PyTorch翻译官网教程-NLP FROM SCRATCH: CLASSIFYING NAMES WITH A CHARACTER-LEVEL RNN
官网链接
NLP From Scratch: Classifying Names with a Character-Level RNN — PyTorch Tutorials 2.0.1+cu117 documentation
使用CHARACTER-LEVEL RNN 对名字分类
我们将建立和训练一个基本的字符级递归神经网络(RNN)来分类单词。本教程以及另外两个“from scratch”的自然语言处理(NLP)教程 NLP From Scratch: Generating Names with a Character-Level RNN 和 NLP From Scratch: Translation with a Sequence to Sequence Network and Attention,演示如何预处理数据以建立NLP模型。特别是,这些教程没有使用torchtext的许多便利功能,因此您可以看到如何简单使用预处理模型NLP。
字符级RNN将单词作为一系列字符来读取 ,每一步输出一个预测和“隐藏状态”,将之前的隐藏状态输入到下一步。我们把最后的预测作为输出,即这个词属于哪个类。
具体来说,我们将训练来自18种语言的几千个姓氏,并根据拼写来预测一个名字来自哪种语言:
$ python predict.py Hinton
(-0.47) Scottish
(-1.52) English
(-3.57) Irish$ python predict.py Schmidhuber
(-0.19) German
(-2.48) Czech
(-2.68) Dutch建议准备
在开始本教程之前,建议您安装PyTorch,并对Python编程语言和张量有基本的了解:
- PyTorch 有关安装说明
- Deep Learning with PyTorch: A 60 Minute Blitz 开始使用PyTorch并学习张量的基础知识
- Learning PyTorch with Examples 使用概述
- PyTorch for Former Torch Users 如果您是前Lua Torch用户
了解rnn及其工作原理也很有用:
- The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Recurrent Neural Networks 展示了一些现实生活中的例子
- Understanding LSTM Networks 是专门关于LSTMs的,但也有关于RNNs的信息
准备数据
从这里下载数据并将其解压缩到当前目录。here
“data/names”目录下包含18个文本文件,文件名为“[Language].txt”。每个文件包含一堆名称,每行一个名称,大多数是罗马化的(但我们仍然需要从Unicode转换为ASCII)。
我们最终会得到一个包含每种语言名称列表的字典,{language: [names ...]}。通用变量“category”和“line”(在本例中表示语言和名称)用于以后的可扩展性。
from io import open
import glob
import osdef findFiles(path): return glob.glob(path)print(findFiles('data/names/*.txt'))import unicodedata
import stringall_letters = string.ascii_letters + " .,;'"
n_letters = len(all_letters)# Turn a Unicode string to plain ASCII, thanks to https://stackoverflow.com/a/518232/2809427
def unicodeToAscii(s):return ''.join(c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'and c in all_letters)print(unicodeToAscii('Ślusàrski'))# Build the category_lines dictionary, a list of names per language
category_lines = {}
all_categories = []# Read a file and split into lines
def readLines(filename):lines = open(filename, encoding='utf-8').read().strip().split('\n')return [unicodeToAscii(line) for line in lines]for filename in findFiles('data/names/*.txt'):category = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(filename))[0]all_categories.append(category)lines = readLines(filename)category_lines[category] = linesn_categories = len(all_categories)输出
['data/names/Arabic.txt', 'data/names/Chinese.txt', 'data/names/Czech.txt', 'data/names/Dutch.txt', 'data/names/English.txt', 'data/names/French.txt', 'data/names/German.txt', 'data/names/Greek.txt', 'data/names/Irish.txt', 'data/names/Italian.txt', 'data/names/Japanese.txt', 'data/names/Korean.txt', 'data/names/Polish.txt', 'data/names/Portuguese.txt', 'data/names/Russian.txt', 'data/names/Scottish.txt', 'data/names/Spanish.txt', 'data/names/Vietnamese.txt']
Slusarski现在我们有了category_lines,这是一个将每个类别(语言)映射到行(名称)列表的字典。我们还记录了all_categories(只是一个语言列表)和n_categories,以供以后参考。
print(category_lines['Italian'][:5])输出
['Abandonato', 'Abatangelo', 'Abatantuono', 'Abate', 'Abategiovanni']
把名字变成张量
现在我们已经组织好了所有的名字,我们需要把它们变成张量来使用它们。
为了表示单个字母,我们使用大小为<1 x n_letters> 的 “one-hot vector”。一个独热向量被0填充,除了当前字母所以处是1。例如:"b" = <0 1 0 0 0 ...>.
为了组成一个单词,我们将一堆这样的单词连接到一个二维矩阵中<line_length x 1 x n_letters>.
额外的1维度是因为PyTorch假设所有的东西都是分批的——我们在这里只是使用1的批大小。
import torch# Find letter index from all_letters, e.g. "a" = 0
def letterToIndex(letter):return all_letters.find(letter)# Just for demonstration, turn a letter into a <1 x n_letters> Tensor
def letterToTensor(letter):tensor = torch.zeros(1, n_letters)tensor[0][letterToIndex(letter)] = 1return tensor# Turn a line into a <line_length x 1 x n_letters>,
# or an array of one-hot letter vectors
def lineToTensor(line):tensor = torch.zeros(len(line), 1, n_letters)for li, letter in enumerate(line):tensor[li][0][letterToIndex(letter)] = 1return tensorprint(letterToTensor('J'))print(lineToTensor('Jones').size())输出
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.,0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.,0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.,0., 0., 0.]])
torch.Size([5, 1, 57])创建网络
在autograd之前,在Torch中创建循环神经网络涉及到在几个时间步上克隆一层的参数。图层包含隐藏状态和梯度,现在完全由图形本身处理。这意味着你可以以一种非常“纯粹”的方式实现RNN,作为常规的前馈层。
这个RNN模块(主要是从the PyTorch for Torch users tutorial复制的)只有2个线性层,在输入和隐藏状态上操作,在输出之后有一个LogSoftmax层。
import torch.nn as nnclass RNN(nn.Module):def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):super(RNN, self).__init__()self.hidden_size = hidden_sizeself.i2h = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, hidden_size)self.h2o = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)def forward(self, input, hidden):combined = torch.cat((input, hidden), 1)hidden = self.i2h(combined)output = self.h2o(hidden)output = self.softmax(output)return output, hiddendef initHidden(self):return torch.zeros(1, self.hidden_size)n_hidden = 128
rnn = RNN(n_letters, n_hidden, n_categories)为了运行这个网络的一个步骤,我们需要传递一个输入(在我们的例子中,是当前字母的张量)和一个先前的隐藏状态(我们一开始将其初始化为零)。我们将返回输出(每种语言的概率)和下一个隐藏状态(我们将其保留到下一步)。
input = letterToTensor('A')
hidden = torch.zeros(1, n_hidden)output, next_hidden = rnn(input, hidden)为了提高效率,我们不想为每一步都创建一个新的张量,所以我们将使用lineToTensor而不是letterToTensor并使用切片。这可以通过预计算张量批次来进一步优化。
input = lineToTensor('Albert')
hidden = torch.zeros(1, n_hidden)output, next_hidden = rnn(input[0], hidden)
print(output)输出
tensor([[-2.9083, -2.9270, -2.9167, -2.9590, -2.9108, -2.8332, -2.8906, -2.8325,-2.8521, -2.9279, -2.8452, -2.8754, -2.8565, -2.9733, -2.9201, -2.8233,-2.9298, -2.8624]], grad_fn=<LogSoftmaxBackward0>)正如您所看到的,输出是一个<1 x n_categories> 张量,其中每个项目是该类别的可能性(越高越有可能)。
训练
训练准备
在开始训练之前,我们应该编写一些辅助函数。首先是解释网络的输出,我们知道这是每个类别的可能性。我们可以用Tensor.topk得到最大值的索引:
def categoryFromOutput(output):top_n, top_i = output.topk(1)category_i = top_i[0].item()return all_categories[category_i], category_iprint(categoryFromOutput(output))输出
('Scottish', 15)我们还需要一种快速获取训练示例(名称及其语言)的方法:
import randomdef randomChoice(l):return l[random.randint(0, len(l) - 1)]def randomTrainingExample():category = randomChoice(all_categories)line = randomChoice(category_lines[category])category_tensor = torch.tensor([all_categories.index(category)], dtype=torch.long)line_tensor = lineToTensor(line)return category, line, category_tensor, line_tensorfor i in range(10):category, line, category_tensor, line_tensor = randomTrainingExample()print('category =', category, '/ line =', line)输出
category = Chinese / line = Hou
category = Scottish / line = Mckay
category = Arabic / line = Cham
category = Russian / line = V'Yurkov
category = Irish / line = O'Keeffe
category = French / line = Belrose
category = Spanish / line = Silva
category = Japanese / line = Fuchida
category = Greek / line = Tsahalis
category = Korean / line = Chang训练网络
现在训练这个网络所需要做的就是给它看一堆例子,让它猜测,然后告诉它是否错了。
对于损失函数nn.NLLLoss是合适的,因为RNN的最后一层是nn.LogSoftmax.。
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()每个训练循环将:
- 创建输入张量和目标张量
- 创建一个零初始隐藏状态
- 读取每个字母
-
- 为下一个字母保存隐藏状态
- 将最终输出与目标进行比较
- 反向传播
- 返回输出和损失
learning_rate = 0.005 # If you set this too high, it might explode. If too low, it might not learndef train(category_tensor, line_tensor):hidden = rnn.initHidden()rnn.zero_grad()for i in range(line_tensor.size()[0]):output, hidden = rnn(line_tensor[i], hidden)loss = criterion(output, category_tensor)loss.backward()# Add parameters' gradients to their values, multiplied by learning ratefor p in rnn.parameters():p.data.add_(p.grad.data, alpha=-learning_rate)return output, loss.item()现在我们只需要用一堆例子来运行它。由于train函数返回输出和损失,我们可以打印它的猜测并跟踪损失以便绘制。由于有1000个示例,我们只打印每个print_every示例,并取损失的平均值。
import time
import mathn_iters = 100000
print_every = 5000
plot_every = 1000# Keep track of losses for plotting
current_loss = 0
all_losses = []def timeSince(since):now = time.time()s = now - sincem = math.floor(s / 60)s -= m * 60return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)start = time.time()for iter in range(1, n_iters + 1):category, line, category_tensor, line_tensor = randomTrainingExample()output, loss = train(category_tensor, line_tensor)current_loss += loss# Print ``iter`` number, loss, name and guessif iter % print_every == 0:guess, guess_i = categoryFromOutput(output)correct = '✓' if guess == category else '✗ (%s)' % categoryprint('%d %d%% (%s) %.4f %s / %s %s' % (iter, iter / n_iters * 100, timeSince(start), loss, line, guess, correct))# Add current loss avg to list of lossesif iter % plot_every == 0:all_losses.append(current_loss / plot_every)current_loss = 0输出
5000 5% (0m 33s) 2.6379 Horigome / Japanese ✓
10000 10% (1m 5s) 2.0172 Miazga / Japanese ✗ (Polish)
15000 15% (1m 39s) 0.2680 Yukhvidov / Russian ✓
20000 20% (2m 12s) 1.8239 Mclaughlin / Irish ✗ (Scottish)
25000 25% (2m 45s) 0.6978 Banh / Vietnamese ✓
30000 30% (3m 18s) 1.7433 Machado / Japanese ✗ (Portuguese)
35000 35% (3m 51s) 0.0340 Fotopoulos / Greek ✓
40000 40% (4m 23s) 1.4637 Quirke / Irish ✓
45000 45% (4m 57s) 1.9018 Reier / French ✗ (German)
50000 50% (5m 30s) 0.9174 Hou / Chinese ✓
55000 55% (6m 2s) 1.0506 Duan / Vietnamese ✗ (Chinese)
60000 60% (6m 35s) 0.9617 Giang / Vietnamese ✓
65000 65% (7m 9s) 2.4557 Cober / German ✗ (Czech)
70000 70% (7m 42s) 0.8502 Mateus / Portuguese ✓
75000 75% (8m 14s) 0.2750 Hamilton / Scottish ✓
80000 80% (8m 47s) 0.7515 Maessen / Dutch ✓
85000 85% (9m 20s) 0.0912 Gan / Chinese ✓
90000 90% (9m 53s) 0.1190 Bellomi / Italian ✓
95000 95% (10m 26s) 0.0137 Vozgov / Russian ✓
100000 100% (10m 59s) 0.7808 Tong / Vietnamese ✓绘制结果
绘制all_losses的历史损失图显示了网络的学习情况:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.ticker as tickerplt.figure()
plt.plot(all_losses)
输出
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7f16606095a0>]评估结果
为了了解网络在不同类别上的表现如何,我们将创建一个混淆矩阵,表示网络猜测(列)的每种语言(行)。为了计算混淆矩阵,使用evaluate(),在网络中运行一堆样本,这与 train() 去掉反向传播相同。
# Keep track of correct guesses in a confusion matrix
confusion = torch.zeros(n_categories, n_categories)
n_confusion = 10000# Just return an output given a line
def evaluate(line_tensor):hidden = rnn.initHidden()for i in range(line_tensor.size()[0]):output, hidden = rnn(line_tensor[i], hidden)return output# Go through a bunch of examples and record which are correctly guessed
for i in range(n_confusion):category, line, category_tensor, line_tensor = randomTrainingExample()output = evaluate(line_tensor)guess, guess_i = categoryFromOutput(output)category_i = all_categories.index(category)confusion[category_i][guess_i] += 1# Normalize by dividing every row by its sum
for i in range(n_categories):confusion[i] = confusion[i] / confusion[i].sum()# Set up plot
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
cax = ax.matshow(confusion.numpy())
fig.colorbar(cax)# Set up axes
ax.set_xticklabels([''] + all_categories, rotation=90)
ax.set_yticklabels([''] + all_categories)# Force label at every tick
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
plt.show()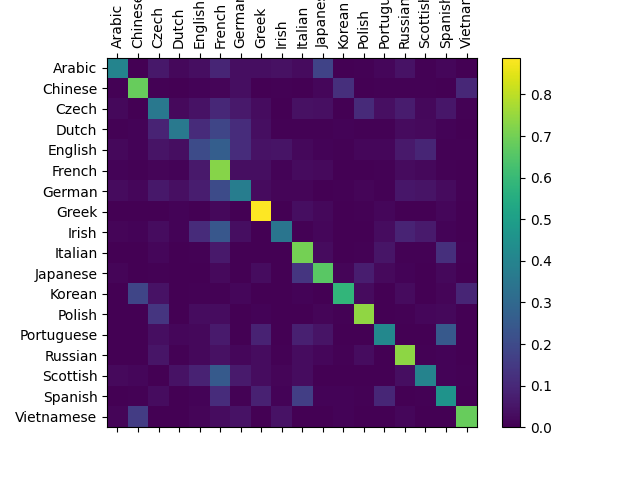
输出
/var/lib/jenkins/workspace/intermediate_source/char_rnn_classification_tutorial.py:445: UserWarning:FixedFormatter should only be used together with FixedLocator/var/lib/jenkins/workspace/intermediate_source/char_rnn_classification_tutorial.py:446: UserWarning:FixedFormatter should only be used together with FixedLocator你可以从主轴上挑出亮点,显示它猜错了哪些语言,例如中文猜错了韩语,西班牙语猜错了意大利语。它似乎在希腊语上表现得很好,而在英语上表现得很差(可能是因为与其他语言重叠)。
运行用户输入
def predict(input_line, n_predictions=3):print('\n> %s' % input_line)with torch.no_grad():output = evaluate(lineToTensor(input_line))# Get top N categoriestopv, topi = output.topk(n_predictions, 1, True)predictions = []for i in range(n_predictions):value = topv[0][i].item()category_index = topi[0][i].item()print('(%.2f) %s' % (value, all_categories[category_index]))predictions.append([value, all_categories[category_index]])predict('Dovesky')
predict('Jackson')
predict('Satoshi')输出
> Dovesky
(-0.57) Czech
(-0.97) Russian
(-3.43) English> Jackson
(-1.02) Scottish
(-1.49) Russian
(-1.96) English> Satoshi
(-0.42) Japanese
(-1.70) Polish
(-2.74) Italianin the Practical PyTorch repo中脚本的最终版本将上述代码拆分为几个文件:
- data.py (加载文件)
- model.py (定义 RNN)
- train.py (执行训练)
- predict.py (运行带有命令行参数的predict() )
- server.py (使用bottle.py作为JSON API提供预测)
运行train.py来训练和保存网络。
运行predict.py并输入一个名称来查看预测:
$ python predict.py Hazaki
(-0.42) Japanese
(-1.39) Polish
(-3.51) Czech运行server.py 并访问http://localhost:5533/Yourname以获得预测的JSON输出。
练习
尝试使用不同的数据集 -> 类别,例如:
- 任何单词->语言
- 名字->性别
- 角色名称->作家
- 页面标题 -> 博客或社交新闻网站子版块
使用一个更大的和/或更好的形状网络,可以获得更好的结果
- 添加更多线性图层
- 试试 nn.LSTM 和 nn.GRU 网络层
- 将这些RNNs组合成一个更高级的网络
相关文章:

PyTorch翻译官网教程-NLP FROM SCRATCH: CLASSIFYING NAMES WITH A CHARACTER-LEVEL RNN
官网链接 NLP From Scratch: Classifying Names with a Character-Level RNN — PyTorch Tutorials 2.0.1cu117 documentation 使用CHARACTER-LEVEL RNN 对名字分类 我们将建立和训练一个基本的字符级递归神经网络(RNN)来分类单词。本教程以及另外两个“from scratch”的自然…...
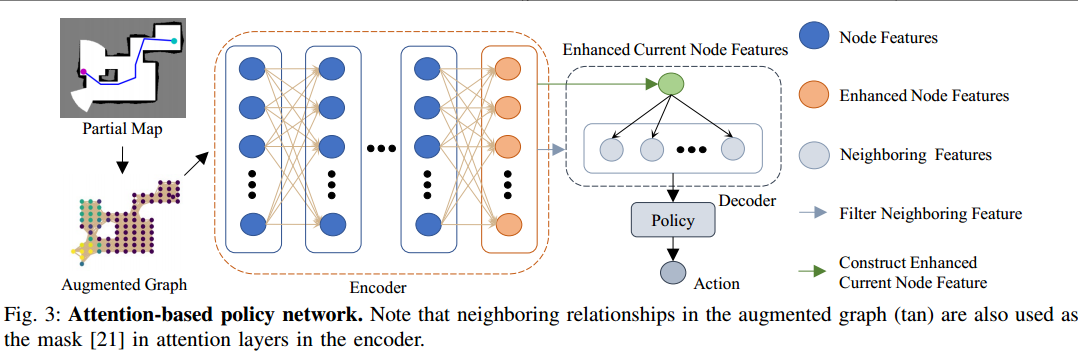
基于注意力神经网络的深度强化学习探索方法:ARiADNE
ARiADNE:A Reinforcement learning approach using Attention-based Deep Networks for Exploration 文章目录 ARiADNE:A Reinforcement learning approach using Attention-based Deep Networks for Exploration机器人自主探索(ARE)ARE的传统边界法非短视路径深度强化学习的方…...
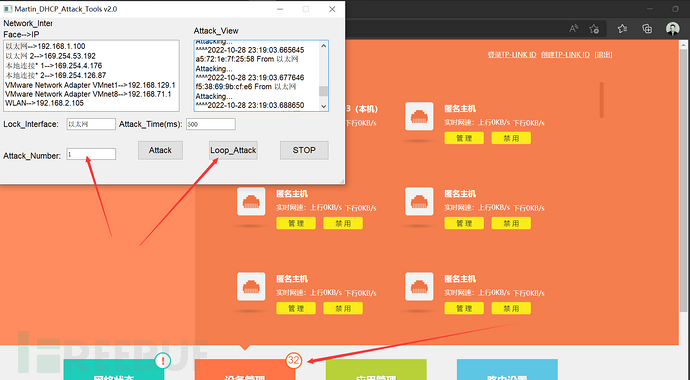
Martin_DHCP_V3.0 (DHCP自动化泛洪攻击GUI)
Github>https://github.com/MartinxMax/Martin_DHCP_V3.0 首页 Martin_DHCP_V3.0 自动化DHCP洪泛攻击 Martin_DHCP_V3.0 使用方法 安装三方库 #python3 1.RunMe_Install_Packet.py 攻击路由器 #python3 Martin_DHCP_Attack.py 填写网卡 填写攻击次数 开始运行...
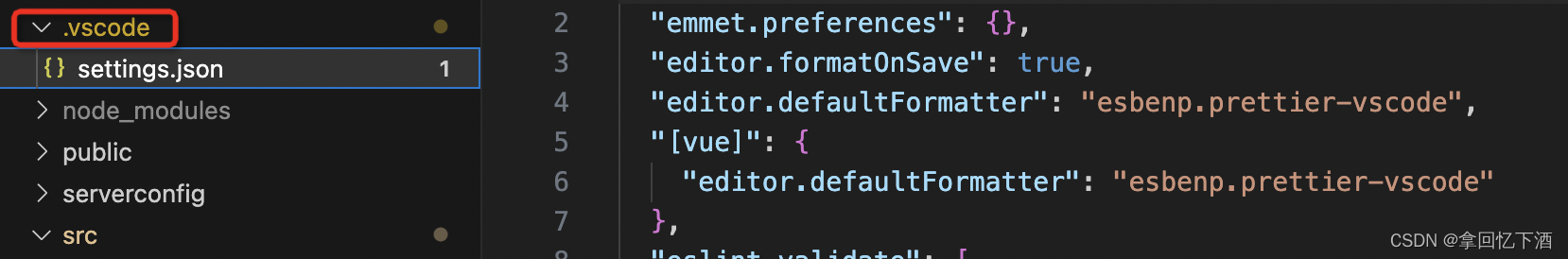
vscode vue3+vite 配置eslint
vue2webpackeslint配置 目前主流项目都在使用vue3vite,因此针对eslint的配置做了一下总结。 引入ESlint、pritter 安装插件,执行以下命令 // eslint // prettier // eslint-plugin-vue // eslint-config-prettier // eslint-plugin-prettier yarn ad…...

【C++学习手札】一文带你初识运算符重载
食用指南:本文在有C基础的情况下食用更佳 🍀本文前置知识: C类 ♈️今日夜电波:クリームソーダとシャンデリア—Edo_Ame江户糖 1:20 ━━━━━━️💟──────── 3:40 …...

javaScript:数组检测
目录 一.前言 二.数组检测方法 1.every() 2.some() 3.filter() 一.前言 数组检测是指在编程中对数组进行验证和检查的过程。数组检测可以涉及以下方面: 确定数组的存在:在使用数…...

【JavaEE基础学习打卡02】是时候了解Java EE了!
目录 前言一、为什么要学习Java EE二、Java EE规范介绍1.什么是规范?2.什么是Java EE规范?3.Java EE版本 三、Java EE应用程序模型1.模型前置说明2.模型具体说明 总结 前言 📜 本系列教程适用于 Java Web 初学者、爱好者,小白白。…...

LeetCode 2813. Maximum Elegance of a K-Length Subsequence【反悔贪心】2582
本文属于「征服LeetCode」系列文章之一,这一系列正式开始于2021/08/12。由于LeetCode上部分题目有锁,本系列将至少持续到刷完所有无锁题之日为止;由于LeetCode还在不断地创建新题,本系列的终止日期可能是永远。在这一系列刷题文章…...

日常BUG——SpringBoot模糊映射
😜作 者:是江迪呀✒️本文关键词:日常BUG、BUG、问题分析☀️每日 一言 :存在错误说明你在进步! 一、问题描述 SpringBoot在启动时报出如下错误: Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateExceptio…...
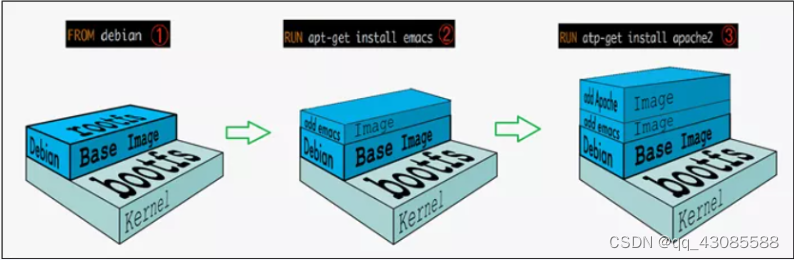
Docker 镜像
1. 什么是镜像? 镜像 是一种轻量级、可执行的独立软件包,它包含运行某个软件所需的所有内容,我们把应用程序和配置依赖打包好形成一个可交付的运行环境(包括代码、运行时需要的库、环境变量和配置文件等),这个打包好的运行环境就…...

Python发送QQ邮件
使用Python的smtplib可以发送QQ邮件,代码如下 #!/usr/bin/python3 import smtplib from email.mime.text import MIMEText from email.header import Headersender 111qq.com # 发送邮箱 receivers [222qq.com] # 接收邮箱 auth_code "abc" # 授权…...

梯度下降求极值,机器学习深度学习
目录 梯度下降求极值 导数 偏导数 梯度下降 机器学习&深度学习 学习形式分类...

【业务功能篇62】Spring boot maven多模块打包时子模块报错问题
程序包 com.xxx.common.utils不存在或者xxx找不到符号 我们项目中一般都是会分成多个module模块,做到解耦,方便后续做微服务拆分模块,可以直接就每个模块进行打包拎出来执行部署这样就会有模块之间的调用,比如API模块会被Service…...
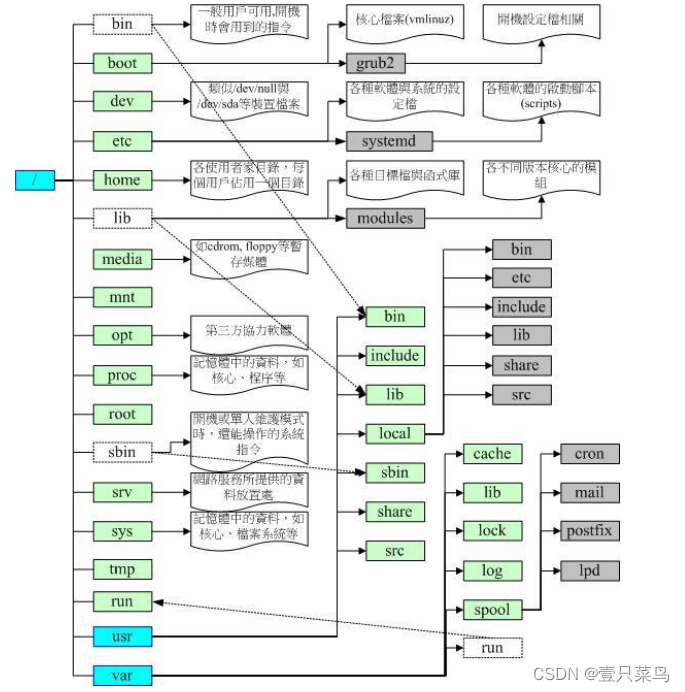
【BASH】回顾与知识点梳理(二十一)
【BASH】回顾与知识点梳理 二十一 二十一. Linux 的文件权限与目录配置21.1 使用者与群组属主(文件拥有者)属组(群组概念)其他人的概念root(万能的天神)Linux 用户身份与群组记录的文件 21.2 Linux 文件权限概念Linux 文件属性Linux 文件权限的重要性 21.3 如何改变文件属性与权…...

从针尖对麦芒,到丝滑入扣,记录那些BT需求
前言: 最近被一个“简单”的需求,搞的有点难受。需求其实很简单,就是记录某成品生产过程数据,然后进行展示,但因需求部门是管理部门。为了能获取足够多的参数来提高生产效率和研发进度。因此需要生产来统计收集对应生产…...

封装vue2局部组件都要注意什么
一. 关于局部组件组成的三个部分(template, script, style) template > 组件的模板结构 (必选) 每个组件对应的模板结构,需要定义到template节点中 <template><!-- 当前组件的dom结构,需…...
第三章 算法从0开始】)
【深入浅出程序设计竞赛(基础篇)第三章 算法从0开始】
深入浅出程序设计竞赛(基础篇)第三章 算法从0开始 第三章 例题例3-1例3-2例3-3例3-4例3-5例3-6例3-7例3-8例3-9例3-10例3-11例3-12 第三章 课后习题3-13-23-33-43-53-63-73-83-9 第三章 例题 例3-1 #include<iostream> using namespace std;int …...
博客目录导读)
安全之安全(security²)博客目录导读
研究方向:安全之安全 研究内容:ARM/RISC-V安全架构、TF-A/TEE之安全、GP安全认证、静态代码分析、FUZZ模糊测试、IDA逆向分析、安全与功耗等,欢迎您的关注💖💖 一、ARM安全架构 1、ARM安全架构及其发展趋势࿰…...

ubuntu安装opencv4
apt 安装 sudo apt install libopencv-dev python3-opencvpkg-config查看安装 sudo apt install pkg-configpkg-config --modversion opencv4pkg-config --libs --cflags opencv4参考 如何在 Ubuntu 20.04 上安装 OpenCV pkg-config 详解...

Qt 当磁盘可用空间小于指定大小时删除早期的文件
1. 需求 用户反应,电脑由于自身磁盘空间只有128G,由于软件执行一次任务,就要录视频记录,导致磁盘空间爆满,电脑卡,无法再次生成视频 2. 分析:当时软件没有写自动删除视频的代码导致的。 可以…...

逻辑回归:给不确定性划界的分类大师
想象你是一名医生。面对患者的检查报告(肿瘤大小、血液指标),你需要做出一个**决定性判断**:恶性还是良性?这种“非黑即白”的抉择,正是**逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)** 的战场&a…...

QMC5883L的驱动
简介 本篇文章的代码已经上传到了github上面,开源代码 作为一个电子罗盘模块,我们可以通过I2C从中获取偏航角yaw,相对于六轴陀螺仪的yaw,qmc5883l几乎不会零飘并且成本较低。 参考资料 QMC5883L磁场传感器驱动 QMC5883L磁力计…...
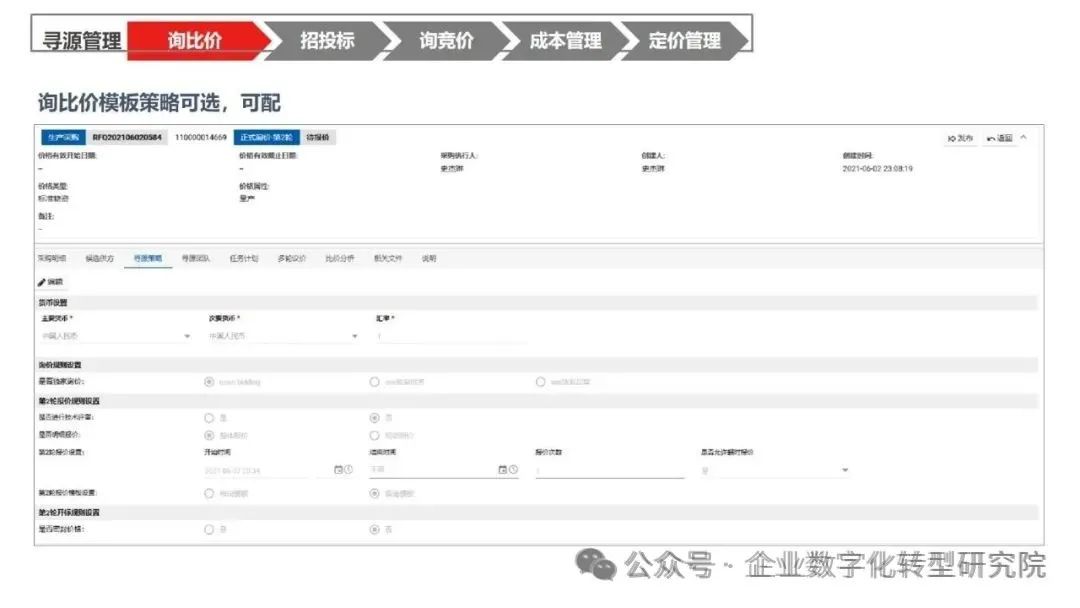
PPT|230页| 制造集团企业供应链端到端的数字化解决方案:从需求到结算的全链路业务闭环构建
制造业采购供应链管理是企业运营的核心环节,供应链协同管理在供应链上下游企业之间建立紧密的合作关系,通过信息共享、资源整合、业务协同等方式,实现供应链的全面管理和优化,提高供应链的效率和透明度,降低供应链的成…...
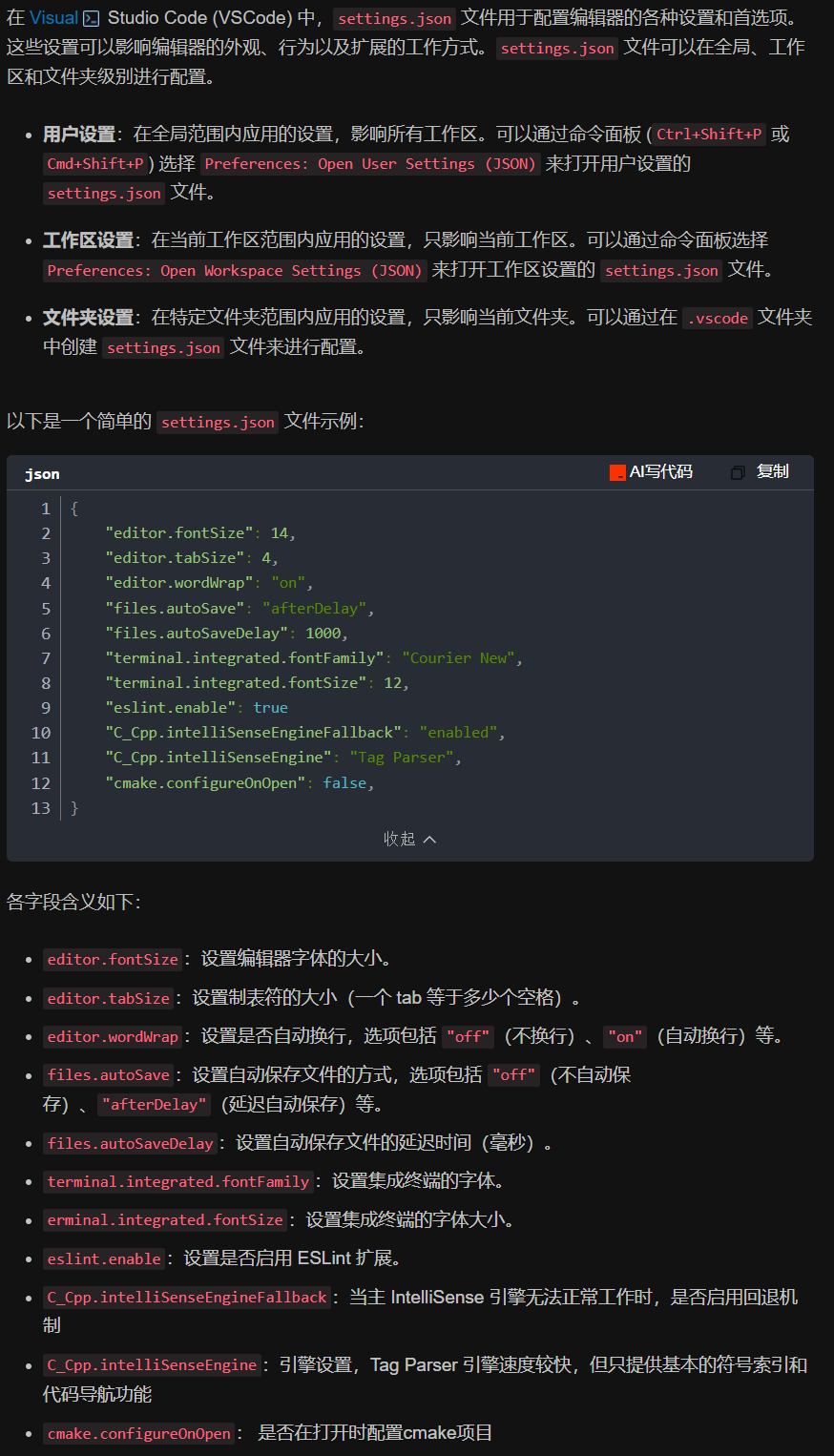
vscode(仍待补充)
写于2025 6.9 主包将加入vscode这个更权威的圈子 vscode的基本使用 侧边栏 vscode还能连接ssh? debug时使用的launch文件 1.task.json {"tasks": [{"type": "cppbuild","label": "C/C: gcc.exe 生成活动文件"…...

FastAPI 教程:从入门到实践
FastAPI 是一个现代、快速(高性能)的 Web 框架,用于构建 API,支持 Python 3.6。它基于标准 Python 类型提示,易于学习且功能强大。以下是一个完整的 FastAPI 入门教程,涵盖从环境搭建到创建并运行一个简单的…...
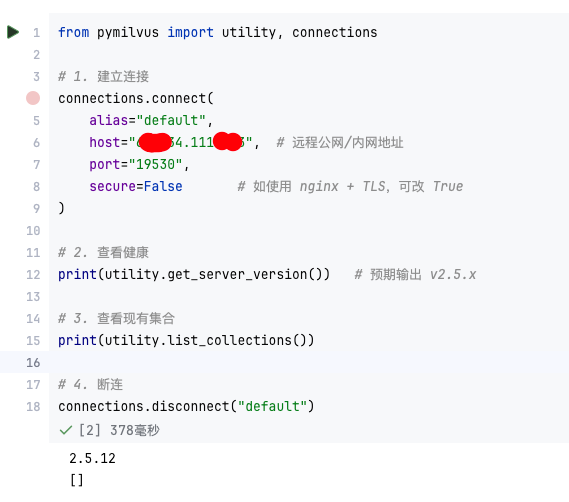
【大模型RAG】Docker 一键部署 Milvus 完整攻略
本文概要 Milvus 2.5 Stand-alone 版可通过 Docker 在几分钟内完成安装;只需暴露 19530(gRPC)与 9091(HTTP/WebUI)两个端口,即可让本地电脑通过 PyMilvus 或浏览器访问远程 Linux 服务器上的 Milvus。下面…...
Mac软件卸载指南,简单易懂!
刚和Adobe分手,它却总在Library里给你写"回忆录"?卸载的Final Cut Pro像电子幽灵般阴魂不散?总是会有残留文件,别慌!这份Mac软件卸载指南,将用最硬核的方式教你"数字分手术"࿰…...
)
WEB3全栈开发——面试专业技能点P2智能合约开发(Solidity)
一、Solidity合约开发 下面是 Solidity 合约开发 的概念、代码示例及讲解,适合用作学习或写简历项目背景说明。 🧠 一、概念简介:Solidity 合约开发 Solidity 是一种专门为 以太坊(Ethereum)平台编写智能合约的高级编…...
用docker来安装部署freeswitch记录
今天刚才测试一个callcenter的项目,所以尝试安装freeswitch 1、使用轩辕镜像 - 中国开发者首选的专业 Docker 镜像加速服务平台 编辑下面/etc/docker/daemon.json文件为 {"registry-mirrors": ["https://docker.xuanyuan.me"] }同时可以进入轩…...

A2A JS SDK 完整教程:快速入门指南
目录 什么是 A2A JS SDK?A2A JS 安装与设置A2A JS 核心概念创建你的第一个 A2A JS 代理A2A JS 服务端开发A2A JS 客户端使用A2A JS 高级特性A2A JS 最佳实践A2A JS 故障排除 什么是 A2A JS SDK? A2A JS SDK 是一个专为 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者设计的强大库ÿ…...
