[Spring]-AOP
AOP场景
AOP: Aspect Oriented Programming (面向切面编程)
OOP: Object Oriented Programming (面向对象编程)
场景设计
- 设计: 编写一个计算器接口和实现类,提供加减乘除四则运算

- 需求: 在加减乘除运算的时候需要记录操作日志(运算前参数、运算后结果)
- 实现方案:
- 硬编码
- 静态代理
- 动态代理
- AOP
硬编码
使用硬编码的方式记录日志
- 创建工程环境: 新建模块, 加一个lombok依赖



- 新建计算器接口和实现类, 并在实现类中, 通过硬编码记录日志
package com.guigu.aop.calculator;// 定义四则运算
public interface MathCalculator {// 加法int add(int i, int b);// 减法int sub(int i, int b);// 乘法int mul(int i , int b);// 除法int div(int i, int b);
}
package com.guigu.aop.calculator.impl;/*** 计算器实现类* 1. 硬编码: 不推荐; 耦合:(通用逻辑 + 专用逻辑)希望不要耦合; 耦合太多就是维护地狱*/
@Component
public class MathCalculatorImpl implements MathCalculator {@Overridepublic int add(int i, int b) {System.out.println("[日志] add开始, 参数:" + i + "," + b);int res = i + b;System.out.println("[日志] add结束, 结果:" + res);return res;}@Overridepublic int sub(int i, int b) {return i -b;}@Overridepublic int mul(int i, int b) {return i * b;}@Overridepublic int div(int i, int b) {return i / b;}
}
- 新建单元测试, 测试一下
package com.guigu.aop;@SpringBootTest
public class MathTest {@AutowiredMathCalculatorImpl mathCalculator;@Testvoid test01() {int add = mathCalculator.add(1, 9);}
}

静态代理
编码时介入: 包装真实对象,对外提供静态代理对象
实现步骤
- 包装被代理对象
- 实现被代理对象的接口
- 运行时调用被代理对象的真实方法
- 外部使用代理对象调用
优点
- 实现简单
缺点
- 需要为不同类型编写不同代理类,导致扩展维护性差
使用静态代理技术, 记录代码日志
package com.guigu.aop.proxy.statics;import com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** 静态代理: 定义代理对象, 帮助目标对象完成一些工作*/
@Component
@Data
public class CalculatorStaticProxy implements MathCalculator {private MathCalculator target; // 目标对象public CalculatorStaticProxy(MathCalculator mc) {this.target = mc;}@Overridepublic int add(int i, int b) {System.out.println("[日志] add开始, 参数:" + i + "," + b);int res = target.add(i, b);System.out.println("[日志] add结束, 结果:" + res);return res;}@Overridepublic int sub(int i, int b) {return target.sub(i, b);}@Overridepublic int mul(int i, int b) {return target.mul(i, b);}@Overridepublic int div(int i, int b) {return target.div(i, b);}
}
package com.guigu.aop;@SpringBootTest
public class MathTest {@AutowiredCalculatorStaticProxy calculatorStaticProxy;@Testvoid test02() {int add = calculatorStaticProxy.add(2, 3);}
}

动态代理
运行时介入: 创建真实对象运行时代理对象
- 实现步骤
- ·Java 反射提供 Proxy.newProxyInstance 的方式创建代理对象
- 优点:
- 节约不同代理类的开发
- 缺点:
- 开发难度大
- 必须有接口,才能创建动态代理
使用动态代理技术, 记录代码日志
- 封装一个日志工具类, 提供记录日志的静态方法
package com.guigu.aop.log;public class LogUtils {public static void logStart(String name, Object... args) {System.out.println("[日志]: [" + name + "]开始, 参数:" + Arrays.toString(args));}public static void logEnd(String name) {System.out.println("[日志]: [" + name + "]结束");}public static void logException(String name, Throwable e) {System.out.println("[日志]: [" +name+ "]异常: 异常信息:" + e.getCause());}public static void logReturn(String name, Object result) {System.out.println("[日志]: [" + name + "]结束, 返回结果:" + result);}
}
- 创建动态代理类 封装一个静态方法, 可以传入任何对象, 返回代理对象
package com.guigu.aop.proxy.dynamic;/*** 动态代理* 1.是java原生支持的技术* 2.运行期间才决定代理关系, 类似于拦截器的思想* 3.目标对象在执行期间会被动态拦截, 可以插入指定逻辑* 4.优点: 可以代理任何对象* 5.缺点: 代码多* 6.强制要求: 目标对象必须有接口(否则报错), 代理的也只是接口规定的方法,*/
@Component
public class DynamicProxy {// 获取目标对象的代理对象public static Object getProxyInstance(Object target) {/*** Proxy是java反射包提供的类* 下面的方法可以创建对象的代理对象, 需要三个参数* Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h)* 参数1: ClassLoader loader, 类加载器 (通过类加载器拿到目标对象)* 参数2: Class<?>[] interfaces, 目标对象实现的接口 (通过接口拿到目标对象实现的方法)* 参数3: InvocationHandler h, 代理对象需要执行的方法, 这个方法中可以插入指定逻辑*//*** 拦截方法说明:* 通过拦截方法, 可以拦截到目标对象方法的调用, 从而做任何事情* (proxy, method, args)-> { }* proxy: 代理对象* method: 准备执行的目标对象的方法* args: 方法调用传递的参数*/return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(),target.getClass().getInterfaces(),(proxy, method, args)-> {String name = method.getName();// 记录开始LogUtils.logStart(name, args);Object result = null;try {result = method.invoke(target, args); // 执行目标对象的方法// 记录返回值LogUtils.logReturn(name, result);} catch (Exception e) {// 记录异常LogUtils.logException(name, e);} finally {// 记录结束LogUtils.logEnd(name);}return result;});}
}
- 使用动态代理类的方法创建代理对象
package com.guigu.aop;@SpringBootTest
public class MathTest {@AutowiredMathCalculatorImpl mathCalculator;@AutowiredDynamicProxy dynamicProxy;@Testvoid test03() {MathCalculator instance =( MathCalculator) dynamicProxy.getProxyInstance(mathCalculator);instance.add(3,5);}
}

AOP使用
了解AOP的术语

AOP基本使用步骤
- 导入AOP依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId></dependency>
- 编写切面Aspect
package com.guigu.aop.aspect;@Component
@Aspect // 告诉spring这个组件是一个切面
public class LogAspect {}
- 编写通知方法
package com.guigu.aop.aspect;@Component
@Aspect // 告诉spring这个组件是一个切面
public class LogAspect {public void logStart() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]开始...");}public void logEnd() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]结束...");}public void logReturn() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]返回结果");}public void logException() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]爬出抛出异常:");}
}
- 指定切入点表达式
package com.guigu.aop.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
@Aspect // 告诉spring这个组件是一个切面
public class LogAspect {/*** 告诉Spring, 以下通知何时何地生效?* 何时?* 通知方法:* @Before: 方法执行前运行* @AfterReturning: 方法执行正常返回结果运行* @AfterThrowing: 方法抛出异常时运行* @After: 方法执行之后运行* 何地:* 切入点表达式:* 1. execution(方法的全签名)* 作用: 根据方法匹配切入点* 全写法: [public] int [com.guigu.aop.calculator].add(int, int) [throws ArithmeticException]* 省略写法: int add(int, int)* 通配符:* *: 表示任意字符* ..: 表示多个参数, 任意类型* 最省略: * *(..)*/@Before("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void logStart() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]开始...");}@After("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void logEnd() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]结束...");}@AfterReturning("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void logReturn() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]返回结果");}@AfterThrowing("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void logException() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]爬出抛出异常:");}
}
- 测试AOP动态织入
package com.guigu.aop;import com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;@SpringBootTest
public class AopTest {@Autowired // 容器中注入的是 MathCalculator 的代理对象MathCalculator mathCalculator;@Testvoid test01() {System.out.println(mathCalculator.getClass()); // 看看代理对象mathCalculator.add(10, 20);}
}

AOP细节
切入点表达式
切入点表达式的写法


package com.guigu.aop.annotation;import java.lang.annotation.*;// 自定义接口
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyAn {
}
package com.guigu.aop.calculator.impl;import com.guigu.aop.annotation.MyAn;
import com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** 计算器实现类* 1. 硬编码: 不推荐; 耦合:(通用逻辑 + 专用逻辑)希望不要耦合; 耦合太多就是维护地狱*/
@Component
public class MathCalculatorImpl implements MathCalculator {@Overridepublic int add(int i, int b) {int res = i + b;return res;}@Overridepublic int sub(int i, int b) {return i -b;}@Overridepublic int mul(int i, int b) {return i * b;}@MyAn@Overridepublic int div(int i, int b) {return i / b;}
}
package com.guigu.aop.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
@Aspect // 告诉spring这个组件是一个切面
public class LogAspect {/*** 告诉Spring, 以下通知何时何地生效?* 何时?* @Before: 方法执行前运行* @AfterReturning: 方法执行正常返回结果运行* @AfterThrowing: 方法抛出异常时运行* @After: 方法执行之后运行* 何地:* 切入点表达式:* 1. execution(方法的全签名)* 作用: 根据方法匹配切入点* 全写法: [public] int [com.guigu.aop.calculator].add(int, int) [throws ArithmeticException]* 省略写法: int add(int, int)* 通配符:* *: 表示任意字符* ..: 表示多个参数, 任意类型* 最省略: * *(..)* 2. args(参数类型或其子类型)* 作用: 根据方法的参数匹配切入点* 3. annotation(注解类型)* 作用: 根据方法的注解匹配切入点, 一般配合自定义注解使用*/@Before("args(int, int)")public void logHaha() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]哈哈...");}@Before("@annotation(com.guigu.aop.annotation.MyAn)")public void logHehe() {System.out.println("[切面-日志]呵呵...");}
}
package com.guigu.aop;@SpringBootTest
public class AopTest {@Autowired // 容器中注入的是 MathCalculator 的代理对象MathCalculator mathCalculator;@Testvoid test02() {// 根据方法的参数匹配切入点mathCalculator.add(1, 2);// 测试方法的注解匹配切入点mathCalculator.div(1, 2);}
}

执行顺序
AOP 的底层原理
1、Spring会为每个被切面切入的组件创建代理对象(Spring CGLIB 创建的代理对象,无视接口)。
2、代理对象中保存了切面类里面所有通知方法构成的增强器链。
3、目标方法执行时,会先去执行增强器链中拿到需要提前执行的通知方法去执行
通知方法的执行顺序
- 正常链路: 前置通知->目标方法->返回通知->后置通知
- 异常链路: 前置通知->目标方法->异常通知->后置通知

连接点信息
通过 JoinPoint 包装了当前目标方法的所有信息
通过 returning 属性可以接收当前方法的返回值
通过 throwing 属性可以接收当前方法的异常信息
package com.guigu.aop.aspect;@Component
@Aspect // 告诉spring这个组件是一个切面
public class LogAspect {@Before("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();// 获取方法的参数值Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();System.out.println("【切面- 日志】【" + name + "】开始:参数列表:【" + Arrays.toString(args) + "】");}@After("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();System.out.println("[切面-日志] " + name + "结束...");}@AfterReturning(value = "execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))",returning = "result")public void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();System.out.println("【切面 -日志】【" + name + "】返回:值:" + result);}@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))",throwing = "e")public void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();System.out.println("【切面 - 日志】【" + name + "】异常:错误信息:【" + e.getMessage() + "】");}}
抽取切入点表达式
使用@Pointcut 注解抽取切入点表达式
package com.guigu.aop.aspect;@Component
@Aspect // 告诉spring这个组件是一个切面
public class LogAspect {@Pointcut("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void pointCut(){};@Before("pointCut()")public void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();// 获取方法的参数值Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();System.out.println("【切面- 日志】【" + name + "】开始:参数列表:【" + Arrays.toString(args) + "】");}@After("pointCut()")public void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();System.out.println("[切面-日志] " + name + "结束...");}@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()",returning = "result")public void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();System.out.println("【切面 -日志】【" + name + "】返回:值:" + result);}@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()",throwing = "e")public void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();System.out.println("【切面 - 日志】【" + name + "】异常:错误信息:【" + e.getMessage() + "】");}}
多切面的执行顺序
默认情况下, 切面方法的执行顺序受切面类的首字母排序影响
通过 Order 注解可以指定切面类的优先级
package com.guigu.aop.aspect;@Order(1) // 数值越小, 优先级越高, 执行越早
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {@Pointcut("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void pointCut(){};@Before("pointCut()")public void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();// 获取方法的参数值Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();System.out.println("【切面- 日志】【" + name + "】开始:参数列表:【" + Arrays.toString(args) + "】");}@After("pointCut()")public void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();System.out.println("[切面-日志] " + name + "结束...");}@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()",returning = "result")public void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();System.out.println("【切面 -日志】【" + name + "】返回:值:" + result);}@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()",throwing = "e")public void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e) {// 拿到方法全签名MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();// 获取方法名String name = signature.getName();System.out.println("【切面 - 日志】【" + name + "】异常:错误信息:【" + e.getMessage() + "】");}
}
package com.guigu.aop.aspect;@Component
@Aspect
public class AuthAspect {@Pointcut("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void pointCut(){};@Before("pointCut()")public void authStart() {System.out.println("[切面-权限] 开始");}@After("pointCut()")public void authEnd() {System.out.println("[切面-权限] 结束");}@AfterReturning("pointCut()")public void authReturn() {System.out.println("【切面 -权限】 返回");}@AfterThrowing("pointCut()")public void authException() {System.out.println("【切面 - 权限】 异常");}}
package com.guigu.aop;@SpringBootTest
public class AopTest {@Testvoid test04() {mathCalculator.add(1, 2);}
}



环绕通知
环绕通知可以控制目标方法是否执行, 修改目标方法的参数和执行结果
package com.guigu.aop.aspect;@Aspect
@Component
public class AroundAspect {/*** 环绕通知的固定写法如下* Object: 返回值* ProceedingJoinPoint: 可以继续推进的切入点*/@Pointcut("execution(int com.guigu.aop.calculator.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void pointCut(){};@Around("pointCut()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {// 获取目标方法的参数Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();System.out.println("[切面-环绕前置]: 参数" + Arrays.toString(args));Object proceed = null;try {// 继续执行目标方法proceed = pjp.proceed(args);System.out.println("[切面-环绕返回]: 返回值" + proceed);} catch (Throwable e) {System.out.println("[切面-环绕异常]: 异常信息" + e.getMessage());throw e; // 抛出异常, 让别人继续感知, 否则异常会被吃掉, 影响后面的程序} finally {System.out.println("[切面-环绕后置]");}// 目标方法执行完毕,返回结果return proceed;}
}
package com.guigu.aop;@SpringBootTest
public class AopTest {@Autowired // 容器中注入的是 MathCalculator 的代理对象MathCalculator mathCalculator;@Testvoid test04() {mathCalculator.add(1, 2);}
}

相关文章:

[Spring]-AOP
AOP场景 AOP: Aspect Oriented Programming (面向切面编程) OOP: Object Oriented Programming (面向对象编程) 场景设计 设计: 编写一个计算器接口和实现类,提供加减乘除四则运算 需求: 在加减乘除运算的时候需要记录操作日志(运算前参数、运算后结果)实现方案:…...

agent 开发
什么是 agent? Agent智能体(又称AI Agent)是一种具备自主感知、决策与行动能力的智能系统,其核心在于模仿人类的认知过程来处理复杂任务。以下是其关键特性和发展现状的综合分析: 一、核心定义与特征 ### 自主决策…...

多系统一键打包docker compose下所有镜像并且使用
本方法适合在已经pull好docker镜像正常使用的机器 将环境迁移到无网络 或者网络不好的机器使用 linux 用法 cd 到 docker-compose.yml 所在目录 ./save_compose_images.sh #!/bin/bash # 拉取镜像并保存为 .tar 文件 docker save $(docker-compose images | awk {print…...

Golang——5、函数详解、time包及日期函数
函数详解、time包及日期函数 1、函数1.1、函数定义1.2、函数参数1.3、函数返回值1.4、函数类型与变量1.5、函数作参数和返回值1.6、匿名函数、函数递归和闭包1.7、defer语句1.8、panic和recover 2、time包以及日期函数2.1、time.Now()获取当前时间2.2、Format方法格式化输出日期…...

【HarmonyOS 5】出行导航开发实践介绍以及详细案例
以下是 HarmonyOS 5 出行导航的核心能力详解(无代码版),聚焦智能交互、多端协同与场景化创新: 一、交互革新:从被动响应到主动服务 意图驱动导航 自然语义理解:用户通过语音指令(如…...
深度学习环境配置指南:基于Anaconda与PyCharm的全流程操作
一、环境搭建前的准备 1. 查看基础环境位置 conda env list 操作说明:通过该命令确认Anaconda默认环境(base)所在磁盘路径(如D盘),后续操作需跳转至该磁盘根目录。 二、创建与激活独立虚拟环境 1. 创…...
--吴恩达)
03 Deep learning神经网络的编程基础 代价函数(Cost function)--吴恩达
深度学习中的损失函数(Cost Function)用于量化模型预测与真实数据的差距,是优化神经网络的核心指标。以下是常见类型及数学表达: 核心原理 逻辑回归通过sigmoid函数将线性预测结果转换为概率: y ^ ( i ) \hat{y}^{(i)}...

打卡day46
知识点回顾: 不同CNN层的特征图:不同通道的特征图什么是注意力:注意力家族,类似于动物园,都是不同的模块,好不好试了才知道。通道注意力:模型的定义和插入的位置通道注意力后的特征图和热力图 内…...

在SpringBoot中使用AWS SDK实现邮箱验证码服务
1.依赖导入(maven) <dependency><groupId>software.amazon.awssdk</groupId><artifactId>ses</artifactId><version>2.31.46</version></dependency> 2.申请两个key 发件人邮箱需要验证: …...

AndroidR车机TextToSpeech音频焦点异常问题分析
一、引言 文章《Android车机之TextToSpeech》介绍了TextToSpeech的使用,当前较多座舱系统语音服务都接入了原生TextToSpeech接口调用。 我司自研语音TTS服务,也接入了此TTS接口调用,对外提供TextToSpeech能力,播报时由客户端Client自行管理音频焦点,播报前申请音频焦点,…...

ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript:使用图层过滤器只显示FeatureLayer的部分要素
文章目录 引言1 需求场景分析2精确过滤实现方案2.1 基础过滤语法2.2 动态过滤实现 3 模糊查询进阶技巧3.1 LIKE操作符使用3.2 特殊字段处理 4. 性能优化与注意事项4.1 服务端vs客户端过滤4.2 最佳实践建议 5 常见问题解答 引言 在地图应用开发中,图层过滤是常见的需…...

深入理解二叉搜索树:原理到实践
1.二叉搜索树的概念 ⼆叉搜索树⼜称⼆叉排序树,它或者是⼀棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的⼆叉树 若它的左树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于或等于根节点的值。若它的右树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于或等于根节点的…...

测试W5500的第11步_使用ARP解析IP地址对应的MAC地址
本文介绍了基于W5500芯片的ARP协议实现方法,详细阐述了ARP请求与回复的工作机制。ARP协议通过广播请求和单播回复实现IP地址与MAC地址的映射,确保局域网设备间的可靠通信。文章提供了完整的STM32F10x开发环境下的代码实现,包括网络初始化、SP…...

终极数据结构详解:从理论到实践
终极数据结构详解:从理论到实践 我将从 底层原理、时间复杂度、空间优化、实际应用 和 代码实现 五个维度,彻底解析数据结构。内容涵盖: 线性结构(数组、链表、栈、队列)非线性结构(树、图)高…...

STM32实战: CAN总线数据记录仪设计方案
以下是基于STM32的CAN总线数据记录仪/转发器的设计与实现方案,结合了核心功能和进阶需求: 系统架构 graph TBA[CAN总线] -->|CAN_H/CAN_L| B(STM32 bxCAN)B --> C[数据处理核心]C --> D[SD卡存储<br>FATFS文件系统]C --> E[串口输出…...

【k8s】k8s集群搭建
k8s集群搭建 一、环境准备1.1 集群类型1.2 安装方式1.3 主机规划1.4 环境配置1.4.1 说明1.4.2 初始化1.4.3 关闭防火墙和禁止防火墙开机启动1.4.4 设置主机名1.4.5 主机名解析1.4.6 时间同步1.4.7 关闭selinux1.4.8 关闭swap分区1.4.9 将桥接的IPv4流量传递到iptables的链1.4.1…...

60天python训练计划----day45
DAY 45 Tensorboard使用介绍 知识点回顾: tensorboard的发展历史和原理tensorboard的常见操作tensorboard在cifar上的实战:MLP和CNN模型 之前的内容中,我们在神经网络训练中,为了帮助自己理解,借用了很多的组件&#x…...
)
Python训练营打卡Day46(2025.6.6)
知识点回顾: 不同CNN层的特征图:不同通道的特征图什么是注意力:注意力家族,类似于动物园,都是不同的模块,好不好试了才知道。通道注意力:模型的定义和插入的位置通道注意力后的特征图和热力图 i…...

C# Wkhtmltopdf HTML转PDF碰到的问题
最近碰到一个Html转PDF的需求,看了一下基本上都是需要依赖Wkhtmltopdf,需要在Windows或者linux安装这个可以后使用。找了一下选择了HtmlToPDFCore,这个库是对Wkhtmltopdf.NetCore简单二次封装,这个库的好处就是通过NuGet安装HtmlT…...

Vue3 (数组push数据报错) 解决Cannot read property ‘push‘ of null报错问题
解决Cannot read property ‘push‘ of null报错问题 错误写法 定义变量 <script setup>const workList ref([{name:,value:}])</script>正确定义变量 <script setup>const workList ref([]) </script>解决咯~...

Lifecycle 核心原理面试回答
1. 核心目标与设计思想 解耦生命周期管理: 将 Activity/Fragment 的生命周期回调逻辑从视图控制器中剥离,让业务组件(如 Presenter, Repository 封装)能独立感知生命周期。 状态驱动: 将离散的生命周期事件 (ON_CREAT…...

PHP:Web 开发的强大基石与未来展望
在当今数字化时代,Web 开发技术日新月异,各种编程语言和框架层出不穷。然而,PHP 作为一种历史悠久且广泛应用的服务器端脚本语言,依然在 Web 开发领域占据着重要地位。 PHP 的历史与现状 PHP(Hypertext Preprocessor…...

html文字红色粗体,闪烁渐变动画效果,中英文切换版本
1. 代码 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"zh"> <head><meta charset"UTF-8"><meta name"viewport" content"widthdevice-width, initial-scale1.0"><title>红色粗体闪烁文字表格 - 中英文切换</t…...

六、【ESP32开发全栈指南:深入解析ESP32 IDF中的WiFi AP模式开发】
1. 引言:AP模式的核心价值 ESP32的AP(Access Point)模式使设备成为独立无线热点,适用于: 设备配网(SmartConfig)无路由器场景的本地组网数据直采终端(传感器集中器)临时…...
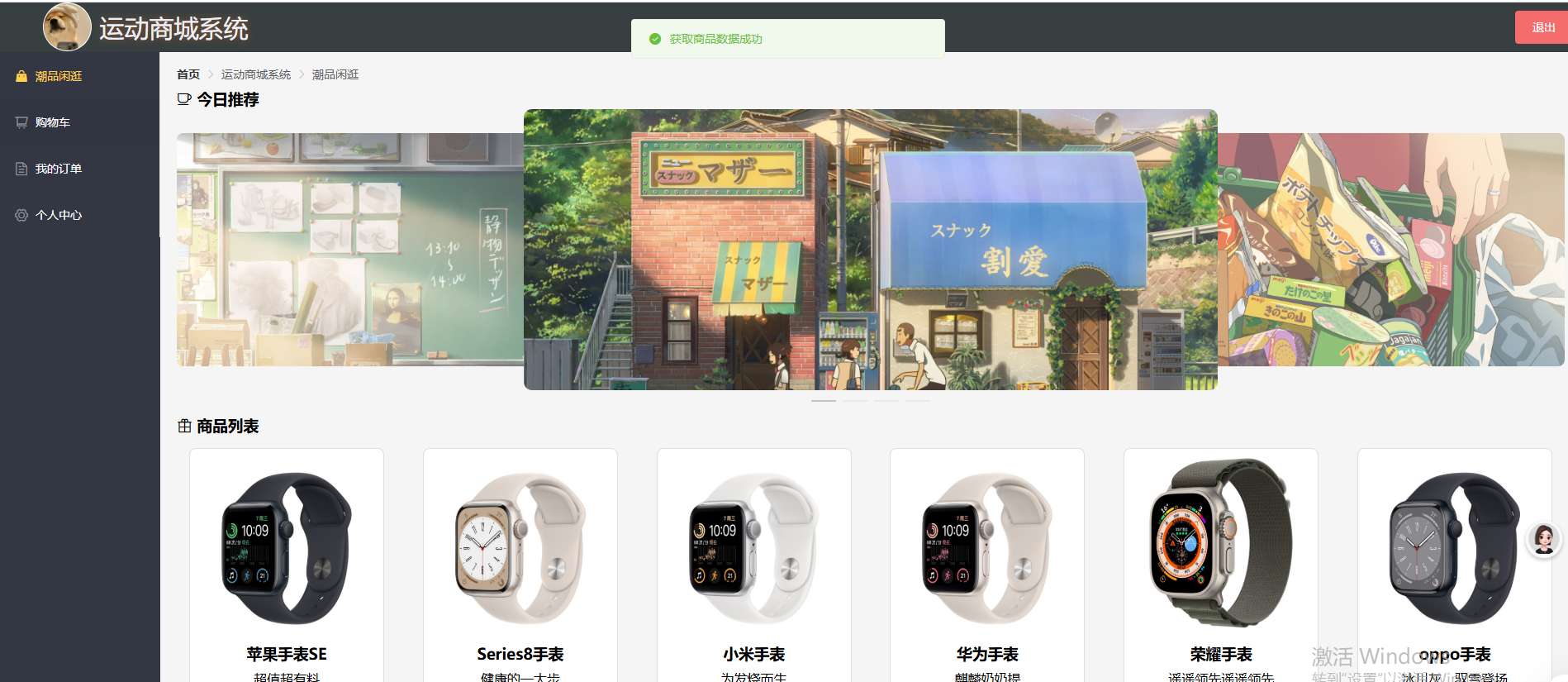
基于Django开发的运动商城系统项目
运动商城系统项目描述 运动商城系统是一个基于现代Web技术构建的电子商务平台,专注于运动类商品的在线销售与管理。该系统采用前后端分离架构,前端使用Vue.js实现动态交互界面,后端基于Django框架提供RESTful API支持,数据库采用…...

Python训练营打卡Day42
知识点回顾 回调函数lambda函数hook函数的模块钩子和张量钩子Grad-CAM的示例 1. 回调函数(Callback Function) 回调函数是作为参数传递给另一个函数的函数,目的是在某个事件发生后执行。 def fetch_data(callback):# 模拟数据获取data {&quo…...

https相比http的区别
https相比http的区别 https相比http的区别在于:https使用了SSL/TLS加密协议,确保数据传输的安全性和完整性,通信时需要证书验证。 https相比于http的区别主要在于安全性。https使用SSL/TLS加密传输数据,确保数据在客户端和服务器之间的通信…...

【Linux】为 Git 设置 Commit 提交模板方法,可统一个人或者项目的提交风格
为 Git 设置 Commit 提交模板 新建模板文件。注意之后不能删除该文件。 gedit ~/.gitmessage.txt粘贴自己的模板。可以给 AI 提自己的需求,定制一个模板,例如 # <type>(<scope>): <description> # # [optional body] # # [optional…...

caliper config.yaml 文件配置,解释了每个配置项的作用和注意事项
以下是添加了详细备注的 config.yaml 文件配置,解释了每个配置项的作用和注意事项: # Caliper 性能测试主配置文件 # 文档参考: https://hyperledger.github.io/caliper/# 测试轮次配置 - 可以定义多个测试轮次,每个轮次测试不同的合约或场景 rounds:# 第一个测试轮次 - 测试…...

结构体和指针1
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string> struct Student{ int age; string name; double score; }; int main() { //静态分配 Student s1 {18,"小明",88.5}; //cout << s1.name<<"的成绩为…...
