用到的C++的相关知识-----未完待续
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、vector函数的使用
- 1.1 构造向量
- 二、常用函数
- 2.1 矩阵输出函数
- 2.2 向量输出函数
- 2.3 矩阵的使用
- 2.4
- 三、new的用法
- 3.1 内存的四种分区
- 3.2 new的作用
- 3.3
- 3.4
- 四、
- 4.1
- 4.2
- 4.3
- 4.4
- 总结
前言
只是为方便学习,不做其他用途
一、vector函数的使用
有关的文章
- C++ vector的用法(整理)
- C++中vector的用法详解
1.1 构造向量
//vector():创建一个空vectorvector<int> v1 = vector<int>(); //v1 = []//vector(int nSize):创建一个vector,元素个数为nSizevector<int> v2 = vector<int>(3); //v2 = [0, 0, 0]//vector(int nSize,const t& t): 创建一个vector,元素个数为nSize,且值均为tvector<int> v3 = vector<int>(3, 10); //v3 = [10, 10, 10]//vector(const vector&): 复制构造函数vector<int> v4 = vector<int>(v3); //v4 = [10, 10, 10]//vector(begin,end): 复制[begin,end)区间内另一个数组的元素到vector中vector<int> v5 = vector<int>(v4.begin(), v4.end() - 1); //v5 = [10, 10]vector<vector<int>> v6 = vector<vector<int>>(3, vector<int>(3);); //v6 = [[0, 0, 0][0, 0, 0][0, 0, 0]]二、常用函数
2.1 矩阵输出函数
// 输出矩阵的各个值
void Print(MatrixXd K)
{for (int j = 0; j < K.rows(); j++){for (int i = 0; i < K.cols(); i++){cout << K(j, i) << " ";}cout << endl;}
}
2.2 向量输出函数
#include <vector>
// 输出向量的各个值
void Print_Vector(vector<double> U)
{for (int i = 0; i < U.size(); i++){cout << " U_ " << i << " = " << U[i] << endl;}
}
2.3 矩阵的使用
eigen库和matlab中对应命令
// A simple quickref for Eigen. Add anything that's missing.
// Main author: Keir Mierle
#include<iostream>
#include <gismo.h>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace Eigen;
using namespace gismo;
using namespace std;
#include <vector>int main()
{gsMatrix<double, 3, 3> A; // Fixed rows and cols. Same as Matrix3d.Matrix<double, 3, Dynamic> B; // Fixed rows, dynamic cols.Matrix<double, Dynamic, Dynamic> C; // Full dynamic. Same as MatrixXd.Matrix<double, 3, 3, RowMajor> E; // Row major; default is column-major.Matrix3f P, Q, R; // 3x3 float matrix.Vector3f x, y, z; // 3x1 float matrix.RowVector3f a, b, c; // 1x3 float matrix.VectorXd v; // Dynamic column vector of doublesdouble s;// Basic usage// Eigen // Matlab // commentsx.size() // length(x) // vector sizeC.rows() // size(C,1) // number of rowsC.cols() // size(C,2) // number of columnsx(i) // x(i+1) // Matlab is 1-basedC(i, j) // C(i+1,j+1) //A.resize(4, 4); // Runtime error if assertions are on.B.resize(4, 9); // Runtime error if assertions are on.A.resize(3, 3); // Ok; size didn't change.B.resize(3, 9); // Ok; only dynamic cols changed.A << 1, 2, 3, // Initialize A. The elements can also be4, 5, 6, // matrices, which are stacked along cols7, 8, 9; // and then the rows are stacked.B << A, A, A; // B is three horizontally stacked A's.A.fill(10); // Fill A with all 10's.// Eigen // MatlabMatrixXd::Identity(rows, cols) // eye(rows,cols)C.setIdentity(rows, cols) // C = eye(rows,cols)MatrixXd::Zero(rows, cols) // zeros(rows,cols)C.setZero(rows, cols) // C = ones(rows,cols)MatrixXd::Ones(rows, cols) // ones(rows,cols)C.setOnes(rows, cols) // C = ones(rows,cols)MatrixXd::Random(rows, cols) // rand(rows,cols)*2-1 // MatrixXd::Random returns uniform random numbers in (-1, 1).C.setRandom(rows, cols) // C = rand(rows,cols)*2-1VectorXd::LinSpaced(size, low, high) // linspace(low,high,size)'v.setLinSpaced(size, low, high) // v = linspace(low,high,size)'// Matrix slicing and blocks. All expressions listed here are read/write.// Templated size versions are faster. Note that Matlab is 1-based (a size N// vector is x(1)...x(N)).// Eigen // Matlabx.head(n) // x(1:n)x.head<n>() // x(1:n)x.tail(n) // x(end - n + 1: end)x.tail<n>() // x(end - n + 1: end)x.segment(i, n) // x(i+1 : i+n)x.segment<n>(i) // x(i+1 : i+n)P.block(i, j, rows, cols) // P(i+1 : i+rows, j+1 : j+cols)P.block<rows, cols>(i, j) // P(i+1 : i+rows, j+1 : j+cols)P.row(i) // P(i+1, :)P.col(j) // P(:, j+1)P.leftCols<cols>() // P(:, 1:cols)P.leftCols(cols) // P(:, 1:cols)P.middleCols<cols>(j) // P(:, j+1:j+cols)P.middleCols(j, cols) // P(:, j+1:j+cols)P.rightCols<cols>() // P(:, end-cols+1:end)P.rightCols(cols) // P(:, end-cols+1:end)P.topRows<rows>() // P(1:rows, :)P.topRows(rows) // P(1:rows, :)P.middleRows<rows>(i) // P(i+1:i+rows, :)P.middleRows(i, rows) // P(i+1:i+rows, :)P.bottomRows<rows>() // P(end-rows+1:end, :)P.bottomRows(rows) // P(end-rows+1:end, :)P.topLeftCorner(rows, cols) // P(1:rows, 1:cols)P.topRightCorner(rows, cols) // P(1:rows, end-cols+1:end)P.bottomLeftCorner(rows, cols) // P(end-rows+1:end, 1:cols)P.bottomRightCorner(rows, cols) // P(end-rows+1:end, end-cols+1:end)P.topLeftCorner<rows, cols>() // P(1:rows, 1:cols)P.topRightCorner<rows, cols>() // P(1:rows, end-cols+1:end)P.bottomLeftCorner<rows, cols>() // P(end-rows+1:end, 1:cols)P.bottomRightCorner<rows, cols>() // P(end-rows+1:end, end-cols+1:end)// Of particular note is Eigen's swap function which is highly optimized.// Eigen // MatlabR.row(i) = P.col(j); // R(i, :) = P(:, i)R.col(j1).swap(mat1.col(j2)); // R(:, [j1 j2]) = R(:, [j2, j1])// Views, transpose, etc; all read-write except for .adjoint().// Eigen // MatlabR.adjoint() // R'R.transpose() // R.' or conj(R')R.diagonal() // diag(R)x.asDiagonal() // diag(x)R.transpose().colwise().reverse(); // rot90(R)R.conjugate() // conj(R)// All the same as Matlab, but matlab doesn't have *= style operators.// Matrix-vector. Matrix-matrix. Matrix-scalar.y = M * x; R = P * Q; R = P * s;a = b * M; R = P - Q; R = s * P;a *= M; R = P + Q; R = P / s;R *= Q; R = s * P;R += Q; R *= s;R -= Q; R /= s;// Vectorized operations on each element independently// Eigen // MatlabR = P.cwiseProduct(Q); // R = P .* QR = P.array() * s.array();// R = P .* sR = P.cwiseQuotient(Q); // R = P ./ QR = P.array() / Q.array();// R = P ./ QR = P.array() + s.array();// R = P + sR = P.array() - s.array();// R = P - sR.array() += s; // R = R + sR.array() -= s; // R = R - sR.array() < Q.array(); // R < QR.array() <= Q.array(); // R <= QR.cwiseInverse(); // 1 ./ PR.array().inverse(); // 1 ./ PR.array().sin() // sin(P)R.array().cos() // cos(P)R.array().pow(s) // P .^ sR.array().square() // P .^ 2R.array().cube() // P .^ 3R.cwiseSqrt() // sqrt(P)R.array().sqrt() // sqrt(P)R.array().exp() // exp(P)R.array().log() // log(P)R.cwiseMax(P) // max(R, P)R.array().max(P.array()) // max(R, P)R.cwiseMin(P) // min(R, P)R.array().min(P.array()) // min(R, P)R.cwiseAbs() // abs(P)R.array().abs() // abs(P)R.cwiseAbs2() // abs(P.^2)R.array().abs2() // abs(P.^2)(R.array() < s).select(P, Q); // (R < s ? P : Q)// Reductions.int r, c;// Eigen // MatlabR.minCoeff() // min(R(:))R.maxCoeff() // max(R(:))s = R.minCoeff(&r, &c) // [s, i] = min(R(:)); [r, c] = ind2sub(size(R), i);s = R.maxCoeff(&r, &c) // [s, i] = max(R(:)); [r, c] = ind2sub(size(R), i);R.sum() // sum(R(:))R.colwise().sum() // sum(R)R.rowwise().sum() // sum(R, 2) or sum(R')'R.prod() // prod(R(:))R.colwise().prod() // prod(R)R.rowwise().prod() // prod(R, 2) or prod(R')'R.trace() // trace(R)R.all() // all(R(:))R.colwise().all() // all(R)R.rowwise().all() // all(R, 2)R.any() // any(R(:))R.colwise().any() // any(R)R.rowwise().any() // any(R, 2)// Dot products, norms, etc.// Eigen // Matlabx.norm() // norm(x). Note that norm(R) doesn't work in Eigen.x.squaredNorm() // dot(x, x) Note the equivalence is not true for complexx.dot(y) // dot(x, y)x.cross(y) // cross(x, y) Requires #include <Eigen/Geometry>// Eigen // MatlabA.cast<double>(); // double(A)A.cast<float>(); // single(A)A.cast<int>(); // int32(A)A.real(); // real(A)A.imag(); // imag(A)// if the original type equals destination type, no work is done// Note that for most operations Eigen requires all operands to have the same type:MatrixXf F = MatrixXf::Zero(3, 3);A += F; // illegal in Eigen. In Matlab A = A+F is allowedA += F.cast<double>(); // F converted to double and then added (generally, conversion happens on-the-fly)// Eigen can map existing memory into Eigen matrices.float array[3];Vector3f::Map(array).fill(10); // create a temporary Map over array and sets entries to 10int data[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };Matrix2i mat2x2(data); // copies data into mat2x2Matrix2i::Map(data) = 2 * mat2x2; // overwrite elements of data with 2*mat2x2MatrixXi::Map(data, 2, 2) += mat2x2; // adds mat2x2 to elements of data (alternative syntax if size is not know at compile time)// Solve Ax = b. Result stored in x. Matlab: x = A \ b.x = A.ldlt().solve(b)); // A sym. p.s.d. #include <Eigen/Cholesky>x = A.llt().solve(b)); // A sym. p.d. #include <Eigen/Cholesky>x = A.lu().solve(b)); // Stable and fast. #include <Eigen/LU>x = A.qr().solve(b)); // No pivoting. #include <Eigen/QR>x = A.svd().solve(b)); // Stable, slowest. #include <Eigen/SVD>// .ldlt() -> .matrixL() and .matrixD()// .llt() -> .matrixL()// .lu() -> .matrixL() and .matrixU()// .qr() -> .matrixQ() and .matrixR()// .svd() -> .matrixU(), .singularValues(), and .matrixV()// Eigenvalue problems// Eigen // MatlabA.eigenvalues(); // eig(A);EigenSolver<Matrix3d> eig(A); // [vec val] = eig(A)eig.eigenvalues(); // diag(val)eig.eigenvectors(); // vec// For self-adjoint matrices use SelfAdjointEigenSolver<>
}2.4
:
三、new的用法
参考文章 c++中new的作用、C++如何让函数返回数组
//可以在new后面直接赋值int* p = new int(3);//也可以单独赋值//*p = 3;//如果不想使用指针,可以定义一个变量,在new之前用“*”表示new出来的内容int q = *new int;q = 1;cout << q << endl;
3.1 内存的四种分区
栈区(stack): 编译器自动分配和释放的,主要存储的是函数的参数值,局部变量等值。发生函数调用时就为函数运行时用到的数据分配内存,函数调用结束后就将之前分配的内存全部销毁。所以局部变量、参数只在当前函数中有效,不能传递到函数外部。栈内存的大小和编译器有关,编译器会为栈内存指定一个最大值,在 VC/VS 下,默认是 1M。
堆区(heap): 动态分配。一般由程序员分配和释放(动态内存申请malloc与释放free),需要手动free。否则会一直存在,若程序员不释放,程序结束时可能由操作系统回收。
全局区(静态区)(static): 静态分配。全局变量和静态变量的存储是放在一块的,该区域在程序结束后由操作系统释放。
代码区:: 通常用来存放程序执行代码(包含类成员函数和全局函数及其他函数代码),这部分区域的大小在程序运行前就已经确定,也有可能包含一些只读的常数变量,例如字符串变量。
3.2 new的作用

用法示例:
int *a = new int[5];
class A {...} //声明一个类 A
A *obj = new A(); //使用 new 创建对象
delete []a;
delete obj;
3.3
:
3.4
:
四、
4.1
:
4.2
:
4.3
:
4.4
:
总结
:
| 二维数 |
相关文章:

用到的C++的相关知识-----未完待续
文章目录前言一、vector函数的使用1.1 构造向量二、常用函数2.1 矩阵输出函数2.2 向量输出函数2.3 矩阵的使用2.4三、new的用法3.1 内存的四种分区3.2 new的作用3.33.4四、4.14.24.34.4总结前言 只是为方便学习,不做其他用途 一、vector函数的使用 有关的文章 C v…...

JavaScript刷LeetCode拿offer-贪心算法
前言 学习算法的时候,总会有一些让人生畏的名词,比方动态规划,贪心算法 等,听着就很难;而这一 part 就是为了攻破之前一直没有系统学习的 贪心算法; 有一说一,做了这些贪心题,其实…...

selenium
下载并安装selenium 安装:cmd中执行 pip install -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple selenium执行完成后 pip show selenium 可查看安装是否成功安装浏览器驱动,查看当前浏览器的版本选择合适的驱动并下载 chrome的链接:https://chromedrive…...

SpringMVC的视图
转发视图ThymeleafView若使用的视图技术为Thymeleaf,在SpringMVC的配置文件中配置了Thymeleaf的视图解析器,由此视图解析器解析之后所得到的是ThymeleafView。解析:当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称没有任何前缀时,此时的视图名称会…...
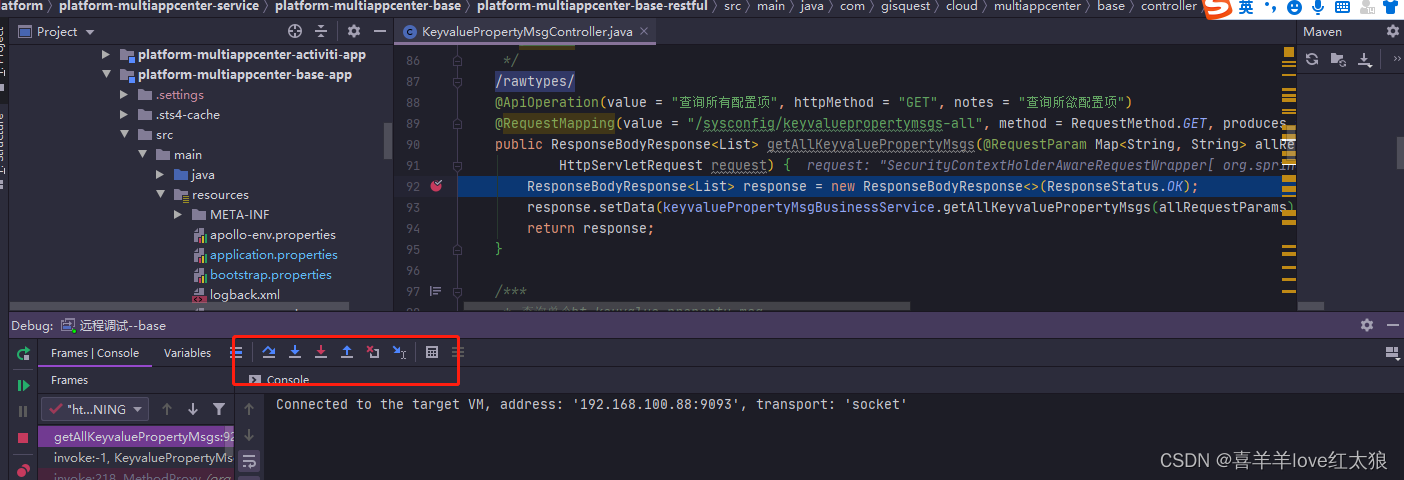
idea使用本地代码远程调试线上运行代码---windows环境
场景: 今天在书上看了一个代码远程调试的方法,自己本地验证了一下感觉十分不错!! windows环境: 启动测试jar包:platform-multiappcenter-base-app-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar 测试工具:postman,idea 应…...
简单记录简单记录
目录1.注册Gmail2.注册ChatGPT3.验证“真人”使用4.开始使用1.注册Gmail 第一步先注册一个谷歌邮箱,你也可以使用微软账号,大部分人选择使用gmail。 申请谷歌邮箱 选择个人用途创建账号即可。 📌温馨提示: 你直接使用guo内的网…...
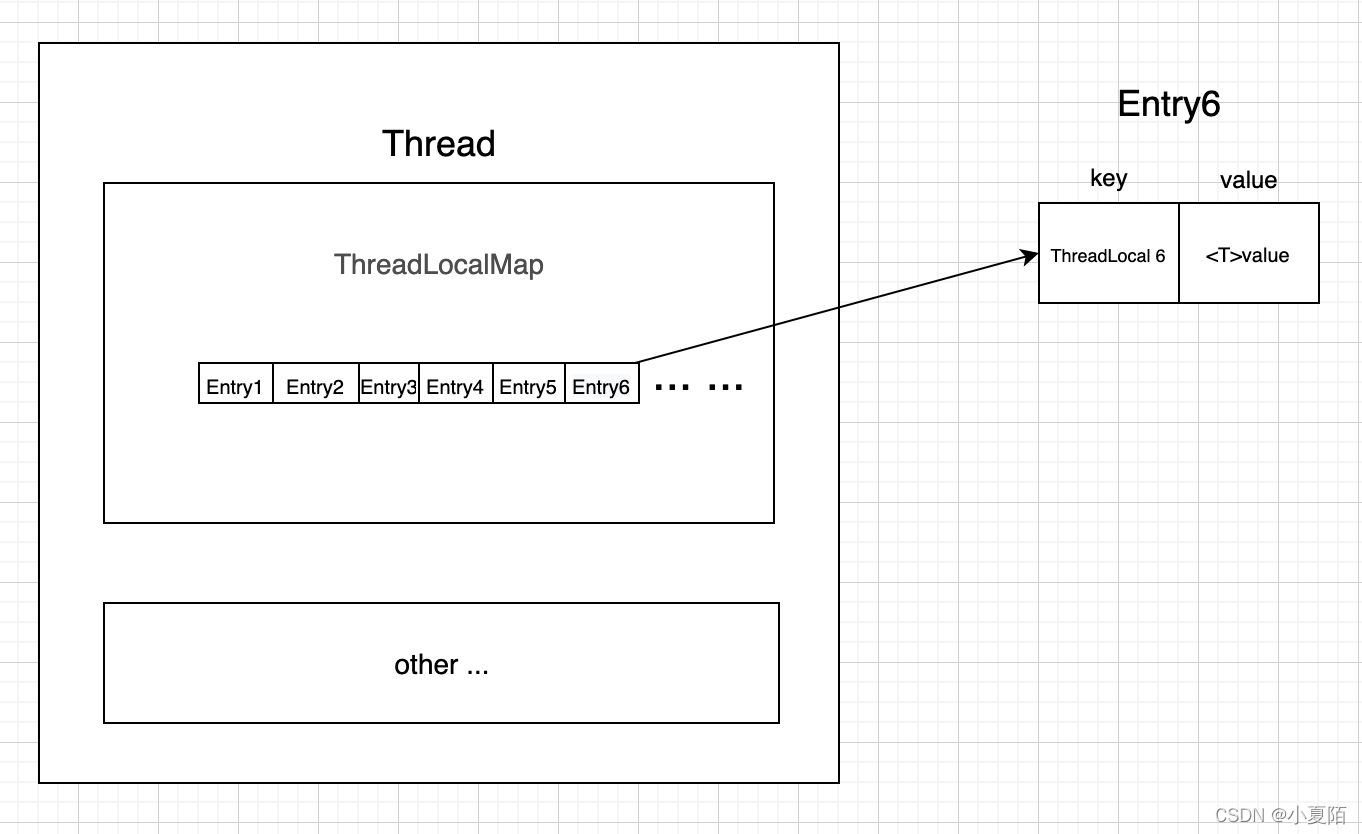
源码系列 之 ThreadLocal
简介 ThreadLocal的作用是做数据隔离,存储的变量只属于当前线程,相当于当前线程的局部变量,多线程环境下,不会被别的线程访问与修改。常用于存储线程私有成员变量、上下文,和用于同一线程,不同层级方法间传…...
——特点及关键字)
C语言入门(1)——特点及关键字
1、C特点及与Java区别 1.1、C特点 面向过程 一般用于嵌入式开发、编写最底层的程序、操作系统 可以直接操作内存 可以封装动态库 不容易跨平台 有指针 可以直接操作串口 线程更加灵活 和硬件打交道速度是最快的 1.2、和Java区别 C是C的增强版,增加了一些新的特性&…...

react中useEffect和useLayoutEffect的区别
布局上 useEffect在浏览器渲染完成后执行useLayoutEffect在DOM更新后执行 特点 useLayoutEffect 总是比 useEffect 先执行;useLayoutEffect与componentDidMount、componentDidUpdate调用时机相同,都是在DOM更新后,页面渲染前调用࿱…...

NoSQL(非关系型数据库)与SQL(关系型数据库)的差别
目录 NoSQL(非关系型数据库)与SQL(关系型数据库)的差别 1.数据结构:结构化与非结构化 2.数据关联:关联性与非关联性 3.查询方式:SQL查询与非SQL查询 4.事务特性:ACID与BASE 分析ACID与BASE的含义: 5.存储方式&am…...

new bing的申请与使用教程
文章目录新必应申请新必应免代使用教程总结新必应申请 下载安装 Edge dev 版本,这个版本可以直接使用 对于没有更新的用户而言,不容易找到入口,所以我们直接使用 集成new bing的dev版本 Edge dev 下载链接:https://www.microso…...

yaml配置文件
最近在写代码,发现随着网络的增加,代码变得越来越冗余,所以就想着写一个网络的配置文件,把网络的配置放到一个文件中,而不再主函数中,这样代码开起来就好看了,调试的时候也方便了。之前写过一篇…...

284. 顶端迭代器
请你在设计一个迭代器,在集成现有迭代器拥有的 hasNext 和 next 操作的基础上,还额外支持 peek 操作。 实现 PeekingIterator 类: PeekingIterator(Iterator nums) 使用指定整数迭代器 nums 初始化迭代器。 int next() 返回数组中的下一个元…...

自学前端最容易犯的10个的错误,入门学前端快来看看
在前端学习过程中,有很多常见的误区,包括过度关注框架和库、缺乏实践、忽视算法和数据结构、忽视浏览器兼容性、缺乏团队合作经验、忽视可访问性、重构次数过多、没有关注性能、缺乏设计知识以及没有持续学习等。要避免这些误区,应该注重基础…...
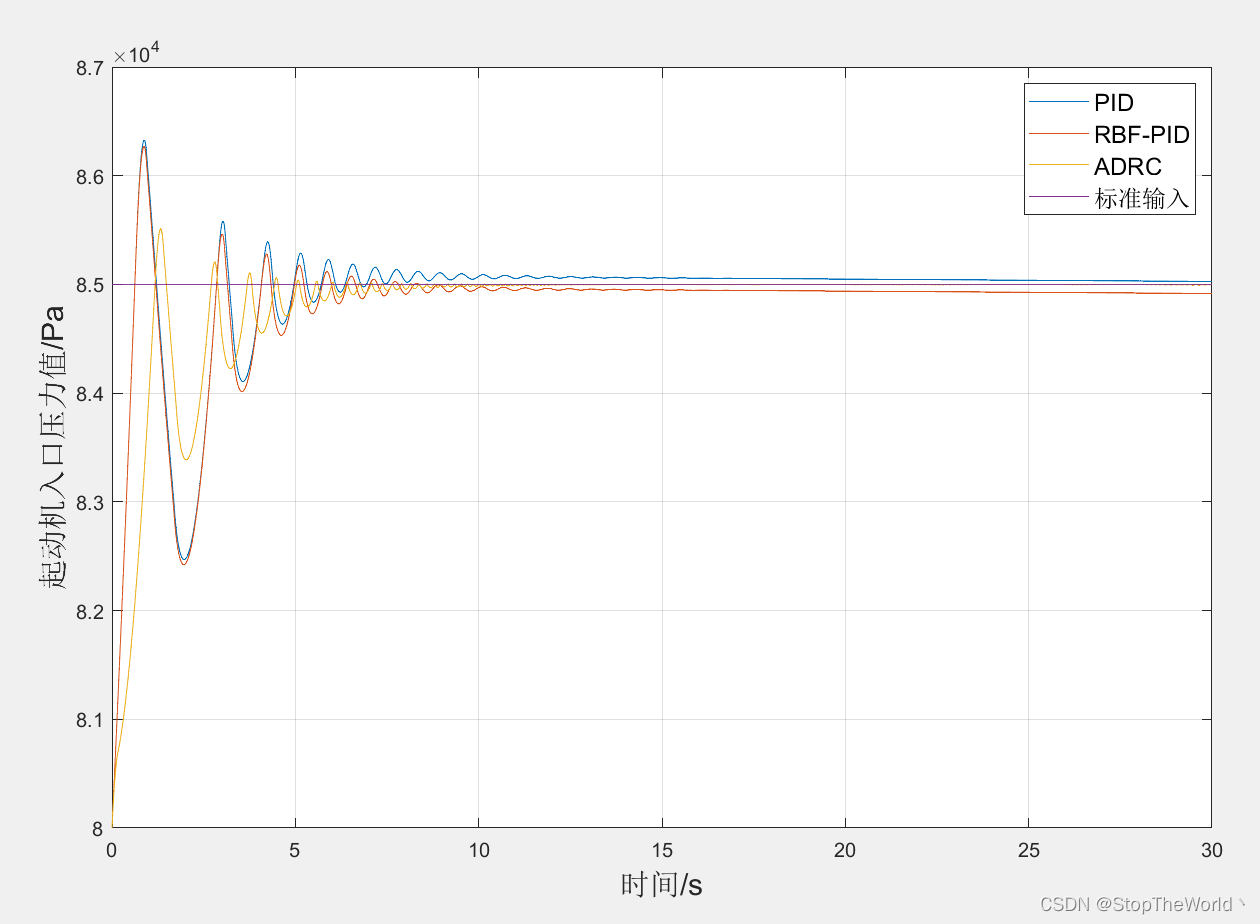
【ADRC控制】使用自抗扰控制器调节起动机入口压力值
以前只知道工业控制中用的是PID控制,然而最近了解到实际生产中还在使用ADRC控制,而且使用效果还优于PID控制,遂找了几篇文献学习学习。 0 引言 自抗扰控制(Active Disturbances Rejection Controller,ADRC)…...
)
剑指 Offer Day2——链表(简单)
目录剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表 原题链接:06. 从尾到头打印链表 最容易想到的思路就是先从头到尾打印下来,然后 reverse 一下,但这里我们使用递归…...

Final Cut Pro 10.6.5
软件介绍Final Cut Pro 10.6.5 已通过小编安装运行测试 100%可以使用。Final Cut Pro 10.6.5 破解版启用了全新的矩形图标,与最新的macOS Ventura设计风格统一,支持最新的macOS 13 文图拉系统,支持Apple M1/M2芯片。经过完整而彻底的重新设计…...
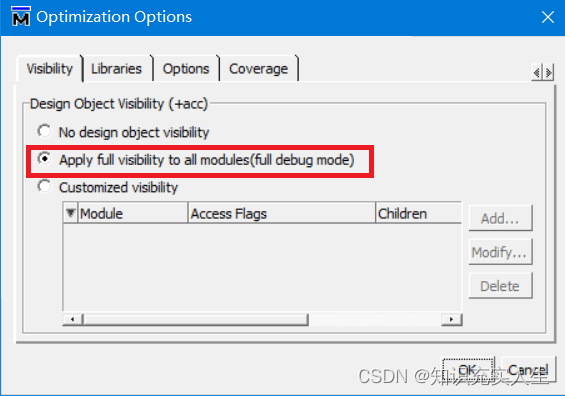
Modelsim仿真操作指导
目录 一、前言 二、仿真分类 三、RTL级仿真 3.1创建库 3.2 仿真配置设置 3.3 运行仿真 四、常见问题 4.1 运行仿真时报错“cant read "Startup(-L)": no such element in array” 4.2 运行仿真时无任何报错,但object窗口为空,可正常运…...

你知道这20个数组方法是怎么实现的吗?
前言你们一定对JavaScript中的数组很熟悉,我们每天都会用到它的各种方法,比如push、pop、forEach、map……等等。但是仅仅使用它就足够了吗?如此出色,您一定不想停在这里。我想和你一起挑战实现20数组方法的功能。1、forEachforEa…...

《系统架构设计》-01-架构和架构师概述
文章目录1. 架构的基本定义1.1 架构组成理论1.1.1 系统元素1)概念2)静态结构和动态结构1.1.2 基本系统属性1.1.3 设计和发展原则1.2 架构的决策理论1.2.1 统一软件过程(Rational Unified Process,统一软件过程)1.2.2 决…...
结构体的进阶应用)
基于算法竞赛的c++编程(28)结构体的进阶应用
结构体的嵌套与复杂数据组织 在C中,结构体可以嵌套使用,形成更复杂的数据结构。例如,可以通过嵌套结构体描述多层级数据关系: struct Address {string city;string street;int zipCode; };struct Employee {string name;int id;…...
)
椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)
一、ECC算法概述 椭圆曲线密码学(Elliptic Curve Cryptography)是基于椭圆曲线数学理论的公钥密码系统,由Neal Koblitz和Victor Miller在1985年独立提出。相比RSA,ECC在相同安全强度下密钥更短(256位ECC ≈ 3072位RSA…...

Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations
Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路 这一题其实就是一个脑筋急转弯,要想要能够将所有的电脑解锁&#x…...
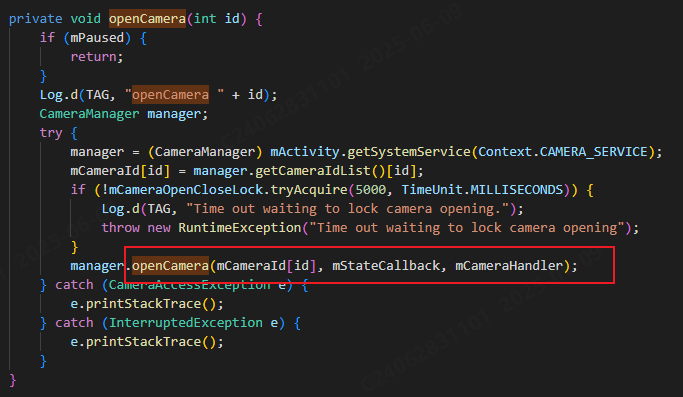
相机从app启动流程
一、流程框架图 二、具体流程分析 1、得到cameralist和对应的静态信息 目录如下: 重点代码分析: 启动相机前,先要通过getCameraIdList获取camera的个数以及id,然后可以通过getCameraCharacteristics获取对应id camera的capabilities(静态信息)进行一些openCamera前的…...
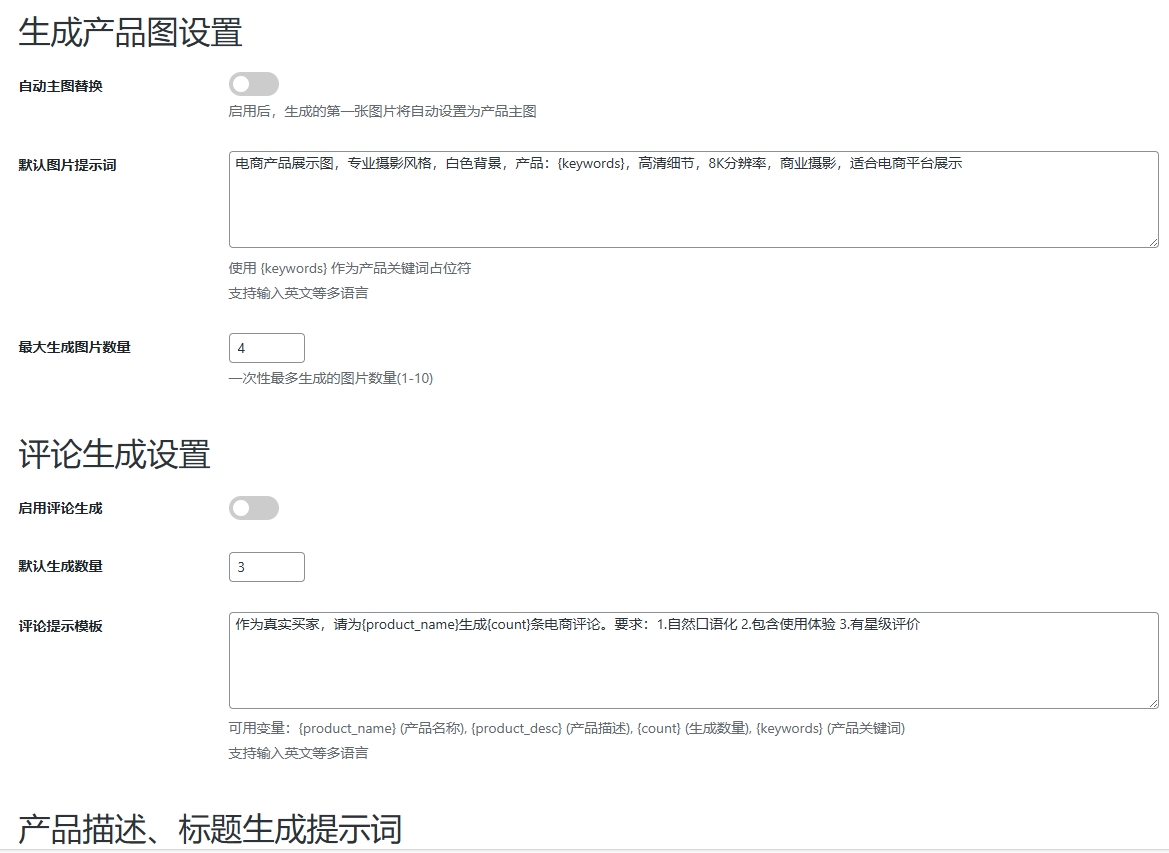
WordPress插件:AI多语言写作与智能配图、免费AI模型、SEO文章生成
厌倦手动写WordPress文章?AI自动生成,效率提升10倍! 支持多语言、自动配图、定时发布,让内容创作更轻松! AI内容生成 → 不想每天写文章?AI一键生成高质量内容!多语言支持 → 跨境电商必备&am…...

OPENCV形态学基础之二腐蚀
一.腐蚀的原理 (图1) 数学表达式:dst(x,y) erode(src(x,y)) min(x,y)src(xx,yy) 腐蚀也是图像形态学的基本功能之一,腐蚀跟膨胀属于反向操作,膨胀是把图像图像变大,而腐蚀就是把图像变小。腐蚀后的图像变小变暗淡。 腐蚀…...

使用Matplotlib创建炫酷的3D散点图:数据可视化的新维度
文章目录 基础实现代码代码解析进阶技巧1. 自定义点的大小和颜色2. 添加图例和样式美化3. 真实数据应用示例实用技巧与注意事项完整示例(带样式)应用场景在数据科学和可视化领域,三维图形能为我们提供更丰富的数据洞察。本文将手把手教你如何使用Python的Matplotlib库创建引…...

Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析
Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析 一、第一轮提问(基础概念问题) 1. 请解释Spring框架的核心容器是什么?它在Spring中起到什么作用? Spring框架的核心容器是IoC容器&#…...

AirSim/Cosys-AirSim 游戏开发(四)外部固定位置监控相机
这个博客介绍了如何通过 settings.json 文件添加一个无人机外的 固定位置监控相机,因为在使用过程中发现 Airsim 对外部监控相机的描述模糊,而 Cosys-Airsim 在官方文档中没有提供外部监控相机设置,最后在源码示例中找到了,所以感…...

三分算法与DeepSeek辅助证明是单峰函数
前置 单峰函数有唯一的最大值,最大值左侧的数值严格单调递增,最大值右侧的数值严格单调递减。 单谷函数有唯一的最小值,最小值左侧的数值严格单调递减,最小值右侧的数值严格单调递增。 三分的本质 三分和二分一样都是通过不断缩…...
