顺序表和链表的各种代码实现
一、线性表
在日常生活中,线性表的例子比比皆是。例如,26个英文字母的字母表(A,B,C,……,Z)是一个线性表,表中的数据元素式单个字母。在稍复杂的线性表中,一个数据元素可以包含若干个数据项。例如在第一章中提到的学生基本信息表,每个学生为一个数据元素,包括学号、姓名、性别、籍贯、专业等数据项。
由以上两例可以看出,它们的数据元素虽然不同,但同一线性表中的元素必定具有相同的特性,即属于同一数据对象,相邻数据元素之间存在这序偶关系。诸如此类由n个数据特性相同的元素构成的有限序列成为线性表。对于非空的线性表或线性结构,其特点是:
(1)、存在唯一的一个被称作”第一个“的数据元素;
(2)、存在唯一的一个被称作”最后一个“的数据元素;
(3)、除第一个之外,结构中的每个数据元素均只有一个前驱;
(4)、除最后一个之外,结构中的每个数据元素均只有一个后继。
二、顺序表和链表
1、顺序表的定义:
顺序表是用一段 物理地址连续 的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表可以分为静态顺序表和动态顺序表:静态顺序表:静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素 。存储结构typedef struct SeqList {SLDataType x;int size; }SeqList动态顺序表:动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。typedef struct SeqList {SLDataType* Array;int size; //顺序表当前的元素个数int capacity; //顺序表的最大容量 }以下是实现顺序表的接口代码:
头文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include <stdio.h> #include <assert.h> #include <stdlib.h>typedef int SLDateType; typedef struct SeqList {SLDateType* a;int size;int capacity; }SeqList;// 对数据的管理:增删查改 void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps); void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps);void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps); void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x); void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x); void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps); void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps);// 顺序表查找 int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x); // 顺序表在pos位置插入x void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLDateType x); // 顺序表删除pos位置的值 void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos); //修改顺序表pos位置的值 void SeqListModify(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLDateType x);
函数实现文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SList.h"void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = (SLDateType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDateType)*4);ps->capacity = 4;ps->size = 0;
}
void SeqListDestroy(SeqList* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->size = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps)
{assert(ps);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);}printf("\n");
}
//检查增容的函数
void CheckCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{if (ps->capacity == ps->size){SLDateType* temp = (SLDateType*)realloc(ps->a, (ps->capacity * 2) * sizeof(SLDateType));if (temp == NULL){perror("mallco fail");return;}else{ps->a = temp;ps->capacity = ps->capacity * 2;}}
}
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x)
{//尾插首先检查增容CheckCapacity(ps);//增容完毕后开始插入数据ps->a[ps->size++] = x;
}
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x)
{//头插首先检查增容CheckCapacity(ps);//开始头插//往后面移动数据,从后往前移int end = 0;for (end = ps->size; end > 0; end--){ps->a[end] = ps->a[end - 1];}ps->a[end] = x;ps->size++;
}
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->size > 0);//头删int end = 0;for (end = 0; end < ps->size-1; end++){ps->a[end] = ps->a[end + 1];}ps->size--;
}
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
{assert(ps->size > 0);assert(ps);ps->size--;
}
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps);int i = 0;while (i < ps->size){if (ps->a[i] == x){return i;}i++;}//下标不可能是-1return -1;
}
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);//检查增容CheckCapacity(ps);int end = 0;for (end = ps->size; end > pos; end--){ps->a[end] = ps->a[end - 1];}ps->a[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos)
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);int end = 0;for (end = pos; end < ps->size - 1; end++){ps->a[end] = ps->a[end + 1];}ps->size--;
}
//修改函数
void SeqListModify(SeqList* ps,int pos,SLDateType x)
{assert(ps);assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);ps->a[pos] = x;
}测试文件:
define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SList.h"void test1()
{SeqList s;SeqListInit(&s);SeqListPushBack(&s, 1);SeqListPushBack(&s, 2);SeqListPushBack(&s, 3);SeqListPushBack(&s, 4);SeqListPushBack(&s, 5);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListPushFront(&s, 5);SeqListPushFront(&s, 4);SeqListPushFront(&s, 3);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListPopFront(&s);SeqListPopFront(&s);SeqListPopFront(&s);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListPopBack(&s);SeqListPopBack(&s);SeqListPopBack(&s);SeqListPopBack(&s);SeqListPopBack(&s);//SeqListPopBack(&s);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListDestroy(&s);
}
void test2()
{SeqList s;SeqListInit(&s);SeqListPushBack(&s, 1);SeqListPushBack(&s, 2);SeqListPushBack(&s, 3);SeqListPushBack(&s, 4);SeqListPushBack(&s, 5);SeqListInsert(&s, 1, 2);SeqListPrint(&s);
}void test3()
{SeqList s;SeqListInit(&s);SeqListPushBack(&s, 1);SeqListPushBack(&s, 2);SeqListPushBack(&s, 3);SeqListPushBack(&s, 4);SeqListPushBack(&s, 5);/*SeqListInsert(&s, 1, 2);SeqListInsert(&s, 6, 6);SeqListInsert(&s, 0, 0);SeqListErase(&s, 0);SeqListErase(&s, 6);*/SeqListPrint(&s);int pos = SeqListFind(&s, 2);SeqListInsert(&s, pos, 3);SeqListPrint(&s);SeqListModify(&s, 1, 2);SeqListPrint(&s);
}
int main()
{//test1();//test2();test3();return 0;
}2、单链表的定义:
概念:链表是一种 物理存储结构上非连续 、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的 逻辑顺序 是通过链表 中的指针链接 次序实现的 。
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SLTypeData;
typedef struct SList
{SLTypeData data;struct SList* next;
}SList;
//打印函数
void SListPrint(SList* phead);
//头插函数
void SListPushFront(SList** pphead,SLTypeData x);
//头删函数
void SListPopFront(SList** pphead);
//尾插函数
void SListPushBack(SList** pphead,SLTypeData x);
//尾删函数
void SListPopBack(SList** pphead);
//查找单链表
SList* SListFind(SList* plist, SLTypeData x);
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
// 分析思考为什么不在pos位置之前插入?
void SListInsertAfter(SList* pos, SLTypeData x);
//单链表的修改
void SListModify(SList* pos, SLTypeData x);
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
// 分析思考为什么不删除pos位置?
void SListEraseAfter(SList* pos);
// 单链表的销毁
void SListDestroy(SList* plist);
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SLTypeData;
typedef struct SList
{SLTypeData data;struct SList* next;
}SList;
//打印函数
void SListPrint(SList* phead);
//头插函数
void SListPushFront(SList** pphead,SLTypeData x);
//头删函数
void SListPopFront(SList** pphead);
//尾插函数
void SListPushBack(SList** pphead,SLTypeData x);
//尾删函数
void SListPopBack(SList** pphead);
//查找单链表
SList* SListFind(SList* plist, SLTypeData x);
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
// 分析思考为什么不在pos位置之前插入?
void SListInsertAfter(SList* pos, SLTypeData x);
//单链表的修改
void SListModify(SList* pos, SLTypeData x);
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
// 分析思考为什么不删除pos位置?
void SListEraseAfter(SList* pos);
// 单链表的销毁
void SListDestroy(SList* plist);
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SList.h"
void test1()
{SList* plist = NULL;SListPushFront(&plist, 1);SListPushFront(&plist, 2);SListPushFront(&plist, 3);SListPushFront(&plist, 4);SListPushFront(&plist, 5);SListPrint(plist);SListPopFront(&plist);SListPopFront(&plist);SListPopFront(&plist);SListPopFront(&plist);SListPopFront(&plist);//SListPopFront(&plist);SListPrint(plist);
}
void test2()
{SList* plist = NULL;SListPushBack(&plist, 1);SListPushBack(&plist, 2);SListPushBack(&plist, 3);SListPushBack(&plist, 4);SListPushBack(&plist, 5);SListPrint(plist);SListPopBack(&plist);SListPopBack(&plist);SListPopBack(&plist);SListPopBack(&plist);SListPopBack(&plist);//SListPopBack(&plist);SListPrint(plist);
}void test3()
{SList* plist = NULL;SListPushBack(&plist, 1);SListPushBack(&plist, 2);SListPushBack(&plist, 3);SListPushBack(&plist, 4);SListPushBack(&plist, 5);SListPrint(plist);SList* pos = SListFind(plist,5);if (pos == NULL){printf("没有找到\n");}else{printf("%d\n", pos->data);}SListInsertAfter(pos, 6);SListPrint(plist);pos = SListFind(plist, 5);SListEraseAfter(pos);SListPrint(plist);SListModify(pos, 4);SListPrint(plist);SListDestroy(plist);
}
int main()
{//test1();//test2();test3();return 0;
}双向带头循环链表的实现:
头文件:
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int STListType;
typedef struct STList
{STListType val;struct STList* prev;struct STList* next;
}STList;
//初始化链表的函数
STList* initSTList();
//新建节点的函数
STList* BuyNode(STListType x);
//头插函数
void STListPushFront(STList* phead, STListType x);
//头删函数
void STListPopFront(STList* phead);
//尾插函数
void STListPushBack(STList* phead, STListType x);
//尾删函数
void STListPopBack(STList* phead);
//判空函数
bool EmptySTList(STList* phead);
//打印函数
void PrintSTList(STList* phead);
//查找函数
STList* FindSTList(STList* phead, STListType x);
//在任意位置插入
void STListPosInsert(STList* phead, STListType x);
//在任意位置删除
void STListPosErase(STList* phead);
//销毁函数
void DesSTList(STList* phead);函数的实现:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "STList.h"
//初始化链表的函数
STList* initSTList()
{STList* phead = malloc(sizeof(STList));phead->val = -1;phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;
}
//新建节点的函数
STList* BuyNode(STListType x)
{STList* newnode = (STList*)malloc(sizeof(STList));newnode->prev = NULL;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->val = x;return newnode;
}
//头插函数
void STListPushFront(STList* phead, STListType x)
{assert(phead);STList* newnode = BuyNode(x);newnode->next = phead->next;phead->next->prev = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;phead->next = newnode;
}
//头删函数
void STListPopFront(STList* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(!EmptySTList(phead));STList* cur = phead->next;STList* next = cur->next;phead->next = next;next->prev = phead;free(cur);cur = NULL;
}
//尾插函数
void STListPushBack(STList* phead, STListType x)
{assert(phead);STList* newnode = BuyNode(x);STList* tail = phead->prev;tail->next = newnode;newnode->prev = tail;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode;
}
//尾删函数
void STListPopBack(STList* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(!EmptySTList(phead));STList* tail = phead->prev;STList* prev = tail->prev;prev->next = phead;phead->prev = prev;
}
//判空函数
bool EmptySTList(STList* phead)
{assert(phead);return phead->next == phead;
}//打印函数
void PrintSTList(STList* phead)
{assert(phead);STList* cur = phead->next;printf("head<==>");while (cur != phead){printf("%d<==>", cur->val);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}//查找函数
STList* FindSTList(STList* phead, STListType x)
{assert(phead);STList* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->val == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}//在任意位置前插入
void STListPosInsert(STList* pos, STListType x)
{assert(pos);STList* newnode = BuyNode(x);STList* prev = pos->prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode;newnode->prev = prev;prev->next = newnode;
}
//在任意位置删除
void STListPosErase(STList* pos)
{assert(pos);STList* prev = pos->prev;STList* next = pos->next;prev->next = next;next->prev = prev;free(pos);
}
//销毁链表
void DesSTList(STList* phead)
{STList* cur = phead;while (cur != phead){STList* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);
}测试文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "STList.h"void test1()
{STList* phead = initSTList();STListPushBack(phead, 1);STListPushBack(phead, 2);STListPushBack(phead, 3);STListPushBack(phead, 4);STListPushBack(phead, 5);PrintSTList(phead);STListPushFront(phead, 5);STListPushFront(phead, 4);STListPushFront(phead, 3);STListPushFront(phead, 2);STListPushFront(phead, 1);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);STListPopBack(phead);PrintSTList(phead);DesSTList(phead);
}
void test2()
{STList* phead = initSTList();STListPushBack(phead, 1);STListPushBack(phead, 2);STListPushBack(phead, 3);STListPushBack(phead, 4);STListPushBack(phead, 5);PrintSTList(phead);STListPushFront(phead, 5);STListPushFront(phead, 4);STListPushFront(phead, 3);STListPushFront(phead, 2);STListPushFront(phead, 1);/*STListPopFront(phead);STListPopFront(phead);STListPopFront(phead);STListPopFront(phead);STListPopFront(phead);STListPopFront(phead);STListPopFront(phead);STListPopFront(phead);STListPopFront(phead);STListPopFront(phead);*/STList* pos = FindSTList(phead, 4);if (pos){STListPosInsert(pos, 40);}PrintSTList(phead);pos = FindSTList(phead, 40);if (pos){STListPosErase(pos);}PrintSTList(phead);
}int main()
{//test1();test2();return 0;
}
相关文章:

顺序表和链表的各种代码实现
一、线性表 在日常生活中,线性表的例子比比皆是。例如,26个英文字母的字母表(A,B,C,……,Z)是一个线性表,表中的数据元素式单个字母。在稍复杂的线性表中,一个数据元素可以包含若干个数据项。例…...

C# 介绍三种不同组件创建PDF文档的方式
1 c# 数据保存为PDF(一) (spire pdf篇) 2 c# 数据保存为PDF(二) (Aspose pdf篇) 3 c# 数据保存为PDF(三) (PdfSharp篇) 组件名称 绘制…...

极简面试题 --- Redis
什么是 Redis? Redis 是一个基于内存的键值存储系统,也被称为数据结构服务器。它支持多种数据结构,例如字符串、哈希表、列表、集合和有序集合,并且可以在内存中快速读写。 Redis 的优势有哪些? 快速:由…...

可视化图表API格式要求有哪些?Sugar BI详细代码示例(4)
Sugar BI中的每个图表可以对应一个数据 API,用户浏览报表时,选定一定的过滤条件,点击「查询」按钮将会通过 API 拉取相应的数据;前面说过,为了确保用户数据的安全性,Sugar BI上的所有数据请求都在Sugar BI的…...
)
学习vue(可与知乎合并)
一:组件及交互 1、什么是组件? 组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,且带有一个名字:在这个例子中是 。我们可以在一个通过 new Vue 创建的 Vue 根实例中,把这个组件作为自定义元素来使用: 声明组件 // 定义一个名…...

【UEFI实战】Linux下如何解析ACPI表
本文介绍如何在Linux下查看ACPI表示。使用的系统是Ubuntu18.04: Linux home 4.15.0-36-generic #39-Ubuntu SMP Mon Sep 24 16:19:09 UTC 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux 可以在如下的目录看到ACPI的基本信息: 但是默认的表都是不可以直接查看的&…...
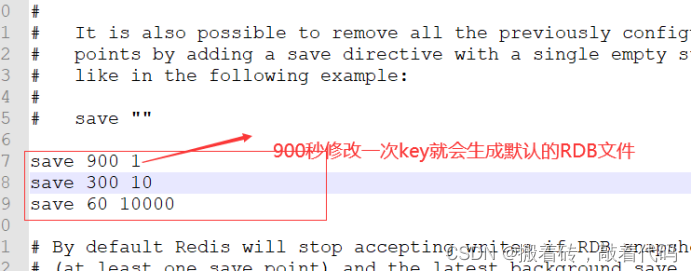
Java-Redis持久化之RDB操作
Java-Redis持久化之RDB操作 1.为什么redis需要持久化?2.什么是RDB操作?3.请你用自己的话讲下RDB的过程?4.如何恢复rdb文件? 1.为什么redis需要持久化? Redis是内存数据库,如果不将内存数据库保存到磁盘,那么服务器进程退出&am…...
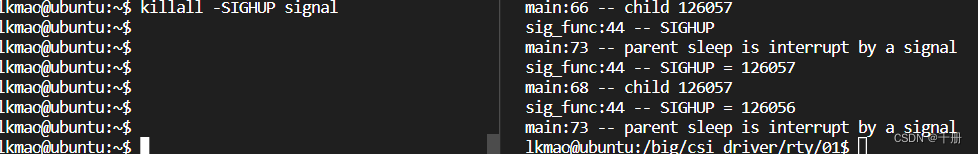
信号signal编程测试
信号会打断系统调用,慎用,就是用的时候测一测。 下面是信号的基础测试 信号 信号(signal)机制是UNIX系统中最为古老的进程之间的通信机制。它用于在一个或多个进程之间传递异步信号。信号可以由各种异步事件产生,例如…...

Linux学习记录——이십삼 进程信号(2)
文章目录 1、可重入函数2、volatile关键字3、如何理解编译器的优化4、SIGCHLD信号 1、可重入函数 两个执行流都执行一个函数时,这个函数就被重入了。比如同一个函数insert,在main中执行时,这个进程时间片到了,嵌入了内核…...
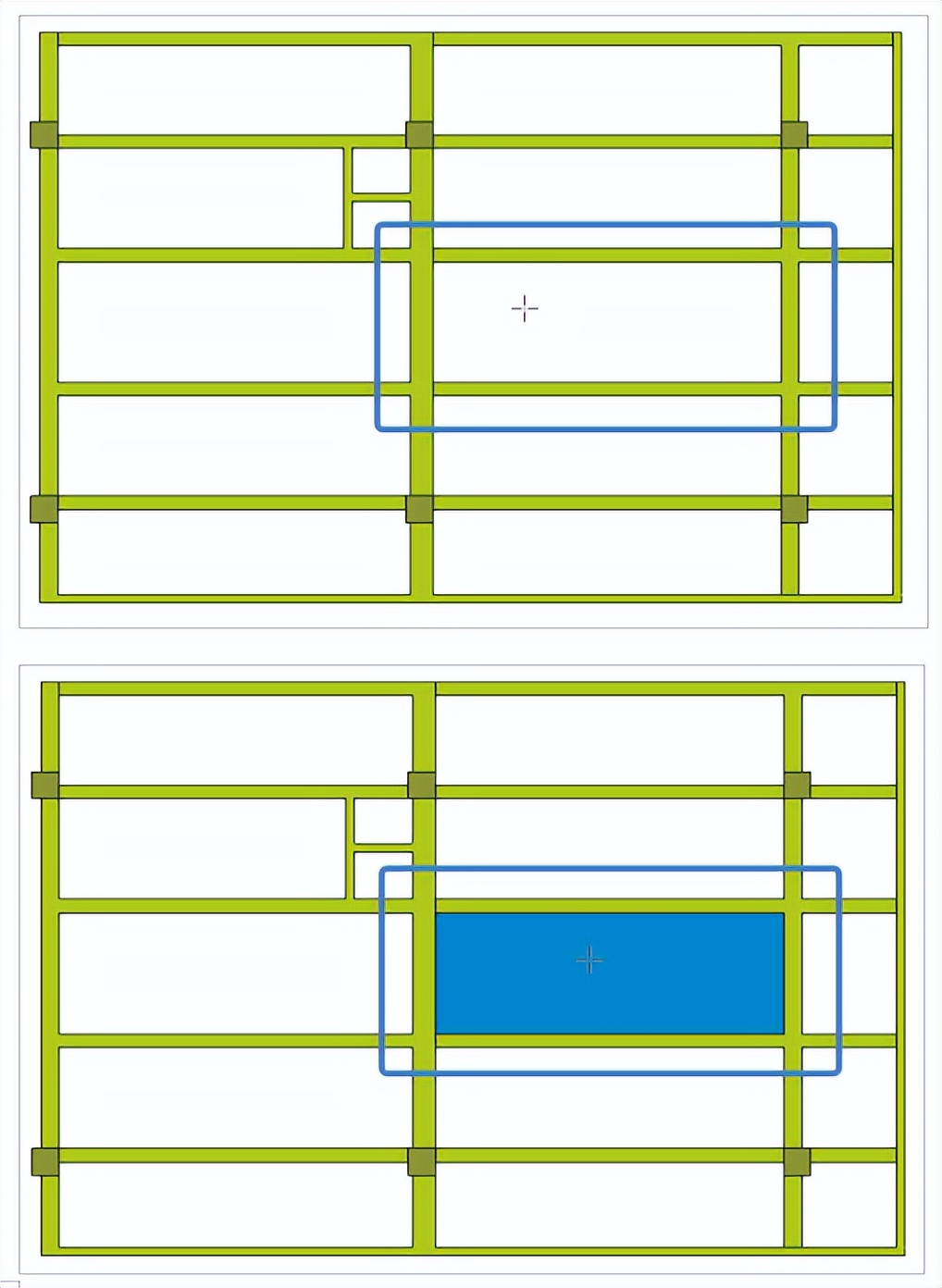
Revit中如何创建曲面嵌板及一键成板
一、Revit中如何创建曲面嵌板 在我们的绘图过程中可能会遇见一些曲面形状,而我们的常规嵌板没办法满足我们绘制的要求,我们今天学习如何在revit中绘制曲面嵌板。 1.新建“自适应公制常规模型”族,创建4个点图元并为其使用自适应。 2.在相同的…...
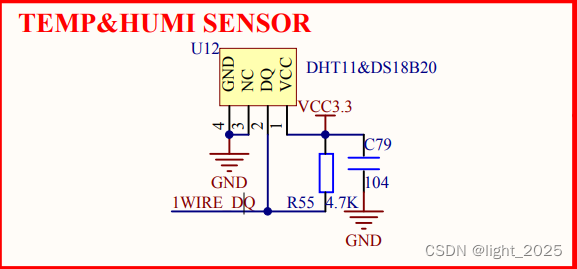
STM32F4_DHT11数字温湿度传感器
目录 前言 1. DHT11简介 2. DHT11数据结构 3. DHT11的传输时序 3.1 DHT11开始发送数据流程 3.2 主机复位信号和DHT11响应信号 3.3 数字 “0” 信号表示方法 3.4 数字 “1” 信号表示方法 4. 硬件分析 5. 实验程序详解 5.1 main.c 5.2 DHT11.c 5.3 DHT11.h 前言 DH…...
WiFi(Wireless Fidelity)基础(十一)
目录 一、基本介绍(Introduction) 二、进化发展(Evolution) 三、PHY帧((PHY Frame ) 四、MAC帧(MAC Frame ) 五、协议(Protocol) 六、安全&#x…...

操作系统—— 精髓与设计原理--期末复习
一、计算机系统概述 1、基本构成 计算机有四个主要的结构化部件: ①处理器(Processor):控制计算机的操作,执行数据处理功能。当只有一个处理器时,它通常指中央处理器(CPU) ②内存…...

每天一道算法练习题--Day21 第一章 --算法专题 --- ----------位运算
我这里总结了几道位运算的题目分享给大家,分别是 136 和 137, 260 和 645, 总共加起来四道题。 四道题全部都是位运算的套路,如果你想练习位运算的话,不要错过哦~~ 前菜 开始之前我们先了解下…...
D1. LuoTianyi and the Floating Islands (Easy Version)(树形dp)
Problem - D1 - Codeforces 这是问题的简化版本。唯一的区别在于在该版本中k≤min(n,3)。只有在两个版本的问题都解决后,才能进行黑客攻击。 琴音和漂浮的岛屿。 洛天依现在生活在一个有n个漂浮岛屿的世界里。这些漂浮岛屿由n−1个无向航线连接,任意两个…...

rk3588移植ubuntu server
ubuntu server 18.04 arm版本. 1、使用qemu运行 安装qemu-system-aarch64 sudo apt install -y qemu-system-arm 2、下载ubuntu server Index of /releases/18.04.3 3、创建虚拟磁盘 qemu-img create ubuntuimg.img 40G 4、创建虚拟机 弹出界面,直接回车选…...

如何更好地刷力扣
之前刷力扣是一口气看很多题目,打算时不时看一会题解,逐渐熟悉套路,争取背过,最后就可以写出来了。我个人是背知识比较喜欢这种方法,但后来发现根本不适用 算法题本身就比较复杂,不经过实际写代码中的思考…...

上采样和下采样
首先,谈谈不平衡数据集。不平衡数据集指的是训练数据中不同类别的样本数量差别较大的情况。在这种情况下,模型容易出现偏差,导致模型对数量较少的类别预测效果不佳。 为了解决这个问题,可以使用上采样和下采样等方法来调整数据集…...

小猪,信息论与我们的生活
前言 动态规划是大家都熟悉与陌生的知识,非常灵活多变,我自己也不敢说自己掌握了,今天给大家介绍一道题,不仅局限于动态规划做题,还会上升到信息论,乃至于启发自己认知世界的角度 因为比较难,本…...
【鸿蒙应用ArkTS开发系列】- http网络库使用讲解和封装
目录 前言http网络库组件介绍http网络库封装创建Har Module创建RequestOption 配置类创建HttpCore核心类创建HttpManager核心类对外组件导出添加网络权限 http网络库依赖和使用依赖http网络库(httpLibrary)使用http网络库(httpLibrary&#x…...
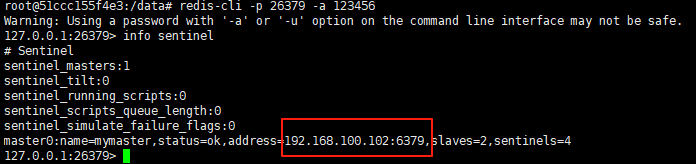
使用docker在3台服务器上搭建基于redis 6.x的一主两从三台均是哨兵模式
一、环境及版本说明 如果服务器已经安装了docker,则忽略此步骤,如果没有安装,则可以按照一下方式安装: 1. 在线安装(有互联网环境): 请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 2. 离线安装(内网环境):请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 说明:假设每台服务器已…...
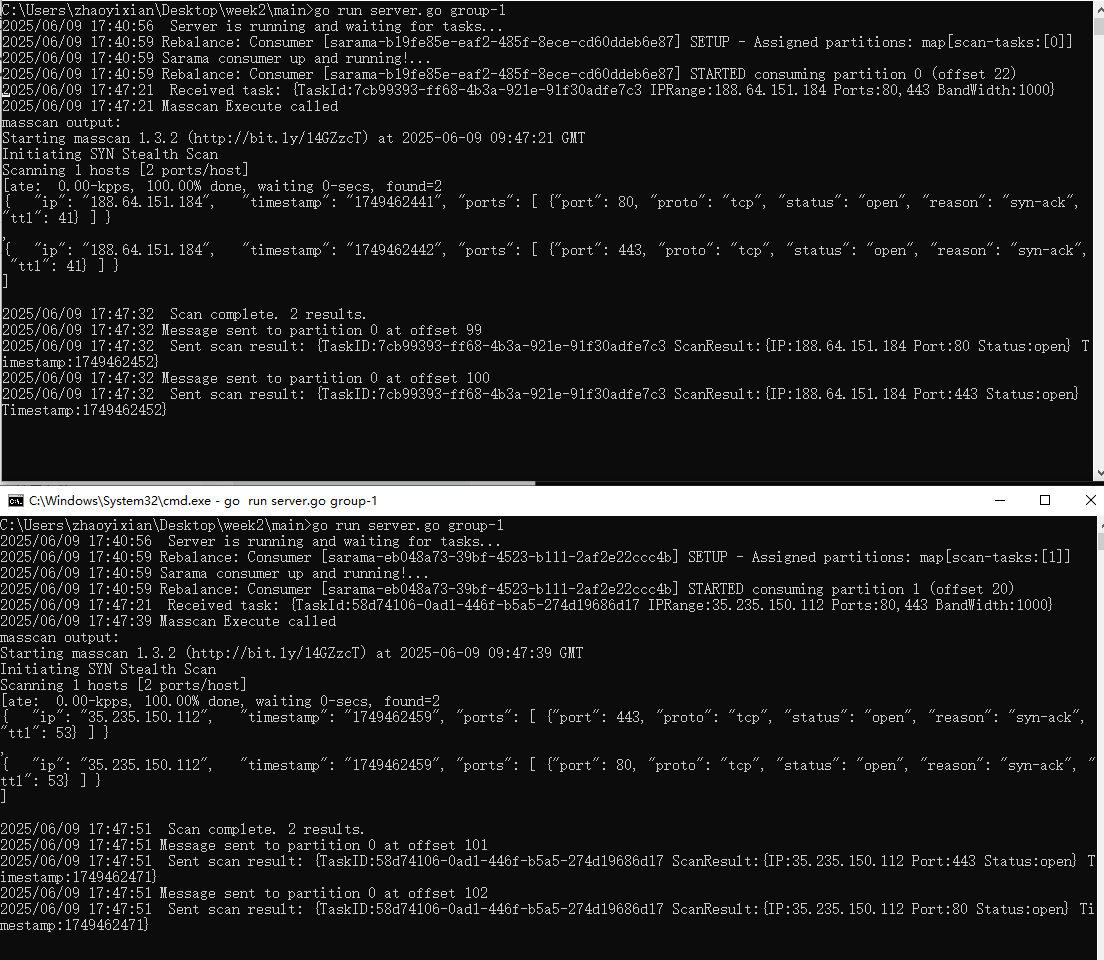
【kafka】Golang实现分布式Masscan任务调度系统
要求: 输出两个程序,一个命令行程序(命令行参数用flag)和一个服务端程序。 命令行程序支持通过命令行参数配置下发IP或IP段、端口、扫描带宽,然后将消息推送到kafka里面。 服务端程序: 从kafka消费者接收…...
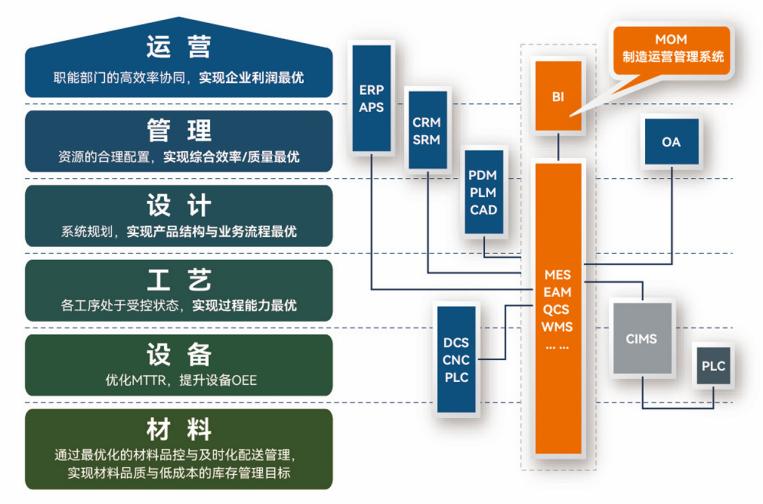
盘古信息PCB行业解决方案:以全域场景重构,激活智造新未来
一、破局:PCB行业的时代之问 在数字经济蓬勃发展的浪潮中,PCB(印制电路板)作为 “电子产品之母”,其重要性愈发凸显。随着 5G、人工智能等新兴技术的加速渗透,PCB行业面临着前所未有的挑战与机遇。产品迭代…...

逻辑回归:给不确定性划界的分类大师
想象你是一名医生。面对患者的检查报告(肿瘤大小、血液指标),你需要做出一个**决定性判断**:恶性还是良性?这种“非黑即白”的抉择,正是**逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)** 的战场&a…...
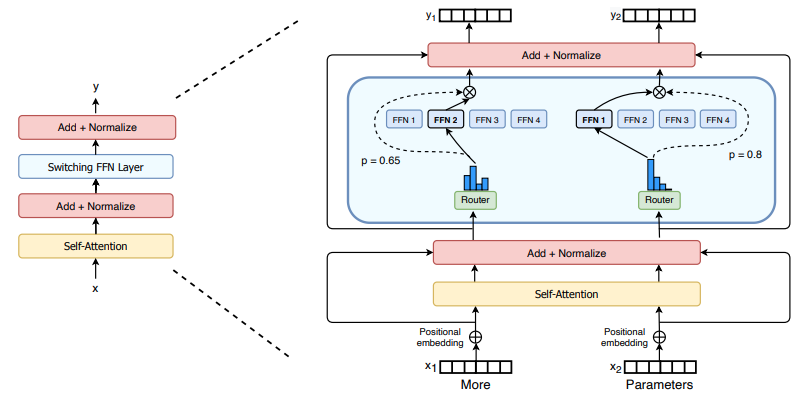
(二)TensorRT-LLM | 模型导出(v0.20.0rc3)
0. 概述 上一节 对安装和使用有个基本介绍。根据这个 issue 的描述,后续 TensorRT-LLM 团队可能更专注于更新和维护 pytorch backend。但 tensorrt backend 作为先前一直开发的工作,其中包含了大量可以学习的地方。本文主要看看它导出模型的部分&#x…...

汽车生产虚拟实训中的技能提升与生产优化
在制造业蓬勃发展的大背景下,虚拟教学实训宛如一颗璀璨的新星,正发挥着不可或缺且日益凸显的关键作用,源源不断地为企业的稳健前行与创新发展注入磅礴强大的动力。就以汽车制造企业这一极具代表性的行业主体为例,汽车生产线上各类…...

什么是EULA和DPA
文章目录 EULA(End User License Agreement)DPA(Data Protection Agreement)一、定义与背景二、核心内容三、法律效力与责任四、实际应用与意义 EULA(End User License Agreement) 定义: EULA即…...
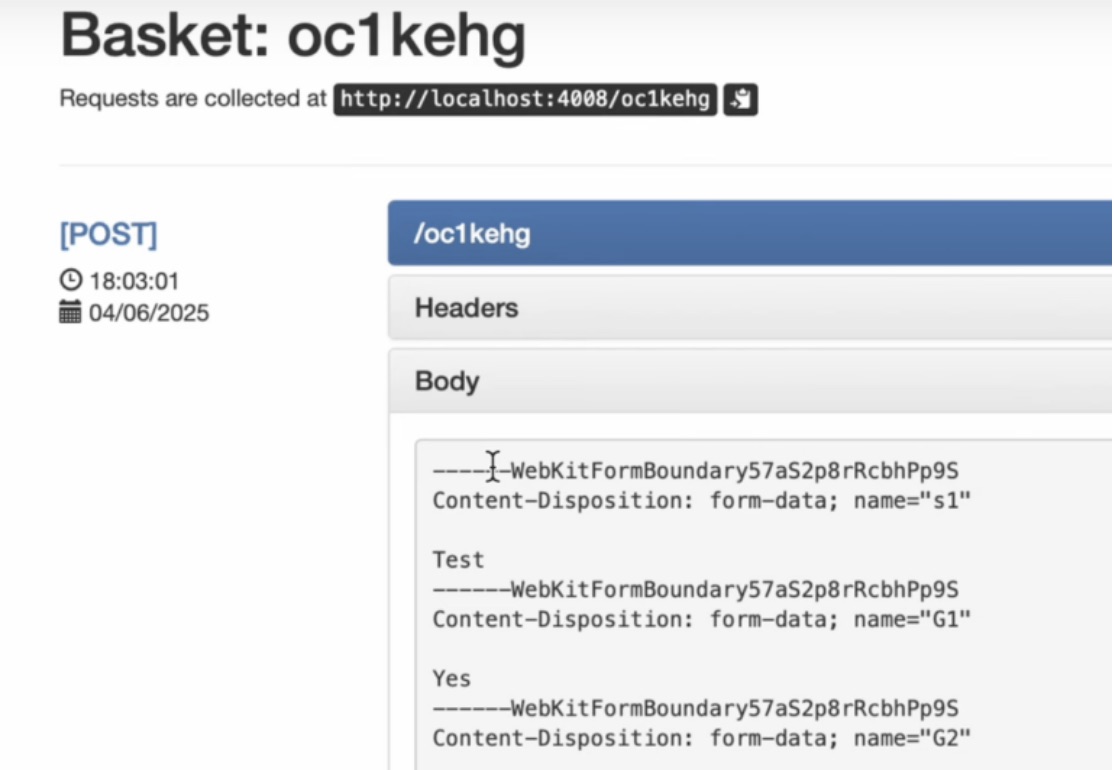
如何在网页里填写 PDF 表格?
有时候,你可能希望用户能在你的网站上填写 PDF 表单。然而,这件事并不简单,因为 PDF 并不是一种原生的网页格式。虽然浏览器可以显示 PDF 文件,但原生并不支持编辑或填写它们。更糟的是,如果你想收集表单数据ÿ…...
相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?)
Redis的发布订阅模式与专业的 MQ(如 Kafka, RabbitMQ)相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?
Redis 的发布订阅(Pub/Sub)模式与专业的 MQ(Message Queue)如 Kafka、RabbitMQ 进行比较,核心的权衡点在于:简单与速度 vs. 可靠与功能。 下面我们详细展开对比。 Redis Pub/Sub 的核心特点 它是一个发后…...

微服务通信安全:深入解析mTLS的原理与实践
🔥「炎码工坊」技术弹药已装填! 点击关注 → 解锁工业级干货【工具实测|项目避坑|源码燃烧指南】 一、引言:微服务时代的通信安全挑战 随着云原生和微服务架构的普及,服务间的通信安全成为系统设计的核心议题。传统的单体架构中&…...
