对极几何与三角化求3D空间坐标
一,使用对极几何约束求R,T
第一步:特征匹配。提取出有效的匹配点
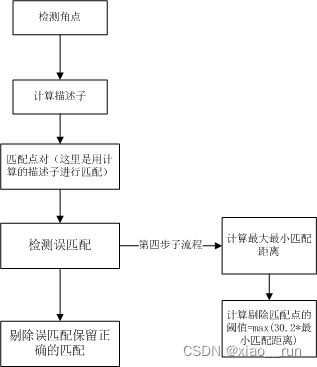
void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,std::vector<DMatch> &matches) {//-- 初始化Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;// used in OpenCV3Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();// use this if you are in OpenCV2// Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );// Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离vector<DMatch> match;// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选double min_dist = 10000, max_dist = 0;//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {double dist = match[i].distance;if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;}printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {if (match[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0)) {matches.push_back(match[i]);}}
}二、使用本质矩阵求解R,T
第二步:根据匹配点对,依据对极几何约束原理,求相机运动的R,t
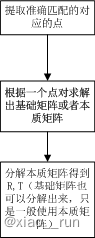
void pose_estimation_2d2d(const std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,const std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,const std::vector<DMatch> &matches,Mat &R, Mat &t) {// 相机内参,TUM Freiburg2Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);//-- 把匹配点转换为vector<Point2f>的形式vector<Point2f> points1;vector<Point2f> points2;for (int i = 0; i < (int) matches.size(); i++) {points1.push_back(keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);points2.push_back(keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);}//-- 计算本质矩阵Point2d principal_point(325.1, 249.7); //相机主点, TUM dataset标定值int focal_length = 521; //相机焦距, TUM dataset标定值Mat essential_matrix;essential_matrix = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, focal_length, principal_point);//-- 从本质矩阵中恢复旋转和平移信息.recoverPose(essential_matrix, points1, points2, R, t, focal_length, principal_point);
}三、由R,T三角化空间坐标
第三步:根据针孔相机模型的公式,由 R,t估计特征点的空间坐标
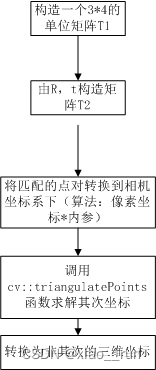
//三角化,根据匹配点和求解到的三维点。存储在points中
void triangulation(const vector<KeyPoint> &keypoint_1,const vector<KeyPoint> &keypoint_2,const std::vector<DMatch> &matches,const Mat &R, const Mat &t,vector<Point3d> &points) {Mat T1 = (Mat_<float>(3, 4) <<1, 0, 0, 0,0, 1, 0, 0,0, 0, 1, 0);//根据求解到的RT构造T2矩阵Mat T2 = (Mat_<float>(3, 4) <<R.at<double>(0, 0), R.at<double>(0, 1), R.at<double>(0, 2), t.at<double>(0, 0),R.at<double>(1, 0), R.at<double>(1, 1), R.at<double>(1, 2), t.at<double>(1, 0),R.at<double>(2, 0), R.at<double>(2, 1), R.at<double>(2, 2), t.at<double>(2, 0));//相机内参Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);vector<Point2f> pts_1, pts_2;for (DMatch m:matches) {// 将像素坐标转换至相机坐标pts_1.push_back(pixel2cam(keypoint_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K));pts_2.push_back(pixel2cam(keypoint_2[m.trainIdx].pt, K));}Mat pts_4d;cv::triangulatePoints(T1, T2, pts_1, pts_2, pts_4d);// 转换成非齐次坐标for (int i = 0; i < pts_4d.cols; i++) {Mat x = pts_4d.col(i);x /= x.at<float>(3, 0); // 归一化Point3d p(x.at<float>(0, 0),x.at<float>(1, 0),x.at<float>(2, 0));points.push_back(p);}
}其中 triangulatePoints()的具体用法为
triangulatePoints(T1, T2, left, right, points_final) ;Mat T1 = (Mat_<float>(3, 4) <<1, 0, 0, 0,0, 1, 0, 0,0, 0, 1, 0);
Mat T2 = (Mat_<float>(3, 4) <<R.at<double>(0, 0), R.at<double>(0, 1), R.at<double>(0, 2), T.at<double>(0, 0),R.at<double>(1, 0), R.at<double>(1, 1), R.at<double>(1, 2), T.at<double>(1, 0),R.at<double>(2, 0), R.at<double>(2, 1), R.at<double>(2, 2), T.at<double>(2, 0));`
triangulatePoints(T1, T2, left, right, points_final) ;其中T2为3x4的[R|T]矩阵,left、right为相机坐标系下的归一化坐标,
因此不能直接使用提取到的像素坐标。应首先将像素坐标通过相机内参转化到相机坐标系下。
所以通过函数pixel2cam可将像素坐标转换到归一化相机坐标系下
归一化坐标:X=(u-u0)/fx
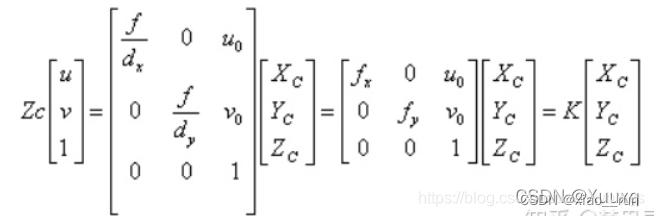
//像素坐标到归一化平面相机坐标的转换
Point2f pixel2cam(const Point2f& p, const Mat& K)
{return Point2f((p.x - K.at<double>(0, 2)) / K.at<double>(0, 0),(p.y - K.at<double>(1, 2)) / K.at<double>(1, 1));
}
四、代码demo
总的代码为:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
// #include "extra.h" // used in opencv2
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,std::vector<DMatch> &matches);void pose_estimation_2d2d(const std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,const std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,const std::vector<DMatch> &matches,Mat &R, Mat &t);void triangulation(const vector<KeyPoint> &keypoint_1,const vector<KeyPoint> &keypoint_2,const std::vector<DMatch> &matches,const Mat &R, const Mat &t,vector<Point3d> &points
);/// 作图用
inline cv::Scalar get_color(float depth) {float up_th = 50, low_th = 10, th_range = up_th - low_th;if (depth > up_th) depth = up_th;if (depth < low_th) depth = low_th;return cv::Scalar(255 * depth / th_range, 0, 255 * (1 - depth / th_range));
}// 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2f pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K);int main(int argc, char **argv) {if (argc != 3) {cout << "usage: triangulation img1 img2" << endl;return 1;}//-- 读取图像Mat img_1 = imread(argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);Mat img_2 = imread(argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;vector<DMatch> matches;find_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches);cout << "一共找到了" << matches.size() << "组匹配点" << endl;//-- 估计两张图像间运动Mat R, t;pose_estimation_2d2d(keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches, R, t);//-- 三角化vector<Point3d> points;//tr是三维点triangulation(keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches, R, t, tr);//-- 验证三角化点与特征点的重投影关系Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);Mat img1_plot = img_1.clone();Mat img2_plot = img_2.clone();for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++) {// 第一个图float depth1 = points[i].z;cout << "depth: " << depth1 << endl;Point2d pt1_cam = pixel2cam(keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt, K);cv::circle(img1_plot, keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt, 2, get_color(depth1), 2);// 第二个图Mat pt2_trans = R * (Mat_<double>(3, 1) << points[i].x, points[i].y, points[i].z) + t;float depth2 = pt2_trans.at<double>(2, 0);cv::circle(img2_plot, keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt, 2, get_color(depth2), 2);}cv::imshow("img 1", img1_plot);cv::imshow("img 2", img2_plot);cv::waitKey();return 0;
}void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,std::vector<DMatch> &matches) {//-- 初始化Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;// used in OpenCV3Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();// use this if you are in OpenCV2// Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );// Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离vector<DMatch> match;// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选double min_dist = 10000, max_dist = 0;//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {double dist = match[i].distance;if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;}printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {if (match[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0)) {matches.push_back(match[i]);}}
}void pose_estimation_2d2d(const std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,const std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,const std::vector<DMatch> &matches,Mat &R, Mat &t) {// 相机内参,TUM Freiburg2Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);//-- 把匹配点转换为vector<Point2f>的形式vector<Point2f> points1;vector<Point2f> points2;for (int i = 0; i < (int) matches.size(); i++) {points1.push_back(keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);points2.push_back(keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);}//-- 计算本质矩阵Point2d principal_point(325.1, 249.7); //相机主点, TUM dataset标定值int focal_length = 521; //相机焦距, TUM dataset标定值Mat essential_matrix;essential_matrix = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, focal_length, principal_point);//-- 从本质矩阵中恢复旋转和平移信息.recoverPose(essential_matrix, points1, points2, R, t, focal_length, principal_point);
}//三角化,根据匹配点和求解到的三维点。存储在points中
void triangulation(const vector<KeyPoint> &keypoint_1,const vector<KeyPoint> &keypoint_2,const std::vector<DMatch> &matches,const Mat &R, const Mat &t,vector<Point3d> &points) {Mat T1 = (Mat_<float>(3, 4) <<1, 0, 0, 0,0, 1, 0, 0,0, 0, 1, 0);//根据求解到的RT构造T2矩阵Mat T2 = (Mat_<float>(3, 4) <<R.at<double>(0, 0), R.at<double>(0, 1), R.at<double>(0, 2), t.at<double>(0, 0),R.at<double>(1, 0), R.at<double>(1, 1), R.at<double>(1, 2), t.at<double>(1, 0),R.at<double>(2, 0), R.at<double>(2, 1), R.at<double>(2, 2), t.at<double>(2, 0));//相机内参Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);vector<Point2f> pts_1, pts_2;for (DMatch m:matches) {// 将像素坐标转换至相机坐标pts_1.push_back(pixel2cam(keypoint_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K));pts_2.push_back(pixel2cam(keypoint_2[m.trainIdx].pt, K));}Mat pts_4d;cv::triangulatePoints(T1, T2, pts_1, pts_2, pts_4d);// 转换成非齐次坐标for (int i = 0; i < pts_4d.cols; i++) {Mat x = pts_4d.col(i);x /= x.at<float>(3, 0); // 归一化Point3d p(x.at<float>(0, 0),x.at<float>(1, 0),x.at<float>(2, 0));points.push_back(p);}
}Point2f pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) {return Point2f((p.x - K.at<double>(0, 2)) / K.at<double>(0, 0),(p.y - K.at<double>(1, 2)) / K.at<double>(1, 1));
}相关文章:
对极几何与三角化求3D空间坐标
一,使用对极几何约束求R,T 第一步:特征匹配。提取出有效的匹配点 void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,std::vector&l…...

英语语法笔记
1.英语五大句型 主谓(主语动词) 主谓宾(主语动词宾语) 主谓宾宾(主语动词简接宾语直接宾语) 主谓宾补(主语动词宾语宾语补语) 主系表(主语系动词主语补语) 1…...
ES6的面向对象编程以及ES6中的类和对象
一、面向对象 1、面向对象 (1)是一种开发思想,并不是具体的一种技术 (2)一切事物均为对象,在项目中主要是对象的分工协作 2、对象的特征 (1)对象是属性和行为的结合体 &#x…...

ConfigMaps in K8s
摘要 ConfigMaps是Kubernetes(K8s)中用于存储应用程序配置信息的一种资源对象。它将key-value对存储为Kubernetes集群中的一个资源,并可以在Pod中以卷或环境变量的形式使用。 ConfigMaps的设计目的是将应用程序配置与应用程序本身解耦。它可…...

《机器人学一(Robotics(1))》_台大林沛群 第 6 周 【轨迹规划_直线转折处抛物线平滑】Quiz 6
步骤: 1、 编程 将PPT 的例子 跑一遍, 确保代码无误 2、根据题目 修改 相关参数 文章目录 求解代码_Python 解决的问题: 线段间转折点 的 速度 不连续 解决方法: 将直线段 两端 修正为 二次方程式 二次项圆滑 求解代码_Python …...
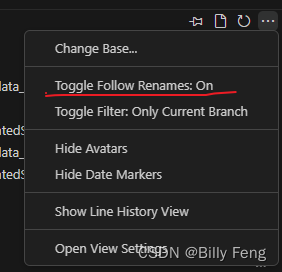
关于vscode的GitLens插件里的FILE HISTORY理解
最近在用vscode的GitLens插件开发项目遇到这个疑问,先看图: 每当我点击FILE HISTORY 一个commit时,正常来说显示器会自动将点击的提交版本和它上一个提交版本进行比较,如果单纯这么理解的话就错了,因为GitLens的File …...
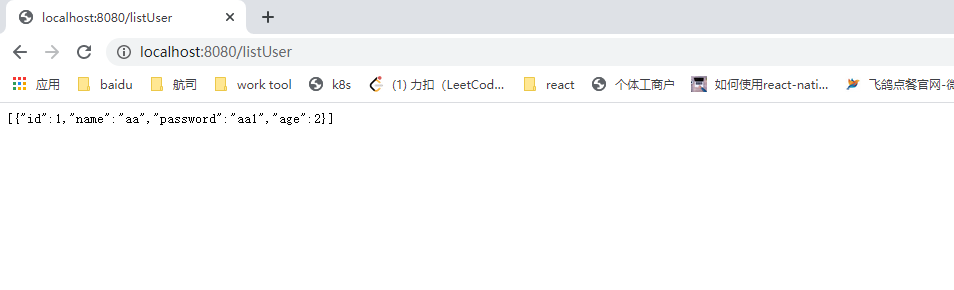
通过idea实现springboot集成mybatys
概述 使用springboot 集成 mybatys后,通过http请求接口,使得通过http请求可以直接直接操作数据库; 完成后端功能框架;前端是准备上小程序,调用https的请求接口用。简单实现后端框架; 详细 springboot 集…...
算法_C++——移位字符串分组)
力扣(LeetCode)算法_C++——移位字符串分组
给定一个字符串,对该字符串可以进行 “移位” 的操作,也就是将字符串中每个字母都变为其在字母表中后续的字母,比如:“abc” -> “bcd”。这样,我们可以持续进行 “移位” 操作,从而生成如下移位序列&am…...

Vue2 与Vue3的区别?面试题
Vue 2和Vue 3是Vue.js框架的不同版本,在面试中经常涉及到它们之间的区别。以下是Vue 2和Vue 3的主要区别: 性能提升:Vue 3在性能方面进行了优化。Vue 3引入了更高效的Diff算法,提高了渲染性能。此外,Vue 3还进行了代码…...

java代码:Random和Scanner应用的小例子-猜数字小游戏
//java代码:Random和Scanner应用的小例子-猜数字小游戏 package com.test; import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; /* * 需求:猜数字小游戏。 * 系统产生一个1-100之间的随机数,请猜出这个数据是多少? * * 分析…...
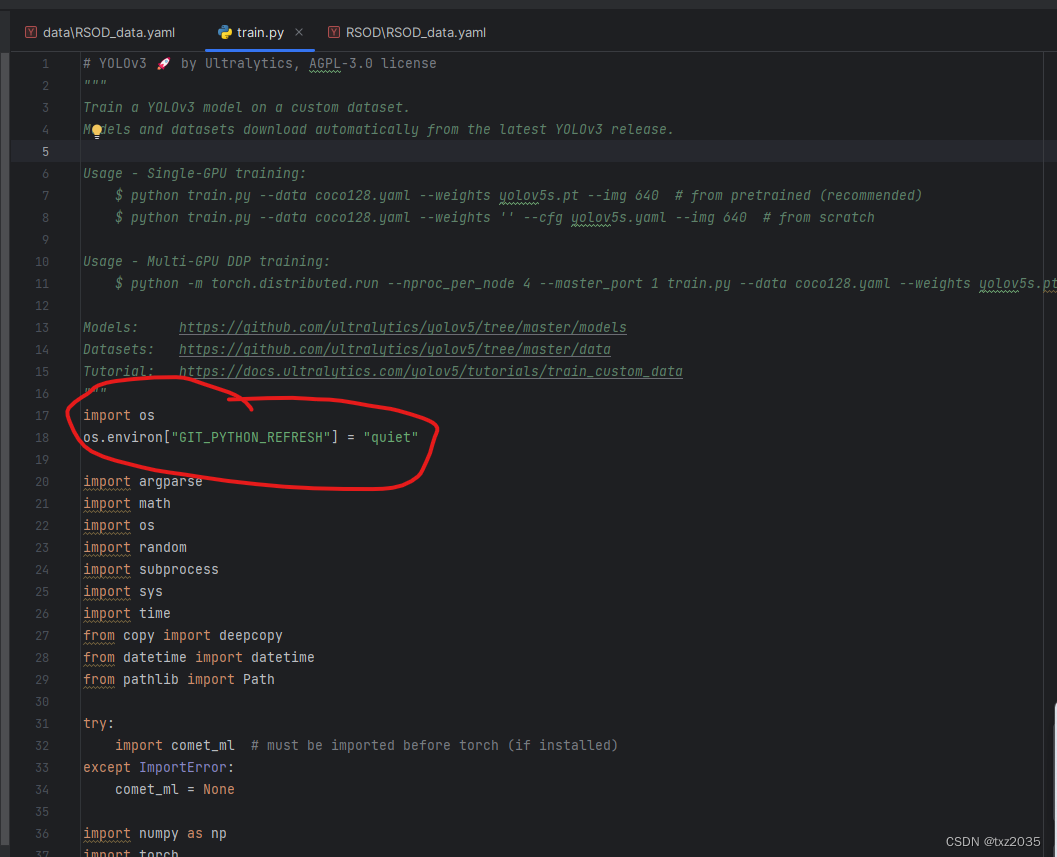
python调用git出错:ImportError: Failed to initialize: Bad git executable.
报错信息 #报错信息 Traceback (most recent call last): File “”, line 1, in File “C:\Python27\lib\site-packages\git_init_.py”, line 85, in raise ImportError(‘Failed to initialize: {0}’.format(exc)) ImportError: Failed to initialize: Bad git executab…...

【C语言】入门——指针
目录 编辑 1.指针是什么 2.指针类型和指针运算 2.1指针-整数 2.2指针-指针 2.3指针的关系运算 3.野指针 3.1野指针成因 👍指针未初始化: 👍指针越界访问: 👍指针指向空间释放: 3.2如何规避野指针 …...

C#_预处理指令
1. 预处理器指令指导编译器在实际编译开始之前对信息进行预处理。 所有的预处理器指令都是以 # 开始。且在一行上,只有空白字符可以出现在预处理器指令之前。预处理器指令不是语句,所以它们不以分号(;)结束。 C# 编译器没有一个单…...
)
容器命令(docker)
文章目录 前言一、docker容器命令0、准备工作1、新建容器并启动2、退出容器3、列出所有的运行的容器4、删除容器5、启动和停止容器的操作 总结 前言 本文主要介绍docker中与容器相关的一些命令,是对狂神课程的一些总结,作为一个手册帮助博主和使用docke…...

Vue3 ElementPlus el-cascader级联选择器动态加载数据
参考了这位的大佬的写法 element el-cascader动态加载数据 (多级联动,落地实现)_el-cascader 动态加载_林邵晨的博客-CSDN博客 <el-cascader style"width: 300px" :props"address" v-model"addressValue" …...
(一、字符串相邻元素删除类型))
leetcode分类刷题:栈(Stack)(一、字符串相邻元素删除类型)
1、在leetcode分类刷题:基于数组的双指针(一、基于元素移除的O(1)类型)题目中,采用双指针之快慢指针的算法来解决。 2、字符串相邻元素的删除问题,用栈来进行管理,会非常有效;这种题型排在后面的…...
你还在找淘宝商品信息查询的接口吗?
你还在找淘宝商品信息查询的接口吗?,不用找了,我这有,免费测试 在很多行业,比如淘客、商品采集、刊登、数据分析行业都需要用到相关的商品接口,但是官方一般又没有开放这些接口,怎么办ÿ…...
dll修复精灵,dll修复工具下载方法分享,mfc140u.dll缺失损坏一键修复
今天,我将为大家分享一个关于mfc140u.dll的问题。首先,我想问一下在座的网友们,有多少人知道mfc140u.dll是什么?又有多少人知道它的作用以及如何解决这个问题呢?在接下来的演讲中,我将详细介绍mfc140u.dll的…...

[LINUX使用] iptables tcpdump
iptables: 收到来自 10.10.10.10 的数据后都丢弃 iptables -I INPUT -s 10.10.10.10 -j DROP 直接 reject 来自 10.10.10.* 网段的数据 iptables -I INPUT -s 10.10.10.0/24 -j REJECT tcpdump: dump eth0的数据到本地 tcpdump -i eth0 -w dump.pcap 只抓 目的地址是 10…...

百度文心一率先言向全社会开放 应用商店搜“文心一言”可直接下载
8月31日,文心一言率先向全社会全面开放。广大用户可以在应用商店下载“文心一言APP”或登陆“文心一言官网”(https://yiyan.baidu.com) 体验。同时,企业用户可以直接登录百度智能云千帆大模型平台官网,调用文心一言能…...
JavaSec-RCE
简介 RCE(Remote Code Execution),可以分为:命令注入(Command Injection)、代码注入(Code Injection) 代码注入 1.漏洞场景:Groovy代码注入 Groovy是一种基于JVM的动态语言,语法简洁,支持闭包、动态类型和Java互操作性,…...
使用rpicam-app通过网络流式传输视频)
树莓派超全系列教程文档--(62)使用rpicam-app通过网络流式传输视频
使用rpicam-app通过网络流式传输视频 使用 rpicam-app 通过网络流式传输视频UDPTCPRTSPlibavGStreamerRTPlibcamerasrc GStreamer 元素 文章来源: http://raspberry.dns8844.cn/documentation 原文网址 使用 rpicam-app 通过网络流式传输视频 本节介绍来自 rpica…...
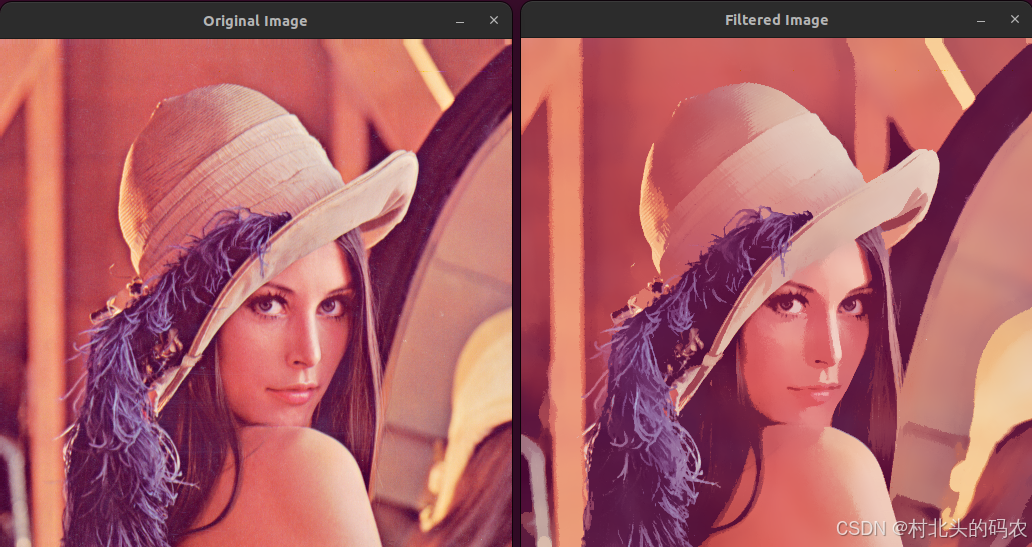
OPenCV CUDA模块图像处理-----对图像执行 均值漂移滤波(Mean Shift Filtering)函数meanShiftFiltering()
操作系统:ubuntu22.04 OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9 IDE:Visual Studio Code 编程语言:C11 算法描述 在 GPU 上对图像执行 均值漂移滤波(Mean Shift Filtering),用于图像分割或平滑处理。 该函数将输入图像中的…...

今日学习:Spring线程池|并发修改异常|链路丢失|登录续期|VIP过期策略|数值类缓存
文章目录 优雅版线程池ThreadPoolTaskExecutor和ThreadPoolTaskExecutor的装饰器并发修改异常并发修改异常简介实现机制设计原因及意义 使用线程池造成的链路丢失问题线程池导致的链路丢失问题发生原因 常见解决方法更好的解决方法设计精妙之处 登录续期登录续期常见实现方式特…...
短视频矩阵系统文案创作功能开发实践,定制化开发
在短视频行业迅猛发展的当下,企业和个人创作者为了扩大影响力、提升传播效果,纷纷采用短视频矩阵运营策略,同时管理多个平台、多个账号的内容发布。然而,频繁的文案创作需求让运营者疲于应对,如何高效产出高质量文案成…...
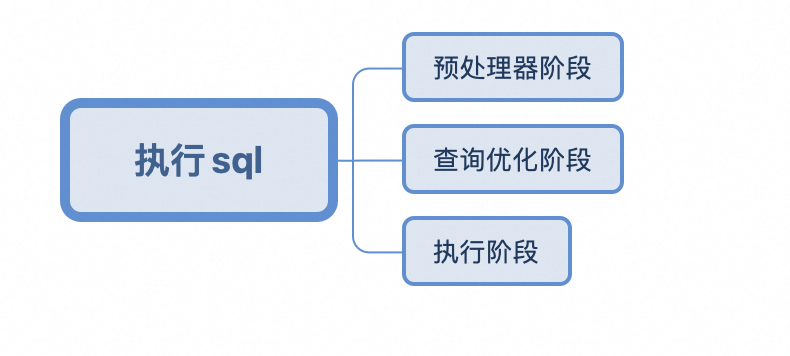
Mysql中select查询语句的执行过程
目录 1、介绍 1.1、组件介绍 1.2、Sql执行顺序 2、执行流程 2.1. 连接与认证 2.2. 查询缓存 2.3. 语法解析(Parser) 2.4、执行sql 1. 预处理(Preprocessor) 2. 查询优化器(Optimizer) 3. 执行器…...
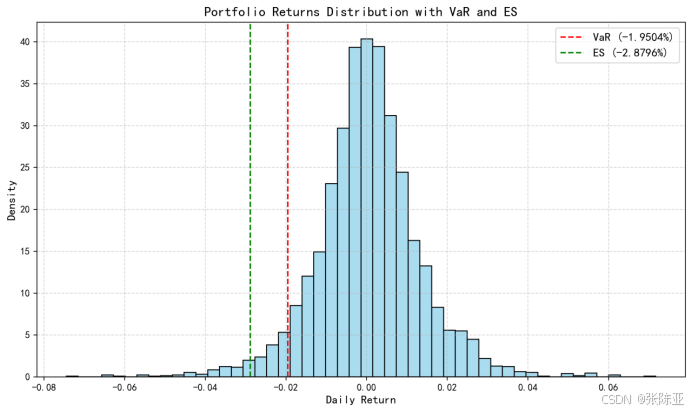
Python基于历史模拟方法实现投资组合风险管理的VaR与ES模型项目实战
说明:这是一个机器学习实战项目(附带数据代码文档),如需数据代码文档可以直接到文章最后关注获取。 1.项目背景 在金融市场日益复杂和波动加剧的背景下,风险管理成为金融机构和个人投资者关注的核心议题之一。VaR&…...
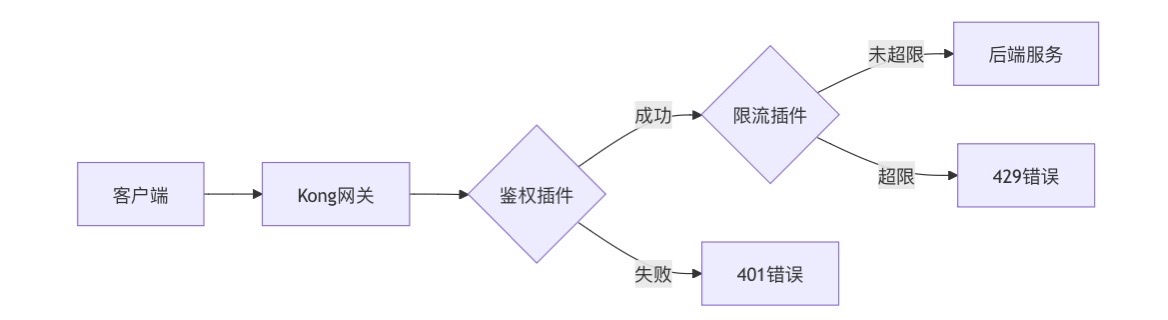
云原生安全实战:API网关Kong的鉴权与限流详解
🔥「炎码工坊」技术弹药已装填! 点击关注 → 解锁工业级干货【工具实测|项目避坑|源码燃烧指南】 一、基础概念 1. API网关(API Gateway) API网关是微服务架构中的核心组件,负责统一管理所有API的流量入口。它像一座…...
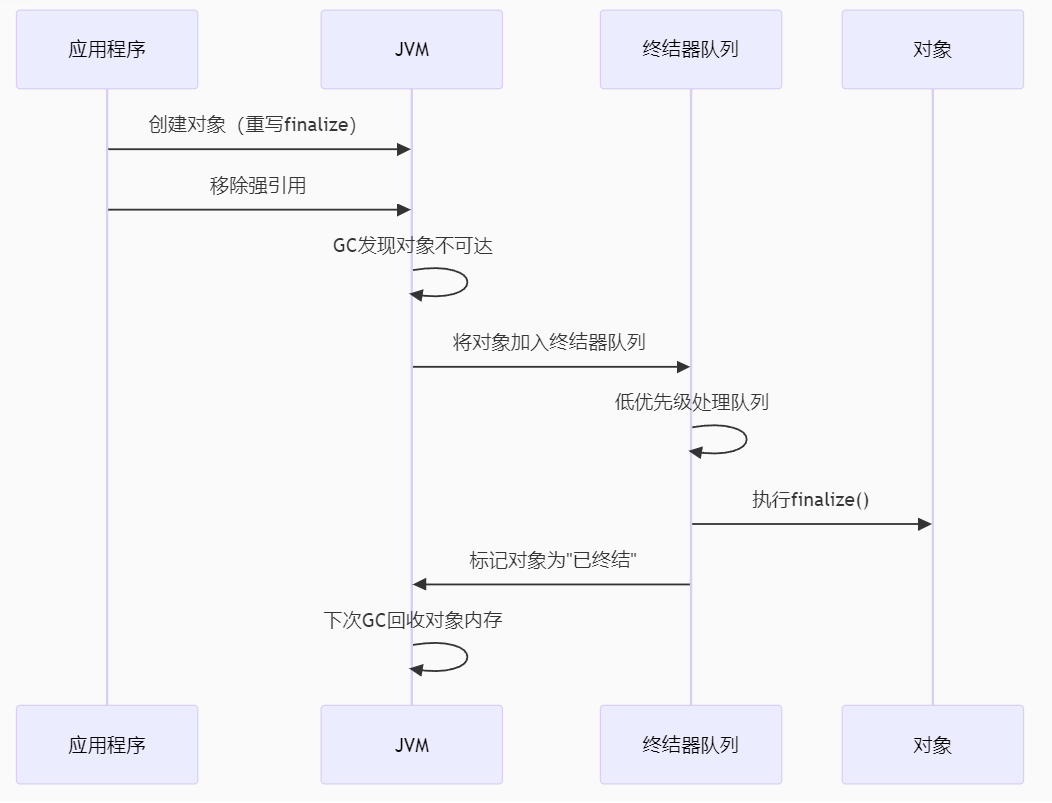
【 java 虚拟机知识 第一篇 】
目录 1.内存模型 1.1.JVM内存模型的介绍 1.2.堆和栈的区别 1.3.栈的存储细节 1.4.堆的部分 1.5.程序计数器的作用 1.6.方法区的内容 1.7.字符串池 1.8.引用类型 1.9.内存泄漏与内存溢出 1.10.会出现内存溢出的结构 1.内存模型 1.1.JVM内存模型的介绍 内存模型主要分…...
STM32---外部32.768K晶振(LSE)无法起振问题
晶振是否起振主要就检查两个1、晶振与MCU是否兼容;2、晶振的负载电容是否匹配 目录 一、判断晶振与MCU是否兼容 二、判断负载电容是否匹配 1. 晶振负载电容(CL)与匹配电容(CL1、CL2)的关系 2. 如何选择 CL1 和 CL…...
