C++学习-入门到精通【14】标准库算法
C++学习-入门到精通【14】标准库算法
目录
- C++学习-入门到精通【14】标准库算法
- 一、对迭代器的最低要求
- 迭代器无效
- 二、算法
- 1.fill、fill_n、generate和generate_n
- 2.equal、mismatch和lexicographical_compare
- 3.remove、remove_if、remove_copy和remove_copy_if
- 4.replace、replace_if、replace_copy和replace_copy_if
- 5.数学算法
- 6.基本查找和排序算法
- 7.swap、iter_swap和swap_ranges
- 8.copy_backward、merge、unique和reverse
- 9.inplace_merge、unique_copy和reverse_copy
- 10.集合操作
- 11.lower_bound、upper_bound和equal_range
- 12.堆排序
- 13.min、max、minmax和minmax_element
- 三、函数对象
- 函数对象较函数指针的优越之处
- 标准模板库中预先定义的函数对象
- 使用标准库的accumulate算法
- 四、lambda表达式
- 五、标准库算法总结
一、对迭代器的最低要求
通常标准库会将算法和容器分离,这样做是为了使添加新算法更容易。每个容器的一个重要部分就是它支持的迭代器类型,这决定了该容器能够使用什么样的算法。所以每个以迭代器为参数的算法的标准库算法,都要求迭代器提供最低限度的功能。例如,如果一个算法需要前向迭代器,那么它就可以使用在支持任何支持前向迭代器、双向迭代器和随机访问迭代器的容器中。
标准库算法并不依赖它们操作的容器的实现细节,只要该容器的迭代器满足算法的需求,那么这个算法就能作用在这个容器上。
在性能允许的情况下使用“最弱的迭代器”,这将有助于产生可用性最大化的组件。例如,一个算法只需要前向迭代器,那么它就可以与支持前向迭代器、双向迭代器或随机访问迭代器的任何容器一起使用,但是如果一个算法需要随机访问迭代器,那么它只能与支持随机访问迭代器的容器一起使用。
迭代器无效
迭代器只是简单地指向容器的元素,因此当对容器进行某些修改时,迭代器就有可能会失效。例如,如果对一个vector对象调用clear函数,那么会间接调用erase函数,将所有元素全部删除。如果在调用clear函数之前,程序中有任何指向该vector对象中元素的迭代器,那么现在这些迭代器就会失效。下面我们总结了在插入和删除操作期间迭代器何时会失效:
插入操作:
- vector —— 如果 vector 对象被重新分配,那么
所有指向这个 vector 对象的迭代器都将变得无效。如果没有重新分配,那么从插入点到这个对象末尾的迭代器都将变为无效(所有元素都会后移); - deque ——
所有迭代器都变为无效;deque通常实现为多个固定大小的数组(被称为块或缓冲区)的集合,这些块由一个中央控制结构(通常是一个数组,被称为映射器)管理,映射器存储指向这些块的指针。所以一个指向deque对象元素的迭代器中通常包含多个组件:指向当前元素的指针、指向当前内存块起始位置的指针、指向当前内存块结束位置的指针和指向映射数组中管理当前内存块的指针的指针。当进行插入操作时触发了映射数组的扩容和重新分配,那么映射数组就移动到了一个新的地址,之前所有迭代器中存储的指向映射数组或其内部指针的指针都变得无效了,即使迭代器之前指向的元素的地址没有发生变化,迭代器也无法再正确地定位它所在的块,所以迭代器会失效。由于用户是无法预知哪一次操作会导致上面情况的发生,所以C++标准规定,当对一个deque对象进行了一次插入之后,之前的所有指向该对象的迭代器都会失效。 - list 或 forward_list ——
所有迭代器都依然有效。它们本身实现就是链表,不管如何插入元素,迭代器都还是会指向原来指向的元素。 - 有序的关联容器 ——
所有迭代器都依然有效。这是因为有序的关联容器基本上都是使用红黑树来实现,而树结构在插入新节点之后,只需要修改节点中的父子指针的指向即可(进行旋转),节点本身的物理地址是没有发生变化的,所以迭代器不会失效。 - 无序的关联容器 ——
所有迭代器都会失效。无序的关联容器使用哈希表来实现,它的内存分布是由一个桶数组(一个连续的内存块)来存储表头指针或是动态数组(存储一个数组其实就是存储该数组首元素的地址)和用于解决冲突的链表或动态数组组成。当进行插入操作后,可能会导致桶数组重新分配,此时桶数组的地址会发生变化,迭代器内会存储桶数组的地址用来寻址,所以迭代器会失效。所以保守起见,C++标准库中规定,只要对一个无序关联容器插入新元素,那么所有的迭代器都会失效;
删除操作:当对容器进行删除操作时,指向被删除元素的迭代器会失效。
- vector —— 从被删除元素到这个 vector 对象末尾的迭代器都会变为无效;
- deque —— 如果处在这个 deque 对象中部的元素被删除,那么所有的迭代器都会变为无效;
迭代器本质上是对底层内存地址的抽象封装。它存储的是一个指向特定内存位置的指针(或者类似指针的东西,当进行插入或删除操作后,原来的元素可能会在内存发生移动,这里再使用原来的迭代器就无法找到对应的元素。这就相当于是你的朋友搬家之后,你仍使用他原来的住址去找他,显然是不合适的)。
二、算法
1.fill、fill_n、generate和generate_n
下面的程序演示了标准库中的fill、fill_n、generate和generate_n算法。
fill 和 fill_n 算法把容器中某个范围内的元素设置为一个指定值。

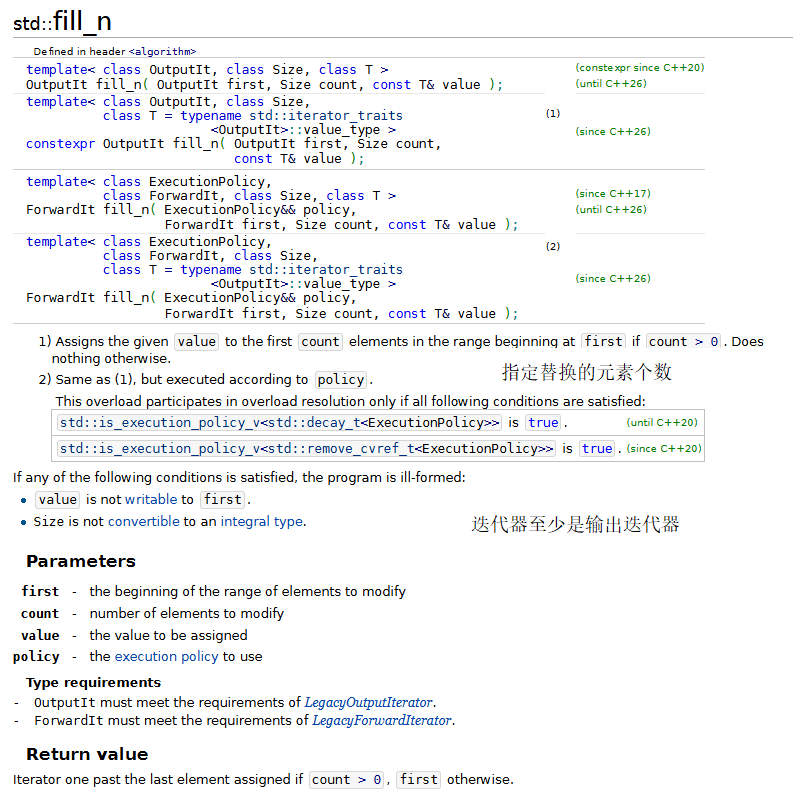
generate 和 generate_n 算法使用一个生成函数为容器中一定范围内的元素创建新的值。


test.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;// 元素生成函数
char nextLetter();int main()
{array<char, 10> chars;ostream_iterator<char> output(cout, " ");fill(chars.begin(), chars.end(), '6'); // 为chars中begin()和end()之间的元素全部分配6cout << "chars after filling with 6:\n";copy(chars.cbegin(), chars.cend(), output);fill_n(chars.begin(), 5, '8'); // 为chars的前5个元素重新分配值为8cout << "\n\nchars after filling five elements with 8:\n";copy(chars.cbegin(), chars.cend(), output);generate(chars.begin(), chars.end(), nextLetter);cout << "\n\nchars after generate letters A-J:\n";copy(chars.cbegin(), chars.cend(), output);// 这里是使用了函数指针generate_n(chars.begin(), 5, nextLetter);cout << "\n\nchars after generate letters K-O:\n";copy(chars.cbegin(), chars.cend(), output);
}char nextLetter()
{static char letter = 'A';return letter++;
}
运行结果:

2.equal、mismatch和lexicographical_compare



示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array <int, SIZE> a1 { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };array <int, SIZE> a2(a1); // 使用拷贝构造函数创建一个array对象array <int, SIZE> a3 { 1, 2, 3, 4, 10000, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "a1 contains: ";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);cout << "\na2 contains: ";copy(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), output);cout << "\na3 contains: ";copy(a3.cbegin(), a3.cend(), output);// 比较a1和a2是否相等bool result = equal(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), a2.cbegin(), a2.cend());cout << "\n\na1 " << (result ? "is " : "is not ") << "equal to a2.\n";// 比较a1和a3是否相等result = equal(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), a3.cbegin(), a3.cend());cout << "a1 " << (result ? "is ": "is not ") << "equal to a3.\n";auto location = mismatch(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), a3.cbegin(), a3.cend());cout << "\nThere is a mismatch between a1 and a3 at location "<< (location.first - a1.cbegin()) << "\nwhere a1 contains "<< *location.first << " and a3 contains " << *location.second << "\n\n";char c1[SIZE] = "HELLO";char c2[SIZE] = "BYE BYE";result = lexicographical_compare(cbegin(c1), cend(c1), cbegin(c2), cend(c2));cout << c1 << (result ? " < " : " >= ") << c2 << endl;
}
运行结果:

3.remove、remove_if、remove_copy和remove_copy_if


注意上面的算法不会改变容器的容量,也并不会真的将删除元素,只是用与参数指定值相同的元素使用它后一个元素替换。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;bool greater9(int);int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array<int, SIZE> init = { 10, 2, 10, 4, 16, 6, 14, 8, 12, 10 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");// 测试removecout << "Testing algorithm \"remove\"\n";array<int, SIZE> a1(init);cout << "a1 before remove all 10:\n";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);auto newLastElement = remove(a1.begin(), a1.end(), 10);cout << "\na1 after remove all 10(newLastElement):\n";copy(a1.begin(), newLastElement, output);cout << "\na1 between a1.cbegin and a1.cend:\n";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);// 测试remove_copycout << "\n\nTesting algorithm \"remove_copy\"\n";array<int, SIZE> a2(init);array<int, SIZE> a3 { };cout << "a2 before removing all 10 and copying:\n";copy(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), output);// 将a2中不是10的元素复制到a3中newLastElement = remove_copy(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), a3.begin(), 10);cout << "\na3 after removing all 10 from a2(newLastElement):\n";copy(a3.begin(), newLastElement, output);cout << "\na3 after removing all 10 from a2:\n";copy(a3.cbegin(), a3.cend(), output);// 测试remove_ifcout << "\n\nTesting algorithm \"remove_if\"\n";array<int, SIZE> a4(init);cout << "a4 before removing all elements greater than 9:\n";copy(a4.cbegin(), a4.cend(), output);// 使用remove_if函数,该函数可以指定条件,“删除”满足条件的元素newLastElement = remove_if(a4.begin(), a4.end(), greater9);cout << "\na4 after removing all elements greater than 9(newLastElement):\n";copy(a4.begin(), newLastElement, output);cout << "\na4 after removing all elements greater than 9:\n";copy(a4.cbegin(), a4.cend(), output);// 测试remove_copy_ifcout << "\n\nTesting algorithm \"remove_copy_if\"\n";array<int, SIZE> a5(init);array<int, SIZE> a6{};cout << "a5 before removing all elements greater than 9 and copying:\n";copy(a5.cbegin(), a5.cend(), output);newLastElement = remove_copy_if(a5.begin(), a5.end(), a6.begin(), greater9);cout << "\na6 after removing all elements greater than 9(newLastElement):\n";copy(a6.begin(), newLastElement, output);cout << "\na6 after removing all elements greater than 9:\n";copy(a6.cbegin(), a6.cend(), output);cout << endl;
}bool greater9(int x)
{return x > 9;
}
运行结果:

从结果我们可以看出上面的这4个版本的算法其实并不会真的将元素删除,仅仅是将容器中与指定元素不同的元素往前移动,并返回一个指向这些与指定元素不同的最后一个元素的迭代器,在这个迭代器之后的元素是什么并不确定。
与容器中实现的成员函数remove比较,算法remove并不会真正的删除元素,而成员函数remove会真正的删除元素。
4.replace、replace_if、replace_copy和replace_copy_if


示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;bool greater9(int);int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array<int, SIZE> init = { 10, 2, 10, 4, 16, 6, 14, 8, 12, 10 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");// 测试replacecout << "Testing of algorithm \"replace\"";array<int, SIZE> a1(init);cout << "\na1 before replacing all 10:\n";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);cout << "\na1 after replacing all 10 with 100:\n";replace(a1.begin(), a1.end(), 10, 100);copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);// 测试replace_copycout << "\n\nTesting of algorithm \"replace_copy\"";array<int, SIZE> a2(init);array<int, SIZE> c1{};cout << "\na2 before replacing all 10 and copying:\n";copy(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), output);cout << "\nc1 after replacing all 10 in a2:\n";replace_copy(a2.begin(), a2.end(), c1.begin(), 10, 100);copy(c1.cbegin(), c1.cend(), output);// 测试replace_ifcout << "\n\nTesting of algorithm \"replace_if\"";array<int, SIZE> a3(init);cout << "\na3 before replacing all elements greater than 9:\n";copy(a3.cbegin(), a3.cend(), output);cout << "\na3 after replacing all elements greater than 9 with 100:\n";replace_if(a3.begin(), a3.end(), greater9, 100);copy(a3.cbegin(), a3.cend(), output);// 测试replace_copy_ifcout << "\n\nTesting of algorithm \"replace_copy_if\"";array<int, SIZE> a4(init);array<int, SIZE> c2{};cout << "\na4 before replacing all greater than 9 and copying:\n";copy(a4.cbegin(), a4.cend(), output);cout << "\nc2 after replacing all greater than 9 in a4:\n";replace_copy_if(a4.begin(), a4.end(), c2.begin(), greater9, 100);copy(c2.cbegin(), c2.cend(), output);cout << endl;
}bool greater9(int x)
{return x > 9;
}
运行结果:

5.数学算法
下面的程序演示了几个常用的数学算法,包括:random_shuffle、count、count_if、min_element、max_element、minmax_element、accumulate、for_each和transform。








示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric> // accumulate算法定义在该头文件中
#include <array>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;bool greater9(int);
void outputSquare(int);
int calculateCube(int);int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array<int, SIZE> a1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");// random_shufflecout << "a1 before random_shuffle: ";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);// 使用默认的rand函数random_shuffle(a1.begin(), a1.end());cout << "\na1 after random_shuffle: ";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);// count和count_ifarray<int, SIZE> a2 = { 100,2,8,1,50,3,8,8,9,10 };cout << "\n\na2 contains: ";copy(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), output);// 计算a2中8的个数auto result = count(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), 8);cout << "\nNumber of elements matching 8: " << result;// 计算a2中大于9的元素的个数result = count_if(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), greater9);cout << "\nNumber of elements greater than 9: " << result;// min_element、max_element和 minmax_elementcout << "\n\nMinimum element in a2 is: "<< *(min_element(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend()));cout << "\nMaximum element in a2 is: "<< *(max_element(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend()));auto minAndMax = minmax_element(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend());cout << "\nThe minimum and maximum elements in a2 are: "<< *minAndMax.first << " and " << *minAndMax.second << ", respectively.";// accumulatecout << "\n\nThe total of the elements in a1 is: "<< accumulate(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), 0);// for_eachcout << "\n\nThe square of every integer in a1 is:\n";for_each(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), outputSquare);array<int,SIZE> cubes;// transformtransform(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), cubes.begin(), calculateCube);cout << "\n\nThe cube of every integer in a1 is:\n";copy(cubes.cbegin(), cubes.cend(), output);cout << endl;
}bool greater9(int x)
{return x > 9;
}void outputSquare(int value)
{cout << value * value << ' ';
}int calculateCube(int value)
{return value * value * value;
}
运行结果:

6.基本查找和排序算法
下面将演示标准库中的几种基本的查找和排序算法,包括:find、find_if、find_if_not、sort、binary_search、all_of、和any_of。




示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;bool greater10(int);
bool less10(int);int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array<int, SIZE> a { 10, 2, 17, 5, 16, 8, 13, 11, 20, 7 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "array a contains: ";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);// find、find_if、find_if_notauto location = find(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 16);if (location != a.cend()) // 范围内存在元素16{// 显示第一个值为16的元素在容器中位置cout << "\n\nFound 16 at location " << (location - a.cbegin()); }elsecout << "\n\n16 not found";location = find(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 100);if (location != a.cend()) // 范围内存在元素100{// 显示第一个值为100的元素在容器中位置cout << "\n\nFound 100 at location " << (location - a.cbegin());}elsecout << "\n\n100 not found";// 查找容器内第一个大于10的元素location = find_if(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), greater10);if (location != a.cend()) {// 显示第一个值大于10的元素在容器中位置cout << "\n\nThe first value greater than 10 is " << *location<< "\nfound at location" << (location - a.cbegin());}elsecout << "\n\nNo values greater than 10 were found.";location = find_if_not(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), less10);if (location != a.cend()){// 显示第一个值大于10的元素在容器中位置cout << "\n\nThe first value not less than 10 is " << *location<< "\nfound at location" << (location - a.cbegin());}elsecout << "\n\nNo values not less than 10 were found.";// sortsort(a.begin(), a.end());cout << "\n\narray a after sort: ";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);// binary_search// 判断容器中是否存在元素13if(binary_search(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 13))cout << "\n\n13 was found in array a";elsecout << "\n\n13 was not found in array a";// 判断容器中是否存在元素13if (binary_search(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 100))cout << "\n\n100 was found in array a";elsecout << "\n\n100 was not found in array a";// all_of、any_of和none_ofif(all_of(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), greater10))cout << "\n\nAll the elements in array a are greater than 10";elsecout << "\n\nSome elements in array a are not greater than 10";if (any_of(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), greater10))cout << "\n\nSome elements in array a are greater than 10";elsecout << "\n\nNone elements in array a are not greater than 10";if (none_of(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), greater10))cout << "\n\nNone elements in array a are greater than 10";elsecout << "\n\nSome elements in array a are not greater than 10";cout << endl;
}bool greater10(int value)
{return value > 10;
}// value 不超过 10 时返回 true
bool less10(int value)
{return value <= 10;
}
运行结果:

7.swap、iter_swap和swap_ranges



注意,在使用swap_ranges时,交换的两个区域不能重叠。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <array>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array<int, SIZE> a = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "Array a contains:\n ";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);swap(a[0], a[5]);cout << "\nArray a after swapping a[0] and a[5] using swap:\n ";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);iter_swap(a.begin(), a.begin() + 5);cout << "\nArray a after swapping a[0] and a[5] using iter_swap:\n ";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);swap_ranges(a.begin(), a.begin() + 5, a.begin() + 5);cout << "\nArray a after swapping the first five elements with the last five elements:\n ";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);cout << endl;
}
运行结果:

8.copy_backward、merge、unique和reverse




示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <array>
using namespace std;int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 5;array<int, SIZE> a1 { 1,3,5,7,9 };array<int, SIZE> a2 { 2,4,5,7,9 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "array a1 contains: ";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);cout << "\narray a2 contains: ";copy(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), output);array<int, SIZE> results {};copy_backward(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), results.end());cout << "\n\nAfter copy_backward, results contains: ";copy(results.cbegin(), results.cend(), output);array<int, SIZE + SIZE> results2;merge(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), results2.begin());cout << "\n\nAfter merge of a1 and a2, results2 contains: ";copy(results2.cbegin(), results2.cend(), output);auto endLocation = unique(results2.begin(), results2.end());cout << "\n\nAfter unique results2 contains (endLocation): ";copy(results2.begin(), endLocation, output);cout << "\nAfter unique results2 contains: ";copy(results2.cbegin(),results2.cend(), output);reverse(a1.begin(), a1.end());cout << "\n\nArray a1 after reverse: ";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);cout << endl;
}
运行结果:

对于上面程序merge算法的使用,我们提前创建了一个array对象用于接收合并后的数据。如果我们事先并不知道被合并的两个容器的总的元素个数是多少,我们应该怎么办呢?使用头文件<iterator>中定义的back_inserter、front_inserter或inserter函数。这些函数会在参数指定的容器中插入元素,它们会返回一个指向将要被插入的位置的迭代器,使用该迭代器进行插入操作。
9.inplace_merge、unique_copy和reverse_copy


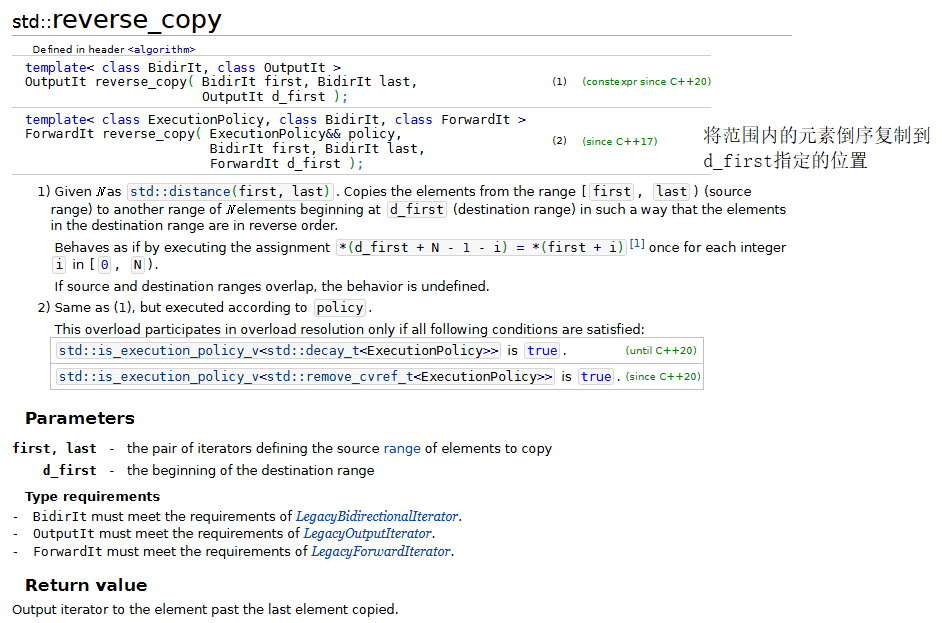
注意在使用inplace_merge之后,序列会自动排序
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array <int, SIZE> a1 = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "array a1 contains: ";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);inplace_merge(a1.begin(), a1.begin() + 5, a1.end());cout << "\nAfter inplace_merge, a1 contains: ";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);vector<int> results1;// 使用 back_inserter 往vector对象中插入新元素unique_copy(a1.cbegin(),a1.cend(), back_inserter(results1));cout << "\nAfter unique_copy, results1 contains: ";copy(results1.cbegin(), results1.cend(), output);vector<int> results2;// 使用 back_inserter 往vector对象中插入新元素reverse_copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), back_inserter(results2));cout << "\nAfter reverse_copy, results2 contains: ";copy(results2.cbegin(), results2.cend(), output);cout << endl;
}
运行结果:

在上面的程序中我们就使用之前提到的back_inserter函数来在vector对象的末端添加新元素。而back_inserter实际上使用vector的push_back函数来在这个vector对象的末端插入新元素,并不是修改已有元素的值。
10.集合操作
标准库中还有一些用来操作有序值集合的算法,包括:includes、set_difference、set_intersection、set_symmetric_difference和set_union。





示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
using namespace std;int main()
{const size_t SIZE1 = 10;const size_t SIZE2 = 5;const size_t SIZE3 = 20;array<int, SIZE1> a1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};array<int, SIZE2> a2 = {4,5,6,7,8};array<int, SIZE2> a3 = {4,5,6,11,15};ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "a1 contains: ";copy(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), output);cout << "\na2 contains: ";copy(a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), output);cout << "\na3 contains: ";copy(a3.cbegin(), a3.cend(), output);// 判断a2是否是a1的子序列if (includes(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), a2.cbegin(), a2.cbegin())){cout << "\n\na1 includes a2";}else{cout << "\n\na1 does not includes a2";}// 判断a3是否是a1的子序列if (includes(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), a3.cbegin(), a3.cbegin())){cout << "\na1 includes a3";}else{cout << "\na1 does not includes a3";}// 测试set_differencearray<int, SIZE1> difference{};auto result1 = set_difference(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(), a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), difference.begin());cout << "\n\nset_difference of a1 and a2 is: ";copy(difference.begin(), result1, output);// 测试set_intersectionarray<int, SIZE1> intersection{};auto result2 = set_intersection(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(),a2.cbegin(), a2.cend(), intersection.begin());cout << "\n\nset_intersection of a1 and a2 is: ";copy(intersection.begin(), result2, output);// 测试set_symmetric_differencearray<int, SIZE1 + SIZE2> symmetric_difference{};auto result3 = set_symmetric_difference(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(),a3.cbegin(), a3.cend(), symmetric_difference.begin());cout << "\n\nset_symmetric_difference of a1 and a3 is: ";copy(symmetric_difference.begin(), result3, output);// 测试set_unionarray<int, SIZE3> unionSet{};auto result4 = set_union(a1.cbegin(), a1.cend(),a3.cbegin(), a3.cend(), unionSet.begin());cout << "\n\nset_union of a1 and a3 is: ";copy(unionSet.begin(), result4, output);cout << endl;
}
运行结果:

11.lower_bound、upper_bound和equal_range



示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <array>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array<int, SIZE> a = { 2,2,4,4,4,6,6,6,6,8 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "array a contains:\n";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);// 找到a中第一个不小于6的元素auto lower = lower_bound(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 6);cout << "\n\nLower bound of 6 is element "<< (lower - a.cbegin()) << " of array a";// 找到a中第一个大于6的元素auto upper = upper_bound(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 6);cout << "\n\nUpper bound of 6 is element "<< (upper - a.cbegin()) << " of array a";auto eq = equal_range(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 6);cout << "\n\nUsing equal_range:\n Lower bound of 6 is element "<< (eq.first - a.cbegin()) << " of array a\n "<< "Upper bound of 6 is element " << (eq.second - a.begin()) << " of array a";// lower_bound的使用场景cout << "\n\nUse lower_bound to locate the first point\n"<< "at which 5 can be inserted in order";lower = lower_bound(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 5);cout << "\n Lower bound of 5 is element "<< (lower - a.cbegin()) << " of array a";// upper_bound的使用场景cout << "\n\nUse upper_bound to locate the last point\n"<< "at which 7 can be inserted in order";upper = upper_bound(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 7);cout << "\n Upper bound of 7 is element "<< (upper - a.cbegin()) << " of array a";// equal_range的使用场景cout << "\n\nUse equal_range to locate the first and\n"<< "last point at which 5 can be inserted in order";eq = equal_range(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), 5);cout << "\n Lower bound of 5 is element "<< (eq.first - a.cbegin()) << " of array a"<< "\n Upper bound of 5 is element " << (eq.second - a.cbegin()) << " of array a"<< endl;
}
运行结果:

12.堆排序
堆排序是一种排序算法,排序时一个数组中的元素被组织成一个特殊的数据结构——堆。关于堆排序的原理,请在“数据结构”课程中学习。
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array<int, SIZE> init { 3, 100, 52, 77, 22, 31, 1, 98, 13, 40 };array<int, SIZE> a(init);ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "Array a before make_heap:\n";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);// 以array对象a中的元素建立一个堆make_heap(a.begin(), a.end());cout << "\nArray a after make_heap:\n";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);// 对堆中的元素进行堆排序sort_heap(a.begin(), a.end());cout << "\nArray a after sort_heap:\n";copy(a.cbegin(), a.cend(), output);cout << "\nArray init contains:\n";copy(init.cbegin(), init.cend(), output); cout << endl;vector<int> v;// 将init中的元素放入v中for (size_t i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i){v.push_back(init[i]);push_heap(v.begin(), v.end());cout << "\nv after push_heap(init[" << i << "]): ";copy(v.cbegin(), v.cend(), output);}cout << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i){cout << "\nv after " << v[0] << " popped from heap\n";pop_heap(v.begin(), v.end() - i);copy(v.cbegin(), v.cend(), output);}cout << endl;
}
运行结果:






13.min、max、minmax和minmax_element




示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{cout << "The minimum of 12 and 7 is: " << min(12, 7);cout << "\nThe maximum of 12 and 7 is: " << max(12, 7);cout << "\nThe minimum of 'G' and 'Z' is: " << min('G', 'Z');cout << "\nThe maximum of 'G' and 'Z' is: " << max('G', 'Z');auto result1 = minmax(12, 7);cout << "\n\nThe minimum of 12 and 7 is: " << result1.first<< "\nThe maximum of 12 and 7 is: " << result1.second;array <int, 10> items { 3, 100, 52, 77, 22, 31, 1, 98, 13, 40 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "\n\nArray itmes contains: ";copy(items.cbegin(), items.cend(), output);auto result2 = minmax_element(items.cbegin(), items.cend());cout << "\nThe minimum element in items is: " << *result2.first<< "\nThe maximum element in items is: " << *result2.second<< endl;
}
运行结果:

三、函数对象
很多算法允许以一个函数指针来作为参数以完成它的任务。例如,上面的minmax_element算法就有一个重载的版本,需要用户提供一个函数来完成元素的比较任务。
任何可以接收函数指针的算法都可以接收一个类的对象,只要这个类提供我们之前学习过的重载函数运算符operator(),且该重载的运算符符合算法的需要。例如在上面的minmax_element算法中,重载的函数运算符必须接收两个参数,并返回一个bool值。这样的类的对象就被称为函数对象,它们在语法和语义上可以像函数或函数指针一样使用。
函数对象较函数指针的优越之处
与函数指针相比,函数对象有若干优点。
编译器可以内联函数对象重载的operator()来提高性能(使用函数指针,每次调用都需要进行函数调用,会产生额外开销)。
而且,由于是类的对象,函数对象可以具有该重载函数运算符用来执行任务的数据成员(函数指针可以使用全局变量或静态变量来做到,但是会存在安全隐患)。
标准模板库中预先定义的函数对象
我们在之前的算法中也曾使用过函数对象less<T>来指定容器元素排序的次序。
| 标准库函数 | 对象类型 |
|---|---|
| divides<T> | 算术 |
| equal_to<T> | 关系 |
| greater<T> | 关系 |
| greater_equal<T> | 关系 |
| less<T> | 关系 |
| less_equal<T> | 关系 |
| logical_and<T> | 逻辑 |
| logical_not<T> | 逻辑 |
| logical_or<T> | 逻辑 |
| minus<t> | 算术 |
| modulus<T> | 算术 |
| negate<T> | 算术 |
| not_equal_to<T> | 关系 |
| plus<T> | 算术 |
| multiplies<T> | 算术 |
使用标准库的accumulate算法
该算法我们在前面数学算法中也已经介绍过了,下面我们将创建一个程序,再次使用该算法,一次使用函数指针,一次使用函数对象。
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <functional>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;int sumSquares(int total, int value)
{return total + value * value;
}template <class T>
class SumSquaresClass
{
public:T operator()(const T& total, const T& value){return total + value * value;}
};int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 10;array <int, SIZE> integers { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");cout << "array integers contains:\n ";copy(integers.cbegin(), integers.cend(), output);// 使用函数指针作为参数,计算序列中元素的平方和int result = accumulate(integers.cbegin(), integers.cend(), 0, sumSquares);cout << "\n\nSum of squares of elements in integers using "<< "binary\nfunction sumSquares: " << result;// 使用函数对象result = accumulate(integers.cbegin(), integers.cend(), 0, SumSquaresClass<int>());cout << "\n\nSum of squares of elements in integers using "<< "binary\nfunction sumSquares: " << result << endl;
}
运行结果:

上面代码中的SumSquaresClass<int>()其实就是,使用特化的类SumSquaresClass<int>调用该类的默认构造函数来实例化了一个函数对象,并将该函数对象作为accumulate算法的参数,之后该算法会使用该对象来调用它的成员函数operator(),从而实现函数调用的功能。
四、lambda表达式
在上面的内容中,我们能够发现有许多的算法可以接收函数指针或函数对象这样的参数。在将函数指针或函数对象传递给算法作参数之前,相应的函数或类必须已经声明。
C++11的lambda表达式(或lambda函数)这一新特性,使程序员可以在将函数对象传递给一个函数的地方定义匿名的函数对象。lambda表达式被局部地定义在函数内,可以(以按值或按引用的方式)获得它所在函数的局部变量,然后在lambda表达式的体中操作这些变量。
下面展示了一个简单的lambda表达式的使用示例,它把一个int类型array对象的每个元素值加倍:
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{const size_t SIZE = 4;array<int, SIZE> values { 1,2,3,4 };// 为指定序列中的每个元素进行同样的处理for_each(values.cbegin(), values.cend(),// 一个 lambda 表达式[](int i){ cout << i * 2 << endl; });int sum = 0;for_each(values.cbegin(), values.cend(),// 一个 lambda 表达式[&sum](int i) { sum += i; });cout << "Sum is " << sum << endl;
}
运行结果:

lambda表达式lambda导引器([]),然后是形参表和函数体。如果函数体是形如return 表达式;的单条语句,那么返回值类型可以自动地被推断出来;否则,默认的返回值类型为void,或者可以显式地使用尾随返回值类型指明。例如,[](int i) -> int { return i * i; }。编译器会将这个lambd表达式转换成一个函数对象。
对于上面的示例代码中第一个的lambda表达式接收一个int类型的参数i,for_each算法将array对象的每个元素传递给这个lambda表达式,由该lambda表达式输出array中元素值的2倍。
第二个lambda表达式接收一个int类型的参数,且它的lambda导引器[&sum]表明该lambda表达式以按引用的方式获得了当前程序中的局部变量sum,因此这个lambda表达式可以修改该局部变量的量。如果没有&符号,则是按值的方式获得局部变量,也就无法修改当前程序中的sum变量的值。
lambda表达式还可以赋值给变量,然后这个变量可以用来调用lambda表达式或者将它传递给其他函数。例如,auto myLambda = [](int i) { cout << i * 2 << endl; };
之后就可以像一个函数名一样使用此变量名来调用该lambda表达式,如下所示:
myLambda(10); // 输出20
五、标准库算法总结
C++标准中将算法分为了几类,包括改变序列的算法、不改变序列的算法、排序及相关算法、广义的数值运算等。
该部分内容较多,请自行前往cppreference查阅。
对于标准模板库中提供的算法,它们提供了实现一种功能的通用方法,所以算法只是将功能抽象出来,使得不同的容器只要能够满足最低的迭代器要求,那么就可以使用相同的算法来实现相同的功能,即使它们容器内部中要实现该功能的函数其实不一样。
对于STL中的容器、算法和迭代器这三个主要组件,容器规定数据的存储结构以及对这些数据的一些操作方法,算法定制了通用功能的实现,而算法通过迭代器来访问容器中的数据,使得定制的功能能够在对应容器中被执行。
相关文章:

C++学习-入门到精通【14】标准库算法
C学习-入门到精通【14】标准库算法 目录 C学习-入门到精通【14】标准库算法一、对迭代器的最低要求迭代器无效 二、算法1.fill、fill_n、generate和generate_n2.equal、mismatch和lexicographical_compare3.remove、remove_if、remove_copy和remove_copy_if4.replace、replace_…...

银行用户评分规则 深度学习
思考模型的实际应用场景。用户的核心疑问在于:在银行真实的评级系统中,基于规则的评级和基于模型的预测评级哪个更有价值?ta担心自己写的代码只是学术练习而没有实际意义。 从用户提到的银行评级规则来看(AAAA到E的划分ÿ…...

HarmonyOS运动语音开发:如何让运动开始时的语音播报更温暖
##鸿蒙核心技术##运动开发##Core Speech Kit(基础语音服务)# 前言 在运动类应用中,语音播报功能不仅可以提升用户体验,还能让运动过程更加生动有趣。想象一下,当你准备开始运动时,一个温暖的声音提醒你“…...

# 从底层架构到应用实践:为何部分大模型在越狱攻击下失守?
从底层架构到应用实践:为何部分大模型在越狱攻击下失守? 引言 近期,我们对多个主流大语言模型(LLM)进行了安全性测试,使用了极具诱导性的越狱提示词,试图绕过其内容安全机制。测试结果显示&am…...

vscode使用系列之快速生成html模板
一.欢迎来到我的酒馆 vscode,yyds! 目录 一.欢迎来到我的酒馆二.vscode下载安装1.关于vscode你需要知道2.开始下载安装 三.vscode快速创建html模板 二.vscode下载安装 1.关于vscode你需要知道 Q:为什么使用vscode? A:使用vscode写…...

Thinkphp6软删除
方法一 从控制器层直接操作 删除 此操作不会直接删除数据 而是在delete_time字段更新删除时间 ->useSoftDelete(delete_time,get_datetime())->delete() 查询 这里的数据库字段需要设置为默认NULL 查询的时候仅查询未更新删除时间的数据 ->whereNull("dele…...

网页前端开发(基础进阶4--axios)
Ajax Ajax(异步的JavaScript和XML) 。 XML是可扩展标记语言,本质上是一种数据格式,可以用来存储复杂的数据结构。 可以通过Ajax给服务器发送请求,并获取服务器响应的数据。 Ajax采用异步交互:可以在不重新加载整个页面的情况下&am…...

软件安全:漏洞利用与渗透测试剖析、流程、方法、案例
在数字时代,软件已深度融入生活与工作的方方面面,从手机应用到企业核心系统,软件安全至关重要。而漏洞利用与渗透测试,作为软件安全领域中相互关联的两个关键环节,一个是黑客攻击的手段,一个是安全防护的方…...

Haproxy的基础配置
1、参考文档 官方文档:HAProxy version 2.2.22 - Configuration Manual 运维派配置手册:Haproxy-基础配置详解 - 运维派 Haproxy 的配置文件haproxy.cfg由两大部分组成,分别是global和proxies部分。 2、haproxy global 配置 global&…...

考研系列—操作系统:冲刺笔记(1-3章)
目录 第一章 计算机系统概述 1.基本概念 2.内核态和用户态 3.中断(外中断)、异常(内中断-与当前执行的) 4.系统调用 5.操作系统引导程序 2021年真题: 6.操作系统结构 大纲新增 (1)分层结构 (2)模块化 (3)外核 7.虚拟机 第二章 进程管理 1.画作业运行的顺序和甘…...
持续集成环境)
使用 Docker Compose 部署 Jenkins(LTS 版)持续集成环境
一、前言 Jenkins 是目前最流行的开源持续集成工具之一。本教程将手把手带你使用 Docker Compose 快速部署 Jenkins LTS(长期支持版本),同时保留数据持久化、Docker 命令转发等功能,适合用于生产或本地开发测试环境。 二、环境准…...

Java调用大模型API实战指南
文章目录 前言调用大模型的流程概述和基本原理获取 DeepSeek 的 API keyJava 实现调用大模型 API 的Demo进阶扩展建议 前言 随着大语言模型(如 OpenAI、DeepSeek、通义千问等)的发展,我们可以很方便地用 API 接口调用这些强大的智能助手。在…...
)
C#中的路由事件(Routed Events)
路由事件的基本概念 路由事件是WPF中特有的事件系统,它允许事件在可视化树中"路由"传递,具有以下特点: 事件路由方向: 冒泡(Tunneling):从事件源向根元素传递 隧道(Bubbling):从根元素向事件源…...

[蓝桥杯]通电
通电 题目描述 2015 年,全中国实现了户户通电。作为一名电力建设者,小明正在帮助一带一路上的国家通电。 这一次,小明要帮助 nn 个村庄通电,其中 1 号村庄正好可以建立一个发电站,所发的电足够所有村庄使用。 现在…...

单片机0-10V电压输出电路分享
一、原理图 二、芯片介绍 GP8101是一个PWM信号转模拟信号转换器,相当于一个PWM信号输入,模拟信号输出的DAC。此 芯片可以将占空比为0%到100%的PWM信号线性转换成0-5V或者0-10V的模拟电压,并且输出电压 精度小于1%。GP8101M可以处理高频调制的…...

从零开始,搭建一个基于 Django 的 Web 项目
🎯 主要步骤概述 1️⃣ 安装 Python 和 pip 2️⃣ 创建虚拟环境 3️⃣ 安装 Django 4️⃣ 创建 Django 项目 5️⃣ 运行开发服务器 6️⃣ 创建一个简单的应用(app) 7️⃣ 配置数据库并迁移 8️⃣ 创建超级用户(admin)…...

大模型模型部署和暴露接口
创建环境 激活案件 安装相关依赖 conda create -n fastApi python3.10 conda activate fastApi conda install -c conda-forge fastapi uvicorn transformers pytorch pip install safetensors sentencepiece protobuf 新建文件夹 mkdir App cd App touch main.py 复制代码…...

2025服装收银系统推荐:智能管理助力服装商家高效经营
在服装批发零售行业,一套高效的收银系统不仅能简化日常经营流程,还能通过数据分析帮助商家优化库存、提升销售。随着AI技术的普及,现代收银系统已不再局限于简单的记账功能,而是能提供智能选品、库存预警、精准营销等进阶服务。 …...

Microsoft Copilot Studio - 尝试一下Agent
1.简单介绍 Microsoft Copilot Studio以前的名字是Power Virtual Agent(简称PVA)。Power Virutal Agent是2019年出现的,是低代码平台Power Platform的一部分。当时Generative AI还没有出现,但是基于已有的Conversation AI技术,即Microsoft L…...

【Python 算法零基础 4.排序 ⑨ 堆排序】
目录 一、问题描述 二、算法对比 1.朴素算法 ① 数组模拟容器 ② 有序数组模拟容器 2.二叉堆 ① 二叉堆特点 ② 数组表示二叉树 ③ 堆 ④ 大顶堆 ⑤ 小顶堆 ⑥ 元素插入 ⑦ 获取堆顶 ⑧ 堆顶元素删除 三、代码分析 1.工具函数 2.调整大顶堆函数 Ⅰ、计算子节点索引 Ⅱ、找出最…...

Deepseek/cherry studio中的Latex公式复制到word中
需要将Deepseek/cherry studio中公式复制到word中,但是deepseek输出Latex公式,比如以下Latex代码段,需要通过Mathtype翻译才能在word中编辑。 $$\begin{aligned}H_1(k1) & H_1(k) \frac{1}{A_1} \left( Q_1 u_1(k) Q_{i1} - Q_2 u_2(k…...

测试设计技术全解析:黑盒与白盒测试的七种武器与覆盖率指标
在软件开发的生命周期中,测试设计技术扮演着至关重要的角色,它直接影响着产品质量和用户体验。测试设计技术主要分为黑盒测试技术和白盒测试技术两大类,它们各有优势和适用场景。黑盒测试技术侧重于从用户视角验证软件功能是否符合需求&#…...
)
AWS中国区IAM相关凭证自行管理策略(只读CodeCommit版)
目标 需要从CodeCommit读取代码。除了设置AWS托管策略:AWSCodeCommitReadOnly。还需要自定义策略,让用户能够自行管理IAM自己的相关凭证。 IAM自定义策略 {"Version": "2012-10-17","Statement": [{"Sid": &…...

极限复习c++
一、核心语法必背 1. 指针 vs 引用(简答题高频) 区别指针引用定义存储地址的变量,可改指向变量的别名,绑定后不可改初始化可空(nullptr)、延迟初始化必须初始化,不能引用空值访问需解引用&…...
32单片机——窗口看门狗
1、WWDG的简介 WWDG:Window watchdog,即窗口看门狗 窗口看门狗本质上是能产生系统复位信号和提前唤醒中断的递减计数器 WWDG产生复位信号的条件: (1)当递减计数器值从0x40减到0x3F时复位(即T6位跳变到0&a…...

javascript中Cookie、BOM、DOM的使用
Cookie 在客户端存储小型文本数据(通常 ≤ 4KB),常用于会话管理、个性化设置等场景。 名称描述作用生命周期存储位置安全性会话 Cookie临时存储,浏览器关闭后自动删除会话管理、个性化设置浏览器关闭内存高持久 Cookie设置过期时…...

IDEA 中 Undo Commit,Revert Commit,Drop Commit区别
一、Undo Commit 适用情况:代码修改完了,已经Commit了,但是还未push,然后发现还有地方需要修改,但是又不想增加一个新的Commit记录。这时可以进行Undo Commit,修改后再重新Commit。如果已经进行了Push&…...

DAY43打卡
浙大疏锦行 kaggle找到一个图像数据集,用cnn网络进行训练并且用grad-cam做可视化 进阶:并拆分成多个文件 fruit_cnn_project/ ├─ data/ # 存放数据集(需手动创建,后续放入图片) │ ├─ train/ …...

Leetcode 1892. 页面推荐Ⅱ
1.题目基本信息 1.1.题目描述 表: Friendship ---------------------- | Column Name | Type | ---------------------- | user1_id | int | | user2_id | int | ---------------------- (user1_id,user2_id) 是 Friendship 表的主键(具有唯一值的列的组合…...

进程——环境变量及程序地址空间
目录 环境变量 概念 补充:命令行参数 引入 其它环境变量 理解 程序地址空间 引入 理解 虚拟地址存在意义 环境变量 概念 环境变量一般是指在操作系统中用来指定操作系统运行环境的一些参数。打个比方,就像你布置房间,这些参数就类…...
