linux系统编程重点复习--线程同步
目录
复习目标:
1 互斥锁
1.1互斥锁的使用步骤
1.2 练习
1.3 死锁
2 读写锁
3 条件变量
4 信号量
复习目标:
- 熟练掌握互斥量的使用
- 说出什么叫死锁以及解决方案
- 熟练掌握读写锁的使用
- 熟练掌握条件变量的使用
- 理解条件变量实现的生产消费者模型
- 理解信号量实现的生产消费者模型
1 互斥锁
1.1互斥锁的使用步骤
- 第1步:创建一把互斥锁
- pthread_mutex_t mutex;
- 初始化互斥锁
- pthread_mutex_init(&mutex);---相当于mutex=1
- 在代码中寻找共享资源(也称为临界区)
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); -- mutex = 0
[临界区代码]
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); -- mutex = 1
- 释放互斥锁资源
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
注意:必须在所有操作共享资源的线程上都加上锁否则不能起到同步的效果
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>//定义一把锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;void *mythread1(void *args)
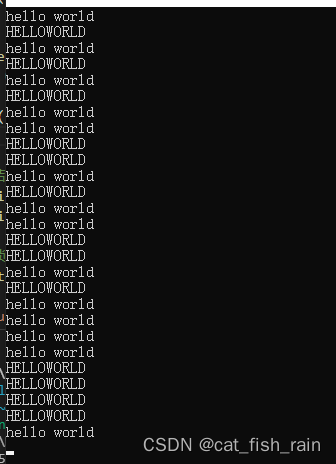
{while (1){//加锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);printf("hello ");sleep(rand() % 3);printf("world\n");//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);sleep(rand() % 3);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}void *mythread2(void *args)
{while (1){//解锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);printf("HELLO");sleep(rand() % 3);printf("WORLD\n");//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);sleep(rand() % 3);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main()
{int ret;pthread_t thread1;pthread_t thread2;//随机数种子srand(time(NULL));//互斥锁初始化pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);ret = pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, mythread1, NULL);if (ret != 0){printf("pthread_create error ,[%s]\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}ret = pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, mythread2, NULL);if (ret != 0){printf("pthread_create error ,[%s]\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}//等待线程结束pthread_join(thread1, NULL);pthread_join(thread2, NULL);//释放互斥锁pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);system("pause");return 0;
}
1.2 练习
- 编写思路:
1 定义一把互斥锁,应该为一全局变量
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
2 在main函数中对mutex进行初始化
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
3 创建两个线程,在两个线程中加锁和解锁
4 主线程释放互斥锁资源
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);


1.3 死锁
死锁并不是linux提供给用户的一种使用方法,而是由于用户使用互斥锁不当引起的一种现象。
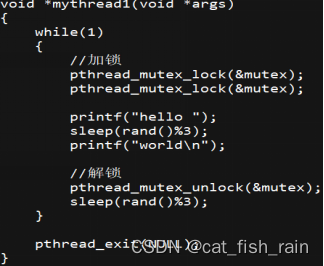
- 常见的死锁有两种:
- 第一种:自己锁自己,如下图代码片段
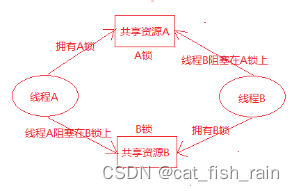
第二种 线程A拥有A锁,请求获得B锁;线程B拥有B锁,请求获得A锁,这样造成线程A和线程B都不释放自己的锁,而且还想得到对方的锁,从而产生死锁,如下图所示:
- 如何解决死锁:
- 让线程按照一定的顺序去访问共享资源
- 在访问其他锁的时候,需要先将自己的锁解开
- 调用pthread_mutex_trylock,如果加锁不成功会立刻返回
2 读写锁
- 什么是读写锁
- 读写锁也叫共享-独占锁。当读写锁以读模式锁住时,它是以共享模式锁住的;当它以写模式锁住时,它是以独占模式锁住的。写独占、读共享。
- 读写锁使用场合
- 读写锁非常适合于对数据结构读的次数远大于写的情况。
- 读写锁特性
- 读写锁是“写模式加锁”时,解锁前,所有对该锁加锁的线程都会被阻塞。
- 读写锁是“读模式加锁”时,如果线程以读模式对其加锁会成功;如果线程以写模式加锁会阻塞。
- 读写锁是“读模式加锁”时, 既有试图以写模式加锁的线程,也有试图以读模式加锁的线程。那么读写锁会阻塞随后的读模式锁请求。优先满足写模式锁。读锁、写锁并行阻塞,写锁优先级高
- 读写锁场景练习:
- 线程A加写锁成功, 线程B请求读锁
- 线程B阻塞
- 线程A持有读锁, 线程B请求写锁
- 线程B阻塞
- 线程A拥有读锁, 线程B请求读锁
- 线程B加锁成功
- 线程A持有读锁, 然后线程B请求写锁, 然后线程C请求读锁
- B阻塞,c阻塞 - 写的优先级高
- A解锁,B线程加写锁成功,C继续阻塞
- B解锁,C加读锁成功
- 线程A持有写锁, 然后线程B请求读锁, 然后线程C请求写锁
- BC阻塞
- A解锁,C加写锁成功,B继续阻塞
- C解锁,B加读锁成功
- 读写锁总结
读并行,写独占,当读写同时等待锁的时候写的优先级高
- 读写锁主要操作函数
- 定义一把读写锁
- pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;
- 初始化读写锁
- int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *restrict rwlock, const pthread_rwlockattr_t *restrict attr);
- 函数参数
- rwlock-读写锁
- attr-读写锁属性,传NULL为默认属性
- 销毁读写锁
int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 加读锁
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 尝试加读锁
int pthread_rwlock_tryrdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 加写锁
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 尝试加写锁
int pthread_rwlock_trywrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 解锁
int pthread_rwlock_unlock(&pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
- 练习:3个线程不定时写同一全局资源,5个线程不定时读同一全局资源。
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>//读写锁测试程序
int number = 0;//定义一把读写锁
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;//读写锁的回调函数
void *thread_write(void *arg)
{int i = *(int *)arg;int cur;while (1){//加读写锁pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);cur = number;cur++;number = cur;printf("[%d]-W:[%d]\n", i, cur);//解锁pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);sleep(rand() % 3);}
}//读回调函数
void *thread_read(void *arg)
{int i = *(int *)arg;int cur;while (1){//加读锁pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);cur = number;printf("[%d]-R:[%d]\n", i, cur);//解锁// pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);sleep(rand() % 3);}
}int main()
{int n = 8;int i = 0;int arr[8];pthread_t thread[8];//读写锁初始化pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);//创建3个写子线程for (i = 0; i < 3; i++){arr[i] = i;pthread_create(&thread[i], NULL, thread_write, &arr[i]);}//创建5个读子线程for (i = 3; i < n; i++){arr[i] = i;pthread_create(&thread[i], NULL, thread_read, &arr[i]);}//回收子线程int j = 0;for (j = 0; j < n; j++){pthread_join(thread[j], NULL);}//释放锁pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock);system("pause");return 0;
}-
3 条件变量
- 条件本身不是锁!但它也可以造成线程阻塞。通常与互斥锁配合使用。给多线程提供一个会合的场所。
- 使用互斥量保护共享数据;
- 使用条件变量可以使线程阻塞, 等待某个条件的发生, 当条件满足的时候解除阻塞.
- 条件变量的两个动作:
- 条件不满足, 阻塞线程
- 条件满足, 通知阻塞的线程解除阻塞, 开始工作.
- 条件变量相关函数
- pthread_cond_t cond;
- 定义一个条件变量
- int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
- 函数描述:初始化条件变量
- 函数参数:
- 函数返回值:成功返回0, 失败返回错误号
- int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
- 函数描述: 销毁条件变量
- 函数参数: 条件变量
- 返回值: 成功返回0, 失败返回错误号
- int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
- 函数描述: 条件不满足, 引起线程阻塞并解锁;
- 函数参数:
- 函数返回值: 成功返回0, 失败返回错误号
- int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
- 函数描述: 唤醒至少一个阻塞在该条件变量上的线程
- 函数参数: 条件变量
- 函数返回值: 成功返回0, 失败返回错误号
cond: 条件变量
attr: 条件变量属性, 通常传NULL
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
条件满足, 解除线程阻塞, 并加锁
cond: 条件变量
mutex: 互斥锁变量
使用条件变量的代码片段


上述代码中,生产者线程调用pthread_cond_signal函数会使消费者线程在pthread_cond_wait处解除阻塞。
//使用条件变量实现生产者和消费者模型
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>typedef struct node
{int data;struct node *next;
} NODE;NODE *head = NULL;//定义一把锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;//定义条件变量
pthread_cond_t cond;//生产者线程
void *producer(void *arg)
{NODE *pNode = NULL;while (1){pNode = (NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE));if (pNode == NULL){perror("malloc error");exit(-1);}pNode->data = rand() % 1000;printf("P:[%d]\n", pNode->data);//加锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);pNode->next = head;head = pNode;//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//通知消费者线程解除阻塞pthread_cond_signal(&cond);sleep(rand() % 3);}
}//消费者线程
void *consumer(void *arg)
{NODE *pNode = NULL;while (1){//加锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);if (head == NULL){//若条件不满足,需要阻塞等待//若条件不满足,则阻塞等待并解锁;//若条件满足(被生成者线程调用pthread_cond_signal函数通知),解除阻塞并加锁pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);}printf("C:[%d]\n", head->data);pNode = head;head = head->next;//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);free(pNode);pNode = NULL;sleep(rand() % 3);}
}int main()
{int ret;pthread_t thread1;pthread_t thread2;//初始化互斥锁pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);//条件变量初始化pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);//创建生产者线程ret = pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, producer, NULL);if (ret != 0){printf("pthread_create error,[%s]\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}//创建消费者线程ret = pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, consumer, NULL);if (ret != 0){printf("pthread_create error,[%s]\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}//等待线程结束pthread_join(thread1, NULL);pthread_join(thread2, NULL);//释放互斥锁pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);//释放条件变量pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);system("pause");return 0;
}多个生产者和消费者
//使用条件变量实现多个生产者和消费者模型
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
typedef struct node
{int data;struct node *next;
}NODE;NODE *head = NULL;//定义一把锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;//定义条件变量
pthread_cond_t cond;//生产者线程
void *producer(void *arg)
{NODE *pNode = NULL;int n = *(int *)arg;while(1){//生产一个节点pNode = (NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE));if(pNode==NULL){perror("malloc error");exit(-1);}pNode->data = rand()%1000;printf("P[%d]:[%d]\n", n, pNode->data);//加锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);pNode->next = head;head = pNode;//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//通知消费者线程解除阻塞pthread_cond_signal(&cond);sleep(rand()%3);}
}//消费者线程
void *consumer(void *arg)
{NODE *pNode = NULL;int n = *(int *)arg;while(1){//加锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);if(head==NULL){//若条件不满足,需要阻塞等待//若条件不满足,则阻塞等待并解锁;//若条件满足(被生成者线程调用pthread_cond_signal函数通知),解除阻塞并加锁 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);}if(head==NULL){//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); continue;}printf("C[%d]:[%d]\n", n, head->data); pNode = head;head = head->next;//解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);free(pNode);pNode = NULL;sleep(rand()%3);}
}int main()
{int ret;int i = 0;pthread_t thread1[5];pthread_t thread2[5];//初始化互斥锁pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);//条件变量初始化pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);int arr[5];for(i=0; i<5; i++){arr[i]= i;//创建生产者线程ret = pthread_create(&thread1[i], NULL, producer, &arr[i]);if(ret!=0){printf("pthread_create error, [%s]\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}//创建消费者线程ret = pthread_create(&thread2[i], NULL, consumer, &arr[i]);if(ret!=0){printf("pthread_create error, [%s]\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}}//等待线程结束for(i=0; i<5; i++){pthread_join(thread1[i], NULL);pthread_join(thread2[i], NULL);}//释放互斥锁pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);//释放条件变量pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);return 0;
}
4 信号量
1 信号量介绍
信号量相当于多把锁, 可以理解为是加强版的互斥锁
2 相关函数
定义信号量 sem_t sem; int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
pshared: 0表示线程同步, 1表示进程同步
value: 最多有几个线程操作共享数据
sem: 信号量变量
3 信号量代码片段:


- 函数描述: 初始化信号量
- 函数参数:
- 函数返回值:成功返回0, 失败返回-1, 并设置errno值
- int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
- 函数描述: 调用该函数一次, 相当于sem--, 当sem为0的时候, 引起阻塞
- 函数参数: 信号量变量
- 函数返回值: 成功返回0, 失败返回-1, 并设置errno值
- int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
- 函数描述: 调用一次, 相当于sem++
- 函数参数: 信号量变量
- 函数返回值: 成功返回0, 失败返回-1, 并设置errno值
- int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem);
- 函数描述: 尝试加锁, 若失败直接返回, 不阻塞
- 函数参数: 信号量变量
- 函数返回值: 成功返回0, 失败返回-1, 并设置errno值
- int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
- 函数描述: 销毁信号量
- 函数参数: 信号量变量
- 函数返回值: 成功返回0, 失败返回-1, 并设置errno值
//使用信号量实现生产者和消费者模型
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
//信号量的头文件
#include <semaphore.h>typedef struct node
{int data;struct node *next;
} NODE;NODE *head = NULL;//定义信号量
sem_t sem_producer;
sem_t sem_consumer;//生产者线程void *producer(void *arg)
{NODE *pNode = NULL;while (1){pNode = (NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE));if (pNode == NULL){perror("malloc error");exit(-1);}pNode->data = rand() % 100;printf("P;[%d]\n", pNode->data);//加锁sem_wait(&sem_producer);pNode->next = head;head = pNode;//解锁sem_post(&sem_consumer);sleep(rand() % 3);}
}void *consumer(void *arg)
{NODE *pNode = NULL;while (1){//加锁sem_wait(&sem_consumer); //相当于--printf("C:[%d]\n", head->data);pNode = head;head = head->next;//解锁sem_post(&sem_producer); //相当于++free(pNode);pNode = NULL;sleep(rand() % 3);}
}int main()
{int ret;pthread_t thread1;pthread_t thread2;//初始化信号量sem_init(&sem_producer, 0, 5);sem_init(&sem_consumer, 0, 0);//创建生产者线程ret = pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, producer, NULL);if (ret != 0){printf("pthread create error,[%s]\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}ret = pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, consumer, NULL);if (ret != 0){printf("pthread create error,[%s]\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}//等待线程结束pthread_join(thread1, NULL);pthread_join(thread2, NULL);//释放信号量资源sem_destroy(&sem_producer);sem_destroy(&sem_consumer);system("pause");return 0;
}相关文章:

linux系统编程重点复习--线程同步
目录 复习目标: 1 互斥锁 1.1互斥锁的使用步骤 1.2 练习 1.3 死锁 2 读写锁 3 条件变量 4 信号量 复习目标: 熟练掌握互斥量的使用说出什么叫死锁以及解决方案熟练掌握读写锁的使用熟练掌握条件变量的使用理解条件变量实现的生产消费者模型理解…...
【Docker 学习笔记】Windows Docker Desktop 安装
文章目录 一、前言二、Windows Docker 安装1. 基于Hyper-V后端和Windows容器的安装2. 基于WSL2后端的安装(推荐)3. 安装Docker Desktop on Windows4. 启动并验证Docker Desktop 一、前言 Docker并非是一个通用的容器工具,它依赖于已存在并运…...

getInputStream has already been called for this request 问题记录
问题背景 HttpServletRequest.getReader() HttpServletRequest.getInputStream() 不能在过滤器中读取一次二进制流(字符流),又在另外一个Servlet中读取一次,即一个InputSteam(BufferedReader)对象在被读取完成后,将无…...
)
日撸代码300行:第60天(小结)
1、自己对于这个专栏的代码抄写也是断断续续,由于种种原因上次在第54天没坚持下来,这次继续希望能抄完。 2、现在代码的阅读和理解能力明显比刚开始抄代码的时候强了不少。感觉坚持到现在收获还是不小。现在基本上来说仔细想一下都能够理清楚代码的意思。…...

python和java哪个更有前景,python和java哪个更有前途
大家好,小编为大家解答python和java哪个好学,零基础的问题。很多人还不知道python和java哪个更容易入门,现在让我们一起来看看吧! 进入编程行业是很多人的梦想,现在越来越多的人都想要通过培训的方式进入IT行业中,但是…...
LeetCode_11. 盛最多水的容器
题目描述 11. 盛最多水的容器 - 力扣(LeetCode)https://leetcode.cn/problems/container-with-most-water/ 思路分析 这题就是典型的是一道很经典的面试题,最优的解法是双指针,但很多人在第一次看到这题的时候很难想到用双指针来…...

【Android】APP电量优化学习笔记
电量优化原因 电量优化在 Android 开发中非常重要,原因如下: 用户体验: 电池续航时间是用户在使用移动设备时非常关注的因素之一。通过进行电量优化,可以延长设备的电池寿命,使用户能够更长时间地使用设备而不必频繁…...
【微信小程序创作之路】- 小程序事件绑定、动态提示Toast、对话框 Modal
【微信小程序创作之路】- 小程序事件绑定、动态提示Toast、对话框 Modal 第六章 小程序事件绑定、动态提示Toast、对话框 Modal 文章目录 【微信小程序创作之路】- 小程序事件绑定、动态提示Toast、对话框 Modal前言一、事件是什么?二、小程序中常用事件三、事件传…...
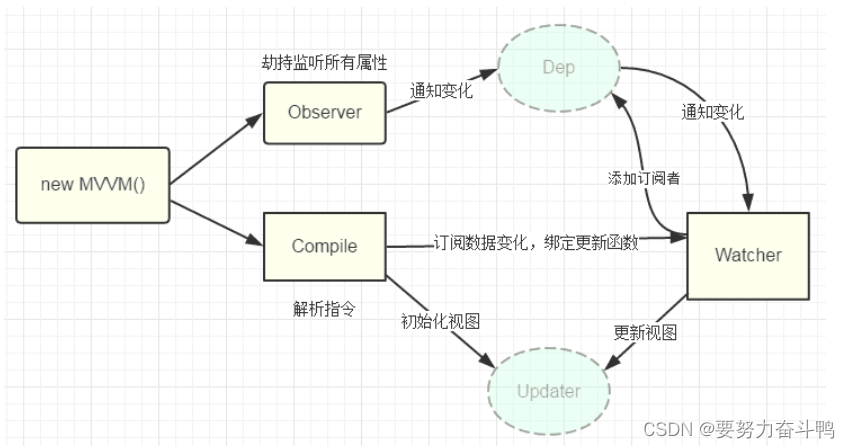
MVC与MVVM模式的区别
一、MVC Model(模型):用于处理应用程序数据逻辑,负责在数据库中存取数据。处理数据的crud View(视图):处理数据显示的部分。通常视图是依据模型数据创建的。 Controller(控制器&…...
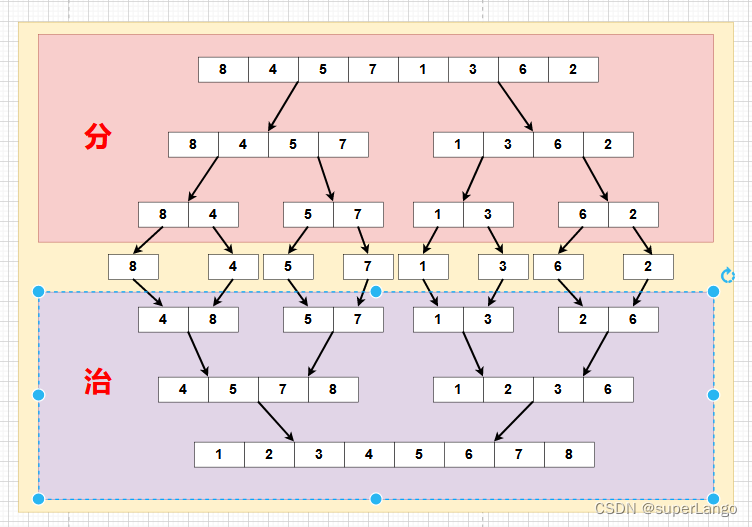
【数据结构与算法】归并排序
归并排序 归并排序(MERGE-SORT)是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法,该算法采用经典的分治(divide-and-conquer)策略(分治法将问题分(divide)成一些小的问题然后递归求解,而…...
OSG3.6.5 + VS2017前期准备及编译
OSG3.6.5 VS2017前期准备及编译 1、前期准备 1.1、osg稳定版本源码 Stable releases (openscenegraph.com) 1.2、osg依赖项 Dependencies (openscenegraph.com) 1.3、osg测试及演示数据 Data Resources (openscenegraph.com) 1.4、安装doxygen和Graphviz(用…...
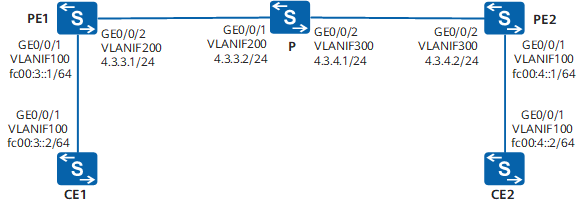
IPv6 over IPv4隧道配置举例
配置IPv6 over IPv4手动隧道示例 组网需求 如图1所示,两台IPv6主机分别通过SwitchA和SwitchC与IPv4骨干网络连接,客户希望两台IPv6主机能通过IPv4骨干网互通。 图1 配置IPv6 over IPv4手动隧道组网图 配置思路 配置IPv6 over IPv4手动隧道的思路如下&…...
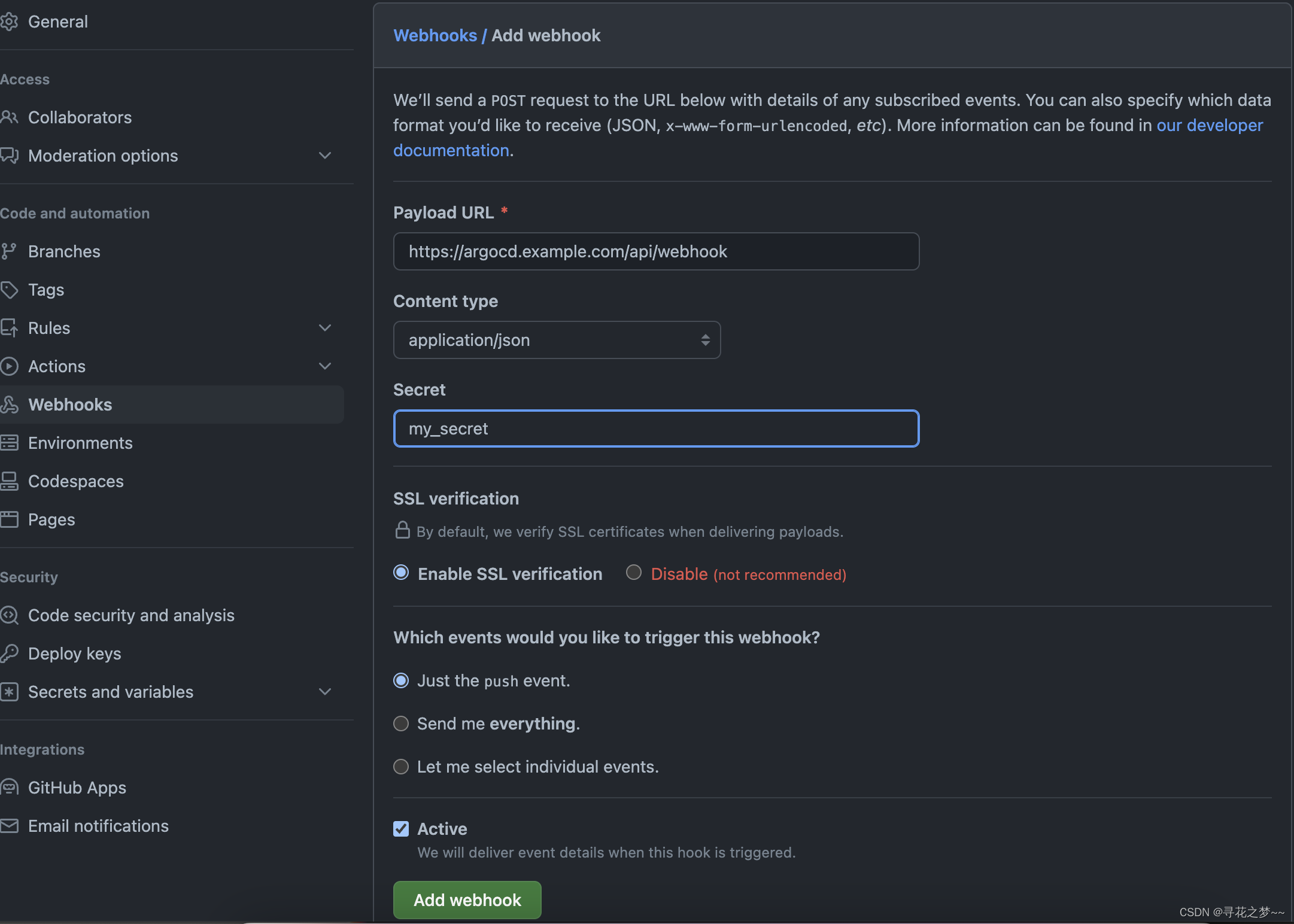
【GitOps系列】使用 ArgoCD 快速打造GitOps工作流
文章目录 ArgoCD简介ArgoCD安装访问ArgoCDGitOps 工作流总览创建 ArgoCD 应用检查 ArgoCD 同步状态访问应用 连接 GitOps 工作流体验 GitOps 工作流生产建议1)修改默认密码2)配置 Ingress 和 TLS3)使用 Webhook 触发 ArgoCD4)将源…...
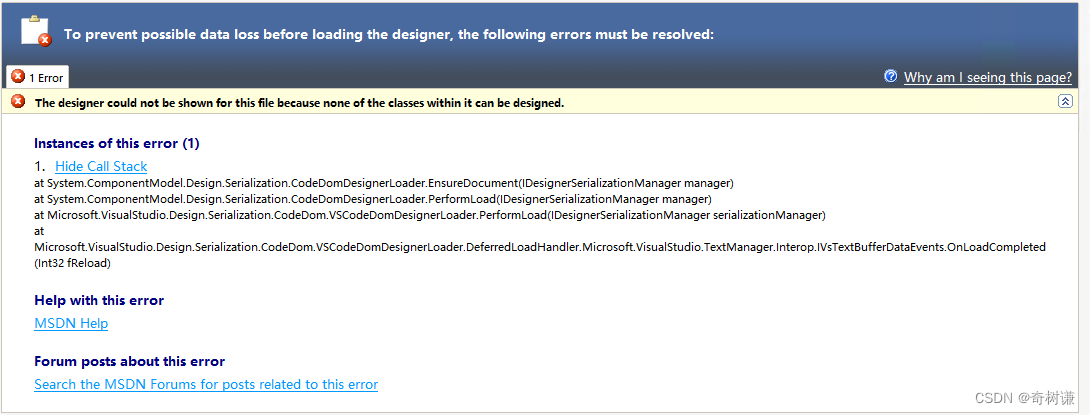
C#|无法打开cs文件设计窗口
报错信息:To prevent possible data loss before loading the designer, the following errors must be resolved: 解决方案:实不相瞒我把项目解决方案名称改短了就可以了。。有其他原因或者解决方案望不吝赐教。。...

【SpringBoot笔记36】SpringBoot自定义WebSocketHandler集成WebSocket
这篇文章,主要介绍SpringBoot自定义WebSocketHandler集成WebSocket。 目录 一、SpringBoot集成WebSocket 1.1、添加WebSocket依赖 1.2、自定义WebSocketHandler 1.3、注册WebSocket服务端...

flutter 图片相关
官方链接:https://api.flutter.dev/flutter/widgets/Image-class.html 图片基本使用 显示本地图片时,要在pubspec.yaml文件里面添加如:(注意空格) assets: - assets/images/logo.png Fit属性: BoxFit.cover最常用 显示可能拉伸,可能裁…...

将上位机程序从PC的window系统迁移至Intel NUC的无桌面版ubuntu系统问题记录
将上位机程序从PC的window系统迁移至Intel NUC的无桌面版ubuntu系统 问题一 网口失效 问题描述:NUC关机状态下,将网口与路由器连接,网络指示灯闪烁;NUC开机后,网络指示灯熄灭,使用ping命令,既…...
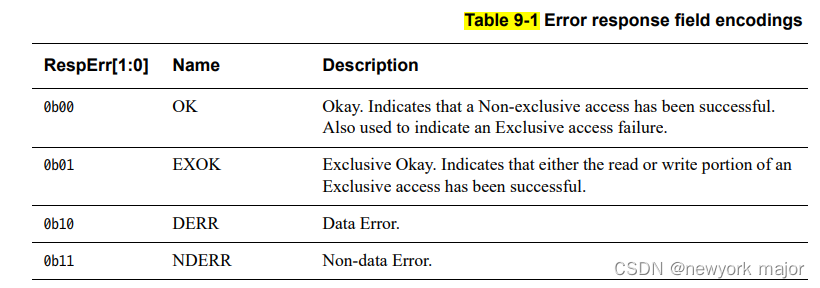
CHI中的error处理
Error Handling Error types 包含两种sub-packet级别的error, 和两种packe级别的error; Packet level error Data Error, DERR □ 访问的地址是正确的,但是访问的数据有错误;通常是在数据崩溃的时候使用,例如ECC…...

如何使用 PHP 进行数据库缓存处理?
当你想要让你的PHP应用程序更快时,数据库缓存是一个重要的工具。它可以帮助你避免频繁地查询数据库,提高应用程序的响应速度。不过,在进行数据库缓存处理时,需要注意一些细节,否则可能会得到相反的结果。下面ÿ…...

新版巨量广告投放技巧分析
新版广告系统,计划出价40,转化成本特别低只有21,同时消耗也比较慢 为什么刚开始成本都比较低,跑着跑着成本就高了,像这种情况一般如何操作? 一: 为什么会出现成本和出价差这么多 1: 系统对账…...
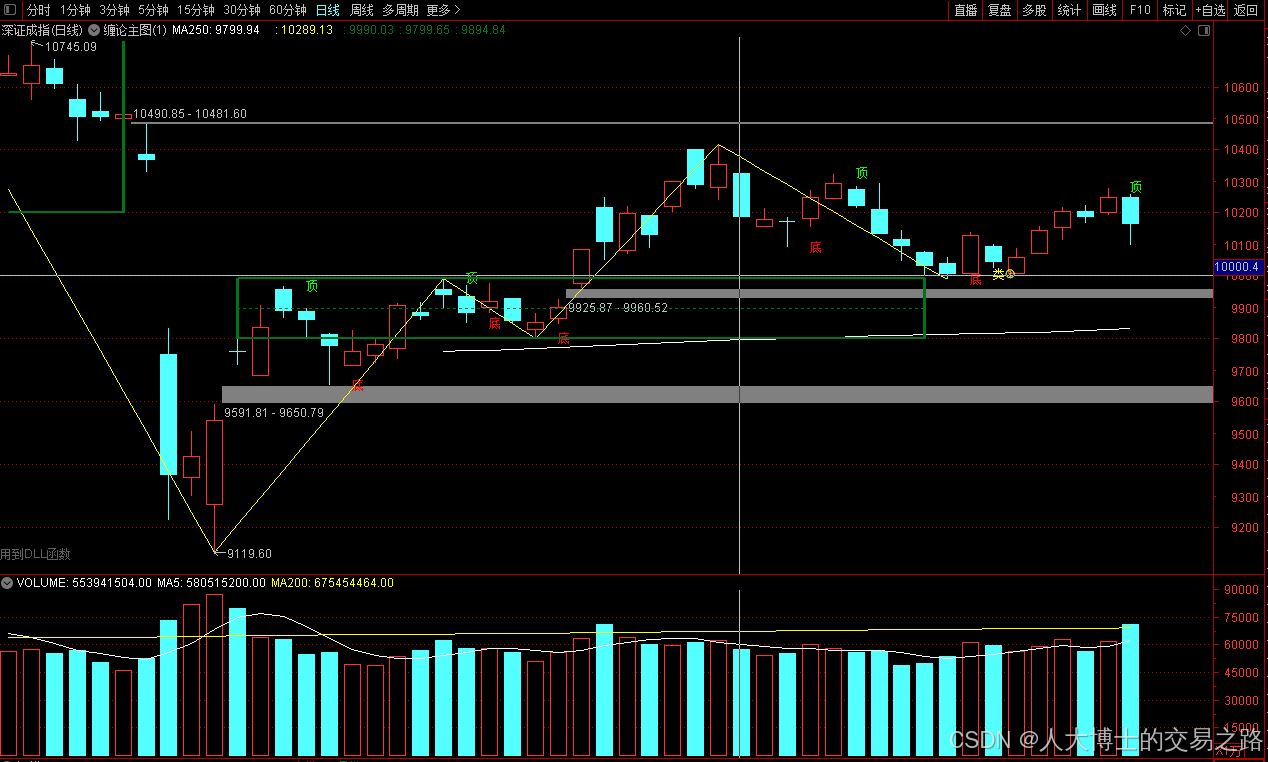
龙虎榜——20250610
上证指数放量收阴线,个股多数下跌,盘中受消息影响大幅波动。 深证指数放量收阴线形成顶分型,指数短线有调整的需求,大概需要一两天。 2025年6月10日龙虎榜行业方向分析 1. 金融科技 代表标的:御银股份、雄帝科技 驱动…...
Cesium相机控制)
三维GIS开发cesium智慧地铁教程(5)Cesium相机控制
一、环境搭建 <script src"../cesium1.99/Build/Cesium/Cesium.js"></script> <link rel"stylesheet" href"../cesium1.99/Build/Cesium/Widgets/widgets.css"> 关键配置点: 路径验证:确保相对路径.…...

汽车生产虚拟实训中的技能提升与生产优化
在制造业蓬勃发展的大背景下,虚拟教学实训宛如一颗璀璨的新星,正发挥着不可或缺且日益凸显的关键作用,源源不断地为企业的稳健前行与创新发展注入磅礴强大的动力。就以汽车制造企业这一极具代表性的行业主体为例,汽车生产线上各类…...
srs linux
下载编译运行 git clone https:///ossrs/srs.git ./configure --h265on make 编译完成后即可启动SRS # 启动 ./objs/srs -c conf/srs.conf # 查看日志 tail -n 30 -f ./objs/srs.log 开放端口 默认RTMP接收推流端口是1935,SRS管理页面端口是8080,可…...

高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景
高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景 高危文件识别旨在检测可能导致安全威胁的文件,如包含恶意代码、敏感数据或欺诈内容的文档,在企业协同办公环境中(如Teams、Google Workspace)尤为重要。结合大模型技术&…...
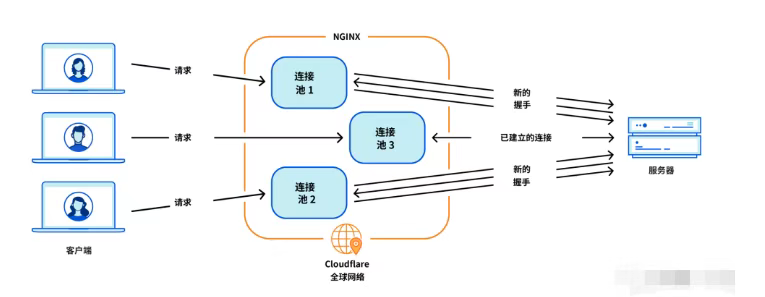
Cloudflare 从 Nginx 到 Pingora:性能、效率与安全的全面升级
在互联网的快速发展中,高性能、高效率和高安全性的网络服务成为了各大互联网基础设施提供商的核心追求。Cloudflare 作为全球领先的互联网安全和基础设施公司,近期做出了一个重大技术决策:弃用长期使用的 Nginx,转而采用其内部开发…...

反射获取方法和属性
Java反射获取方法 在Java中,反射(Reflection)是一种强大的机制,允许程序在运行时访问和操作类的内部属性和方法。通过反射,可以动态地创建对象、调用方法、改变属性值,这在很多Java框架中如Spring和Hiberna…...
)
WEB3全栈开发——面试专业技能点P2智能合约开发(Solidity)
一、Solidity合约开发 下面是 Solidity 合约开发 的概念、代码示例及讲解,适合用作学习或写简历项目背景说明。 🧠 一、概念简介:Solidity 合约开发 Solidity 是一种专门为 以太坊(Ethereum)平台编写智能合约的高级编…...

MySQL中【正则表达式】用法
MySQL 中正则表达式通过 REGEXP 或 RLIKE 操作符实现(两者等价),用于在 WHERE 子句中进行复杂的字符串模式匹配。以下是核心用法和示例: 一、基础语法 SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name REGEXP pattern; …...

如何在最短时间内提升打ctf(web)的水平?
刚刚刷完2遍 bugku 的 web 题,前来答题。 每个人对刷题理解是不同,有的人是看了writeup就等于刷了,有的人是收藏了writeup就等于刷了,有的人是跟着writeup做了一遍就等于刷了,还有的人是独立思考做了一遍就等于刷了。…...
