26 用lsqnonlin求解最小二乘问题(matlab程序)
1.简述
函数语法
x = lsqnonlin(fun,x0)
函数用于:
解决非线性最小二乘(非线性数据拟合)问题
解决非线性最小二乘曲线拟合问题的形式
变量x的约束上下限为ub和lb,
x = lsqnonlin(fun,x0)从x0点开始,找到fun中描述的函数的最小平方和。函数fun应该返回一个向量(或数组),而不是值的平方和。(该算法隐式地计算了fun(x)元素的平方和。)
2.代码
主程序:
%% 用lsqnonlin求解最小二乘问题
clear all
x0 = [0.3 0.4]; % 初值点
[x,resnorm] = lsqnonlin(@f1211,x0) % 调用最优化函数求 x 和 平方和残差
子程序:
function [xCurrent,Resnorm,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA,JACOB] = lsqnonlin(FUN,xCurrent,LB,UB,options,varargin)
%LSQNONLIN solves non-linear least squares problems.
% LSQNONLIN attempts to solve problems of the form:
% min sum {FUN(X).^2} where X and the values returned by FUN can be
% X vectors or matrices.
%
% LSQNONLIN implements two different algorithms: trust region reflective
% and Levenberg-Marquardt. Choose one via the option Algorithm: for
% instance, to choose Levenberg-Marquardt, set
% OPTIONS = optimoptions('lsqnonlin', 'Algorithm','levenberg-marquardt'),
% and then pass OPTIONS to LSQNONLIN.
%
% X = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0) starts at the matrix X0 and finds a minimum X to
% the sum of squares of the functions in FUN. FUN accepts input X
% and returns a vector (or matrix) of function values F evaluated
% at X. NOTE: FUN should return FUN(X) and not the sum-of-squares
% sum(FUN(X).^2)). (FUN(X) is summed and squared implicitly in the
% algorithm.)
%
% X = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,LB,UB) defines a set of lower and upper bounds on
% the design variables, X, so that the solution is in the range LB <= X
% <= UB. Use empty matrices for LB and UB if no bounds exist. Set LB(i)
% = -Inf if X(i) is unbounded below; set UB(i) = Inf if X(i) is
% unbounded above.
%
% X = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,LB,UB,OPTIONS) minimizes with the default
% optimization parameters replaced by values in OPTIONS, an argument
% created with the OPTIMOPTIONS function. See OPTIMOPTIONS for details.
% Use the SpecifyObjectiveGradient option to specify that FUN also
% returns a second output argument J that is the Jacobian matrix at the
% point X. If FUN returns a vector F of m components when X has length n,
% then J is an m-by-n matrix where J(i,j) is the partial derivative of
% F(i) with respect to x(j). (Note that the Jacobian J is the transpose
% of the gradient of F.)
%
% X = LSQNONLIN(PROBLEM) solves the non-linear least squares problem
% defined in PROBLEM. PROBLEM is a structure with the function FUN in
% PROBLEM.objective, the start point in PROBLEM.x0, the lower bounds in
% PROBLEM.lb, the upper bounds in PROBLEM.ub, the options structure in
% PROBLEM.options, and solver name 'lsqnonlin' in PROBLEM.solver. Use
% this syntax to solve at the command line a problem exported from
% OPTIMTOOL.
%
% [X,RESNORM] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...) returns
% the value of the squared 2-norm of the residual at X: sum(FUN(X).^2).
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...) returns the value of the
% residual at the solution X: RESIDUAL = FUN(X).
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL,EXITFLAG] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...) returns an
% EXITFLAG that describes the exit condition. Possible values of EXITFLAG
% and the corresponding exit conditions are listed below. See the
% documentation for a complete description.
%
% 1 LSQNONLIN converged to a solution.
% 2 Change in X too small.
% 3 Change in RESNORM too small.
% 4 Computed search direction too small.
% 0 Too many function evaluations or iterations.
% -1 Stopped by output/plot function.
% -2 Bounds are inconsistent.
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...) returns a
% structure OUTPUT with the number of iterations taken in
% OUTPUT.iterations, the number of function evaluations in
% OUTPUT.funcCount, the algorithm used in OUTPUT.algorithm, the number
% of CG iterations (if used) in OUTPUT.cgiterations, the first-order
% optimality (if used) in OUTPUT.firstorderopt, and the exit message in
% OUTPUT.message.
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,X0,...)
% returns the set of Lagrangian multipliers, LAMBDA, at the solution:
% LAMBDA.lower for LB and LAMBDA.upper for UB.
%
% [X,RESNORM,RESIDUAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA,JACOBIAN] = LSQNONLIN(FUN,
% X0,...) returns the Jacobian of FUN at X.
%
% Examples
% FUN can be specified using @:
% x = lsqnonlin(@myfun,[2 3 4])
%
% where myfun is a MATLAB function such as:
%
% function F = myfun(x)
% F = sin(x);
%
% FUN can also be an anonymous function:
%
% x = lsqnonlin(@(x) sin(3*x),[1 4])
%
% If FUN is parameterized, you can use anonymous functions to capture the
% problem-dependent parameters. Suppose you want to solve the non-linear
% least squares problem given in the function myfun, which is
% parameterized by its second argument c. Here myfun is a MATLAB file
% function such as
%
% function F = myfun(x,c)
% F = [ 2*x(1) - exp(c*x(1))
% -x(1) - exp(c*x(2))
% x(1) - x(2) ];
%
% To solve the least squares problem for a specific value of c, first
% assign the value to c. Then create a one-argument anonymous function
% that captures that value of c and calls myfun with two arguments.
% Finally, pass this anonymous function to LSQNONLIN:
%
% c = -1; % define parameter first
% x = lsqnonlin(@(x) myfun(x,c),[1;1])
%
% See also OPTIMOPTIONS, LSQCURVEFIT, FSOLVE, @, INLINE.
% Copyright 1990-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
% ------------Initialization----------------
defaultopt = struct(...
'Algorithm','trust-region-reflective',...
'DerivativeCheck','off',...
'Diagnostics','off',...
'DiffMaxChange',Inf,...
'DiffMinChange',0,...
'Display','final',...
'FinDiffRelStep', [], ...
'FinDiffType','forward',...
'FunValCheck','off',...
'InitDamping', 0.01, ...
'Jacobian','off',...
'JacobMult',[],...
'JacobPattern','sparse(ones(Jrows,Jcols))',...
'MaxFunEvals',[],...
'MaxIter',400,...
'MaxPCGIter','max(1,floor(numberOfVariables/2))',...
'OutputFcn',[],...
'PlotFcns',[],...
'PrecondBandWidth',Inf,...
'ScaleProblem','none',...
'TolFun', 1e-6,...
'TolFunValue', 1e-6, ...
'TolPCG',0.1,...
'TolX',1e-6,...
'TypicalX','ones(numberOfVariables,1)',...
'UseParallel',false );
% If just 'defaults' passed in, return the default options in X
if nargin==1 && nargout <= 1 && strcmpi(FUN,'defaults')
xCurrent = defaultopt;
return
end
if nargin < 5
options = [];
if nargin < 4
UB = [];
if nargin < 3
LB = [];
end
end
end
problemInput = false;
if nargin == 1
if isa(FUN,'struct')
problemInput = true;
[FUN,xCurrent,LB,UB,options] = separateOptimStruct(FUN);
else % Single input and non-structure.
error(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InputArg'));
end
end
% No options passed. Set options directly to defaultopt after
allDefaultOpts = isempty(options);
% Prepare the options for the solver
options = prepareOptionsForSolver(options, 'lsqnonlin');
% Set options to default if no options were passed.
if allDefaultOpts
% Options are all default
options = defaultopt;
end
if nargin < 2 && ~problemInput
error(message('optim:lsqnonlin:NotEnoughInputs'))
end
% Check for non-double inputs
msg = isoptimargdbl('LSQNONLIN', {'X0','LB','UB'}, ...
xCurrent,LB, UB);
if ~isempty(msg)
error('optim:lsqnonlin:NonDoubleInput',msg);
end
caller = 'lsqnonlin';
[funfcn,mtxmpy,flags,sizes,~,xstart,lb,ub,EXITFLAG,Resnorm,FVAL,LAMBDA, ...
JACOB,OUTPUT,earlyTermination] = lsqnsetup(FUN,xCurrent,LB,UB,options,defaultopt, ...
allDefaultOpts,caller,nargout,length(varargin));
if earlyTermination
return % premature return because of problem detected in lsqnsetup()
end
xCurrent(:) = xstart; % reshape back to user shape before evaluation
% Catch any error in user objective during initial evaluation only
switch funfcn{1}
case 'fun'
try
initVals.F = feval(funfcn{3},xCurrent,varargin{:});
catch userFcn_ME
optim_ME = MException('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN', ...
getString(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN')));
userFcn_ME = addCause(userFcn_ME,optim_ME);
rethrow(userFcn_ME)
end
initVals.J = [];
case 'fungrad'
try
[initVals.F,initVals.J] = feval(funfcn{3},xCurrent,varargin{:});
catch userFcn_ME
optim_ME = MException('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN', ...
getString(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN')));
userFcn_ME = addCause(userFcn_ME,optim_ME);
rethrow(userFcn_ME)
end
case 'fun_then_grad'
try
initVals.F = feval(funfcn{3},xCurrent,varargin{:});
catch userFcn_ME
optim_ME = MException('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN', ...
getString(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN')));
userFcn_ME = addCause(userFcn_ME,optim_ME);
rethrow(userFcn_ME)
end
try
initVals.J = feval(funfcn{4},xCurrent,varargin{:});
catch userFcn_ME
optim_ME = MException('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidFUN', ...
getString(message('optim:lsqnonlin:InvalidJacobFun')));
userFcn_ME = addCause(userFcn_ME,optim_ME);
rethrow(userFcn_ME)
end
otherwise
error(message('optim:lsqnonlin:UndefCallType'))
end
% Check for non-double data typed values returned by user functions
if ~isempty( isoptimargdbl('LSQNONLIN', {'F','J'}, initVals.F, initVals.J) )
error('optim:lsqnonlin:NonDoubleFunVal',getString(message('optimlib:commonMsgs:NonDoubleFunVal','LSQNONLIN')));
end
% Flag to determine whether to look up the exit msg.
flags.makeExitMsg = logical(flags.verbosity) || nargout > 4;
[xCurrent,Resnorm,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA,JACOB] = ...
lsqncommon(funfcn,xCurrent,lb,ub,options,defaultopt,allDefaultOpts,caller,...
initVals,sizes,flags,mtxmpy,varargin{:});
3.运行结果
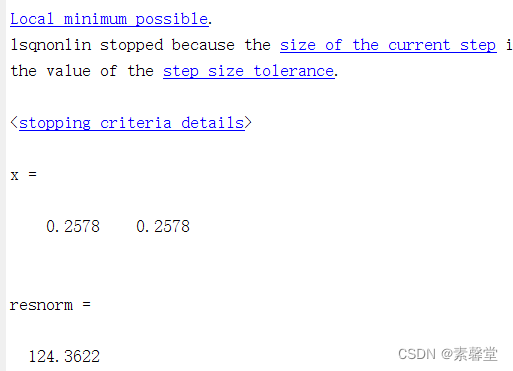
相关文章:

26 用lsqnonlin求解最小二乘问题(matlab程序)
1.简述 函数语法 x lsqnonlin(fun,x0) 函数用于: 解决非线性最小二乘(非线性数据拟合)问题 解决非线性最小二乘曲线拟合问题的形式 变量x的约束上下限为ub和lb, x lsqnonlin(fun,x0)从x0点开始,找到fun中描述的函数的最小平方和。函数fu…...

Verilog语法学习——LV6_多功能数据处理器
LV6_多功能数据处理器 题目来源于牛客网 [牛客网在线编程_Verilog篇_Verilog快速入门 (nowcoder.com)](https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj?page1&tabVerilog篇&topicId301) 题目 描述 根据指示信号select的不同,对输入信号a,b实现不同的运算。输入信号a…...

发送信息----策略模式
发送信息----策略模式 发送信息 发送信息 发送信息到手机、邮箱等,可扩展 package mainimport ("errors""fmt" )type PushContext struct {Phone, Email, Message stringTage int }type PaymentStrategy interface {Push(*P…...
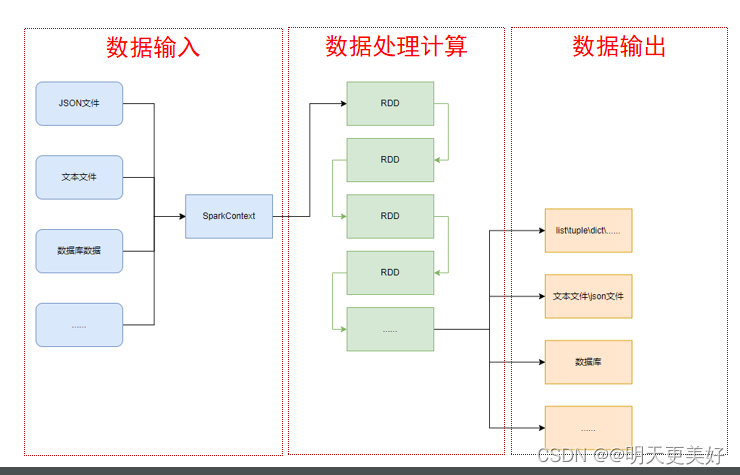
PySpark介绍与安装
Spark是什么 定义:Apache Spark是用于大规模数据(large-scala data)处理的统一(unified)分析引擎。 简单来说,Spark是一款分布式的计算框架,用于调度成百上千的服务器集群,计算TB、…...
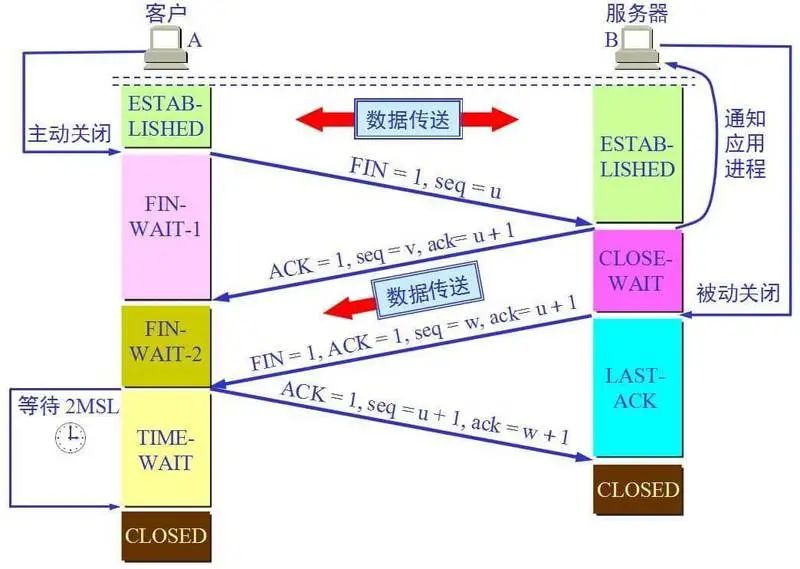
细讲TCP三次握手四次挥手(三)
TCP/IP 协议族 在互联网使用的各种协议中最重要和最著名的就是 TCP/IP 两个协议。现在人们经常提到的 TCP/IP 并不一定是单指 TCP 和 IP 这两个具体的协议,而往往是表示互联网所使用的整个 TCP/IP 协议族。 互联网协议套件(英语:Internet Pr…...

vue 组件中 data 为什么必须是函数
在Vue组件中,data选项为什么必须是函数而不是对象的原因是为了确保每个组件实例都拥有独立的数据副本。 当data选项是一个对象时,如果你有多个相同组件的实例,它们会共享同一个对象引用,这意味着一个组件的数据变化会影响到其他相…...

从零开始学python(十二)如何成为一名优秀的爬虫工程师
前言 回顾之前讲述了python语法编程 必修入门基础和网络编程,多线程/多进程/协程等方面的内容,后续讲到了数据库编程篇MySQL,Redis,MongoDB篇,和机器学习,全栈开发,数据分析前面没看的也不用往…...

为高性能计算构建,由亚马逊云科技Amazon Graviton3E驱动的最新实例正式可用
亚马逊云科技宣布两款基于最新一代自研芯片Amazon Graviton3E的新实例Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud(Amazon EC2)Hpc7g和Amazon EC2 C7gn正式可用。 其中,Hpc7g实例专为计算和网络密集型高性能计算(HPC)工作负载而构建…...
)
BUUCTF题目Crypto部分wp(持续更新)
Url编码 题目密文是%66%6c%61%67%7b%61%6e%64%20%31%3d%31%7d,根据题目名字使用python的urllib模块解码即可。flag{and 11} from urllib.parse import quote, unquotec r%66%6c%61%67%7b%61%6e%64%20%31%3d%31%7d m unquote(c, encodingutf-8) print(m)c2 quot…...
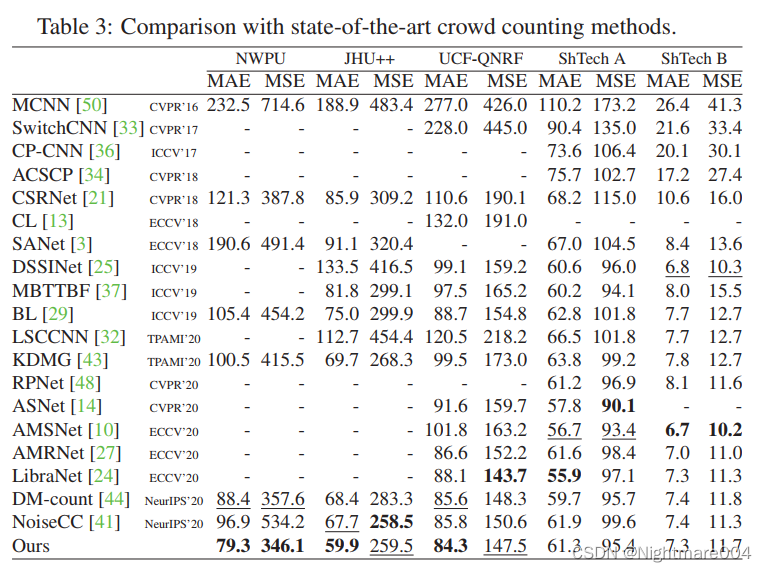
A Generalized Loss Function for Crowd Counting and Localization阅读笔记
简单来说,就是用了UOT来解决人群计数问题 代码:https://github.com/jia-wan/GeneralizedLoss-Counting-Pytorch.git 我改了一点的:https://github.com/Nightmare4214/GeneralizedLoss-Counting-Pytorch.git loss 设density map为 A { ( a…...

SocketD协议单链接双向RPC模式怎么实现
SocketD是一个基于Socket的通信框架,支持单链接双向RPC模式。在实现单链接双向RPC模式时,需要按照一定的协议进行通信,以下是一个简单的实现示例: 定义通信协议:首先,需要定义客户端和服务端之间的通信协议…...

apache poi 设置背景颜色
apache poi 设置背景颜色 要设置 Apache POI 中 HSSFCellStyle 的背景颜色,你可以按照以下步骤进行操作: 首先,创建一个 HSSFWorkbook 对象来表示你的 Excel 工作簿: HSSFWorkbook workbook new HSSFWorkbook();然后ÿ…...

Vue2-Vue3组件间通信-EventBus方式-函数封装
Vue3中采用EventBus方式进行组件间通信与Vue2有一定区别 1.创建EventBus 在Vue2中,我们可以在main.js中创建一个全局的EventBus,代码如下: // EventBus.js import Vue from vue const EventBus new Vue() export default EventBus// main.…...
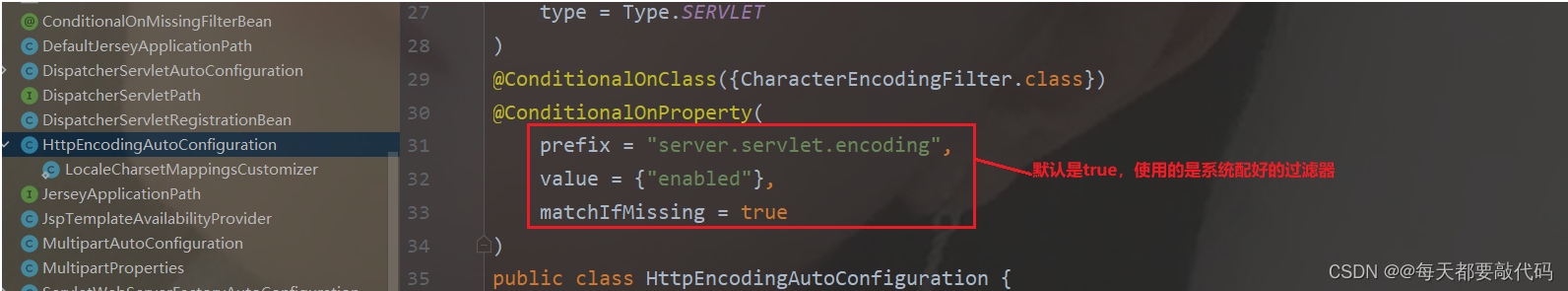
【SpringBoot】| SpringBoot 和 web组件
目录 一:SpringBoot 和 web组件 1. SpringBoot中使用拦截器(重点) 2. SpringBoot中使用Servlet 3. SpringBoot中使用过滤器(重点) 4. 字符集过滤器的应用 一:SpringBoot 和 web组件 1. SpringBoot中使…...
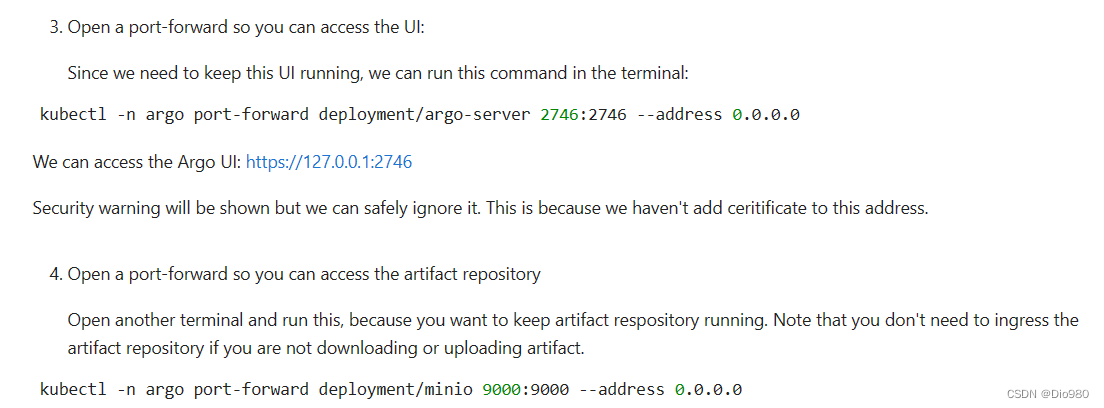
dflow工作流使用1——架构和基本概念
对于容器技术、工作流等概念完全不懂的情况下理解dflow的工作方式会很吃力,这里记录一下个人理解。 dflow涉及的基本概念 工作流的概念很好理解,即某个项目可以分为多个步骤,每个步骤可以实现独立运行,只保留输入输出接口&#x…...
python小游戏课程设计报告,python游戏课程设计报告
大家好,给大家分享一下python2048游戏课程设计报告,很多人还不知道这一点。下面详细解释一下。现在让我们来看看!...
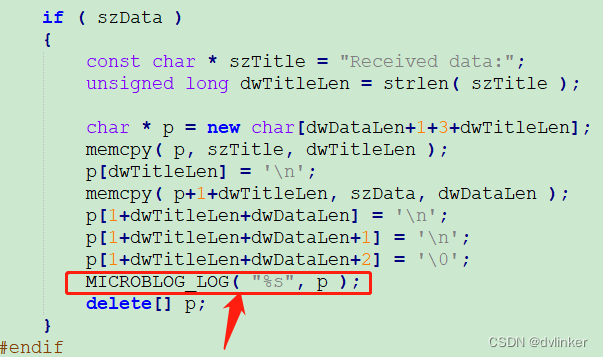
使用Windbg分析从系统应用程序日志中找到的系统自动生成的dump文件去排查问题
目录 1、尝试将Windbg附加到目标进程上进行动态调试,但Windbg并没有捕获到 2、在系统应用程序日志中找到了系统在程序发生异常时自动生成的dump文件 2.1、查看应用程序日志的入口 2.2、在应用程序日志中找到系统自动生成的dump文件 3、使用Windbg静态分析dump文…...

后端技术趋势指南|如何选择自己的技术方向
编程多条路,条条通罗马 后台大佬 后台路线都是面对后台服务器业务,比如web后台服务器,视频后台服务器,搜索后台服务器,游戏后台服务器,直播后台服务器,社交IM后台服务器等等,大部分…...

Delphi XE的原生JSONObject如何判断键值是否存在?
【问题现象】 Delphi XE的原生JSONObject,取出键值的时候如下: //json是传入的参数,里面包括"food_name"等之类的键值,没有food_type键值 procedure XXXXFunciton(json:TJSONObject) var strFoodName,strFoodType:S…...

Go Runtime功能初探
以下内容,是对 运行时 runtime的神奇用法[1] 的学习与记录 目录: 1.获取GOROOT环境变量 2.获取GO的版本号 3.获取本机CPU个数 4.设置最大可同时执行的最大CPU数 5.设置cup profile 记录的速录 6.查看cup profile 下一次堆栈跟踪数据 7.立即执行一次垃圾回收 8.给变量…...
接口测试中缓存处理策略
在接口测试中,缓存处理策略是一个关键环节,直接影响测试结果的准确性和可靠性。合理的缓存处理策略能够确保测试环境的一致性,避免因缓存数据导致的测试偏差。以下是接口测试中常见的缓存处理策略及其详细说明: 一、缓存处理的核…...
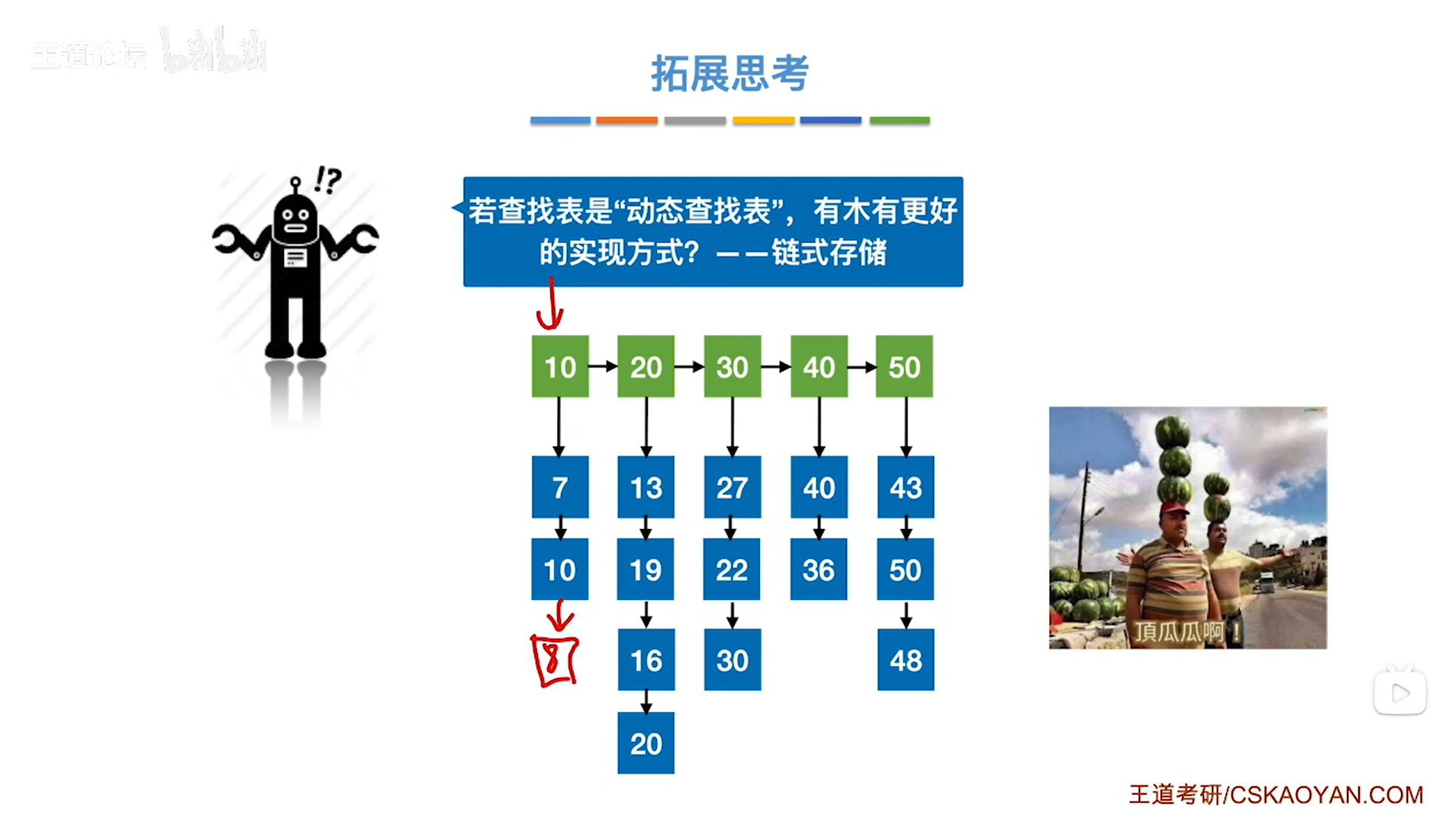
7.4.分块查找
一.分块查找的算法思想: 1.实例: 以上述图片的顺序表为例, 该顺序表的数据元素从整体来看是乱序的,但如果把这些数据元素分成一块一块的小区间, 第一个区间[0,1]索引上的数据元素都是小于等于10的, 第二…...
。】2022-5-15)
【根据当天日期输出明天的日期(需对闰年做判定)。】2022-5-15
缘由根据当天日期输出明天的日期(需对闰年做判定)。日期类型结构体如下: struct data{ int year; int month; int day;};-编程语言-CSDN问答 struct mdata{ int year; int month; int day; }mdata; int 天数(int year, int month) {switch (month){case 1: case 3:…...

ubuntu搭建nfs服务centos挂载访问
在Ubuntu上设置NFS服务器 在Ubuntu上,你可以使用apt包管理器来安装NFS服务器。打开终端并运行: sudo apt update sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server创建共享目录 创建一个目录用于共享,例如/shared: sudo mkdir /shared sud…...
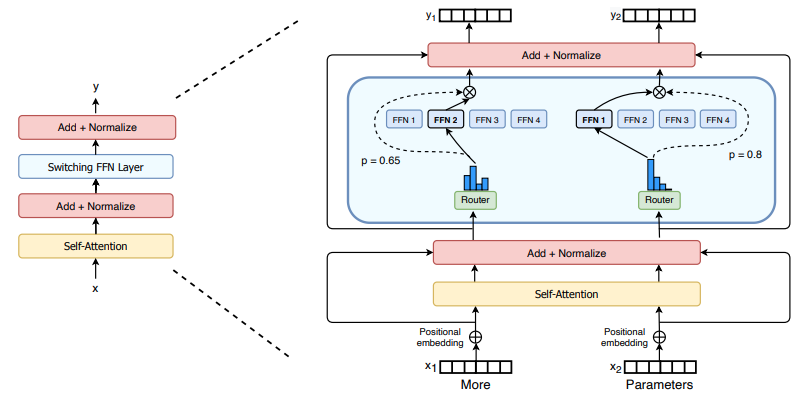
(二)TensorRT-LLM | 模型导出(v0.20.0rc3)
0. 概述 上一节 对安装和使用有个基本介绍。根据这个 issue 的描述,后续 TensorRT-LLM 团队可能更专注于更新和维护 pytorch backend。但 tensorrt backend 作为先前一直开发的工作,其中包含了大量可以学习的地方。本文主要看看它导出模型的部分&#x…...

条件运算符
C中的三目运算符(也称条件运算符,英文:ternary operator)是一种简洁的条件选择语句,语法如下: 条件表达式 ? 表达式1 : 表达式2• 如果“条件表达式”为true,则整个表达式的结果为“表达式1”…...

基于数字孪生的水厂可视化平台建设:架构与实践
分享大纲: 1、数字孪生水厂可视化平台建设背景 2、数字孪生水厂可视化平台建设架构 3、数字孪生水厂可视化平台建设成效 近几年,数字孪生水厂的建设开展的如火如荼。作为提升水厂管理效率、优化资源的调度手段,基于数字孪生的水厂可视化平台的…...

高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景
高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景 高危文件识别旨在检测可能导致安全威胁的文件,如包含恶意代码、敏感数据或欺诈内容的文档,在企业协同办公环境中(如Teams、Google Workspace)尤为重要。结合大模型技术&…...

【git】把本地更改提交远程新分支feature_g
创建并切换新分支 git checkout -b feature_g 添加并提交更改 git add . git commit -m “实现图片上传功能” 推送到远程 git push -u origin feature_g...

Java面试专项一-准备篇
一、企业简历筛选规则 一般企业的简历筛选流程:首先由HR先筛选一部分简历后,在将简历给到对应的项目负责人后再进行下一步的操作。 HR如何筛选简历 例如:Boss直聘(招聘方平台) 直接按照条件进行筛选 例如:…...
