex就是MAX_VALUE。而只要firstWriteIndex为MAX_VALUE,那么就可以不断允许获取读锁。
(7)先获取写锁 + 再获取写锁的情形分析
如果客户端线程1先获取了写锁,然后后面客户端线程2来获取这个写锁。此时线程2会发现自己创建的节点排在节点列表中的第二,不是第一。于是获取写锁失败,进行阻塞挂起。等线程1释放了写锁后,才会唤醒线程2继续尝试获取写锁。
4.Curator的MultiLock源码
(1)Curator的MultiLock的使用
(2)Curator的MultiLock的源码
(1)Curator的MultiLock的使用
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 3);final CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("127.0.0.1:2181",//zk的地址5000,//客户端和zk的心跳超时时间,超过该时间没心跳,Session就会被断开3000,//连接zk时的超时时间retryPolicy);client.start();System.out.println("已经启动Curator客户端,完成zk的连接");//MultiLockInterProcessLock lock1 = new InterProcessMutex(client, "/locks/lock_01");InterProcessLock lock2 = new InterProcessMutex(client, "/locks/lock_02");InterProcessLock lock3 = new InterProcessMutex(client, "/locks/lock_03");List<InterProcessLock> locks = new ArrayList<InterProcessLock>();locks.add(lock1);locks.add(lock2);locks.add(lock3);InterProcessMultiLock multiLock = new InterProcessMultiLock(locks);}
}(2)Curator的MultiLock的源码
MultiLock原理:依次遍历获取每个锁,阻塞直到获取每个锁为止,然后返回true。如果过程中有报错,依次释放已经获取到的锁,然后返回false。
public class InterProcessMultiLock implements InterProcessLock {private final List<InterProcessLock> locks;public InterProcessMultiLock(List<InterProcessLock> locks) {this.locks = ImmutableList.copyOf(locks);}//获取锁@Overridepublic void acquire() throws Exception {acquire(-1, null);}@Overridepublic boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {Exception exception = null;List<InterProcessLock> acquired = Lists.newArrayList();boolean success = true;//依次遍历获取每个锁,阻塞直到获取每个锁为止for (InterProcessLock lock : locks) {try {if (unit == null) {lock.acquire();acquired.add(lock);} else {if (lock.acquire(time, unit)) {acquired.add(lock);} else {success = false;break;}}} catch (Exception e) {ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(e);success = false;exception = e;}}if (!success) {for (InterProcessLock lock : reverse(acquired)) {try {lock.release();} catch (Exception e) {ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(e);// ignore}}}if (exception != null) {throw exception;}return success;}@Overridepublic synchronized void release() throws Exception {Exception baseException = null;for (InterProcessLock lock : reverse(locks)) {try {lock.release();} catch (Exception e) {ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(e);if (baseException == null) {baseException = e;} else {baseException = new Exception(baseException);}}}if (baseException != null) {throw baseException;}}...
}5.Curator的Semaphore源码
(1)基于InterProcessSemaphoreV2使用Semaphore
(2)InterProcessSemaphoreV2的初始化
(3)InterProcessSemaphoreV2.acquire()方法获取Semaphore的Lease
(4)InterProcessSemaphoreV2.returnLease()方法释放Semaphore的Lease
Semaphore信号量,就是指定同时可以有多个线程获取到锁。
(1)基于InterProcessSemaphoreV2使用Semaphore
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 3);final CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient("127.0.0.1:2181",//zk的地址5000,//客户端和zk的心跳超时时间,超过该时间没心跳,Session就会被断开3000,//连接zk时的超时时间retryPolicy);client.start();System.out.println("已经启动Curator客户端,完成zk的连接");//获取SemaphoreInterProcessSemaphoreV2 semaphore = new InterProcessSemaphoreV2(client, "/semaphore", 3);Lease lease = semaphore.acquire();//获取Semaphore的一个锁Thread.sleep(3000);semaphore.returnLease(lease);//向Semaphore返还一个锁}
}(2)InterProcessSemaphoreV2的初始化
public class InterProcessSemaphoreV2 {private final WatcherRemoveCuratorFramework client;private final InterProcessMutex lock;private final String leasesPath;private volatile int maxLeases;...//maxLeases表示该实例可以允许获取的lease数量public InterProcessSemaphoreV2(CuratorFramework client, String path, int maxLeases) {this(client, path, maxLeases, null);}//初始化InterProcessSemaphoreV2时,传入的参数path = "/semaphore",参数maxLeases = 3private InterProcessSemaphoreV2(CuratorFramework client, String path, int maxLeases, SharedCountReader count) {this.client = client.newWatcherRemoveCuratorFramework();path = PathUtils.validatePath(path);//锁的path是ZKPaths.makePath(path, LOCK_PARENT) => '/semaphore/locks'//初始化一个InterProcessMutex分布式锁this.lock = new InterProcessMutex(client, ZKPaths.makePath(path, LOCK_PARENT));this.maxLeases = (count != null) ? count.getCount() : maxLeases;//lease的path是:'/semaphore/leases'this.leasesPath = ZKPaths.makePath(path, LEASE_PARENT);...}...
}(3)InterProcessSemaphoreV2.acquire()方法获取Semaphore的Lease
客户端线程尝试获取Semaphore的一个Lease。
步骤一:首先会获取初始化时创建的锁InterProcessMutex
锁的路径是:/semaphore/locks。当多个客户端线程同时执行acquire()获取Lease时只会有一个线程成功,而其他线程会基于锁路径下的临时顺序节点来排队获取锁。
步骤二:获取锁成功后才会尝试获取Semaphore的Lease
Lease的路径是:/semaphore/leases。此时会先到'/semaphore/leases'目录下创建一个临时顺序节点,然后会调用InterProcessSemaphoreV2的makeLease()方法创建一个Lease。这个Lease对象就是客户端线程成功获取Semaphore的一个Lease。
创建完Lease对象后,接着会进入一个for循环,会先获取/semaphore/leases目录下的所有临时顺序节点,并添加监听。然后判断/semaphore/leases目录下节点的数量是否大于maxLeases。如果临时顺序节点的数量小于maxLeases,那么说明当前客户端线程成功获取Semaphore的Lease,于是退出循环。如果临时顺序节点的数量大于maxLeases,那么当前客户端线程就要调用wait()进行阻塞等待。
public class InterProcessSemaphoreV2 {private final InterProcessMutex lock;private final Watcher watcher = new Watcher() {@Overridepublic void process(WatchedEvent event) {//唤醒在InterProcessSemaphoreV2对象中执行wait()而被阻塞的线程client.postSafeNotify(InterProcessSemaphoreV2.this);}};...public Lease acquire() throws Exception {Collection<Lease> leases = acquire(1, 0, null);return leases.iterator().next();}public Collection<Lease> acquire(int qty, long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {long startMs = System.currentTimeMillis();boolean hasWait = (unit != null);long waitMs = hasWait ? TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(time, unit) : 0;Preconditions.checkArgument(qty > 0, "qty cannot be 0");ImmutableList.Builder<Lease> builder = ImmutableList.builder();boolean success = false;try {while (qty-- > 0) {int retryCount = 0;long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();boolean isDone = false;while (!isDone) {switch (internalAcquire1Lease(builder, startMs, hasWait, waitMs)) {case CONTINUE: {isDone = true;break;}case RETURN_NULL: {return null;}case RETRY_DUE_TO_MISSING_NODE: {if (!client.getZookeeperClient().getRetryPolicy().allowRetry(retryCount++, System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis, RetryLoop.getDefaultRetrySleeper())) {throw new KeeperException.NoNodeException("Sequential path not found - possible session loss");}//try againbreak;}}}}success = true;} finally {if (!success) {returnAll(builder.build());}}return builder.build();}private InternalAcquireResult internalAcquire1Lease(ImmutableList.Builder<Lease> builder, long startMs, boolean hasWait, long waitMs) throws Exception {if (client.getState() != CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) {return InternalAcquireResult.RETURN_NULL;}if (hasWait) {long thisWaitMs = getThisWaitMs(startMs, waitMs);if (!lock.acquire(thisWaitMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {return InternalAcquireResult.RETURN_NULL;}} else {//1.首先获取一个分布式锁lock.acquire();}Lease lease = null;boolean success = false;try {//2.尝试获取Semaphore的Lease:创建一个临时顺序节点PathAndBytesable<String> createBuilder = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL);String path = (nodeData != null) ? createBuilder.forPath(ZKPaths.makePath(leasesPath, LEASE_BASE_NAME), nodeData) : createBuilder.forPath(ZKPaths.makePath(leasesPath, LEASE_BASE_NAME));String nodeName = ZKPaths.getNodeFromPath(path);lease = makeLease(path);...try {synchronized(this) {for(;;) {List<String> children;//3.获取./lease目录下的所有临时顺序节点,并添加watcher监听children = client.getChildren().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(leasesPath);...//4.判断临时顺序节点的数量是否大于maxLeases//maxLeases表示最多允许多少个客户端线程获取Semaphore的Leaseif (children.size() <= maxLeases) {//如果临时顺序节点的数量小于maxLeases//那么说明当前客户端线程成功获取Semaphore的Lease,于是退出循环break;}//如果临时顺序节点的数量大于maxLeases//那么当前客户端线程就要调用wait()进行阻塞等待if (hasWait) {long thisWaitMs = getThisWaitMs(startMs, waitMs);if (thisWaitMs <= 0) {return InternalAcquireResult.RETURN_NULL;}...wait(thisWaitMs);} else {...wait();}}success = true;}} finally {if (!success) {returnLease(lease);}client.removeWatchers();}} finally {//释放掉之前获取的锁lock.release();}builder.add(Preconditions.checkNotNull(lease));return InternalAcquireResult.CONTINUE;}...
}(4)InterProcessSemaphoreV2.returnLease()方法释放Semaphore的Lease
执行InterProcessSemaphoreV2的returnLease()方法时,最终会执行makeLease()生成的Lease对象的close()方法,而close()方法会删除在/semaphore/leases目录下创建的临时顺序节点。
当/semaphore/leases目录下的节点发生变化时,那些对该目录进行Watcher监听的客户端就会收到通知,于是就会执行Watcher里的process()方法,唤醒执行wait()时被阻塞的线程,从而让这些没有成功获取Semaphore的Lease的线程继续尝试获取Lease。
public class InterProcessSemaphoreV2 {...public void returnLease(Lease lease) {//执行Lease的close()方法CloseableUtils.closeQuietly(lease);}private Lease makeLease(final String path) {return new Lease() {@Overridepublic void close() throws IOException {try {client.delete().guaranteed().forPath(path);} catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) {log.warn("Lease already released", e);} catch (Exception e) {ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(e);throw new IOException(e);}}@Overridepublic byte[] getData() throws Exception {return client.getData().forPath(path);}@Overridepublic String getNodeName() {return ZKPaths.getNodeFromPath(path);}};}...
}相关文章:

分布式锁—7.Curator的分布式锁
大纲 1.Curator的可重入锁的源码 2.Curator的非可重入锁的源码 3.Curator的可重入读写锁的源码 4.Curator的MultiLock源码 5.Curator的Semaphore源码 1.Curator的可重入锁的源码 (1)InterProcessMutex获取分布式锁 (2)InterProcessMutex的初始化 (3)InterProcessMutex.…...

【笔记】STM32L4系列使用RT-Thread Studio电源管理组件(PM框架)实现低功耗
硬件平台:STM32L431RCT6 RT-Thread版本:4.1.0 目录 一.新建工程 二.配置工程 编辑 三.移植pm驱动 四.配置cubeMX 五.修改驱动文件,干掉报错 六.增加用户低功耗逻辑 1.设置唤醒方式 2.设置睡眠时以及唤醒后动作 编辑 3.增加测试命…...

C++什么是深复制和浅复制,构造函数和析构函数,哪一个可以写成虚函数,为什么?
在C之中深复制是指对于值类型复制它的值,对于指针类型不仅仅复制指针指向的值,还会重新分配一个内存空间用于放置复制的值(对动态分配的内存进行重新分配和内存复制),这种深复制不会出现悬空指针的问题,但是…...

从连接到交互:SDN 架构下 OpenFlow 协议的流程与报文剖析
在SDN架构中,交换机与控制器之间的通信基于 OpenFlow协议,其设计目的是实现控制平面与数据平面的解耦。以下是 交换机连接控制器 和 数据包进入交换机触发交互 的详细流程及协议报文分析: 一、交换机连接控制器的流程(初始化阶段&…...

第七课:Python反爬攻防战:Headers/IP代理与验证码
在爬虫开发过程中,反爬虫机制成为了我们必须面对的挑战。本文将深入探讨Python爬虫中常见的反爬机制,并详细解析如何通过随机User-Agent生成、代理IP池搭建以及验证码识别来应对这些反爬策略。文章将包含完整的示例代码,帮助读者更好地理解和…...

Golang学习笔记_47——访问者模式
Golang学习笔记_44——命令模式 Golang学习笔记_45——备忘录模式 Golang学习笔记_46——状态模式 文章目录 一、核心概念1. 定义2. 解决的问题3. 核心角色4. 类图 二、特点分析三、适用场景1. 编译器实现2. 财务系统3. UI组件系统 四、Go语言实现示例完整实现代码执行结果 五、…...

软件高级架构师 - 软件工程
补充中 测试 测试类型 静态测试 动态测试 测试阶段 单元测试中,包含性能测试,如下: 集成测试中,包含以下: 维护 遗留系统处置 高水平低价值:采取集成 对于这类系统,采取 集成 的方式&…...

IDEA 基础配置: maven配置 | 服务窗口配置
文章目录 IDEA版本与MAVEN版本对应关系maven配置镜像源插件idea打开服务工具窗口IDEA中的一些常见问题及其解决方案IDEA版本与MAVEN版本对应关系 查找发布时间在IDEA版本之前的dea2021可以使用maven3.8以及以前的版本 比如我是idea2021.2.2 ,需要将 maven 退到 apache-maven-3.…...

Qt之QGraphicsView图像操作
QGraphicsView图像操作:旋转、放大、缩小、移动、图层切换 1 摘要 GraphicsView框架结构主要包含三个主要的类QGraphicsScene(场景)、QGraphicsView(视图)、QGraphicsItem(图元)。QGraphicsScene本身不可见,是一个存储图元的容器,必须通过与之相连的QGraphicsView视图来显…...

人工智能之数学基础:对线性代数中逆矩阵的思考?
本文重点 逆矩阵是线性代数中的一个重要概念,它在线性方程组、矩阵方程、动态系统、密码学、经济学和金融学以及计算机图形学等领域都有广泛的应用。通过了解逆矩阵的定义、性质、计算方法和应用,我们可以更好地理解和应用线性代数知识,解决各种实际问题。 关于逆矩阵的思…...

嵌入式开发之串行数据处理
前题 前面几篇文章写了关于嵌入式软件开发时,关于串行数据处理的一些相关内容,有兴趣的可以看看《嵌入式开发:软件架构、驱动开发与串行数据处理》、《嵌入式软件开发之生产关系模型》和《嵌入式开发之Modbus-RTU协议解析》相关的内容。从业十…...

机器学习(六)
一,决策树: 简介: 决策树是一种通过构建类似树状的结构(颠倒的树),从根节点开始逐步对数据进行划分,最终在叶子节点做出预测结果的模型。 结构组成: 根节点:初始的数据集…...

结合unittest和pytest进行虚拟数据库测试
使用 pytest 和 MagicMock 模拟数据库操作,并测试假设的 create_user 函数,将用户添加到数据库中。 代码实现 from datetime import date from typing import List, Optional from unittest.mock import MagicMock from pydantic import BaseModel, Fi…...
详细教程)
Spring Boot 监听器(Listeners)详细教程
Spring Boot 监听器(Listeners)详细教程 目录 Spring Boot 监听器概述监听器核心概念最佳使用场景实现步骤高级配置详细使用场景总结 1. Spring Boot 监听器概述 Spring Boot 监听器(Listeners)基于 Spring Framework 的事件机制…...

工具介绍《githack》以及Git 命令行
一、Githack 工具介绍 Githack 是一个用于检测和利用网站 .git 目录泄露漏洞的安全工具。当网站错误配置导致 .git 目录可公开访问时,攻击者可通过该工具下载 .git 中的版本控制文件,并重建完整的项目源代码。 核心用途 检测 .git 目录泄露漏洞。从泄…...

【hello git】git rebase、git merge、git stash、git cherry-pick
目录 一、git merge:保留了原有分支的提交结构 二、git rebase:提交分支更加整洁 三、git stash 四、git cherry-pick 共同点:将 一个分支的提交 合并到 到另一个上分支上去 一、git merge:保留了原有分支的提交结构 现有一个模型…...

MR的环形缓冲区(底层)
MapReduce的大致流程: 1、HDFS读取数据; 2、按照规则进行分片,形成若干个spilt; 3、进行Map 4、打上分区标签(patition) 5、数据入环形缓冲区(KVbuffer) 6、原地排序ÿ…...

下载Hugging Face模型的几种方式
1.网页下载 直接访问Hugging Face模型页面,点击“File and versions”选项卡,选择所需的文件进行下载。 2.使用huggingface-cli 首先,安装huggingface_hub: pip install huggingface_hub 然后,使用以下命令下载模型࿱…...

Java 第十一章 GUI编程(2)
目录 GUI 事件处理 基本思路 添加事件监听器 对话框 实例 GUI 事件处理 对于采用了图形用户界面的程序来说,事件控制是非常重要的;到目前为止, 我们编写的图形用户界面程序都仅仅只是完成了界面,而没有任何实际的功能&…...
)
Redis数据结构深度解析:从String到Stream的奇幻之旅(一)
Redis系列文章 《半小时掌握Redis核心操作:从零开始的实战指南》-CSDN博客 Redis数据结构深度解析:从String到Stream的奇幻之旅(一)-CSDN博客 Redis数据结构深度解析:从String到Stream的奇幻之旅(二&…...
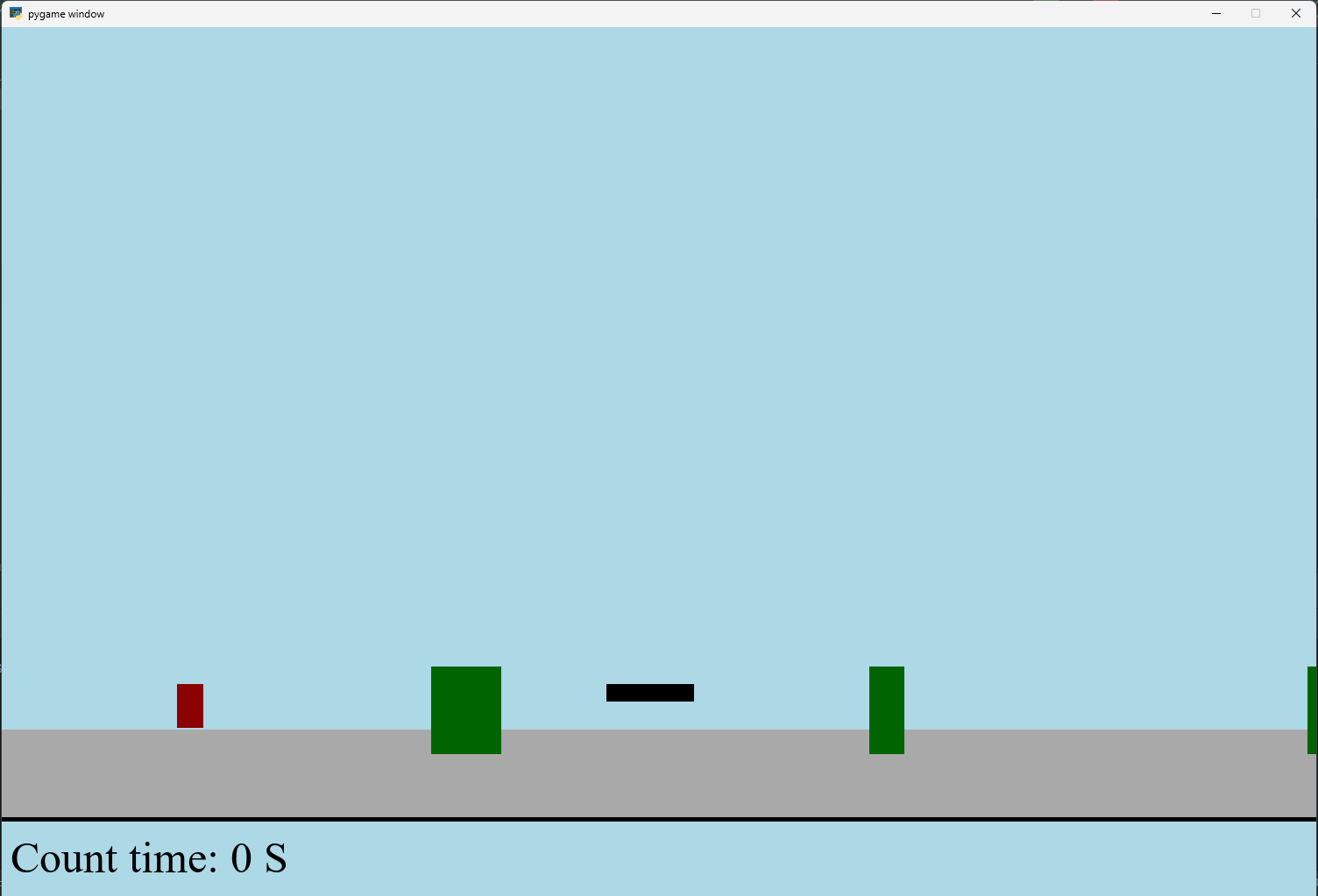
【Python】 -- 趣味代码 - 小恐龙游戏
文章目录 文章目录 00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架代码结构和功能游戏流程总结01 小恐龙游戏程序设计02 百度网盘地址00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架 这段代码是一个基于 Pygame 的简易跑酷游戏的完整实现,玩家控制一个角色(龙)躲避障碍物(仙人掌和乌鸦)。以下是代码的详细介绍:…...
【入坑系列】TiDB 强制索引在不同库下不生效问题
文章目录 背景SQL 优化情况线上SQL运行情况分析怀疑1:执行计划绑定问题?尝试:SHOW WARNINGS 查看警告探索 TiDB 的 USE_INDEX 写法Hint 不生效问题排查解决参考背景 项目中使用 TiDB 数据库,并对 SQL 进行优化了,添加了强制索引。 UAT 环境已经生效,但 PROD 环境强制索…...

MVC 数据库
MVC 数据库 引言 在软件开发领域,Model-View-Controller(MVC)是一种流行的软件架构模式,它将应用程序分为三个核心组件:模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)。这种模式有助于提高代码的可维护性和可扩展性。本文将深入探讨MVC架构与数据库之间的关系,以…...
保姆级教程:在无网络无显卡的Windows电脑的vscode本地部署deepseek
文章目录 1 前言2 部署流程2.1 准备工作2.2 Ollama2.2.1 使用有网络的电脑下载Ollama2.2.2 安装Ollama(有网络的电脑)2.2.3 安装Ollama(无网络的电脑)2.2.4 安装验证2.2.5 修改大模型安装位置2.2.6 下载Deepseek模型 2.3 将deepse…...
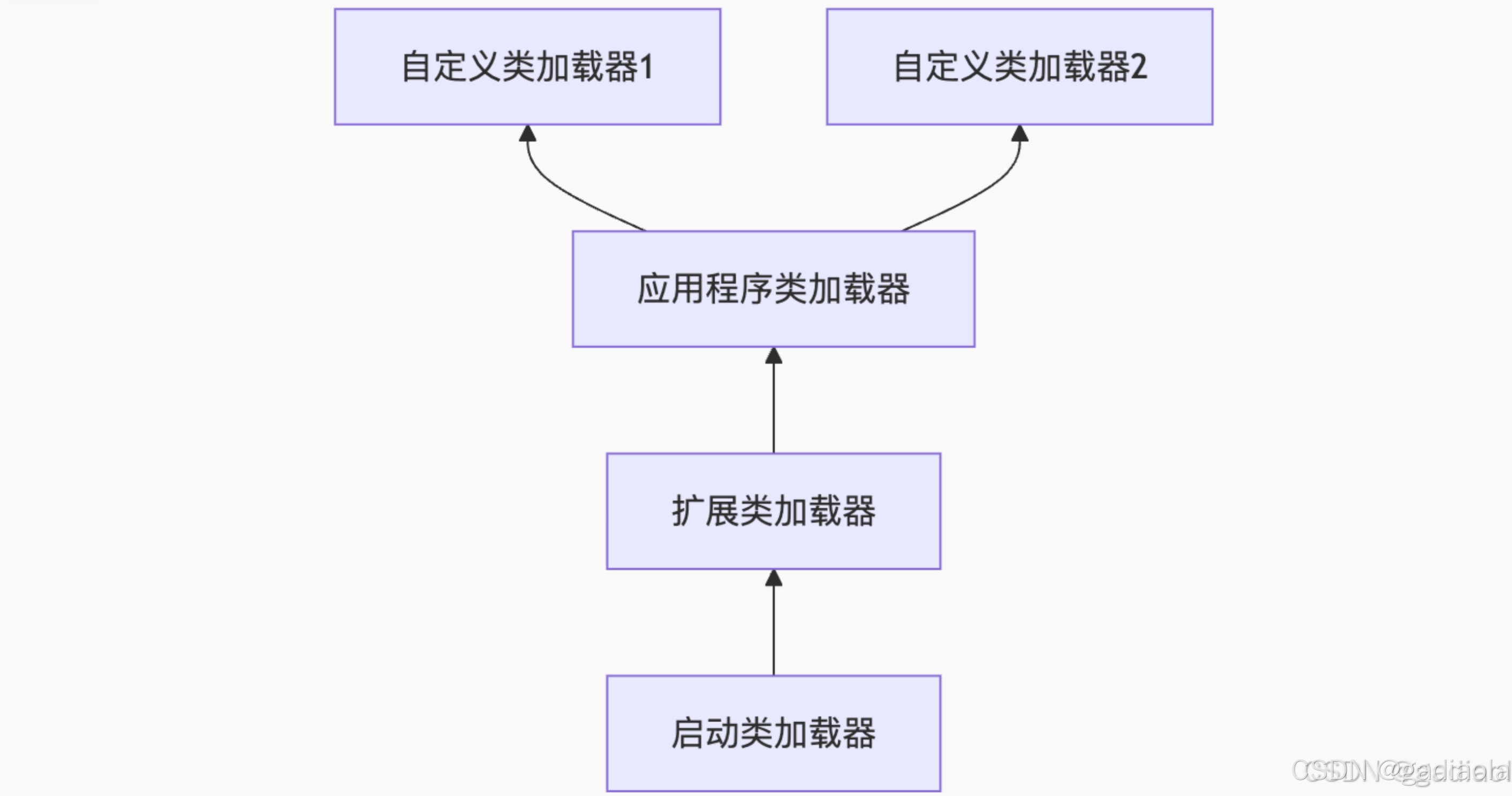
【JVM面试篇】高频八股汇总——类加载和类加载器
目录 1. 讲一下类加载过程? 2. Java创建对象的过程? 3. 对象的生命周期? 4. 类加载器有哪些? 5. 双亲委派模型的作用(好处)? 6. 讲一下类的加载和双亲委派原则? 7. 双亲委派模…...
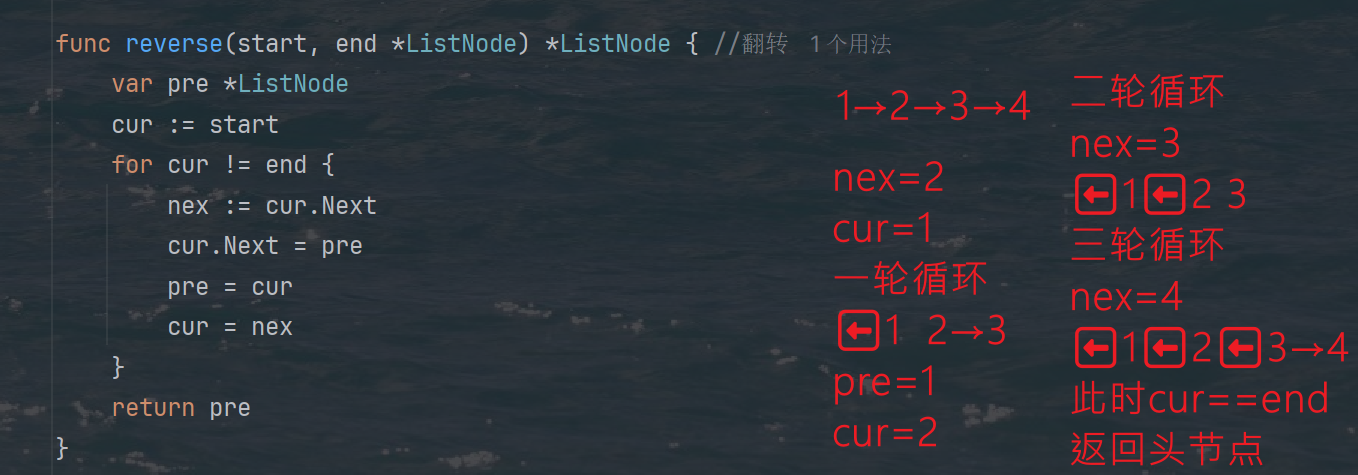
力扣热题100 k个一组反转链表题解
题目: 代码: func reverseKGroup(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode {cur : headfor i : 0; i < k; i {if cur nil {return head}cur cur.Next}newHead : reverse(head, cur)head.Next reverseKGroup(cur, k)return newHead }func reverse(start, end *ListNode) *ListN…...
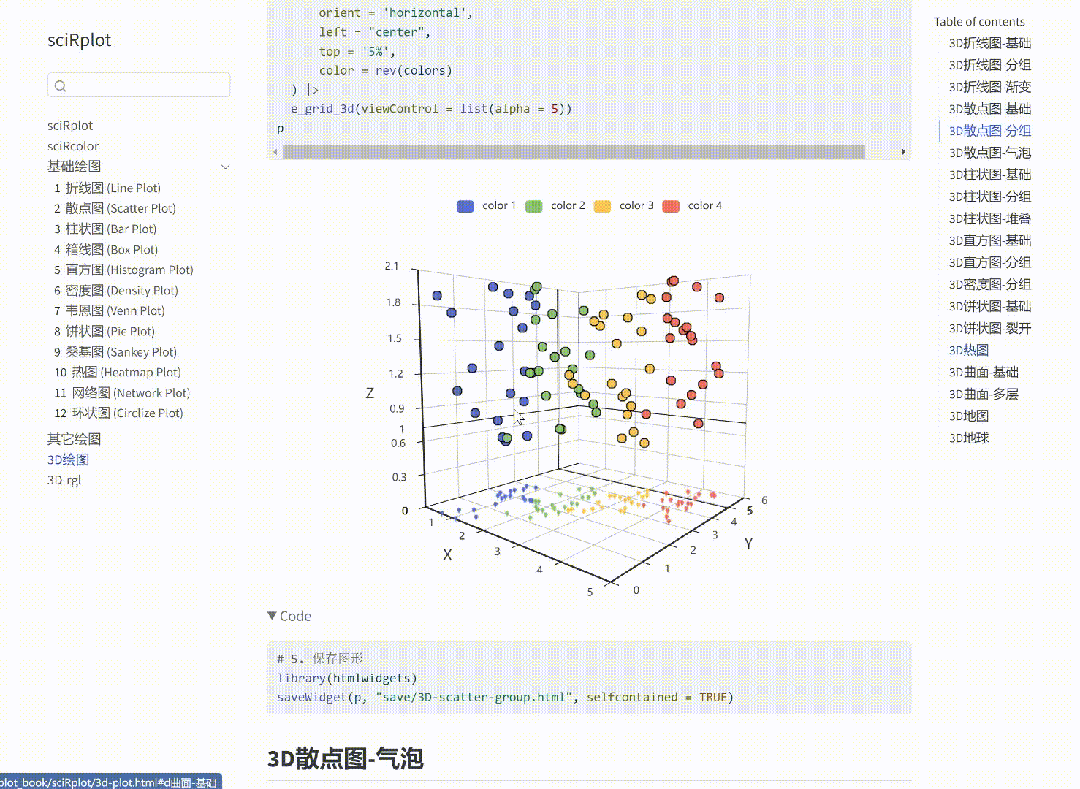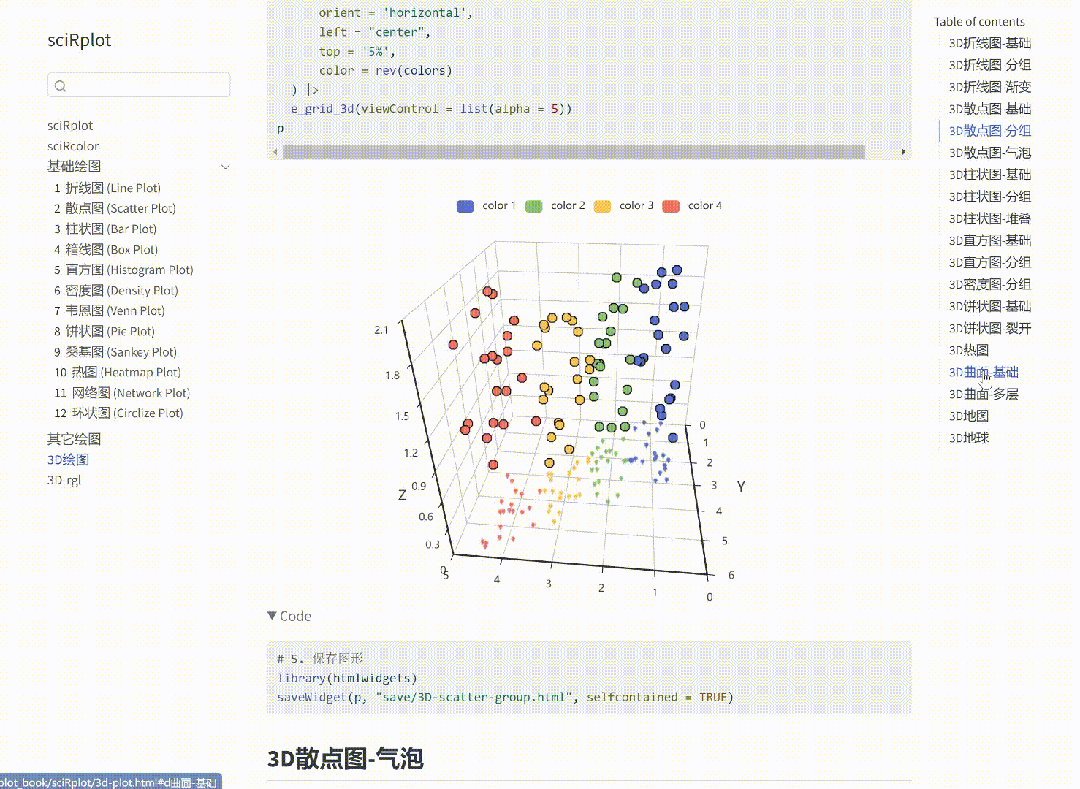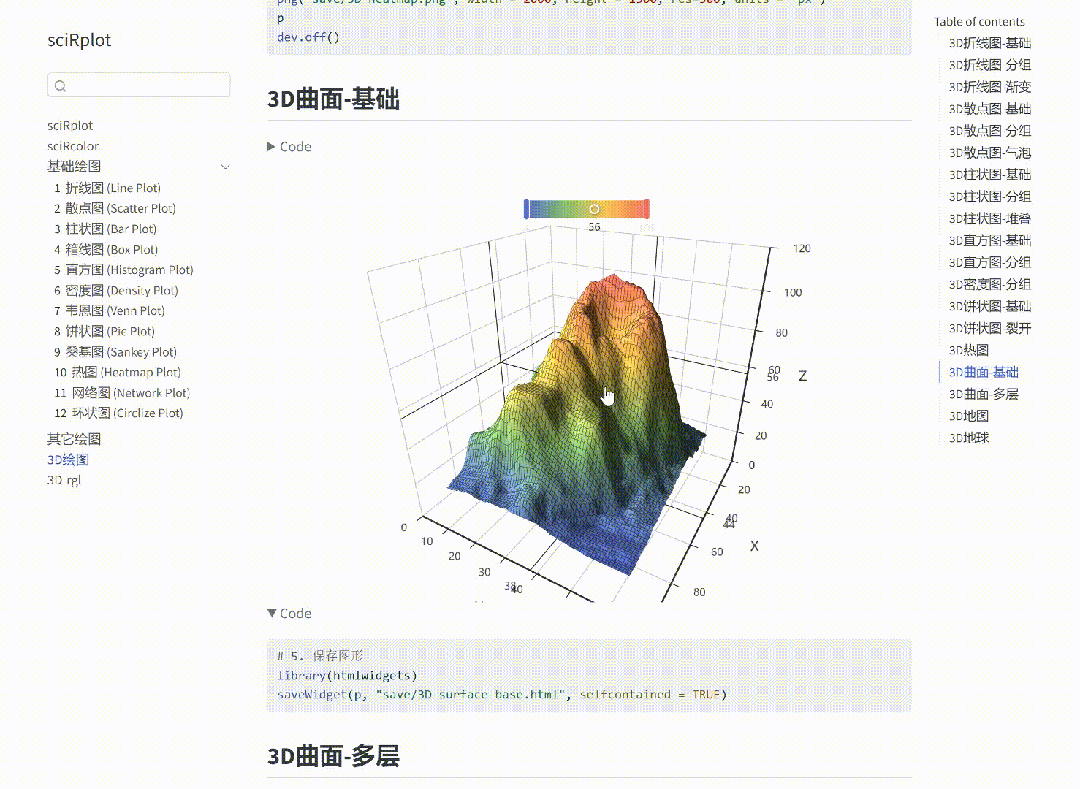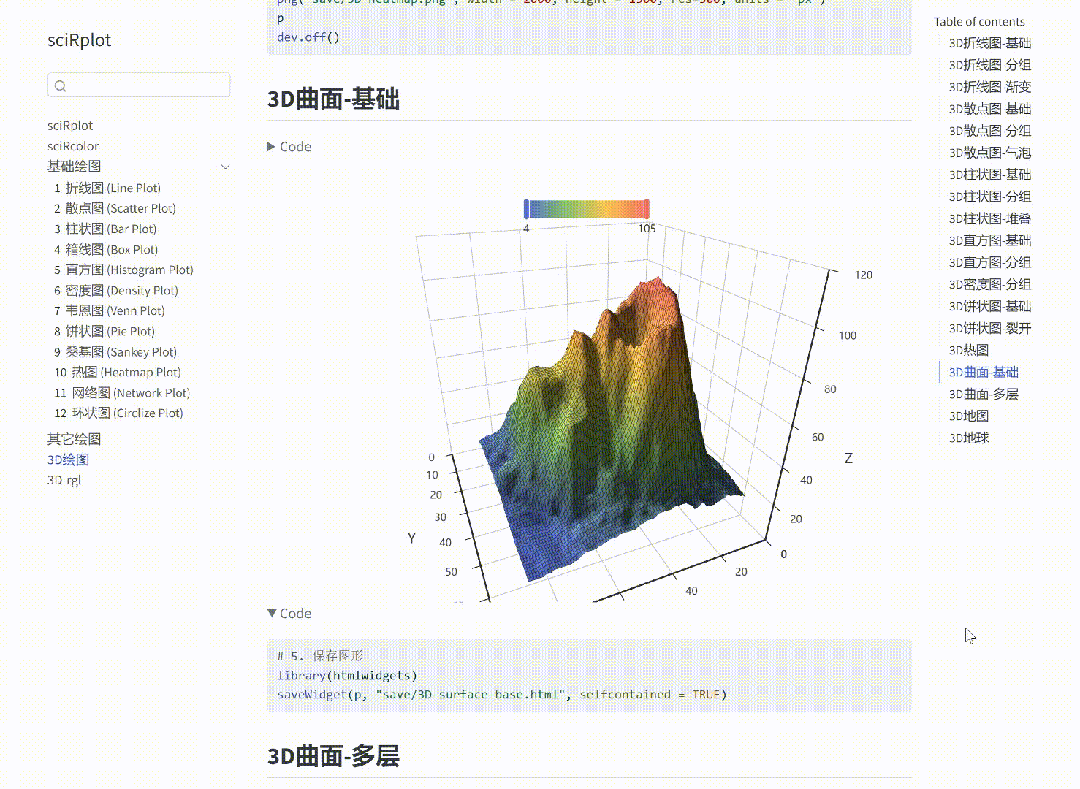
R 语言科研绘图第 55 期 --- 网络图-聚类
在发表科研论文的过程中,科研绘图是必不可少的,一张好看的图形会是文章很大的加分项。 为了便于使用,本系列文章介绍的所有绘图都已收录到了 sciRplot 项目中,获取方式: R 语言科研绘图模板 --- sciRplothttps://mp.…...

MySQL 索引底层结构揭秘:B-Tree 与 B+Tree 的区别与应用
文章目录 一、背景知识:什么是 B-Tree 和 BTree? B-Tree(平衡多路查找树) BTree(B-Tree 的变种) 二、结构对比:一张图看懂 三、为什么 MySQL InnoDB 选择 BTree? 1. 范围查询更快 2…...
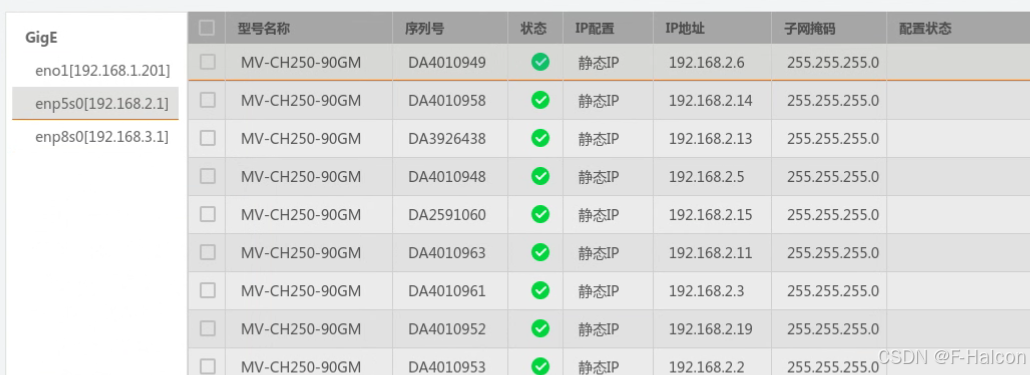
Ubuntu系统多网卡多相机IP设置方法
目录 1、硬件情况 2、如何设置网卡和相机IP 2.1 万兆网卡连接交换机,交换机再连相机 2.1.1 网卡设置 2.1.2 相机设置 2.3 万兆网卡直连相机 1、硬件情况 2个网卡n个相机 电脑系统信息,系统版本:Ubuntu22.04.5 LTS;内核版本…...
一些实用的chrome扩展0x01
简介 浏览器扩展程序有助于自动化任务、查找隐藏的漏洞、隐藏自身痕迹。以下列出了一些必备扩展程序,无论是测试应用程序、搜寻漏洞还是收集情报,它们都能提升工作流程。 FoxyProxy 代理管理工具,此扩展简化了使用代理(如 Burp…...
