C++容器——list的模拟实现
目录
一.list的基本结构
二. 接下来就是对list类构造函数的设计了:
三.链表数据的增加:
四.接下来就是迭代器的创建了:
四.简单函数的实现:
五.构造与析构
六.拷贝构造和赋值重载
传统写法:
现代写法:
七.迭代器模板类型
一.list的基本结构
想要模拟实现list类,就需要先了解它的底层架构,上篇博客讲到:list容器的底层是双向链表,那么就需要自定义一个节点类,通过节点类可以创建节点,设置节点的前后指针和数据值。之后便可以通过该类类型创建list类的成员变量。
template<class T>
struct list_node { //该类为内部类,是list的内部类list_node(const T& val):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(val) {}//成员变量list_node* _next; //后指针list_node* _prev; //前指针T _data; //值
};template<class T>
class list {public:typedef list_node<T> node; //将节点类作为类类型private:node* _head; //指向堆区空间链表的指针size_t _size; //计数
};
node* 类型就好比是对节点类的封装。
二. 接下来就是对list类构造函数的设计了:
template<class T>
class list {public:typedef list_node<T> node; //将节点类作为类类型//初始化操作void empty_Init() {_head = new node(T());_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list() //构造函数:_head(nullptr),_size(0){empty_Init();}private:node* _head; //指向堆区空间链表的指针size_t _size; //计数
};对构造函数的初始化设计就是:创建哨兵位头结点,让链表指针指向哨兵位头结点,由哨兵头节点去控制节点的增删查改,避免了由链表指针去控制,操作和形式上都方便了很多。
注:哨兵位头结点的创建是在empty_Init()函数中进行的!
三.链表数据的增加:
template<class T>
class list{public:typedef Node<T> node;//尾插 void push_back(const T& val) {node* newnode = new node(val);node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;++_size;}//尾删void pop_back() {assert(!empty());node* tail = _head->_prev;node* last = tail->_prev;last->_next = _head;_head->_prev = last;delete tail;--_size;}//头插void push_front(const T& val) {node* newnode = new node(val);node* first = _head->_next;_head->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = _head->_next;newnode->_next = first;first->_prev = newnode;++_size;}//头删void pop_front() {assert(!empty());node* first = _head->_next;node* second = first->_next;_head->_next = second;second->_prev = _head->_next;delete first;--_size;}//任意位置的插入iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val=T()) {if (pos == this->begin()) {push_front(val); //复用代码}else if (pos == this->end()) {push_back(val); //复用代码}else {node* newnode = new node(val);node* cur = pos.phead;node* last = cur->_prev;last->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = last;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;++_size;}return pos;}//任意位置的删除iterator erase(iterator pos) {assert(!empty());if (pos == this->begin()) {pop_front();}else if (pos == this->end()) {pop_back();}else {node* cur = pos.phead;node* tail = cur->_next;node* last = cur->_prev;last->_next = tail;tail->_prev = last;delete cur;--_size;}return pos;}private:node* _head; //指向堆区空间链表的指针size_t _size; //计数};对于数据的增加和删除,头插头删、尾插尾删简单就不说了,重点是insert和erase函数的实现,如上代码,在insert和erase中,各有三种情况,其中头尾的操作直接复用函数即可,对于中间位置的插入删除情况,我想说的是,指定的pos参数是iterator类型——自定义迭代器类,它是指针!!! 它只是指向该节点元素的位置,所以想要获取该位置的节点,就需要pos.phead才能获取到该节点,只有获取到该节点,才能使用该节点附近的前后指针!
四.接下来就是迭代器的创建了:
在对vector、String容器的模拟实现中,我并没有单独创建迭代器,这是因为这两个容器的底层都是数组,是一段连续的地址空间,对于迭代器中的成员begin、end都是可以直接让指针进行类型的字节++/--进行的,很方便的,是使用原生指针来确定位置
而对于list容器来说,它的底层是链表,各个节点的位置是不连续的,随机的。使用原生指针并不能遍历到每一个对象的元素!所以针对list容器,需要创建一个自定义类型的迭代器进行链表的遍历。
template<class T>struct list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> node;node* _pnode; //成员变量list_iterator(node* p) //构造函数:_pnode(p){}T& operator*(){ //指针解引用return _pnode->_data;}list_iterator<T>& operator++(){ //指针++_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}bool operator!=(const list_iterator<T>& it){ //!=运算符重载return _pnode != it._pnode;}};template<class T>class list{public:typedef list_node<T> node;typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){//iterator it(_head);//return it;return iterator(_head);}};
在自定义的迭代器类中,我根据平常练习vector、String的迭代器代码中,写了几个一定会用到的运算符重载函数:解引用、指针++,遍历所用到的!=等函数。
写好自定义迭代器类后,需要在list类中重命名该类。
写好迭代器后,我们就可以试验一下了:
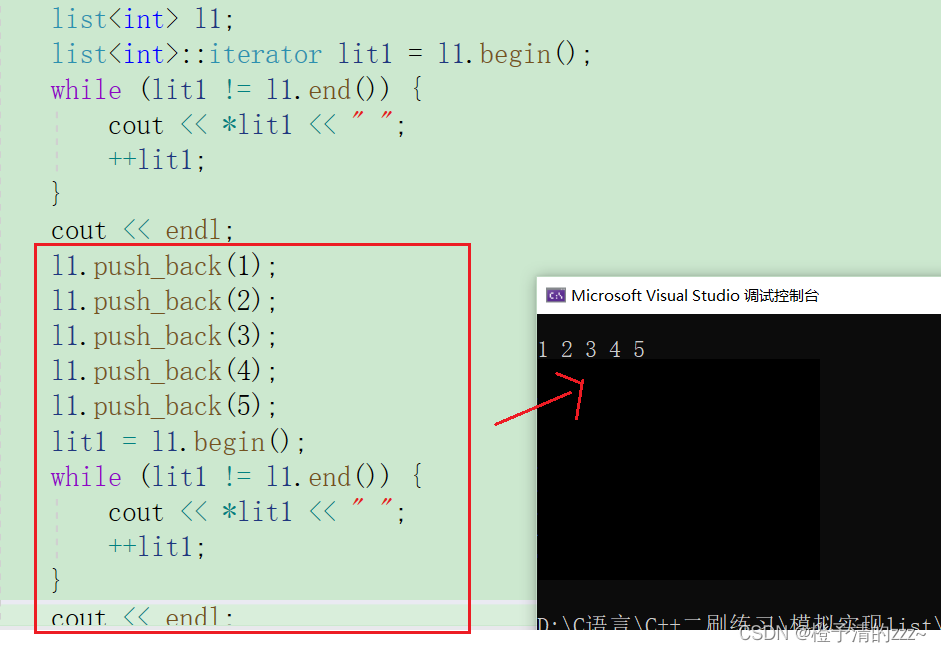
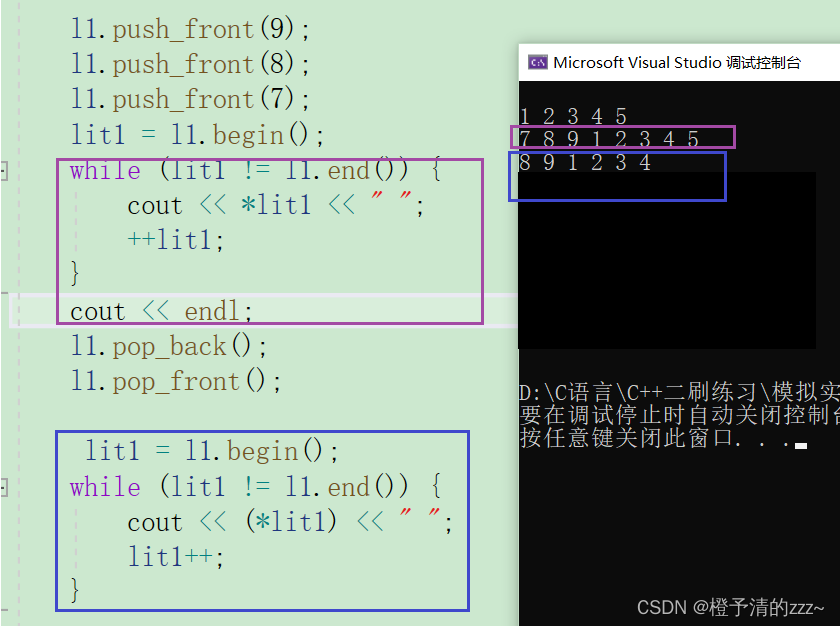
注:上面的迭代器只是普通迭代器的实现,还会有const迭代器、反向迭代器需要实现,意味着还得再写两个迭代器类。
四.简单函数的实现:
template<class T>
class list{public:size_t size()const {return _size;//方法2:利用指针遍历,每遍历一次记一次数}bool empty() const {//方法1:return _size == 0;//方法2:return _head->next==_head;}void clear() {node* cur = _head->_next;while (cur != _head) {node* del = cur;cur = cur->_next;delete del;}cur->_next = _head;cur->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}T& front() {return this->begin().phead->_data;}T& back() {return this->end().phead->_prev->_data;}private:node* _head;size_t _size;};
五.构造与析构
有了迭代器,我们就可以对list构造函数进行迭代器区间构造实现了:
template<class T>
class list{
public://迭代器区间构造函数template<class Inputiterator>list(Inputiterator first, Inputiterator last) { empty_Init();while (first != last) {push_back(*first);++first;}}void empty_Init() {_head = new node(T());_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list() //无参构造{empty_Init();}//析构函数~list() {this->clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;_size = 0;}
private:node* _head;size_t _size;
};析构函数就是遍历链表中每个节点都进行遍历释放,置空指针,置零变量。
六.拷贝构造和赋值重载
传统写法:
//拷贝构造——传统写法list(const list<T>& lt) {empty_Init();for (auto& e : lt) {this->push_back(e);}}//赋值重载函数——传统写法list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& lt) {if (this != <) {this->clear();}for (const auto& e : lt) {this->push_back(e);}return *this;}拷贝构造和赋值重载本质上都相同,都是复制已有的list对象,然后深拷贝数据给自己。深拷贝就是创建一个属于自己的头结点,剩下的数据就是浅拷贝(无脑将数据以遍历的方式让自己的头指针进行指针链接)。
现代写法:
//调用std库中swap函数进行成员交换void Swap(list<T>& lt) {std::swap(this->_head, lt._head);std::swap(this->_size, lt._size);} //拷贝构造——现代写法list(const list<T>& lt) {empty_Init();list<T> tmp(lt.begin(), lt.end()); //调用迭代器区间构造函数this->Swap(tmp);}//赋值重载——现代写法list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt) {this->Swap(lt); //值传递,形参的改变不影响实参return *this;}
七.迭代器模板类型
上面讲迭代器的最后说了,迭代器有普通版、const版、反向版、反向const版,意味着我们需要创建四个迭代器类型,但迭代器能用到的运算符重载函数都一样,都是解引用、指针++、!=运算符。
//自定义普通迭代器类
template<class T>struct list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> node;node* _pnode;list_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p){}T& operator*(){return _pnode->_data;}list_iterator<T>& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}list_iterator<T>& operator--(){_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return *this;}bool operator!=(const list_iterator<T>& it){return _pnode != it._pnode;}};//const迭代器类template<class T>struct list_const_iterator{typedef list_node<T> node;node* _pnode;list_const_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p){}const T& operator*(){return _pnode->_data;}list_const_iterator<T>& operator++(){_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}list_const_iterator<T>& operator--(){_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return *this;}bool operator!=(const list_const_iterator<T>& it){return _pnode != it._pnode;}};template<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> node;public:typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}如上,普通迭代器类和const迭代器类唯一的区别:是在遍历上,const迭代器类的解引用运算符重载函数中不能用*it修改数据,那么这俩迭代器类中其他函数的实现完全一样,这极大的造成了代码的冗余,降低了可读性!!!
于是为了在一种迭代器类中体现不同类型的迭代器,可以这样做:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct _list_iterator {typedef list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T, Ref,Ptr> Self; //Self是T与ref,ptr 模板类型的另一种别称//迭代器构造函数_list_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p) {}//解引用Ref operator*() {return _pnode->_data;}//箭头只有是结构体才可以用Ptr operator->() {return &_pnode->_data; //返回的是该结点的地址}Self& operator++() {_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;}//后置++,使用占位符int,与前置++以示区分Self operator++(int) {Self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_next;return tmp;}//前置--Self& operator--() {_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return *this;}//后置--Self operator--(int) {Self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& lt) const {return _pnode != lt._pnode;}bool operator==(const Self& lt) const{return _pnode == lt._pnode;}node* _pnode;
};
在迭代器类中,采用了三个模板参数。这三个模板参数:T代表泛型值,Ref代表泛型引用,Ptr代表泛型指针,这三种参数主要应用于运算符重载函数的函数返回值,函数形参,相当方便,一举多得,通过不同实参的传递就可以调用不同类型的函数。
template<class T>
class list {
public:typedef list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;//typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;typedef _list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;完整模拟实现代码 .h文件:
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>using std::cout;
using std::endl;template<class T>
struct list_node { //该类为内部类,是list的内部类list_node(const T& val):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(val) {}//成员变量list_node* _next;list_node* _prev;T _data;
};//typedef list_iterator<T, T&> iterator;
//typedef list_iterator<T, const T&> const_iterator;//这种写法来源:vector<int>,vector<string>,vector<vector<int>>
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr> //新增一个模板参数 ,T是一种类型,ref是一种类型
struct list_iterator {typedef list_node<T> node;typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; //Self是T与ref,ptr 模板类型的另一种别称//迭代器构造函数list_iterator(node* p):_pnode(p) {}//在下面的运算符重载中,const版与非const版只有解引用运算符重载函数的类型不同,其他运算符重载都一样//所以operator* 的类型需要使用ref,ref可以理解为constT&, 而非const对象也可以调用const函数,权限够//const对象不可调用非const函数,权限不够,所以使用ref//解引用Ref operator*() {return _pnode->_data;}//箭头只有是结构体才可以用Ptr operator->() {return &_pnode->_data; //返回的是该结点的地址}//前置++,//为啥要用引用? 原因:return *this ,this(迭代器对象)出了该函数体,还存在(this的生命周期在该类中是全局的)Self& operator++() {_pnode = _pnode->_next;return *this;//既然this还在,那么直接用引用返回,栈帧中不开临时空间,减少拷贝次数,提高效率//记住:使用引用返回的前提是,要返回的值出了函数体仍在才可以使用,否则会报错}//后置++,使用占位符int,与前置++以示区分Self operator++(int) {Self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_next;return tmp;//返回tmp后,tmp为临时对象,出了函数就消失了,tmp对象不在,需要拷贝,那就得用传值返回,在栈帧中//创建一个临时空间去接收返回的tmp对象数据。设置一个默认参数和前置++做区分,构成函数重载。//若使用引用返回,那么该函数结束后,返回的tmp已经不存在了,引用返回返回野指针(随机值)就会报错!!!}Self& operator--() {_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return *this;}//后置--Self operator--(int) {Self tmp(*this);_pnode = _pnode->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& lt) const {return _pnode != lt._pnode;}bool operator==(const Self& lt) const{return _pnode == lt._pnode;}node* _pnode;
};//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------template<class T>
class list {
public:typedef list_node<T> node;typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;void empty_Init() {_head = new node(T());_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(){empty_Init();}//析构~list() {this->clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;_size = 0;}template<class Inputiterator>list(Inputiterator first, Inputiterator last) { //拷贝构造的天选打工人//先初始化,给头节点,否则没法继续empty_Init();while (first != last) {push_back(*first);++first;}}void swap(list<T>& lt) {std::swap(this->_head, lt._head);std::swap(this->_size, lt._size);}void clear() {iterator it = this->begin();while (it != this->end()) {it = this->erase(it);}}//拷贝构造——传统写法/*list(const list<T>& lt) {empty_Init();for (auto& e : lt) {this->push_back(e);}}*///拷贝构造——现代写法list(const list<T>& lt) {empty_Init();list<T> tmp(lt.begin(), lt.end()); //调用迭代器区间构造函数this->swap(tmp);}//赋值重载——传统写法/*list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& lt) {if (this != <) {this->clear();}for (const auto& e : lt) {this->push_back(e);}return *this;}*///赋值重载——现代写法list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt) {this->swap(lt);return *this;}//迭代器iterator begin() {return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end() {return iterator(_head);}//const迭代器const_iterator begin() const {return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const {return const_iterator(_head);}//尾插void push_back(const T& val) {node* newnode = new node(T(val));node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;}//insertiterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val) {node* newnode = new node(T(val));node* cur = pos._pnode;node* first = cur->_prev;first->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = first;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;_size++;//insert后返回新节点的位置,那么下一次pos就会指向最近一次创建新节点的位置了return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos) {//pos不能指向哨兵位头节点,因为pos一旦指向哨兵位头,那么该链表一定为空,空链表是不能再删数据的assert(pos != end());node* first = pos._pnode->_prev;node* last = pos._pnode->_next;first->_next = last;last->_prev = first;delete pos._pnode;pos._pnode = nullptr;--_size;return iterator(last);}void push_front(const T& val) {insert(begin(), val);}void pop_back() {erase(--end());}void pop_front() {erase(begin());}size_t size() const{/*size_t s = 0;iterator it = this->begin();while (it != this->end()) {++it;++s;}return s;*///复用insert和erase//因为在链表中,一切的新增和减少都是复用的insert和erase,所以在insert和erase中size++,size--即可return _size;}bool empty() const {//return _head->_next == _head;//也可以复用size()return _size == 0;}private:node* _head; //头节点size_t _size;
};
相关文章:

C++容器——list的模拟实现
目录 一.list的基本结构 二. 接下来就是对list类构造函数的设计了: 三.链表数据的增加: 四.接下来就是迭代器的创建了: 四.简单函数的实现: 五.构造与析构 六.拷贝构造和赋值重载 传统写法: 现代写法: 七.迭…...

VUE3 祖孙组件传值调用方法
1.在 Vue 3 中,你可以使用 provide/inject 来实现祖孙组件之间的传值和调用方法。 首先,在祖组件中使用 provide 来提供数据或方法,例如: // 祖组件 import { provide } from vue;export default {setup() {const data Hello;c…...

我的网安之路
机缘 我目前从事网安工作,一转眼我从发布的第一篇文章到现在已经过去了4年了,感慨时间过得很快 曾经我是一名Java开发工程师所以我的第一篇文章是跟开发相关的那个时候还是实习生被安排 一个很难的工作是完成地图实时定位以及根据GPS信息模拟海上追捕,这对刚入职的我来说很难 …...

langchain-ChatGLM源码阅读:webui.py
样式定制 使用gradio设置页面的视觉组件和交互逻辑 import gradio as gr import shutilfrom chains.local_doc_qa import LocalDocQA from configs.model_config import * import nltk import models.shared as shared from models.loader.args import parser from models.load…...

<C++>二、 类和对象
1.面向对象和面向过程 C语言是面向过程的,关注的是过程,分析出求解问题的步骤, 通过函数调用逐步解决问题。 C是基于面向对象的,关注的是对象,将一件事情拆分成不同的对象,靠对象之间的交互完成。 2. C类 C…...

【HttpRunnerManager】搭建接口自动化测试平台实战
目录 一、需要准备的知识点 二、我搭建的环境 三、搭建过程 四、访问链接 五、两个问题点 【整整200集】超超超详细的Python接口自动化测试进阶教程,真实模拟企业项目实战!! 一、需要准备的知识点 1. linux: 安装 python3、nginx 安装和…...

【adb】adb常用命令
Android Debug Bridge (adb) Android 调试桥 (adb) 是一种功能多样的命令行工具,可让您与设备进行通信。adb 命令可用于执行各种设备操作,例如安装和调试应用。adb 提供对 Unix shell(可用来在设备上运行各种命令)的访问权限。它…...

SAP 委外副产品业务
SAP 委外副产品业务 1.订单bom设置数量为负 2.采购收货时,副产品O库存增加,545 O 借:原材料 贷:委外加工-发出材料 3.从O库存调拨回本地库存,542...
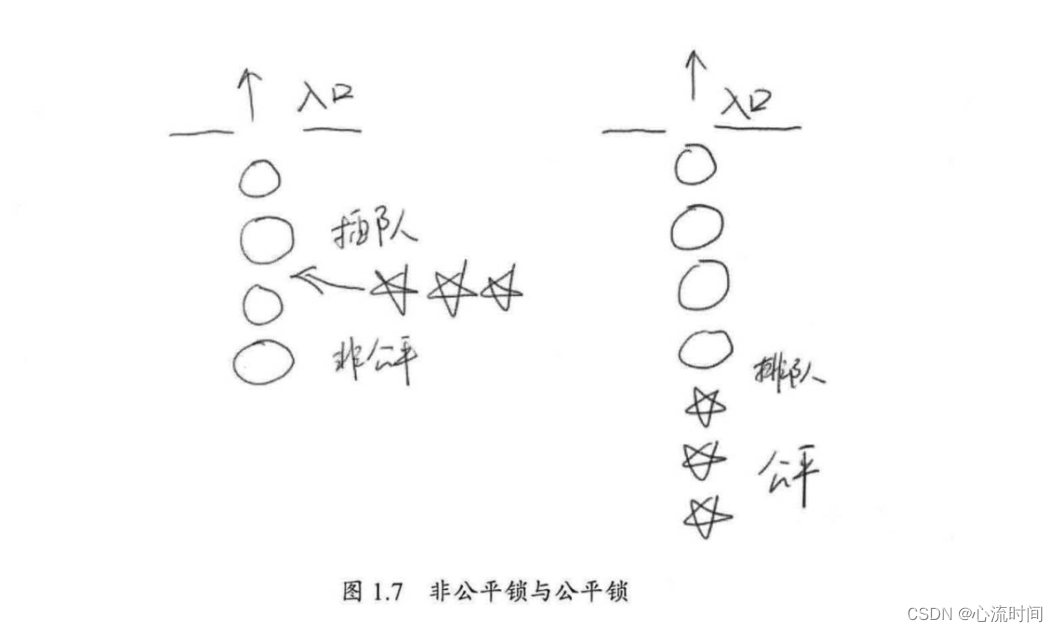
高并发编程-2. 并发级别
此文章为笔记,为阅读其他文章的感受、补充、记录、练习、汇总,非原创,感谢每个知识分享者。 原文 文章目录 阻塞无饥饿(Starvation-Free)无障碍(Obstruction-Free)无锁(Lock-Free)无等待 由于临界区的存在,多线程之间的并发必须受…...

牛客网Verilog刷题——VL47
牛客网Verilog刷题——VL47 题目答案 题目 实现4bit位宽的格雷码计数器。 电路的接口如下图所示: 输入输出描述: 信号类型输入/输出位宽描述clkwireIntput1时钟信号rst_nwireIntput1异步复位信号,低电平有效gray_outregOutput4输出格雷码计数…...
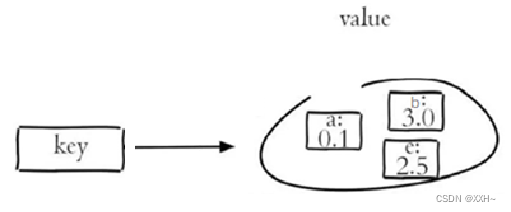
Redis以及Java使用Redis
一、Redis的安装 Redis是一个基于内存的 key-value 结构数据库。 基于内存存储,读写性能高 适合存储热点数据(热点商品、资讯、新闻) 企业应用广泛 官网:https://redis.io 中文网:https://www.redis.net.cn/ Redis…...

Apipost教程?一篇文章玩转Apipost
你是否经常遇到接口开发过程中的各种问题?或许你曾为接口测试与调试的繁琐流程而烦恼。不要担心!今天我将向大家介绍一款功能强大、易于上手的接口测试工具——Apipost,并带你深入了解如何玩转它,轻松实现接口测试与调试。 什么是…...
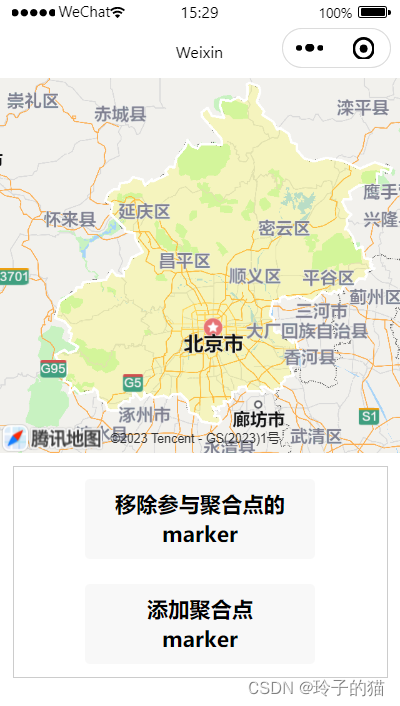
微信小程序开发学习之--地图绘制行政区域图
不知道大家有没有感觉就是在做微信小程序地图功能时刚刚接触时候真的感觉好迷茫呀,文档看不懂,资料找不到,就很难受呀,比如我现在的功能就想想绘制出一个区域的轮廓图,主要是为了显眼,效果图如下࿱…...
在windows下安装ruby使用gem
在windows下安装ruby使用gem 1.下载安装ruby环境2.使用gem3.gem换源 1.下载安装ruby环境 ruby下载地址 选择合适的版本进行下载和安装: 在安装的时候,请勾选Add Ruby executables to your PATH这个选项,添加环境变量: 安装Ruby成…...

【Ajax】笔记-设置CORS响应头实现跨域
CORS CORS CORS是什么? CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing),跨域资源共享。CORS是官方的跨域解决方案,它的特点是不需要在客户端做任何特殊的操作,完全在服务器中进行处理,支持get和post请求。跨域资源共享标准新增了一组HTTP首…...
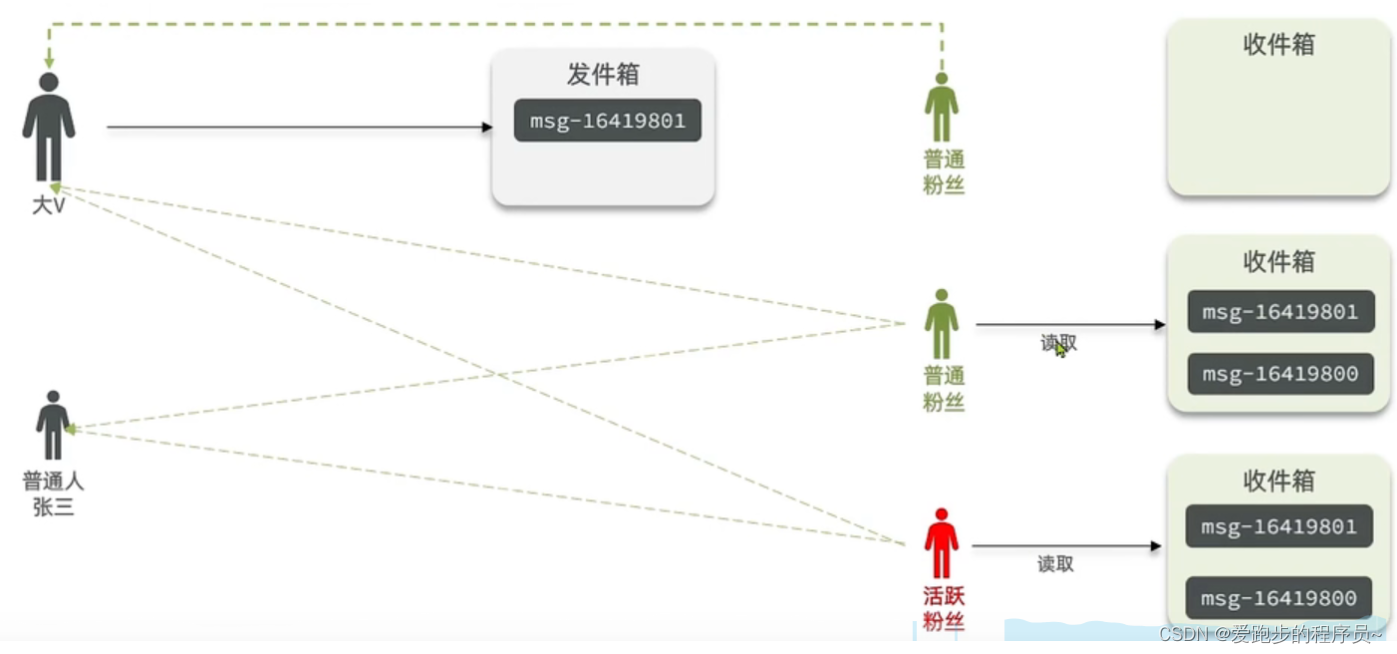
实现Feed流的三种模式:拉模式、推模式和推拉结合模式
在互联网产品中,Feed流是一种常见的功能,它可以帮助我们实时获取我们关注的用户的最新动态。Feed流的实现有多种模式,包括拉模式、推模式和推拉结合模式。在本文中,我们将详细介绍这三种模式,并通过Java代码示例来实现…...

Vue中使用Typescript及Typescript基础
准备工作 新建一个基于ts的vue项目 通过官方脚手架构建安装 # 1. 如果没有安装 Vue CLI 就先安装 npm install --global vue/cli最新的Vue CLI工具允许开发者 使用 TypeScript 集成环境 创建新项目。 只需运行vue create my-app 然后选择选项,箭头键选择 Manuall…...

MySQL数据库 【索引事务】
目录 一、概念 二、索引的优缺点 1、索引的优点 2、索引的缺陷 三、索引的使用 1、查看索引 2、创建索引 3、删除索引 四、索引底层的数据结构 1、B树 2、B树 五、索引事务 1、概念和回滚 2、事务的使用 3、事务的基本特性 4、并发会遇到的问题 (…...

源码阅读:classnames
源码阅读:classnames 源码阅读:classnames简介源码解读indexdedupebind类型声明 学习与收获 源码阅读:classnames 简介 classnames 一个简单的 JavaScript 实用程序,用于有条件地将类名连接在一起。 可以通过 npm 包管理器从 n…...

【解惑笔记】树莓派+OpenCV+YOLOv5目标检测(Pytorch框架)
【学习资料】 子豪兄的零基础树莓派教程https://github.com/TommyZihao/ZihaoTutorialOfRaspberryPi/blob/master/%E7%AC%AC2%E8%AE%B2%EF%BC%9A%E6%A0%91%E8%8E%93%E6%B4%BE%E6%96%B0%E6%89%8B%E6%97%A0%E7%97%9B%E5%BC%80%E6%9C%BA%E6%8C%87%E5%8D%97.md#%E7%83%A7%E5%BD%95…...
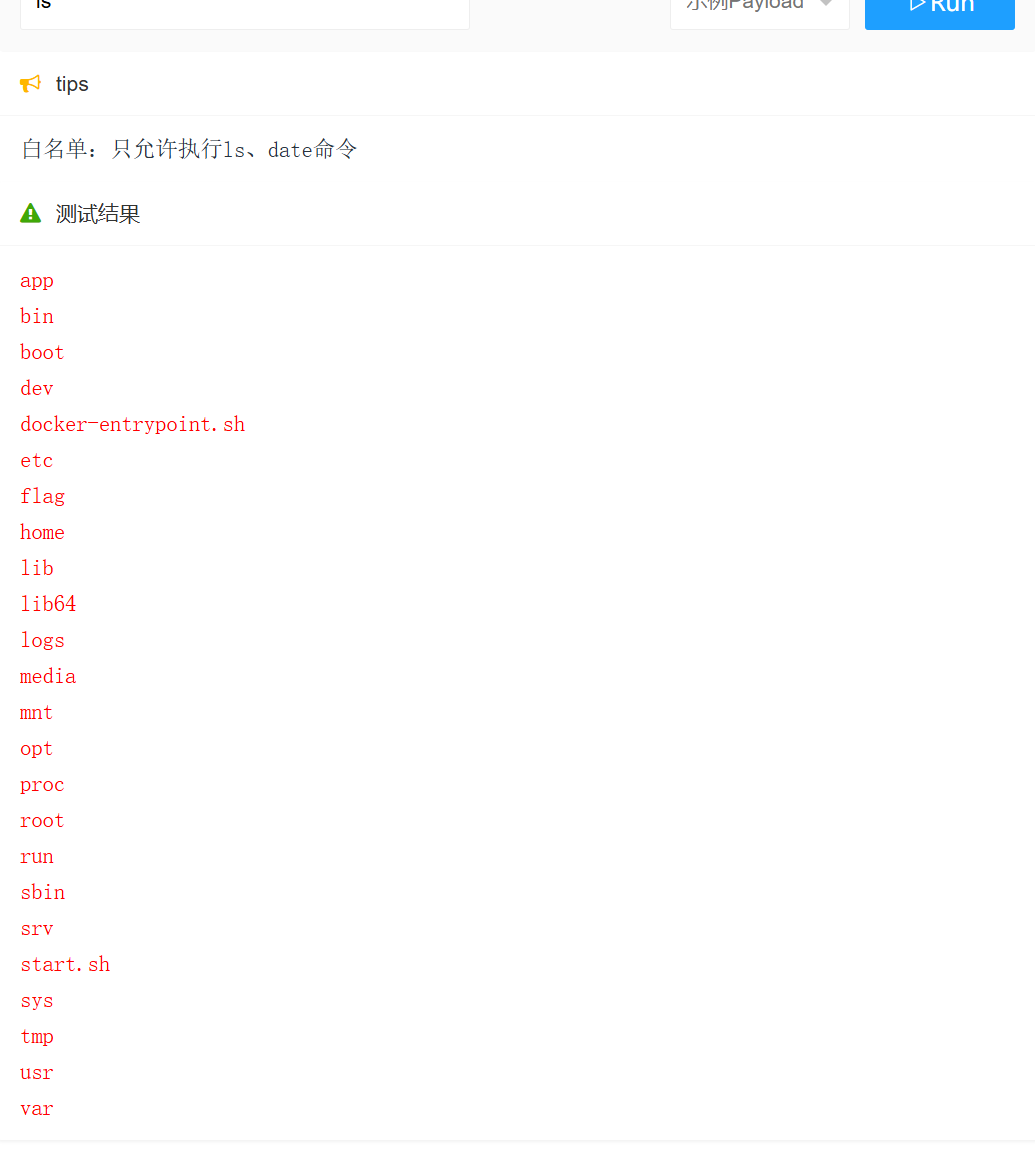
JavaSec-RCE
简介 RCE(Remote Code Execution),可以分为:命令注入(Command Injection)、代码注入(Code Injection) 代码注入 1.漏洞场景:Groovy代码注入 Groovy是一种基于JVM的动态语言,语法简洁,支持闭包、动态类型和Java互操作性,…...

Ascend NPU上适配Step-Audio模型
1 概述 1.1 简述 Step-Audio 是业界首个集语音理解与生成控制一体化的产品级开源实时语音对话系统,支持多语言对话(如 中文,英文,日语),语音情感(如 开心,悲伤)&#x…...

JDK 17 新特性
#JDK 17 新特性 /**************** 文本块 *****************/ python/scala中早就支持,不稀奇 String json “”" { “name”: “Java”, “version”: 17 } “”"; /**************** Switch 语句 -> 表达式 *****************/ 挺好的ÿ…...

使用Matplotlib创建炫酷的3D散点图:数据可视化的新维度
文章目录 基础实现代码代码解析进阶技巧1. 自定义点的大小和颜色2. 添加图例和样式美化3. 真实数据应用示例实用技巧与注意事项完整示例(带样式)应用场景在数据科学和可视化领域,三维图形能为我们提供更丰富的数据洞察。本文将手把手教你如何使用Python的Matplotlib库创建引…...

苹果AI眼镜:从“工具”到“社交姿态”的范式革命——重新定义AI交互入口的未来机会
在2025年的AI硬件浪潮中,苹果AI眼镜(Apple Glasses)正在引发一场关于“人机交互形态”的深度思考。它并非简单地替代AirPods或Apple Watch,而是开辟了一个全新的、日常可接受的AI入口。其核心价值不在于功能的堆叠,而在于如何通过形态设计打破社交壁垒,成为用户“全天佩戴…...

微服务通信安全:深入解析mTLS的原理与实践
🔥「炎码工坊」技术弹药已装填! 点击关注 → 解锁工业级干货【工具实测|项目避坑|源码燃烧指南】 一、引言:微服务时代的通信安全挑战 随着云原生和微服务架构的普及,服务间的通信安全成为系统设计的核心议题。传统的单体架构中&…...
Mac flutter环境搭建
一、下载flutter sdk 制作 Android 应用 | Flutter 中文文档 - Flutter 中文开发者网站 - Flutter 1、查看mac电脑处理器选择sdk 2、解压 unzip ~/Downloads/flutter_macos_arm64_3.32.2-stable.zip \ -d ~/development/ 3、添加环境变量 命令行打开配置环境变量文件 ope…...

[QMT量化交易小白入门]-六十二、ETF轮动中简单的评分算法如何获取历史年化收益32.7%
本专栏主要是介绍QMT的基础用法,常见函数,写策略的方法,也会分享一些量化交易的思路,大概会写100篇左右。 QMT的相关资料较少,在使用过程中不断的摸索,遇到了一些问题,记录下来和大家一起沟通,共同进步。 文章目录 相关阅读1. 策略概述2. 趋势评分模块3 代码解析4 木头…...

linux设备重启后时间与网络时间不同步怎么解决?
linux设备重启后时间与网络时间不同步怎么解决? 设备只要一重启,时间又错了/偏了,明明刚刚对时还是对的! 这在物联网、嵌入式开发环境特别常见,尤其是开发板、树莓派、rk3588 这类设备。 解决方法: 加硬件…...
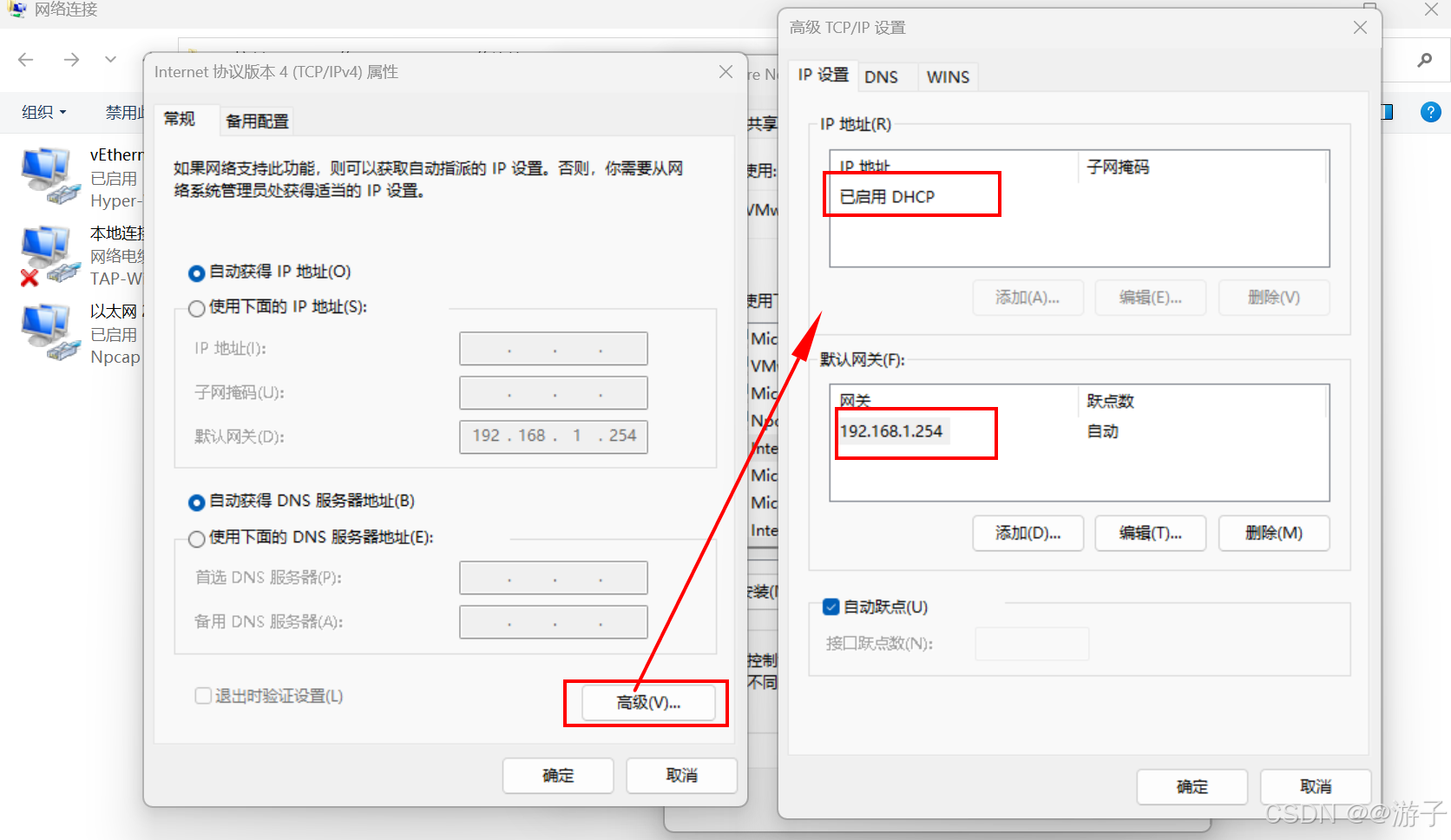
虚拟机网络不通的问题(这里以win10的问题为主,模式NAT)
当我们网关配置好了,DNS也配置好了,最后在虚拟机里还是无法访问百度的网址。 第一种情况: 我们先考虑一下,网关的IP是否和虚拟机编辑器里的IP一样不,如果不一样需要更改一下,因为我们访问百度需要从物理机…...
