LinkedList与链表
目录
一、Arraylist的缺陷
二、链表
2.1 链表的概念和结构
2.2 链表的实现
三、链表面试题
3.1 删除链表中所有值为val的节点
3.2 反转一个单链表
3.3 链表的中间节点
3.4 将有序链表合并
3.5 输出倒数第k个节点
3.6 链表分割
3.7 链表的回文结构
3.8 找两个链表的公共节点
3.9 判断链表是否有环
3.10 找链表入环的第一个节点
四、LinkedList的模拟实现
五、LinkedList的使用
5.1 什么是LinkedList
5.2 LinkedList的使用
六、ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
一、Arraylist的缺陷
ArrayList底层使用数组来存储元素
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
// ...
// 默认容量是10
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
//...
// 数组:用来存储元素
transient Object[] elementData;
// 有效元素个数
private int size;
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}//...
}
ArrayList底层是一段连续空间,当在ArrayList任意位置插入或者删除元素时,需要将后序元素整体往前或者往后搬移,时间复杂度为O(n),效率比较低,因此ArrayList不适合做任意位置插入和删除比较多的场景。因此:java集合中引入LinkedList,即链表结构。
二、链表
2.1 链表的概念和结构
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的。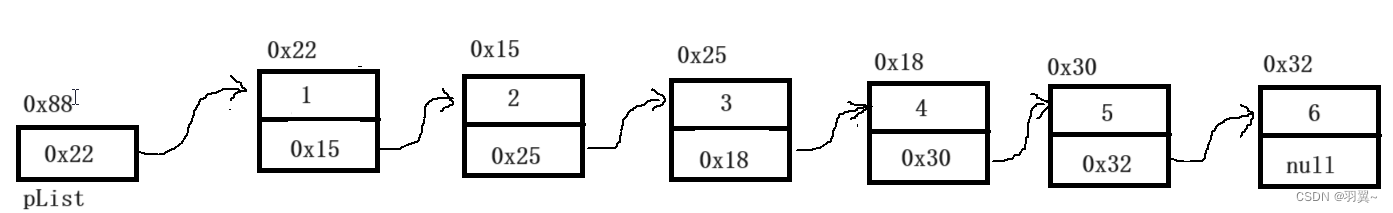
链式结构在逻辑上连续,但在物理上不一定连续;节点一般都是从堆上申请出来的;从堆上申请的空间,是按照一定的策略来分配的,两次申请的空间可能连续,也可能不连续。
实际中的链表结构非常多,以下请况组合起来就有8种:
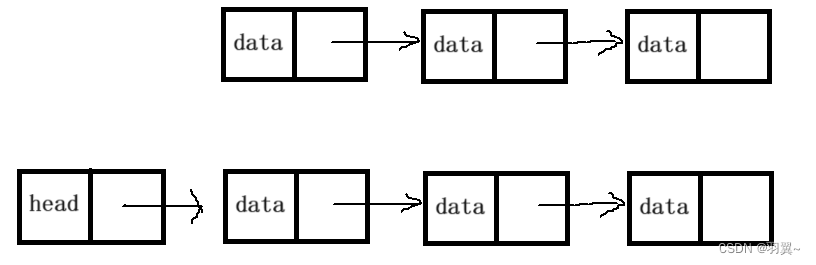
1. 单向或双向

2. 带头或不带头
3. 循环或非循环
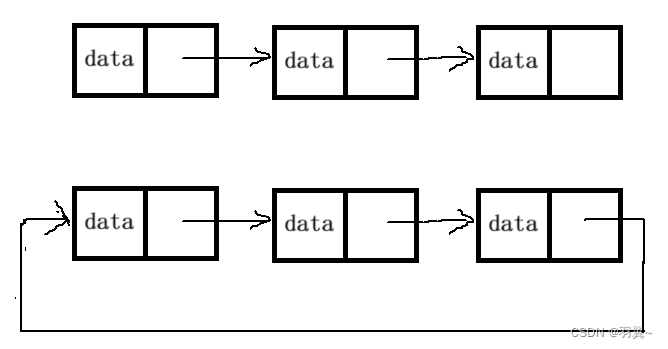
链表有很多,重点掌握两种:
无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多

无头双向链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
2.2 链表的实现
//无头单向非循环链表实现
public class SingleLinkedList {
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
}//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
}//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
}//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
return false;
}//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
}//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
}//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
return -1;
}//清空
public void clear() {
}//打印
public void display() {
}
}
三、链表面试题
3.1 删除链表中所有值为val的节点
删除链表中等于给定值val的所有节点 链接
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {} ;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
解法1:遍历整个链表,将其中值为val的节点删除(将要删除节点前的节点的next指向要删除节点后的第一个节点)。
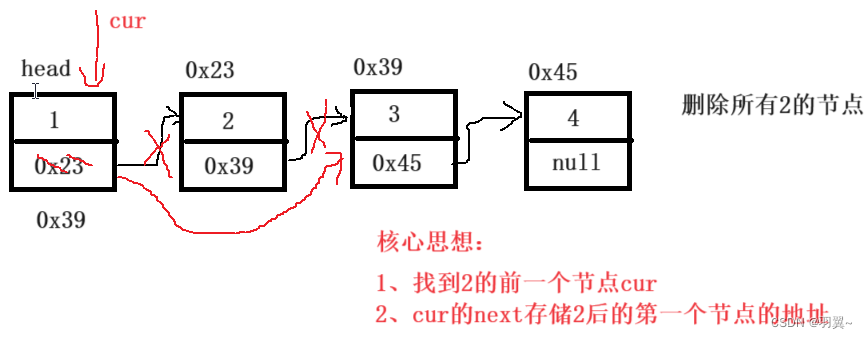
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
//原链表是空链表
if(head==null)
return head;
ListNode cur=head;
//从第二个节点判断
while(cur.next!=null){
//下一个节点的值
if(cur.next.val==val){
cur.next=cur.next.next;
}
else{
cur=cur.next;
}
}
//判断头节点
if(head.val==val){
head=head.next;
}
return head;
}
解法2:遍历整个链表,将所有值不是给定值val的节点放入新链表中,返回新链表。
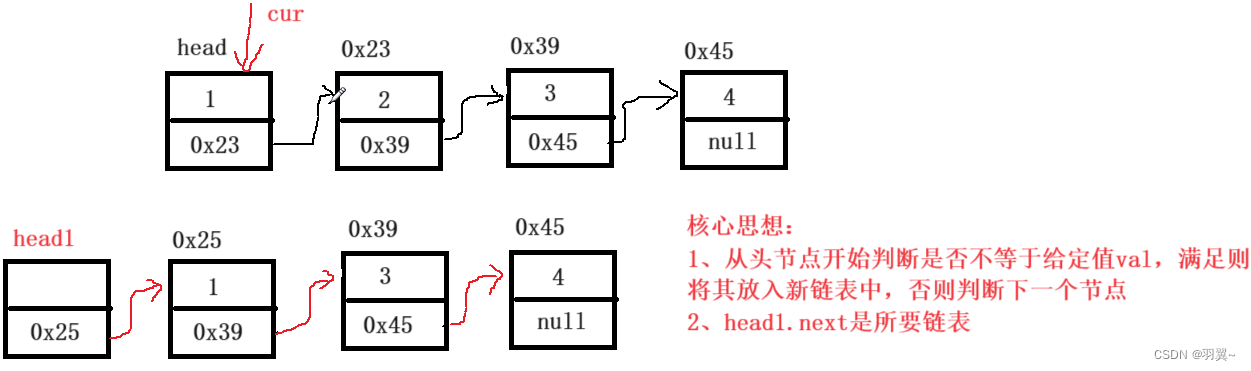
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
//原链表是空链表
if(head==null)
return head;
//新链表的头节点
ListNode head1=new ListNode();
//新链表的节点
ListNode cur1=head1;
//原来链表的节点
ListNode cur=head;
//遍历原来链表
while(cur!=null){
//当前节点的值
if(cur.val==val)
cur=cur.next;
else{
cur1.next=cur;
cur=cur.next;
cur1=cur1.next;
}
}
//如果新链表的尾节点不是原来链表的尾节点,将next置空
if(cur1.next!=null)
cur1.next=null;
return head1.next;
}
3.2 反转一个单链表
链接
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
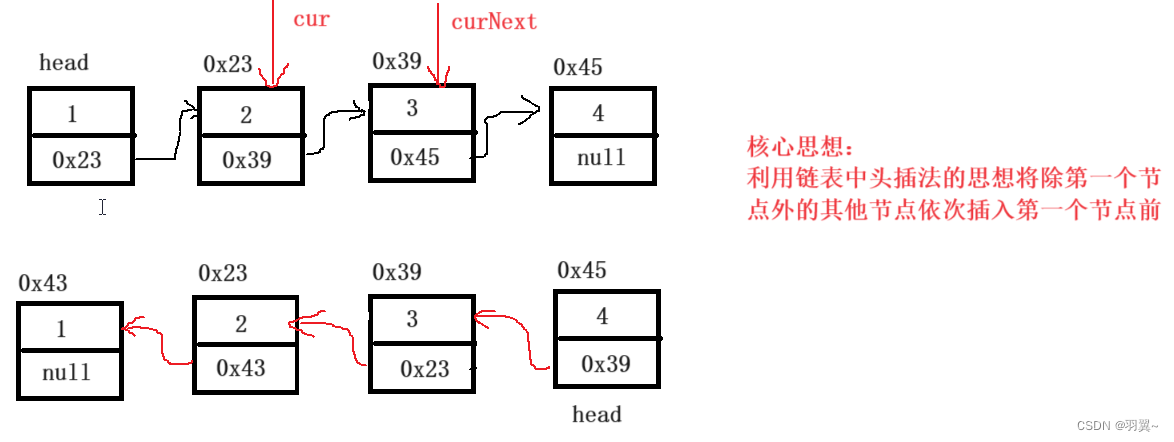
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//原链表为空
if(head==null)
return null;
//原链表只有一个节点
if(head.next==null)
return head;
//原链表的第二个节点开始
ListNode cur=head.next;
head.next=null;
//遍历链表
while(cur!=null){
//curNext为当前节点的下一个节点
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
//头插法插入节点
cur.next=head;
head=cur;
//当前节点指向原链表位置的下一个节点
cur=curNext;
}
return head;
}
3.3 链表的中间节点
给一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点 链接
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
解法1:先求链表长度,获取长度一半的节点
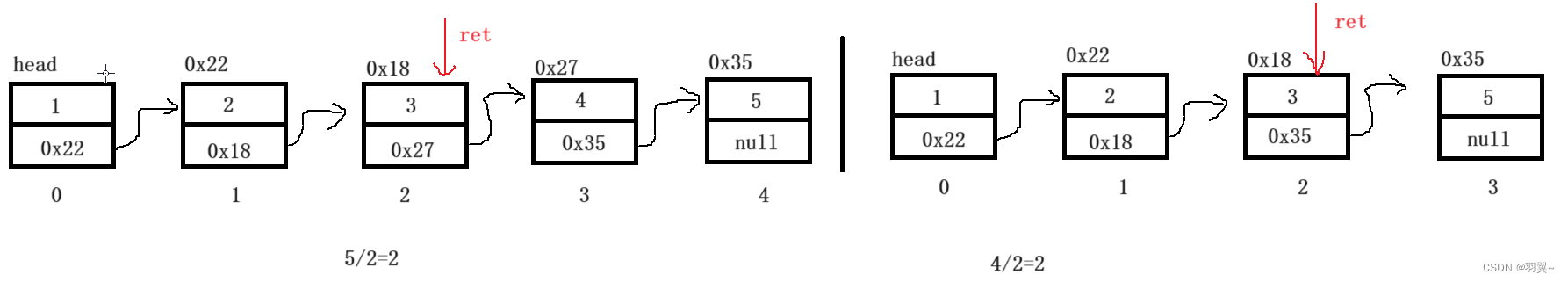
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur=head;
//链表的长度
int count=0;
while(cur!=null){
cur=cur.next;
count++;
}
int BinaCount=count/2;
ListNode ret=head;
for(int i=0;i<BinaCount;i++){
ret=ret.next;
}
return ret;
}
缺陷:需要两次遍历才能找到中间节点,当节点较多时,时间复杂度较大。
解法2:在一次遍历中找到中间节点,两个引用fast和slow分别走两步和一步
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
3.4 将有序链表合并
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的 链接
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}

public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode NewHead=new ListNode();
//Newcur 新链表的尾节点
ListNode Newcur=NewHead;
while(list1!=null&&list2!=null){
if(list1.val<list2.val){
Newcur.next=list1;
list1=list1.next;
}else{
Newcur.next=list2;
list2=list2.next;
}
Newcur=Newcur.next;
}
//list1还有数
if(list1!=null){
Newcur.next=list1;
}
//list2还有数
if(list2!=null){
Newcur.next=list2;
}
return NewHead.next;
}
3.5 输出倒数第k个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点 链接
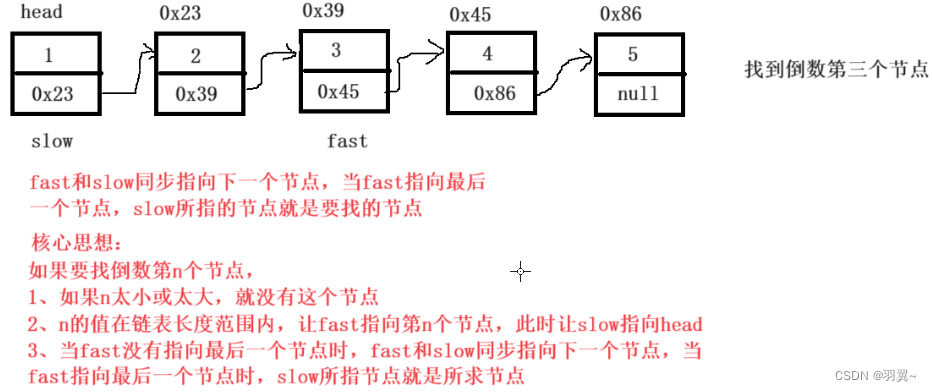
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
//链表为空或k太小
if(k<=0||head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
//fast指向第k个节点
while(k>1){
fast=fast.next;
//当k太大
if(fast==null){
return null;
}
k--;
}
ListNode slow=head;
//fast没有指向最后一个节点
while(fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
3.6 链表分割
编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前 链接
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}

public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
//pmin链表存小于x的节点
ListNode pmin = null;
//pin为pmin的尾节点
ListNode pin = null;
//pmin链表存大于等于x的节点
ListNode pmax = null;
//pax为pmax的尾节点
ListNode pax = null;
//遍历链表pHead,将小于x和大于等于x的存入pmin和pmax中
ListNode cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < x) {
if (pmin == null) {
//pmin为空
pmin = cur;
pin = cur;
} else {
//pmin不为空
pin.next = cur;
pin = pin.next;
}
} else {
if (pmax == null) {
//pmax为空
pmax = cur;
pax = cur;
} else {
//pmax不为空
pax.next = cur;
pax = pax.next;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(pmin==null){
//没有小于x的
return pmax;
}
if(pmax==null){
//没有大于等于x的return pmin;
}
//将pmin与pmax串联起来(pmin的尾节点指向pmax的头节点)
pin.next=pmax;
if(pax.next!=null){
pax.next=null;
}
return pmin;
}
3.7 链表的回文结构
链接
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
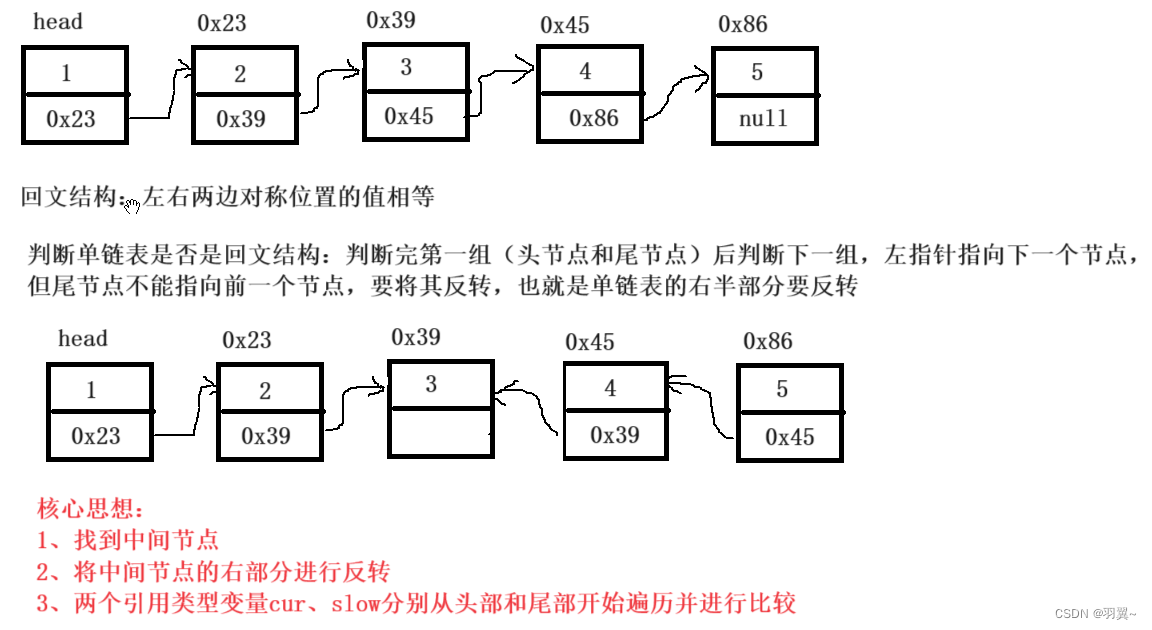
反转:
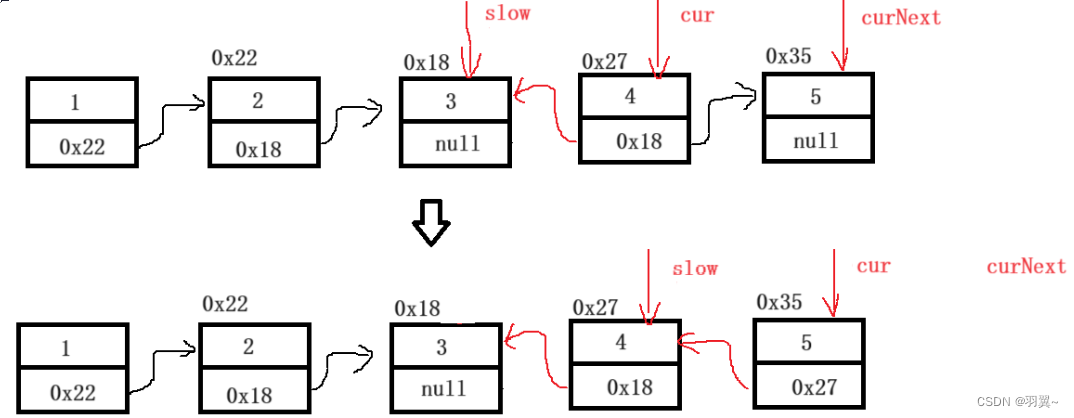
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
ListNode fast = A;
//1、找中间节点slow
ListNode slow = A;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//2、中间节点之后的反转
//cur是节点后的第一个节点
ListNode cur = slow.next;
slow.next=null;
while (cur!= null) {
//保存cur后的第一个节点
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
//反转结束后,slow指向最后一个节点
//3、从第一个节点开始判断
cur = A;
while (cur != slow && cur.next != slow) {
if (cur.val != slow.val) {
return false;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
}
return true;
}
3.8 找两个链表的公共节点
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点 链接
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}

public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
//lenA、lenB分别为链表headA和链表headB的长度
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
while(curA != null){
lenA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while( curB != null){
lenB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
//pl指向最长链表,ps指向最短链表
ListNode pl = headA;
ListNode ps = headB;
//长度差值len
int len = lenA-lenB;
if(len<0){
//修正pl、ps、len
pl = headB;
ps = headA;
len = lenB-lenA;
}
//pl走差值步
while(len>0){
pl = pl.next;
len--;
}
//同步走
while(pl != ps){
pl = pl.next;
ps = ps.next;
}
//pl为空,没有公共节点
if(pl == null){
return null;
}
return pl;
}
3.9 判断链表是否有环
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环 链接

class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
//快慢指针
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
//相遇->有环
if(fast==slow){
return true;
}
}
//循环结束->无环
return false;
}
3.10 找链表入环的第一个节点
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点, 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL 链接
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
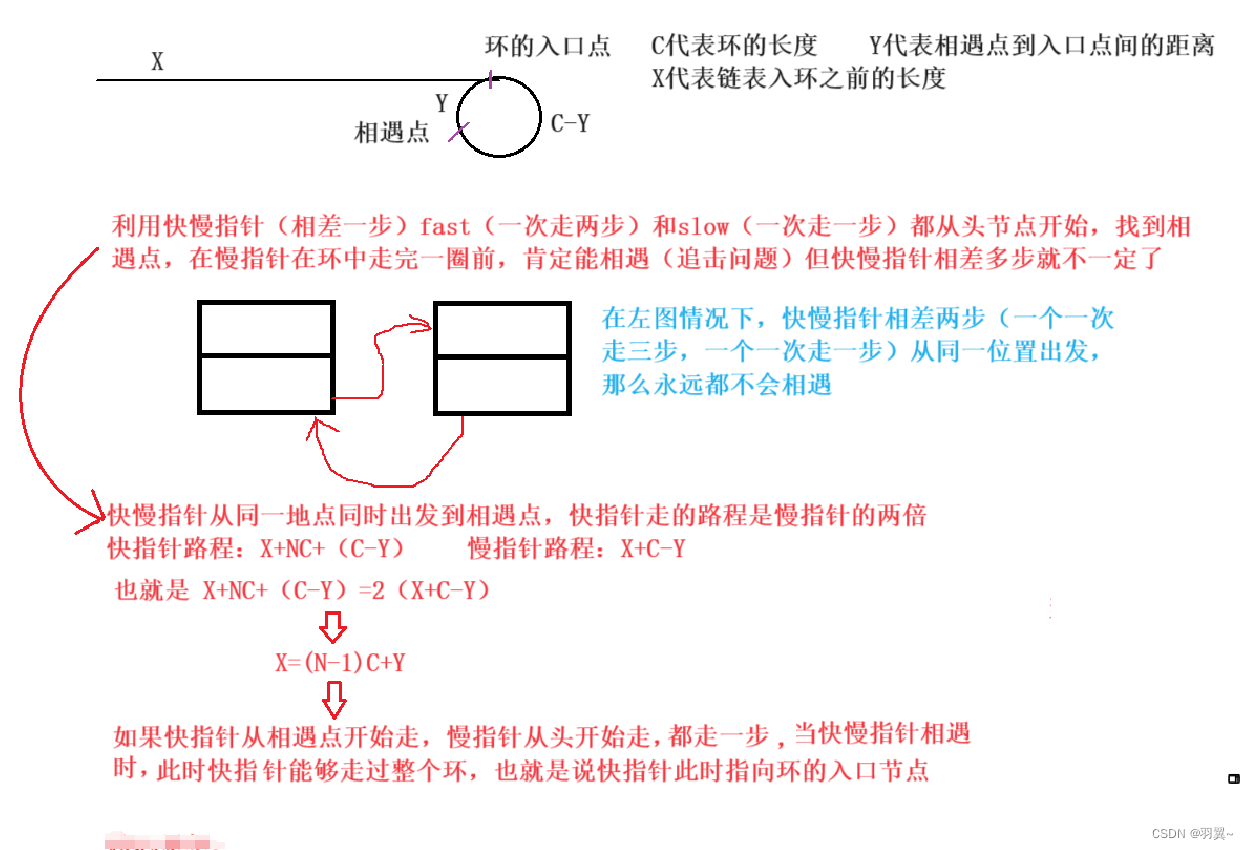

public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
//快慢指针
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
//找相遇节点
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
//相遇
if(fast==slow){
break;
}
}
//fast=null或fast.next=bull->链表不为环,也就没有入环的第一个节点
if(fast==null||fast.next==null){
return null;
}
//慢指针从头开始
slow=head;
while(slow!=fast){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next;
}
//循环结束,slow和fast都指向入环的第一个节点
return slow;
}
结论:让一个指针从链表起始位置开始走,同时让一个指针从判环时相遇点的位置开始走,两个指针每次均走一步,最终肯定会在环的入口点的位置相遇。
四、LinkedList的模拟实现
无头双向链表实现public class MyLinkedList {//头插法public void addFirst(int data){ }//尾插法public void addLast(int data){}//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标public void addIndex(int index,int data){}//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中public boolean contains(int key){}//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点public void remove(int key){}//删除所有值为key的节点public void removeAllKey(int key){}//得到单链表的长度public int size(){}//打印链表public void display (){}//清空链表public void clear (){}}
//无头双向链表的操作 public interface IOPeration {//头插法public void addFirst(int data);//尾插法public void addLast(int data);//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标public boolean addIndex(int index,int data);//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中public boolean contains(int key);//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点public void remove(int key);//删除所有值为key的节点public void removeAllKey(int key);//得到单链表的长度public int size();//打印链表public void display();//清空链表public void clear(); }
public class MySidesLinkList implements IOPeration{static class ListNode {int val;ListNode pre;ListNode next;public ListNode(int data){val=data;}}private int usedSize;private ListNode head;private ListNode last;@Overridepublic void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null){head = node;last = node;}else {node.next = head;head.pre = node;head = node;}usedSize++;}@Overridepublic void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(last == null){head = node;last = node;}else {last.next = node;node.pre = last;last = node;}usedSize++;}@Overridepublic boolean addIndex(int index, int data) {if(index<0||index>usedSize){throw new IndexEception("下标异常:"+index);}if(index == 0){addFirst(data);return true;}if(index == usedSize){addLast(data);return true;}ListNode cur=head;while(index>0){cur = cur.next;index--;}ListNode node = new ListNode(data);cur.pre.next = node;node.next=cur;node.pre = cur.pre;cur.pre = node;usedSize++;return true;}@Overridepublic boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while(cur != null){if(cur.val == key){return true;}else {cur=cur.next;}}return false;}@Overridepublic void remove(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while(cur != null){if(cur.val == key){if(cur == head){head = head.next;head.pre = null;cur.next = null;}else if(cur == last){last = last.pre;last.next = null;cur.pre = null;}else {cur.pre.next = cur.next;cur.next.pre = cur.pre;}usedSize--;return;}else {cur = cur.next;}}}@Overridepublic void removeAllKey(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while(cur != null){if(cur.val == key){ListNode curNext=cur.next;if(cur == head){head = head.next;head.pre = null;cur.next = null;}else if(cur == last){last = last.pre;last.next = null;cur.pre = null;}else {cur.pre.next = cur.next;cur.next.pre = cur.pre;}usedSize--;cur=curNext;}else {cur = cur.next;}}}@Overridepublic int size() {return usedSize;}@Overridepublic void display() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null){System.out.print(cur.val+" ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}@Overridepublic void clear() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null){ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.pre = null;cur.next = null;cur=curNext;}head = null;last = null;}
}
//下标异常类
public class IndexEception extends RuntimeException{public IndexEception (String massage){super(massage);}
}
五、LinkedList的使用
5.1 什么是LinkedList
LinkedList的底层是双向链表结构,链表没有将元素存储在连续空间中,而是存储在单独的节 点中,通过引用将节点连接起来了,因此在任意位置插入或者删除元素时,不需要搬移元素,效率较高。
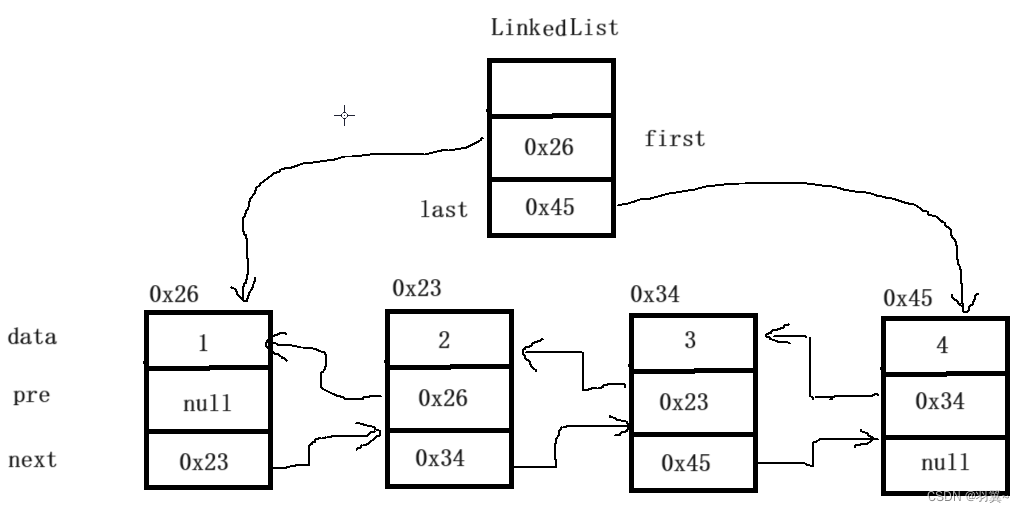
在集合框架中,LinkedList也实现了List接口:
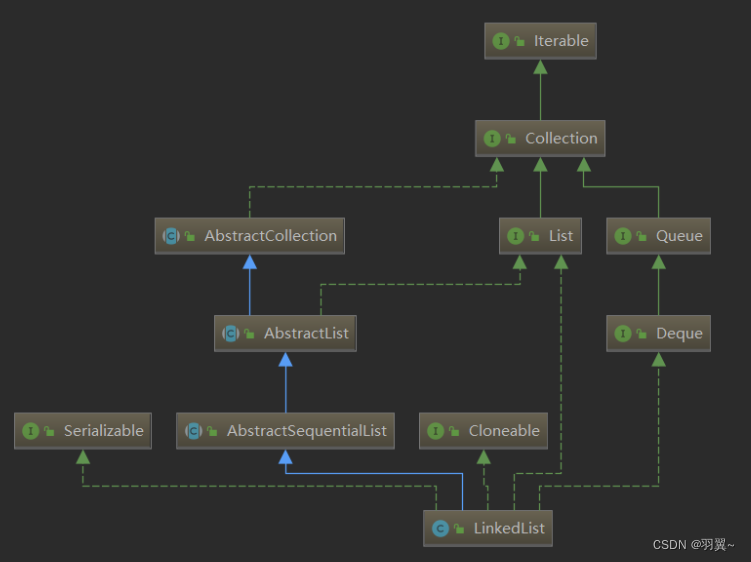
LinkedList实现了List接口,底层使用双向链表;没有实现RandomAccess接口,不支持随机访问;LinkedList在任意位置插入和删除效率较高,时间复杂度为O(1);适合任意位置插入的场景。
5.2 LinkedList的使用
1. LinkedList的构造
| 方法 | 解释 |
| public LinkedList(); | 无参构造 |
| public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) | 使用其他集合容器中元素构造List |
public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();list1.addLast(1);list1.addLast(2);list1.addLast(3);//打印链表for (Integer x:list1) {System.out.print(x+" ");}System.out.println();/*使用list1中的元素构造list2* 其中list1的类型是与list2是同类型或是list2的子类类型* 存储元素的类型保持一致*/LinkedList<Integer> list2 = new LinkedList<>(list1);//打印链表for (Integer x:list2) {System.out.print(x+" ");}System.out.println();
}
2. LinkedList其他常用方法
| 方法 | 解释 |
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 将下标 index 位置 元素设置为 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在链表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf (Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();list.add(1);//尾插list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);list.add(5);System.out.println(list.size()); //5System.out.println(list); //[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]System.out.println("====");list.add(2,10);//在 index 位置插入元素list.addFirst(10);//头插list.addLast(10);//尾插System.out.println(list); //[10, 1, 2, 10, 3, 4, 5, 10]System.out.println("====");list.remove();//默认删除第一个元素System.out.println(list); //[1, 2, 10, 3, 4, 5, 10]list.removeFirst();//删除第一个元素System.out.println(list); //[2, 10, 3, 4, 5, 10]list.removeLast();//删除最后一个元素System.out.println(list); //[2, 10, 3, 4, 5]list.remove(1);//删除index位置的元素System.out.println(list); //[2, 3, 4, 5]System.out.println("====");//contains(elem)判断elem元素是否存在System.out.println(list.contains(5));//true//从前向后找第一个elem出现的位置System.out.println(list.indexOf(3));//从后向前找第一个elem出现的位置System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(4));System.out.println("====");//获取index位置的元素int elem = list.get(0);//set设置index位置的值为elemlist.set(0,100);System.out.println(list); //[100, 3, 4, 5]System.out.println("====");//subList截取部分(左闭右开)并返回,返回值类型为List<E>List<Integer> list2 = list.subList(0,2);System.out.println(list2); //[100, 3]
}
3. LinkedList的遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);list.add(5);//遍历链表//foreach遍历for (int x:list) {System.out.print(x+" ");//1 2 3 4 5}System.out.println();//迭代器遍历ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();while (it.hasNext()){System.out.print(it.next()+" ");//1 2 3 4 5}System.out.println();//反向迭代器遍历ListIterator<Integer> reverseIt = list.listIterator(list.size());while (reverseIt.hasPrevious()){System.out.print(reverseIt.previous()+" ");//5 4 3 2 1 }
}
六、ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
| 不同点 | ArrayList | LinkedList |
| 存储空间上 | 物理上一定连续 | 逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持O(1) | 不支持O(N) |
| 头插 | 需要移动元素,效率低O(N) | 只需修改引用的指向,O(1) |
| 插入 | 空间不够需要扩容 | 没有容量的概念 |
| 应用场景 | 元素高效存储、频繁访问 | 任意位置插入和删除频繁 |
相关文章:

LinkedList与链表
目录 一、Arraylist的缺陷 二、链表 2.1 链表的概念和结构 2.2 链表的实现 三、链表面试题 3.1 删除链表中所有值为val的节点 3.2 反转一个单链表 3.3 链表的中间节点 3.4 将有序链表合并 3.5 输出倒数第k个节点 3.6 链表分割 3.7 链表的回文结构 3.8 找两个链表的公共节…...
纳米软件芯片自动化测试系统测试电源芯片稳压反馈的方法
在一些电源芯片或稳压芯片中,通常内部都会有稳压反馈电路,这些电路可以将输入电压通过内部调整后输出一个稳定的输出电压,以满足电路中的稳定电源需求。也就是说芯片的稳压反馈就是内部稳压反馈电路中的电压。 芯片稳压反馈原理介绍 稳压反馈…...
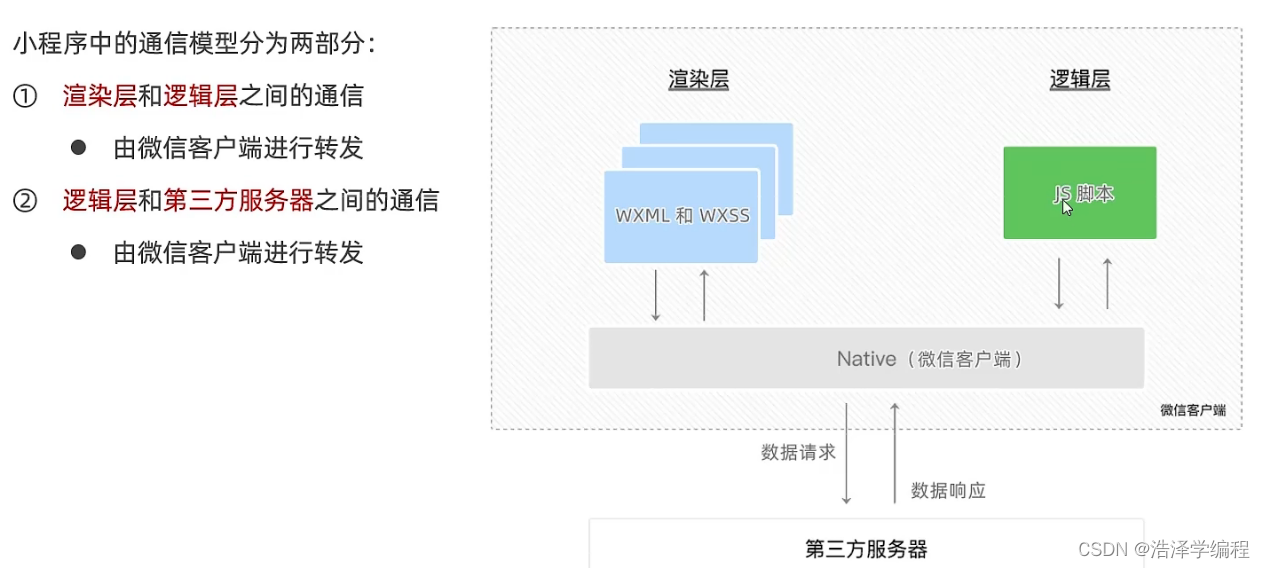
微信小程序之项目基本结构、页面的基础及宿主环境
文章目录 前言一、基本组成结构基本组成小程序页面的组成部分JSON配置文件作用 二、页面基础pagesWXML和HTML的区别WXSS和CSS的区别小程序中js文件分类 三、小程序宿主环境总结 前言 微信小程序的项目基本结构、页面的基础及宿主环境 一、基本组成结构 基本组成 新建一个微信…...

C/C++鸡尾酒疗法 2023年5月电子学会青少年软件编程(C/C++)等级考试一级真题答案解析
目录 C/C鸡尾酒疗法 一、题目要求 1、编程实现 2、输入输出 二、解题思路 1、案例分析 三、程序代码 四、程序说明 五、运行结果 六、考点分析 C/C鸡尾酒疗法 2020年6月 C/C编程等级考试一级编程题 一、题目要求 1、编程实现 鸡尾酒疗法,原指“高效抗…...

人工智能及大模型简介
一、人工智能介绍 人工智能(Artificial Intelligence),英文缩写为AI。它试图赋予机器智能的能力,使它们能够像人类一样思考、学习和做出决策。它的核心要素是数据、模型和算力。 数据是人工智能的基础,数据的质量和…...

基于springboot消防员招录系统
博主主页:猫头鹰源码 博主简介:Java领域优质创作者、CSDN博客专家、公司架构师、全网粉丝5万、专注Java技术领域和毕业设计项目实战 主要内容:毕业设计(Javaweb项目|小程序等)、简历模板、学习资料、面试题库、技术咨询 文末联系获取 项目介绍…...
手把手教你制作登录、注册界面 SpringBoot+Vue.js(cookie的灵活运用,验证码功能)
一、用户登录界面 实现思路:用户在界面输入用户名和密码传入变量。用post方法传输到后端,后端接收整个实体对象。将用户名提取出。在dao层方法中通过select注解查询,返回数据库对应的数据对象。如果返回为空则return false。不为空则通过比对…...
C++ Qt零基础入门进阶与企业级项目实战教程与学习方法分享
Qt是一个卓越的客户端跨平台开发框架,可以在Windows、Linux、macOS进行客户端开发,无缝切换,一统三端;当然除了桌面端,在移动端的早期,Qt也展现了其多才多艺,在Android和ios也可以使用Qt编写app…...

TypeScript学习记录
一、TS开发环境的搭建 1、下载并安装node.js 2、使用npm全局安装typeScript 进入命令行输入:npm i -g typescript 3、创建一个ts文件 4、使用tsc对ts文件进行编译 进入命令行进入ts文件所在目录执行命令:tsc 文件名.ts 二、TS基本变量 1、类型声…...
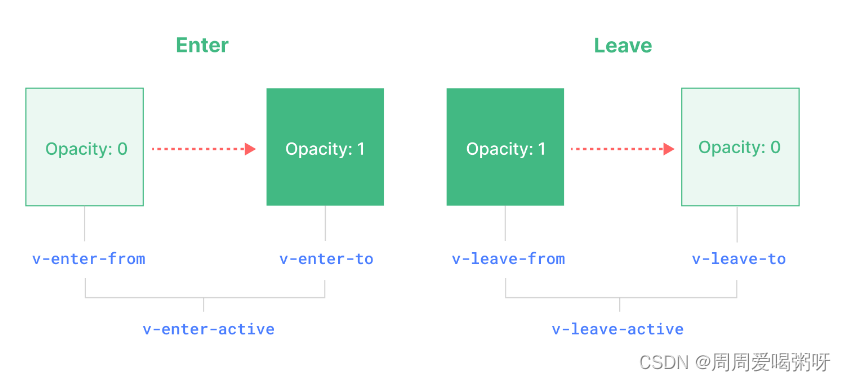
vue内置组件Transition的详解
1. Transition定义 Vue 提供了两个内置组件,可以帮助你制作基于状态变化的过渡和动画: <Transition>会在一个元素或组件进入和离开 DOM 时应用动画。 <TransitionGroup> 会在一个 v-for 列表中的元素或组件被插入,移动࿰…...

中秋节听夜曲,Android OpenGL 呈现周董专属的玉兔主题音乐播放器
概述 前几天发现QQ音乐有个好玩的功能,为用户提供了多种 播放器主题,其中 原神 的主题让我眼前一亮: 当然,诸如 换肤、主题 类的功能已经屡见不鲜,但这类沉浸式播放器的听歌体验确实不错。 见猎心喜,正好…...

008_第一代软件系统架构
第一代软件系统架构 文章目录 第一代软件系统架构项目介绍软件架构和软件构架系统框架硬件组成运行系统基础库软件层 系统架构 关键字: Qt、 Qml、 关键字3、 关键字4、 关键字5 项目介绍 欢迎来到我们的 QML & C 项目!这个项目结合了 QML&…...
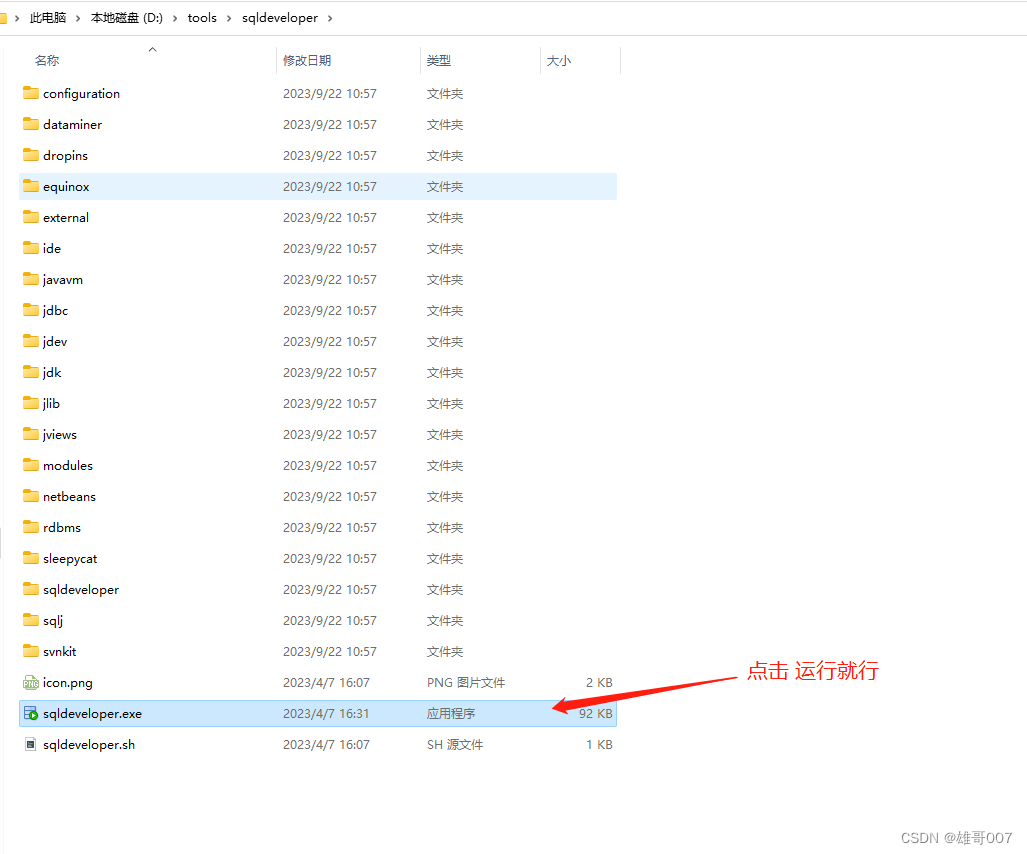
oracle客户端的安装(SQL Developer)
参考资料 软件首页:https://www.oracle.com/database/sqldeveloper/ 官方文档:https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/sql-developer/ 下载地址:https://www.oracle.com/database/sqldeveloper/technologies/download/ 安装指南&#…...

Mysql索引优化1
关闭查询缓存 set global query_cache_size 0; set global query_cache_type 0; force index(索引)where 条件 强制走索引 一般不推荐,因为mysql结构中会通过cost计算出最优sql路线 索引下推 5.6之前 会先从辅助索引表也就是二级索引…...
)
Spring常考知识点(IOC、事务、容器等)
作者:逍遥Sean 简介:一个主修Java的Web网站\游戏服务器后端开发者 主页:https://blog.csdn.net/Ureliable 觉得博主文章不错的话,可以三连支持一下~ 如有需要我的支持,请私信或评论留言! Spring需要理解的问…...

Leetcode 2867. Count Valid Paths in a Tree
Leetcode 2867. Count Valid Paths in a Tree 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:2867. Count Valid Paths in a Tree 1. 解题思路 这一题思路上的话由于要求路径上有且仅有一个质数点,因此,一个直接的思路就是考察所有质数的点作为中心点时…...

Jtti:Ubuntu下如何创建XFS文件系统的LVM
在 Ubuntu 下创建一个 XFS 文件系统的 LVM(Logical Volume Manager)分区需要一系列步骤。以下是详细的步骤: 1. 创建物理卷 (PV) 首先,将要用于 LVM 的硬盘分区(物理卷)初始化为物理卷。假设你有一个硬盘…...

做销售管理分析需要看哪些关键指标?
做销售管理分析需要看哪些关键指标? 销售管理分析时抓取关键指标,有着能够【分析和判断销售趋势、为销售决策提供数据支持、优化销售流程和客户管理】等的好处 在了解了分析关键指标的目的之后,我们就可以根据企业的需求来确定关键指标&…...

【Python】自动完成手写字体图片贴入以及盖章工具
简介 该工具完成了如下功能: 1.将文字转换为手写体填入到模板文件中 2.自动将文字转换为盖章格式填入到模板文件中 3.字体格式可以替换 4.有配置文件进行扩展功能 功能模块 1.界面模块 import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMessageBox, QWid…...
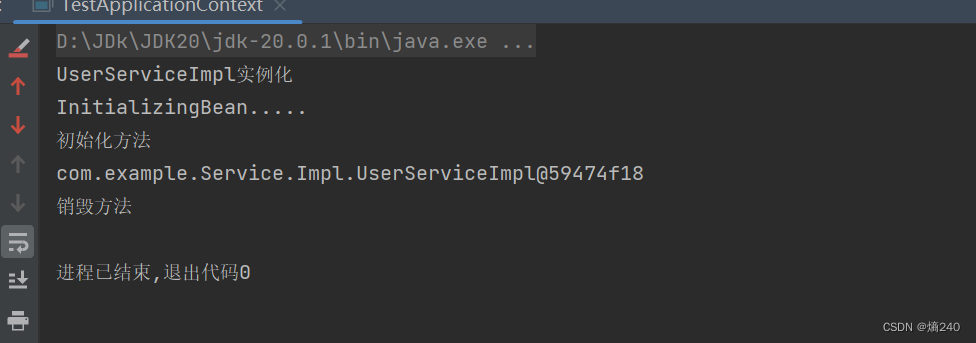
基于Xml方式Bean的配置-初始化方法和销毁方法
SpringBean的配置详解 Bean的初始化和销毁方法配置 Bean在被实例化后,可以执行指定的初始化方法完成一些初始化的操作,Bean在销毁之前也可以执行指定的销毁方法完成一些操作,初始化方法名称和销毁方法名称通过 <bean id"userService…...
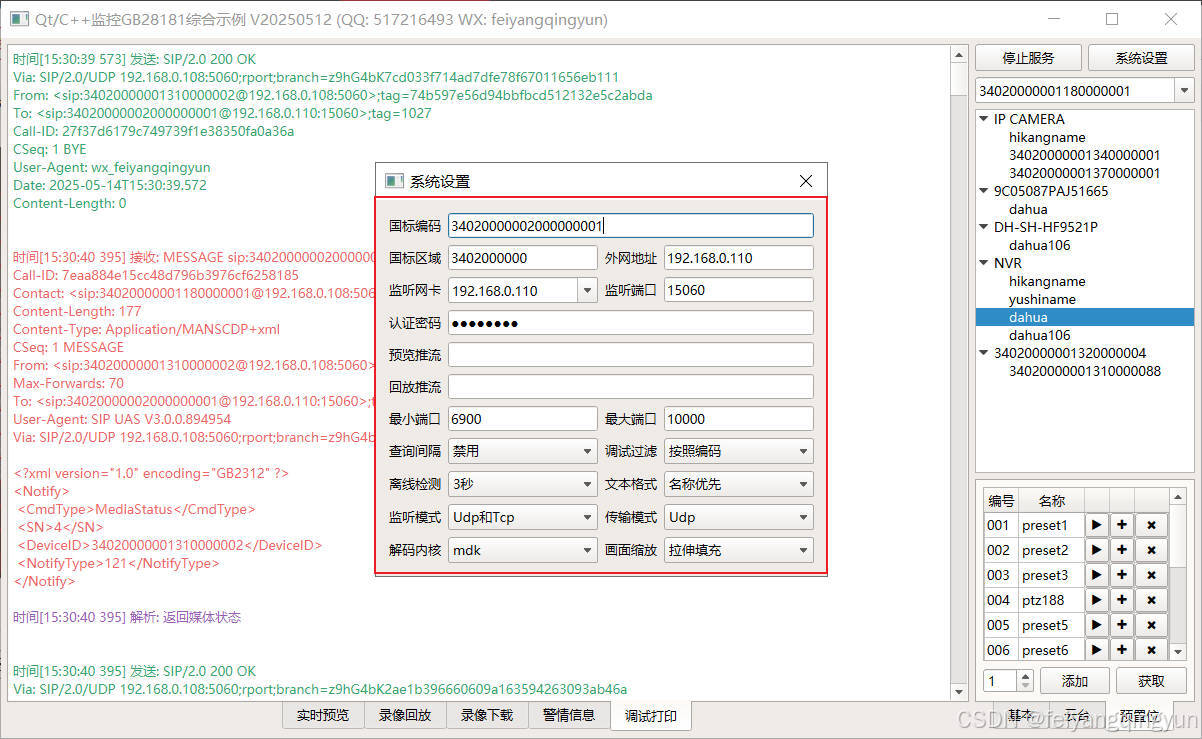
Qt/C++开发监控GB28181系统/取流协议/同时支持udp/tcp被动/tcp主动
一、前言说明 在2011版本的gb28181协议中,拉取视频流只要求udp方式,从2016开始要求新增支持tcp被动和tcp主动两种方式,udp理论上会丢包的,所以实际使用过程可能会出现画面花屏的情况,而tcp肯定不丢包,起码…...
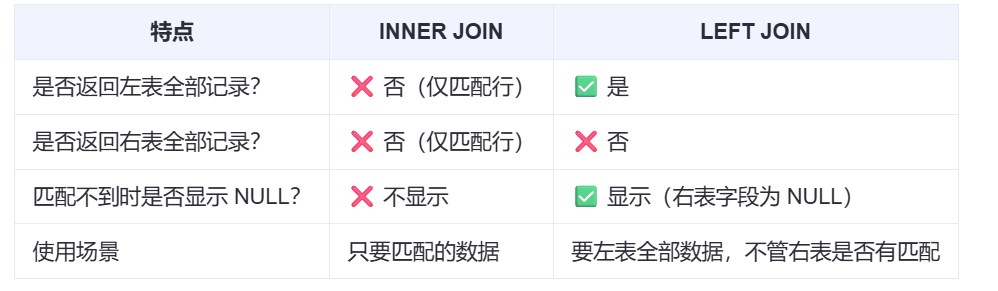
【SQL学习笔记1】增删改查+多表连接全解析(内附SQL免费在线练习工具)
可以使用Sqliteviz这个网站免费编写sql语句,它能够让用户直接在浏览器内练习SQL的语法,不需要安装任何软件。 链接如下: sqliteviz 注意: 在转写SQL语法时,关键字之间有一个特定的顺序,这个顺序会影响到…...

数据链路层的主要功能是什么
数据链路层(OSI模型第2层)的核心功能是在相邻网络节点(如交换机、主机)间提供可靠的数据帧传输服务,主要职责包括: 🔑 核心功能详解: 帧封装与解封装 封装: 将网络层下发…...
Mobile ALOHA全身模仿学习
一、题目 Mobile ALOHA:通过低成本全身远程操作学习双手移动操作 传统模仿学习(Imitation Learning)缺点:聚焦与桌面操作,缺乏通用任务所需的移动性和灵活性 本论文优点:(1)在ALOHA…...
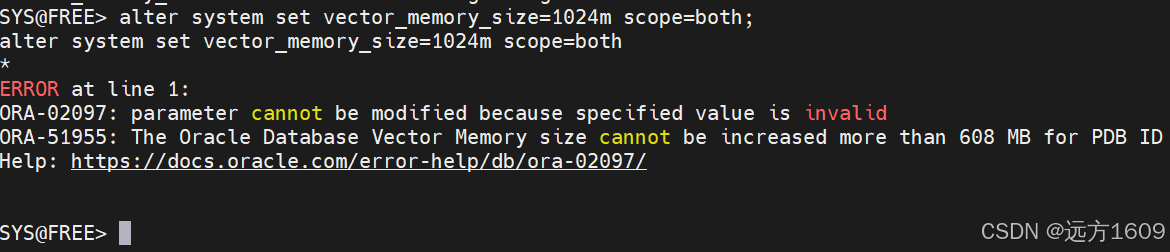
10-Oracle 23 ai Vector Search 概述和参数
一、Oracle AI Vector Search 概述 企业和个人都在尝试各种AI,使用客户端或是内部自己搭建集成大模型的终端,加速与大型语言模型(LLM)的结合,同时使用检索增强生成(Retrieval Augmented Generation &#…...

Python 包管理器 uv 介绍
Python 包管理器 uv 全面介绍 uv 是由 Astral(热门工具 Ruff 的开发者)推出的下一代高性能 Python 包管理器和构建工具,用 Rust 编写。它旨在解决传统工具(如 pip、virtualenv、pip-tools)的性能瓶颈,同时…...

招商蛇口 | 执笔CID,启幕低密生活新境
作为中国城市生长的力量,招商蛇口以“美好生活承载者”为使命,深耕全球111座城市,以央企担当匠造时代理想人居。从深圳湾的开拓基因到西安高新CID的战略落子,招商蛇口始终与城市发展同频共振,以建筑诠释对土地与生活的…...

6.计算机网络核心知识点精要手册
计算机网络核心知识点精要手册 1.协议基础篇 网络协议三要素 语法:数据与控制信息的结构或格式,如同语言中的语法规则语义:控制信息的具体含义和响应方式,规定通信双方"说什么"同步:事件执行的顺序与时序…...

RabbitMQ 各类交换机
为什么要用交换机? 交换机用来路由消息。如果直发队列,这个消息就被处理消失了,那别的队列也需要这个消息怎么办?那就要用到交换机 交换机类型 1,fanout:广播 特点 广播所有消息:将消息…...
多模态学习路线(2)——DL基础系列
目录 前言 一、归一化 1. Layer Normalization (LN) 2. Batch Normalization (BN) 3. Instance Normalization (IN) 4. Group Normalization (GN) 5. Root Mean Square Normalization(RMSNorm) 二、激活函数 1. Sigmoid激活函数(二分类&…...
