【C++初阶】模拟实现list

👦个人主页:@Weraphael
✍🏻作者简介:目前学习C++和算法
✈️专栏:C++航路
🐋 希望大家多多支持,咱一起进步!😁
如果文章对你有帮助的话
欢迎 评论💬 点赞👍🏻 收藏 📂 加关注✨
目录
- 一、简单剖析list源码
- 二、准备工作
- 三、模拟实现list常见操作
- 3.1 默认构造函数
- 3.2 push_back - 尾插
- 3.3 迭代器(重点)
- 3.4 const的迭代器(重点)
- 3.5 insert - 插入
- 3.6 erase - 删除
- 3.7 头插 - push_front
- 3.8 尾删 - pop_back
- 3.9 头删 - pop_front
- 3.10 个数 - size
- 3.11 析构
- 3.12 清空 - clear
- 3.13 拷贝构造
- 3.14 交换
- 3.15 赋值运算符重载
- 四、源码
一、简单剖析list源码
在模拟vector容量讲过,要想快速了解STL源码,首先要看成员变量:
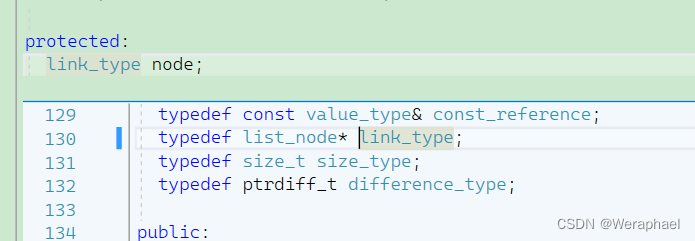
node从名字上猜测是一个节点,其类型是list_node。然后我发现list_node也是重命名出来的:
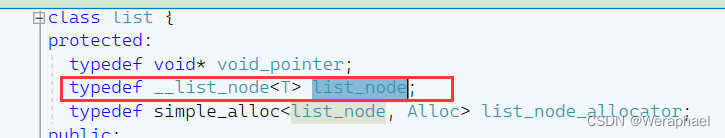
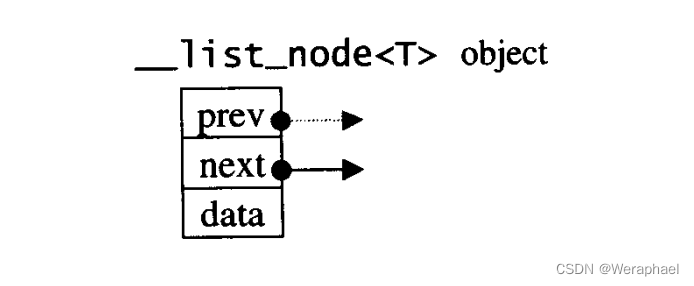
而__list_node<T>又是什么东西呢?如下所示:
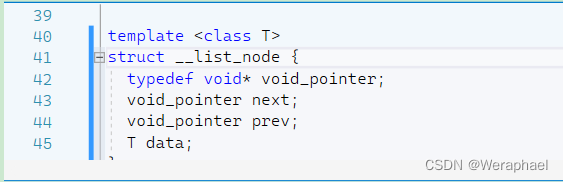
显然这是一个双向链表,并且__list_node是用来定义结点的
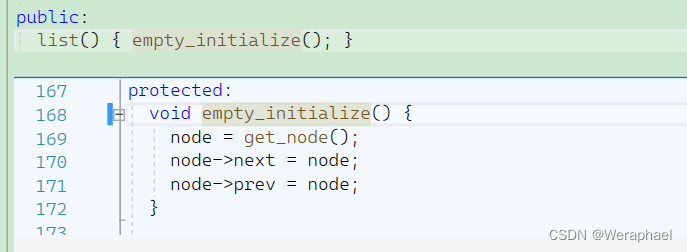
接下来就应该分析构造函数:
get_node从名字上是得到结点,那么应该是开辟空间的。我们可以简单看看:
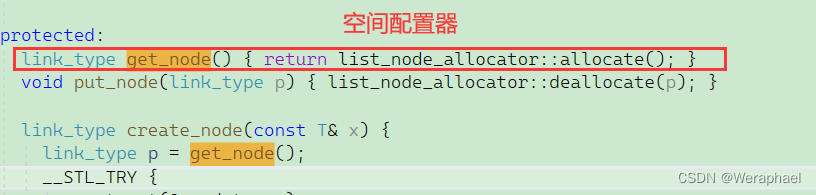
空间配置器讲起来有点麻烦,直接使用new和delete也是够用的
然后node的next和prev都指向自己。因此list的底层是一个带头(哨兵位)双向循环链表,因此list的成员变量应该是哨兵位结点。
大致结构我们已经知道了,不妨再来看看插入操作:
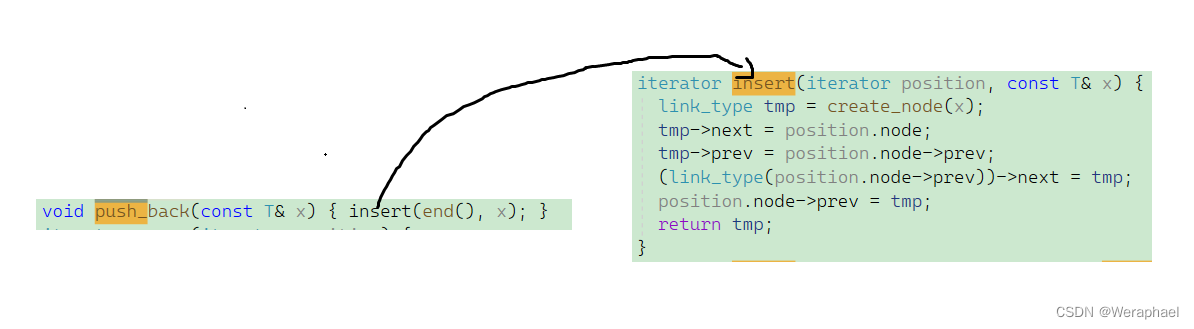
这和以往学习过的双向循环链表很相似,无非就是创造新的结点,然后再把它们链接起来。
大致内容已经了解了,直接开始实现吧~
二、准备工作
为了方便管理代码,分两个文件来写:
Test.cpp- 测试代码逻辑list.h- 模拟实现list
三、模拟实现list常见操作
3.1 默认构造函数
namespace wj
{template<class T>struct list_node // 定义结点{list_node<T>* _next; list_node<T>* _prev;T _val;};template<class T>class list{public:list(){// 为哨兵位头结点开空间_head = new list_node<T>;// 自己指向自己_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;}private:list_node<T> _head; // 哨兵位(不存储有效数据)};
}
定义结点的成员变量最好是公有的,方便类外可以随时访问。注意:此处的struct可不是C语言的结构体,在C++中已经升级成了类,并且默认成员都是公有的。当然使用class也是没问题的,只是要加上public。
以上代码还能简化,我们知道类模板和普通类是不同的,普通类的类名即是类型,而类模板的类名是类名<T>。而有许多人会很容易忘记加上<T>,因此我们可以对list_node<T>进行重命名typedef:
namespace wj
{template<class T>struct list_node // 定义结点{list_node<T>* _next; list_node<T>* _prev;T _val;};template<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:list(){// 为哨兵位头结点开空间_head = new Node;// 自己指向自己_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;}private:list_node<T> _head; // 哨兵位(不存储有效数据)};
}
- 为了防止与库的
list冲突,要重新写一个命名空间域wjtypedef在类中是有讲究的。如果typedef放在public段中,则可以在类外部使用;而如果放在private段中,则只能在类内使用。注意:上述代码是只能在类中使用!
3.2 push_back - 尾插
void push_back(const T& val)
{//1. 找尾(哨兵位的prev)Node* tail = _head->_prev;// 2. 开辟一个新节点Node* newnode = new Node(val); // 3. 链接 _head tail newnodetail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;
}
尾插就容易多了,下面有图帮助大家理解:
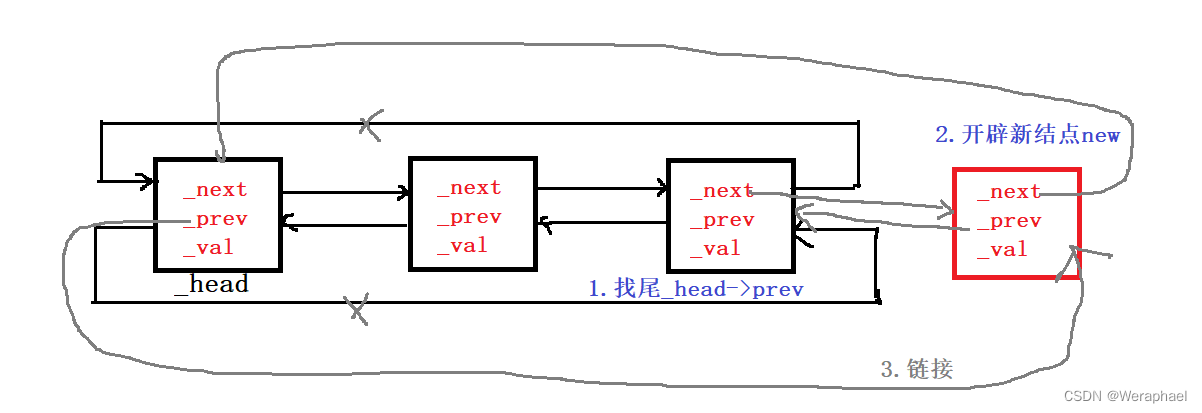
注意:new对于自定义类型除了开空间,还会调用构造函数。初始化_val
struct list_node // 结点的定义
{list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _val; list_node(const T& val = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _val(val){}
};
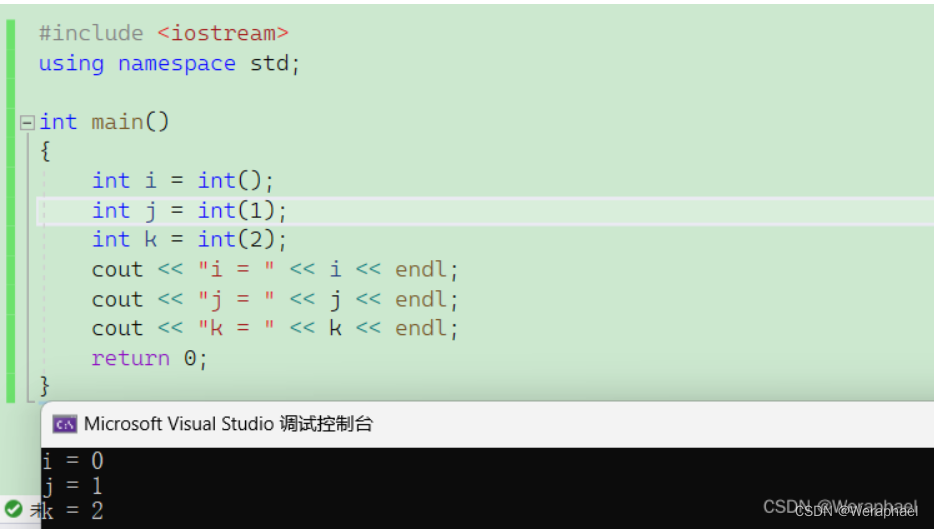
缺省值给T()相信看过模拟实现vector都不陌生。不能直接给0,这样就写死能,只能int类型适用,对于string就不行了。因此可以给个匿名对象,它会调用T类型的默认构造。内置类型也是有默认构造的:
3.3 迭代器(重点)
能否定义类似像vector的迭代器?如下所示:
typedef Node* iterator;
答案当然不行!list不能像vector一样以原生指针(普通指针)作为迭代器。
vector类似于数组,数据在内存中是连续存储的。对迭代器(指针)++,就可以跳过一个对象的大小,并且解引用也能得到对应的数据;然而,list的节点不能保证一定在内存空间中连续存在,导致++/--不一定能找到下一个节点,并且对其解引用得到的是结点而不是有效数据。
那问题来了,如何定义list的迭代器呢?
我们可以封装一个类,然后用重载运算符去改变指针的行为。为什么可以这样呢?原因是:内置类型的++是行为规定的,但是自定义类型的++是自己说的算。可以联想以往实现的日期类->点击跳转
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{cout << *it << ' ';++it;
}
我们可以对照以上代码一步一步实现迭代器
begin() + end()
在这个类中,只需要一个结点类的指针成员变量,用于指向list某一个结点, 在一开始定义迭代器时,需要一个构造函数,用于迭代器的初始化。注意:begin和end需要定义在list类中,因为它们本身就是list内置的接口函数
// 封装一个类实现迭代器
template<class T>
struct __list_iterator
{typedef list_node<T> Node;Node* _node; //指向某个节点的指针// 迭代器的初始化__list_iterator(Node* node) :_node(node){}
};template<class T>
class list
{typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:typedef __list_iterator<T> iterator; iterator begin(){return _head->_next;// return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return _head;//return iterator(_head);}
private:Node* _head;
};
这里还有一个知识点,begin和end返回类型为迭代器,怎么能返回结点的指针呢?— 这是因为单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换。
!=、==、*、++、--
封装一个类,然后用重载运算符去改变指针的行为
// 封装一个类实现迭代器
template<class T>
struct __list_iterator
{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T> self;Node* _node; //指向某个节点的指针__list_iterator(Node* node) // 迭代器的初始化:_node(node){}
/// 用结点的指针比bool operator!=(const self& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _node == it._node;}
/T& operator*(){// 出了作用域,结点还在,引用返回return _node->_val;}
/// 迭代器++返回的还是迭代器self& operator++() //前置{_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator--() // 前置{_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int) // 后置{self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}self operator++(int) // 后置{self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}
};
前置++和后置++会发生一个问题:函数名会相同。因此,C++规定:后置(++/--)重载时多增加一个int类型的参数,但调用函数时该参数不用传递。
3.4 const的迭代器(重点)
现在又有一个问题,const的迭代器也能否像类似于vector一样设计?如下所示:
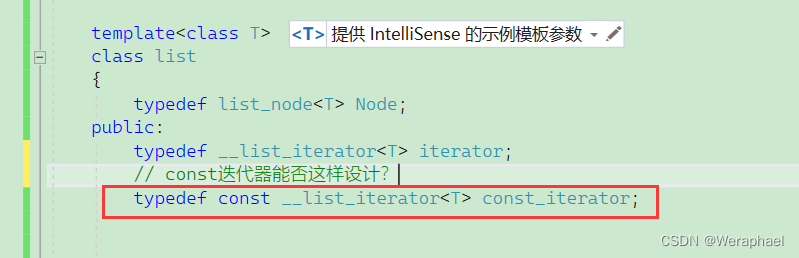
答案当然是不可以的!这是因为 const迭代器要求的是迭代器指向的内容不可以被修改,而对一个类加上一个const,这是让这个类对象无法被修改啊。也就是类的成员变量都不可以被修改,这样一来,这个迭代器里面的指针无法移动了。(const的迭代器指针是可以移动的,但是指向的内容不可被修改)
那么const的迭代器该如何设计呢?我们知道,list迭代器输出数据是依靠解引用的,因此可以在返回值加上const
template<class T>
struct __list_iterator
{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T> selfNode* _node; //指向某个节点的指针__list_iterator(Node* node) // 迭代器的初始化:_node(node){}// 用结点的指针比bool operator!=(const self& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _node == it._node;}T& operator*(){// 出了作用域,结点还在,引用返回return _node->_val;}// 迭代器++返回的还是迭代器self& operator++() //前置{_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator--() // 前置{_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int) // 后置{self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}self operator++(int) // 后置{self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}
};template<class T>
struct __list_iterator
{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T> self;Node* _node; //指向某个节点的指针__list_iterator(Node* node) // 迭代器的初始化:_node(node){}// 用结点的指针比bool operator!=(const self& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _node == it._node;}const T& operator*(){// 出了作用域,结点还在,引用返回return _node->_val;}// 迭代器++返回的还是迭代器self& operator++() //前置{_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator--() // 前置{_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int) // 后置{self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}self operator++(int) // 后置{self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}
};
但以上代码显得有点冗余,只有两个函数的返回值不一样,其它都是一样的。那还有什么别的设计方法呢?
注意:上面两个函数只要返回值的类型不一样,因此可以通过一个类型来控制返回值 -> 即增加一个模板参数(库里也是这么实现的~)
// 封装一个类实现迭代器
template<class T, class Ref> // 增加一个模板参数
struct __list_iterator
{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref> self;Node* _node; //指向某个节点的指针__list_iterator(Node* node) // 迭代器的初始化:_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}
}template<class T>
class list
{typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}
private:list_node<T> _head; // 哨兵位(不存储有效数据)
};
补充:除了重载*运算符,当然也要重载->操作符
T* operator->()
{return &_node->_val;
}
那什么时候会用到->操作符呢?下面有个例子:
#include <iostream>
#include "list.h"
using namespace std;struct A
{A(int a = 0):_a(a){}int _a;
};
int main()
{wj::list<A> lt;lt.push_back(A(1));lt.push_back(A(2));lt.push_back(A(3));lt.push_back(A(4));lt.push_back(A(5));wj::list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << it->_a << " ";it++;}cout << endl;
}
【输出结果】
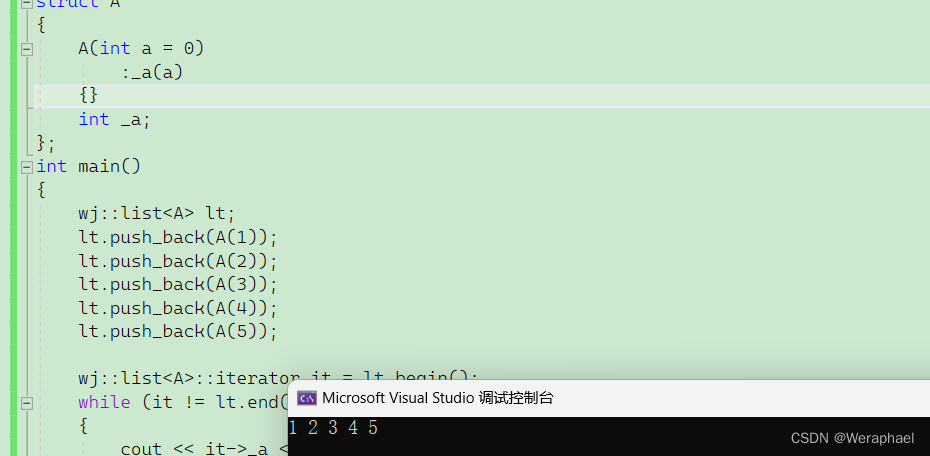
有没有发现operator->非常怪,首先我们这个运算符重载返回的是什么呢?是T*,也就是A*,也就是说它还需要一次->才能打印_a。严格来说,it->->_a,才是符合语法的。那么这里为什么还能编译通过呢?因为运算符重载要求可读性,那么编译器特殊处理,省略了一个->
但是以上代码还是不够完善,由于->只针对普通对象,如果是const对象,其返回值应该是const T*,这个问题就和运算符重载*类似了,再增加一个模板参数,因此完整代码如下:
template<class T, class Ref, class ptr>
struct __list_iterator // 迭代器
{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, ptr> self;Node* _node; //指向某个节点的指针__list_iterator(Node* node) // 迭代器的初始化:_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;// 出了作用域,结点还在,要加&}ptr operator->() {return &_node->_val;}
}template<class T> // 为list提供
class list
{typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator; iterator begin(){// return iterator(_head->_next);return _head->_next;}iterator end(){// return iterator(_head);return _head;}
private:Node* _head; // 哨兵位(不存储有效数据)
};
3.5 insert - 插入
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{// pos 不需要检查 // 假设在node前插入// head newnode node tail// 步骤如下// 1. 开辟新的结点Node* newnode = new Node(x);// 2. 找到要删除的结点nodeNode* cur = pos._node;// 3. 以及node的前一个节点Node* prev = cur->_prev;// 4. 链接prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;return newnode;// 返回新插入元素的位置
}
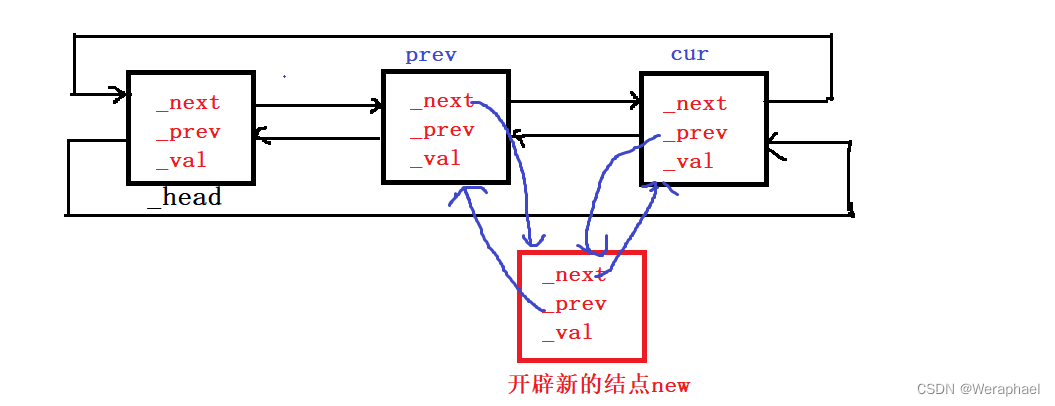
3.6 erase - 删除
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{// 检查pos的有效性assert(pos != end());// 1.分别找到pos的前一个节点和后一个节点Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;// 2, 链接prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;// 3. 删除delete cur;// 注意:list的erase会有迭代器失效问题// 返回删除元素的下一个位置return next;
}
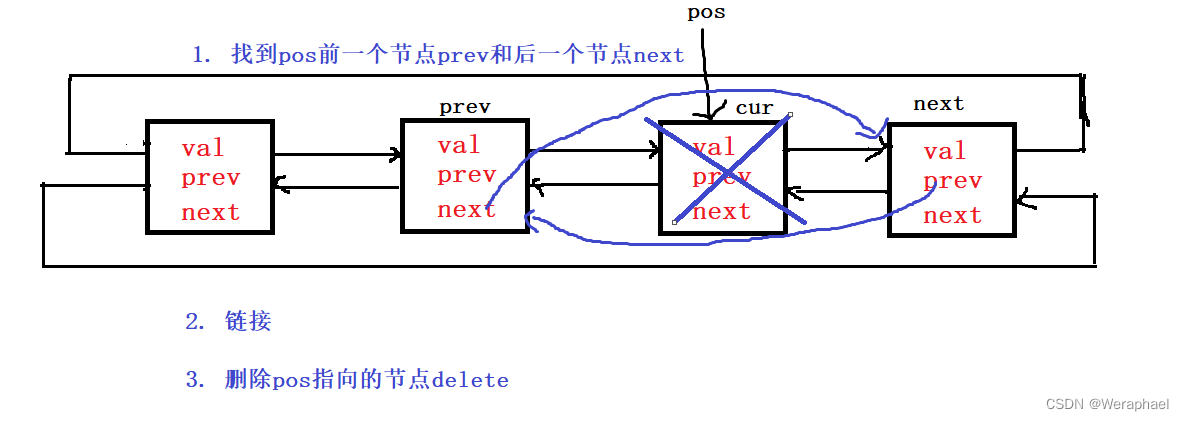
3.7 头插 - push_front
复用insert
void push_front(const T& val)
{insert(begin(), val);
}
3.8 尾删 - pop_back
复用erase
void pop_back()
{erase(--end());
}
3.9 头删 - pop_front
void pop_front()
{erase(begin());
}
3.10 个数 - size
遍历即可
size_t size()
{size_t count = 0;iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){++count;++it;}return count;
}
或者还可以在成员变量中定义size_t _size,每次插入数据++,以及删除数据--即可
3.11 析构
~list()
{clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;
}
3.12 清空 - clear
void clear()
{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}
}
3.13 拷贝构造
list(const list<T>& it)
{_head = new Node;_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;for (auto& e : it){push_back(e);}
}
3.14 交换
void swap(list<T> it)
{std::swap(_head, it._head);std::swap(this->size(), it._size());
}
3.15 赋值运算符重载
list<T>& operator=(const list<T> it)
{swap(it);return *this;
}
四、源码
#pragma once
#include <assert.h>namespace wj
{template<class T> struct list_node {list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _val; list_node(const T& val = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _val(val){}};template<class T, class Ref, class ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, ptr> self;Node* _node; __list_iterator(Node* node) :_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}ptr operator->() {return &_node->_val;}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self& operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _node == it._node;}};template<class T> class list{typedef list_node<T> Node; public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator; iterator begin(){// return iterator(_head->_next);return _head->_next;}iterator end(){// return iterator(_head);return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{//return _head->_next;return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return _head;//return const_iterator(_head);}list(){_head = new Node;_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;_size = 0;}list(const list<T>& it){_head = new Node;_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;_size = 0;for (auto& x : it){push_back(x);}}void push_back(const T& val){Node* tail = _head->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(val);tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;_size++;}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;_size++;return newnode;}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;_size--;return next;}void push_front(const T& val){insert(begin(), val);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}size_t size(){/*size_t count = 0;iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){++count;++it;}return count;*/return _size;}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}_size = 0;}void swap(list<T> it){std::swap(_head, it._head);std::swap(_size, it._size);}list<T>& operator=(const list<T> it){swap(it);return *this;}private:Node* _head; size_t _size;};
}
测试代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "list.h"int main()
{// 默认构造wj::list<int> ll;// 尾插测试ll.push_back(1);ll.push_back(2);ll.push_back(3);ll.push_back(4);// 迭代器测试wj::list<int>::iterator it = ll.begin();while (it != ll.end()){cout << *it << ' ';it++;}cout << endl;// 范围for(底层迭代器)for (auto& x : ll){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;// insert测试// 在3的前面插入30it = ll.begin();for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){it++;}ll.insert(it, 30);for (auto& x : ll){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;// erase测试it = ll.begin();// 删除30for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){it++;}ll.erase(it);for (auto x : ll){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;// 头插测试// 头插100ll.push_front(100);for (auto x : ll){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;// 尾删测试ll.pop_back(); // 100 1 2 3for (auto x : ll){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;// 头删测试ll.pop_front(); // 1 2 3for (auto x : ll){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;// size测试cout << "个数为:" << ll.size() << endl; // 3// 清空ll.clear();for (auto x : ll){cout << x << ' '; // 无输出}cout << endl;// 拷贝构造ll.push_back(1);ll.push_back(2);ll.push_back(3);ll.push_back(4);ll.push_back(5);wj::list<int> lll(ll);for (auto x : lll){cout << x << ' '; // 1 2 3 4 5}cout << endl;// 赋值运算符重载wj::list<char> a;a.push_back('a');wj::list<char> b;b.push_back('b');b.push_back('b');b.push_back('b');a = b;for (auto x : a){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;// 交换wj::list<char> c;a.push_back('c');wj::list<char> d;b.push_back('d');b.push_back('d');b.push_back('d');d.swap(c);for (auto x : c){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;for (auto x : d){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;return 0;
}
相关文章:

【C++初阶】模拟实现list
👦个人主页:Weraphael ✍🏻作者简介:目前学习C和算法 ✈️专栏:C航路 🐋 希望大家多多支持,咱一起进步!😁 如果文章对你有帮助的话 欢迎 评论💬 点赞…...
三维模拟推演电子沙盘虚拟数字沙盘开发教程第13课
三维模拟推演电子沙盘虚拟数字沙盘开发教程第13课 该数据库中只提供 成都市火车南站附近的数据请注意,104.0648,30.61658 在SDK中为了方便三方数据的接入,引入了一个用户层接口。主要是完成三方数据的接入,含动态数据(如GPS&…...

flask中GET和POST的区别
GET和POST是HTTP协议中两种常用的请求方法,它们在如何向服务器发送数据以及数据传输方式上有所不同。下面是GET和POST的主要区别: 一、数据传输位置: GET:将数据通过URL的查询字符串部分(即URL的参数)传递…...
基于Spring Boot的游泳馆管理系统的设计与实现(Java+spring boot+MySQL)
获取源码或者论文请私信博主 演示视频: 基于Spring Boot的游泳馆管理系统的设计与实现(Javaspring bootMySQL) 使用技术: 前端:html css javascript jQuery ajax thymeleaf 微信小程序 后端:Java spring…...
)
git冲突处理(已commit但忘pull的情况)
一般来说,你只要记得先拉再传就不会有问题,但如果pull后没有立刻push,这段时间刚好有人push了,就会导致冲突,那么你可以使用以下方法进行版本回退之后合并代码 步骤: git log查看所有的commit,…...

嵌入式设备应用开发(发现需求和提升价值)
【 声明:版权所有,欢迎转载,请勿用于商业用途。 联系信箱:feixiaoxing @163.com】 很多做技术的同学,都会陷入到技术的窠臼之中。对于如何做具体的产品、实现具体的技术,他们可能很感兴趣。但是做出来的东西做什么用,或者说是有没有竞争力,事实上他们不是很关心…...

Redis Replication
Redis Replication 1、前言 在单节点搞事情, 存在的问题包括存量问题和增量问题两类, 解决方案就是1个不行上N个, 做到单机维度宕机但服务维度是可用的。 1.1 存量问题 如果目前的单节点QPS满足(也就是综合瓶颈还没达到), 那么只有宕机能影响到。如果业务量不大, 又是出于成…...
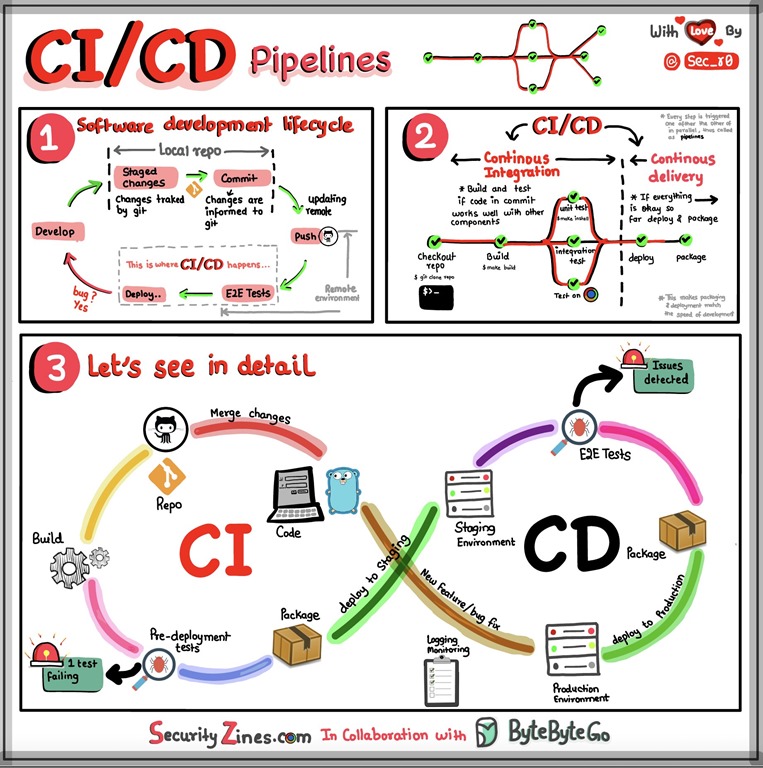
软件研发CI/CD流水线图解
当谈到现代软件开发流程时,持续集成(Continuous Integration,简称CI)和持续交付(Continuous Delivery,简称CD)是两个关键的实践。它们旨在加速开发流程、提高软件质量,并使软件发布更…...

代码随想录第五十九天
代码随想录第五十九天 Leetcode 503. 下一个更大元素 IILeetcode 42. 接雨水 Leetcode 503. 下一个更大元素 II 题目链接: 下一个更大元素 II 自己的思路:没想到哈哈哈哈!! 正确思路:这个题在单调栈的情况下转了一个弯,就是需要取一个模操作…...

“yarn“、“npm“、“cnpm“和“pnpm“的区别
"yarn"、"npm"、"cnpm"和"pnpm"的区别 npm优点:缺点: yarn优点:缺点: cnpm优点:缺点: pnpm优点:缺点: 总结: npm npm…...

批量将txt文件转化为excel文件
可以使用Python的内置库csv和openpyxl来完成这个任务。以下是一个基本的代码示例: import csv from openpyxl import Workbook # 遍历目录中的所有.txt文件 for filename in glob.glob(*.txt): with open(filename, r) as infile: reader csv.reader(…...

StringIndexOutOfBoundsException: String index out of range: 458
报错信息: org.springframework.dao.TransientDataAccessResourceException: ### Error updating database. Cause: java.sql.SQLException: java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException: String index out of range: 458 ... ... ... 问题原因: <i…...
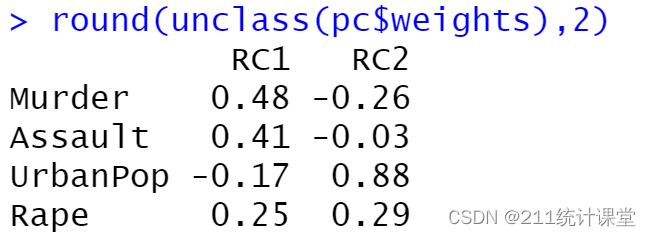
R语言主成分分析
R语言主成分分析 之前介绍过怎么用SPSS进行主成分分析(PCA),已经忘了的朋友们可以到主页看看 今天主要介绍下R语言主成分分析的几种方法。都是入门级别,跟着我一步步走,一点都不难哈~ 首先调用R语言自带的数据集,USArrests。这…...
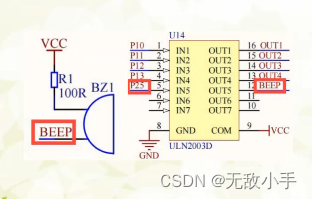
单片机学习-蜂鸣器如何发出声音
硬件电路 软件编写 ①发出声音 #include "reg52.h" typedef unsigned int u16; // 重新定义 类型 typedef unsigned char u8; // 重新定义 类型sbit BEEP P2^5; //定义 P2第五个管教 为BEEP // 延时函数 void delay_time(u16 times) {while(times--); } vo…...
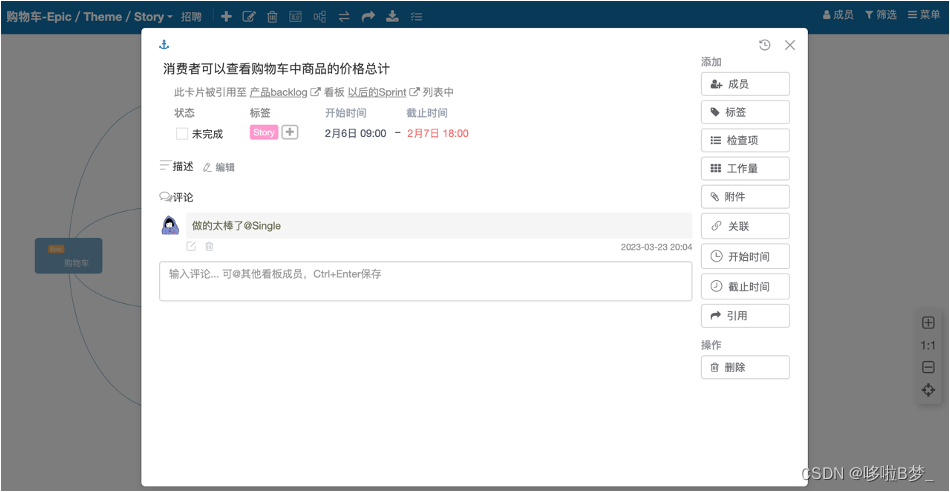
利用敏捷开发工具实现敏捷项目管理的实践经验分享
Scrum中非常强调公开、透明、直接有效的沟通,这也是“可视化的管理工具”在敏捷开发中如此重要的原因之一。通过“可视化的管理工具”让所有人直观的看到需求,故事,任务之间的流转状态,可以使团队成员更加快速适应敏捷开发流程。 …...

代码随想录训练营 贪心02
代码随想录训练营 贪心01 🌸55. 跳跃游戏🌸代码 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II45. 跳跃游戏 II 🌸55. 跳跃游戏🌸 给你一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的 第一个下标 。数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的…...
)
Linux安装NVM(简洁版)
安装目录 mkdir /opt/nvm && cd /opt/nvm 安装包下载 wget https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm/archive/refs/tags/v0.39.5.tar.gz 注意:https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm/tags获取下载链接并替换 安装包解压 for file in *.tar.gz; do tar -zxvf "$file&quo…...
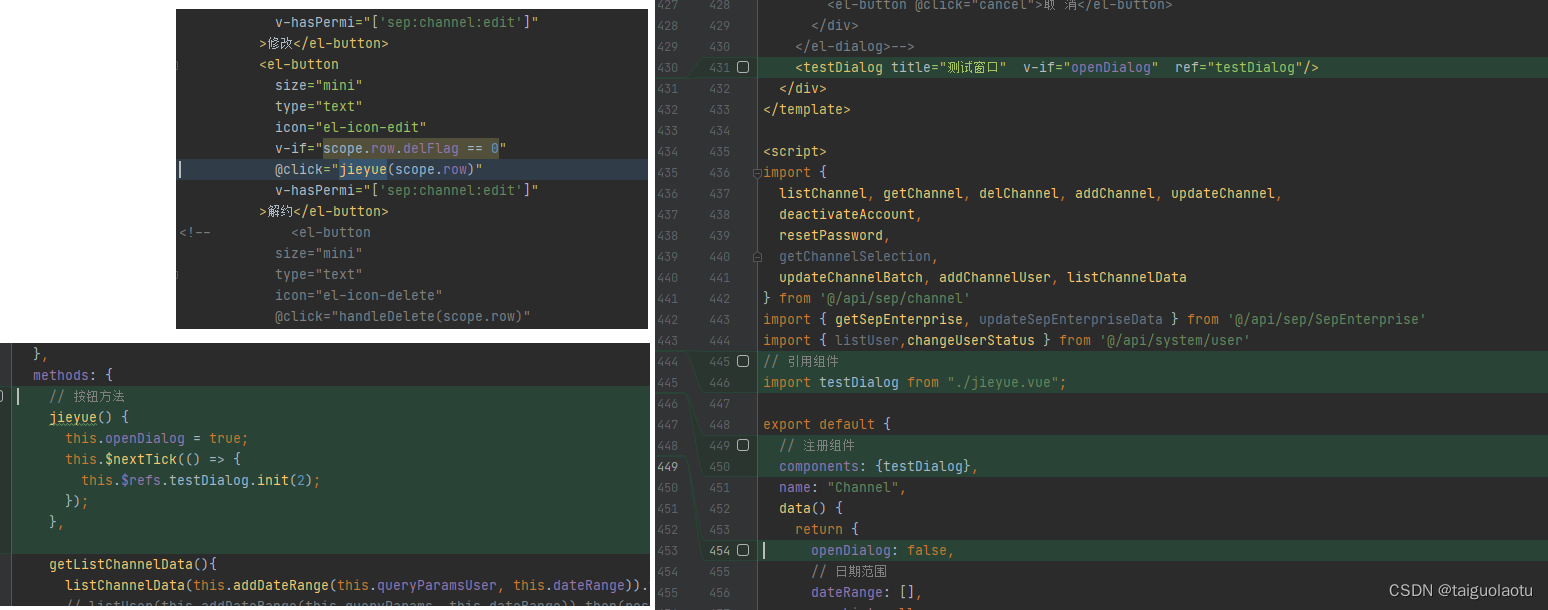
vue 弹出框 引入另一个vue页面
为什么要这么做,适用于在一个页面逻辑比较多的时候,可以搞多个页面,防止出错 index页面点击解约按钮,弹出框 进入jieyue.vue 核心代码 <el-buttonsize"mini"type"text"icon"el-icon-edit"v-if"scope.row.delFlag 0"click"j…...
为Android做一个ShowModal窗口
大家知道,用Delphi实现一个Form,并用ShowModal显示出来,在Android平台是非阻塞的,即执行了Form.ShowModal,代码会继续往下执行而不是等待,这跟在Windows平台是完全不一样的。如果我们需要类似阻塞的效果&am…...
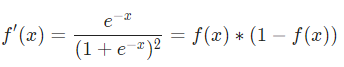
神经网络的工作原理
目录 神经网络的介绍 神经网络的组成 神经网络的工作原理 Numpy 实现神经元 Numpy 实现前向传播 Numpy 实现一个可学习的神经网络 神经网络的介绍 神经网络受人类大脑启发的算法。简单来说,当你睁开眼睛时,你看到的物体叫做数据,再由你…...
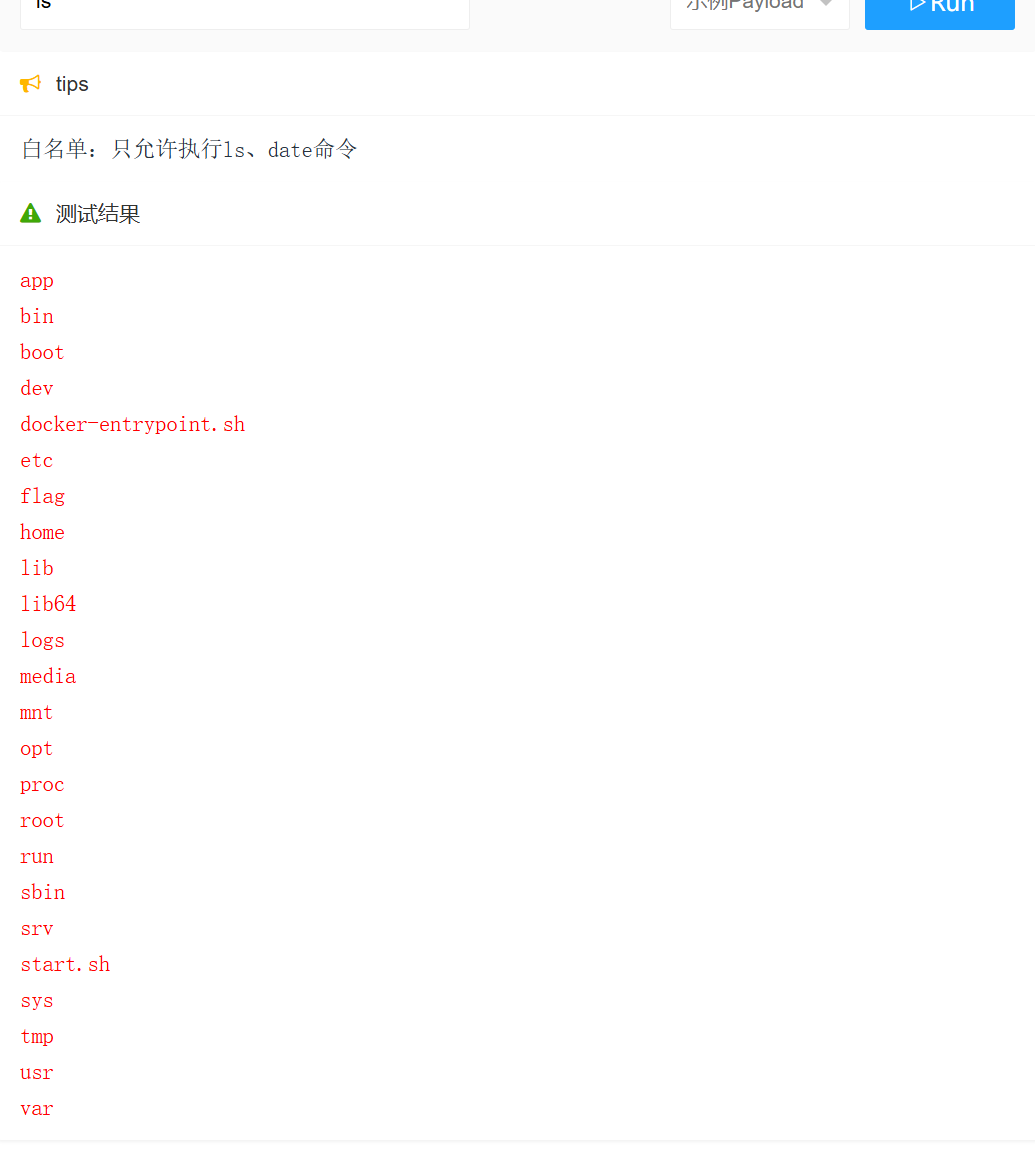
JavaSec-RCE
简介 RCE(Remote Code Execution),可以分为:命令注入(Command Injection)、代码注入(Code Injection) 代码注入 1.漏洞场景:Groovy代码注入 Groovy是一种基于JVM的动态语言,语法简洁,支持闭包、动态类型和Java互操作性,…...

从零实现富文本编辑器#5-编辑器选区模型的状态结构表达
先前我们总结了浏览器选区模型的交互策略,并且实现了基本的选区操作,还调研了自绘选区的实现。那么相对的,我们还需要设计编辑器的选区表达,也可以称为模型选区。编辑器中应用变更时的操作范围,就是以模型选区为基准来…...
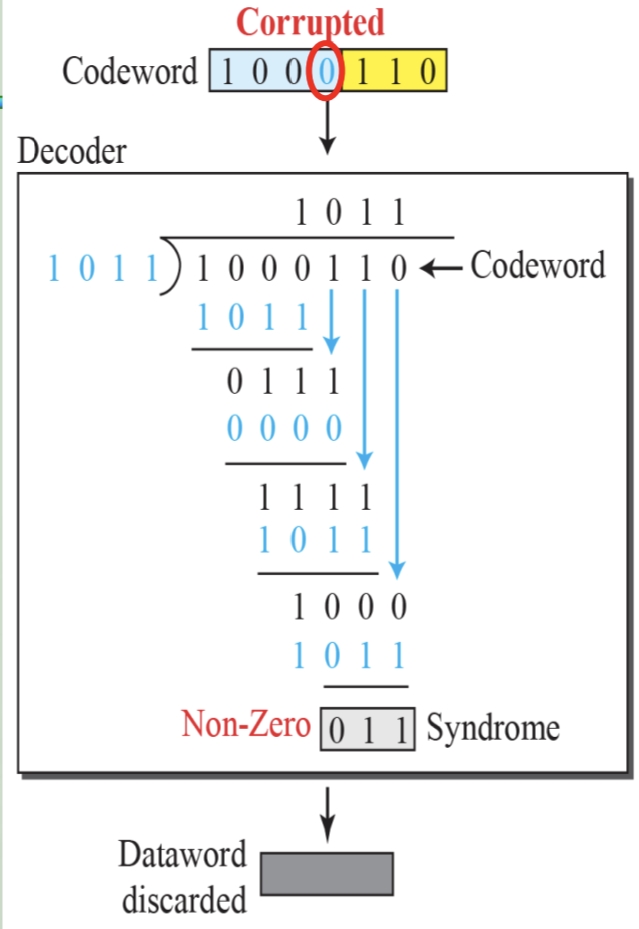
循环冗余码校验CRC码 算法步骤+详细实例计算
通信过程:(白话解释) 我们将原始待发送的消息称为 M M M,依据发送接收消息双方约定的生成多项式 G ( x ) G(x) G(x)(意思就是 G ( x ) G(x) G(x) 是已知的)࿰…...

Objective-C常用命名规范总结
【OC】常用命名规范总结 文章目录 【OC】常用命名规范总结1.类名(Class Name)2.协议名(Protocol Name)3.方法名(Method Name)4.属性名(Property Name)5.局部变量/实例变量(Local / Instance Variables&…...
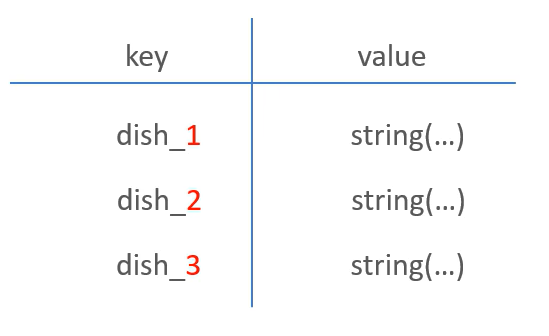
苍穹外卖--缓存菜品
1.问题说明 用户端小程序展示的菜品数据都是通过查询数据库获得,如果用户端访问量比较大,数据库访问压力随之增大 2.实现思路 通过Redis来缓存菜品数据,减少数据库查询操作。 缓存逻辑分析: ①每个分类下的菜品保持一份缓存数据…...

工业自动化时代的精准装配革新:迁移科技3D视觉系统如何重塑机器人定位装配
AI3D视觉的工业赋能者 迁移科技成立于2017年,作为行业领先的3D工业相机及视觉系统供应商,累计完成数亿元融资。其核心技术覆盖硬件设计、算法优化及软件集成,通过稳定、易用、高回报的AI3D视觉系统,为汽车、新能源、金属制造等行…...

【HTTP三个基础问题】
面试官您好!HTTP是超文本传输协议,是互联网上客户端和服务器之间传输超文本数据(比如文字、图片、音频、视频等)的核心协议,当前互联网应用最广泛的版本是HTTP1.1,它基于经典的C/S模型,也就是客…...
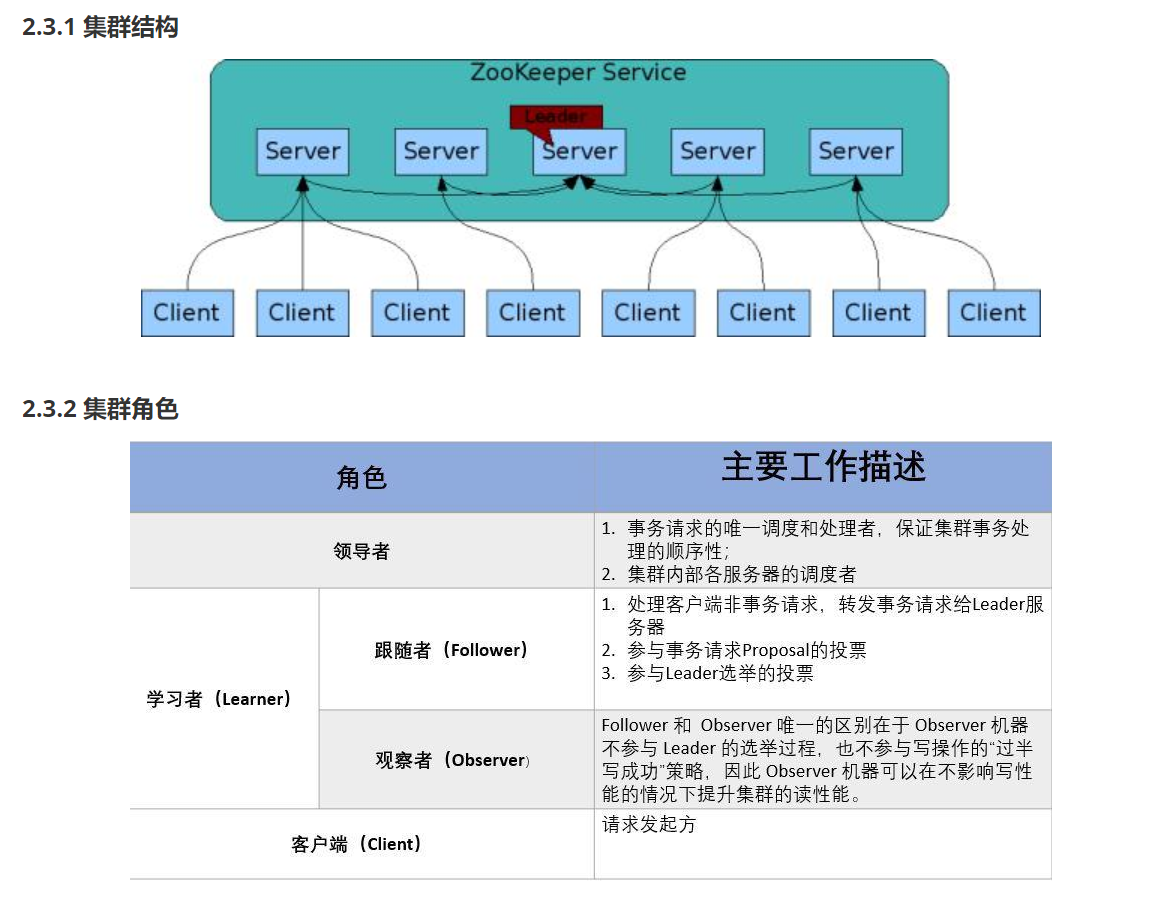
HDFS分布式存储 zookeeper
hadoop介绍 狭义上hadoop是指apache的一款开源软件 用java语言实现开源框架,允许使用简单的变成模型跨计算机对大型集群进行分布式处理(1.海量的数据存储 2.海量数据的计算)Hadoop核心组件 hdfs(分布式文件存储系统)&a…...

A2A JS SDK 完整教程:快速入门指南
目录 什么是 A2A JS SDK?A2A JS 安装与设置A2A JS 核心概念创建你的第一个 A2A JS 代理A2A JS 服务端开发A2A JS 客户端使用A2A JS 高级特性A2A JS 最佳实践A2A JS 故障排除 什么是 A2A JS SDK? A2A JS SDK 是一个专为 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者设计的强大库ÿ…...
mac 安装homebrew (nvm 及git)
mac 安装nvm 及git 万恶之源 mac 安装这些东西离不开Xcode。及homebrew 一、先说安装git步骤 通用: 方法一:使用 Homebrew 安装 Git(推荐) 步骤如下:打开终端(Terminal.app) 1.安装 Homebrew…...