Java-day13(IO流)
IO流
凡是与输入,输出相关的类,接口等都定义在java.io包下

1.File类的使用
-
File类可以有构造器创建其对象,此对象对应着一个文件(.txt,.avi,.doc,.mp3等)或文件目录
-
File类对象是与平台无关的
-
File中的方法仅涉及到如何创建,删除,重命名等操作,不涉及文件内容的修改(需IO流来操作)
-
File类对象常作为io流的具体类的构造器的形参
常见的方法

熟练掌握红色标记的方法
例:
import java.io.File;
import java.sql.Date;import org.junit.Test;
public class test10{@Testpublic void test1(){//绝对路径File f1 = new File("C:/Users/Cat God 007/Desktop/hello.txt"); //文件File f2 = new File("C:/Users/Cat God 007/Desktop");//文件目录//相对路径File f3 = new File("hello.txt");System.out.println("=============访问文件名================");System.out.println(f3.getName());//返回文件名 System.out.println(f3.getPath());//返回文件路径System.out.println(f3.getAbsoluteFile());//返回文件的绝对路径System.out.println(f3.getParent());//返回上一级文件目录System.out.println(f3.getAbsolutePath());//返回完整的文件路径System.out.println("=============================");System.out.println(f2.getName());//返回文件目录名System.out.println(f2.getPath());//返回文件目录路径System.out.println(f2.getAbsoluteFile());//返回文件目录的绝对路径System.out.println(f2.getParent());//返回上一级文件目录System.out.println(f2.getAbsolutePath());//返回完整的文件目录路径System.out.println("============文件检测=========");System.out.println(f1.exists());//检测文件是否存在System.out.println(f1.canRead());//检测文件是否可读System.out.println(f1.canWrite());//检测文件是否可写System.out.println(f1.isFile());//检测此对象是否不是文件System.out.println(f1.isDirectory());//检测此对象是否不是文件目录System.out.println("============获取常规文件信息=========");System.out.println(new Date(f1.lastModified()));//获取文件最后修改时间System.out.println(f1.length());//获取文件大小}@Testpublic void test2(){File f1 = new File("C:/Users/Cat God 007/Desktop/hello.txt"); File f2 = new File("C:/Users/Cat God 007/Desktop/test/tes1-test9");System.out.println(f1.delete());//删除文件if(!f1.exists()){boolean b1 = f1.createNewFile();//创建文件System.out.println(b1);}if(!f2.exists()){boolean b2 = f2.mkdir();//mkdirs()可以递归创建文件夹,mkdir只创建最后的文件目录,若它上层没有创建,则它也不会创建System.out.println(b2);}File f3 = new File("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\javacode\\day13");String[] list = f3.list();for(int i = 0;i < list.length;i++){System.out.println(list[i]);//以String方式读取出f3下的文件}File[] files = f3.listFiles();for(int i = 0;i < files.length;i++){System.out.println(files[i].getName());//以文件方式读取出f3下的文件}}
}
2.IO流原理及其分类
- IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输
- 按数据单位可分为:
字节流(8bit),字符流(16bit) - 按流的流向可分为:
输入流,输出流 - 按流的角色可分为:
节点流(直接作为于文件),处理流
| 抽象基类 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 输入流 | InputStream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
IO流设计40多个类,都是从以上4个抽象基类派生由这四个类派生出的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀
IO流体系

- 访问文件的类也被称为节点流,文件流,其他类被称为处理流
3.文件流
FileInputStream
例:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.junit.Test;public class test11{@Test
//读取硬盘文件内容到程序中,使用FileInputStream(读取的文件一定要存在,否则会报文件找不到的异常)
public void test1()throws Exception{//1.创建Filen类型的对象File file = new File("hello.txt");//2.创建FileInputStream类型的对象FileInputStream files = new FileInputStream(file); //3.调用FileInputStream的方法,实现file文件的读取//read():读取文件的一个字节,当执行到文件结尾时,返回-1//方式一int b = files.read();while(b != -1){System.out.println((char)b);//int转字符(否则打印出来的是对应的Ascll码)b = files.read();}//方式二int c;while((c = files.read()) != -1){System.out.println((char)c);}//4.关闭相应的流files.close();
}@Test//测试test1的优化,确保每次流都能被关闭public void test2(){FileInputStream files = null;try {File file = new File("hello.txt");files = new FileInputStream(file);int c;while((c = files.read()) != -1){System.out.println((char)c);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(files != null){try{files.close();}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}
}@Testpublic void test3(){FileInputStream files = null;try{File file = new File("hello.txt");files = new FileInputStream(file);byte[] b = new byte[5];//将读取到的数据写入数组中int len;//每次读入到byte中的字节长度while((len = files.read(b)) != -1){// 方式一:运行for循环实现遍历输出// 成功案例:for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){System.out.print((char)b[i]);}//错误案例:使用b.length时,在读取到最后(此时只读取了1个元素),但依旧会传入5个元素的数组{1个新元素+4个旧元素}// for(int i = 0;i < b.length;i++){// System.out.print((char)b[i]);// }//方式二:运行String构造器实现遍历输出// String str = new String(b, 0, len);// System.out.println(str);}}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(files != null){try{files.close();}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
FileOutputStream
简单编写
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.junit.Test;public class test12{@Testpublic void testFileOutputSteam(){//1.创建要写入文件的文件路径的File对象,此文件路径可以不存在(会自动创建),若存在,就会用新写入的数据覆盖原来的数据File file = new File("hello1.txt");//2.创建FileOutputStream对象,将之前的File对象作形参传入FileOutputStream的构造器中FileOutputStream f = null;try{ f = new FileOutputStream(file);//3.写入数据f.write(new String("I Love China").getBytes());//这里用到了字符串转字节数组}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{//关闭输出流if(f != null){try{f.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
练习:编写非文本文件复制的方法
主要实现
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.junit.Test;public class test12{@Test//从硬盘中读入数据,将此数据写入到另一位置(相当文件复制)public void testFileInputOutputSteam(){//1.提供读,写的文件路径File file1 = new File("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\t1.jpg");File file2 = new File("C:\\\\Users\\\\Cat God 007\\\\Desktop\\\\tt.jpg");//2.提供读,写流FileOutputStream fos = null;FileInputStream fis = null;try{ fis = new FileInputStream(file1);fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);//3.实现文件复制byte [] b = new byte[20];int len;while ((len = fis.read(b)) != -1) {fos.write(b,0,len); }}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{//4.关闭读,写流if(fos != null){try{fos.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}if(fis != null){try{fis.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
最后包装成方法,并进行测试
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;public class test12{public static void main(String[] args) { testFileInputOutputSteam("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\t1.jpg", "C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\tt1.jpg");}public static void testFileInputOutputSteam(String src,String dest){File file1 = new File(src);File file2 = new File(dest);FileOutputStream fos = null;FileInputStream fis = null;try{fis = new FileInputStream(file1);fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);byte [] b = new byte[20];int len;while ((len = fis.read(b)) != -1) {fos.write(b,0,len); }}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(fos != null){try{fos.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}if(fis != null){try{fis.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
FileReader,FileWriter(字符流)
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import org.junit.Test;public class test13{//使用FileReader,FileWriter可以实现文本文件的复制@Testpublic void testFileReaderWriter(){ FileReader fr = null;FileWriter fw = null; try{File src = new File("hello.txt");//读File desc = new File("hello1.txt");//写fr = new FileReader(src);fw = new FileWriter(desc);char[] c = new char[20];int len;while ((len = fr.read(c)) != -1) {fw.write(c,0,len); }}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(fr != null){try{fr.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}if(fw != null){try{fw.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
}
- 文本文件用字符流,非文本文件(视频文件,音频文件,图片)用字节流,效率较高
4.缓冲流(主要使用)
-
可以提高处理数据的效率
-
每次处理完后,都需要刷新(
flush())数组,方便下次元素不够写入的情况
使用 BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream 实现非文本文件的复制
例:
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.junit.Test;public class test14{@Testpublic void testBufferedInputOutputStream(){BufferedInputStream bis = null;BufferedOutputStream bos = null;try{ //1.提供读写文件File file1 = new File("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\t1.jpg");File file2 = new File(".\\1.jpg");//2.创建相应的节点流FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);//3.将创建的节点流的对象作为形参传递给缓冲流的构造器中bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);//4.实现文本文件byte[] b = new byte[1024];int len;while ((len = bis.read(b)) != -1) {bos.write(b, 0, len);bos.flush();//刷新一下}}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{//5.关闭相应的流if(bis != null){try{bis.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}if(bos != null){try{bos.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
}
}
使用BufferedReader,BufferedWriter实现文本文件的复制
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import org.junit.Test;public class test{
// BufferedReader()的readLine()方法(一行一行读)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import org.junit.Test;public class test14{@Testpublic void testBufferedReader(){BufferedReader br = null;BufferedWriter bw = null;try{ File file = new File("hello.txt");File file1 = new File("hell1o.txt");FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file1);br = new BufferedReader(fr);bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);// char[] c = new char[1024];// int len;// while ((len = br.read(c)) != -1) {// String str = new String(c, 0, len);// System.out.print(str);// }String str;while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {//System.out.println(str);bw.write(str + "\n");//bw.newLine();//换行bw.flush();}}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(bw != null){try{bw.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}if(br != null){try{br.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
5.转换流
-
提供在字节流和字符流之间的转换
-
字节流中的数据都是字符时,转换成字符流操作更高效
-
编码(字符串====>字节数组),解码(字节数组====>字符串)
-
提供两个转换流
InputStreamReader(解码),OutputStreamWriter(编码)
例:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;import org.junit.Test;public class test16{@Testpublic void test1(){BufferedReader br = null;BufferedWriter bw = null;try{ //解码(字节数组====>字符串)File file = new File("hello.txt");FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");br = new BufferedReader(isr);//编码(字符串====>字节数组)File file1 = new File("hello123.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file1);OutputStreamWriter isw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "UTF-8");bw = new BufferedWriter(isw);String str;while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {//System.out.println(str);isw.write(str + "\n");//bw.newLine();//换行isw.flush();}}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(bw != null){try{bw.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}if(br != null){try{br.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
6.标准的输入输出流
- 标准的输出流:
System.out - 标准的输入流:
System.in
例:

import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;import org.junit.Test;public class test16{@Testpublic void test(){BufferedReader br = null;try{ InputStream is = System.in;//接受传入的字节流InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is); //字节转字符br = new BufferedReader(isr); //包装成带缓冲的字符流String str;while(true){System.out.println("请输入字符串:");str = br.readLine();//忽略大小写if(str.equalsIgnoreCase("e") || str.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")){break;}String str1 = str.toUpperCase();//转化成大写System.out.println(str1);}}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(br != null){try{br.close();}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
练习
在一个目录下创建test.txt文件,并写入以下内容:
云计算是一个比较庞大的概念,入门云计算,首先要从掌握基本概念和基础知识开始,然后通过掌握完全面向云计算的特定供应商的平台或技术等重要领域来增强其专业知识水平,
这样可以更快的学好云计算。你需要学习这些知识:
计算机与网络的基础知识
安全基础知识
编程语言基础
脚本语言
linux基础知识
分布式系统
读取test.txt文件的内容,并打印出来
复制test.txt文件为cloudcompute.txt文件
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;import org.junit.Test;public class test17{@Test//字节流写入文本文件数据public void test1(){BufferedOutputStream bos = null;try{ File file = new File("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\test.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);String str = "\u4E91\u8BA1\u7B97\u662F\u4E00\u4E2A\u6BD4\u8F83\u5E9E\u5927\u7684\u6982\u5FF5\uFF0C\u5165\u95E8\u4E91\u8BA1\u7B97\uFF0C\u9996\u5148\u8981\u4ECE\u638C\u63E1\u57FA\u672C\u6982\u5FF5\u548C\u57FA\u7840\u77E5\u8BC6\u5F00\u59CB\uFF0C\u7136\u540E\u901A\u8FC7\u638C\u63E1\u5B8C\u5168\u9762\u5411\u4E91\u8BA1\u7B97\u7684\u7279\u5B9A\u4F9B\u5E94\u5546\u7684\u5E73\u53F0\u6216\u6280\u672F\u7B49\u91CD\u8981\u9886\u57DF\u6765\u589E\u5F3A\u5176\u4E13\u4E1A\u77E5\u8BC6\u6C34\u5E73\uFF0C\r\n" + //"\u8FD9\u6837\u53EF\u4EE5\u66F4\u5FEB\u7684\u5B66\u597D\u4E91\u8BA1\u7B97\u3002\u4F60\u9700\u8981\u5B66\u4E60\u8FD9\u4E9B\u77E5\u8BC6\uFF1A\r\n" + //"\u8BA1\u7B97\u673A\u4E0E\u7F51\u7EDC\u7684\u57FA\u7840\u77E5\u8BC6\r\n" + //"\u5B89\u5168\u57FA\u7840\u77E5\u8BC6\r\n" + //"\u7F16\u7A0B\u8BED\u8A00\u57FA\u7840\r\n" + //"\u811A\u672C\u8BED\u8A00\r\n" + //"linux\u57FA\u7840\u77E5\u8BC6\r\n" + //"\u5206\u5E03\u5F0F\u7CFB\u7EDF";bos.write(str.getBytes());}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(bos != null){try{bos.flush();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}@Test//字符流写入文本文件数据public void test2(){BufferedWriter bw = null;try{bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\test.txt")));String str = "\u4E91\u8BA1\u7B97\u662F\u4E00\u4E2A\u6BD4\u8F83\u5E9E\u5927\u7684\u6982\u5FF5\uFF0C\u5165\u95E8\u4E91\u8BA1\u7B97\uFF0C\u9996\u5148\u8981\u4ECE\u638C\u63E1\u57FA\u672C\u6982\u5FF5\u548C\u57FA\u7840\u77E5\u8BC6\u5F00\u59CB\uFF0C\u7136\u540E\u901A\u8FC7\u638C\u63E1\u5B8C\u5168\u9762\u5411\u4E91\u8BA1\u7B97\u7684\u7279\u5B9A\u4F9B\u5E94\u5546\u7684\u5E73\u53F0\u6216\u6280\u672F\u7B49\u91CD\u8981\u9886\u57DF\u6765\u589E\u5F3A\u5176\u4E13\u4E1A\u77E5\u8BC6\u6C34\u5E73\uFF0C\r\n" + //"\u8FD9\u6837\u53EF\u4EE5\u66F4\u5FEB\u7684\u5B66\u597D\u4E91\u8BA1\u7B97\u3002\u4F60\u9700\u8981\u5B66\u4E60\u8FD9\u4E9B\u77E5\u8BC6\uFF1A\r\n" + //"\u8BA1\u7B97\u673A\u4E0E\u7F51\u7EDC\u7684\u57FA\u7840\u77E5\u8BC6\r\n" + //"\u5B89\u5168\u57FA\u7840\u77E5\u8BC6\r\n" + //"\u7F16\u7A0B\u8BED\u8A00\u57FA\u7840\r\n" + //"\u811A\u672C\u8BED\u8A00\r\n" + //"linux\u57FA\u7840\u77E5\u8BC6\r\n" + //"\u5206\u5E03\u5F0Fw\u7CFB\u7EDF";bw.write(str);}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(bw != null){try{bw.flush();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}@Test//字符流输出文本文件数据public void test3(){BufferedReader br = null;try{br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\test.txt"));String str;while((str = br.readLine()) != null){System.out.println(str);}}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(br != null){try{br.close();}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}@Test//字符流实现复制public void test4(){BufferedWriter bw = null;BufferedReader br = null;try{br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\test.txt"));bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\cloudcompute.txt"));String str;while((str = br.readLine()) != null){bw.write(str + "\n");} }catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(bw != null){try{bw.close();}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}if(br != null){try{br.close();}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
7.打印流
PrintStream:字节流printWriter:字符流
例:
public class test18{@Test//打印流public void printStreamTest(){FileOutputStream fos = null;try{ fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\test.txt");}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}//创建打印输出流,设置为自动刷新模式(写入换行符就或字节'\n'时都会刷新输出缓冲区)PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(fos,true);if(ps != null){//把标准输出流改成文件System.setOut(ps);//修改输出打印的位置为ps}for(int i = 0;i < 255;i++){System.out.print((char)i);if(i % 50 == 0){//每50数据一行System.out.println();//换行}}ps.close();}
}
8.数据流

- 用来处理基本数据类型,String,字节数组的数据
例:
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;import org.junit.Test;public class test19{@Test//数据流写入public void testData(){DataOutputStream dos = null;try { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\test.txt");dos = new DataOutputStream(fos);dos.writeUTF("你好");dos.writeInt(467876543);dos.writeDouble(1289.789);dos.writeBoolean(true);}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(dos != null){try {dos.close();} catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}@Test//数据流读取public void testData1(){DataInputStream dis = null;try { dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Cat God 007\\Desktop\\test.txt"));String str = dis.readUTF();System.out.println(str);int i = dis.readInt();System.out.println(i);double d = dis.readDouble();System.out.println(d);boolean b = dis.readBoolean();System.out.println(b);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(dis != null){try {dis.close();} catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
9.对象流
ObjectOutputStream 和 ObjectInputStream
-
用于存储和读取对象的处理流,可以把Java中的对象写入到数据源中,也能把对象从数据源中还原回来
-
序列化(Serialize):用 ObjectOutputStream 类将Java对象写入IO流中

-
反序列化(Deserialize):用 ObjectInputStream 类从IO流中恢复该Java对象
-
ObjectOutputStream 和
ObjectInputStream不能序列化static和transient(短暂的)修饰的成员变量
例:
i
mport java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.junit.Test;public class test20{@Test// 反序列化--ObjectInputStreampublic void testObjectInputStream(){ObjectInputStream ois = null;try { ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\\\Users\\\\Cat God 007\\\\Desktop\\\\test.txt"));Person p1 = (Person)ois.readObject();//读取一个对象System.out.println(p1.toString());//打印一个对象Person p2 = (Person) ois.readObject();//读取对象System.out.println(p2);//打印对象}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(ois != null){try{ois.close();}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}@Test//对象序列化---ObjectOutputStreampublic void testObjectOutputStream(){Person p1 = new Person("张三", 20,new Pet("张二"));Person p2 = new Person("李四", 21,new Pet("李三"));ObjectOutputStream oos = null;try{oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\\\Users\\\\Cat God 007\\\\Desktop\\\\test.txt"));oos.writeObject(p1);oos.flush();oos.writeObject(p2);oos.flush(); }catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(oos != null){try {oos.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
/** 实现序列化的类:* 1.此类可序列化,需要此类实现Serializable接口* 2.此类可序列化,需要类的属性同样实现Serializable接口* 3.版本号:凡是实现Serializable接口的类都有一个表示序列化版本标识符的静态变量,表明类的不同版本间的兼容性,如果没有定义,那在运行时会自动生成,如果源码修改,版本号(自动生成的)可能会变化* 如:private static final long serialVersionUID = 1234678876543L; */
class Person implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 12343128876543L; String name;Integer age;Pet pet;public Person(String name, Integer age,Pet pet) { this.name = name;this.age = age; this.pet = pet;}@Overridepublic String toString() { return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age + '\'' +", pet=" + pet + '\'' +'}';}
}
class Pet implements Serializable{String name;public Pet(String name) {this.name = name;}
}
10.随机存取文件流
-
RandomAccessFile类支持"随机访问"的方式,程序可以直接跳到文件的任意地方来读,写文件-
可以向已存在的文件后追加内容
-
支持只访问文件的部分内容
-
-
RandomAccessFile对象包含一个记录指针,用于标示当前读写处的位置。RandomAccessFile类类对象可以自由移动记录指针-
long getFilePointer():获取文件记录指针的当前位置 -
void seek(long pos):将文件记录指针定位到pos位置

-
例:
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;import org.junit.Test;public class test21{@Test//进行文件的读,写public void test(){RandomAccessFile raf1 = null;RandomAccessFile raf2 = null;try{ raf1 = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt","r");raf2 = new RandomAccessFile("hello1.txt","rw");byte[] b = new byte[4];int len;while((len = raf1.read(b))!=-1){raf2.write(b,0,len);}}catch(Exception e){{e.printStackTrace();}}finally{if(raf2 != null){try{raf2.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}if(raf1 != null){try{raf1.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}@Test//在指定位置进行文件的读写,实际上实现的是覆盖的效果public void test1(){RandomAccessFile raf = null;try{raf = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt","rw");raf.seek(3);//把指针调到第三个的位置raf.write("123456789".getBytes());}catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(raf != null){try{raf.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}@Test//实现在指定位置的插入效果public void test2(){RandomAccessFile raf = null;try{raf = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt","rw");raf.seek(3);byte[] b = new byte[10];int len;StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();//可变的字符序列,相当于Stringwhile((len = raf.read(b)) != -1){sb.append(new String(b,0,len));}raf.seek(3);//把指针调到第三个的位置raf.write("123456789".getBytes());//写入要插入的内容raf.write(sb.toString().getBytes());//写入原来的后面字符}catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(raf != null){try{raf.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}@Test//实现在指定位置的插入效果(在test2的基础上进行优化,使之更通用)public void test3(){RandomAccessFile raf = null;try{raf = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt","rw");raf.seek(3);String str = raf.readLine();//读取出要插入处之后的所有字符// long l = raf.getFilePointer();//获取当前指针的位置// System.out.println(l);//12raf.seek(3);//把指针调到第三个的位置raf.write("123456789".getBytes());//写入要插入的内容raf.write(str.getBytes());//写入原来的后面字符}catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally{if(raf != null){try{raf.close();}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}
IO流练习

import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class test1 {public static void main(String[] args) { test1 t = new test1();System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");String str = t.nextString();System.out.println(str);int j = t.nextInt();System.out.println(j + 20);}public String nextString() {InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);String str = null;try {str = br.readLine();}catch(IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return str;}public int nextInt() {return Integer.parseInt(nextString());}public boolean nextBoolean() {return Boolean.parseBoolean(nextString());}}
感谢大家的支持,关注,评论,点赞!
参考资料:
尚硅谷宋红康20天搞定Java基础下部
相关文章:

Java-day13(IO流)
IO流 凡是与输入,输出相关的类,接口等都定义在java.io包下 1.File类的使用 File类可以有构造器创建其对象,此对象对应着一个文件(.txt,.avi,.doc,.mp3等)或文件目录 File类对象是与平台无关的 File中的方法仅涉及到如何创建,…...
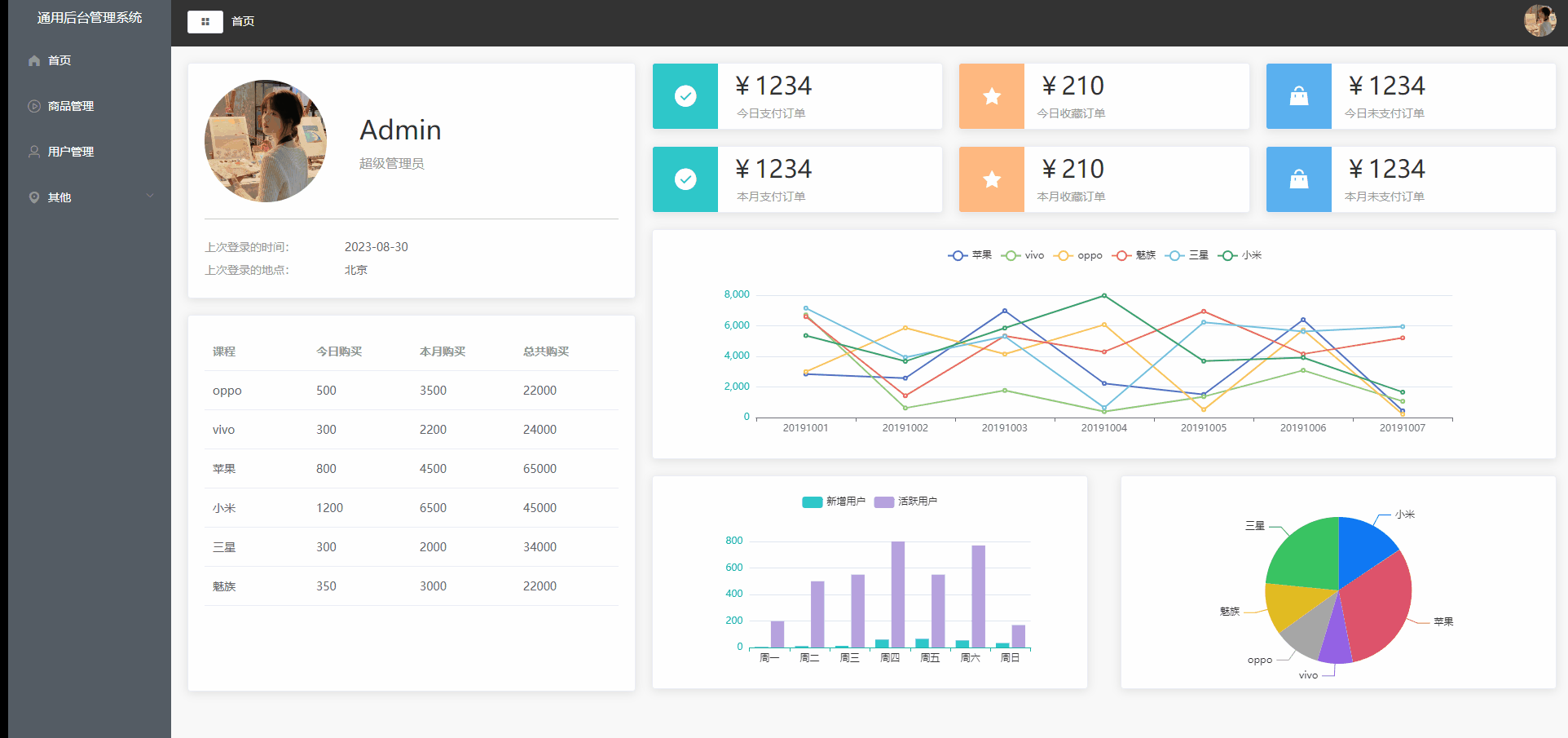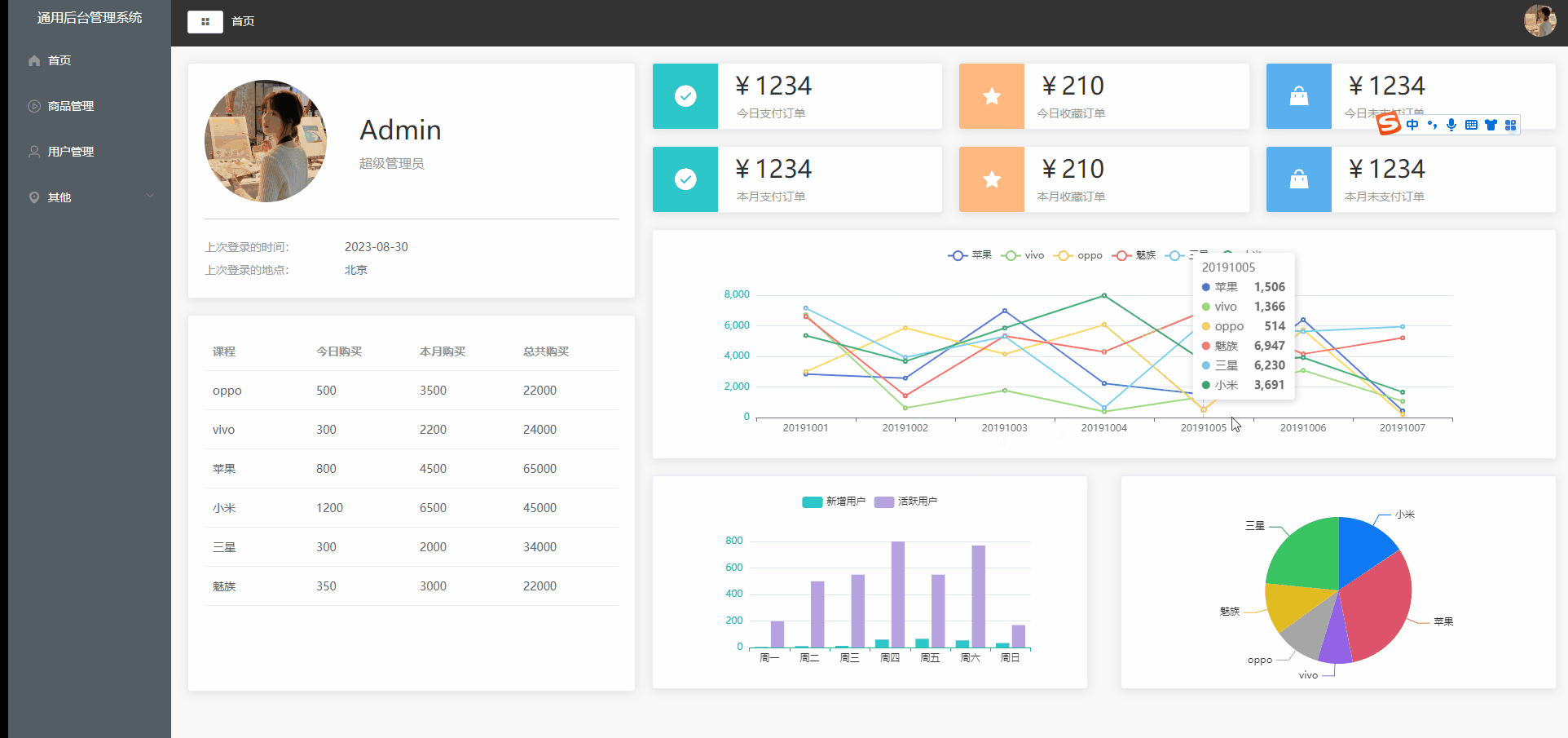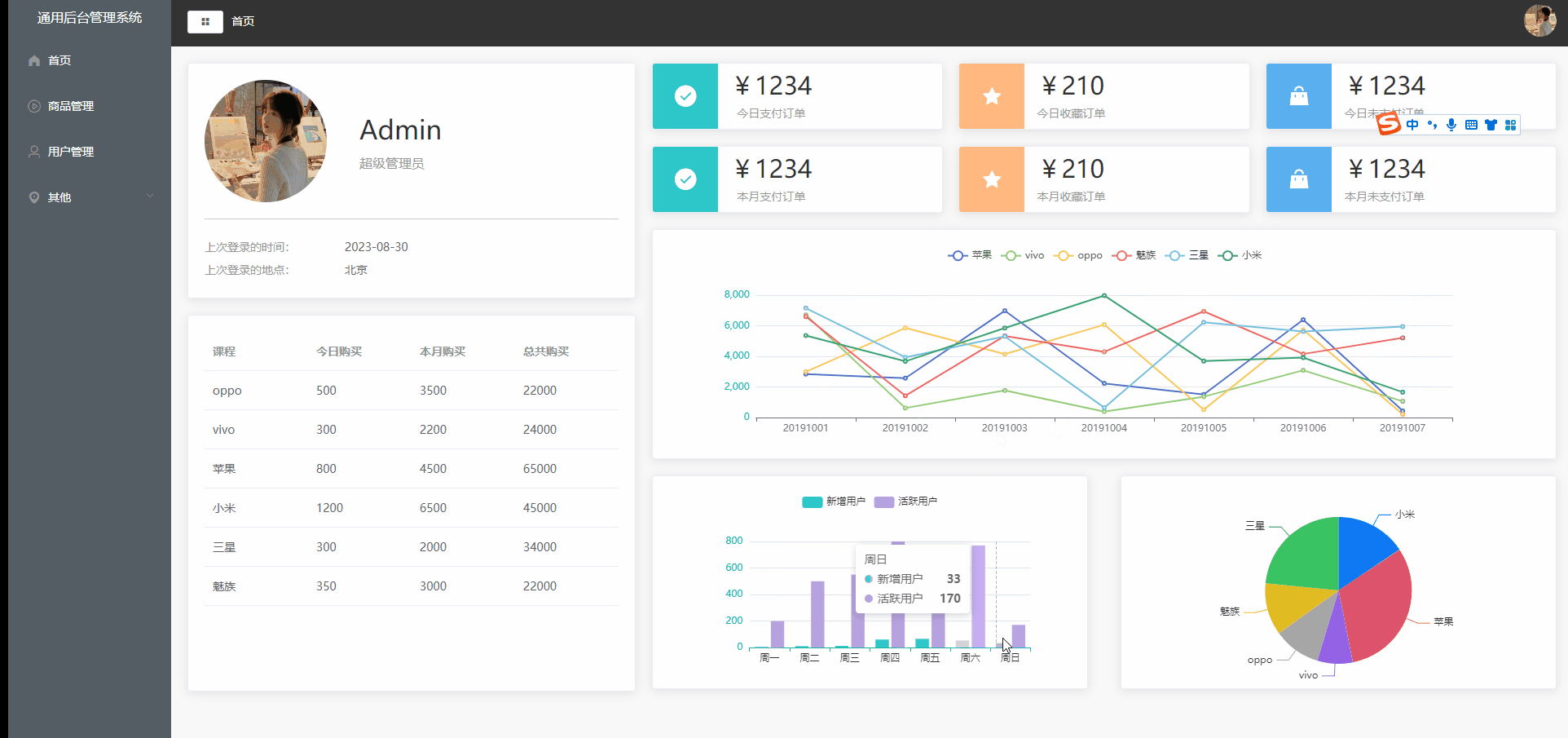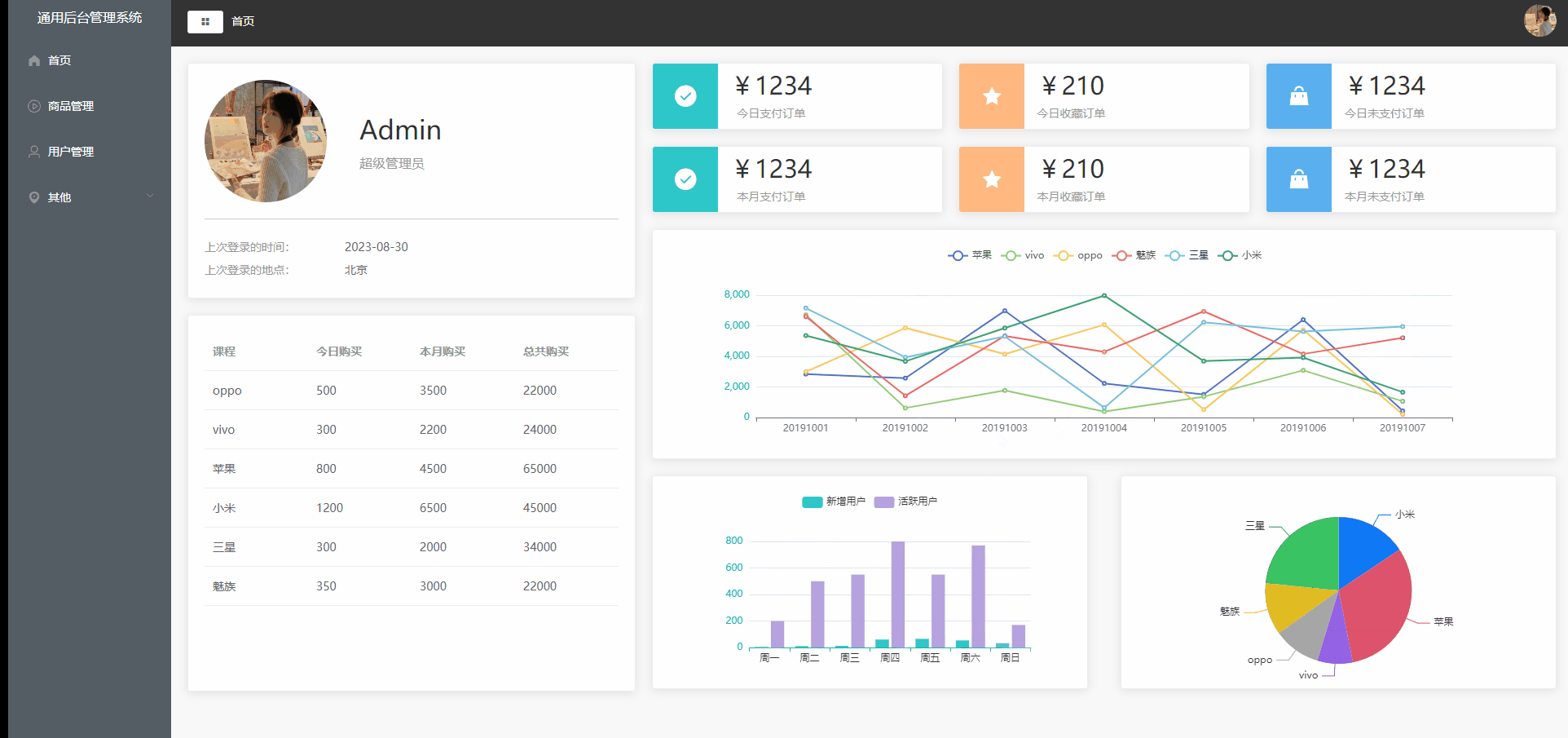
Vue2项目练手——通用后台管理项目第四节
Vue2项目练手——通用后台管理项目 数据的请求mock数据模拟实战文件目录src/api/mock.jssrc/api/mockServeData/home.jsmain.js 首页组件布局可视化图表可视化图表布局Home.vue echarts表Home.vue 数据的请求 mock数据模拟实战 mock官方文档 前端用来模拟后端接口的工具&…...
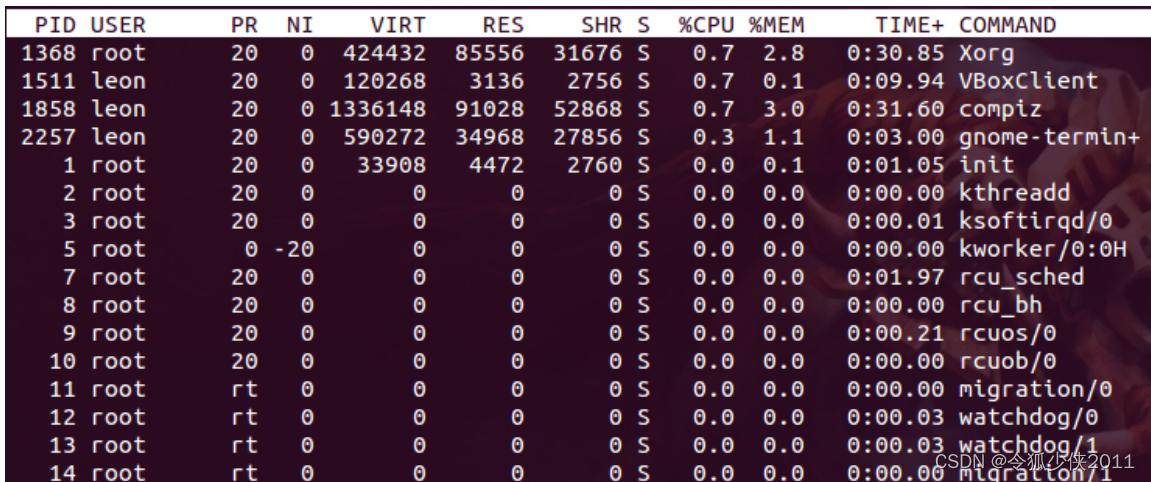
linux运维(二)内存占用分析
一、centos内存高,查看占用内存, top命令详解 1.1: free 命令是 free 单位K free -m 单位M free -h 单位Gfree最常规的查看内存占用情况的命令 1.2: 参数说明 total 总物理内存 used 已经使用的内存 free 没有使用的内存 shared 多进程共享内存 buff/cache 读写…...

go logger 不侵入业务代码 用slog 替换 zap 并实现 callerSkip
快速体验 以下是 项目中 已经用slog替换 zap 后的 logger 使用方法,无任何感知,与之前一模一样 package mainimport "github.com/webws/go-moda/logger"func main() {// 格式化打印 {"time":"2023-09-08T01:25:21.31346308:00","level&qu…...

vuez 与 Vue3 响应式比较
Vue2 的响应式 对象:通过 defineProperty 对对象的已有属性值的读取和修改进行劫持(监视/拦被)。 数组:通过重写数组、更新数组等一系列更新元素的方法来实现元素修改的劫持。 存在的问题如下: &#…...

【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
文章目录 TASK系列解析文章前言PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER功能简介PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER相关配置PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER流程QP问题的标准类型定义:优化变量设计目标函数约束条件相关矩阵二次项系数矩阵 H H H一次项系数向量 q q q设定OSQP求…...

CNI、CSI 和 CRI在 Docker 中的角色和作用
摘要 CNI(Container Network Interface): CNI 是用于容器网络的接口标准,它定义了容器和网络插件之间的通信协议。CNI 的主要作用是为容器创建和管理网络接口。当创建一个容器时,CNI 插件会被调用来为容器创建一个网络…...

「Docker」M1 Pro 打包docker image问题合集
运行docker 遇到 The requested images platform (linux/arm64/v8) does not match the detected host platform (linux/amd64/v4) and no specific platform was requested 说明打包的镜像没有 linux/amd64 解决方案:重新打包镜像 docker buildx build --platfor…...
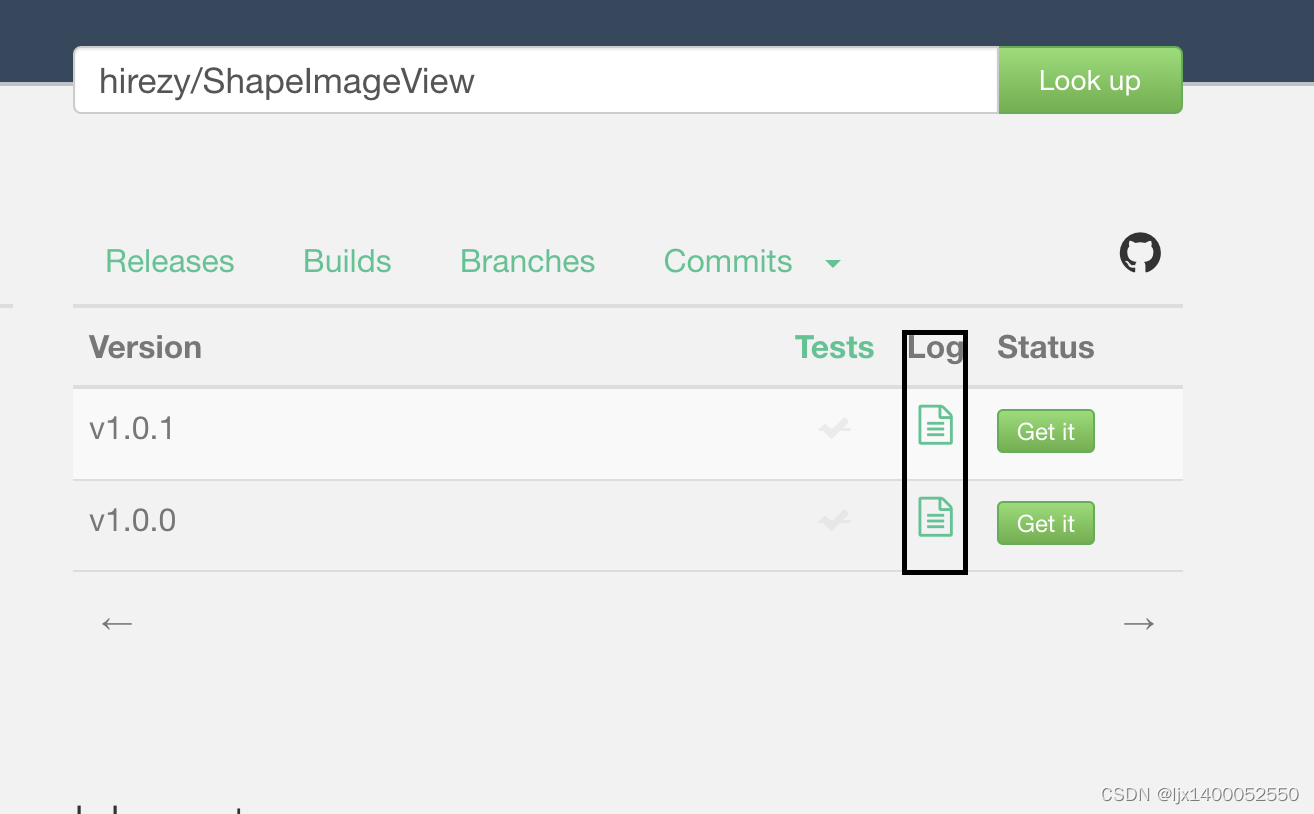
Android发布依赖到 Jitpack
前言 我们在日常开发中,经常会用到第三方开源的库文件,有的来自JCenter,Maven Central,google等。但是随着JCenter的弃用,现在用的最多的还是Maven Central,google。今天我们就自己亲自发布一个依赖。 现…...
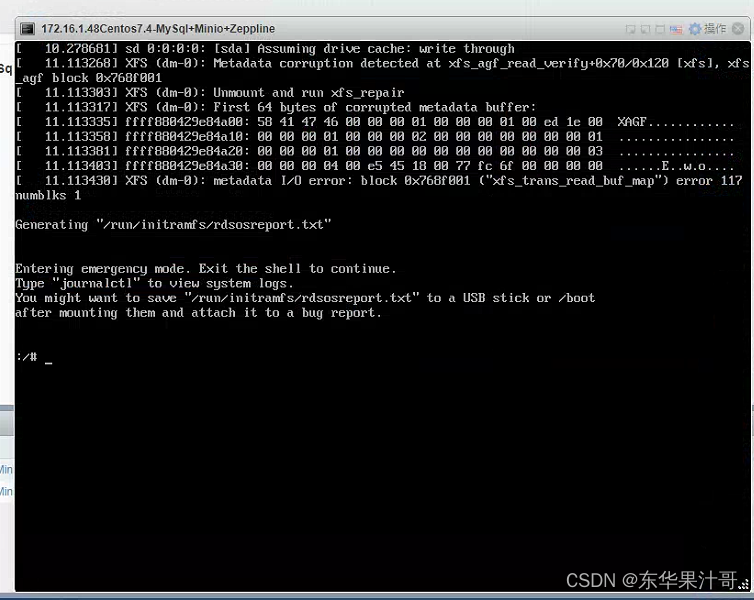
【虚拟机开不了】linux、centOS虚拟机出现entering emergency mode解决方案
按他的操作输入journalctl之后输入shiftg到日志最后查看报错发现是xfs(dm-0有问题) xfs_repair -v -L /dev/dm-0 reboot解决问题...

嘉泰实业举行“互联网金融知识社区”“安全理财风险讲座”等活动
每一次暖心的沟通都是一次公益,真诚不会因为它的渺小而被忽略;每一声问候都是一次公益,善意不会因为它的普通而被埋没。熟悉嘉泰实业的人都知道,这家企业不但擅长在金融理财领域里面呼风唤雨,同时也非常擅长在公益事业当中践行,属于企业的责任心,为更多有困难的群体带来大爱的传…...

《C++设计模式》——结构型
前言 结构模式可以让我们把很多小的东西通过结构模式组合起来成为一个打的结构,但是又不影响各自的独立性,尽可能减少各组件之间的耦合。 Adapter Class/Object(适配器) Bridge(桥接) Composite(组合) Decorator(装饰) 动态…...
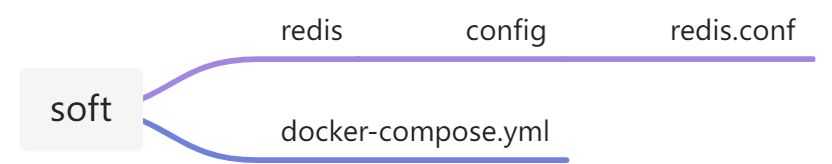
docker-compose安装redis
基于docker-compose快速安装redis 目录 一、目录结构 1、docker-compose.yml 2、redis.conf 二、连接使用 一、目录结构 1、docker-compose.yml version: 3 services:redis:image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/zhengqing/redis:6.0.8 # 镜像red…...
机器学习基础之《分类算法(6)—决策树》
一、决策树 1、认识决策树 决策树思想的来源非常朴素,程序设计中的条件分支结构就是if-else结构,最早的决策树就是利用这类结构分割数据的一种分类学习方法 2、一个对话的例子 想一想这个女生为什么把年龄放在最上面判断!!&…...

2023国赛数学建模C题思路模型 - 蔬菜类商品的自动定价与补货决策
# 1 赛题 在生鲜商超中,一般蔬菜类商品的保鲜期都比较短,且品相随销售时间的增加而变差, 大部分品种如当日未售出,隔日就无法再售。因此, 商超通常会根据各商品的历史销售和需 求情况每天进行补货。 由于商超销售的蔬菜…...

【Docker】Docker网络与存储(三)
前言: Docker网络与存储的作用是实现容器之间的通信和数据持久化,以便有效地部署、扩展和管理容器化应用程序。 文章目录 Docker网络桥接网络容器之间的通信 覆盖网络创建一个覆盖网络 Docker存储卷 总结 Docker网络 Docker网络是在容器之间提供通信的机…...

python面向对象的一个简单实例
#发文福利# #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-students {id001: {name: serena, age: 18, address: beijing},id002: {name: fanbingbing, age: 42, address: anhui},id003: {name: kahn, age: 20, address: shanghai}}class Student:def __init__(self, xid, na…...

微信小程序通过npm引入tdesign包进行构建的时候报错
问题 在通过npm 引入 tdesign时:https://tdesign.tencent.com/miniprogram/getting-started 通过微信小程序IDE进行npm构建的时候出现:无法构建,应该怎么办? 解决方法: 1 输入: npm init -y命令 2 重新点…...

三次握手四次挥手
TCP协议是一种面向连接的、可靠的、基于字节流的运输层通信协议。它通过三次握手来建立连接,通过四次挥手来断开连接。 三次握手 所谓三次握手,是指建立一个TCP连接时,需要客户端和服务器总共发送3个报文。三次握手的目的是连接服务器指定端…...

Redis持久化、主从与哨兵架构详解
Redis持久化 RDB快照(snapshot) 在默认情况下, Redis 将内存数据库快照保存在名字为 dump.rdb 的二进制文件中。 你可以对 Redis 进行设置, 让它在“ N 秒内数据集至少有 M 个改动”这一条件被满足时, 自动保存一次数…...
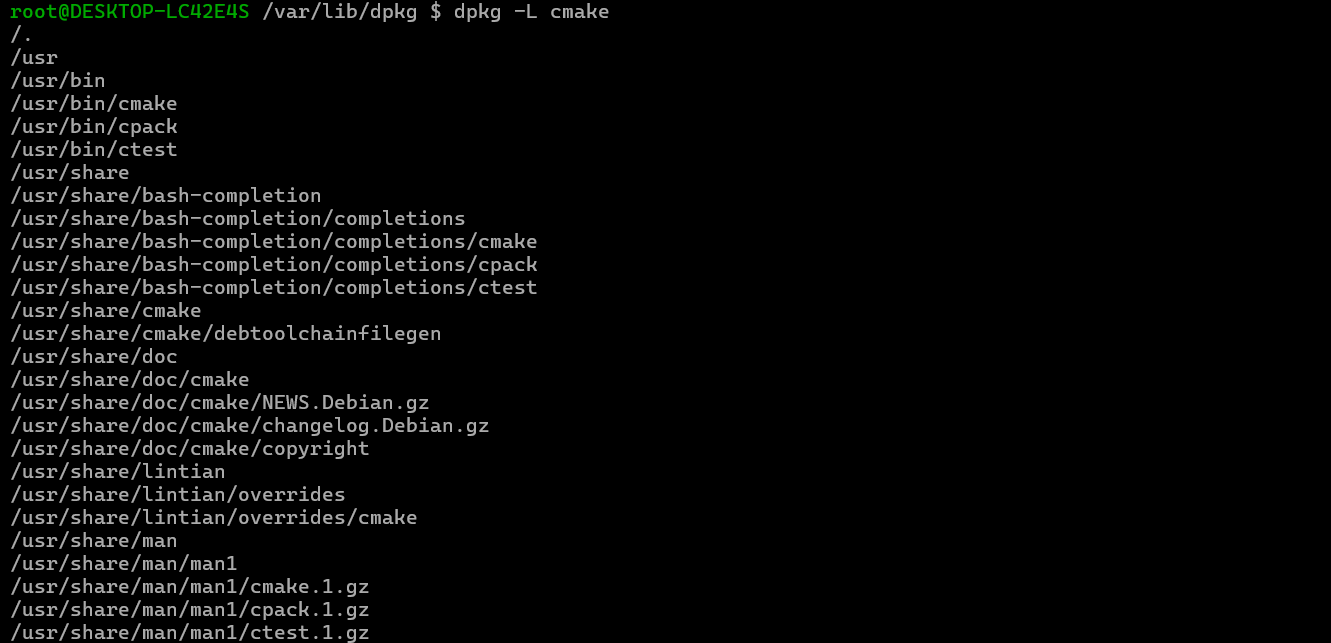
Debian系统简介
目录 Debian系统介绍 Debian版本介绍 Debian软件源介绍 软件包管理工具dpkg dpkg核心指令详解 安装软件包 卸载软件包 查询软件包状态 验证软件包完整性 手动处理依赖关系 dpkg vs apt Debian系统介绍 Debian 和 Ubuntu 都是基于 Debian内核 的 Linux 发行版ÿ…...

macOS多出来了:Google云端硬盘、YouTube、表格、幻灯片、Gmail、Google文档等应用
文章目录 问题现象问题原因解决办法 问题现象 macOS启动台(Launchpad)多出来了:Google云端硬盘、YouTube、表格、幻灯片、Gmail、Google文档等应用。 问题原因 很明显,都是Google家的办公全家桶。这些应用并不是通过独立安装的…...
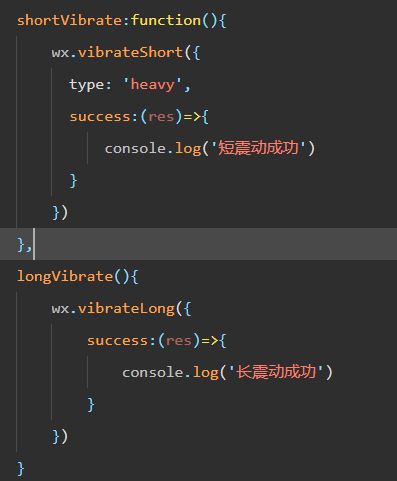
微信小程序 - 手机震动
一、界面 <button type"primary" bindtap"shortVibrate">短震动</button> <button type"primary" bindtap"longVibrate">长震动</button> 二、js逻辑代码 注:文档 https://developers.weixin.qq…...

【Go】3、Go语言进阶与依赖管理
前言 本系列文章参考自稀土掘金上的 【字节内部课】公开课,做自我学习总结整理。 Go语言并发编程 Go语言原生支持并发编程,它的核心机制是 Goroutine 协程、Channel 通道,并基于CSP(Communicating Sequential Processes࿰…...
ArcGIS Pro制作水平横向图例+多级标注
今天介绍下载ArcGIS Pro中如何设置水平横向图例。 之前我们介绍了ArcGIS的横向图例制作:ArcGIS横向、多列图例、顺序重排、符号居中、批量更改图例符号等等(ArcGIS出图图例8大技巧),那这次我们看看ArcGIS Pro如何更加快捷的操作。…...

laravel8+vue3.0+element-plus搭建方法
创建 laravel8 项目 composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel8 8.* 安装 laravel/ui composer require laravel/ui 修改 package.json 文件 "devDependencies": {"vue/compiler-sfc": "^3.0.7","axios": …...

wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像
wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像https://www.cnblogs.com/haodafeng/p/10431387.html 如果你在寻找能够快速在image控件刷新大图像(比如分辨率3000*3000的图像)的办法,尤其是想把内存中的裸数据(只有图像的数据,不包…...
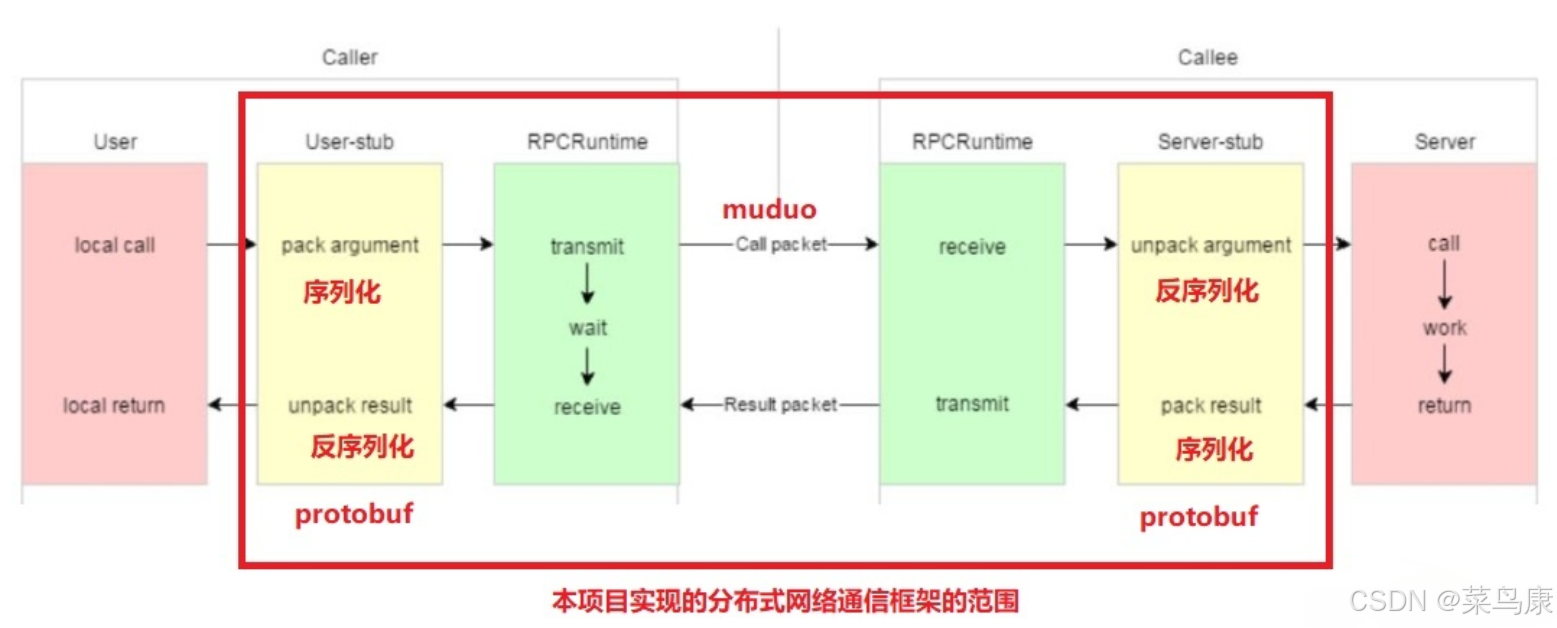
C++实现分布式网络通信框架RPC(2)——rpc发布端
有了上篇文章的项目的基本知识的了解,现在我们就开始构建项目。 目录 一、构建工程目录 二、本地服务发布成RPC服务 2.1理解RPC发布 2.2实现 三、Mprpc框架的基础类设计 3.1框架的初始化类 MprpcApplication 代码实现 3.2读取配置文件类 MprpcConfig 代码实现…...
自然语言处理——文本分类
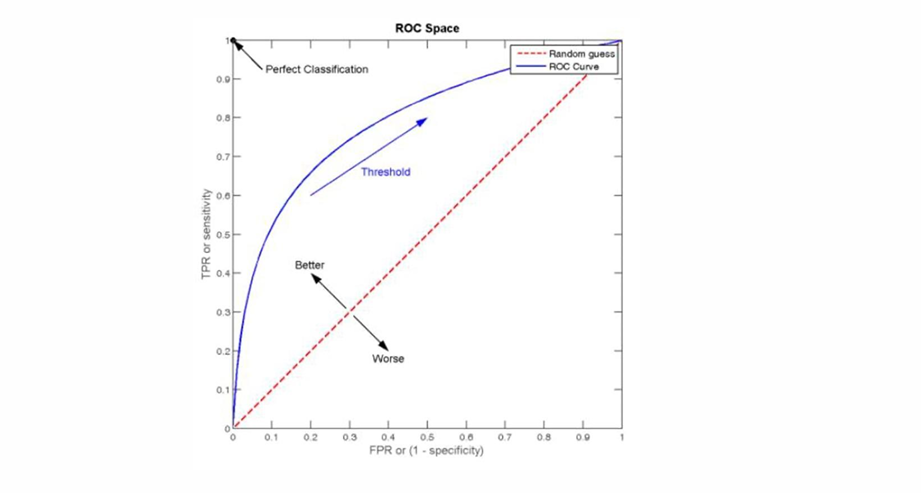
文本分类 传统机器学习方法文本表示向量空间模型 特征选择文档频率互信息信息增益(IG) 分类器设计贝叶斯理论:线性判别函数 文本分类性能评估P-R曲线ROC曲线 将文本文档或句子分类为预定义的类或类别, 有单标签多类别文本分类和多…...

Pydantic + Function Calling的结合
1、Pydantic Pydantic 是一个 Python 库,用于数据验证和设置管理,通过 Python 类型注解强制执行数据类型。它广泛用于 API 开发(如 FastAPI)、配置管理和数据解析,核心功能包括: 数据验证:通过…...
