【ConcurrentHashMap1.7源码】十分钟带你深入ConcurrentHashMap并发解析
ConcurrentHashMap1.7源码
四个核心要点
- 初始化
- PUT
- 扩容
- GET
Unsafe
初始化
五个构造方法
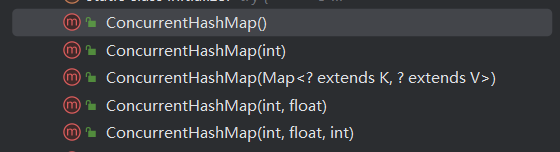
/*** Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16).*/public ConcurrentHashMap() {}/*** Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size* accommodating the specified number of elements without the need* to dynamically resize.** @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal* sizing to accommodate this many elements.* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of* elements is negative*/public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));this.sizeCtl = cap;}/*** Creates a new map with the same mappings as the given map.** @param m the map*/public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;putAll(m);}/*** Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}) and* initial table density ({@code loadFactor}).** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,* given the specified load factor.* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for* establishing the initial table size* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of* elements is negative or the load factor is nonpositive** @since 1.6*/public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);}/*** Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}), table* density ({@code loadFactor}), and number of concurrently* updating threads ({@code concurrencyLevel}).** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,* given the specified load factor.* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for* establishing the initial table size* @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently* updating threads. The implementation may use this value as* a sizing hint.* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is* negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are* nonpositive*/public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many binsinitialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threadslong size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);this.sizeCtl = cap;}
无参构造方法
/*** Creates a new, empty map with a default initial capacity (16),* load factor (0.75) and concurrencyLevel (16).*/public ConcurrentHashMap() {this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);}
四个参数
- initialCapacity-初始容量
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
- loadFactor-加载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
- concurrencyLevel-并发等级(最大支持线程)
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
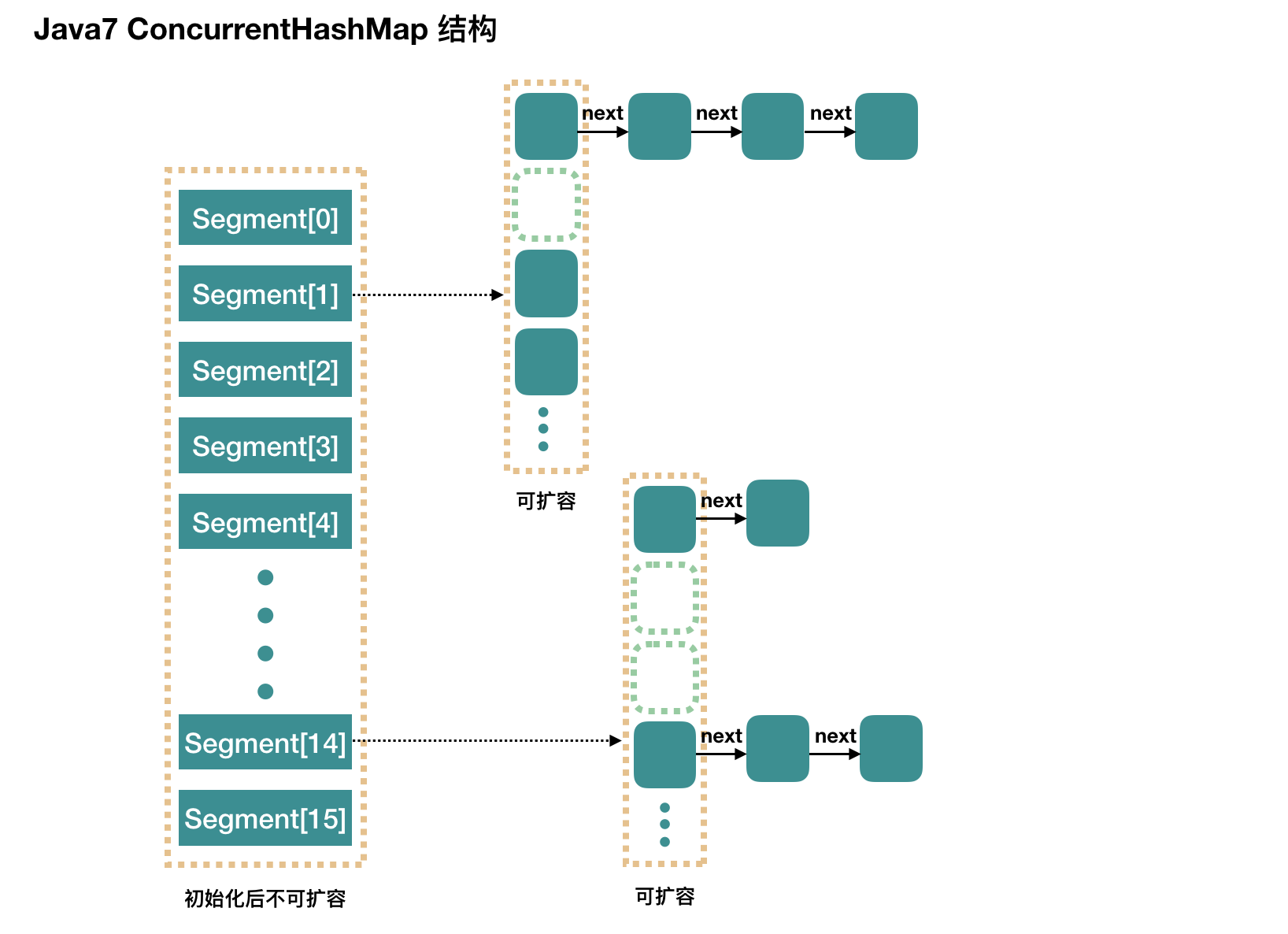
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {// 参数校验if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS)concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS;// Find power-of-two sizes best matching argumentsint sshift = 0;// 关键int ssize = 1;// 1 < 16 2 < 16 4 < 16 8 < 16 最后ssize=16// 假如传入concurrencyLevel = 9 ,ssize = 16// 也就是找一个大于concurrencyLevel的2次幂数给ssizewhile (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {++sshift;ssize <<= 1;}this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;// 以默认值为例c=16/16=1int c = initialCapacity / ssize;// 如果是initialCapacity=9,concurrencyLevel=8// 下面是向上取整,要确保要这么多容量if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)++c;// static final int MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY = 2;// cap = 2,所以初始化的时候cap=2int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY;// 保证cap容量是2的幂次方数while (cap < c)cap <<= 1;// create segments and segments[0]Segment<K, V> s0 =new Segment<K, V>(loadFactor, (int) (cap * loadFactor),(HashEntry<K, V>[]) new HashEntry[cap]);Segment<K, V>[] ss = (Segment<K, V>[]) new Segment[ssize];// 默认先在Segment数组里放了一个segments[0],里面是一个new HashEntry[cap]// 后面会以这个默认进行扩容UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0]this.segments = ss;}
注意:默认初始化的时候,HashEntry数组默认是16x2=32个,而不是16个
Segment
继承了ReentrantLock,方便lock
static final class Segment<K, V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;/*** The maximum number of times to tryLock in a prescan before* possibly blocking on acquire in preparation for a locked* segment operation. On multiprocessors, using a bounded* number of retries maintains cache acquired while locating* nodes.*/static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES =Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1;/*** The per-segment table. Elements are accessed via* entryAt/setEntryAt providing volatile semantics.*/transient volatile HashEntry<K, V>[] table;/*** The number of elements. Accessed only either within locks* or among other volatile reads that maintain visibility.*/transient int count;/*** The total number of mutative operations in this segment.* Even though this may overflows 32 bits, it provides* sufficient accuracy for stability checks in CHM isEmpty()* and size() methods. Accessed only either within locks or* among other volatile reads that maintain visibility.*/transient int modCount;/*** The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold.* (The value of this field is always <tt>(int)(capacity ** loadFactor)</tt>.)*/transient int threshold;/*** The load factor for the hash table. Even though this value* is same for all segments, it is replicated to avoid needing* links to outer object.** @serial*/final float loadFactor;Segment(float lf, int threshold, HashEntry<K, V>[] tab) {this.loadFactor = lf;this.threshold = threshold;this.table = tab;}
PUT方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public V put(K key, V value) {Segment<K, V> s;if (value == null)throw new NullPointerException();// 计算hash值int hash = hash(key);// segmentMask = ssize - 1// 下面算segment的下标int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;// 判断segment是不是nullif ((s = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegments = ensureSegment(j);// segment不为空直接putreturn s.put(key, hash, value, false);}
创建segment
只需要一个线程来创建segment,另一个线程也是得到同一个Segment
/*** Returns the segment for the given index, creating it and* recording in segment table (via CAS) if not already present.** @param k the index* @return the segment*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private Segment<K, V> ensureSegment(int k) {final Segment<K, V>[] ss = this.segments;long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; // raw offsetSegment<K, V> seg;// 只有一个线程拿到ss是null,一个线程进入ifif ((seg = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) {// 原型模式Segment<K, V> proto = ss[0]; // use segment 0 as prototypeint cap = proto.table.length;float lf = proto.loadFactor;// 0.75x16 = 12int threshold = (int) (cap * lf);HashEntry<K, V>[] tab = (HashEntry<K, V>[]) new HashEntry[cap];// DCLif ((seg = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))== null) { // recheck// 创建Segment对象Segment<K, V> s = new Segment<K, V>(lf, threshold, tab);while ((seg = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))== null) {// 把新segment放入数组if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null, seg = s))break;}}}return seg;}
PUT
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {// 两个线程进来,tryLock(),拿到锁就可以走下面流程放入元素,没有的话就可以走scanAndLockForPut流程// 在等待锁的过程中可以执行相关代码,也就是自旋// lock是阻塞,trylock是非阻塞HashEntry<K, V> node = tryLock() ? null :scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);V oldValue;try {HashEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;// 计算HashEntry tab的下标int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;HashEntry<K, V> first = entryAt(tab, index);// 以下就是hashmap的代码for (HashEntry<K, V> e = first; ; ) {if (e != null) {K k;if ((k = e.key) == key ||(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {oldValue = e.value;if (!onlyIfAbsent) {e.value = value;++modCount;}break;}e = e.next;} else {if (node != null)node.setNext(first);elsenode = new HashEntry<K, V>(hash, key, value, first);int c = count + 1;if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)rehash(node);elsesetEntryAt(tab, index, node);++modCount;count = c;oldValue = null;break;}}} finally {unlock();}return oldValue;}
scanAndLockForPut
保证一定要Segment加上锁
/*** Scans for a node containing given key while trying to* acquire lock, creating and returning one if not found. Upon* return, guarantees that lock is held. UNlike in most* methods, calls to method equals are not screened: Since* traversal speed doesn't matter, we might as well help warm* up the associated code and accesses as well.** @return a new node if key not found, else null*/private HashEntry<K, V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) {HashEntry<K, V> first = entryForHash(this, hash);HashEntry<K, V> e = first;HashEntry<K, V> node = null;int retries = -1; // negative while locating node// 自旋锁,等待的过程可以执行其他流程// 下面可以创建HashEntry node对象while (!tryLock()) {HashEntry<K, V> f; // to recheck first belowif (retries < 0) {// e 是头节点,如果e==null,表示遍历到链表最后if (e == null) {if (node == null) // speculatively create nodenode = new HashEntry<K, V>(hash, key, value, null);retries = 0;// 如果key已经存在,则不创建node对象} else if (key.equals(e.key))retries = 0;else// 相当于遍历链表e = e.next;// static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES =// Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1;} else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {// 超过阈值就会保证加上锁lock();break;// retries & 1 保证偶数次重试的时候,判断头节点是不是一样的// 如果头节点不一样表示头节点被修改,插入了元素} else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&(f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {// 保证是最新的头节点e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changedretries = -1;}}return node;}
GET方法
/*** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.** <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)},* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)** @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null*/public V get(Object key) {Segment<K, V> s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overheadHashEntry<K, V>[] tab;int h = hash(key);long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;if ((s = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&(tab = s.table) != null) {for (HashEntry<K, V> e = (HashEntry<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long) (((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);e != null; e = e.next) {K k;if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))return e.value;}}return null;}
Size方法
本质上是遍历每一个segment,加上所有的node节点
public int size() {// Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to// continuous async changes in table, resort to locking.final Segment<K, V>[] segments = this.segments;int size;boolean overflow; // true if size overflows 32 bitslong sum; // sum of modCountslong last = 0L; // previous sumint retries = -1; // first iteration isn't retrytry {for (; ; ) {if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation}sum = 0L;size = 0;overflow = false;// 遍历每一个segmentsfor (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) {Segment<K, V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j);if (seg != null) {sum += seg.modCount;int c = seg.count;if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0)overflow = true;}}if (sum == last)break;last = sum;}} finally {if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)segmentAt(segments, j).unlock();}}return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size;}
总结
ConcurrentHashMap采用了分段锁的设计,当需要put元素的时候,并不是对整个hashmap进行加锁,而是先通过hashcode来知道要放在哪一个分段中,然后对这个分段进行加锁,所以当多线程put的时候,只要不是放在一个分段中,就没有锁竞争,实现真正的并行插入。相比于对整个Map加锁的设计,分段锁大大的提高了高并发环境下的处理能力。但同时,由于不是对整个Map加锁,导致一些需要扫描整个Map的方法(如size(), containsValue())需要使用特殊的实现,另外一些方法(如clear())甚至放弃了对一致性的要求(ConcurrentHashMap是弱一致性的)。
假如new ConcurrentHashMap(32, 0.75, 16)就是新建了一个ConcurrentHashMap,他的容量是32,分段锁的个数是16,也就是每个Segment里面HashEntry[]数组的长度是2。但是new ConcurrentHashMap()时,每个Segment里面HashEntry[]数组的长度也是2,因为ConcurrentHashMap规定了Segment数组中HashEntry数组的长度是2。
相关文章:

【ConcurrentHashMap1.7源码】十分钟带你深入ConcurrentHashMap并发解析
ConcurrentHashMap1.7源码 四个核心要点 初始化PUT扩容GET Unsafe 初始化 五个构造方法 /*** Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16).*/public ConcurrentHashMap() {}/*** Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size* accommodati…...
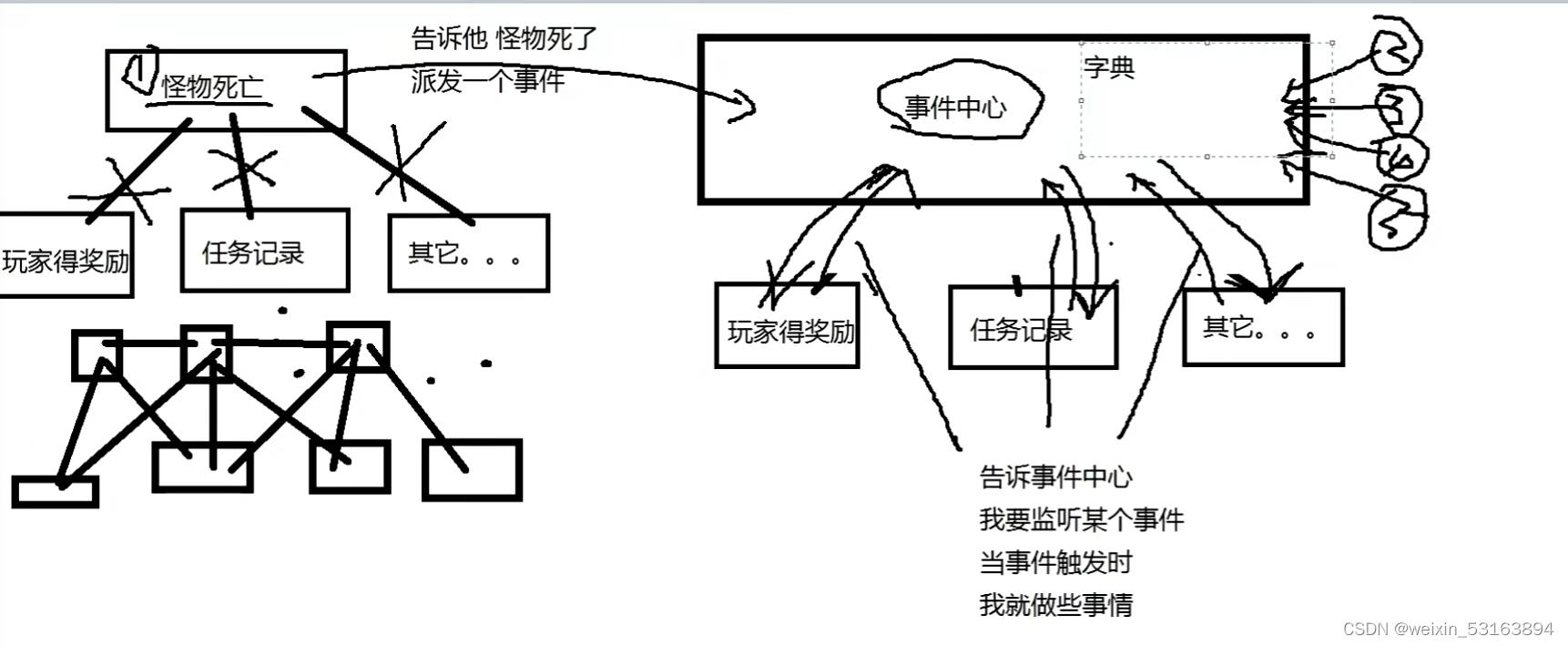
程序框架-事件中心模块-观察者模式
一、观察者模式 1.1 观察者模式定义 意图: 定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变是,所有依赖于它的对象都能得到通知并自动更新。 适用性: 当一个对象状态的改变需要改变其他对象, 或实际对…...

通过AOP的ProceedingJoinPoint获取方法信息
文章目录 ProceedingJoinPoint用法 ProceedingJoinPoint用法 获得切点对应的方法(Method) 本处Method指的是java.lang.reflect.Method 若切入点表达式是方法,则获得的是切入点方法的信息。若切入点表达式是注解,则获得的是使用了…...
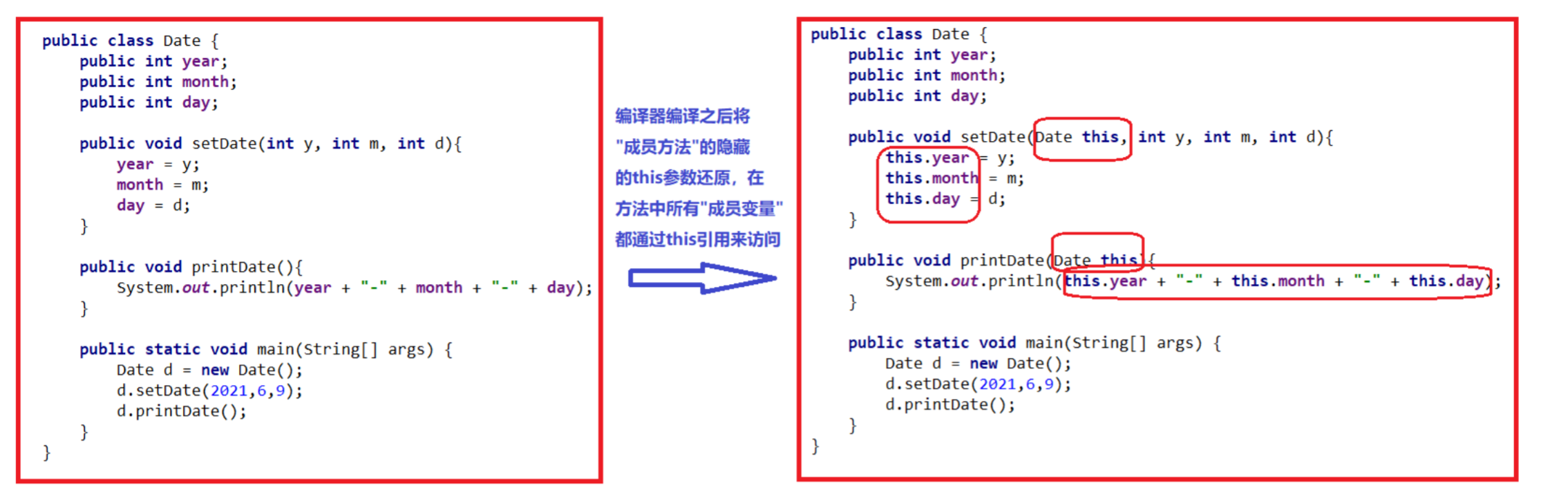
【JavaSE】初步认识类和对象
【本节目标】 1. 掌握类的定义方式以及对象的实例化 2. 掌握类中的成员变量和成员方法的使用 3. 掌握对象的整个初始化过程 目录 1. 面向对象的初步认知 2. 类定义和使用 3. 类的实例化 4. this引用 1. 面向对象的初步认知 1.1 什么是面向对象 Java是一门纯面向对象的语…...
)
python中的matplotlib画饼图(数据分析与可视化)
直接开始 1、先安装pandas和matplotlib pip install pandas pip install matplotlib2、然后在py文件中导入 import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt3、然后直接写代码 import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as pltpd.set_option("max_columns&…...

用Rust实现23种设计模式之 职责链模式
关注我,学习Rust不迷路!! 优点 解耦:职责链模式将请求发送者和接收者解耦,使得多个对象都有机会处理请求,而不是将请求的发送者和接收者紧密耦合在一起。灵活性:可以动态地改变或扩展处理请求…...

进销存管理中的技术创新和数字化转型
在进销存管理中,技术创新和数字化转型可以通过以下具体的应用案例来实现: 自动化仓储系统:利用自动化技术和机器人系统来管理仓库操作,包括货物的装卸、分拣和存储。这可以提高仓库的运作效率,减少人力成本࿰…...

与“云”共舞,联想凌拓的新科技与新突破
伴随着数字经济的高速发展,IT信息技术在数字中国建设中起到的驱动和支撑作用也愈发凸显。特别是2023年人工智能和ChatGPT在全球的持续火爆,更是为整个IT产业注入了澎湃动力。那么面对日新月异的IT信息技术,再结合疫情之后截然不同的经济环境和…...
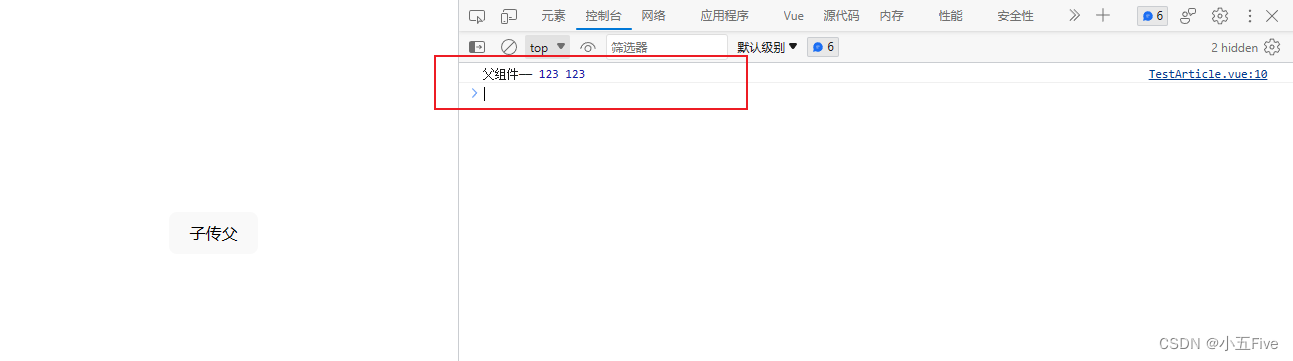
【超细节】Vue3组件事件怎么声明,defineEmits与emit
目录 前言 一、基本语法 1. 子组件触发 2. 父组件监听 二、 事件参数 1. 传值 2. 接收值 三、 事件校验 四、注意事项 前言 组件事件是 Vue 组件之间进行通信的一种方式。它允许一个组件触发一个自定义事件,并且其他组件可以监听并响应这个事件。 一、基本…...

java Selenium 实现简单的网页操作
官方文档:入门指南 | Selenium Selenium是一个用于Web应用测试的工具。Selenium测试直接运行在浏览器中,就像真正的用户在操作一样。 所以使用这个前端测试话工具,可以自动化做很多事情,比如自动化抓取网页内容,俗称网…...

(数据库系统概论|王珊)第一章绪论-第一节:数据库系统概论
目录 一:四大基本概念 (1)数据(Data) (2)数据库(DataBase,DB) (3)数据库管理系统(DataBase Management System,DBMS) (4)数据库系统(Database System,DBS…...
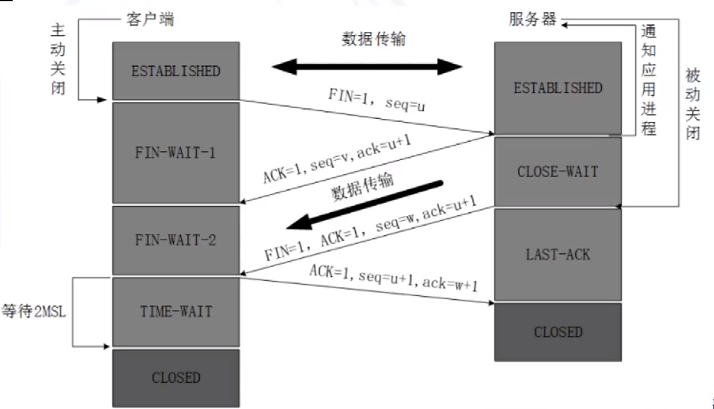
深入理解TCP三次握手:连接可靠性与安全风险
目录 导言TCP简介和工作原理的回顾TCP三次握手的目的和步骤TCP三次握手过程中可能出现的问题和安全风险为什么TCP三次握手是必要的?是否可以增加或减少三次握手的次数?TCP四次挥手与三次握手的异同点 导言 在网络通信中,TCP(Tra…...

基于人工智能的智能矿山解决方案
什么是智能矿山? 智能矿山是一种运用先进技术和智能化系统来管理和监控矿山运营的概念。它利用传感器、无线通信、数据分析和人工智能等技术,实现对矿山内部各个环节的实时监测、自动化控制和智能决策,从而提高矿山的效率、安全性和可持续性。…...
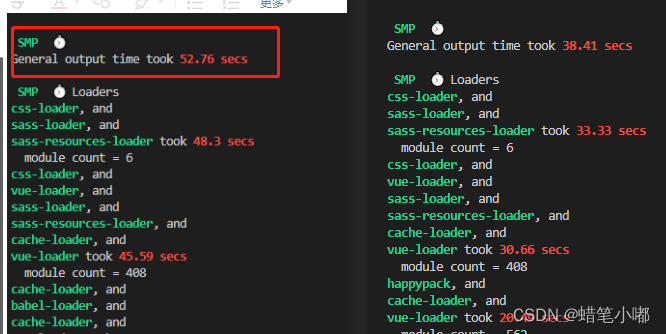
vue-cli3项目优化
首先添加两个量化的插件,方便对项目目前的情况进行分析: 1.添加speed-measure-webpack-plugin插件 —量化的指标可以看出前后对比 使用步骤: 安装speed-measure-webpack-plugin依赖 npm install speed-measure-webpack-plugin -D配置vue.c…...
Windows环境下VSCode安装PlatformIO Cero报错ERROR: HTTP error 403 while getting
安装PlatformIO插件成功,初始化失败 错误信息判断问题尝试访问https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/platformio/成功点击文件后报错如下: 解决问题- 换源 ( Windows下有两个地方需要更改)cmd命令行Pip文件 总结:…...
git bash 安装sdkadmin
1.下载相关安装包,复制到git 安装目录 D:\software\Git\mingw64\bin 2. 运行 curl -s "https://get.sdkman.io" | bash...

如何在IEEE论文中添加伪代码pseudocode
前言 记录写论文过程中需要重复用的一些小技巧: 一、如何在IEEE论文中添加伪代码pseudocode pseudocode是经常需要在论文中使用的流程图,掌握如何写伪代码图是必须得。 1.引入库 代码如下(示例): # 头部添加不可少的…...

【css】css隐藏元素
display:none:可以隐藏元素。该元素将被隐藏,并且页面将显示为好像该元素不在其中。visibility:hidden: 可以隐藏元素。但是,该元素仍将占用与之前相同的空间。元素将被隐藏,但仍会影响布局。 代码: <!…...

JUC并发编程(二)ForkJoinPool、Future、CompletableFuture、CAS
文章目录 ForkJoin分治工作窃取ForkJoinPool与ThreadPoolExecutor使用案例不带返回值的计算--RecursiveAction带返回值的计算--RecursiveTask Future 异步回调烧水案例join实现FutureTask实现 CompletableFuture为什么叫CompletableFuture?创建异步任务supplyAsyncrunAsync获取…...

大数据课程F2——HIve的安装操作
文章作者邮箱:yugongshiye@sina.cn 地址:广东惠州 ▲ 本章节目的 ⚪ 了解HIve的安装概念; ⚪ 掌握HIve安装步骤和Linux常用命令; ⚪ 掌握HIve安装的连接池jar包冲突和日志打印jar包冲突; ⚪ 掌握HIve安装的Hadoop安装配置; ⚪ 掌握HIve安装的JDK安装配…...

C++:std::is_convertible
C++标志库中提供is_convertible,可以测试一种类型是否可以转换为另一只类型: template <class From, class To> struct is_convertible; 使用举例: #include <iostream> #include <string>using namespace std;struct A { }; struct B : A { };int main…...

逻辑回归:给不确定性划界的分类大师
想象你是一名医生。面对患者的检查报告(肿瘤大小、血液指标),你需要做出一个**决定性判断**:恶性还是良性?这种“非黑即白”的抉择,正是**逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)** 的战场&a…...

蓝桥杯 2024 15届国赛 A组 儿童节快乐
P10576 [蓝桥杯 2024 国 A] 儿童节快乐 题目描述 五彩斑斓的气球在蓝天下悠然飘荡,轻快的音乐在耳边持续回荡,小朋友们手牵着手一同畅快欢笑。在这样一片安乐祥和的氛围下,六一来了。 今天是六一儿童节,小蓝老师为了让大家在节…...

解决本地部署 SmolVLM2 大语言模型运行 flash-attn 报错
出现的问题 安装 flash-attn 会一直卡在 build 那一步或者运行报错 解决办法 是因为你安装的 flash-attn 版本没有对应上,所以报错,到 https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases 下载对应版本,cu、torch、cp 的版本一定要对…...

大模型多显卡多服务器并行计算方法与实践指南
一、分布式训练概述 大规模语言模型的训练通常需要分布式计算技术,以解决单机资源不足的问题。分布式训练主要分为两种模式: 数据并行:将数据分片到不同设备,每个设备拥有完整的模型副本 模型并行:将模型分割到不同设备,每个设备处理部分模型计算 现代大模型训练通常结合…...

拉力测试cuda pytorch 把 4070显卡拉满
import torch import timedef stress_test_gpu(matrix_size16384, duration300):"""对GPU进行压力测试,通过持续的矩阵乘法来最大化GPU利用率参数:matrix_size: 矩阵维度大小,增大可提高计算复杂度duration: 测试持续时间(秒&…...

UR 协作机器人「三剑客」:精密轻量担当(UR7e)、全能协作主力(UR12e)、重型任务专家(UR15)
UR协作机器人正以其卓越性能在现代制造业自动化中扮演重要角色。UR7e、UR12e和UR15通过创新技术和精准设计满足了不同行业的多样化需求。其中,UR15以其速度、精度及人工智能准备能力成为自动化领域的重要突破。UR7e和UR12e则在负载规格和市场定位上不断优化…...
【分享】推荐一些办公小工具
1、PDF 在线转换 https://smallpdf.com/cn/pdf-tools 推荐理由:大部分的转换软件需要收费,要么功能不齐全,而开会员又用不了几次浪费钱,借用别人的又不安全。 这个网站它不需要登录或下载安装。而且提供的免费功能就能满足日常…...
的使用)
Go 并发编程基础:通道(Channel)的使用
在 Go 中,Channel 是 Goroutine 之间通信的核心机制。它提供了一个线程安全的通信方式,用于在多个 Goroutine 之间传递数据,从而实现高效的并发编程。 本章将介绍 Channel 的基本概念、用法、缓冲、关闭机制以及 select 的使用。 一、Channel…...
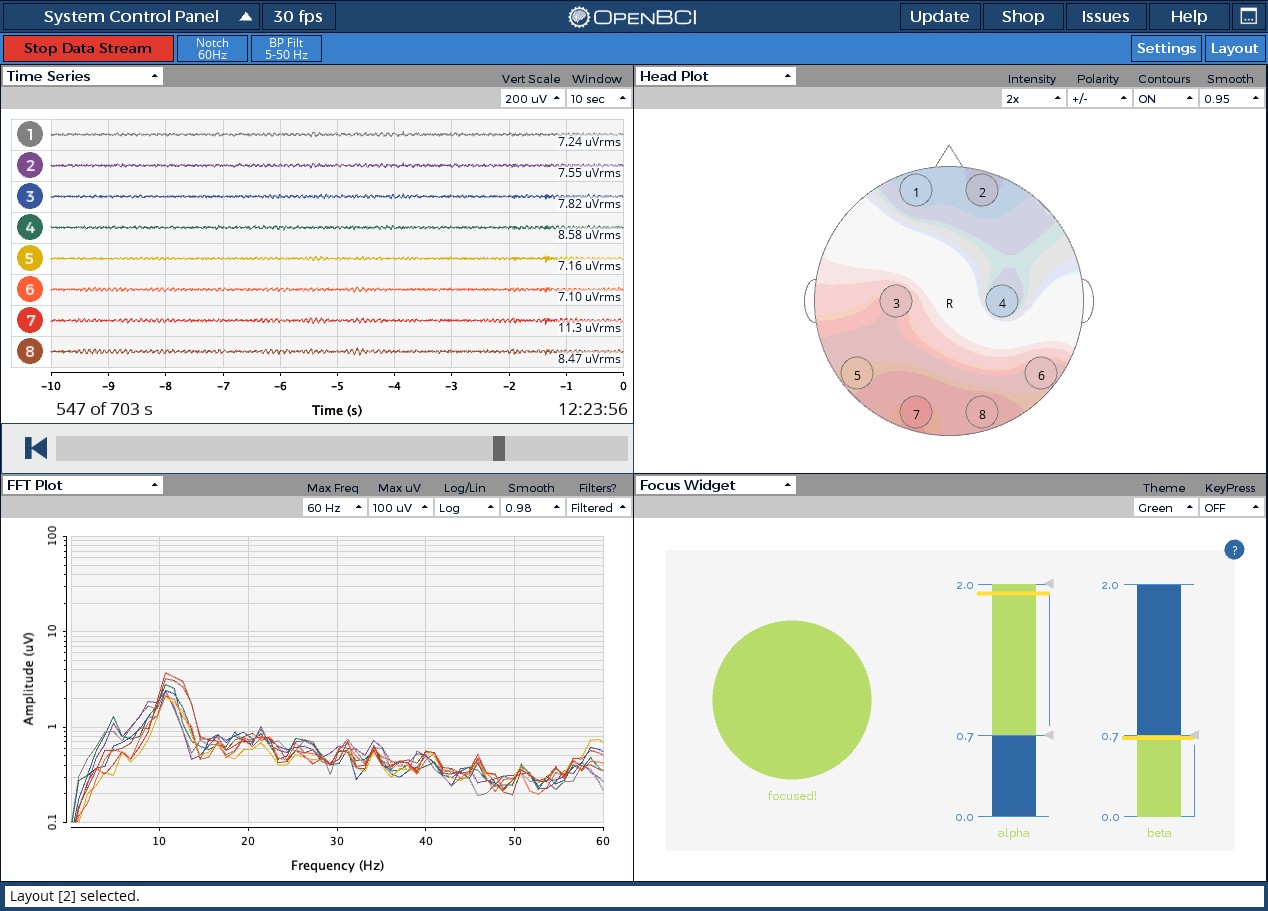
脑机新手指南(七):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(上)
一、OpenBCI_GUI 项目概述 (一)项目背景与目标 OpenBCI 是一个开源的脑电信号采集硬件平台,其配套的 OpenBCI_GUI 则是专为该硬件设计的图形化界面工具。对于研究人员、开发者和学生而言,首次接触 OpenBCI 设备时,往…...