为什么创建 Redis 集群时会自动错开主从节点?
哈喽大家好,我是咸鱼
在《一台服务器上部署 Redis 伪集群》这篇文章中,咸鱼在创建 Redis 集群时并没有明确指定哪个 Redis 实例将担任 master,哪个将担任 slave
/usr/local/redis-4.0.9/src/redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 192.168.149.131:6379 192.168.149.131:26379 192.168.149.131:6380 192.168.149.131:26380 192.168.149.131:6381 192.168.149.131:26381
然而 Redis 却自动完成了主从节点的分配工作
如果大家在多台服务器部署过 Redis 集群的话,比如说在三台机器上部署三主三从的 redis 集群,你会观察到 Redis 自动地将主节点和从节点的部署位置错开
举个例子: master 1 和 slave 3 在同一台机器上; master 2和 slave 1 在同一台机器上; master 3 和 slave 2 在同一台机器上
这是为什么呢?
我们知道老版本的 Redis 集群管理命令是 redis-trib.rb,新版本则换成了 redis-cli
这两个可执行文件其实是一个用 C 编写的脚本,小伙伴们如果看过这两个文件的源码就会发现原因就在下面这段代码里
/* Return the anti-affinity score, which is a measure of the amount of* violations of anti-affinity in the current cluster layout, that is, how* badly the masters and slaves are distributed in the different IP* addresses so that slaves of the same master are not in the master* host and are also in different hosts.** The score is calculated as follows:** SAME_AS_MASTER = 10000 * each slave in the same IP of its master.* SAME_AS_SLAVE = 1 * each slave having the same IP as another slaveof the same master.* FINAL_SCORE = SAME_AS_MASTER + SAME_AS_SLAVE** So a greater score means a worse anti-affinity level, while zero* means perfect anti-affinity.** The anti affinity optimization will try to get a score as low as* possible. Since we do not want to sacrifice the fact that slaves should* not be in the same host as the master, we assign 10000 times the score* to this violation, so that we'll optimize for the second factor only* if it does not impact the first one.** The ipnodes argument is an array of clusterManagerNodeArray, one for* each IP, while ip_count is the total number of IPs in the configuration.** The function returns the above score, and the list of* offending slaves can be stored into the 'offending' argument,* so that the optimizer can try changing the configuration of the* slaves violating the anti-affinity goals. */
static int clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(clusterManagerNodeArray *ipnodes,int ip_count, clusterManagerNode ***offending, int *offending_len)
{...return score;
}static void clusterManagerOptimizeAntiAffinity(clusterManagerNodeArray *ipnodes,int ip_count)
{...
}
通过注释我们可以得知,clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore 函数是用来计算反亲和性得分,这个得分表示了当前 Redis 集群布局中是否符合反亲和性的要求
反亲和性指的是 master 和 slave 不应该在同一台机器上,也不应该在相同的 IP 地址上
那如何计算反亲和性得分呢?
- 如果有多个 slave 与同一个 master 在相同的 IP 地址上,那么对于每个这样的 slave,得分增加 10000
- 如果有多个 slave 在相同的 IP 地址上,但它们彼此之间不是同一个 master,那么对于每个这样的 slave,得分增加 1
- 最终得分是上述两部分得分之和
也就是说,得分越高,亲和性越高;得分越低,反亲和性越高;得分为零表示完全符合反亲和性的要求
获得得分之后,就会对得分高(反亲和性低)的节点进行优化
为了让 Redis 主从之间的反亲和性更高,clusterManagerOptimizeAntiAffinity 函数会对那些反亲和性很低的节点进行优化,它会尝试通过交换从节点的主节点,来改善集群中主从节点分布,从而减少反亲和性低问题
接下来我们分别来看下这两个函数
反亲和性得分计算
static int clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(clusterManagerNodeArray *ipnodes,int ip_count, clusterManagerNode ***offending, int *offending_len)
{...
}
可以看到,该函数接受了四个参数:
ipnodes:一个包含多个clusterManagerNodeArray结构体的数组,每个结构体表示一个 IP 地址上的节点数组ip_count:IP 地址的总数offending:用于存储违反反亲和性规则的节点的指针数组(可选参数)offending_len:存储offending数组中节点数量的指针(可选参数)
第一层 for 循环是遍历 ip 地址,第二层循环是遍历每个 IP 地址的节点数组
...for (i = 0; i < ip_count; i++) {clusterManagerNodeArray *node_array = &(ipnodes[i]);dict *related = dictCreate(&clusterManagerDictType);char *ip = NULL;for (j = 0; j < node_array->len; j++) {...}...
我们来看下第二层 for 循环
for (i = 0; i < ip_count; i++) {/* 获取每个 IP 地址的节点数组 */clusterManagerNodeArray *node_array = &(ipnodes[i]);/* 创建字典 related */dict *related = dictCreate(&clusterManagerDictType);char *ip = NULL;for (j = 0; j < node_array->len; j++) {/* 获取当前节点 */clusterManagerNode *node = node_array->nodes[j];.../* 在 related 字典中查找是否已经存在相应的键 */dictEntry *entry = dictFind(related, key);if (entry) types = sdsdup((sds) dictGetVal(entry));else types = sdsempty();if (node->replicate) types = sdscat(types, "s");else {sds s = sdscatsds(sdsnew("m"), types);sdsfree(types);types = s;}dictReplace(related, key, types);}
首先遍历每个 IP 地址的节点数组,对于每个 IP 地址上的节点数组,函数通过字典related来记录相同主节点和从节点的关系
其中字典 related的 key 是节点的名称,value 是一个字符串,表示该节点类型 types
对于每个节点,根据节点构建一个字符串类型的关系标记(types),将主节点标记为 m,从节点标记为 s
然后通过字典将相同关系标记的节点关联在一起,构建了一个记录相同主从节点关系的字典 related
... /* 创建字典迭代器,用于遍历节点分组信息 */dictIterator *iter = dictGetIterator(related);dictEntry *entry;while ((entry = dictNext(iter)) != NULL) {/* key 是节点名称,value 是 types,即节点类型 */sds types = (sds) dictGetVal(entry);sds name = (sds) dictGetKey(entry);int typeslen = sdslen(types);if (typeslen < 2) continue;/* 计算反亲和性得分 */if (types[0] == 'm') score += (10000 * (typeslen - 1));else score += (1 * typeslen);...}
上面代码片段可知,while 循环遍历字典 related中的分组信息,计算相同主从节点关系的得分
- 获取节点类型信息并长度
- 如果是主节点类型,得分 += (10000 * (
typeslen- 1));否则,得分 += (1 *typeslen)
如果有提供 offending 参数,将找到违反反亲和性规则的节点并存储到 offending 数组中,同时更新违反规则节点的数量,如下代码所示
if (offending == NULL) continue;/* Populate the list of offending nodes. */listIter li;listNode *ln;listRewind(cluster_manager.nodes, &li);while ((ln = listNext(&li)) != NULL) {clusterManagerNode *n = ln->value;if (n->replicate == NULL) continue;if (!strcmp(n->replicate, name) && !strcmp(n->ip, ip)) {*(offending_p++) = n;if (offending_len != NULL) (*offending_len)++;break;}}
最后返回得分 score,完整函数代码如下
static int clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(clusterManagerNodeArray *ipnodes,int ip_count, clusterManagerNode ***offending, int *offending_len)
{int score = 0, i, j;int node_len = cluster_manager.nodes->len;clusterManagerNode **offending_p = NULL;if (offending != NULL) {*offending = zcalloc(node_len * sizeof(clusterManagerNode*));offending_p = *offending;}/* For each set of nodes in the same host, split by* related nodes (masters and slaves which are involved in* replication of each other) */for (i = 0; i < ip_count; i++) {clusterManagerNodeArray *node_array = &(ipnodes[i]);dict *related = dictCreate(&clusterManagerDictType);char *ip = NULL;for (j = 0; j < node_array->len; j++) {clusterManagerNode *node = node_array->nodes[j];if (node == NULL) continue;if (!ip) ip = node->ip;sds types;/* We always use the Master ID as key. */sds key = (!node->replicate ? node->name : node->replicate);assert(key != NULL);dictEntry *entry = dictFind(related, key);if (entry) types = sdsdup((sds) dictGetVal(entry));else types = sdsempty();/* Master type 'm' is always set as the first character of the* types string. */if (node->replicate) types = sdscat(types, "s");else {sds s = sdscatsds(sdsnew("m"), types);sdsfree(types);types = s;}dictReplace(related, key, types);}/* Now it's trivial to check, for each related group having the* same host, what is their local score. */dictIterator *iter = dictGetIterator(related);dictEntry *entry;while ((entry = dictNext(iter)) != NULL) {sds types = (sds) dictGetVal(entry);sds name = (sds) dictGetKey(entry);int typeslen = sdslen(types);if (typeslen < 2) continue;if (types[0] == 'm') score += (10000 * (typeslen - 1));else score += (1 * typeslen);if (offending == NULL) continue;/* Populate the list of offending nodes. */listIter li;listNode *ln;listRewind(cluster_manager.nodes, &li);while ((ln = listNext(&li)) != NULL) {clusterManagerNode *n = ln->value;if (n->replicate == NULL) continue;if (!strcmp(n->replicate, name) && !strcmp(n->ip, ip)) {*(offending_p++) = n;if (offending_len != NULL) (*offending_len)++;break;}}}//if (offending_len != NULL) *offending_len = offending_p - *offending;dictReleaseIterator(iter);dictRelease(related);}return score;
}
反亲和性优化
计算出反亲和性得分之后,对于那些得分很低的节点,redis 就需要对其进行优化,提高集群中节点的分布,以避免节点在同一主机上
static void clusterManagerOptimizeAntiAffinity(clusterManagerNodeArray *ipnodes, int ip_count){ clusterManagerNode **offenders = NULL;int score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes, ip_count,NULL, NULL);if (score == 0) goto cleanup; ...
cleanup:zfree(offenders);
}
从上面的代码可以看到,如果得分为 0 ,说明反亲和性已经很好,无需优化。直接跳到 cleanup 去释放 offenders 节点的内存空间
如果得分不为 0 ,则就会设置一个最大迭代次数maxiter,这个次数跟节点的数量成正比,然后 while 循环在有限次迭代内进行优化操作
...int maxiter = 500 * node_len; // Effort is proportional to cluster size...while (maxiter > 0) {...maxiter--;}...
这个函数的核心就在 while 循环里,我们来看一下其中的一些片段
首先 offending_len 来存储违反规则的节点数,然后如果之前有违反规则的节点(offenders != NULL)则释放掉(zfree(offenders))
然后重新计算得分,如果得分为0或没有违反规则的节点,退出 while 循环
int offending_len = 0; if (offenders != NULL) {zfree(offenders); // 释放之前存储的违反规则的节点offenders = NULL;}score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes,ip_count,&offenders,&offending_len);if (score == 0 || offending_len == 0) break;
接着去随机选择一个违反规则的节点,尝试交换分配的 master
int rand_idx = rand() % offending_len;clusterManagerNode *first = offenders[rand_idx],*second = NULL;// 创建一个数组,用来存储其他可交换 master 的 slaveclusterManagerNode **other_replicas = zcalloc((node_len - 1) *sizeof(*other_replicas));
然后遍历集群中的节点,寻找能够交换 master 的 slave。如果没有找到,那就退出循环
while ((ln = listNext(&li)) != NULL) {clusterManagerNode *n = ln->value;if (n != first && n->replicate != NULL)other_replicas[other_replicas_count++] = n;}if (other_replicas_count == 0) {zfree(other_replicas);break;}
如果找到了,就开始交换并计算交换后的反亲和性得分
// 随机选择一个可交换的节点作为交换目标rand_idx = rand() % other_replicas_count;second = other_replicas[rand_idx];// 交换两个 slave 的 master 分配char *first_master = first->replicate,*second_master = second->replicate;first->replicate = second_master, first->dirty = 1;second->replicate = first_master, second->dirty = 1;// 计算交换后的反亲和性得分int new_score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes,ip_count,NULL, NULL);
如果交换后的得分比之前的得分还大,说明白交换了,还不如不交换,就会回顾;如果交换后的得分比之前的得分小,说明交换是没毛病的
if (new_score > score) {first->replicate = first_master;second->replicate = second_master;}
最后释放资源,准备下一次 while 循环
zfree(other_replicas);maxiter--;
总结一下:
- 每次
while循环会尝试随机选择一个违反反亲和性规则的从节点,并与另一个随机选中的从节点交换其主节点分配,然后重新计算交换后的反亲和性得分 - 如果交换后的得分变大,说明交换不利于反亲和性,会回滚交换
- 如果交换后得分变小,则保持,后面可能还需要多次交换
- 这样,通过多次随机的交换尝试,最终可以达到更好的反亲和性分布
最后则是一些收尾工作,像输出日志信息,释放内存等,这里不过多介绍
char *msg;int perfect = (score == 0);int log_level = (perfect ? CLUSTER_MANAGER_LOG_LVL_SUCCESS :CLUSTER_MANAGER_LOG_LVL_WARN);if (perfect) msg = "[OK] Perfect anti-affinity obtained!";else if (score >= 10000)msg = ("[WARNING] Some slaves are in the same host as their master");elsemsg=("[WARNING] Some slaves of the same master are in the same host");clusterManagerLog(log_level, "%s\n", msg);
下面是完整代码
static void clusterManagerOptimizeAntiAffinity(clusterManagerNodeArray *ipnodes,int ip_count)
{clusterManagerNode **offenders = NULL;int score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes, ip_count,NULL, NULL);if (score == 0) goto cleanup;clusterManagerLogInfo(">>> Trying to optimize slaves allocation ""for anti-affinity\n");int node_len = cluster_manager.nodes->len;int maxiter = 500 * node_len; // Effort is proportional to cluster size...srand(time(NULL));while (maxiter > 0) {int offending_len = 0;if (offenders != NULL) {zfree(offenders);offenders = NULL;}score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes,ip_count,&offenders,&offending_len);if (score == 0 || offending_len == 0) break; // Optimal anti affinity reached/* We'll try to randomly swap a slave's assigned master causing* an affinity problem with another random slave, to see if we* can improve the affinity. */int rand_idx = rand() % offending_len;clusterManagerNode *first = offenders[rand_idx],*second = NULL;clusterManagerNode **other_replicas = zcalloc((node_len - 1) *sizeof(*other_replicas));int other_replicas_count = 0;listIter li;listNode *ln;listRewind(cluster_manager.nodes, &li);while ((ln = listNext(&li)) != NULL) {clusterManagerNode *n = ln->value;if (n != first && n->replicate != NULL)other_replicas[other_replicas_count++] = n;}if (other_replicas_count == 0) {zfree(other_replicas);break;}rand_idx = rand() % other_replicas_count;second = other_replicas[rand_idx];char *first_master = first->replicate,*second_master = second->replicate;first->replicate = second_master, first->dirty = 1;second->replicate = first_master, second->dirty = 1;int new_score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes,ip_count,NULL, NULL);/* If the change actually makes thing worse, revert. Otherwise* leave as it is because the best solution may need a few* combined swaps. */if (new_score > score) {first->replicate = first_master;second->replicate = second_master;}zfree(other_replicas);maxiter--;}score = clusterManagerGetAntiAffinityScore(ipnodes, ip_count, NULL, NULL);char *msg;int perfect = (score == 0);int log_level = (perfect ? CLUSTER_MANAGER_LOG_LVL_SUCCESS :CLUSTER_MANAGER_LOG_LVL_WARN);if (perfect) msg = "[OK] Perfect anti-affinity obtained!";else if (score >= 10000)msg = ("[WARNING] Some slaves are in the same host as their master");elsemsg=("[WARNING] Some slaves of the same master are in the same host");clusterManagerLog(log_level, "%s\n", msg);
cleanup:zfree(offenders);
}
相关文章:

为什么创建 Redis 集群时会自动错开主从节点?
哈喽大家好,我是咸鱼 在《一台服务器上部署 Redis 伪集群》这篇文章中,咸鱼在创建 Redis 集群时并没有明确指定哪个 Redis 实例将担任 master,哪个将担任 slave /usr/local/redis-4.0.9/src/redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 192.168.149…...
分布式 - 服务器Nginx:基础系列之Nginx静态资源配置优化sendfile | tcp_nopush | tcp_nodelay
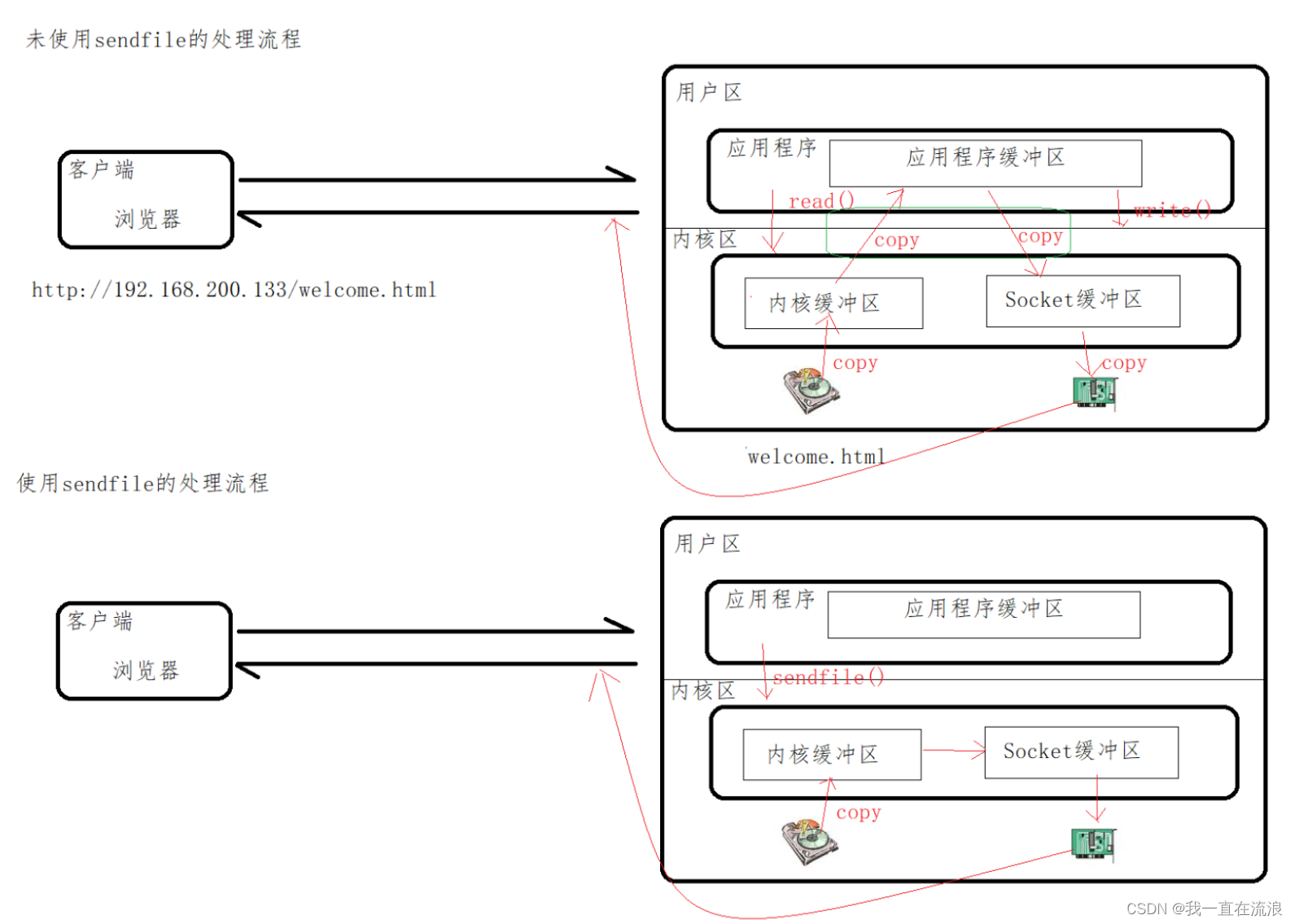
文章目录 1. sendfile 指令2. tcp_nopush 指令3. tcp_nodelay 指令 1. sendfile 指令 请求静态资源的过程:客户端通过网络接口向服务端发送请求,操作系统将这些客户端的请求传递给服务器端应用程序,服务器端应用程序会处理这些请求ÿ…...

【动手学深度学习】--语言模型
文章目录 语言模型1.学习语言模型2.马尔可夫模型与N元语法3.自然语言统计4.读取长序列数据4.1随机采样4.2顺序分区 语言模型 学习视频:语言模型【动手学深度学习v2】 官方笔记:语言模型和数据集 在【文本预处理】中了解了如何将文本数据映射为词元&…...

uni-app 之 目录结构
目录结构: 工程简介 | uni-app官网 (dcloud.net.cn) pages/index/index.vue 页面元素等 static 静态文件,图片 字体文件等 App.vue 应用配置,用来配置App全局样式以及监听 应用生命周期 index.html 项目运行最终生成的文件 main.js 引用的…...

批量上传图片添加水印
思路: 1、循环图片列表,批量添加水印。 2、与之对应的html页面也要魂环并添加水印。 代码实现: <view style"width: 0;height: 0;overflow: hidden;position:fixed;left: 200%;"><canvas v-for"(item,index) in …...

CPU和GPU性能优化
在Unity游戏开发中,优化CPU和GPU的性能是非常重要的,可以提高游戏的运行效率、降低功耗和延迟,并提高用户体验。以下是一些优化CPU和GPU性能的方法: 1.优化游戏逻辑和算法 减少不必要的计算和内存操作,例如避免频繁的…...
虚拟机(三)VMware Workstation 桥接模式下无法上网
目录 一、背景二、解决方式方式一:关闭防火墙方式二:查看桥接模式下的物理网卡是否对应正确方式三:查看物理主机的网络属性 一、背景 今天在使用 VMware Workstation 里面安装的 Windows 虚拟机的时候,发现虽然在 NAT 模式下可以…...

[BFS] 广度优先搜索
1. 数字操作 常见的模板 // 使用一个数组判断元素是否入过队 int inqueue[N] {0}; // 层数或者可以称为深度 int step 0; // 判断是否可以入队的条件 int isvalid(){ } BFS(int x){ // 将初始的元素压入队列 // 注意每次压队的时候都要将inque[x] 1,表明入队过…...
)
蓝桥杯官网填空题(矩形切割)
题目描述 本题为填空题,只需要算出结果后,在代码中使用输出语句将所填结果输出即可。 小明有一些矩形的材料,他要从这些矩形材料中切割出一些正方形。 当他面对一块矩形材料时,他总是从中间切割一刀,切出一块最大的…...
通过Docker Compose安装MQTT
一、文件和目录说明 1、MQTT安装时的文件和目录 EMQX 安装完成后会创建一些目录用来存放运行文件和配置文件,存储数据以及记录日志。 不同安装方式得到的文件和目录位置有所不同,具体如下: 注意: 压缩包解压安装时,目…...

Golang企业面试题
Golang企业面试题 基础 高级 Golang有哪些优势?Golang数据类型有哪些Golang中的包如何使用Go 支持什么形式的类型转换?什么是 Goroutine?你如何停止它?如何在运行时检查变量类型?Go 两个接口之间可以存在什么关系&a…...
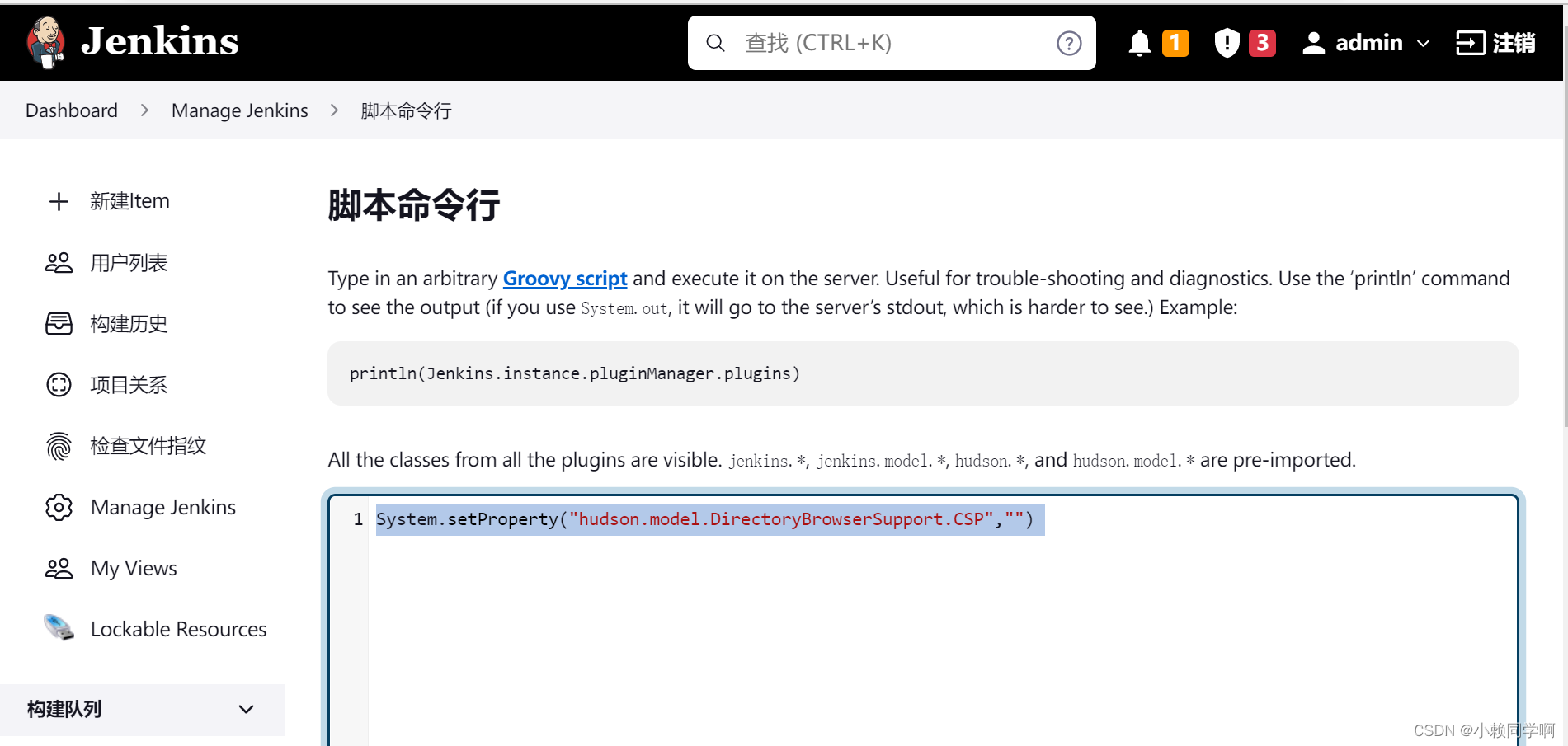
Jenkins测试报告样式优化
方式一:修改Content Security Policy(临时解决,Jenkins重启后失效) 1、jenkins首页—>ManageJenkins—>Tools and Actions标题下—>Script Console 2、粘贴脚本输入框中:System.setProperty("hudson.model.Directo…...
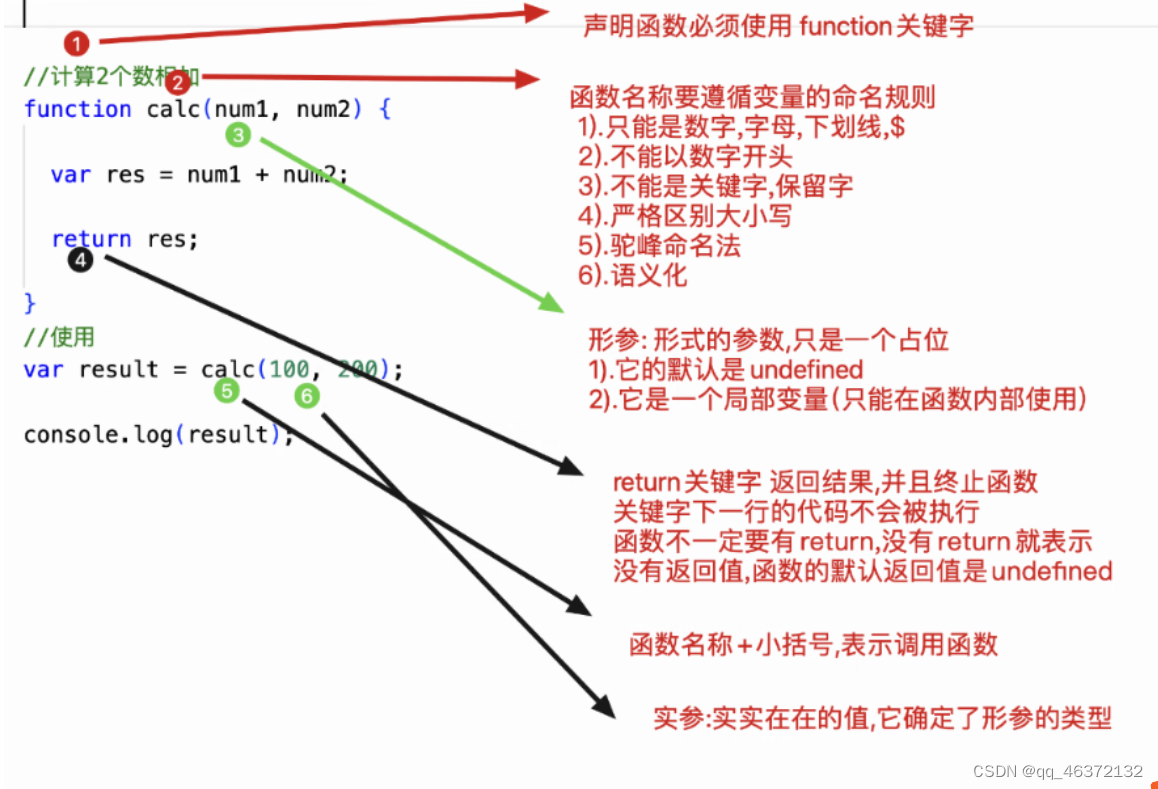
函数相关概念
4.函数 1.函数的概念 1.什么是函数? 把特点的代码片段,抽取成为独立运行的实体 2.使用函数的好处1.重复使用,提供效率2.提高代码的可读性3.有利用程序的维护 3.函数的分类1.内置函数(系统函数)已经提高的alert(); prompt();confirm();print()document.write(),console.log()…...

2023软考学习营
...
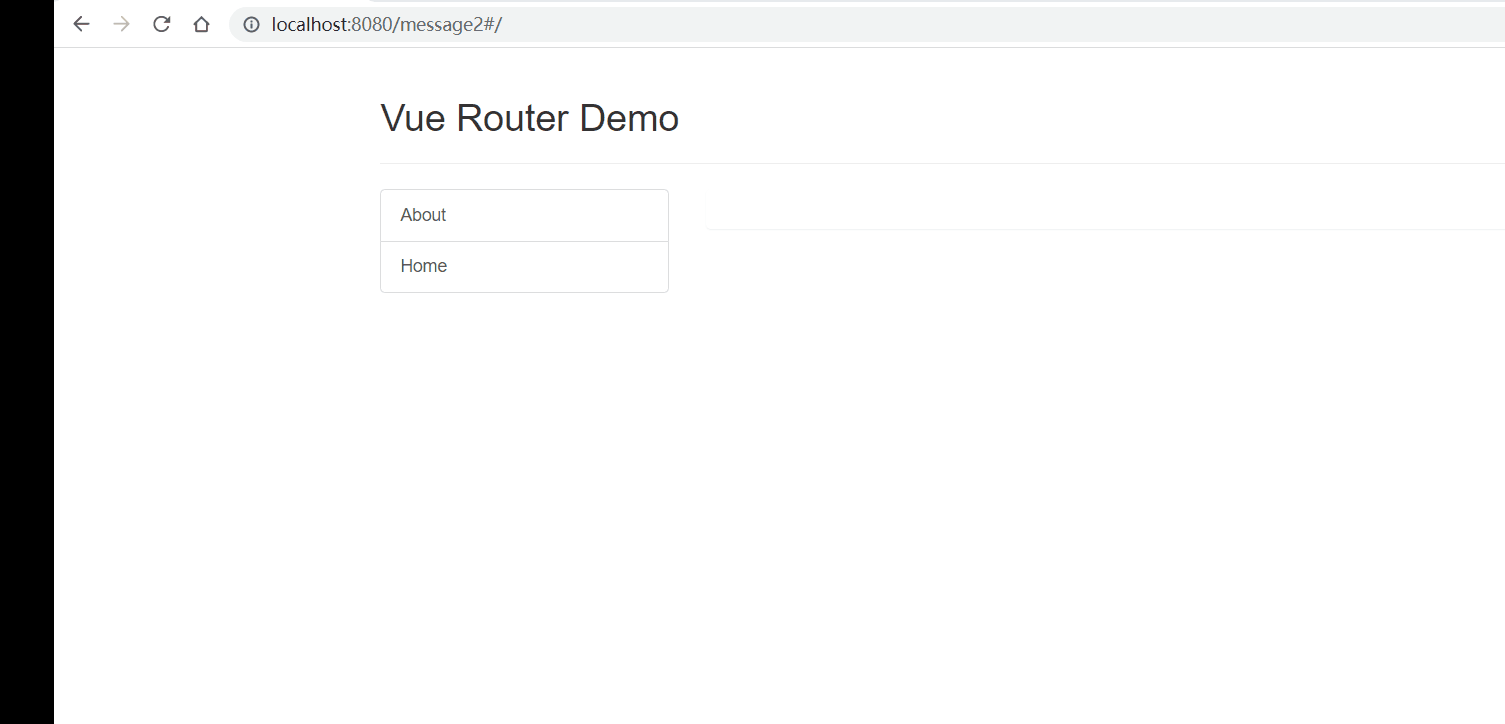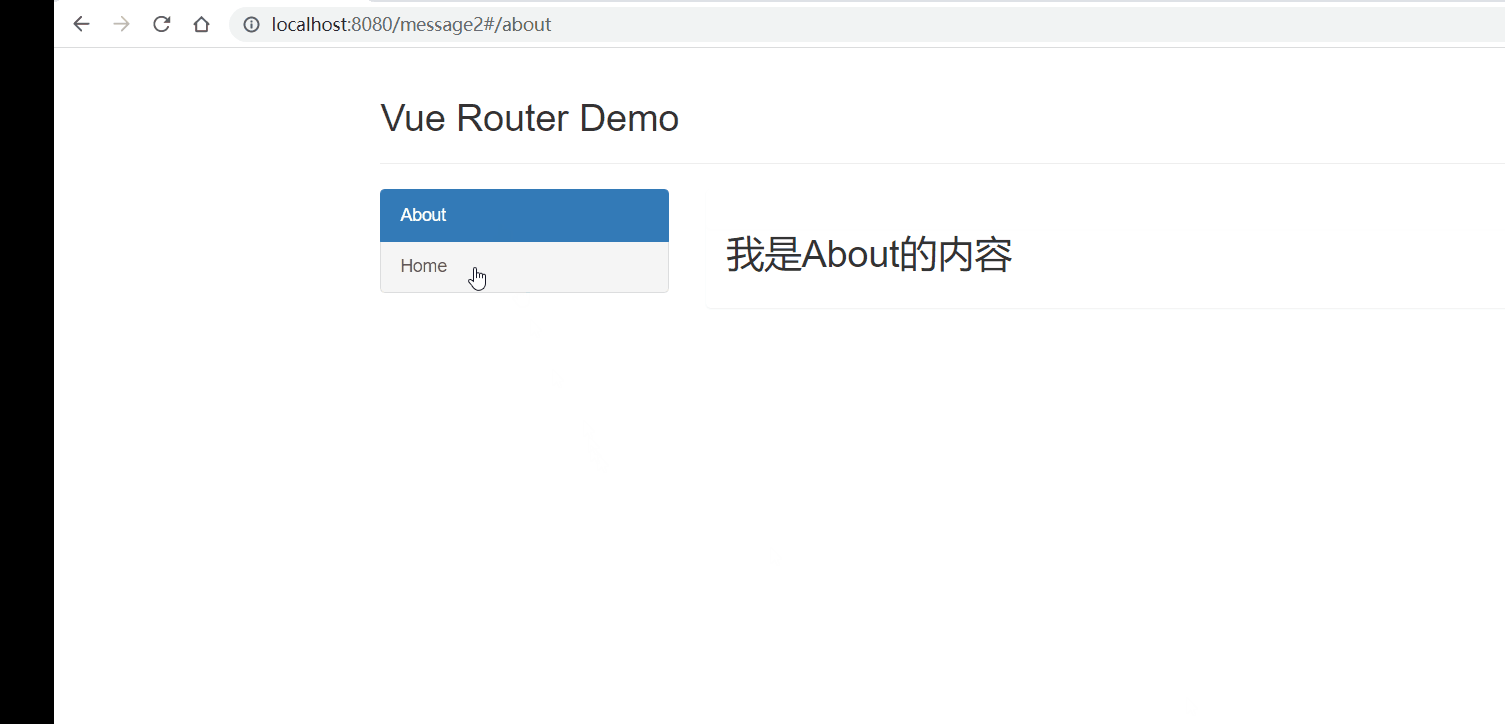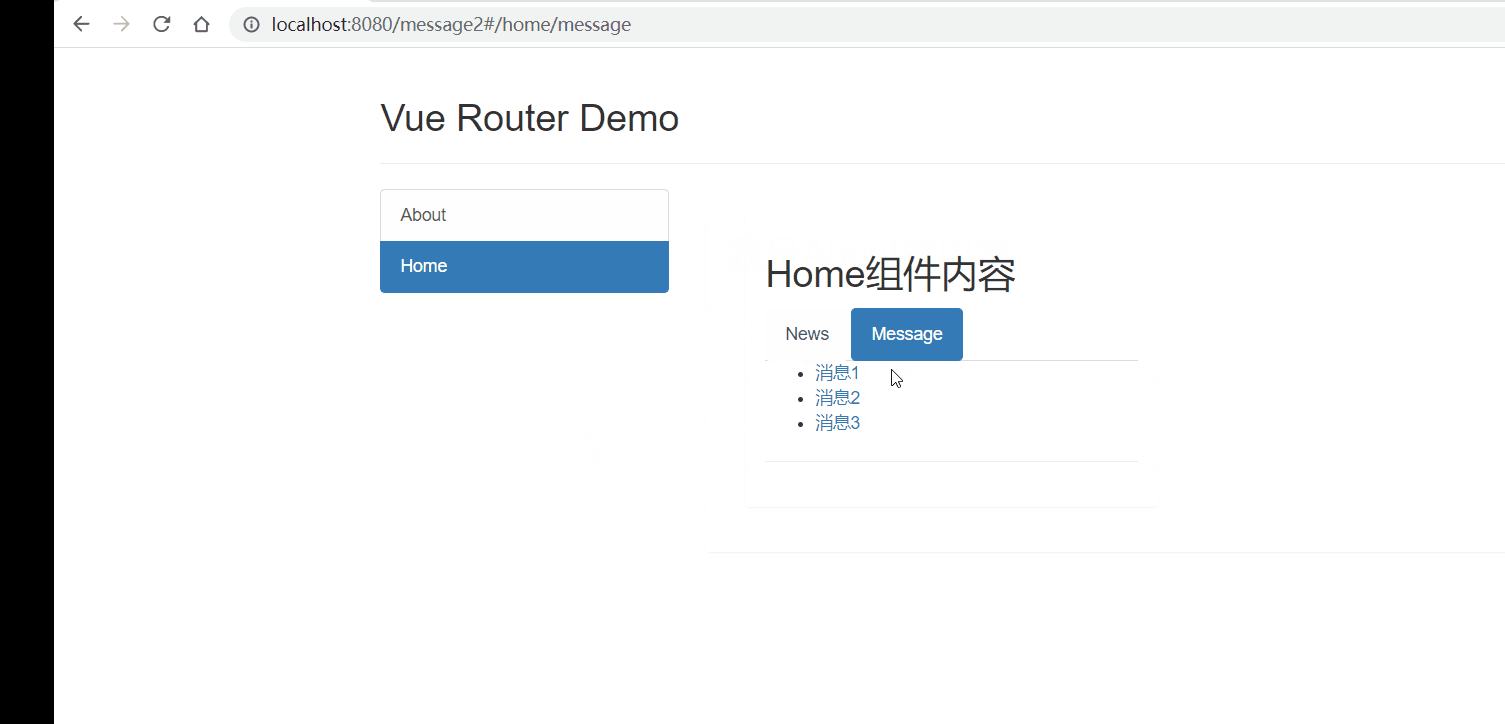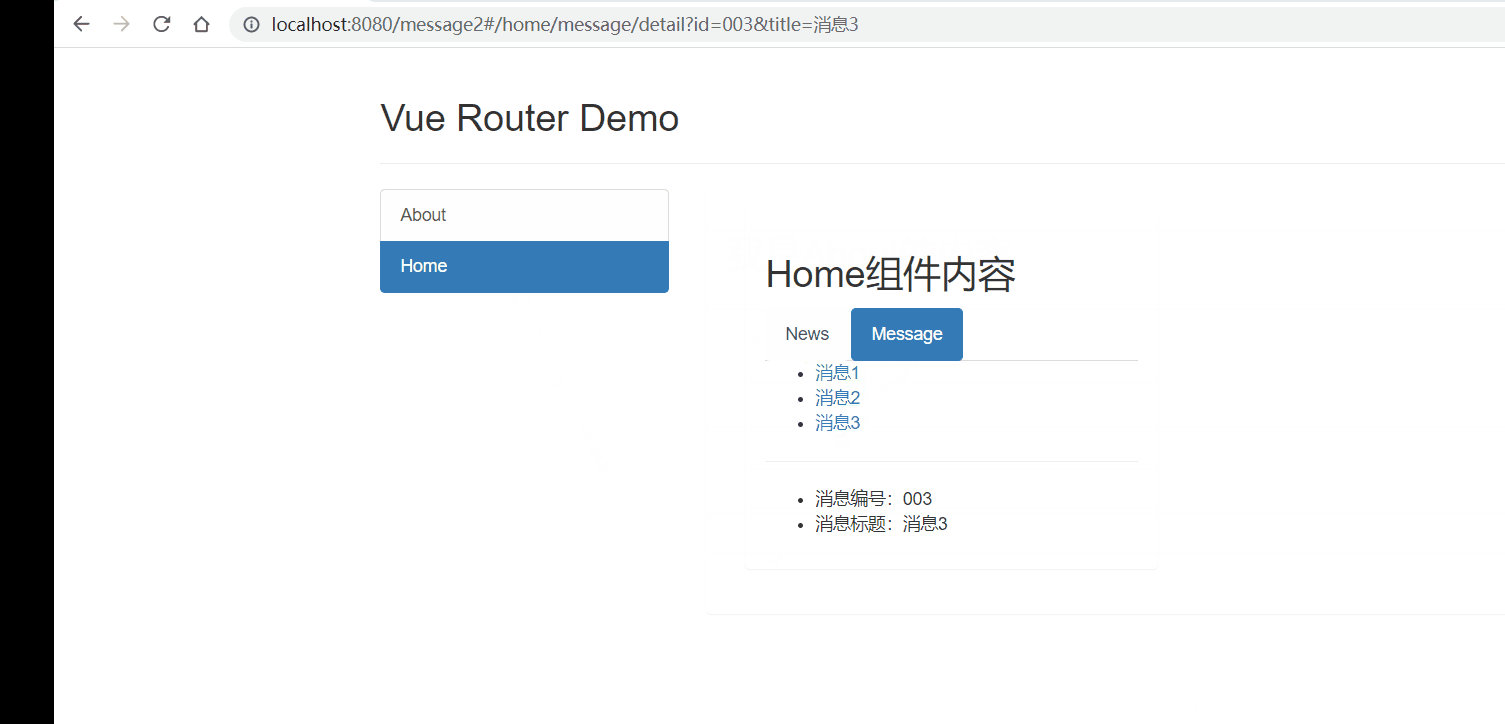
Vue2进阶篇学习笔记
文章目录 Vue2进阶学习笔记前言1、Vue脚手架学习1.1 Vue脚手架概述1.2 Vue脚手架安装1.3 常用属性1.4 插件 2、组件基本概述3、非单文件组件3.1 非单文件组件的基本使用3.2 组件的嵌套 4、单文件组件4.1 快速体验4.2 Todo案例 5、浏览器本地存储6、组件的自定义事件6.1 使用自定…...

Python 正则表达式:强大的文本处理工具
概念: 正则表达式是一种强大的文本匹配和处理工具,它可以用来在字符串中查找、替换和提取符合某种规则的内容。在Python中,使用re模块可以轻松地操作正则表达式,它提供了丰富的功能和灵活的语法。 场景: 正则表达式…...

Linux如何查看系统时间
文章目录 一、使用date命令查看系统时间二、通过/var/log/syslog文件查看系统时间三、通过/proc/uptime文件查看系统运行时间四、通过hwclock命令查看硬件时间五、通过timedatectl命令设置系统时区六、通过NTP协议同步网络时间七、通过ntpstat命令检查NTP同步状态八、使用cal命…...

46. 出勤率问题
文章目录 题目需求实现一题目来源 题目需求 现有用户出勤表(user_login)如下。 user_id (用户id)course_id (课程id)login_in (登录时间)login_out (登出时间)112022-06-02 09:08:242022-06-02 10:09:361…...
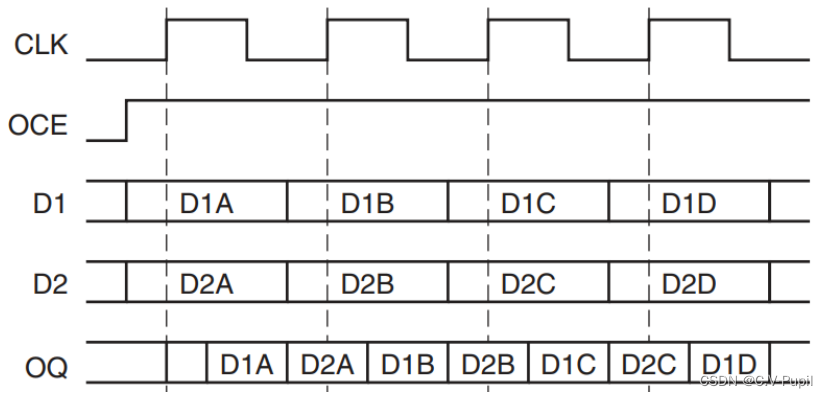
Xilinx IDDR与ODDR原语的使用
文章目录 ODDR原语1. OPPOSITE_EDGE 模式2. SAME_EDGE 模式 ODDR原语 例化模板: ODDR #(.DDR_CLK_EDGE("OPPOSITE_EDGE"), // "OPPOSITE_EDGE" or "SAME_EDGE" .INIT(1b0), // Initial value of Q: 1b0 or 1b1.SRTYPE("SYNC…...

面试系列 - 序列化和反序列化详解
Java 序列化是一种将对象转换为字节流的过程,可以将对象的状态保存到磁盘文件或通过网络传输。反序列化则是将字节流重新转换为对象的过程。Java 提供了一个强大的序列化框架,允许你在对象的持久化和网络通信中使用它。 一、Java 序列化的基本原理 Jav…...

利用最小二乘法找圆心和半径
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <Eigen/Dense> // 需安装Eigen库用于矩阵运算 // 定义点结构 struct Point { double x, y; Point(double x_, double y_) : x(x_), y(y_) {} }; // 最小二乘法求圆心和半径 …...
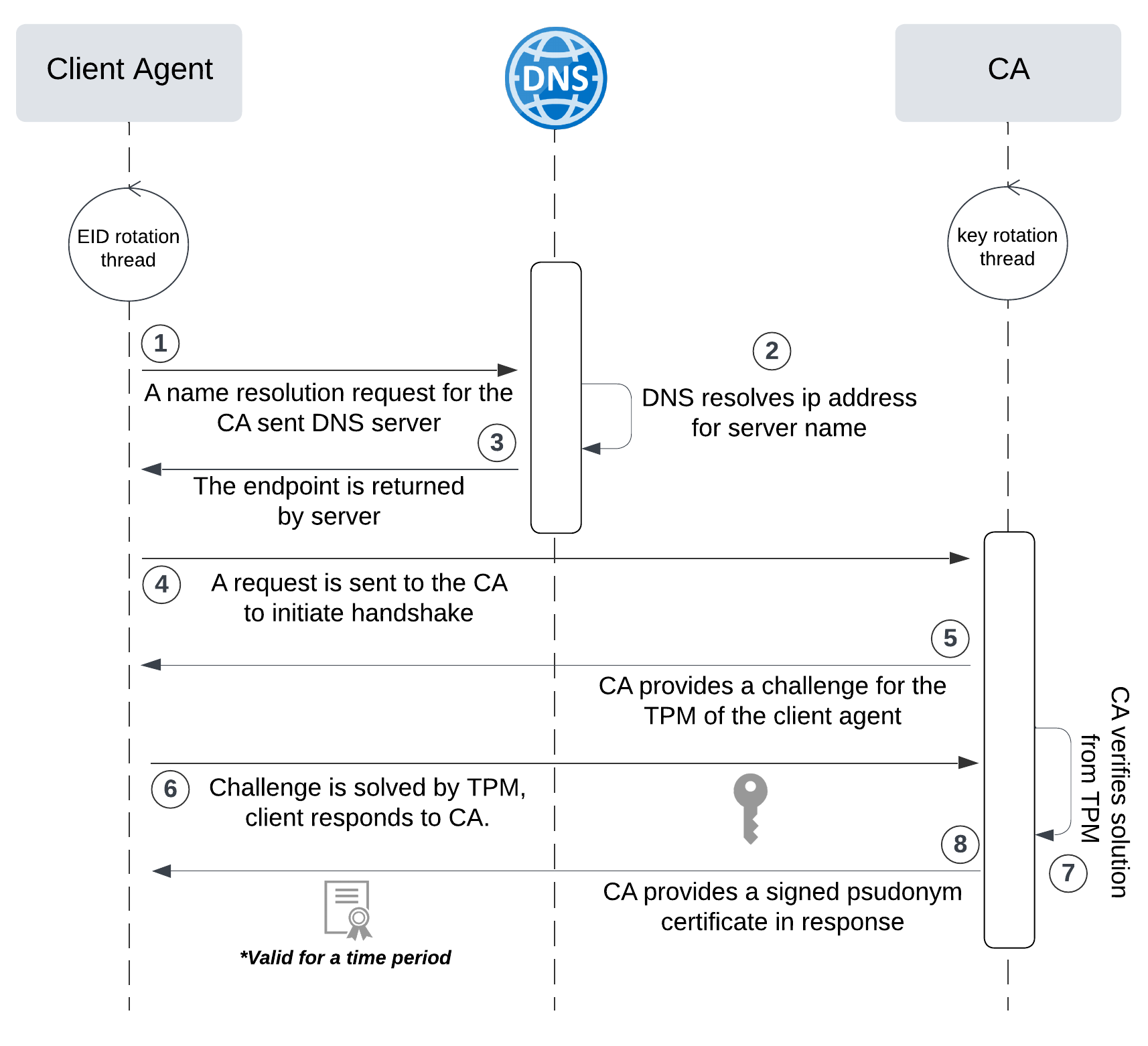
网络六边形受到攻击
大家读完觉得有帮助记得关注和点赞!!! 抽象 现代智能交通系统 (ITS) 的一个关键要求是能够以安全、可靠和匿名的方式从互联车辆和移动设备收集地理参考数据。Nexagon 协议建立在 IETF 定位器/ID 分离协议 (…...
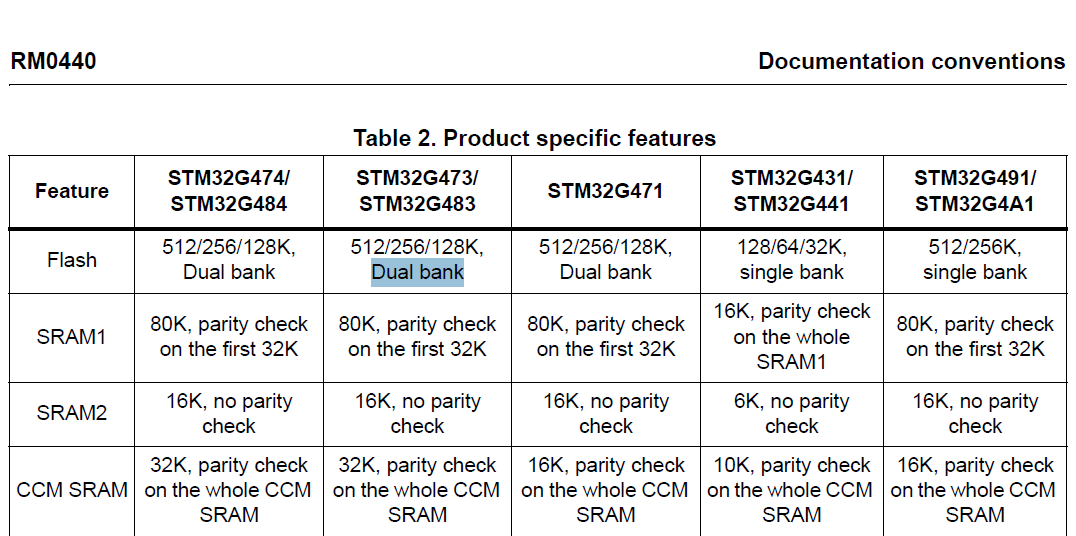
stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?
今天突然有人stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?由于时间太久,我真忘记了。搜搜发现,还真有人和我一样。见下面的链接:https://shequ.stmicroelectronics.cn/forum.php?modviewthread&tid644563 根据STM32G4系列参考手…...

css实现圆环展示百分比,根据值动态展示所占比例
代码如下 <view class""><view class"circle-chart"><view v-if"!!num" class"pie-item" :style"{background: conic-gradient(var(--one-color) 0%,#E9E6F1 ${num}%),}"></view><view v-else …...
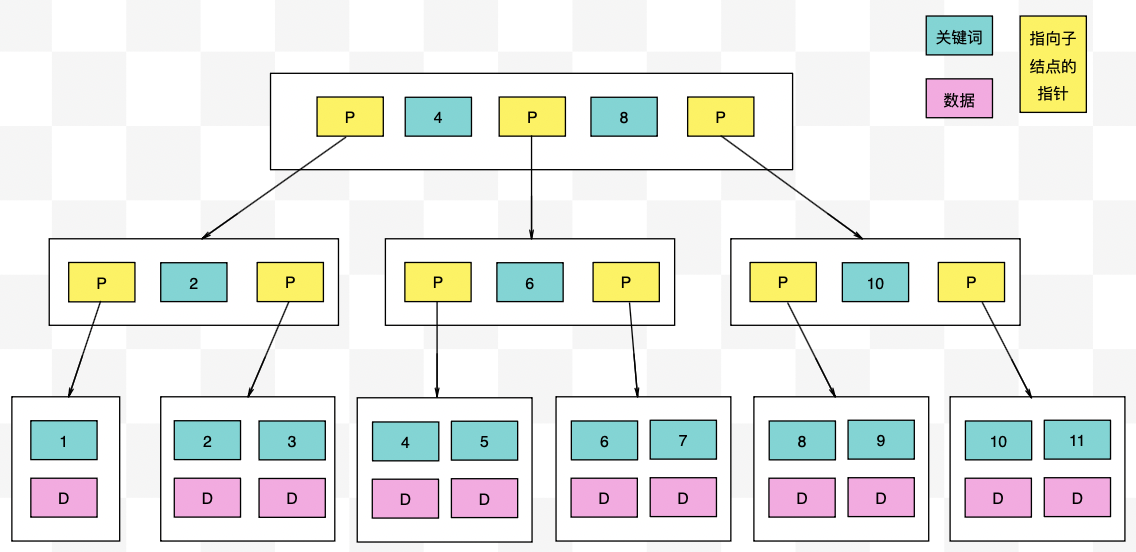
【力扣数据库知识手册笔记】索引
索引 索引的优缺点 优点1. 通过创建唯一性索引,可以保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。2. 可以加快数据的检索速度(创建索引的主要原因)。3. 可以加速表和表之间的连接,实现数据的参考完整性。4. 可以在查询过程中,…...

mongodb源码分析session执行handleRequest命令find过程
mongo/transport/service_state_machine.cpp已经分析startSession创建ASIOSession过程,并且验证connection是否超过限制ASIOSession和connection是循环接受客户端命令,把数据流转换成Message,状态转变流程是:State::Created 》 St…...
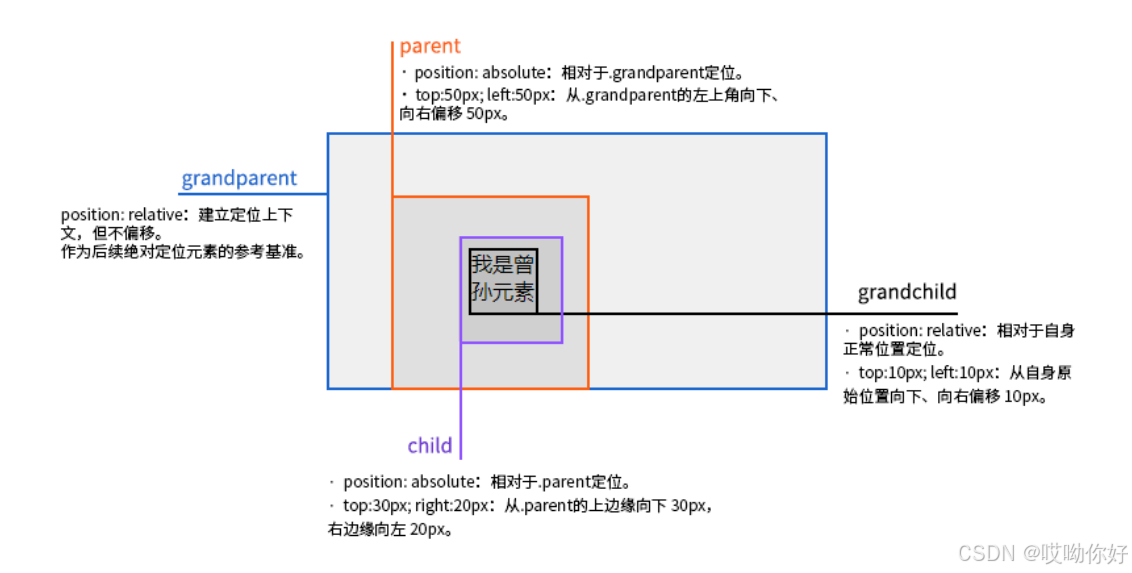
【CSS position 属性】static、relative、fixed、absolute 、sticky详细介绍,多层嵌套定位示例
文章目录 ★ position 的五种类型及基本用法 ★ 一、position 属性概述 二、position 的五种类型详解(初学者版) 1. static(默认值) 2. relative(相对定位) 3. absolute(绝对定位) 4. fixed(固定定位) 5. sticky(粘性定位) 三、定位元素的层级关系(z-i…...
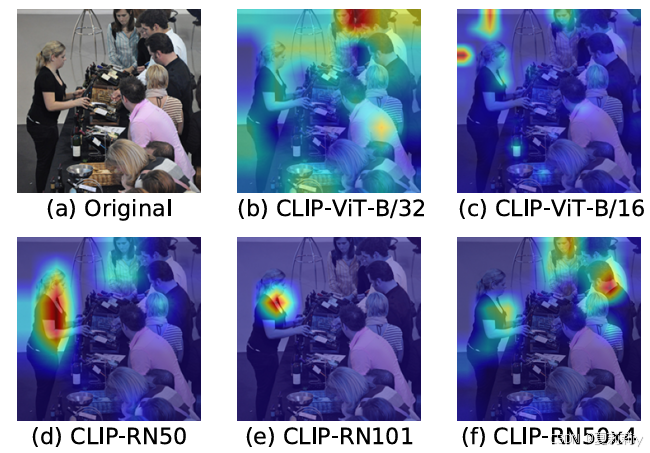

[ICLR 2022]How Much Can CLIP Benefit Vision-and-Language Tasks?
论文网址:pdf 英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用 目录 1. 心得 2. 论文逐段精读 2.1. Abstract 2…...
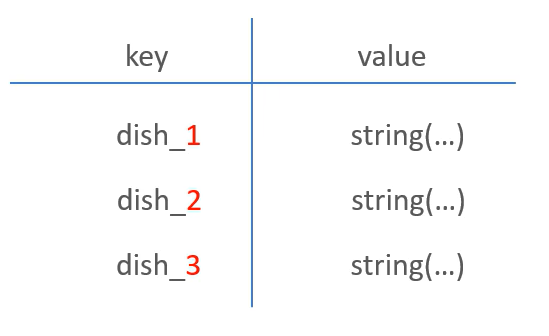
苍穹外卖--缓存菜品
1.问题说明 用户端小程序展示的菜品数据都是通过查询数据库获得,如果用户端访问量比较大,数据库访问压力随之增大 2.实现思路 通过Redis来缓存菜品数据,减少数据库查询操作。 缓存逻辑分析: ①每个分类下的菜品保持一份缓存数据…...
SpringBoot+uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序设计与实现,论文初版实现
摘要 本论文旨在设计并实现基于 SpringBoot 和 uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序,以满足俱乐部线上活动推广、会员管理、社交互动等需求。通过 SpringBoot 搭建后端服务,提供稳定高效的数据处理与业务逻辑支持;利用 uniapp 实现跨平台前…...
