WebGL矩阵变换库
目录
矩阵变换库:
Matrix4对象所支持的方法和属性如表所示:
方法属性规范:
虽然平移、旋转、缩放等变换操作都可以用一个4×4的矩阵表示,但是在写WebGL程序的时候,手动计算每个矩阵很耗费时间。为了简化编程,大多数WebGL开发者都使用矩阵操作函数库来隐藏矩阵计算的细节,简化与矩阵有关的操作。目前已经有一些开源的矩阵库。以下是一个比较好的矩阵变换库可供大家学习使用。有了矩阵函数库,进行如“平移,然后旋转”等各种复合的变换就很简单了。
Matrix4是该矩阵库提供的新类型 ,顾名思义,Matrix4对象(实例)表示一个4×4的矩阵。该对象内部使用类型化数组Floated2Array来存储矩阵的元素。
矩阵变换库:
/*** Constructor of Matrix4* If opt_src is specified, new matrix is initialized by opt_src.* Otherwise, new matrix is initialized by identity matrix.* @param opt_src source matrix(option)*/
var Matrix4 = function(opt_src) {var i, s, d;if (opt_src && typeof opt_src === 'object' && opt_src.hasOwnProperty('elements')) {s = opt_src.elements;d = new Float32Array(16);for (i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {d[i] = s[i];}this.elements = d;} else {this.elements = new Float32Array([1,0,0,0, 0,1,0,0, 0,0,1,0, 0,0,0,1]);}
};/*** Set the identity matrix.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.setIdentity = function() {var e = this.elements;e[0] = 1; e[4] = 0; e[8] = 0; e[12] = 0;e[1] = 0; e[5] = 1; e[9] = 0; e[13] = 0;e[2] = 0; e[6] = 0; e[10] = 1; e[14] = 0;e[3] = 0; e[7] = 0; e[11] = 0; e[15] = 1;return this;
};/*** Copy matrix.* @param src source matrix* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.set = function(src) {var i, s, d;s = src.elements;d = this.elements;if (s === d) {return;}for (i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {d[i] = s[i];}return this;
};/*** Multiply the matrix from the right.* @param other The multiply matrix* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.concat = function(other) {var i, e, a, b, ai0, ai1, ai2, ai3;// Calculate e = a * be = this.elements;a = this.elements;b = other.elements;// If e equals b, copy b to temporary matrix.if (e === b) {b = new Float32Array(16);for (i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {b[i] = e[i];}}for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {ai0=a[i]; ai1=a[i+4]; ai2=a[i+8]; ai3=a[i+12];e[i] = ai0 * b[0] + ai1 * b[1] + ai2 * b[2] + ai3 * b[3];e[i+4] = ai0 * b[4] + ai1 * b[5] + ai2 * b[6] + ai3 * b[7];e[i+8] = ai0 * b[8] + ai1 * b[9] + ai2 * b[10] + ai3 * b[11];e[i+12] = ai0 * b[12] + ai1 * b[13] + ai2 * b[14] + ai3 * b[15];}return this;
};
Matrix4.prototype.multiply = Matrix4.prototype.concat;/*** Multiply the three-dimensional vector.* @param pos The multiply vector* @return The result of multiplication(Float32Array)*/
Matrix4.prototype.multiplyVector3 = function(pos) {var e = this.elements;var p = pos.elements;var v = new Vector3();var result = v.elements;result[0] = p[0] * e[0] + p[1] * e[4] + p[2] * e[ 8] + e[12];result[1] = p[0] * e[1] + p[1] * e[5] + p[2] * e[ 9] + e[13];result[2] = p[0] * e[2] + p[1] * e[6] + p[2] * e[10] + e[14];return v;
};/*** Multiply the four-dimensional vector.* @param pos The multiply vector* @return The result of multiplication(Float32Array)*/
Matrix4.prototype.multiplyVector4 = function(pos) {var e = this.elements;var p = pos.elements;var v = new Vector4();var result = v.elements;result[0] = p[0] * e[0] + p[1] * e[4] + p[2] * e[ 8] + p[3] * e[12];result[1] = p[0] * e[1] + p[1] * e[5] + p[2] * e[ 9] + p[3] * e[13];result[2] = p[0] * e[2] + p[1] * e[6] + p[2] * e[10] + p[3] * e[14];result[3] = p[0] * e[3] + p[1] * e[7] + p[2] * e[11] + p[3] * e[15];return v;
};/*** Transpose the matrix.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.transpose = function() {var e, t;e = this.elements;t = e[ 1]; e[ 1] = e[ 4]; e[ 4] = t;t = e[ 2]; e[ 2] = e[ 8]; e[ 8] = t;t = e[ 3]; e[ 3] = e[12]; e[12] = t;t = e[ 6]; e[ 6] = e[ 9]; e[ 9] = t;t = e[ 7]; e[ 7] = e[13]; e[13] = t;t = e[11]; e[11] = e[14]; e[14] = t;return this;
};/*** Calculate the inverse matrix of specified matrix, and set to this.* @param other The source matrix* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.setInverseOf = function(other) {var i, s, d, inv, det;s = other.elements;d = this.elements;inv = new Float32Array(16);inv[0] = s[5]*s[10]*s[15] - s[5] *s[11]*s[14] - s[9] *s[6]*s[15]+ s[9]*s[7] *s[14] + s[13]*s[6] *s[11] - s[13]*s[7]*s[10];inv[4] = - s[4]*s[10]*s[15] + s[4] *s[11]*s[14] + s[8] *s[6]*s[15]- s[8]*s[7] *s[14] - s[12]*s[6] *s[11] + s[12]*s[7]*s[10];inv[8] = s[4]*s[9] *s[15] - s[4] *s[11]*s[13] - s[8] *s[5]*s[15]+ s[8]*s[7] *s[13] + s[12]*s[5] *s[11] - s[12]*s[7]*s[9];inv[12] = - s[4]*s[9] *s[14] + s[4] *s[10]*s[13] + s[8] *s[5]*s[14]- s[8]*s[6] *s[13] - s[12]*s[5] *s[10] + s[12]*s[6]*s[9];inv[1] = - s[1]*s[10]*s[15] + s[1] *s[11]*s[14] + s[9] *s[2]*s[15]- s[9]*s[3] *s[14] - s[13]*s[2] *s[11] + s[13]*s[3]*s[10];inv[5] = s[0]*s[10]*s[15] - s[0] *s[11]*s[14] - s[8] *s[2]*s[15]+ s[8]*s[3] *s[14] + s[12]*s[2] *s[11] - s[12]*s[3]*s[10];inv[9] = - s[0]*s[9] *s[15] + s[0] *s[11]*s[13] + s[8] *s[1]*s[15]- s[8]*s[3] *s[13] - s[12]*s[1] *s[11] + s[12]*s[3]*s[9];inv[13] = s[0]*s[9] *s[14] - s[0] *s[10]*s[13] - s[8] *s[1]*s[14]+ s[8]*s[2] *s[13] + s[12]*s[1] *s[10] - s[12]*s[2]*s[9];inv[2] = s[1]*s[6]*s[15] - s[1] *s[7]*s[14] - s[5] *s[2]*s[15]+ s[5]*s[3]*s[14] + s[13]*s[2]*s[7] - s[13]*s[3]*s[6];inv[6] = - s[0]*s[6]*s[15] + s[0] *s[7]*s[14] + s[4] *s[2]*s[15]- s[4]*s[3]*s[14] - s[12]*s[2]*s[7] + s[12]*s[3]*s[6];inv[10] = s[0]*s[5]*s[15] - s[0] *s[7]*s[13] - s[4] *s[1]*s[15]+ s[4]*s[3]*s[13] + s[12]*s[1]*s[7] - s[12]*s[3]*s[5];inv[14] = - s[0]*s[5]*s[14] + s[0] *s[6]*s[13] + s[4] *s[1]*s[14]- s[4]*s[2]*s[13] - s[12]*s[1]*s[6] + s[12]*s[2]*s[5];inv[3] = - s[1]*s[6]*s[11] + s[1]*s[7]*s[10] + s[5]*s[2]*s[11]- s[5]*s[3]*s[10] - s[9]*s[2]*s[7] + s[9]*s[3]*s[6];inv[7] = s[0]*s[6]*s[11] - s[0]*s[7]*s[10] - s[4]*s[2]*s[11]+ s[4]*s[3]*s[10] + s[8]*s[2]*s[7] - s[8]*s[3]*s[6];inv[11] = - s[0]*s[5]*s[11] + s[0]*s[7]*s[9] + s[4]*s[1]*s[11]- s[4]*s[3]*s[9] - s[8]*s[1]*s[7] + s[8]*s[3]*s[5];inv[15] = s[0]*s[5]*s[10] - s[0]*s[6]*s[9] - s[4]*s[1]*s[10]+ s[4]*s[2]*s[9] + s[8]*s[1]*s[6] - s[8]*s[2]*s[5];det = s[0]*inv[0] + s[1]*inv[4] + s[2]*inv[8] + s[3]*inv[12];if (det === 0) {return this;}det = 1 / det;for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {d[i] = inv[i] * det;}return this;
};/*** Calculate the inverse matrix of this, and set to this.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.invert = function() {return this.setInverseOf(this);
};/*** Set the orthographic projection matrix.* @param left The coordinate of the left of clipping plane.* @param right The coordinate of the right of clipping plane.* @param bottom The coordinate of the bottom of clipping plane.* @param top The coordinate of the top top clipping plane.* @param near The distances to the nearer depth clipping plane. This value is minus if the plane is to be behind the viewer.* @param far The distances to the farther depth clipping plane. This value is minus if the plane is to be behind the viewer.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.setOrtho = function(left, right, bottom, top, near, far) {var e, rw, rh, rd;if (left === right || bottom === top || near === far) {throw 'null frustum';}rw = 1 / (right - left);rh = 1 / (top - bottom);rd = 1 / (far - near);e = this.elements;e[0] = 2 * rw;e[1] = 0;e[2] = 0;e[3] = 0;e[4] = 0;e[5] = 2 * rh;e[6] = 0;e[7] = 0;e[8] = 0;e[9] = 0;e[10] = -2 * rd;e[11] = 0;e[12] = -(right + left) * rw;e[13] = -(top + bottom) * rh;e[14] = -(far + near) * rd;e[15] = 1;return this;
};/*** Multiply the orthographic projection matrix from the right.* @param left The coordinate of the left of clipping plane.* @param right The coordinate of the right of clipping plane.* @param bottom The coordinate of the bottom of clipping plane.* @param top The coordinate of the top top clipping plane.* @param near The distances to the nearer depth clipping plane. This value is minus if the plane is to be behind the viewer.* @param far The distances to the farther depth clipping plane. This value is minus if the plane is to be behind the viewer.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.ortho = function(left, right, bottom, top, near, far) {return this.concat(new Matrix4().setOrtho(left, right, bottom, top, near, far));
};/*** Set the perspective projection matrix.* @param left The coordinate of the left of clipping plane.* @param right The coordinate of the right of clipping plane.* @param bottom The coordinate of the bottom of clipping plane.* @param top The coordinate of the top top clipping plane.* @param near The distances to the nearer depth clipping plane. This value must be plus value.* @param far The distances to the farther depth clipping plane. This value must be plus value.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.setFrustum = function(left, right, bottom, top, near, far) {var e, rw, rh, rd;if (left === right || top === bottom || near === far) {throw 'null frustum';}if (near <= 0) {throw 'near <= 0';}if (far <= 0) {throw 'far <= 0';}rw = 1 / (right - left);rh = 1 / (top - bottom);rd = 1 / (far - near);e = this.elements;e[ 0] = 2 * near * rw;e[ 1] = 0;e[ 2] = 0;e[ 3] = 0;e[ 4] = 0;e[ 5] = 2 * near * rh;e[ 6] = 0;e[ 7] = 0;e[ 8] = (right + left) * rw;e[ 9] = (top + bottom) * rh;e[10] = -(far + near) * rd;e[11] = -1;e[12] = 0;e[13] = 0;e[14] = -2 * near * far * rd;e[15] = 0;return this;
};/*** Multiply the perspective projection matrix from the right.* @param left The coordinate of the left of clipping plane.* @param right The coordinate of the right of clipping plane.* @param bottom The coordinate of the bottom of clipping plane.* @param top The coordinate of the top top clipping plane.* @param near The distances to the nearer depth clipping plane. This value must be plus value.* @param far The distances to the farther depth clipping plane. This value must be plus value.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.frustum = function(left, right, bottom, top, near, far) {return this.concat(new Matrix4().setFrustum(left, right, bottom, top, near, far));
};/*** Set the perspective projection matrix by fovy and aspect.* @param fovy The angle between the upper and lower sides of the frustum.* @param aspect The aspect ratio of the frustum. (width/height)* @param near The distances to the nearer depth clipping plane. This value must be plus value.* @param far The distances to the farther depth clipping plane. This value must be plus value.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.setPerspective = function(fovy, aspect, near, far) {var e, rd, s, ct;if (near === far || aspect === 0) {throw 'null frustum';}if (near <= 0) {throw 'near <= 0';}if (far <= 0) {throw 'far <= 0';}fovy = Math.PI * fovy / 180 / 2;s = Math.sin(fovy);if (s === 0) {throw 'null frustum';}rd = 1 / (far - near);ct = Math.cos(fovy) / s;e = this.elements;e[0] = ct / aspect;e[1] = 0;e[2] = 0;e[3] = 0;e[4] = 0;e[5] = ct;e[6] = 0;e[7] = 0;e[8] = 0;e[9] = 0;e[10] = -(far + near) * rd;e[11] = -1;e[12] = 0;e[13] = 0;e[14] = -2 * near * far * rd;e[15] = 0;return this;
};/*** Multiply the perspective projection matrix from the right.* @param fovy The angle between the upper and lower sides of the frustum.* @param aspect The aspect ratio of the frustum. (width/height)* @param near The distances to the nearer depth clipping plane. This value must be plus value.* @param far The distances to the farther depth clipping plane. This value must be plus value.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.perspective = function(fovy, aspect, near, far) {return this.concat(new Matrix4().setPerspective(fovy, aspect, near, far));
};/*** Set the matrix for scaling.* @param x The scale factor along the X axis* @param y The scale factor along the Y axis* @param z The scale factor along the Z axis* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.setScale = function(x, y, z) {var e = this.elements;e[0] = x; e[4] = 0; e[8] = 0; e[12] = 0;e[1] = 0; e[5] = y; e[9] = 0; e[13] = 0;e[2] = 0; e[6] = 0; e[10] = z; e[14] = 0;e[3] = 0; e[7] = 0; e[11] = 0; e[15] = 1;return this;
};/*** Multiply the matrix for scaling from the right.* @param x The scale factor along the X axis* @param y The scale factor along the Y axis* @param z The scale factor along the Z axis* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.scale = function(x, y, z) {var e = this.elements;e[0] *= x; e[4] *= y; e[8] *= z;e[1] *= x; e[5] *= y; e[9] *= z;e[2] *= x; e[6] *= y; e[10] *= z;e[3] *= x; e[7] *= y; e[11] *= z;return this;
};/*** Set the matrix for translation.* @param x The X value of a translation.* @param y The Y value of a translation.* @param z The Z value of a translation.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.setTranslate = function(x, y, z) {var e = this.elements;e[0] = 1; e[4] = 0; e[8] = 0; e[12] = x;e[1] = 0; e[5] = 1; e[9] = 0; e[13] = y;e[2] = 0; e[6] = 0; e[10] = 1; e[14] = z;e[3] = 0; e[7] = 0; e[11] = 0; e[15] = 1;return this;
};/*** Multiply the matrix for translation from the right.* @param x The X value of a translation.* @param y The Y value of a translation.* @param z The Z value of a translation.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.translate = function(x, y, z) {var e = this.elements;e[12] += e[0] * x + e[4] * y + e[8] * z;e[13] += e[1] * x + e[5] * y + e[9] * z;e[14] += e[2] * x + e[6] * y + e[10] * z;e[15] += e[3] * x + e[7] * y + e[11] * z;return this;
};/*** Set the matrix for rotation.* The vector of rotation axis may not be normalized.* @param angle The angle of rotation (degrees)* @param x The X coordinate of vector of rotation axis.* @param y The Y coordinate of vector of rotation axis.* @param z The Z coordinate of vector of rotation axis.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.setRotate = function(angle, x, y, z) {var e, s, c, len, rlen, nc, xy, yz, zx, xs, ys, zs;angle = Math.PI * angle / 180;e = this.elements;s = Math.sin(angle);c = Math.cos(angle);if (0 !== x && 0 === y && 0 === z) {// Rotation around X axisif (x < 0) {s = -s;}e[0] = 1; e[4] = 0; e[ 8] = 0; e[12] = 0;e[1] = 0; e[5] = c; e[ 9] =-s; e[13] = 0;e[2] = 0; e[6] = s; e[10] = c; e[14] = 0;e[3] = 0; e[7] = 0; e[11] = 0; e[15] = 1;} else if (0 === x && 0 !== y && 0 === z) {// Rotation around Y axisif (y < 0) {s = -s;}e[0] = c; e[4] = 0; e[ 8] = s; e[12] = 0;e[1] = 0; e[5] = 1; e[ 9] = 0; e[13] = 0;e[2] =-s; e[6] = 0; e[10] = c; e[14] = 0;e[3] = 0; e[7] = 0; e[11] = 0; e[15] = 1;} else if (0 === x && 0 === y && 0 !== z) {// Rotation around Z axisif (z < 0) {s = -s;}e[0] = c; e[4] =-s; e[ 8] = 0; e[12] = 0;e[1] = s; e[5] = c; e[ 9] = 0; e[13] = 0;e[2] = 0; e[6] = 0; e[10] = 1; e[14] = 0;e[3] = 0; e[7] = 0; e[11] = 0; e[15] = 1;} else {// Rotation around another axislen = Math.sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z);if (len !== 1) {rlen = 1 / len;x *= rlen;y *= rlen;z *= rlen;}nc = 1 - c;xy = x * y;yz = y * z;zx = z * x;xs = x * s;ys = y * s;zs = z * s;e[ 0] = x*x*nc + c;e[ 1] = xy *nc + zs;e[ 2] = zx *nc - ys;e[ 3] = 0;e[ 4] = xy *nc - zs;e[ 5] = y*y*nc + c;e[ 6] = yz *nc + xs;e[ 7] = 0;e[ 8] = zx *nc + ys;e[ 9] = yz *nc - xs;e[10] = z*z*nc + c;e[11] = 0;e[12] = 0;e[13] = 0;e[14] = 0;e[15] = 1;}return this;
};/*** Multiply the matrix for rotation from the right.* The vector of rotation axis may not be normalized.* @param angle The angle of rotation (degrees)* @param x The X coordinate of vector of rotation axis.* @param y The Y coordinate of vector of rotation axis.* @param z The Z coordinate of vector of rotation axis.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.rotate = function(angle, x, y, z) {return this.concat(new Matrix4().setRotate(angle, x, y, z));
};/*** Set the viewing matrix.* @param eyeX, eyeY, eyeZ The position of the eye point.* @param centerX, centerY, centerZ The position of the reference point.* @param upX, upY, upZ The direction of the up vector.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.setLookAt = function(eyeX, eyeY, eyeZ, centerX, centerY, centerZ, upX, upY, upZ) {var e, fx, fy, fz, rlf, sx, sy, sz, rls, ux, uy, uz;fx = centerX - eyeX;fy = centerY - eyeY;fz = centerZ - eyeZ;// Normalize f.rlf = 1 / Math.sqrt(fx*fx + fy*fy + fz*fz);fx *= rlf;fy *= rlf;fz *= rlf;// Calculate cross product of f and up.sx = fy * upZ - fz * upY;sy = fz * upX - fx * upZ;sz = fx * upY - fy * upX;// Normalize s.rls = 1 / Math.sqrt(sx*sx + sy*sy + sz*sz);sx *= rls;sy *= rls;sz *= rls;// Calculate cross product of s and f.ux = sy * fz - sz * fy;uy = sz * fx - sx * fz;uz = sx * fy - sy * fx;// Set to this.e = this.elements;e[0] = sx;e[1] = ux;e[2] = -fx;e[3] = 0;e[4] = sy;e[5] = uy;e[6] = -fy;e[7] = 0;e[8] = sz;e[9] = uz;e[10] = -fz;e[11] = 0;e[12] = 0;e[13] = 0;e[14] = 0;e[15] = 1;// Translate.return this.translate(-eyeX, -eyeY, -eyeZ);
};/*** Multiply the viewing matrix from the right.* @param eyeX, eyeY, eyeZ The position of the eye point.* @param centerX, centerY, centerZ The position of the reference point.* @param upX, upY, upZ The direction of the up vector.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.lookAt = function(eyeX, eyeY, eyeZ, centerX, centerY, centerZ, upX, upY, upZ) {return this.concat(new Matrix4().setLookAt(eyeX, eyeY, eyeZ, centerX, centerY, centerZ, upX, upY, upZ));
};/*** Multiply the matrix for project vertex to plane from the right.* @param plane The array[A, B, C, D] of the equation of plane "Ax + By + Cz + D = 0".* @param light The array which stored coordinates of the light. if light[3]=0, treated as parallel light.* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.dropShadow = function(plane, light) {var mat = new Matrix4();var e = mat.elements;var dot = plane[0] * light[0] + plane[1] * light[1] + plane[2] * light[2] + plane[3] * light[3];e[ 0] = dot - light[0] * plane[0];e[ 1] = - light[1] * plane[0];e[ 2] = - light[2] * plane[0];e[ 3] = - light[3] * plane[0];e[ 4] = - light[0] * plane[1];e[ 5] = dot - light[1] * plane[1];e[ 6] = - light[2] * plane[1];e[ 7] = - light[3] * plane[1];e[ 8] = - light[0] * plane[2];e[ 9] = - light[1] * plane[2];e[10] = dot - light[2] * plane[2];e[11] = - light[3] * plane[2];e[12] = - light[0] * plane[3];e[13] = - light[1] * plane[3];e[14] = - light[2] * plane[3];e[15] = dot - light[3] * plane[3];return this.concat(mat);
}/*** Multiply the matrix for project vertex to plane from the right.(Projected by parallel light.)* @param normX, normY, normZ The normal vector of the plane.(Not necessary to be normalized.)* @param planeX, planeY, planeZ The coordinate of arbitrary points on a plane.* @param lightX, lightY, lightZ The vector of the direction of light.(Not necessary to be normalized.)* @return this*/
Matrix4.prototype.dropShadowDirectionally = function(normX, normY, normZ, planeX, planeY, planeZ, lightX, lightY, lightZ) {var a = planeX * normX + planeY * normY + planeZ * normZ;return this.dropShadow([normX, normY, normZ, -a], [lightX, lightY, lightZ, 0]);
};/*** Constructor of Vector3* If opt_src is specified, new vector is initialized by opt_src.* @param opt_src source vector(option)*/
var Vector3 = function(opt_src) {var v = new Float32Array(3);if (opt_src && typeof opt_src === 'object') {v[0] = opt_src[0]; v[1] = opt_src[1]; v[2] = opt_src[2];} this.elements = v;
}/*** Normalize.* @return this*/
Vector3.prototype.normalize = function() {var v = this.elements;var c = v[0], d = v[1], e = v[2], g = Math.sqrt(c*c+d*d+e*e);if(g){if(g == 1)return this;} else {v[0] = 0; v[1] = 0; v[2] = 0;return this;}g = 1/g;v[0] = c*g; v[1] = d*g; v[2] = e*g;return this;
};/*** Constructor of Vector4* If opt_src is specified, new vector is initialized by opt_src.* @param opt_src source vector(option)*/
var Vector4 = function(opt_src) {var v = new Float32Array(4);if (opt_src && typeof opt_src === 'object') {v[0] = opt_src[0]; v[1] = opt_src[1]; v[2] = opt_src[2]; v[3] = opt_src[3];} this.elements = v;
}
Matrix4对象所支持的方法和属性如表所示:

 * 单位阵在矩阵乘法中的行为,就像数字1在乘法中的行为一样。将一个矩阵乘以单位阵,得到的结果和原矩阵完全相同。在单位阵中,对角线上的元素为1.0,其余的元素为0.0。
* 单位阵在矩阵乘法中的行为,就像数字1在乘法中的行为一样。将一个矩阵乘以单位阵,得到的结果和原矩阵完全相同。在单位阵中,对角线上的元素为1.0,其余的元素为0.0。
方法属性规范:
从上表中可见,Matrix4对象有两种方法:一种方法的名称中含有前缀set,另一种则不含。包含set前缀的方法会根据参数计算出变换矩阵,然后将变换矩阵写入到自身中;而不含set前缀的方法,会先根据参数计算出变换矩阵,然后将自身与刚刚计算得到的变换矩阵相乘,然后把最终得到的结果再写入到Matrix4对象中。
如上表所示,Matrix4对象的方法十分强大且灵活。更重要的是,有了这些函数,进行变换就会变得轻而易举。
相关文章:

WebGL矩阵变换库
目录 矩阵变换库: Matrix4对象所支持的方法和属性如表所示: 方法属性规范: 虽然平移、旋转、缩放等变换操作都可以用一个44的矩阵表示,但是在写WebGL程序的时候,手动计算每个矩阵很耗费时间。为了简化编程…...

block层:8. deadline调度器
deadline 源码基于5.10 0. 私有数据 struct deadline_data {/** run time data*//** requests (deadline_rq s) are present on both sort_list and fifo_list*/struct rb_root sort_list[2];struct list_head fifo_list[2];/** next in sort order. read, write or both ar…...

DTO,VO,PO的意义与他们之间的转换
DTO(Data Transfer Object):数据传输对象,这个概念来源于J2EE的设计模式,原来的目的是为了EJB的分布式应用提供粗粒度的数据实体,以减少分布式调用的次数,从而提高分布式调用的性能和降低网络负…...

Java 集合框架2
一、关于set接口的常用类 1.HashSet类 用来处理无序的单列数据,没有重复的元素,重复的元素算一个 i.构造方法 //HashSet类是set接口的子类,是无序的单列数据,没有重复的元素,重复的元素算一个 //HashSet的构造方法 //HashSet() …...
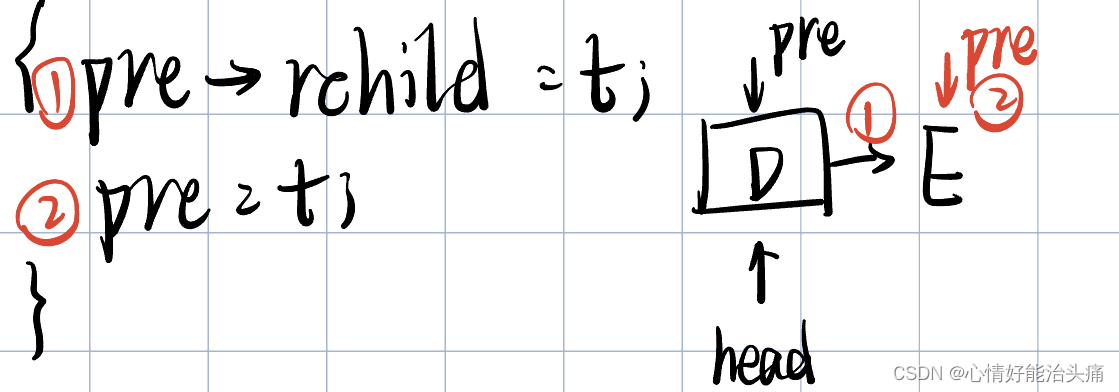
2024王道408数据结构P144 T16
2024王道408数据结构P144 T16 思考过程 首先看题目,要求我们把二叉树的叶子结点求出来并且用链表的方式存储,链接时用叶结点的右指针来存放单链表指针。我们很清楚可以看出来能用中序遍历递归的方式实现,因为第一个叶子结点在整棵树的最左下…...

【ARM Coresight 系列文章 22 -- linux frace 与 trace-cmd】
文章目录 ftrace 介绍trace-cmd 介绍trace-cmd 常用跟踪事件ftrace 与 trace-cmd 关系ftrace 编译依赖 ftrace 介绍 ftrace 是 Linux 内核中的一个跟踪工具,主要用于帮助开发者分析和调试内核的行为。ftrace 的名字来源于 “function tracer”,它最初是…...

MyBatis的一级缓存和二级缓存是怎么样的?
目录 1. 一级缓存 2. 一级缓存失效的几种情况 3. 二级缓存 4.二级缓存失效的情况 5. 二级缓存的相关配置 6. 缓存的查询顺序 MyBatis 的缓存共分为一级缓存和二级缓存。 1. 一级缓存 一级缓存是 SqlSession 级别的,通过同一个 SqlSession 查询到的数据会被缓…...

下载的文件被Windows 11 安全中心自动删除
今天从CSDN上下载了自己曾经上传的文件,但是浏览器下载完之后文件被Windows安全中心自动删除,说是带病毒。实际是没有病毒的,再说了即便有病毒也不应该直接删除啊,至少给用户一个保留或删除的选项。 研究了一番,可以暂…...
)
【Java List与数组】List<T>数组和数组List<T>的区别(124)
List数组:存储List的数组,即:数组中的元素是:List; 数组List:存储数组的List,即:List中的数据是类型的数组; 测试案例: import java.util.ArrayList; impor…...

Nuxt 菜鸟入门学习笔记四:静态资源
文章目录 public 目录assets 目录全局样式导入 Nuxt 官网地址: https://nuxt.com/ Nuxt 使用以下两个目录来处理 CSS、fonts 和图片等静态资源: public 目录 public 目录用作静态资产的公共服务器,可通过应用程序定义的 URL 公开获取。 换…...
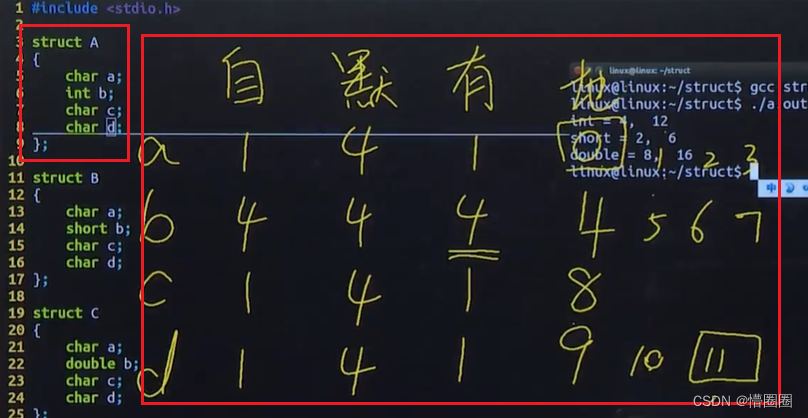
C语言 - 结构体、结构体数组、结构体指针和结构体嵌套
结构体的意义 问题:学籍管理需要每个学生的下列数据:学号、姓名、性别、年龄、分数,请用 C 语言程序存储并处理一组学生的学籍。 单个学生学籍的数据结构: 学号(num): int 型姓名(…...

python安装playwright问题记录
python安装playwright这个时候,有得时候会https timeout 有的时候会 not found。 我最后使用的方法三,挺好用的。 PyPI The Python Package Index 可以尝试使用的方法 1. 更换pip源:使用国内的pip源可以提高下载速度并减少超时问题。例如,…...

关于gRPC微服务利弊之谈
gRPC微服务架构包括以下几个主要组件: 服务定义:定义服务的接口和消息格式,使用Protocol Buffers或其他的消息格式进行描述。服务实现:实现定义的服务接口和消息处理逻辑。服务器端实现:在服务器端,需要实…...

【Terraform学习】使用 Terraform创建Lambda函数启动EC2(Terraform-AWS最佳实战学习)
本站以分享各种运维经验和运维所需要的技能为主 《python》:python零基础入门学习 《shell》:shell学习 《terraform》持续更新中:terraform_Aws学习零基础入门到最佳实战 《k8》暂未更新 《docker学习》暂未更新 《ceph学习》ceph日常问题解…...

Mac软件删除方法?如何删除不会有残留
Mac电脑如果有太多无用的应用程序,很有可能会拖垮Mac系统的运行速度。因此,卸载电脑中无用的软件是优化Mac系统运行速度的最佳方式之一。Mac卸载应用程序的方式是和Windows有很大的区别,特别对于Mac新用户来说,如何无残留的卸载删…...

编程之道:【性能优化】提高软件效率的实际建议和避免常见陷阱
在今天的数字化世界中,软件性能是应用程序成功的关键之一。无论是网页加载速度、移动应用的响应时间还是后端服务器的处理速度,性能都直接影响着用户满意度。在追求高性能时,开发人员需要采取一系列实际建议,同时避免常见的陷阱。…...
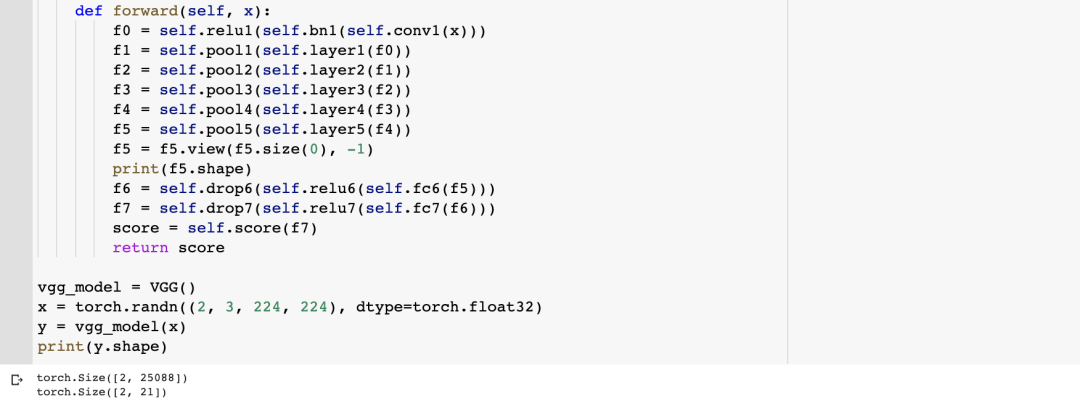
VGG的结构:视觉几何组(Visual Geometry Group)
目录 1. VGG 的结构 2. VGG 的网络细节 3. VGG 的代码实现 1. VGG 的结构 牛津大学的视觉几何组(Visual Geometry Group)设计了 VGGNet(也称为 VGG),一种经典的卷积神经网络 (CNN) 架构。在 2014 年 ILSVRC 分类任务中,VGG 取…...

VBA:按照Excel工作表中的名称列自动汇总多个工作薄中对应sheet中所需要的数据
需求如下: B列为产品名为合并单元格,C列为供应商名,G、H列为金额数据;数据源放在同一个文件夹内,B列产品名来源于工作薄名称中间的字符串,C列供应商名来源于工作薄中的sheet名;G、H列金额数据来…...
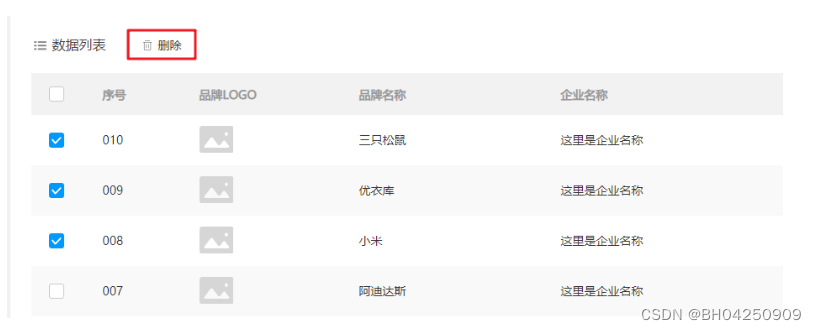
Mybatis1.9 批量删除
1.9 批量删除 1.9.1 编写接口方法1.9.2 编写SQL语句1.9.3 编写测试方法 如上图所示,用户可以选择多条数据,然后点击上面的 删除 按钮,就会删除数据库中对应的多行数据。 1.9.1 编写接口方法 在 BrandMapper 接口中定义删除多行数据的方法。…...
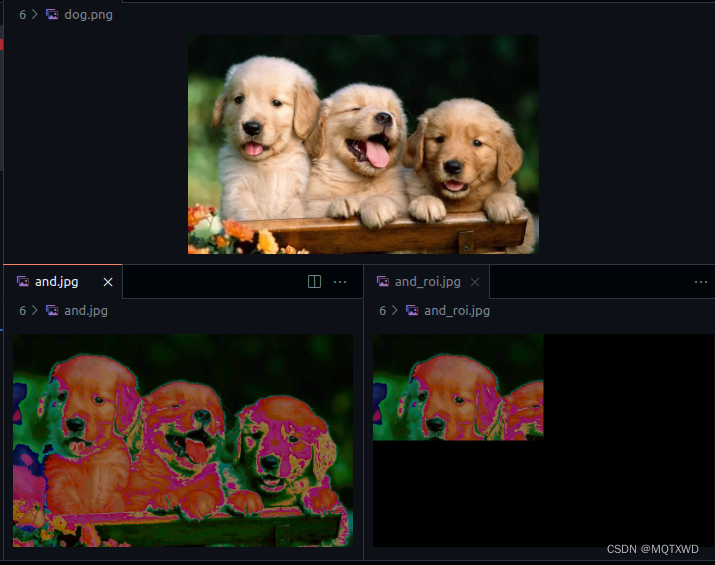
CUDA小白 - NPP(2) -图像处理-算数和逻辑操作(2)
cuda小白 原始API链接 NPP GPU架构近些年也有不少的变化,具体的可以参考别的博主的介绍,都比较详细。还有一些cuda中的专有名词的含义,可以参考《详解CUDA的Context、Stream、Warp、SM、SP、Kernel、Block、Grid》 常见的NppStatus…...

超短脉冲激光自聚焦效应
前言与目录 强激光引起自聚焦效应机理 超短脉冲激光在脆性材料内部加工时引起的自聚焦效应,这是一种非线性光学现象,主要涉及光学克尔效应和材料的非线性光学特性。 自聚焦效应可以产生局部的强光场,对材料产生非线性响应,可能…...

【OSG学习笔记】Day 18: 碰撞检测与物理交互
物理引擎(Physics Engine) 物理引擎 是一种通过计算机模拟物理规律(如力学、碰撞、重力、流体动力学等)的软件工具或库。 它的核心目标是在虚拟环境中逼真地模拟物体的运动和交互,广泛应用于 游戏开发、动画制作、虚…...
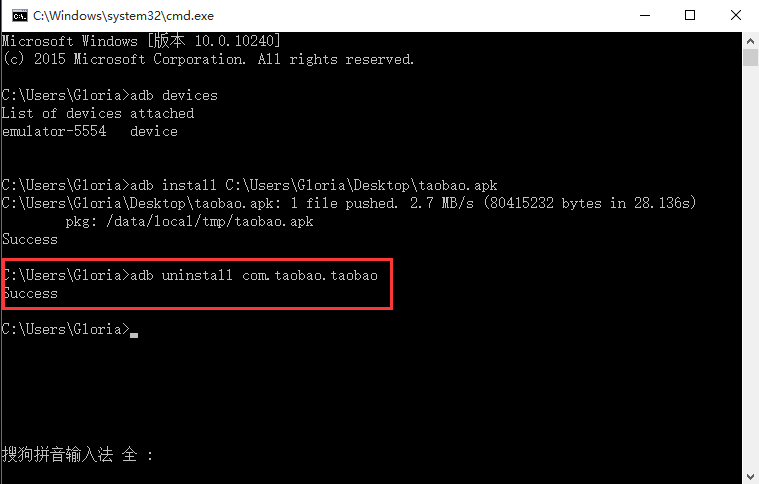
Appium+python自动化(十六)- ADB命令
简介 Android 调试桥(adb)是多种用途的工具,该工具可以帮助你你管理设备或模拟器 的状态。 adb ( Android Debug Bridge)是一个通用命令行工具,其允许您与模拟器实例或连接的 Android 设备进行通信。它可为各种设备操作提供便利,如安装和调试…...
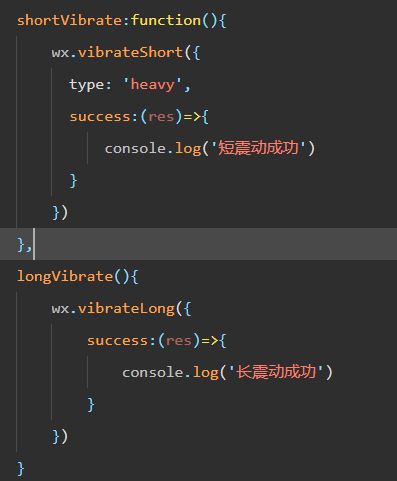
微信小程序 - 手机震动
一、界面 <button type"primary" bindtap"shortVibrate">短震动</button> <button type"primary" bindtap"longVibrate">长震动</button> 二、js逻辑代码 注:文档 https://developers.weixin.qq…...
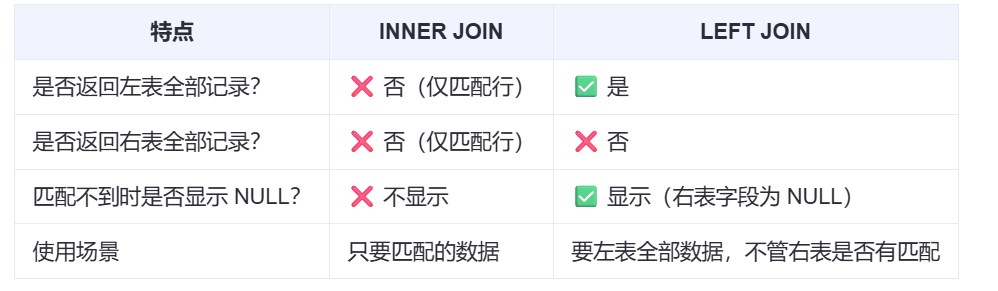
【SQL学习笔记1】增删改查+多表连接全解析(内附SQL免费在线练习工具)
可以使用Sqliteviz这个网站免费编写sql语句,它能够让用户直接在浏览器内练习SQL的语法,不需要安装任何软件。 链接如下: sqliteviz 注意: 在转写SQL语法时,关键字之间有一个特定的顺序,这个顺序会影响到…...
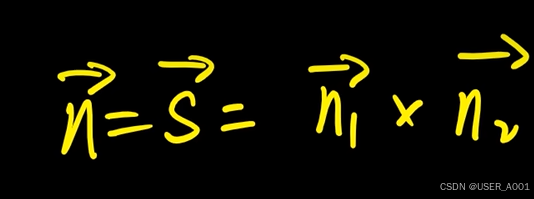
高等数学(下)题型笔记(八)空间解析几何与向量代数
目录 0 前言 1 向量的点乘 1.1 基本公式 1.2 例题 2 向量的叉乘 2.1 基础知识 2.2 例题 3 空间平面方程 3.1 基础知识 3.2 例题 4 空间直线方程 4.1 基础知识 4.2 例题 5 旋转曲面及其方程 5.1 基础知识 5.2 例题 6 空间曲面的法线与切平面 6.1 基础知识 6.2…...

AI编程--插件对比分析:CodeRider、GitHub Copilot及其他
AI编程插件对比分析:CodeRider、GitHub Copilot及其他 随着人工智能技术的快速发展,AI编程插件已成为提升开发者生产力的重要工具。CodeRider和GitHub Copilot作为市场上的领先者,分别以其独特的特性和生态系统吸引了大量开发者。本文将从功…...

【JavaSE】绘图与事件入门学习笔记
-Java绘图坐标体系 坐标体系-介绍 坐标原点位于左上角,以像素为单位。 在Java坐标系中,第一个是x坐标,表示当前位置为水平方向,距离坐标原点x个像素;第二个是y坐标,表示当前位置为垂直方向,距离坐标原点y个像素。 坐标体系-像素 …...

蓝桥杯3498 01串的熵
问题描述 对于一个长度为 23333333的 01 串, 如果其信息熵为 11625907.5798, 且 0 出现次数比 1 少, 那么这个 01 串中 0 出现了多少次? #include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std;int n 23333333;int main() {//枚举 0 出现的次数//因…...

蓝桥杯 冶炼金属
原题目链接 🔧 冶炼金属转换率推测题解 📜 原题描述 小蓝有一个神奇的炉子用于将普通金属 O O O 冶炼成为一种特殊金属 X X X。这个炉子有一个属性叫转换率 V V V,是一个正整数,表示每 V V V 个普通金属 O O O 可以冶炼出 …...
