算法18:LeetCode_链表相关算法题
链表无小事,只要是涉及到链表的算法题,边界值的设定尤为重要,而且及其容易出错误。这就要求我们平时多加练习。但是,我们在面试和笔试的过程中往往会碰到链表相关的题目,所以我们在笔试的时候一般都会借助系统提供的工具类进行解答,但是在面试的过程中,面试官往往想听到的答案是和链表直接相关的解答。这就要求我们有2套不同的应答方案。
题目1:给定一个单链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构
package code03.链表_01;import java.util.Stack;/*** 给定一个单链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构* https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/** 1)哈希表方法特别简单(笔试用)* 2)改原链表的方法就需要注意边界了(面试用)*/
public class Palindrome_01 {static class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;ListNode() {}ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }}//笔试用, 怎么简单怎么来,安全保险最重要public boolean isPalindrome (ListNode head){//Letcode 默认仅有一个节点的链表也是回文if (head == null /*|| head.next == null*/) {return false;}//后进先出,正好和node是反着的Stack stack = new Stack();ListNode node = head;while (node != null) {stack.push(node);node = node.next;}boolean isPadinDrom = true;while (head != null) {if (head.val != ((ListNode) stack.pop()).val) {isPadinDrom = false;break;}head = head.next;}return isPadinDrom;}//面试用, 对链表进行操作,大体思路对即可,高端大气上档次//这种写法节省了额外空间复杂度 Stackpublic boolean isPalindrome2 (ListNode header){//Letcode 默认仅有一个节点的链表也是回文if (header == null /*|| header.next == null*/) {return false;}ListNode fast = header;ListNode slow = header;while (fast != null && fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { // fast.next.next != null 判断特别重要fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}//奇数,slow正好是中间节点。 偶数,slow是2个中间节点靠后的一个ListNode next = slow.next;slow.next = null;ListNode reverseNode = slow; //前一个逆转的node节点、ListNode node2 = null;//逆转回文后半部分链表节点//假设原有链表是1->2->3->2->1 逆转后得到 1 ->2 -> 3 ->null 和 1 -> 2 ->3 -> null结构//假设原有链表是1->2->3->3->2->1 逆转后得到 1 ->2 -> 3 ->null 和 1 -> 2 ->3 -> 3->null结构while (next != null && reverseNode != null) {node2 = next.next; //记录下一个节点next.next = reverseNode; //当前节点指向之前被逆转的节点reverseNode = next; //更新被逆转的节点next = node2; //当前节点来到下一个节点处}//开始比较//因为我们根据快慢指针进行切割并且第一个3作为中间节点,前一段链表是标准的结构;后一段链表存在以下2种情况//1) 奇数,前后链表相同个数;偶数,厚一点链表多一个值。 因此以第一个链表为参考即可. 参考上一个while的备注ListNode cur = header;boolean isPadinDrom = true;node2 = reverseNode;while (cur!= null) {if (cur.val != reverseNode.val) {isPadinDrom = false;break;}cur = cur.next;reverseNode = reverseNode.next;}/*** 如果我们不在意原有链表是否被破坏,那么以下while可以省略* 如果我们还想要保持原有链表结构不被破坏,此处我们需要修复原有链表* 假设原有链表是1->2->3->2->1 逆转后得到 1 ->2 -> 3 ->null 和 1 -> 2 ->3 -> null结构* 假设原有链表是1->2->3->3->2->1 逆转后得到 1 ->2 -> 3 ->null 和 1 -> 2 ->3 -> 3->null结构* 两个链表的最后一个节点在内存中是相同的,因此仅需要参考后一个链表进行修复即可(此处需要重点理解)*/reverseNode = null;while (node2 != null) {next = node2.next;node2.next = reverseNode;reverseNode = node2;node2 = next;}return isPadinDrom;}public static void printNode (ListNode node) {if (node == null) {System.out.println("链表不存在");}System.out.println("当前链表的值为: " + node.val);//递归的方式逐层打印Node的子节点if(node.next != null) {printNode(node.next);}}public static void main(String[] args) {Palindrome_01 test = new Palindrome_01();ListNode node = new ListNode(1);node.next = new ListNode(2);node.next.next = new ListNode(3);node.next.next.next = new ListNode(2);node.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(1);//node.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);boolean isPadinDrom = test.isPalindrome(node);System.out.println(isPadinDrom);boolean isPadinDrom2 = test.isPalindrome2(node);System.out.println("测试原链表是否被修复");printNode(node);System.out.println(isPadinDrom2);ListNode node2 = new ListNode(1);node2.next = new ListNode(2);node2.next.next = new ListNode(3);node2.next.next.next = new ListNode(3);node2.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(2);node2.next.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(1);//node2.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);boolean isPadinDrom3 = test.isPalindrome(node2);System.out.println(isPadinDrom3);boolean isPadinDrom4 = test.isPalindrome2(node2);System.out.println("测试原链表是否被修复");printNode(node2);System.out.println(isPadinDrom4);}
}
题目2:将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
笔试用:
package code03.链表_01;import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;/*** 将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式* 笔试用,典型的快排*/
public class SmallEqualBig_02 {static class Node {int value;Node next;Node(int value) {this.value = value;}}public static void swap(Node[] nodeArr, int a, int b) {Node tmp = nodeArr[a];nodeArr[a] = nodeArr[b];nodeArr[b] = tmp;}public void partition (Node[] nodes, int left, int right) {//以最后一个值为参考值Node pavoit = nodes[right];int min = left;int max = right;int cur = left;while (cur < max) {if (nodes[cur].value < pavoit.value) {swap(nodes, min++, cur++);}else if (nodes[cur].value > pavoit.value) {swap(nodes, cur, --max);}else {cur++;}}swap(nodes, cur, right);}public Node sort(Node node){if(node == null || node.next == null) {return node;}int n = 0;Node cur = node;while (cur != null) {cur = cur.next;n++;}Node[] arr = new Node[n];cur = node;for (int i =0; i < arr.length; i++) {arr[i] = cur;cur = cur.next;}partition(arr, 0, n-1);cur = arr[0];node = cur;for (int i =1; i < arr.length; i++) {cur.next = arr[i];cur = cur.next;}cur.next = null;return node;}public static void printNode (Node node) {if (node == null) {System.out.println("链表不存在");}System.out.println("当前链表的值为: " + node.value);//递归的方式逐层打印Node的子节点if(node.next != null) {printNode(node.next);}}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head1 = new Node(7);head1.next = new Node(9);head1.next.next = new Node(1);head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);SmallEqualBig_02 test = new SmallEqualBig_02();System.out.println("排序前的节点");printNode(head1);System.out.println("=================");Node n2 = test.sort(head1);printNode(n2);}
}
面试用:
package code03.链表_01;//将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
public class SmallEqualBig_03 {static class Node {int value;Node next;Node(int value) {this.value = value;}}//笔试用, 不借助任何的新对象,纯粹借住现有的链表结构进行操作public Node sort(Node node, int povit) {Node maxStart = null;Node maxEnd = null;Node minStart = null;Node minEnd = null;Node equalStart = null;Node equalEnd = null;while (node != null) {if(node.value < povit) {if (minStart == null) {minStart = node;minEnd = node;}else {minEnd.next = node;minEnd = node;}}else if(node.value > povit) {if (maxStart == null) {maxStart = node;maxEnd = node;}else {maxEnd.next = node;maxEnd = node;}}else {if (equalStart == null) {equalStart = node;equalEnd = node;}else {equalEnd.next = node;equalEnd = node;}}node = node.next;}if (minEnd != null) {if (equalStart != null) {minEnd.next = equalStart;equalEnd.next = null;}else if (maxStart != null) {minEnd.next = maxStart;maxEnd.next = null;}}if (equalEnd != null){if (maxStart != null) {equalEnd.next = maxStart;maxEnd.next = null;}else{equalEnd.next = null;}}return minStart != null ? minStart : equalStart != null ? equalStart : maxStart;}public static void printNode (Node node) {if (node == null) {System.out.println("链表不存在");}System.out.println("当前链表的值为: " + node.value);//递归的方式逐层打印Node的子节点if(node.next != null) {printNode(node.next);}}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head1 = new Node(7);head1.next = new Node(9);head1.next.next = new Node(1);head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);SmallEqualBig_03 test = new SmallEqualBig_03();System.out.println("排序前的节点");printNode(head1);System.out.println("=================");Node n2 = test.sort(head1, 5);printNode(n2);}}
题目3:
一种特殊的单链表节点类描述如下
class Node {
int value;
Node next;
Node rand;
Node(int val) { value = val; }
}
rand指针是单链表节点结构中新增的指针,rand可能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向null。
给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点 head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表的复制,并返回复制的新链表的头节点。
【要求】
时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)
package code03.链表_01;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;/*** 一种特殊的单链表节点类描述如下* class Node {* int value;* Node next;* Node rand;* Node(int val) { value = val; }* }* rand指针是单链表节点结构中新增的指针,rand可能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向null。* 给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点 head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表的复制,并返回复制的新链表的头节点。* 【要求】* 时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)** 解题思路:* 1. 借助系统容器,逐个深拷贝每个指针对象,然后将拷贝的指针串成新指针返回 (笔试用)** 2.深拷贝每个指针对象,并且串联进当前的指针当中,然后将当前链表进行切割,生成新链表并返回(面试用)*/
public class DeepCopyNode_04
{static class Node {int value;Node next;Node rand;Node(int val) {value = val;}}//借助系统容器,笔试用(快准稳)public Node deepCopy1 (Node node){//额外空间复杂度O(1), 此处只生成了一个map对象//而深拷贝N个指针,是题目本身就要求的事情,因此可以忽略题目要求的O(N)空间复杂度Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();if (node == null) {return node;}//深拷贝每个nodeNode cur = node;while (cur != null) {Node n = new Node(cur.value);map.put(cur, n);cur = cur.next;}//构造新链表cur = node;while (cur != null) {map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);cur = cur.next;}return (Node) map.get(node);}//纯链表实现,面试用public Node deepCopy2 (Node node){if (node == null) {return node;}Node cur = node;//假设链表为1-2-3 拷贝完以后就是 1-1-2-2-3-3while (cur != null) {//深拷贝Node n = new Node(cur.value);Node next = cur.next;cur.next = n;n.next = next;cur = next;}cur = node;Node copy = cur.next;//rand有可能是后面指向前面,所以不能提前断开,否则找不到copy后后面的指针对象的randwhile (cur != null && cur.next != null) { //cur.next != null等价于copy != null//假设 b 是copy a的节点,那么b的rand节点肯定就在a.rand节点后面copy.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null;cur = cur.next.next; //等价于cur = copy.nextcopy = cur != null ? cur.next : null;}//最后分离cur = node;copy = cur.next;Node ans = copy;while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {Node curNext = cur.next.next;Node copyNext = curNext != null ? curNext.next : null;cur.next = curNext;copy.next = copyNext;cur = curNext;copy = copyNext;}return ans;}public static void printNode (Node node) {if (node == null) {System.out.println("链表不存在");}System.out.println("当前链表的值为: " + node.value);System.out.println("当前链表的random值为: " + (node.rand == null ? null : node.rand.value));//递归的方式逐层打印Node的子节点if(node.next != null) {printNode(node.next);}}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head1 = new Node(7);head1.next = new Node(9);head1.next.next = new Node(1);head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head1.next.next.rand = head1.next.next.next.next;head1.next.next.next.next.next.next.rand = head1;DeepCopyNode_04 test = new DeepCopyNode_04();Node n = test.deepCopy1(head1);printNode(n);System.out.println("==================");Node n2 = test.deepCopy2(head1);printNode(n2);}
}
题目4:给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
package code03.链表_01;/*** 给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。** 如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。* 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。* 注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。** 如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。* 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle*/
public class LoopNode_05 {static class ListNode {int value;ListNode next;ListNode(int value) {this.value = value;}}public boolean hasCycle(ListNode node){//需要使用快慢指针if (node == null || node.next == null || node.next.next == null) {return false;}ListNode fast = node.next.next;ListNode slow = node.next;//跳出当前循环//1) fast == slow 循环链表//2) fast.next 或 fast.next.next 为 null 不是循环链表while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {if (fast == slow) {break;}fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}//无环链表if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) {return false;}return true;}}
题目5:给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
package code03.链表_01;/*** 给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。** 如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。* 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。* 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。* https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii*/
public class LoopNode_05_2
{static class ListNode {int value;ListNode next;ListNode(int value) {this.value = value;}}public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode node){//需要使用快慢指针if (node == null || node.next == null || node.next.next == null) {return null;}ListNode fast = node.next.next;ListNode slow = node.next;//跳出当前循环//1) fast == slow 循环链表//2) fast.next 或 fast.next.next 为 null 不是循环链表while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {if (fast == slow) {break;}fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}//无环链表if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) {return null;}//有环链表fast = node;//备注1: 找出第一个相交节点,此处根据数据推导公式得出while (fast != slow) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}//返回fast 或 slow 都对return fast;}public static void main(String[] args) {ListNode head1 = new ListNode(7);ListNode head2 = new ListNode(9); head1.next = head2;ListNode head3 = new ListNode(1); head2.next = head3;ListNode head4 = new ListNode(8); head3.next = head4;ListNode head5 = new ListNode(5); head4.next = head5;ListNode head6 = new ListNode(6); head5.next = head6;ListNode head7 = new ListNode(5); head6.next = head7;LoopNode_05_2 loop = new LoopNode_05_2();//测试无环ListNode loopNode = loop.detectCycle(head1);System.out.println((loopNode != null ? loopNode.value : "null"));//测试有环head7.next = head4; // head4作为环形链表的第一个值ListNode loopNode2 = loop.detectCycle(head1);System.out.println("第一个入环节点的值为: " + (loopNode2 != null ? loopNode2.value : "null"));}
}
此处,需要对代码中的 “备注1” 进行解释一下,为什么fast = node; while (fast != slow) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next;} 当 fast = slow的时候,fast或slow就是相交的第一个节点? 不理解这一点,下面的题目无法继续进行下去

由此图,我们可知: 快指针从A点重新出现,跑了x距离。 那么慢指针就是跑 N圈额外加z一段距离,此时他们正好会在第一个相交的节点相遇。
题目6:给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
package code03.链表_01;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;/*** 给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。* 题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。* https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/**/
public class DoubleLoopNodes_06
{static class ListNode {int value;ListNode next;ListNode(int value) {this.value = value;}}//借助java系统提供的容器public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB){if (headA == null || headB == null) {return null;}Map<ListNode, ListNode> map = new HashMap();ListNode cur = headA;while (cur != null) {map.put(cur, cur);cur = cur.next;}cur = headB;while (cur != null) {if (map.containsKey(cur)) {return map.get(cur);}cur = cur.next;}return null;}//纯链表实现public ListNode getIntersectionNode2(ListNode headA, ListNode headB){if (headA == null || headB == null) {return null;}ListNode cur = headA;int n = 0;while (cur != null) {n++;cur = cur.next;}cur = headB;while (cur != null) {n--;cur = cur.next;}ListNode lNode = n > 0 ? headA : headB; //长链表ListNode sNode = lNode == headA ? headB : headA; //短链表n = Math.abs(n);while (n > 0) {lNode = lNode.next;n--;}//此刻,长链表剩下的节点和短链表剩下的节点个数相同while (lNode != sNode) {lNode = lNode.next;sNode = sNode.next;if(lNode == null || sNode == null) {return null;}}return lNode;}public static void main(String[] args) {//链表1ListNode node1 = new ListNode(4);ListNode node2 = new ListNode(1);//链表2ListNode node3 = new ListNode(5);ListNode node4 = new ListNode(6);ListNode node5 = new ListNode(2);//相交节点ListNode node6 = new ListNode(8);ListNode node7 = new ListNode(7);ListNode node8 = new ListNode(3);node1.next = node2; node2.next = node6; node6.next = node7; node7.next = node8;node3.next = node4; node4.next = node5; node5.next = node6;DoubleLoopNodes_06 test = new DoubleLoopNodes_06();ListNode n1 = test.getIntersectionNode(node1, node3);System.out.println("相交节点的值为 :" + (n1 != null ? n1.value : null));ListNode n2 = test.getIntersectionNode2(node1, node3);System.out.println("相交节点的值为 :" + (n2 != null ? n2.value : null));}
}
说了这么多,终极大boss终于要登场了。
题目7:给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2。请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的 第一个节点。如果不相交,返回null
【要求】
如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度 请达到O(1)
解题思路:根据排除所得,要么两条链表无环相交,要么有环相交,只存在这两种情况
package code03.链表_01;/*** 给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2。请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的 第一个节点。如果不相交,返回null* 【要求】* 如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度 请达到O(1)。** 解题思路:根据排除所得,要么两条链表无环相交,要么有环相交,只存在这两种情况*/
public class DoubleLoopNodes_06_2
{static class ListNode {int value;ListNode next;ListNode(int value) {this.value = value;}}//获取单链表相交的第一个节点,不想交则返回nullpublic ListNode getLoopNode(ListNode node){//需要使用快慢指针if (node == null || node.next == null || node.next.next == null) {return null;}ListNode fast = node.next.next;ListNode slow = node.next;//跳出当前循环//1) fast == slow 循环链表//2) fast.next 或 fast.next.next 为 null 不是循环链表while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {if (fast == slow) {break;}fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}//无环链表if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) {return null;}//有环链表fast = node;//备注1: 找出第一个相交节点,此处根据数据推导公式得出while (fast != slow) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}//返回fast 或 slow 都对return fast;}//两个都没有循环链表的相交节点public ListNode bothNoCycleNodes(ListNode headA, ListNode headB){if (headA == null || headB == null) {return null;}ListNode cur = headA;int n = 0;while (cur != null) {n++;cur = cur.next;}cur = headB;while (cur != null) {n--;cur = cur.next;}ListNode lNode = n > 0 ? headA : headB; //长链表ListNode sNode = lNode == headA ? headB : headA; //短链表n = Math.abs(n);while (n > 0) {lNode = lNode.next;n--;}//此刻,长链表剩下的节点和短链表剩下的节点个数相同while (lNode != sNode) {lNode = lNode.next;sNode = sNode.next;if(lNode == null || sNode == null) {return null;}}return lNode;}public ListNode bothCycleNodes(ListNode headA, ListNode loopA, ListNode headB, ListNode loopB){//2种情况: 环外相交,正好第一个相交节点相交。 这种情况可以视为2个无环链表相交if (loopA == loopB) {int n = 0;ListNode cur = headA;while (cur != loopA) {n++;cur = cur.next;}cur = headB;while (cur != loopB) {n--;cur = cur.next;}ListNode lNode = n > 0 ? headA : headB; //长链表ListNode sNode = lNode == headA ? headB : headA; //短链表n = Math.abs(n);while (n > 0) {lNode = lNode.next;n--;}//此刻,长链表剩下的节点和短链表剩下的节点个数相同while (lNode != sNode) {lNode = lNode.next;sNode = sNode.next;}return lNode;}else { //环内相交ListNode cur1 = loopA.next;while (cur1 != loopA) { //如果跑一圈都没找到相交节点,则无相交节点if (cur1 == loopB) { //中途找到了相交节点return loopB; //返回loopA 或 loopB 都行。 环内相交,说不清谁是第一个}cur1 = cur1.next;}return null;}}public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode node1, ListNode node2){if (node1 == null || node2 == null) {return null;}ListNode loopNode1 = getLoopNode(node1);ListNode loopNode2 = getLoopNode(node2);ListNode ansNode = null;if (loopNode1 == null && loopNode2 == null) { //两个都没有环的节点ansNode = bothNoCycleNodes(node1, node2);}else if (loopNode1 != null && loopNode2 != null) { //两个环形链表相交ansNode = bothCycleNodes(node1,loopNode1, node2,loopNode2);}return ansNode;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("================测试2个无环聊表相交===========================");//链表1ListNode node1 = new ListNode(4);ListNode node2 = new ListNode(1);//链表2ListNode node3 = new ListNode(5);ListNode node4 = new ListNode(6);ListNode node5 = new ListNode(2);//相交节点ListNode node6 = new ListNode(8);ListNode node7 = new ListNode(7);ListNode node8 = new ListNode(3);node1.next = node2; node2.next = node6; node6.next = node7; node7.next = node8;node3.next = node4; node4.next = node5;DoubleLoopNodes_06_2 test = new DoubleLoopNodes_06_2();//不相交ListNode m1 = test.getIntersectionNode(node1, node3);System.out.println("无环 不相交 :" + (m1 != null ? m1.value : null));//相交node5.next = node6;ListNode m2 = test.getIntersectionNode(node1, node3);System.out.println("无环 相交节点的值为 :" + (m2 != null ? m2.value : null));System.out.println("================测试2个环形链表 环外 相交===========================");//链表1ListNode n1 = new ListNode(4);ListNode n2 = new ListNode(1);//链表2ListNode n3 = new ListNode(5);ListNode n4 = new ListNode(6);ListNode n5 = new ListNode(2);//相交节点ListNode n6 = new ListNode(8);ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7);ListNode n8 = new ListNode(3);n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n2;n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; n7.next = n8; n8.next = n6;ListNode m3 = test.getIntersectionNode(n1, n5);System.out.println("有环 不相交 :" + (m3 != null ? m3.value : null)); //不相交n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n3;n6.next = n7; n7.next = n8; n8.next = n3;ListNode m4 = test.getIntersectionNode(n1, n6);System.out.println("有环 第一个相交点相交 :" + (m4 != null ? m4.value : null)); //n3对应的值是5n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n3;n6.next = n7; n7.next = n8; n8.next = n2;ListNode m5 = test.getIntersectionNode(n1, n6);System.out.println("有环 环外相交 :" + (m5 != null ? m5.value : null)); //n2对应的值是1System.out.println("================测试2个环形链表 环内 相交===========================");n6.next = n7; n7.next = n8; n8.next = n4;ListNode m6 = test.getIntersectionNode(n1, n6);System.out.println("有环 环外相交 :" + (m6 != null ? m6.value : null)); //n2对应的值是1 n4对应6}
}
相关文章:

算法18:LeetCode_链表相关算法题
链表无小事,只要是涉及到链表的算法题,边界值的设定尤为重要,而且及其容易出错误。这就要求我们平时多加练习。但是,我们在面试和笔试的过程中往往会碰到链表相关的题目,所以我们在笔试的时候一般都会借助系统提供的工…...
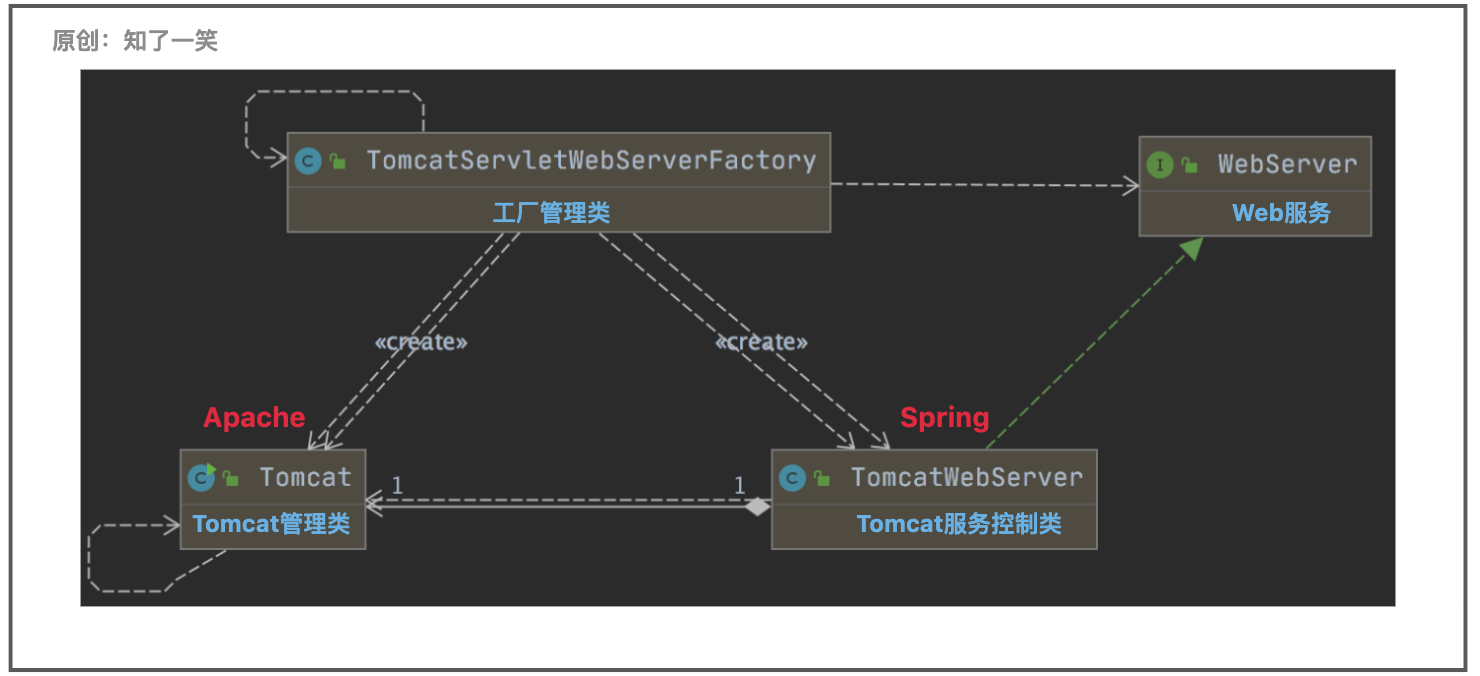
SpringBoot集成Tomcat服务
文章目录一、Tomcat集成1、依赖层级2、自动化配置二、Tomcat架构三、Tomcat配置1、基础配置2、属性配置类3、配置加载分析四、周期管理方法1、控制类2、核心方法使用的成本越低,内部封装越复杂; 一、Tomcat集成 1、依赖层级 在SpringBoot框架的web依赖…...

【机器学习】决策树-C4.5算法
1.C4.5算法 C4.5算法与ID3相似,在ID3的基础上进行了改进,采用信息增益比来选择属性。ID3选择属性用的是子树的信息增益,ID3使用的是熵(entropy, 熵是一种不纯度度量准则),也就是熵的变化值&…...
actipro-winforms-controls-23.1.0 Crack
actipro-winforms一组用于构建漂亮的 Windows 窗体桌面应用程序的 UI 控件,用于构建 IDE 的高级停靠窗口、MDI、属性网格、树控件和文件夹/文件浏览器,用于常见数据类型、自动完成、屏蔽编辑和代码编辑的强大编辑器,功能区、图表、微型图表、…...

适合打游戏用的蓝牙耳机有哪些?吃鸡无延迟的蓝牙耳机推荐
现在手游的兴起,让游戏市场变得更加火爆,各种可以提高玩家体验的外设也越来越多,除了提升操作的外置按键与手柄外,能带来更出色音质与舒心使用的游戏耳机,整体氛围感更好,让玩家在细节上占据优势࿰…...

1000:入门测试题目[不一样的题解][85种写法]【A+B问题】
题目: 1000:入门测试题目 时间限制: 1000 ms 内存限制: 32768 KB 提交数: 262857 通过数: 158152 【题目描述】 求两个整数的和。 【输入】 一行,两个用空格隔开的整数。 【输出】 两个整数的和。 【输入样例】 2 3 【输出样例】…...
FastReport .NET 2023.1.13 Crack
FastReport .NET 使用来自 ADO .NET 数据源的数据。它可以排序和过滤数据行,使用主从关系和查找数据列。一切都可以通过点击几下鼠标来完成。 直接连接到 ADO、MS SQL 或基于 xml 的数据库。其他连接器可作为插件使用。 能够从 IEnumerable 类型的业务对象中获取数…...

unzip: cannot find zipfile directory in one of
下面是执行flutter doctor 后报错内容 End-of-central-directory signature not found. Either this file is not a zipfile, or it constitutes one disk of a multi-part archive. In the latter case the central directory and zipfile comment will be found on the last …...
;CONFIG_CRYPTO_GCM)
RFC4543: Galois Message Authentication Code (GMAC);CONFIG_CRYPTO_GCM
在2010年这个算法被Linux社区加进来:说明算法还是挺重要,普遍使用。 commit 73c89c15b959adf06366722c4be8d2eddec0a529 Author: Tobias Brunner <tobias@strongswan.org> Date: Sun Jan 17 21:52:11 2010 +1100crypto: gcm - Add RFC4543 wrapper for GCMThis patc…...
【YOLOv5】 02-标注图片,训练并使用自己的模型
在上一篇文章中,我们完成了YOLOv5的安装和测试。如果想检测自定义目标,就需要用到LabelImg来对图片打标签,本篇文章介绍了LabelImg安装与使用,以及如何训练并使用自己的模型。一、安装LabelImg输入如下命令进行安装:pi…...
)
2023.2.15日学习内容(用户的增删改查)
1,如果前端时间需要年月日,不需要时分秒,则一般情况下再数据库里面操作即可2.正常情况下,以后所有的查询都不能用* 查询所有列3.删除思路逻辑1)点击删除按钮需要对其进行监听2)对于重要的信息删除应该给用户…...

车载以太网 - 测试用例设计 - 时间参数 - 11
前面已经介绍过DoIP相关的时间参数信息,然而对于时间参数信息相关的测试用例该如何设计呢?个人认为这是用例中最好设计的一类,这类的用例只需要按照定义去设计写测试用例即可,难的是自动化脚本开发和手动测试执行。毕竟时间参数一般都是毫秒级的验证,就算是秒级的我们也很…...

【C#个人错题笔记】
观前提醒 记录一些我不会或者少见的内容,不一定适合所有人 字符串拼接 int a3,b8; Console.WriteLine(ab);//11 Console.WriteLine("ab");//ab Console.WriteLine(a""b);//38 Console.WriteLine("ab"ab);//ab38 Console.WriteLine…...
JavaScript刷LeetCode拿offer-树的遍历
什么是树 一种分层数据的抽象模型。前端工作中常见的树包括:DOM树,级联选择,树形控件JS中没有树,可以用Object和Array构建树树的常用操作:深度/广度优先遍历,先中后序遍历 深度优先遍历 访问根节点对根节…...
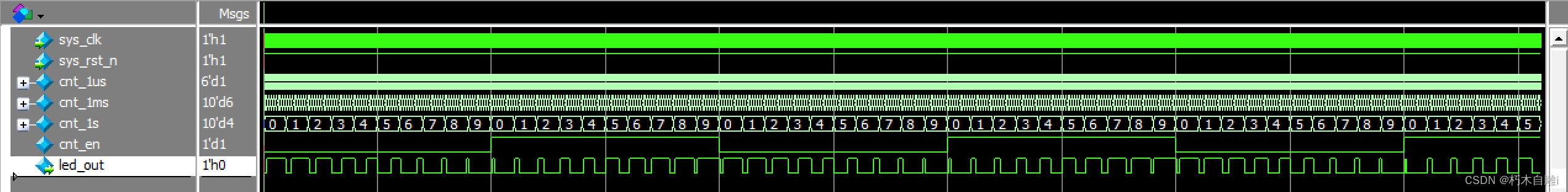
《FPGA学习》->呼吸灯
🍎与其担心未来,不如现在好好努力。在这条路上,只有奋斗才能给你安全感。你若努力,全世界都会为你让路。呼吸灯,简而言之就像人类呼吸一样,有节奏的让LED灯从:灭->微微亮->微亮->亮-&g…...
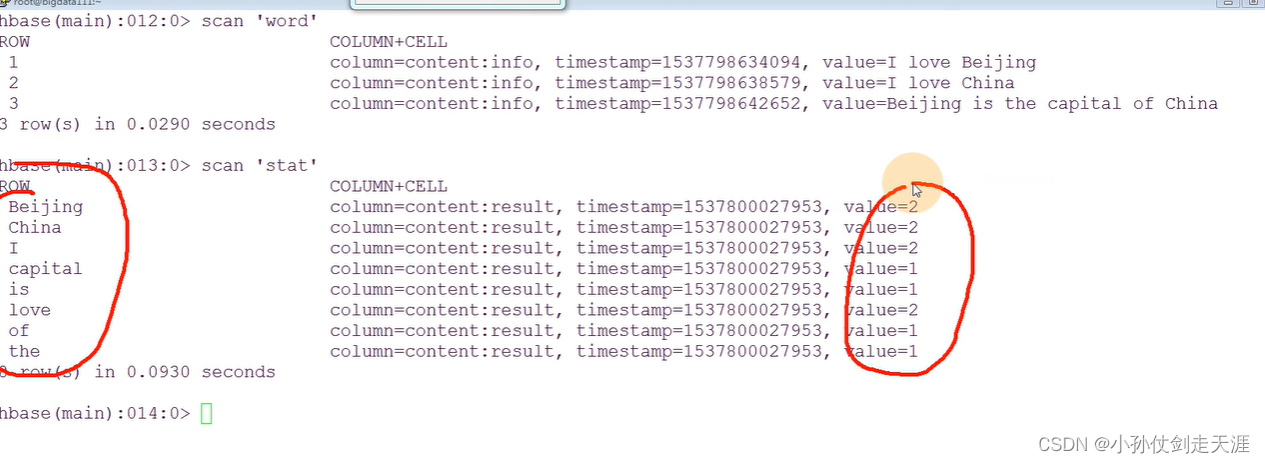
【大数据离线开发】7.4 HBase数据保存和过滤器
7.4 数据保存的过程 注意:数据的存储,都需要注意Region的分裂 HDFS:数据的平衡 ——> 数据的移动(拷贝)HBase:数据越来越多 ——> Region的分裂 ——> 数据的移动(拷贝) …...
CentOS7安装MariaDB步骤
文章目录1.配置MariaDB yum源2.安装MariaDBMariaDB数据库管理系统是MySQL的一个分支,主要由开源社区在维护,采用GPL授权许可。 MariaDB的目的是完全兼容MySQL,包括API和命令行,使之能轻松成为MySQL的代替品。 CentOS 6 或早期的版…...

软件测试13个最容易犯的错误
目录 一、 输入框测试 二、 搜索功能测试 三、 添加/修改功能 四、 删除功能 五、 上传图片功能测试 六、 查询结果列表 七、 返回键检查 八、 回车键检查 九、 刷新键检查 十、 直接URL链接检查(盗链问题) 十一、并发问题 十二、 业务流程测…...
)
华为OD机试真题Java实现【5键键盘的输出】真题+解题思路+代码(20222023)
🔥系列专栏 华为OD机试(Python)真题目录汇总华为OD机试(JAVA)真题目录汇总华为OD机试(C++)真题目录汇总华为OD机试(JavaScript)真题目录汇总文章目录 🔥系列专栏题目输入输出描述:示例1:示例2:解题思路代码实现运行结果:版权说明:题目...
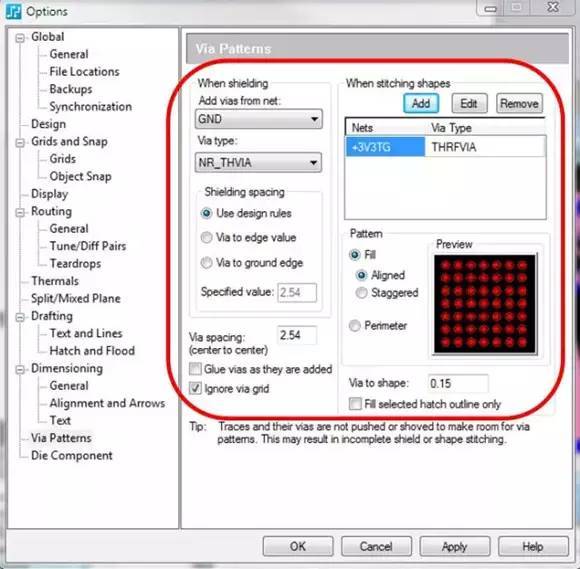
化解射频和微波设计挑战的六个技巧
即使是最自信的设计人员,对于射频电路也往往望而却步,因为它会带来巨大的设计挑战,并且需要专业的设计和分析工具。这里将为您介绍六条技巧,来帮助您简化任何射频PCB 设计任务和减轻工作压力! 1、保持完好、精确的射频…...

Docker 离线安装指南
参考文章 1、确认操作系统类型及内核版本 Docker依赖于Linux内核的一些特性,不同版本的Docker对内核版本有不同要求。例如,Docker 17.06及之后的版本通常需要Linux内核3.10及以上版本,Docker17.09及更高版本对应Linux内核4.9.x及更高版本。…...
: K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?)
云原生核心技术 (7/12): K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?
大家好,欢迎来到《云原生核心技术》系列的第七篇! 在上一篇,我们成功地使用 Minikube 或 kind 在自己的电脑上搭建起了一个迷你但功能完备的 Kubernetes 集群。现在,我们就像一个拥有了一块崭新数字土地的农场主,是时…...
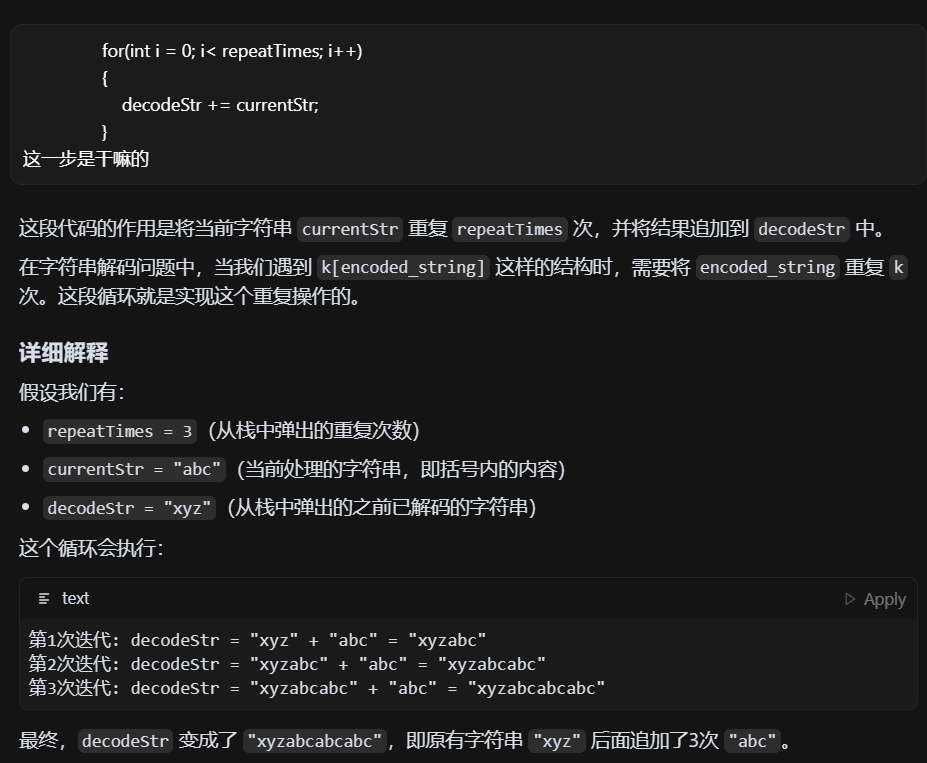
LeetCode - 394. 字符串解码
题目 394. 字符串解码 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路 使用两个栈:一个存储重复次数,一个存储字符串 遍历输入字符串: 数字处理:遇到数字时,累积计算重复次数左括号处理:保存当前状态&a…...

MVC 数据库
MVC 数据库 引言 在软件开发领域,Model-View-Controller(MVC)是一种流行的软件架构模式,它将应用程序分为三个核心组件:模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)。这种模式有助于提高代码的可维护性和可扩展性。本文将深入探讨MVC架构与数据库之间的关系,以…...

spring:实例工厂方法获取bean
spring处理使用静态工厂方法获取bean实例,也可以通过实例工厂方法获取bean实例。 实例工厂方法步骤如下: 定义实例工厂类(Java代码),定义实例工厂(xml),定义调用实例工厂ÿ…...

html-<abbr> 缩写或首字母缩略词
定义与作用 <abbr> 标签用于表示缩写或首字母缩略词,它可以帮助用户更好地理解缩写的含义,尤其是对于那些不熟悉该缩写的用户。 title 属性的内容提供了缩写的详细说明。当用户将鼠标悬停在缩写上时,会显示一个提示框。 示例&#x…...

python爬虫——气象数据爬取
一、导入库与全局配置 python 运行 import json import datetime import time import requests from sqlalchemy import create_engine import csv import pandas as pd作用: 引入数据解析、网络请求、时间处理、数据库操作等所需库。requests:发送 …...
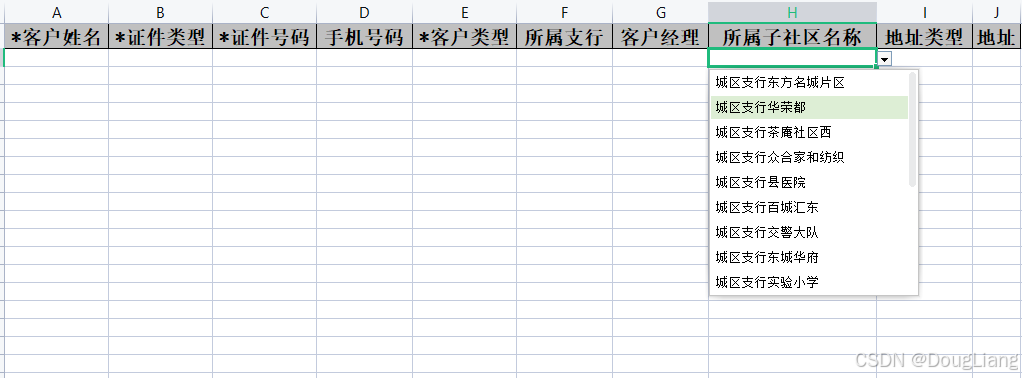
关于easyexcel动态下拉选问题处理
前些日子突然碰到一个问题,说是客户的导入文件模版想支持部分导入内容的下拉选,于是我就找了easyexcel官网寻找解决方案,并没有找到合适的方案,没办法只能自己动手并分享出来,针对Java生成Excel下拉菜单时因选项过多导…...
SQL注入篇-sqlmap的配置和使用
在之前的皮卡丘靶场第五期SQL注入的内容中我们谈到了sqlmap,但是由于很多朋友看不了解命令行格式,所以是纯手动获取数据库信息的 接下来我们就用sqlmap来进行皮卡丘靶场的sql注入学习,链接:https://wwhc.lanzoue.com/ifJY32ybh6vc…...

Python的__call__ 方法
在 Python 中,__call__ 是一个特殊的魔术方法(magic method),它允许一个类的实例像函数一样被调用。当你在一个对象后面加上 () 并执行时(例如 obj()),Python 会自动调用该对象的 __call__ 方法…...
