heap pwn 入门大全 - 1:glibc heap机制与源码阅读(上)
本文为笔者学习heap pwn时,学习阅读glibc ptmalloc2源码时的笔记,与各位分享。可能存在思维跳跃或错误之处,敬请见谅,欢迎在评论中指出。本文也借用了部分外网和其他前辈的素材图片,向各位表示诚挚的感谢!如有侵权,请联系笔者删除。
glibc的堆管理器为ptmalloc2
heap management
堆管理器向kernel申请批量内存,自己管理,堆的内存管理空间称为 arena,堆管理器与用户的内存交易发生在arena中
operations
- malloc
n=0时,返回允许的堆的最小内存块n<0时,size_t 为无符号数,通常无法分配这么大的内存,返回ERRNOMEM
- free
- p 为空指针:无操作
- p 已经释放后,double free
- 当释放较大内存块后,manager通过系统调用将内存直接还给系统
syscalls
-
(s)brk
-
堆的内存布局由两个指针控制:
start_brk,brk,分别为开始和结尾

-
mmap
-
malloc 使用mmap创建独立的匿名映射段,可以申请全0内存,且此内存仅被调用进程所调用
-
void *mmap(void addr[.length], size_t length, int prot, int flags,int fd, off_t offset); -
Flags -
MAP_ANONYMOUS: 该区域为匿名映射,不与任何文件关联,内存赋初值为0 -
当单次申请超过128KB内存,并且arena中没有剩余空间,则直接调用mmap申请内存,而不是brk
-
多线程支持
与之前实现中多线程共享一个堆不同,ptmalloc2中,所有的线程共享多个堆,在堆申请、释放时,不需要等待其他线程退出临界区 critical area
使用pthread多线程,自线程申请的堆单独建立,

上图为thread malloc(0x32000)后的vmmap情况,其中:
-
heap: 为main_arena空间,为初始化大小
0x21000 -
vmmap堆创建时,总共会申请得到1MB内存(
0x7ffff00- ~ 0x7ffff40-),其中仅有132KB(0x7ffff0000000 ~ 0x7ffff0021000=0x21000B)内存可以作为堆内存进行读写,这是堆默认初始大小,当malloc大于0x20000,会直接使用mmap而不是在堆中创建 -
由于申请的size大于initial heap size,于是进行了扩充
-
pwndbg> heap // in thread 2 Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE | NON_MAIN_ARENA Addr: 0x7ffff00008c0 // tcache_perthread_struct Size: 0x290 (with flag bits: 0x295)Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE | NON_MAIN_ARENA Addr: 0x7ffff0000b50 // printf in use Size: 0x410 (with flag bits: 0x415)Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE | NON_MAIN_ARENA Addr: 0x7ffff0000f60 // 0x32000 user space allocated Size: 0x32010 (with flag bits: 0x32015)Top chunk | PREV_INUSE Addr: 0x7ffff0032f70 // remainder / top chunk Size: 0x90 (with flag bits: 0x91)
其他多线程支持机制:
- 单次malloc映射的132KB内存(in main thread)称为
arena - 当heap空间不足,可以通过扩充arena进行拓展,空间剩余过多时则可以进行shrink
- thread arena 的数量受限于机器的核数,64bit 系统,最大
8*cores
Chunk
chunk是堆管理中的基本结构,无论chunk状态如何,都使用同一个结构体表示:
code in malloc.c
struct malloc_chunk {INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if free. */struct malloc_chunk* bk;/* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if free. */struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize;
};
-
INTERNAL_SIZE_T: 用于存储chunk size的数据类型,一般为size_t -
SIZE_SZ: size ofINTERNAL_SIZE_T, 8 in 64-bit system -
MALLOC_ALIGNMENT:2 * SIZE_SZ,为chunk size 对齐宽度 -
prev_size, 如果该 chunk 的**物理相邻的前一地址 chunk(两个指针的地址差值为前一 chunk 大小)**是空闲的话,那该字段记录的是前一个 chunk 的大小 (包括 chunk 头)。否则,该字段可以用来存储物理相邻的前一个 chunk 的数据。这里的前一 chunk 指的是较低地址的 chunk 。
-
size,该 chunk 的大小,大小必须是 2 *
SIZE_SZ的整数倍。如果申请的内存大小不是 2 *SIZE_SZ的整数倍,会被转换满足大小的最小的 2 *SIZE_SZ的倍数。32 位系统中,SIZE_SZ是 4;64 位系统中,SIZE_SZ是 8。 该字段的低三个比特位对 chunk 的大小没有影响,它们从高到低分别表示NON_MAIN_ARENA,记录当前 chunk 是否不属于主线程,1 表示不属于,0 表示属于。IS_MAPPED,记录当前 chunk 是否是由 mmap 分配的。 若该位被置位,则其他bit被忽略,因为mmap分配的块不属于arena,也不会与其他free chunk物理相邻。PREV_INUSE,记录前一个(物理相邻) chunk 块是否被分配。一般来说,堆中第一个被分配的内存块的 size 字段的 P 位都会被设置为 1,以便于防止访问前面的非法内存。当一个 chunk 的 size 的 P 位为 0 时,我们能通过 prev_size 字段来获取上一个 chunk 的大小以及地址。这也方便进行空闲 chunk 之间的合并。
-
fd, bk: forward, back,只在空闲时使用。当chunk空闲时,会被添加到空闲块管理列表中,为双向链表。fd为下一个,bk为上一个,注意,指针指向非物理相邻的free chunk
-
fd_nextsize, bk_nextsize: 只在空闲时,且大chunk时使用,记录下/上一个块的大小
- free large chunk一般会由大到小排列,避免挨个遍历
structure of a malloced-chunk:
chunk-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| Size of previous chunk, if unallocated (P clear) |+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| Size of chunk, in bytes |A|M|P|mem-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| User data starts here... .. .. (malloc_usable_size() bytes) .
next . |
chunk-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| (size of chunk, but used for application data) |+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| Size of next chunk, in bytes |A|0|1|+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
- 对于下一个chunk,
prev_inuse=1 - malloc返回的指针位于user data的起始处,末尾三位为
010

structure of a free chunk:
chunk-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| Size of previous chunk, if unallocated (P clear) |+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
`head:' | Size of chunk, in bytes |A|0|P|mem-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| Forward pointer to next chunk in list |+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| Back pointer to previous chunk in list |+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| Unused space (may be 0 bytes long) .. .next . |
chunk-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
`foot:' | Size of chunk, in bytes |+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+| Size of next chunk, in bytes |A|0|0|+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
- 对于一个free chunk,有两个地方可以保存其大小,一个是该chunk的size,另一个是
next_chunk的prev_size
注意事项:
- 一般情况下,物理相邻的两个chunk会自动合并为一个
- fastbin中的free chunk在堆管理器看来是一个allocated chunk
chunk 相关宏
-
INTERNAL_SIZE_T: 用于存储chunk size的数据类型,一般为size_t -
SIZE_SZ: size ofINTERNAL_SIZE_T, 8 in 64-bit system -
MALLOC_ALIGNMENT:2 * SIZE_SZ,为chunk size 对齐宽度 -
chunk与user data空间头部指针的转换:
/* conversion from malloc headers to user pointers, and back */ #define chunk2mem(p) ((void *) ((char *) (p) + 2 * SIZE_SZ)) #define mem2chunk(mem) ((mchunkptr)((char *) (mem) -2 * SIZE_SZ)) -
最小chunk大小
/* The smallest possible chunk */ #definMIN_CHUNK_SIZE (offsetof(struct malloc_chunk, fd_nextsize)) // 32 Byteoffsetof计算结构体中成员的偏置,即该成员前所有成员的大小之和- 最小的chunk至少要包含两个指针 (fd,bk),以及前面的两个size,共32B
-
检查是否对齐
#define aligned_OK(m) (((unsigned long) (m) & MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) == 0) -
请求字节数检查,避免超限
/*Check if a request is so large that it would wrap around zero whenpadded and aligned. To simplify some other code, the bound is madelow enough so that adding MINSIZE will also not wrap around zero.*/#define REQUEST_OUT_OF_RANGE(req) \((unsigned long) (req) >= (unsigned long) (INTERNAL_SIZE_T)(-2 * MINSIZE)) -
将用户请求字节数转化为chunk size
/* pad request bytes into a usable size -- internal version */ //MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK = 2 * SIZE_SZ -1 #define request2size(req) \(((req) + SIZE_SZ + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK < MINSIZE) \? MINSIZE \: ((req) + SIZE_SZ + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) & ~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK)/* Same, except also perform argument check */#define checked_request2size(req, sz) \if (REQUEST_OUT_OF_RANGE(req)) { \__set_errno(ENOMEM); \return 0; \} \(sz) = request2size(req); -
chunk_at_offset:将一个ptr+offset处的内存视为一个内存块
当一个 chunk 处于已分配状态时,它的物理相邻的下一个 chunk 的 prev_size 字段必然是无效的,故而这个字段就可以被当前这个 chunk 使用。这就是 ptmalloc 中 chunk 间的复用。
- request size + chunk header
2 * SIZE_SZ,但复用了prev_size,只需要一个SIZE_SZ即可
chunk 申请流程
- 首先,利用 REQUEST_OUT_OF_RANGE 判断是否可以分配用户请求的字节大小的 chunk。
- 其次,需要注意的是用户请求的字节是用来存储数据的,即 chunk header 后面的部分。与此同时,由于 chunk 间复用,所以可以使用下一个 chunk 的 prev_size 字段。因此,这里只需要再添加 SIZE_SZ 大小即可以完全存储内容。
- 由于系统中所允许的申请的 chunk 最小是 MINSIZE,所以与其进行比较。如果不满足最低要求,那么就需要直接分配 MINSIZE 字节。
- 如果大于的话,因为系统中申请的 chunk 需要 2 * SIZE_SZ 对齐,所以这里需要加上 MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK 以便于对齐。
-
标记位相关宏:
/* size field is or'ed with PREV_INUSE when previous adjacent chunk in use */ #define PREV_INUSE 0x1/* extract inuse bit of previous chunk */ #define prev_inuse(p) ((p)->mchunk_size & PREV_INUSE)/* size field is or'ed with IS_MMAPPED if the chunk was obtained with mmap() */ #define IS_MMAPPED 0x2/* check for mmap()'ed chunk */ #define chunk_is_mmapped(p) ((p)->mchunk_size & IS_MMAPPED)/* size field is or'ed with NON_MAIN_ARENA if the chunk was obtainedfrom a non-main arena. This is only set immediately before handingthe chunk to the user, if necessary. */ #define NON_MAIN_ARENA 0x4/* Check for chunk from main arena. */ #define chunk_main_arena(p) (((p)->mchunk_size & NON_MAIN_ARENA) == 0)/* Mark a chunk as not being on the main arena. */ #define set_non_main_arena(p) ((p)->mchunk_size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA)/*Bits to mask off when extracting sizeNote: IS_MMAPPED is intentionally not masked off from size field inmacros for which mmapped chunks should never be seen. This shouldcause helpful core dumps to occur if it is tried by accident bypeople extending or adapting this malloc.*/ #define SIZE_BITS (PREV_INUSE | IS_MMAPPED | NON_MAIN_ARENA) -
get chunk size
/* Get size, ignoring use bits */ #define chunksize(p) (chunksize_nomask(p) & ~(SIZE_BITS))/* Like chunksize, but do not mask SIZE_BITS. */ #define chunksize_nomask(p) ((p)->mchunk_size) -
Get next chunk position which is physical adjacent to the current chunk
/* Ptr to next physical malloc_chunk. */ #define next_chunk(p) ((mchunkptr)(((char *) (p)) + chunksize(p))) -
access info about previous chunk
/* Size of the chunk below P. Only valid if !prev_inuse (P). */ #define prev_size(p) ((p)->mchunk_prev_size)/* Set the size of the chunk below P. Only valid if !prev_inuse (P). */ #define set_prev_size(p, sz) ((p)->mchunk_prev_size = (sz))/* Ptr to previous physical malloc_chunk. Only valid if !prev_inuse (P). */ #define prev_chunk(p) ((mchunkptr)(((char *) (p)) - prev_size(p))) -
操作chunk当前状态
/* extract p's inuse bit */ #define inuse(p) \((((mchunkptr)(((char *) (p)) + chunksize(p)))->mchunk_size) & PREV_INUSE)/* set/clear chunk as being inuse without otherwise disturbing */ #define set_inuse(p) \((mchunkptr)(((char *) (p)) + chunksize(p)))->mchunk_size |= PREV_INUSE#define clear_inuse(p) \((mchunkptr)(((char *) (p)) + chunksize(p)))->mchunk_size &= ~(PREV_INUSE) -
获取指定偏移的chunk
/* Treat space at ptr + offset as a chunk */ #define chunk_at_offset(p, s) ((mchunkptr)(((char *) (p)) + (s)))
Top chunk
位于arena 顶端的chunk
-
是内存分配中寻找的最后一个chunk,若前面的各个bin都无法满足要求,则从top chunk中split
-
如果位置不足,则调用sbrk进行扩容。
-
top chunk 只能split,不能直接被使用
-
PREV_INUSE标志位恒为1,避免前面的chunk合并到top chunk中- 前面chunk consolidate时会进行检查,若为top chunk,则直接进行合并
/*TopThe top-most available chunk (i.e., the one bordering the end ofavailable memory) is treated specially. It is never included inany bin, is used only if no other chunk is available, and isreleased back to the system if it is very large (seeM_TRIM_THRESHOLD). Because top initiallypoints to its own bin with initial zero size, thus forcingextension on the first malloc request, we avoid having any specialcode in malloc to check whether it even exists yet. But we stillneed to do so when getting memory from system, so we makeinitial_top treat the bin as a legal but unusable chunk during theinterval between initialization and the first call tosysmalloc. (This is somewhat delicate, since it relies onthe 2 preceding words to be zero during this interval as well.)*//* Conveniently, the unsorted bin can be used as dummy top on first call */
#define initial_top(M) (unsorted_chunks(M))
程序第一次进行malloc时,会初始化heap,剩余部分作为 top chunk。初始状态下,将unsorted chunk作为top chunk
Last remainder chunk
是最近一次split产生的chunk。当当前chunk没有合适的大小时,会将一个大的chunk分为两部分,一部分给用户空间使用,另一部分作为last remainder chunk,该部分同样会存入unsorted bin中
bin
用户释放的chunk不会马上归还给系统,ptmalloc会统一管理heap和mmap映射区域中的空闲chunk。
ptmalloc采用分箱方式进行chunk管理。根据chunk大小和使用状态对chunk进行分类:
- fast bins
- Large bins
- small bins
- unsorted bins
在每个bin中有更多细分,同类bin使用双向链表相连。
除了fast bin,ptmalloc将他们维护在同一个数组中,bin对应的数据结构存放在arrena header数据结构——malloc_state中。
typedef struct malloc_chunk* mchunkptr;
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2];
- 每个bin使用两个指针描述,第一个记录bin的
HEAD,即fd,第二个记录bin的TAIL - 整个bin使用
malloc_chunk的结构体,也就是说,可以被当作chunk使用,这样就不需要单独处理header chunk。相邻的两个header chunk互相重叠,只使用fd,bk两个指针,offset通过下面宏中所提到的bin_at计算
Fast bin 单独拥有一个维护数组:
typedef struct malloc_chunk *mfastbinptr;
mfastbinptr fastbinsY[]; // Array of pointers to chunks
bins组织如下:(序号为宏计算前的序号,非bins中的offset)
-
第 1 个为unsorted bin,chunk未排序,存储较为混乱。注意:没有0号bin
-
共有62个small bins, index = 2 ~ 63,每一个small bin链表中chunk长度相同;相邻两个bins 大小相差两个字长 16B in 64-bit OS(即malloc),遵循队列分配(FIFO)
- small bins 大小依次为:32, 48, …, 1008 共62个
-
共有63个large bins,每个bin中的chunk size 为一个范围
-
相邻两个bin间隔按照类似指数的规则排列
64 bins of size 16 [ Small bins] // 62 bins in deed 32 bins of size 64 [ Large bins] // start from 1024 16 bins of size 512 [ Large bins] 8 bins of size 4096 [ .. ] 4 bins of size 32768 2 bins of size 262144 1 bin of size what's left- 如上图所示,第一个large bin (index=64) 为:
1024~1087, 第二个是1088~1151
- 如上图所示,第一个large bin (index=64) 为:
-
最小的large bin 大小
MIN_LARGE_SIZE=1024 -
large bin 内,相同size的chunk按照FIFO规划
-
- 原则:任意两个物理相邻的空闲chunk不能在一起,物理相邻的两个chunk都free时会进行合并
bin 相关宏
typedef struct malloc_chunk *mbinptr;/* addressing -- note that bin_at(0) does not exist */
#define bin_at(m, i) \(mbinptr)(((char *) &((m)->bins[ ((i) -1) * 2 ])) - \offsetof(struct malloc_chunk, fd))/* analog of ++bin */
//获取下一个bin的地址
#define next_bin(b) ((mbinptr)((char *) (b) + (sizeof(mchunkptr) << 1)))/* Reminders about list directionality within bins */
// 这两个宏可以用来遍历bin
// 获取 bin 的位于链表头的 chunk
#define first(b) ((b)->fd)
// 获取 bin 的位于链表尾的 chunk
#define last(b) ((b)->bk)
bin_at: 通过index查询到对应的bin,其中减去offset是为了将header chunk作为chunk使用,同时完成空间压缩,一个header chunk,我们只使用两个双向链表指针,其他位置是别的chunk的位置,所以0号位置不能使用,否则继续使用offset将会OOB
bin 的 组织如下:
To simplify use in double-linked lists, each bin header acts as a malloc_chunk. This avoids special-casing for headers. But to conserve space and improve locality, we allocate only the fd/bk pointers of bins, and then use repositioning tricks to treat these as the fields of a malloc_chunk*
- 一个bin 占用两个bins中的元素,一个代表fd,另一个为bk,为双向链表的两个指针,通过
bin_at查询对应索引的bin,从而直接使用两个链表指针参数
fast bin
由于大多数程序经常申请较小chunk,花费在split和merge上的时间过多,使用fast chunk缓解这个问题。使用fastbinsY数组进行储存
/*FastbinsAn array of lists holding recently freed small chunks. Fastbinsare not doubly linked. It is faster to single-link them, andsince chunks are never removed from the middles of these lists,double linking is not necessary. Also, unlike regular bins, theyare not even processed in FIFO order (they use faster LIFO) sinceordering doesn't much matter in the transient contexts in whichfastbins are normally used.Chunks in fastbins keep their inuse bit set, so they cannotbe consolidated with other free chunks. malloc_consolidatereleases all chunks in fastbins and consolidates them withother free chunks.*/typedef struct malloc_chunk *mfastbinptr;
#define fastbin(ar_ptr, idx) ((ar_ptr)->fastbinsY[idx])// .../* The maximum fastbin request size we support */
#define MAX_FAST_SIZE (80 * SIZE_SZ / 4)#define NFASTBINS (fastbin_index (request2size (MAX_FAST_SIZE)) + 1)mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];
-
fast bin 不进行合并操作
-
每个fast bin中的chunk size相同
-
采用单链表存储结构,因为从不会从中间将chunk移除
-
使用FILO顺序进行管理,所有操作在头部进行
-
fast bins 将IN_USE位始终置1
typedef struct malloc_chunk *mfastbinptr;
#define fastbin(ar_ptr, idx) ((ar_ptr)->fastbinsY[idx])/* offset 2 to use otherwise unindexable first 2 bins */
#define fastbin_index(sz) \((((unsigned int) (sz)) >> (SIZE_SZ == 8 ? 4 : 3)) - 2)/* The maximum fastbin request size we support */
#define MAX_FAST_SIZE (80 * SIZE_SZ / 4)#define NFASTBINS (fastbin_index (request2size (MAX_FAST_SIZE)) + 1)
- 默认支持到128B,最多支持
MAX_FAST_SIZE = 160Bin 64-bit OS- 通过
do_set_mxfast修改最大支持fast bin 大小 - 初始化时设置为默认支持fast bin 大小
- 通过
- 每个fast bin 间隔 16B
- 共有10个fast bin,依次为32B, 48B…
内存整理:
/*FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD is the size of a chunk in free()that triggers automatic consolidation of possibly-surroundingfastbin chunks. This is a heuristic, so the exact value should notmatter too much. It is defined at half the default trim threshold as acompromise heuristic to only attempt consolidation if it is likelyto lead to trimming. However, it is not dynamically tunable, sinceconsolidation reduces fragmentation surrounding large chunks evenif trimming is not used.*/#define FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD (65536UL)
- 当目前需要free的chunk size大于
fastbin_consolidation_threshold时,该free chunk周围较多内存碎片,需要调用malloc_consolidate将fast bin中的chunk进行合并 malloc_consolidate将所有fastbin释放,并合并为小块

small bin
small bin 相关宏:
#define NBINS 128
#define NSMALLBINS 64 // is 63 in total, actually
#define SMALLBIN_WIDTH MALLOC_ALIGNMENT
#define SMALLBIN_CORRECTION (MALLOC_ALIGNMENT > 2 * SIZE_SZ)
#define MIN_LARGE_SIZE ((NSMALLBINS - SMALLBIN_CORRECTION) * SMALLBIN_WIDTH)#define in_smallbin_range(sz) \((unsigned long) (sz) < (unsigned long) MIN_LARGE_SIZE)#define smallbin_index(sz) \((SMALLBIN_WIDTH == 16 ? (((unsigned) (sz)) >> 4) : (((unsigned) (sz)) >> 3))\+ SMALLBIN_CORRECTION)
-
smallbin_index用于计算chunk 位于 smallbin中的序号,当32B(最小chunk)被free时,将得到idx=2,在unsorted bin之后 -
small bin malloc使用队列分配,FIFO
-
small bin的free操作,需要检查物理相邻块,并将相邻free chunk合并,合并后的chunk加入unsorted chunk中

large bin
-
大于等于1024B的chunk都为large chunk,在largin bin中管理
-
同一个bin中的chunk size可以不同
-
large bin支持随机存取
-
具体的size规范见bin概述
-
bin中chunk降序排列,HEAD上是最大的chunk
-
nextsize查找速度优化-
对于large bin,每个bin中的size各不相同,也可能出现多个相同size的chunk
-
每次在large bin中查找chunk,若遍历所有chunk,可能效率低下
-
nextsize将相邻不同size的chunk组合成链表,如下图所示,会跳过相同size chunk(仍可以通过fd和bk查询到)
- 独立的chunk,两个
nextsize指针为空
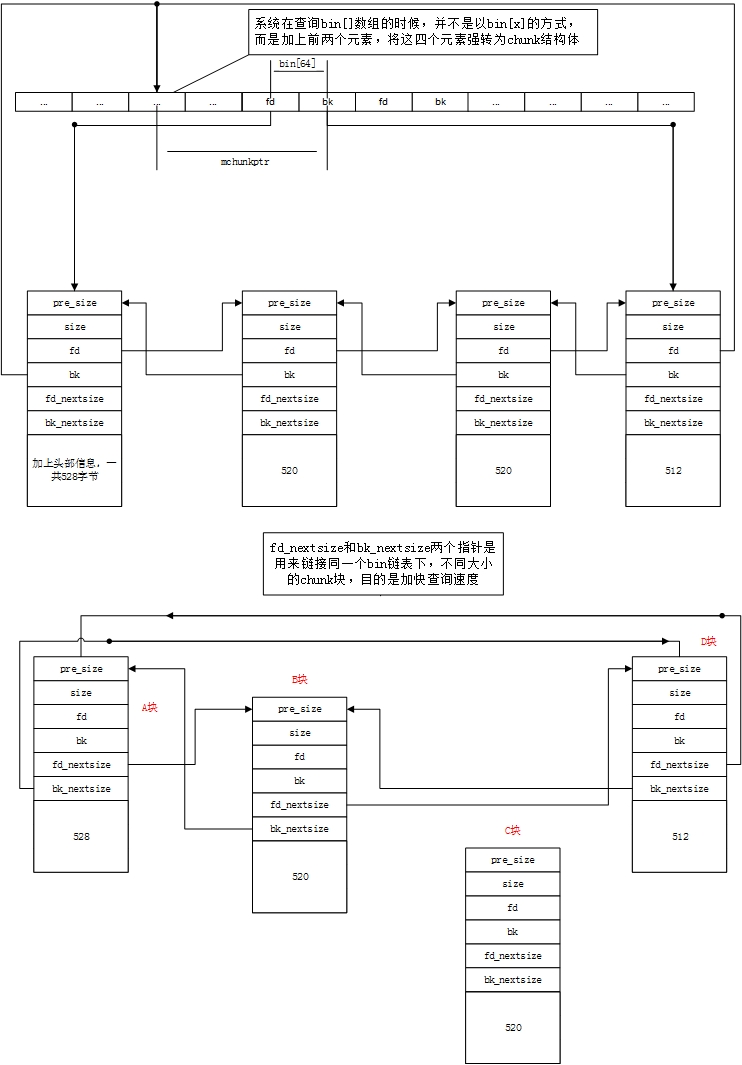
- 独立的chunk,两个
-
malloc 操作:
- 首先确定用户请求的大小属于哪个bin,再在bin中寻找可用的最小chunk
- 若大于用户请求量,则拆分后返回给用户,剩余部分加入unsroted bin
- 若当前bin没有合适chunk,则依次向后寻找bin,否则向top chunk索取
- 优化:Binmap
- motivation: 由于不同的bin较多,依次遍历将消耗较多时间,特别是在warm-up阶段,绝大多数bin都是空的情况下
- 用于记录bin是否为空,使用bitmap映射
- 偏否的蒙特卡洛算法,bit位置1,对应bin不一定非空,但若为0,则一定为空

unsorted bin
/*Unsorted chunksAll remainders from chunk splits, as well as all returned chunks,are first placed in the "unsorted" bin. They are then placedin regular bins after malloc gives them ONE chance to be used beforebinning. So, basically, the unsorted_chunks list acts as a queue,with chunks being placed on it in free (and malloc_consolidate),and taken off (to be either used or placed in bins) in malloc.The NON_MAIN_ARENA flag is never set for unsorted chunks, so itdoes not have to be taken into account in size comparisons.*//* The otherwise unindexable 1-bin is used to hold unsorted chunks. */
#define unsorted_chunks(M) (bin_at (M, 1))
为chunk管理提供缓冲区
-
若free chunk过大,则放置到缓冲区中
-
split后的chunk也会放到unsroted bin中
-
循环双链表结构,FIFO管理
-
任何大小的chunk都可以放到unsroted bin中
-
unsorted bin 中的 non_main_arena一定为0

bin 初始化
malloc_init_state过程:
static void
malloc_init_state (mstate av)
{int i;mbinptr bin;/* Establish circular links for normal bins */for (i = 1; i < NBINS; ++i){bin = bin_at (av, i);bin->fd = bin->bk = bin;}#if MORECORE_CONTIGUOUSif (av != &main_arena)
#endifset_noncontiguous (av);if (av == &main_arena)set_max_fast (DEFAULT_MXFAST);atomic_store_relaxed (&av->have_fastchunks, false);av->top = initial_top (av);
}
- 将各个bin中的链表头尾都指向header bin,初始化为空链表
- 设置
noncontiguous - 初始化fast bin
- 初始化当前top chunk为unsorted bin,因为bin为空,所以第一次进行malloc时必然触发brk扩充
arena & heap
-
Arena 是glibc申请一次内存得到的空间,用于管理chunks
-
每个线程至多有一个arena
-
arena 最多数量为
8 * cores + 1(in 64-bit system) -
在2.31中,arena结构体大小为
0x898B -
主线程的arena称为
main_arena,只有它关联到程序的heap段;其余arena通过mmap分配,通过mmap分配的arena通过指针进行串联static struct malloc_state main_arena = {.mutex = _LIBC_LOCK_INITIALIZER,.next = &main_arena,.attached_threads = 1 }; -
利用锁机制进行线程间共享,除了访问fastbin是原子性操作外,其他访问都需要获取mutex
-
首次调用malloc时,在不超过arena上限的情况下,会为其分配并初始化一个arena。否则将选择一个可用的arena提供给线程使用

上图为一个arena的示意图,多个arena之间通过arena->next链接
heap info
对于非main_arena,其内存由mmap分配,每个mmap块称为heap,每个heap 拥有一个heap_info结构体,其中的ar_ptr均指向同一个arena,arena位于第一个mmap heap中
typedef struct _heap_info
{mstate ar_ptr; /* Arena for this heap. */struct _heap_info *prev; /* Previous heap. */size_t size; /* Current size in bytes. */size_t mprotect_size; /* Size in bytes that has been mprotectedPROT_READ|PROT_WRITE. *//* Make sure the following data is properly aligned, particularlythat sizeof (heap_info) + 2 * SIZE_SZ is a multiple ofMALLOC_ALIGNMENT. */char pad[-6 * SIZE_SZ & MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK];
} heap_info;
- 其中,pad将heap_info 对齐到
MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK
data structure
arena 通过malloc_state结构体实现
struct malloc_state
{/* Serialize access. */__libc_lock_define (, mutex); // 并发锁/* Flags (formerly in max_fast). */int flags; // for example, continuous bit/* Set if the fastbin chunks contain recently inserted free blocks. *//* Note this is a bool but not all targets support atomics on booleans. */int have_fastchunks;/* Fastbins */mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];/* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin */mchunkptr top; // top chunk ptr/* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */mchunkptr last_remainder;/* Normal bins packed as described above */mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2]; // bins header chunk (packed)/* Bitmap of bins */unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];/* Linked list */struct malloc_state *next;/* Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serializedby free_list_lock in arena.c. */struct malloc_state *next_free;/* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is onthe free list. Access to this field is serialized byfree_list_lock in arena.c. */INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads;/* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
}
- main_arena的结构体数据保存在glibc的data segment中
- Main_arena 初始化后的heap size为132KB(0x21000)
- 非main_arena的
malloc_state结构体在heap的第一个块(0x290 size)的0x20偏移处,前0x20 bytes为heap_info

gdb instructions for debugging heap
-
heap: display heap chunk info allheapbase: display base address of a heapParse heap: display heap chunk in another way
-
bins: display bins on current thread all- specifie bin type to diplay corresponding bin chunks
-
arena: display detailed info on current thread allarenas: list all arenas of current processarenainfo: similar toarena
-
chunk
chunkinfo *victimdisplay chunk informationchunkptr *user_ptrdisplay chunk information by user pointerMerge info *victimdisplay merge information of a chunk
-
tcache: display tcache infotcache bins: display bins in tcache
-
bmemoryself-defined- break at malloc and free
- cannot use “step” to trace those functions, probably because it doesn’t support indirect jump trace?
相关文章:

heap pwn 入门大全 - 1:glibc heap机制与源码阅读(上)
本文为笔者学习heap pwn时,学习阅读glibc ptmalloc2源码时的笔记,与各位分享。可能存在思维跳跃或错误之处,敬请见谅,欢迎在评论中指出。本文也借用了部分外网和其他前辈的素材图片,向各位表示诚挚的感谢!如…...
树莓派RP2040 用Arduino IDE安装和编译
目录 1 Arduino IDE 1.1 IDE下载 1.2 安装 arduino mbed os rp2040 boards 2 编程-烧录固件 2.1 打开点灯示例程序 2.2 选择Raspberry Pi Pico开发板 2.3 编译程序 2.4 烧录程序 2.4.1 Raspberry Pi Pico开发板首次烧录提示失败 2.4.2 解决首次下载失败问题 2.4.2.1…...
云安全攻防(八)之 Docker Remote API 未授权访问逃逸
Docker Remote API 未授权访问逃逸 基础知识 Docker Remote API 是一个取代远程命令行界面(rcli)的REST API,其默认绑定2375端口,如管理员对其配置不当可导致未授权访问漏洞。攻击者利用 docker client 或者 http 直接请求就可以…...

2023-08-13 LeetCode每日一题(合并两个有序数组)
2023-08-13每日一题 一、题目编号 88. 合并两个有序数组二、题目链接 点击跳转到题目位置 三、题目描述 给你两个按 非递减顺序 排列的整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,另有两个整数 m 和 n ,分别表示 nums1 和 nums2 中的元素数目。 请你 合并 nums2 到 …...

nbcio-boot升级springboot、mybatis-plus和JSQLParser后的LocalDateTime日期json问题
升级后,运行显示项目的时候出现下面错误 2023-08-12 10:57:39.174 [http-nio-8080-exec-3] [1;31mERROR[0;39m [36morg.jeecg.common.aspect.DictAspect:104[0;39m - json解析失败Java 8 date/time type java.time.LocalDateTime not supported by default: add Mo…...
「C/C++」C/C++搭建程序框架
✨博客主页何曾参静谧的博客📌文章专栏「C/C」C/C程序设计📚全部专栏「UG/NX」NX二次开发「UG/NX」BlockUI集合「VS」Visual Studio「QT」QT5程序设计「C/C」C/C程序设计「Win」Windows程序设计「DSA」数据结构与算法「File」数据文件格式 目录 1. 分离职…...
Android 内存泄漏
名词解释 内存泄漏:即memory leak。是指内存空间使用完毕后无法被释放的现象,虽然Java有垃圾回收机制(GC),但是对于还保持着引用, 该内存不能再被分配使用,逻辑上却已经不会再用到的对象,垃圾回…...

Android上的基于协程的存储框架
在Android上,经常会需要持久化本地数据,比如我们需要缓存用户的配置信息、用户的数据、缓存数据、离线缓存数据等等。我们通常使用的工具为SharePreference、MMKV、DataStore、Room、文件等等。通过使用现有的存储框架,结合协程,我…...

虚拟现实与增强现实技术的商业应用
章节一:引言 随着科技的不断发展,虚拟现实(Virtual Reality,简称VR)与增强现实(Augmented Reality,简称AR)技术正日益成为商业领域中的重要创新力量。这两种技术为企业带来了前所未…...

每日后端面试5题 第六天
1. Java中有几种类型的流 字符流、字节流 输入流、输出流 节点流、处理流 2 .Spring支持的几种bean的作用域 五种: 1.singleton bean在每个ioc容器中只有一个实例 2.prototype 可以有多个实例 3-5在web环境中才生效 3.request 每次请求才创建bean 4.se…...

LeetCode150道面试经典题-- 两数之和(简单)
1.题目 给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。 你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。 你可以按任意…...
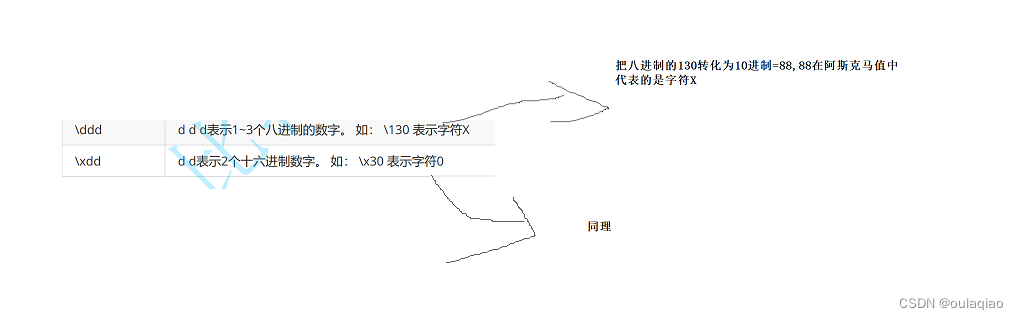
转义字符\
转移字符,就是通过字符,来转变原来字符的意思 常见的转义字符: 1、 2 注:" 的作用和他是类似的 3 4、 当打印\a时,电脑会出现一个警告,蜂鸣的声音 5、 阿斯克码表...
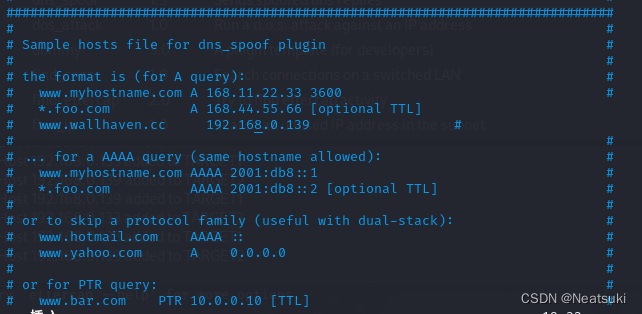
什么是DNS欺骗及如何进行DNS欺骗
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 前言一、什么是 DNS 欺骗?二、开始1.配置2.Ettercap启动3.操作 总结 前言 我已经离开了一段时间,我现在回来了,我终于在做一个教…...
Android核心开发之——OpenGL
OpenGL是一种用于编程计算机图形的应用程序编程接口(API)。它提供了一系列函数和方法,用于绘制2D和3D图形,以及进行渲染和图形处理。OpenGL可以跨平台使用,支持各种操作系统和硬件设备。它被广泛应用于游戏开发、虚拟现…...

公共服务领域:西安新小区业主自立业主委员会年底分红83万以及103万事件区块链资金透明监管与投票解决方案的尝试
公共服务领域:西安新小区业主自立业主委员会年底分红83万以及103万事件区块链资金透明监管与投票解决方案的尝试 作者 重庆电子工程职业学院 | 向键雄 杜小敏 前言 本项目想法来源于,西安新小区业主开出物业自立业主委员会年底分红83万以及103万事件,对于此类事件,我们刨…...

ID3 决策树
西瓜数据集D如下: 编号色泽根蒂敲声纹理脐部触感好瓜1青绿蜷缩浊响清晰凹陷硬滑是2乌黑蜷缩沉闷清晰凹陷硬滑是3乌黑蜷缩浊响清晰凹陷硬滑是4青绿蜷缩沉闷清晰凹陷硬滑是5浅白蜷缩浊响清晰凹陷硬滑是6青绿稍蜷浊响清晰稍凹软粘是7乌黑稍蜷浊响稍糊稍凹软粘是8乌黑稍蜷浊响清晰…...

简单线性回归:预测事物间简单关系的利器
文章目录 🍀简介🍀什么是简单线性回归?🍀简单线性回归的应用场景使用步骤:注意事项: 🍀代码演示🍀结论 🍀简介 在数据科学领域,线性回归是一种基本而强大的统…...
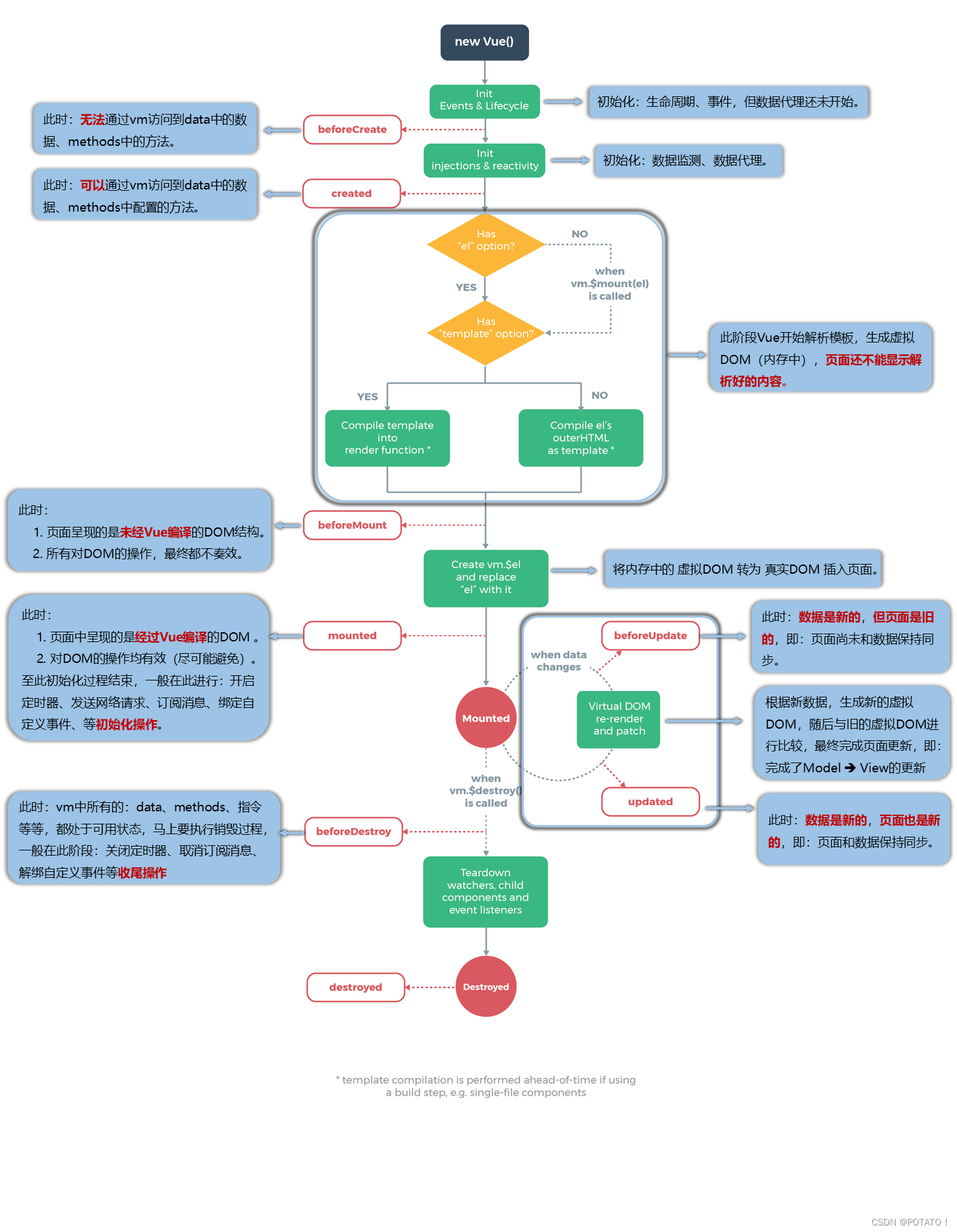
Vue2-收集表单数据、过滤器、内置指令与自定义指令、Vue生命周期
🥔:我徒越万重山 千帆过 万木自逢春 更多Vue知识请点击——Vue.js VUE2-Day4 收集表单数据1、不同标签的value属性2、v-model的三个修饰符 过滤器内置指令与自定义指令1、内置指令2、自定义指令定义语法(1)函数式(2&am…...

正则表达式学习详解
正则表达式 正则表达式(Regular Expression),通常简称为正则或正则表达式,是一种用于描述字符串模式的工具。它是由一系列字符和特殊字符组成的字符串,用于定义搜索模式或进行字符串匹配、替换、提取等操作。 正则表…...

R语言AI模型部署方案:精准离线运行详解
R语言AI模型部署方案:精准离线运行详解 一、项目概述 本文将构建一个完整的R语言AI部署解决方案,实现鸢尾花分类模型的训练、保存、离线部署和预测功能。核心特点: 100%离线运行能力自包含环境依赖生产级错误处理跨平台兼容性模型版本管理# 文件结构说明 Iris_AI_Deployme…...
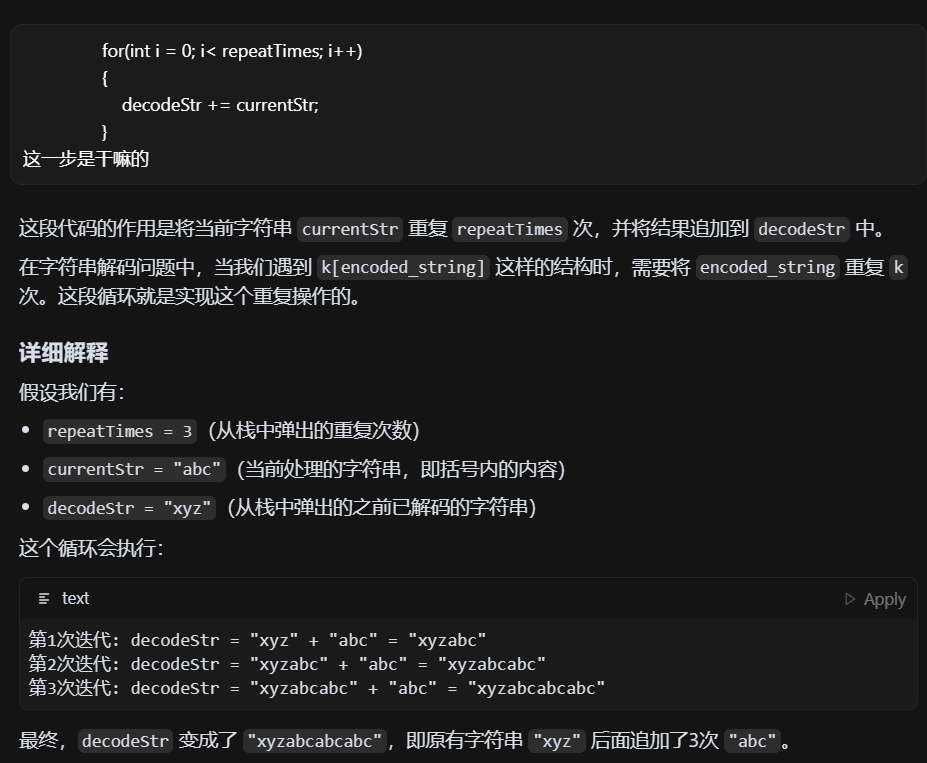
LeetCode - 394. 字符串解码
题目 394. 字符串解码 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路 使用两个栈:一个存储重复次数,一个存储字符串 遍历输入字符串: 数字处理:遇到数字时,累积计算重复次数左括号处理:保存当前状态&a…...

el-switch文字内置
el-switch文字内置 效果 vue <div style"color:#ffffff;font-size:14px;float:left;margin-bottom:5px;margin-right:5px;">自动加载</div> <el-switch v-model"value" active-color"#3E99FB" inactive-color"#DCDFE6"…...
)
OpenLayers 分屏对比(地图联动)
注:当前使用的是 ol 5.3.0 版本,天地图使用的key请到天地图官网申请,并替换为自己的key 地图分屏对比在WebGIS开发中是很常见的功能,和卷帘图层不一样的是,分屏对比是在各个地图中添加相同或者不同的图层进行对比查看。…...
VM虚拟机网络配置(ubuntu24桥接模式):配置静态IP
编辑-虚拟网络编辑器-更改设置 选择桥接模式,然后找到相应的网卡(可以查看自己本机的网络连接) windows连接的网络点击查看属性 编辑虚拟机设置更改网络配置,选择刚才配置的桥接模式 静态ip设置: 我用的ubuntu24桌…...

LangChain知识库管理后端接口:数据库操作详解—— 构建本地知识库系统的基础《二》
这段 Python 代码是一个完整的 知识库数据库操作模块,用于对本地知识库系统中的知识库进行增删改查(CRUD)操作。它基于 SQLAlchemy ORM 框架 和一个自定义的装饰器 with_session 实现数据库会话管理。 📘 一、整体功能概述 该模块…...
MySQL 知识小结(一)
一、my.cnf配置详解 我们知道安装MySQL有两种方式来安装咱们的MySQL数据库,分别是二进制安装编译数据库或者使用三方yum来进行安装,第三方yum的安装相对于二进制压缩包的安装更快捷,但是文件存放起来数据比较冗余,用二进制能够更好管理咱们M…...
【C++特殊工具与技术】优化内存分配(一):C++中的内存分配
目录 一、C 内存的基本概念 1.1 内存的物理与逻辑结构 1.2 C 程序的内存区域划分 二、栈内存分配 2.1 栈内存的特点 2.2 栈内存分配示例 三、堆内存分配 3.1 new和delete操作符 4.2 内存泄漏与悬空指针问题 4.3 new和delete的重载 四、智能指针…...
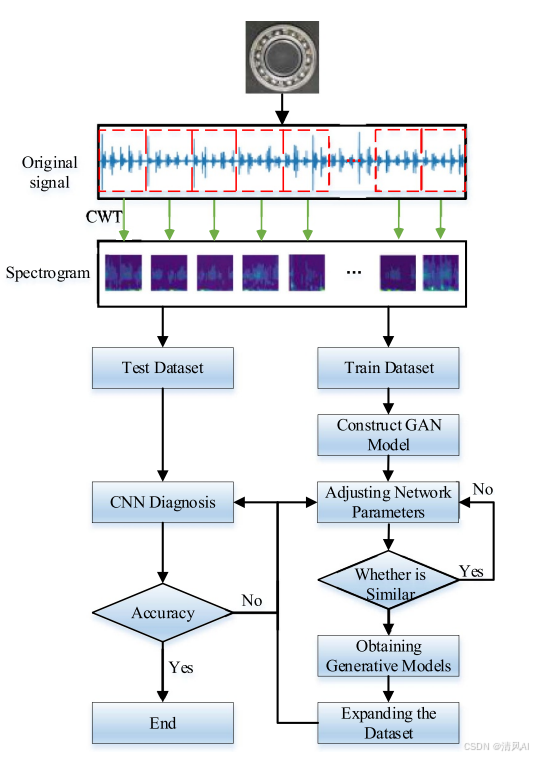
基于IDIG-GAN的小样本电机轴承故障诊断
目录 🔍 核心问题 一、IDIG-GAN模型原理 1. 整体架构 2. 核心创新点 (1) 梯度归一化(Gradient Normalization) (2) 判别器梯度间隙正则化(Discriminator Gradient Gap Regularization) (3) 自注意力机制(Self-Attention) 3. 完整损失函数 二…...
: 一刀斩断视频片头广告)
快刀集(1): 一刀斩断视频片头广告
一刀流:用一个简单脚本,秒杀视频片头广告,还你清爽观影体验。 1. 引子 作为一个爱生活、爱学习、爱收藏高清资源的老码农,平时写代码之余看看电影、补补片,是再正常不过的事。 电影嘛,要沉浸,…...

