贪心算法应用:最小反馈顶点集问题详解

贪心算法应用:最小反馈顶点集问题详解
1. 问题定义与背景
1.1 反馈顶点集定义
反馈顶点集(Feedback Vertex Set, FVS)是指在一个有向图中,删除该集合中的所有顶点后,图中将不再存在任何有向环。换句话说,反馈顶点集是破坏图中所有环所需删除的顶点集合。
1.2 最小反馈顶点集问题
最小反馈顶点集问题是指在一个给定的有向图中,寻找一个最小的反馈顶点集,即包含顶点数量最少的反馈顶点集。这是一个经典的NP难问题,在实际应用中有着广泛的需求。
1.3 应用场景
- 死锁检测与预防:在操作系统中识别和打破进程间的循环等待
- 电路设计:避免逻辑电路中的反馈循环
- 生物信息学:分析基因调控网络
- 软件工程:分析程序控制流图中的循环结构
2. 贪心算法原理
2.1 贪心算法基本思想
贪心算法是一种在每一步选择中都采取当前状态下最优的选择,从而希望导致结果是全局最优的算法策略。对于最小反馈顶点集问题,贪心算法的基本思路是:
- 识别图中最有可能破坏多个环的顶点
- 将该顶点加入反馈顶点集
- 从图中移除该顶点及其相关边
- 重复上述过程直到图中不再有环
2.2 贪心策略选择
常见的贪心策略包括:
- 最大度数优先:选择当前图中度数最大的顶点
- 最大环参与度:选择参与最多环的顶点
- 权重策略:在有顶点权重的情况下,选择权重与度数比最优的顶点
3. Java实现详细解析
3.1 图的数据结构表示
我们首先需要定义图的表示方式。在Java中,可以使用邻接表来表示有向图。
import java.util.*;public class DirectedGraph {private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> adjacencyList;private Set<Integer> vertices;public DirectedGraph() {this.adjacencyList = new HashMap<>();this.vertices = new HashSet<>();}public void addVertex(int vertex) {vertices.add(vertex);adjacencyList.putIfAbsent(vertex, new ArrayList<>());}public void addEdge(int from, int to) {addVertex(from);addVertex(to);adjacencyList.get(from).add(to);}public List<Integer> getNeighbors(int vertex) {return adjacencyList.getOrDefault(vertex, new ArrayList<>());}public Set<Integer> getVertices() {return new HashSet<>(vertices);}public DirectedGraph copy() {DirectedGraph copy = new DirectedGraph();for (int v : vertices) {for (int neighbor : adjacencyList.get(v)) {copy.addEdge(v, neighbor);}}return copy;}public void removeVertex(int vertex) {vertices.remove(vertex);adjacencyList.remove(vertex);for (List<Integer> neighbors : adjacencyList.values()) {neighbors.removeIf(v -> v == vertex);}}
}
3.2 环检测实现
在实现贪心算法前,我们需要能够检测图中是否存在环。这里使用深度优先搜索(DFS)来实现环检测。
public boolean hasCycle() {Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();Set<Integer> recursionStack = new HashSet<>();for (int vertex : vertices) {if (!visited.contains(vertex) && hasCycleUtil(vertex, visited, recursionStack)) {return true;}}return false;
}private boolean hasCycleUtil(int vertex, Set<Integer> visited, Set<Integer> recursionStack) {visited.add(vertex);recursionStack.add(vertex);for (int neighbor : adjacencyList.getOrDefault(vertex, new ArrayList<>())) {if (!visited.contains(neighbor)) {if (hasCycleUtil(neighbor, visited, recursionStack)) {return true;}} else if (recursionStack.contains(neighbor)) {return true;}}recursionStack.remove(vertex);return false;
}
3.3 贪心算法实现
基于最大度数优先策略的贪心算法实现:
public Set<Integer> greedyFVS() {Set<Integer> fvs = new HashSet<>();DirectedGraph graphCopy = this.copy();while (graphCopy.hasCycle()) {// 选择当前图中度数最大的顶点int vertexToRemove = selectVertexWithMaxDegree(graphCopy);// 添加到反馈顶点集fvs.add(vertexToRemove);// 从图中移除该顶点graphCopy.removeVertex(vertexToRemove);}return fvs;
}private int selectVertexWithMaxDegree(DirectedGraph graph) {int maxDegree = -1;int selectedVertex = -1;for (int vertex : graph.getVertices()) {int outDegree = graph.getNeighbors(vertex).size();int inDegree = 0;// 计算入度for (int v : graph.getVertices()) {if (graph.getNeighbors(v).contains(vertex)) {inDegree++;}}int totalDegree = outDegree + inDegree;if (totalDegree > maxDegree) {maxDegree = totalDegree;selectedVertex = vertex;}}return selectedVertex;
}
3.4 改进的贪心策略实现
更复杂的贪心策略可以考虑顶点参与环的数量:
public Set<Integer> improvedGreedyFVS() {Set<Integer> fvs = new HashSet<>();DirectedGraph graphCopy = this.copy();while (graphCopy.hasCycle()) {// 选择参与最多环的顶点int vertexToRemove = selectVertexInMostCycles(graphCopy);fvs.add(vertexToRemove);graphCopy.removeVertex(vertexToRemove);}return fvs;
}private int selectVertexInMostCycles(DirectedGraph graph) {Map<Integer, Integer> cycleCount = new HashMap<>();// 初始化所有顶点的环计数for (int vertex : graph.getVertices()) {cycleCount.put(vertex, 0);}// 使用DFS检测环并计数for (int vertex : graph.getVertices()) {Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<>();countCyclesUtil(graph, vertex, visited, path, cycleCount);}// 选择参与最多环的顶点return Collections.max(cycleCount.entrySet(), Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).getKey();
}private void countCyclesUtil(DirectedGraph graph, int vertex, Set<Integer> visited, Stack<Integer> path, Map<Integer, Integer> cycleCount) {if (path.contains(vertex)) {// 发现环,增加路径上所有顶点的计数int index = path.indexOf(vertex);for (int i = index; i < path.size(); i++) {int v = path.get(i);cycleCount.put(v, cycleCount.get(v) + 1);}return;}if (visited.contains(vertex)) {return;}visited.add(vertex);path.push(vertex);for (int neighbor : graph.getNeighbors(vertex)) {countCyclesUtil(graph, neighbor, visited, path, cycleCount);}path.pop();
}
4. 算法分析与优化
4.1 时间复杂度分析
-
基本贪心算法:
- 每次环检测:O(V+E)
- 每次选择顶点:O(V^2)(因为要计算每个顶点的度数)
- 最坏情况下需要移除O(V)个顶点
- 总时间复杂度:O(V^3 + V*E)
-
改进的贪心算法:
- 环计数实现较为复杂,最坏情况下为指数时间
- 实际应用中通常需要限制DFS的深度或使用近似方法
4.2 近似比分析
贪心算法提供的是一种近似解法。对于最小反馈顶点集问题:
- 基本贪心算法的近似比为O(log n log log n)
- 更复杂的贪心策略可以达到O(log n)近似比
- 在特殊类型的图中可能有更好的近似比
4.3 优化策略
- 局部搜索优化:在贪心算法得到的解基础上进行局部优化
- 混合策略:结合多种贪心策略,选择最优解
- 并行计算:并行计算各顶点的环参与度
- 启发式剪枝:限制DFS深度或使用随机游走估计环参与度
5. 完整Java实现示例
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class FeedbackVertexSet {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建示例图DirectedGraph graph = new DirectedGraph();graph.addEdge(1, 2);graph.addEdge(2, 3);graph.addEdge(3, 4);graph.addEdge(4, 1); // 形成环1-2-3-4-1graph.addEdge(2, 5);graph.addEdge(5, 6);graph.addEdge(6, 2); // 形成环2-5-6-2graph.addEdge(7, 8);graph.addEdge(8, 7); // 形成环7-8-7System.out.println("原始图是否有环: " + graph.hasCycle());// 使用基本贪心算法Set<Integer> basicFVS = graph.greedyFVS();System.out.println("基本贪心算法找到的FVS: " + basicFVS);System.out.println("大小: " + basicFVS.size());// 使用改进贪心算法Set<Integer> improvedFVS = graph.improvedGreedyFVS();System.out.println("改进贪心算法找到的FVS: " + improvedFVS);System.out.println("大小: " + improvedFVS.size());// 验证解的正确性DirectedGraph testGraph = graph.copy();for (int v : improvedFVS) {testGraph.removeVertex(v);}System.out.println("移除FVS后图是否有环: " + testGraph.hasCycle());}
}class DirectedGraph {// ... 前面的图实现代码 ...// 添加一个更高效的贪心算法实现public Set<Integer> efficientGreedyFVS() {Set<Integer> fvs = new HashSet<>();DirectedGraph graphCopy = this.copy();// 使用优先队列来高效获取最大度数顶点PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b.getValue() - a.getValue());// 初始化度数表Map<Integer, Integer> degreeMap = new HashMap<>();for (int v : graphCopy.getVertices()) {int degree = graphCopy.getNeighbors(v).size();// 计算入度int inDegree = 0;for (int u : graphCopy.getVertices()) {if (graphCopy.getNeighbors(u).contains(v)) {inDegree++;}}degreeMap.put(v, degree + inDegree);}maxHeap.addAll(degreeMap.entrySet());while (graphCopy.hasCycle()) {if (maxHeap.isEmpty()) break;Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry = maxHeap.poll();int vertex = entry.getKey();int currentDegree = degreeMap.getOrDefault(vertex, 0);// 检查度数是否最新(因为图可能已经改变)int actualDegree = graphCopy.getNeighbors(vertex).size();int actualInDegree = 0;for (int u : graphCopy.getVertices()) {if (graphCopy.getNeighbors(u).contains(vertex)) {actualInDegree++;}}int totalDegree = actualDegree + actualInDegree;if (totalDegree < currentDegree) {// 度数已变化,重新插入entry.setValue(totalDegree);maxHeap.add(entry);continue;}// 添加到FVSfvs.add(vertex);// 更新邻居的度数for (int neighbor : graphCopy.getNeighbors(vertex)) {if (degreeMap.containsKey(neighbor)) {degreeMap.put(neighbor, degreeMap.get(neighbor) - 1);}}// 更新指向该顶点的邻居for (int u : graphCopy.getVertices()) {if (graphCopy.getNeighbors(u).contains(vertex)) {if (degreeMap.containsKey(u)) {degreeMap.put(u, degreeMap.get(u) - 1);}}}// 从图中移除顶点graphCopy.removeVertex(vertex);degreeMap.remove(vertex);}return fvs;}// 添加一个基于随机游走的近似环计数方法private int selectVertexInMostCyclesApprox(DirectedGraph graph, int walks, int steps) {Map<Integer, Integer> cycleCount = new HashMap<>();Random random = new Random();List<Integer> vertices = new ArrayList<>(graph.getVertices());for (int v : graph.getVertices()) {cycleCount.put(v, 0);}for (int i = 0; i < walks; i++) {int startVertex = vertices.get(random.nextInt(vertices.size()));int currentVertex = startVertex;Set<Integer> visitedInWalk = new HashSet<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();for (int step = 0; step < steps; step++) {List<Integer> neighbors = graph.getNeighbors(currentVertex);if (neighbors.isEmpty()) break;int nextVertex = neighbors.get(random.nextInt(neighbors.size()));if (path.contains(nextVertex)) {// 发现环int index = path.indexOf(nextVertex);for (int j = index; j < path.size(); j++) {int v = path.get(j);cycleCount.put(v, cycleCount.get(v) + 1);}break;}path.add(nextVertex);currentVertex = nextVertex;}}return Collections.max(cycleCount.entrySet(), Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).getKey();}
}
6. 测试与验证
6.1 测试用例设计
为了验证算法的正确性和效率,我们需要设计多种测试用例:
- 简单环图:单个环或多个不相交的环
- 复杂环图:多个相交的环
- 无环图:验证算法不会返回不必要的顶点
- 完全图:所有顶点之间都有边
- 随机图:随机生成的有向图
6.2 验证方法
- 移除返回的反馈顶点集后,检查图中是否确实无环
- 比较不同算法得到的解的大小
- 测量算法运行时间
6.3 性能测试示例
public class PerformanceTest {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] sizes = {10, 50, 100, 200, 500};for (int size : sizes) {System.out.println("\n测试图大小: " + size);DirectedGraph graph = generateRandomGraph(size, size * 2);long start, end;start = System.currentTimeMillis();Set<Integer> basicFVS = graph.greedyFVS();end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.printf("基本贪心算法: %d 顶点, 耗时 %d ms%n", basicFVS.size(), end - start);start = System.currentTimeMillis();Set<Integer> efficientFVS = graph.efficientGreedyFVS();end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.printf("高效贪心算法: %d 顶点, 耗时 %d ms%n", efficientFVS.size(), end - start);// 对于大图,改进算法可能太慢,可以跳过if (size <= 100) {start = System.currentTimeMillis();Set<Integer> improvedFVS = graph.improvedGreedyFVS();end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.printf("改进贪心算法: %d 顶点, 耗时 %d ms%n", improvedFVS.size(), end - start);}}}private static DirectedGraph generateRandomGraph(int vertexCount, int edgeCount) {DirectedGraph graph = new DirectedGraph();Random random = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {graph.addVertex(i);}for (int i = 0; i < edgeCount; i++) {int from = random.nextInt(vertexCount);int to = random.nextInt(vertexCount);if (from != to) {graph.addEdge(from, to);}}return graph;}
}
7. 实际应用与扩展
7.1 加权反馈顶点集
在实际应用中,顶点可能有不同的权重,我们需要寻找权重和最小的反馈顶点集:
public Set<Integer> weightedGreedyFVS(Map<Integer, Integer> vertexWeights) {Set<Integer> fvs = new HashSet<>();DirectedGraph graphCopy = this.copy();while (graphCopy.hasCycle()) {// 选择(度数/权重)最大的顶点int vertexToRemove = -1;double maxRatio = -1;for (int vertex : graphCopy.getVertices()) {int outDegree = graphCopy.getNeighbors(vertex).size();int inDegree = 0;for (int v : graphCopy.getVertices()) {if (graphCopy.getNeighbors(v).contains(vertex)) {inDegree++;}}double ratio = (outDegree + inDegree) / (double) vertexWeights.get(vertex);if (ratio > maxRatio) {maxRatio = ratio;vertexToRemove = vertex;}}fvs.add(vertexToRemove);graphCopy.removeVertex(vertexToRemove);}return fvs;
}
7.2 并行化实现
对于大型图,可以并行计算各顶点的环参与度:
public Set<Integer> parallelGreedyFVS() {Set<Integer> fvs = new HashSet<>();DirectedGraph graphCopy = this.copy();ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());while (graphCopy.hasCycle()) {List<Future<VertexCycleCount>> futures = new ArrayList<>();for (int vertex : graphCopy.getVertices()) {futures.add(executor.submit(() -> {int count = countCyclesForVertex(graphCopy, vertex);return new VertexCycleCount(vertex, count);}));}VertexCycleCount best = new VertexCycleCount(-1, -1);for (Future<VertexCycleCount> future : futures) {try {VertexCycleCount current = future.get();if (current.count > best.count) {best = current;}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}if (best.vertex != -1) {fvs.add(best.vertex);graphCopy.removeVertex(best.vertex);}}executor.shutdown();return fvs;
}private static class VertexCycleCount {int vertex;int count;VertexCycleCount(int vertex, int count) {this.vertex = vertex;this.count = count;}
}private int countCyclesForVertex(DirectedGraph graph, int vertex) {// 简化的环计数实现int count = 0;Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<>();return countCyclesUtil(graph, vertex, visited, path);
}private int countCyclesUtil(DirectedGraph graph, int vertex, Set<Integer> visited, Stack<Integer> path) {if (path.contains(vertex)) {return 1;}if (visited.contains(vertex)) {return 0;}visited.add(vertex);path.push(vertex);int total = 0;for (int neighbor : graph.getNeighbors(vertex)) {total += countCyclesUtil(graph, neighbor, visited, path);}path.pop();return total;
}
8. 总结
最小反馈顶点集问题是一个具有挑战性的NP难问题,贪心算法提供了一种有效的近似解决方案。本文详细介绍了:
- 问题的定义和应用背景
- 贪心算法的基本原理和多种策略
- 完整的Java实现,包括基础和改进版本
- 时间复杂度分析和优化策略
- 测试验证方法和性能考虑
- 实际应用扩展和并行化实现
贪心算法虽然不能保证得到最优解,但在实际应用中通常能提供令人满意的近似解,特别是在处理大规模图数据时。通过选择合适的贪心策略和优化技巧,可以在解的质量和计算效率之间取得良好的平衡。
对于需要更高精度解的场景,可以考虑将贪心算法与其他技术如分支限界、动态规划或元启发式算法结合使用。
更多资源:
https://www.kdocs.cn/l/cvk0eoGYucWA
本文发表于【纪元A梦】,关注我,获取更多免费实用教程/资源!
相关文章:

贪心算法应用:最小反馈顶点集问题详解
贪心算法应用:最小反馈顶点集问题详解 1. 问题定义与背景 1.1 反馈顶点集定义 反馈顶点集(Feedback Vertex Set, FVS)是指在一个有向图中,删除该集合中的所有顶点后,图中将不再存在任何有向环。换句话说,反馈顶点集是破坏图中所…...

游戏引擎学习第259天:OpenGL和软件渲染器清理
回顾并为今天的内容做好铺垫 今天,我们将对游戏的分析器进行升级。在之前的修复中,我们解决了分析器的一些敏感问题,例如它无法跨代码重新加载进行分析,以及一些复杂的小问题。现在,我们的分析器看起来已经很稳定了。…...

一篇文章看懂时间同步服务
Linux 系统时间与时区管理 一、时间与时钟类型 时钟类型说明管理工具系统时钟由 Linux 内核维护的软件时钟,基于时区配置显示时间timedatectl硬件时钟 (RTC)主板上的物理时钟,通常以 UTC 或本地时间存储,用于系统启动时初始化时间hwclock …...

12.模方ModelFun工具-立面修整
摘要:本文主要介绍模方ModelFun修模工具——立面修整的操作方法。 点击工具栏即可找到立面修整工具,点击可打开并使用该工具,如下图: 图 工具菜单栏 (1)截面绘制: 快速绘制竖直矩形࿱…...

git命令常见用法【持续更新中……】
一、已有本地代码,在gitee创建了空仓库后想将代码与该仓库相连 在本地项目目录下初始化Git # 1. 初始化本地仓库 git init# 2. 添加所有文件到暂存区 git add .# 3. 提交第一个版本 git commit -m "Initial commit: 项目初始化"将本地仓库关联到Gitee 根…...

Docker 渡渡鸟镜像同步站 使用教程
Docker 渡渡鸟镜像同步站 使用教程 🚀 介绍 Docker.aityp.com(渡渡鸟镜像同步站)是一个专注于为国内开发者提供 Docker 镜像加速和同步服务的平台。它通过同步官方镜像源(如 Docker Hub、GCR、GHCR 等),为…...

Python TensorFlow库【深度学习框架】全面讲解与案例
一、TensorFlow 基础知识 1. 核心概念 张量 (Tensor): 多维数组,是 TensorFlow 的基本数据单位(标量、向量、矩阵等)。计算图 (Graph): 早期版本中的静态图机制(TF2.x 默认启用动态图)。会话 (Session): 在 TF1.x 中用于执行计算图(TF2.x 中已弃用)。2. 基本操作 impo…...

火影bug,未保证短时间数据一致性,拿这个例子讲一下Redis
本文只拿这个游戏的bug来举例Redis,如果有不妥的地方,联系我进行删除 描述:今天在高速上打火影(有隧道,有时候会卡),发现了个bug,我点了两次-1000的忍玉(大概用了1千七百…...

Power Query 是 Excel 和 Power BI 中强大的数据获取、转换和加载工具
Power Query 链接是什么 Power Query 是 Excel 和 Power BI 中强大的数据获取、转换和加载工具。Power Query 链接指的是在 Excel 或 Power BI 里通过 Power Query 建立的与外部数据源的连接。这些数据源可以是各种类型,像文本文件(CSV、TXT)…...

探索元生代:ComfyUI 工作流与计算机视觉的奇妙邂逅
目录 一、引言 二、蓝耘元生代和 ComfyUI 工作流初印象 (一)蓝耘元生代平台简介 (二)ComfyUI 工作流创建是啥玩意儿 三、计算机视觉是个啥 (一)计算机视觉的基本概念 (二)计算…...

Unity-Shader详解-其五
关于Unity的Shader部分的基础知识其实已经讲解得差不多了,今天我们来一些实例分享: 溶解 效果如下: 代码如下: Shader "Chapter8/chapter8_1" {Properties{// 定义属性[NoScaleOffset]_Albedo("Albedo", 2…...

【Java 专题补充】流程控制语句
流程控制语句是用来控制程序中各语句执行顺序的语句,是程序中既基本又非常关键的部分。流程控制语句可以把单个的语句组合成有意义的、能完成一定功能的小逻辑模块。最主要的流程控制方式是结构化程序设计中规定的三种基本流程结构。 1.1 结构化程序设计的三种基本流…...

恶心的win11更新DIY 设置win11更新为100年
打开注册表编辑器:按下Win R键,输入regedit,然后按回车打开注册表编辑器。12导航到指定路径:在注册表编辑器中,依次展开HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsUpdate\UX\Settings新建DWORD值&…...

【ArcGIS微课1000例】0146:将多个文件夹下的影像移动到一个目标文件夹(以Landscan数据为例)
本文讲述将多个文件夹下的影像移动到一个目标文件夹,便于投影变换、裁剪等操作。 文章目录 一、数据准备二、解压操作三、批量移动四、查看效果五、ArcGIS操作一、数据准备 全球人口数据集Landscan2000-2023如下所示,每年数据位一个压缩包: 二、解压操作 首先将其解压,方…...

【redis】分片方案
Redis分片(Sharding)是解决单机性能瓶颈的核心技术,其本质是将数据分散存储到多个Redis节点(实例)中,每个实例将只是所有键的一个子集,通过水平扩展提升系统容量和性能。 分片的核心价值 性能提…...

springboot+mysql+element-plus+vue完整实现汽车租赁系统
目录 一、项目介绍 二、项目截图 1.项目结构图 三、系统详细介绍 管理后台 1.登陆页 2.管理后台主页 3.汽车地点管理 4.汽车类别 5.汽车品牌 6.汽车信息 7.用户管理 8.举报管理 9.订单管理 10.轮播图管理 11.交互界面 12.图表管理 汽车租赁商城 1.首页 2.汽…...

Linux第四节:进程控制
一、进程创建 1.1 fork函数 1. fork函数有两个返回值问题 返回的本质就是写入!所以,谁先返回,谁就先写入id,因为进程具有独立性,会发生写时拷贝,父进程和子进程各自指向return语句。 2. fork返回后&#x…...

Qt 编译 sqldrivers之psql
编译postgres pgsql驱动 下载驱动源码修改配置文件编译 下载驱动源码 // 源代码下载 https://download.qt.io/archive/qt/5.15/5.15.2/submodules/驱动目录:qtbase-everywhere-src-5.15.2\src\plugins\sqldrivers 修改配置文件 打开pro文件 右键点击添加库 此处的为debu…...

382_C++_在用户会话结束时,检查是否有其他会话仍然来自同一个客户端 IP 地址,没有连接状态设置为断开,否则为连接
之前出现的问题:重启管理机,工作机上面热备连接状态显示未连接 (此时是有一个工作机连接管理机的),所以正常应该是连接状态解决:根因分析: 重启管理机后,管理机给过来的cookie是空的,导致工作机同时存在两个管理机的session,在其中一个超时后,调用回调函数通知会话断开…...
的配置文件(moveitcpp))
RViz(机器人可视化工具)的配置文件(moveitcpp)
1. Panels(面板设置) 面板是RViz界面中的各个功能区域,用于显示和操作不同的数据。 Displays(显示面板) Class: rviz_common/Displays 指定面板的类型,这里是显示面板。 Help Height: 78 帮助区域的高度…...

Redis中6种缓存更新策略
Redis作为一款高性能的内存数据库,已经成为缓存层的首选解决方案。然而,使用缓存时最大的挑战在于保证缓存数据与底层数据源的一致性。缓存更新策略直接影响系统的性能、可靠性和数据一致性,选择合适的策略至关重要。 本文将介绍Redis中6种缓…...

如何使用极狐GitLab 软件包仓库功能托管 terraform?
极狐GitLab 是 GitLab 在中国的发行版,关于中文参考文档和资料有: 极狐GitLab 中文文档极狐GitLab 中文论坛极狐GitLab 官网 Terraform 模块库 (BASIC ALL) 基础设施仓库和 Terraform 模块仓库合并到单个 Terraform 模块仓库功能引入于极狐GitLab 15.1…...

观测云:安全、可信赖的监控观测云服务
引言 近日,“TikTok 遭欧盟隐私监管机构调查并处以 5.3 亿欧元”一案,再次引发行业内对数据合规等话题的热议。据了解,仅 2023 年一年就产生了超过 20 亿美元的 GDPR 罚单。这凸显了在全球化背景下,企业在数据隐私保护方面所面临…...

【python】使用Python和BERT进行文本摘要:从数据预处理到模型训练与生成
《Python OpenCV从菜鸟到高手》带你进入图像处理与计算机视觉的大门! 解锁Python编程的无限可能:《奇妙的Python》带你漫游代码世界 随着信息爆炸时代的到来,海量文本数据的高效处理与理解成为亟待解决的问题。文本摘要作为自然语言处理(NLP)中的关键任务,旨在自动生成…...

【PostgreSQL数据分析实战:从数据清洗到可视化全流程】5.3 相关性分析(PEARSON/SPEARMAN相关系数)
👉 点击关注不迷路 👉 点击关注不迷路 👉 点击关注不迷路 文章大纲 5.3 相关性分析(PEARSON/SPEARMAN相关系数)5.3.1 相关性分析理论基础5.3.1.1 相关系数定义与分类5.3.1.2 Pearson相关系数( Pearson Corr…...

Redis面试 实战贴 后面持续更新链接
redis是使用C语言写的。 面试问题列表: Redis支持哪些数据类型?各适用于什么场景? Redis为什么采用单线程模型?优势与瓶颈是什么? RDB和AOF持久化的区别?如何选择?混合持久化如何实现&#x…...
)
小程序滚动条隐藏(uniapp版本)
单独指定页面隐藏(找到对应的scroll-view) <style> /* 全局隐藏滚动条样式 */ ::-webkit-scrollbar { display: none; width: 0; height: 0; color: transparent; background: transparent; } /* 确保scroll-view组件也隐藏滚动条 */ …...
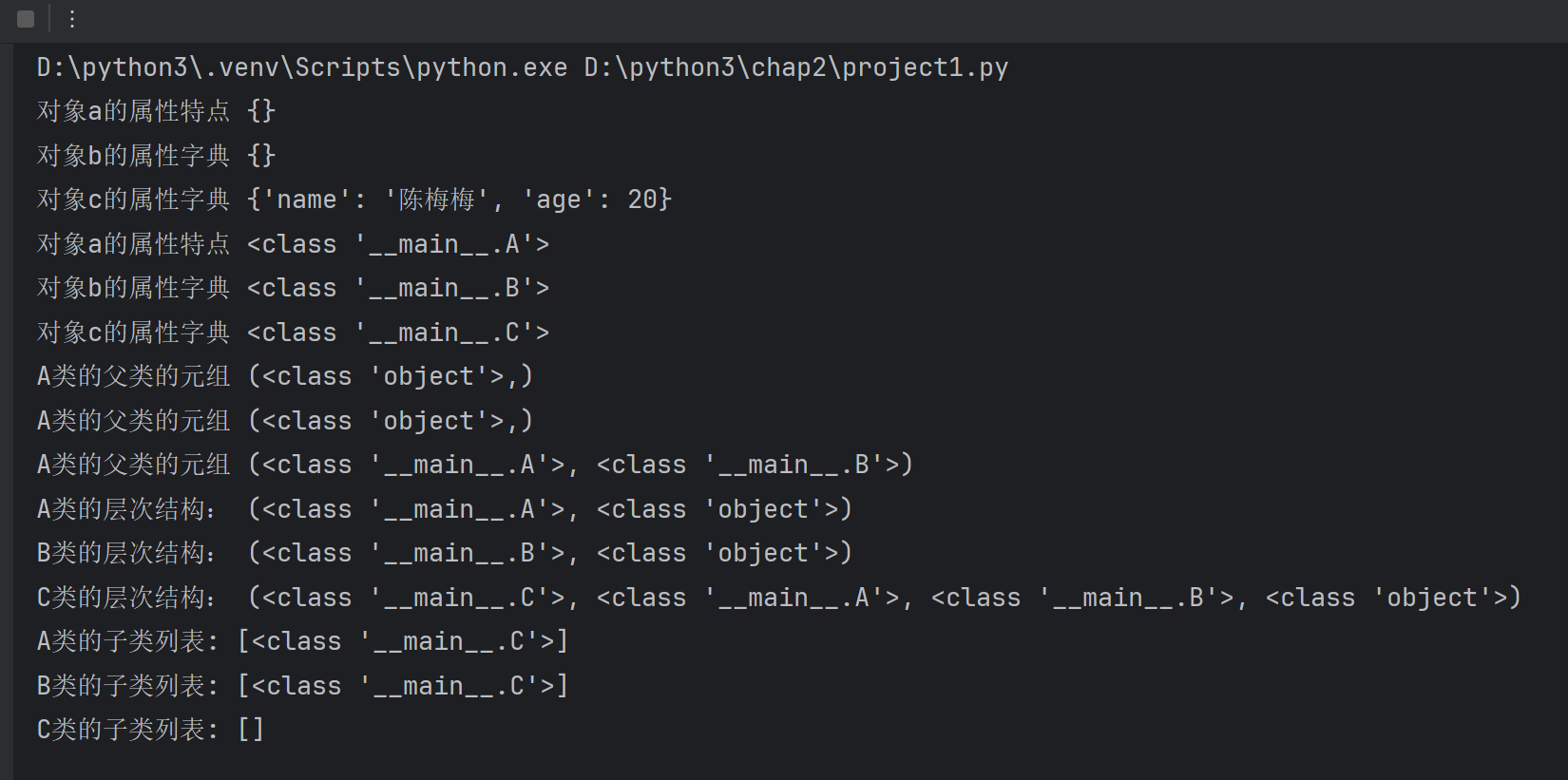
python基础:序列和索引-->Python的特殊属性
一.序列和索引 1.1 用索引检索字符串中的元素 # 正向递增 shelloworld for i in range (0,len(s)):# i是索引print(i,s[i],end\t\t) print(\n--------------------------) # 反向递减 for i in range (-10,0):print(i,s[i],end\t\t)print(\n--------------------------) print(…...

java反射(2)
package 反射;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Arrays;public class demo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 通过类的全限定名获取对应的 Class 对象…...

C++核心概念全解析:从析构函数到运算符重载的深度指南
目录 前言一、构析函数1.1 概念1.2 语法格式 1.3 核心特性1.4 调用时机1.5 构造函数 vs 析构函数1.6 代码示例 二、this关键字2.1 基本概念2.2 核心特性2.3 使用场景2.3.1 区分成员与局部变量2.3.2 返回对象自身(链式调用)2.3.3 成员函数间传递当前对象2…...
