Android 高性能列表:RecyclerView + DiffUtil
文章目录
- 背景
- 介绍
- 一般刷新 notifyDataSetChanged()
- 局部刷新
- 实现
- 调用代码
- 准备工作
- 创建 MyDiffUtilCallback 类继承 DiffUtil.Callback 抽象类
- MyAdpter 类代码实现
- 步骤总结
- 通过 log 证实 diffutil 的局部刷新
- diffutil 优化
- 后台线程参考
- 主线程参考
- diff 更新优化后写法
- 相关参考
背景
- 学习记录
- 针对
recyclerview实现的多数据列表展示,进一步优化数据频繁更新时的性能
介绍
Android在Support:v7-24.2.0中,recyclerview支持库开始支持了DiffUtil工具类的使用DiffUtil内部使用Eugene W. Myers’s difference算法:进行两个数据集的对比,找出新数据与旧数据之间最小的变化部分,和RecyclerView一起使用可以实现列表的局部更新
一般刷新 notifyDataSetChanged()
public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyAdapter.ViewHolder> {...// 一般刷新方式public void notifyUpdate(List<CoderBean> mCoderList){this.mCoderList = mCoderList;if (mCoderList == null || mCoderList.size() == 0){this.mCoderList = new ArrayList<>();}notifyDataSetChanged();}
}
主要缺点:
- 粗暴的刷新整个列表的可见区域,这时候就会触发每个
item的视图重绘,当onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position)中的处理逻辑比较复杂,容易出现卡顿
局部刷新
为了进一步优化上面的缺点,recyclerview 提供了局部刷新的方式,如下:
# notifyItemChanged(int)
# notifyItemInserted(int)
# notifyItemRemoved(int)
# notifyItemRangeChanged(int, int)
# notifyItemRangeInserted(int, int)
# notifyItemRangeRemoved(int, int)
上面的几个 recyclerview 提供的局部刷新方法,都只会刷新指定 position 位置的 item,就不会存在一般刷新方式出现的缺点。
但是如果数据量多,且需要更新的 item 也较多,那么这将会需要我们提供较为复杂的局部刷新调用处理逻辑,这无疑是一场灾难。
所以后面 Google 也注意到了这点,后续推出了工具类: DiffUtil ,用来专门计算哪些位置的数据需要进行更新。
实现
调用代码
这里先给出调用的代码,我们来看下相关 api :
public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyAdapter.ViewHolder> {...// diff 更新方式public void diffUpdate(final List<CoderBean> newCoderList){final MyDiffUtilCallback diffUtilCallback = new MyDiffUtilCallback(this.mCoderList, newCoderList);// 获取差异结果(注意这里是耗时操作,如果数据量大的时候需要放到后台线程处理差异,否则会阻塞主线程)final DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(diffUtilCallback);cloneData(newCoderList);// DiffResult 再把差异分发给 Adapter,adapter 最后根据接收到的差异数据做更新diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(MyAdapter.this);}// 拷贝一份数据给到当前数据集 mCoderListprivate void cloneData(List<CoderBean> newCoderList) {this.mCoderList.clear();this.mCoderList.addAll(newCoderList);}
}
- 首先
MyAdapter就是简单的展示数据逻辑:构建itemView、获取数据,绑定数据展示 mCoderList是上一次的数据集,newCoderList是通过参数新传进来的新的数据集- 需要一个
DiffUtil.Callback对象。MyDiffUtilCallback继承了DiffUtil.Callback抽象类
准备工作
- 创建实体类
CoderBean
package com.example.diffutildemo.bean;import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;/*** 搬砖工 实体*/
public class CoderBean implements Parcelable {private int id;private String name;public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic int describeContents() {return 0;}@Overridepublic void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {dest.writeInt(this.id);dest.writeString(this.name);}public CoderBean() {}protected CoderBean(Parcel in) {this.id = in.readInt();this.name = in.readString();}public static final Parcelable.Creator<CoderBean> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<CoderBean>() {@Overridepublic CoderBean createFromParcel(Parcel source) {return new CoderBean(source);}@Overridepublic CoderBean[] newArray(int size) {return new CoderBean[size];}};
}创建 MyDiffUtilCallback 类继承 DiffUtil.Callback 抽象类
代码如下:
package com.example.diffutildemo.callback;import android.text.TextUtils;import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.DiffUtil;import com.example.diffutildemo.bean.CoderBean;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class MyDiffUtilCallback extends DiffUtil.Callback {private List<CoderBean> oldCoderList = new ArrayList<>();private List<CoderBean> newCoderList = new ArrayList<>();// 通过构造传入新旧数据集public MyDiffUtilCallback(List<CoderBean> oldCoderList, List<CoderBean> newCoderList) {this.oldCoderList = oldCoderList;this.newCoderList = newCoderList;}@Overridepublic int getOldListSize() {return oldCoderList == null ? 0 : oldCoderList.size();}@Overridepublic int getNewListSize() {return newCoderList == null ? 0 : newCoderList.size();}@Overridepublic boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {CoderBean oldCoderBean = oldCoderList.get(oldItemPosition);CoderBean newCoderBean = oldCoderList.get(newItemPosition);if (oldCoderBean != null && newCoderBean != null){int oldId = oldCoderList.get(oldItemPosition).getId();int newId = newCoderList.get(newItemPosition).getId();if (oldId == newId){return true;}}return false;}@Overridepublic boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {String oldName = oldCoderList.get(oldItemPosition).getName();String newName = newCoderList.get(newItemPosition).getName();if (TextUtils.isEmpty(oldName) || TextUtils.isEmpty(newName)){return false;}if (oldName.equals(newName)){return true;}return false;}@Nullable@Overridepublic Object getChangePayload(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {System.out.println(":> getChangePayload +++ old: " + oldItemPosition+ ", +++ new: " + newItemPosition);return super.getChangePayload(oldItemPosition, newItemPosition);}
}- public int getOldListSize() :
返回旧列表数据集的数量。
- public int getNewListSize():
返回新列表数据集的数量。
- public boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition):
两个位置的对象是否是同一个 item。一般通过实体类中定义的 id 属性值是否相同来进行判断:返回 true 表示是同一个,反之则不是。
- public boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition):
用来判断新旧 item 的各内容属性值是否相同(自己实现,也相对简单)。
只有当 areItemsTheSame() 返回 true 时才会触发调用:返回 true
表示是相同的各属性内容,反之则存在属性内容的变化。
- public Object getChangePayload(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition):
当 areItemsTheSame() 返回 true ,并且 areContentsTheSame() 返回 false 时触发调用。
这里可以自己实现返回差异数据,会从 DiffResult 分发给 notifyItemRangeChanged(position,
count, payload) 方法,最终交给 Adapter 的 onBindViewHolder(… List< Object >
payloads) 处理。
MyAdpter 类代码实现
package com.example.diffutildemo.adatper;import android.content.Context;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.DiffUtil;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;import com.example.diffutildemo.R;
import com.example.diffutildemo.bean.CoderBean;
import com.example.diffutildemo.callback.MyDiffUtilCallback;
import com.example.diffutildemo.executor.DiffMainThreadExecutor;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyAdapter.ViewHolder> {private List<CoderBean> mCoderList = new ArrayList<>();private LayoutInflater inflater;private ViewHolder holder;private Context context;public MyAdapter(Context context, List<CoderBean> mCoderList) {this.mCoderList = mCoderList;this.context = context;this.inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);}@NonNull@Overridepublic ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {System.out.println(":> onCreateViewHolder +++ ");View itemView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.recyclerview_itemview_coder, parent, false);holder = new ViewHolder(itemView);return holder;}@Overridepublic void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position) {System.out.println(":> onBindViewHolder +++ " + position);String name = mCoderList.get(position).getName();holder.tv_coder.setText(name);}@Overridepublic void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull ViewHolder holder, int position, @NonNull List<Object> payloads) {
// System.out.println(":> onBindViewHolder +++ payloads");super.onBindViewHolder(holder, position, payloads);}@Overridepublic int getItemCount() {return (mCoderList == null) ? 0 : mCoderList.size();}public class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {TextView tv_coder;public ViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {super(itemView);tv_coder = itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_coder);}}@Overridepublic int getItemViewType(int position) {return super.getItemViewType(position);}// 一般刷新方式public void notifyUpdate(List<CoderBean> mCoderList){this.mCoderList = mCoderList;if (mCoderList == null || mCoderList.size() == 0){this.mCoderList = new ArrayList<>();}notifyDataSetChanged();}// diff 更新方式public void diffUpdate(final List<CoderBean> newCoderList){final MyDiffUtilCallback diffUtilCallback = new MyDiffUtilCallback(this.mCoderList, newCoderList);// 获取差异结果(注意这里是耗时操作,如果数据量大的时候需要放到后台线程处理差异,否则会阻塞主线程)final DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(diffUtilCallback);cloneData(newCoderList);// DiffResult 再把差异分发给 Adapter,adapter 最后根据接收到的差异数据做更新diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(MyAdapter.this);}private void cloneData(List<CoderBean> newCoderList) {this.mCoderList.clear();this.mCoderList.addAll(newCoderList);}}- 代码简单,不过多说明。
步骤总结
所以使用 DiffUtil 工具类进行局部刷新可以简单分为下面几步:
- 自实现
DiffUtil.callback - 计算得到
DiffResult
final DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(diffUtilCallback);
- 将
DiffResult分发给Adapter进行局部更新
cloneData(newCoderList);
// DiffResult 再把差异分发给 Adapter,adapter 最后根据接收到的差异数据做更新
diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(MyAdapter.this);
计算出 DiffResult 后,咱们必须要将新数据设置给 Adapter,然后才能调用DiffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(Adapter) 刷新ui
private void cloneData(List<CoderBean> newCoderList) {this.mCoderList.clear();this.mCoderList.addAll(newCoderList);
}
通过 log 证实 diffutil 的局部刷新
原始数据初始化代码:
private void initData() {coderList.clear();for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){CoderBean bean = new CoderBean();bean.setId(i);bean.setName("原始数据 coder +00" + i);coderList.add(bean);}}
一般更新模拟设置数据代码:
// 一般更新数据模拟,前两个数据保持不变private List<CoderBean> getNewData(){List<CoderBean> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){CoderBean bean = new CoderBean();bean.setId(i);bean.setName("一般更新 coder +00" + i);if (i < 2){bean.setName("原始数据 coder +00" + i);}list.add(bean);}return list;}
diff 更新模拟设置数据代码:
// diff 更新模拟设置数据 前两个数据保持不变private List<CoderBean> getNewDiffData(){List<CoderBean> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){CoderBean bean = new CoderBean();bean.setId(i);bean.setName("Diff更新 coder +00" + i);if (i < 2){bean.setName("原始数据 coder +00" + i);}list.add(bean);}return list;}
一般更新调用测试:
// 一般更新btn_update.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View v) {if (adapter != null){adapter.notifyUpdate(getNewData());}}});
日志打印如下:
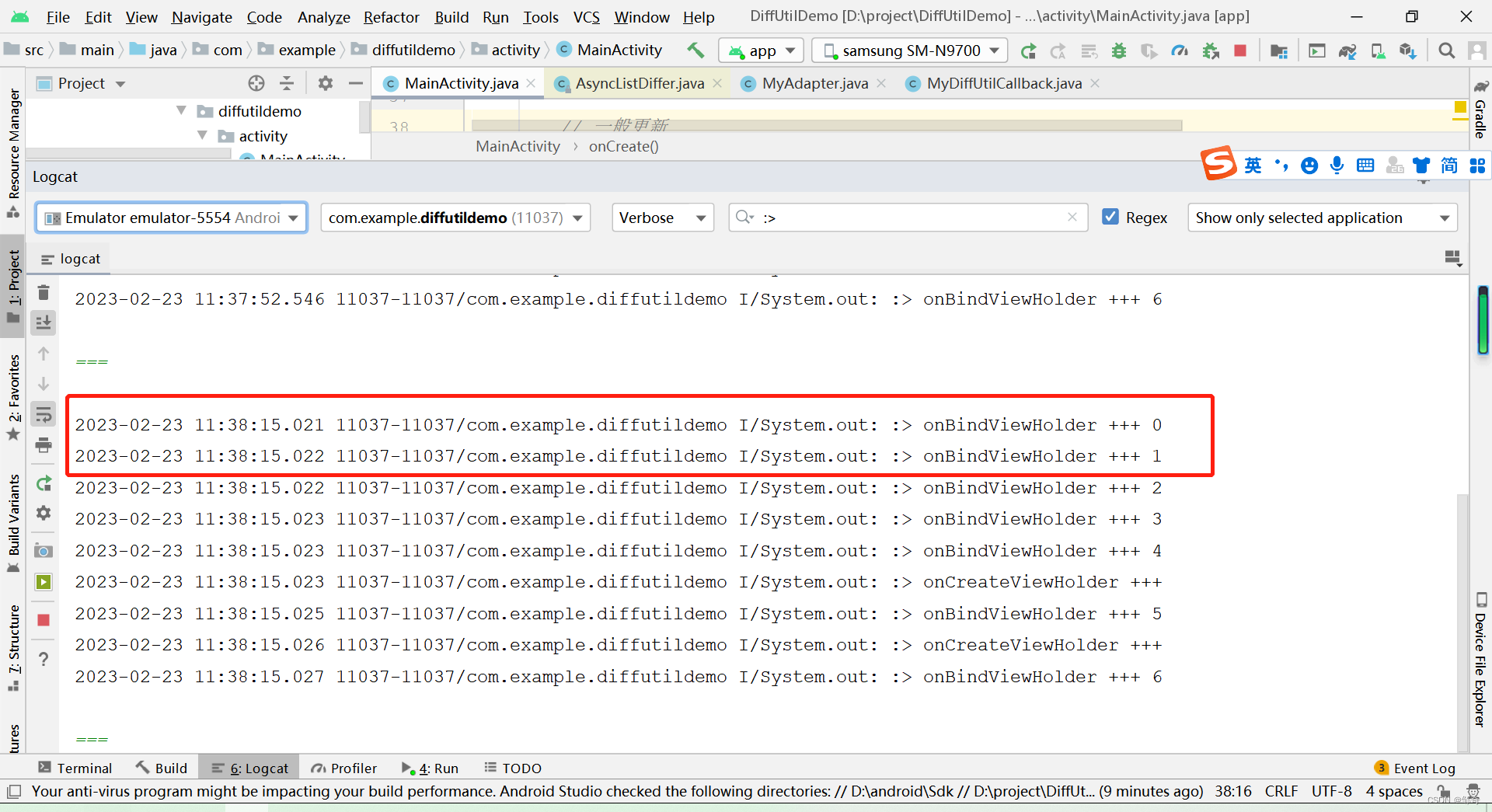
上图可知:即使前两个 item 的数据一样,一般更新也会重新绘制前两个 itemview 的视图。
diff 更新调用测试:
// diff 更新btn_update_diff.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View v) {if (adapter != null){adapter.diffUpdate(getNewDiffData());}}});
日志打印如下:
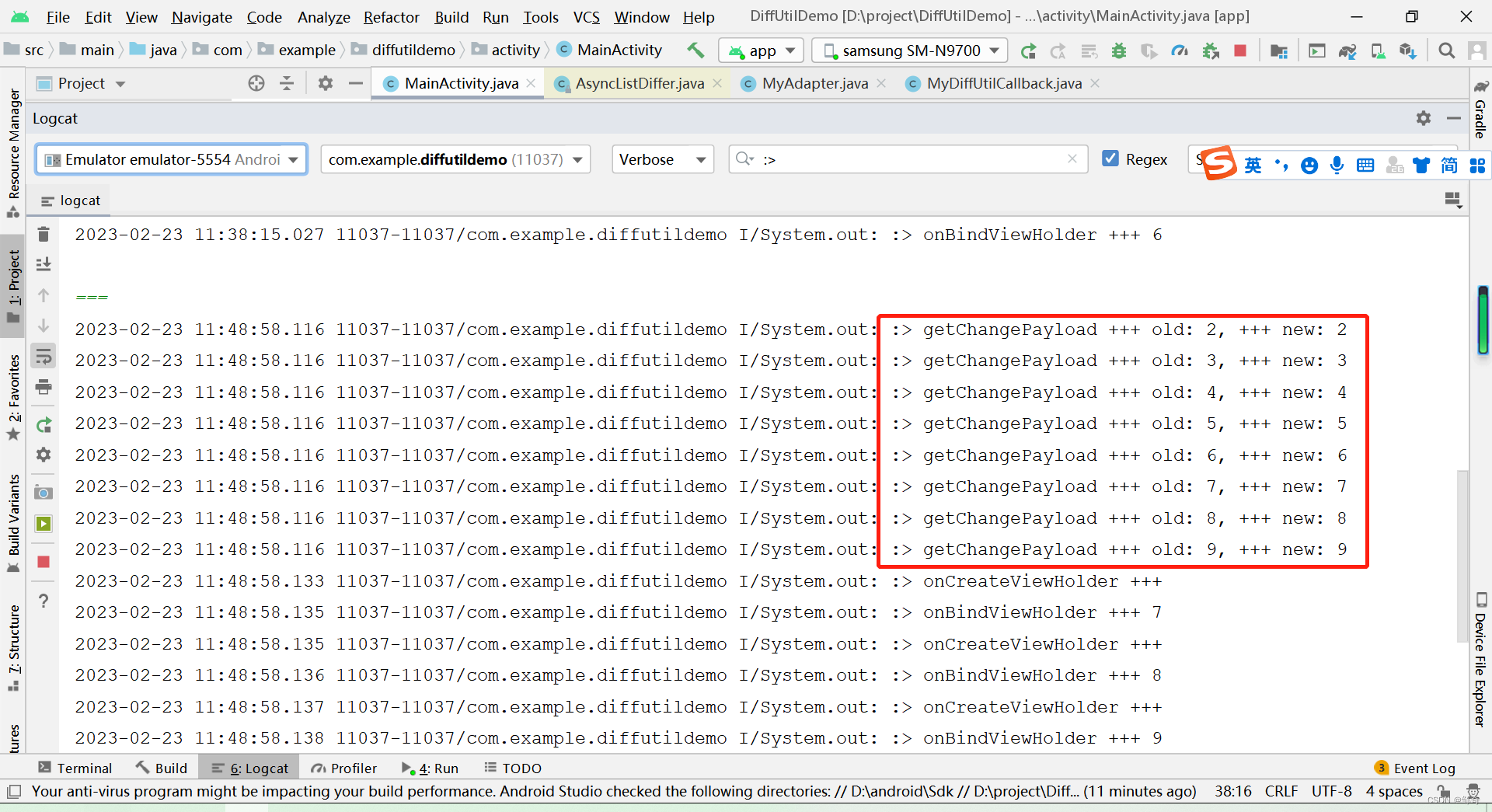
完整打印如下:
2023-02-23 11:48:58.116 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> getChangePayload +++ old: 2, +++ new: 2
2023-02-23 11:48:58.116 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> getChangePayload +++ old: 3, +++ new: 3
2023-02-23 11:48:58.116 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> getChangePayload +++ old: 4, +++ new: 4
2023-02-23 11:48:58.116 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> getChangePayload +++ old: 5, +++ new: 5
2023-02-23 11:48:58.116 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> getChangePayload +++ old: 6, +++ new: 6
2023-02-23 11:48:58.116 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> getChangePayload +++ old: 7, +++ new: 7
2023-02-23 11:48:58.116 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> getChangePayload +++ old: 8, +++ new: 8
2023-02-23 11:48:58.116 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> getChangePayload +++ old: 9, +++ new: 9
2023-02-23 11:48:58.133 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onCreateViewHolder +++
2023-02-23 11:48:58.135 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onBindViewHolder +++ 7
2023-02-23 11:48:58.135 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onCreateViewHolder +++
2023-02-23 11:48:58.136 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onBindViewHolder +++ 8
2023-02-23 11:48:58.137 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onCreateViewHolder +++
2023-02-23 11:48:58.138 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onBindViewHolder +++ 9
2023-02-23 11:48:58.138 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onCreateViewHolder +++
2023-02-23 11:48:58.140 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onBindViewHolder +++ 2
2023-02-23 11:48:58.140 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onCreateViewHolder +++
2023-02-23 11:48:58.142 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onBindViewHolder +++ 3
2023-02-23 11:48:58.142 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onCreateViewHolder +++
2023-02-23 11:48:58.142 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onBindViewHolder +++ 4
2023-02-23 11:48:58.143 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onCreateViewHolder +++
2023-02-23 11:48:58.144 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onBindViewHolder +++ 5
2023-02-23 11:48:58.144 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onCreateViewHolder +++
2023-02-23 11:48:58.145 11037-11037/com.example.diffutildemo I/System.out: :> onBindViewHolder +++ 6
由上面日志打印可知,前两个位置的 item 的视图没有重新绘制,也就是说明做到了局部刷新。
相比 notifyDataSetChanged(),性能大有提高。
如果在 Adapter 的 onBindViewHolder(… List< Object > payloads)
中进一步判断,可以做到进一步优化,只改变控件的内容,不用进行重绘,这里就不展开细讲了。
diffutil 优化
- 如果列表很大,
DiffUtil的计算操作会花费很多时间。所以官方建议在后台线程计算差异,在主线程应用计算结果DiffResult。
Google 当然也考虑到了这个问题,后面推出了 AsyncListDiffer工具类。所以我们来看下这个工具类的源码实现,然后自己参考进行优化即可。
后台线程参考
AsyncListDiffer.java 这个工具类的源码,大家根据自己依赖的库找就行。
找到 public void submitList(@Nullable final List<T> newList, @Nullable final Runnable commitCallback) 这个方法的实现,如下:
/*** Pass a new List to the AdapterHelper. Adapter updates will be computed on a background* thread.* <p>* If a List is already present, a diff will be computed asynchronously on a background thread.* When the diff is computed, it will be applied (dispatched to the {@link ListUpdateCallback}),* and the new List will be swapped in.* <p>* The commit callback can be used to know when the List is committed, but note that it* may not be executed. If List B is submitted immediately after List A, and is* committed directly, the callback associated with List A will not be run.** @param newList The new List.* @param commitCallback Optional runnable that is executed when the List is committed, if* it is committed.*/@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")public void submitList(@Nullable final List<T> newList,@Nullable final Runnable commitCallback) {// incrementing generation means any currently-running diffs are discarded when they finishfinal int runGeneration = ++mMaxScheduledGeneration;if (newList == mList) {// nothing to do (Note - still had to inc generation, since may have ongoing work)if (commitCallback != null) {commitCallback.run();}return;}final List<T> previousList = mReadOnlyList;// fast simple remove allif (newList == null) {//noinspection ConstantConditionsint countRemoved = mList.size();mList = null;mReadOnlyList = Collections.emptyList();// notify last, after list is updatedmUpdateCallback.onRemoved(0, countRemoved);onCurrentListChanged(previousList, commitCallback);return;}// fast simple first insertif (mList == null) {mList = newList;mReadOnlyList = Collections.unmodifiableList(newList);// notify last, after list is updatedmUpdateCallback.onInserted(0, newList.size());onCurrentListChanged(previousList, commitCallback);return;}final List<T> oldList = mList;mConfig.getBackgroundThreadExecutor().execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {final DiffUtil.DiffResult result = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(new DiffUtil.Callback() {@Overridepublic int getOldListSize() {return oldList.size();}@Overridepublic int getNewListSize() {return newList.size();}@Overridepublic boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {T oldItem = oldList.get(oldItemPosition);T newItem = newList.get(newItemPosition);if (oldItem != null && newItem != null) {return mConfig.getDiffCallback().areItemsTheSame(oldItem, newItem);}// If both items are null we consider them the same.return oldItem == null && newItem == null;}@Overridepublic boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {T oldItem = oldList.get(oldItemPosition);T newItem = newList.get(newItemPosition);if (oldItem != null && newItem != null) {return mConfig.getDiffCallback().areContentsTheSame(oldItem, newItem);}if (oldItem == null && newItem == null) {return true;}// There is an implementation bug if we reach this point. Per the docs, this// method should only be invoked when areItemsTheSame returns true. That// only occurs when both items are non-null or both are null and both of// those cases are handled above.throw new AssertionError();}@Nullable@Overridepublic Object getChangePayload(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {T oldItem = oldList.get(oldItemPosition);T newItem = newList.get(newItemPosition);if (oldItem != null && newItem != null) {return mConfig.getDiffCallback().getChangePayload(oldItem, newItem);}// There is an implementation bug if we reach this point. Per the docs, this// method should only be invoked when areItemsTheSame returns true AND// areContentsTheSame returns false. That only occurs when both items are// non-null which is the only case handled above.throw new AssertionError();}});mMainThreadExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {if (mMaxScheduledGeneration == runGeneration) {latchList(newList, result, commitCallback);}}});}});}
定位到 mConfig.getBackgroundThreadExecutor() 这个地方:
public final class AsyncDifferConfig<T> {...@NonNullprivate final Executor mBackgroundThreadExecutor;@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")@NonNullpublic Executor getBackgroundThreadExecutor() {return mBackgroundThreadExecutor;}
}然后我们再继续在 AsyncDifferConfig.java 中找 mBackgroundThreadExecutor 是怎么创建的。
最后定位到 public AsyncDifferConfig<T> build() 这个方法,如下:
public final class AsyncDifferConfig<T> {...@NonNullprivate final Executor mBackgroundThreadExecutor;/*** Creates a {@link AsyncListDiffer} with the given parameters.** @return A new AsyncDifferConfig.*/@NonNullpublic AsyncDifferConfig<T> build() {if (mBackgroundThreadExecutor == null) {synchronized (sExecutorLock) {if (sDiffExecutor == null) {sDiffExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);}}mBackgroundThreadExecutor = sDiffExecutor;}return new AsyncDifferConfig<>(mMainThreadExecutor,mBackgroundThreadExecutor,mDiffCallback);}
}
到这里就找到后台线程的创建方式了,如下:
sDiffExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
mBackgroundThreadExecutor = sDiffExecutor;
使用如下:
Executor background = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);background.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {// 计算差异的耗时操作放到这里执行}});
后面我们就可以将计算差异的耗时操作放到后台线程中进行。
主线程参考
主线程 mMainThreadExecutor 的创建位于 AsyncListDiffer.java 中,如下:
public class AsyncListDiffer<T> {...Executor mMainThreadExecutor;private static class MainThreadExecutor implements Executor {final Handler mHandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());MainThreadExecutor() {}@Overridepublic void execute(@NonNull Runnable command) {mHandler.post(command);}}// TODO: use MainThreadExecutor from supportlib once one existsprivate static final Executor sMainThreadExecutor = new MainThreadExecutor();/*** Create a AsyncListDiffer with the provided config, and ListUpdateCallback to dispatch* updates to.** @param listUpdateCallback Callback to dispatch updates to.* @param config Config to define background work Executor, and DiffUtil.ItemCallback for* computing List diffs.** @see DiffUtil.DiffResult#dispatchUpdatesTo(RecyclerView.Adapter)*/@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")public AsyncListDiffer(@NonNull ListUpdateCallback listUpdateCallback,@NonNull AsyncDifferConfig<T> config) {mUpdateCallback = listUpdateCallback;mConfig = config;if (config.getMainThreadExecutor() != null) {mMainThreadExecutor = config.getMainThreadExecutor();} else {mMainThreadExecutor = sMainThreadExecutor;}}public void submitList(@Nullable final List<T> newList,@Nullable final Runnable commitCallback) {...mConfig.getBackgroundThreadExecutor().execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {...mMainThreadExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {if (mMaxScheduledGeneration == runGeneration) {latchList(newList, result, commitCallback);}}});}});}}
可以看到如果 config 获取不到主线程对象时,会用默认的 sMainThreadExecutor,如下:
if (config.getMainThreadExecutor() != null) {mMainThreadExecutor = config.getMainThreadExecutor();} else {mMainThreadExecutor = sMainThreadExecutor;}
这里就找到了源码中主线程的创建方式,我们可以用来参考。如下:
private static class MainThreadExecutor implements Executor {final Handler mHandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());MainThreadExecutor() {}@Overridepublic void execute(@NonNull Runnable command) {mHandler.post(command);}}
使用如下:
new MainThreadExecutor().execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {// 这里执行主线程刷新操作}});
diff 更新优化后写法
public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyAdapter.ViewHolder> {...// diff 更新方式 优化public void diffUpdate(final List<CoderBean> newCoderList){final MyDiffUtilCallback diffUtilCallback = new MyDiffUtilCallback(this.mCoderList, newCoderList);// 获取差异结果(注意这里是耗时操作,如果数据量大的时候需要放到后台线程处理差异,否则会阻塞主线程)Executor background = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);background.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {final DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(diffUtilCallback);new DiffMainThreadExecutor().execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {cloneData(newCoderList);// DiffResult 再把差异分发给 Adapter,adapter 最后根据接收到的差异数据做更新diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(MyAdapter.this);}});}});}}
DiffMainThreadExecutor.java 如下:
package com.example.diffutildemo.executor;import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Looper;import java.util.concurrent.Executor;public class DiffMainThreadExecutor implements Executor {private final Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());public DiffMainThreadExecutor(){}@Overridepublic void execute(Runnable command) {try {handler.post(command);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}到这里就完成了对 DiffUtil 的一个使用与说明,更多还是需要同学们自己在实际中多实践应用,最后希望 DiffUtil 带给同学们一个更流畅的数据展示效果。
相关参考
Android高性能列表:RecyclerView + DiffUtil
AsyncListDiffer-RecyclerView最好的伙伴
技术永不眠!下期见!
相关文章:

Android 高性能列表:RecyclerView + DiffUtil
文章目录背景介绍一般刷新 notifyDataSetChanged()局部刷新实现调用代码准备工作创建 MyDiffUtilCallback 类继承 DiffUtil.Callback 抽象类MyAdpter 类代码实现步骤总结通过 log 证实 diffutil 的局部刷新diffutil 优化后台线程参考主线程参考diff 更新优化后写法相关参考背景…...

为什么派生类的构造函数必须在初始化列表中调用基类的构造函数
调用派生类的构造函数时,可能会调用继承自基类的函数,也就可能会用到基类的数据成员,因此,调用派生类的构造函数时,必须确保继承自基类的数据成员已构造完毕,而将基类构造函数的调用写在初始化列表中&#…...
2023年2月初某企业网络工程师面试题【建议收藏】
拓扑图如下,主机A与主机B能互相通信,但是A不能ping通RA的F0接口,这是为什么?RA上f0接口上配置了ACL,禁止源ip为主机A,目的ip为RA f0的数据包的发送; 第一个路由器上只有到主机B网段的路由&#…...
单点登录)
分布式下(sso)单点登录
目录标题一、基于rediscookie的单点登录二、基于jwtcookie的单点登录一、基于rediscookie的单点登录 传统单机应用登录 传统单机应用,一般是结合session和cookie实现认证、授权。用户通过输入账号密码登录系统,登录成功后在系统创建一个session来保存用…...

PMP真的有那么厉害?你需要考PMP吗?
这个含金量是有的,是目前项目管理界含金量较高的证书,但也要分人, 因为这是职业证书,主要用于提高职场工作能力,不搞这一行的,PMP证书含金量再高也是一张废纸,可以看下下面这张图,这…...

高通平台开发系列讲解(WIFI篇)802.11 基本概念
文章目录 一、WLAN概述二、802.11发展历程三、802.11基本概念沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄 📢本文将基于高通平台介绍802.11基本概念。 一、WLAN概述 WLAN是Wireless Local Area Network的简称,指应用无线通信技术将计算机设备互联起来,构成可以互相通…...

扬帆优配|反弹涨超70%,昨收三连板,稀土行业或迎大事件
本年第一批稀土挖掘锻炼目标行将发放。 2月22日晚,东易日盛公告称,公司收到董事、副总经理兼财务总监李双侠出具的《关于未严格执行股份减持方案的致歉函》,其此次减持方案已施行结束,但在施行减持方案时,因操作失误&a…...
 | 机试题+算法思路+考点+代码解析 【2023】)
华为OD机试 - 工号不够用了(Java) | 机试题+算法思路+考点+代码解析 【2023】
工号不够用了 3020年,空间通信集团的员工人数突破20亿人,即将遇到现有工号不够用的窘境。 现在,请你负责调研新工号系统。继承历史传统,新的工号系统由小写英文字母(a-z)和数字(0-9)两部分构成。新工号由一段英文字母开头,之后跟随一段数字,比如"aaahw0001&qu…...

Python学习-----lambda式匿名函数
目录 前言: 1.什么是lambda函数 2.使用示例 (1)示例1:与def对比 (2)示例2:与三目运算符 (3)示例3:lambda作为参数传入其他函数 (4ÿ…...
)
华为OD机试真题Python实现【求解连续数列】真题+解题思路+代码(20222023)
求解连续数列 题目 已知连续正整数数列{K}=K1,K2,K3… Ki的各个数相加之和为S, i = N (0 < S < 100000, 0 < N < 100000), 求此数列K。 🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥👉👉👉👉👉👉 华为OD机试(Python)真题目录汇总 ## 输入 输入包含两个参数 连续正整数数…...

每日学术速递2.22
CV - 计算机视觉 | ML - 机器学习 | RL - 强化学习 | NLP 自然语言处理 Subjects: cs.CV 1.PriSTI: A Conditional Diffusion Framework for Spatiotemporal Imputation 标题:PriSTI:时空插补的条件扩散框架 作者:Mingzhe Liu, Han Huan…...
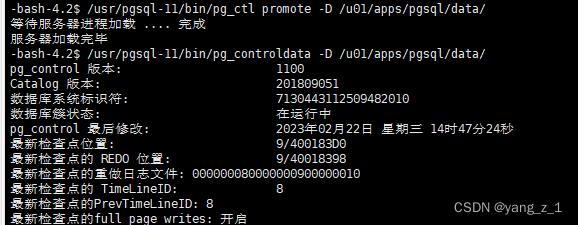
postgresql 数据库 主从切换 测试
postgresql 数据库 主从切换 测试 文章目录postgresql 数据库 主从切换 测试前言环境:主从切换1. 查看数据库状态:2. 备库切换主库3. 旧主库切换成备库;4 查看状态后记前言 因数据库等保需要,需要对老系统的数据库进行主从切换来…...
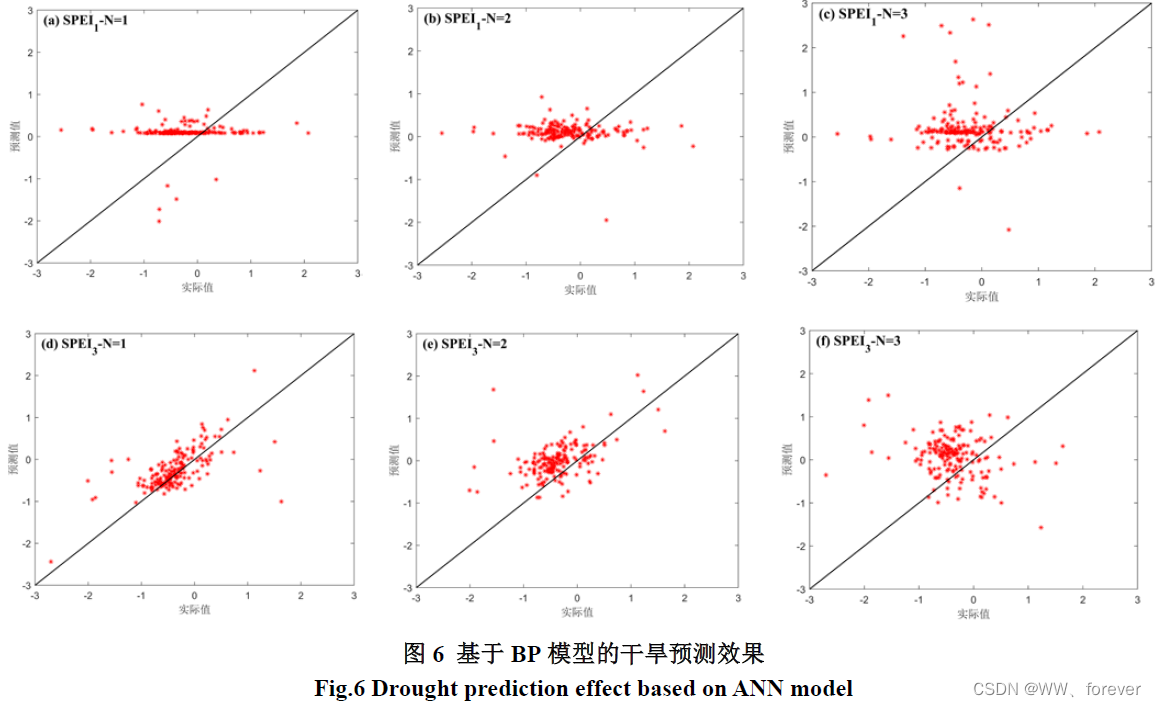
干旱预测方法总结及基于人工神经网络的干旱预测案例分析(MATLAB全代码)
本案例采用SPEI干旱指数,构建ANN和BP神经网络预测模型,并开展1~3个月预见期的干旱预测,对比分析干旱预测模型的适用性,为流域干旱预警和管理提供技术依据。 干旱预测 1 干旱预测方法 1.1 统计学干旱预测 根据历史降水或气温等…...
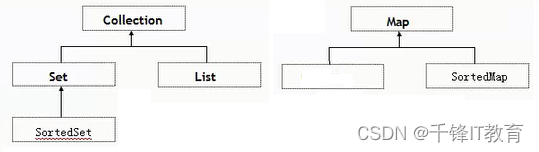
一篇文章弄清楚啥是数组和集合
数组和集合多语言都有,数组是集合的一种,是一种有序的集合,不面向对象,面向过程的也有。1.数组逻辑结构:线性的物理结构:顺序的存储结构申请内存:一次申请一大段连续的空间,一旦申请…...
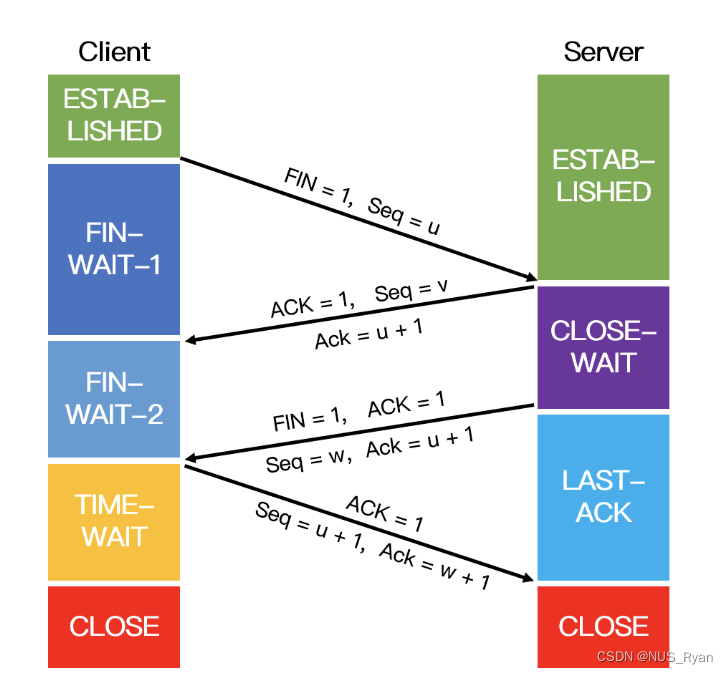
计算机网络(五):三次握手和四次挥手,TCP,UDP,TIME-WAIT,CLOSE-WAIT,拥塞避免,
文章目录零. TCP和UDP的区别以及TCP详解TCP是如何保证可靠性的TCP超时重传的原理TCP最大连接数限制TCP流量控制和拥塞控制流量控制拥塞控制TCP粘包问题一、三次握手和四次挥手二、为什么要进行三次握手?两次握手可以吗?三、为什么要进行四次挥手…...

【数据结构】二叉树(C语言实现)
文章目录一、树的概念及结构1.树的概念2.树的相关概念名词3.树的表示4.树在实际中的运用二、二叉树概念及结构1.二叉树的概念2.特殊的二叉树3.二叉树的性质4.二叉树的存储结构三、二叉树链式结构的实现1.结构的定义2.构建二叉树3.二叉树前序遍历4.二叉树中序遍历5.二叉树后序遍…...
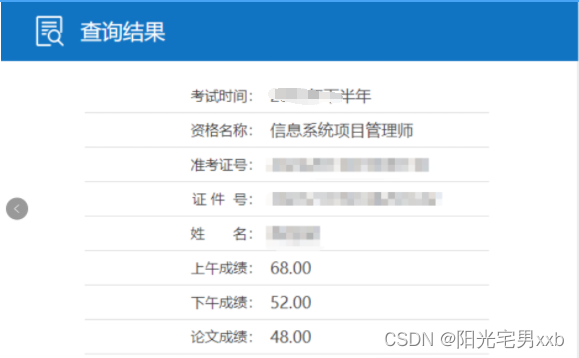
高级信息系统项目管理(高项 软考)原创论文——成本管理(2)
1、如果您想了解如何高分通过高级信息系统项目管理师(高项)你可以点击链接: 高级信息系统项目管理师(高项)高分通过经验分享_高项经验 2、如果您想了解更多的高级信息系统项目管理(高项 软考)原创论文,您可以点击链接:...

代码签名即将迎来一波新关注
在数字化高度发展的当下,个人隐私及信息安全保护已经成了大家关注的重点,包括日常使用的电脑软件,手机APP等,由于包含了大量的用户信息,已经成了重点关注对象,任何一个疏忽就可能泄露大量用户信息。所以权威…...

黑盒渗透盲打lampiao
一、查找主机ip,通过Nmap扫描工具排查出我的靶机的IP 为.134 python tools.py ip -i 192.168.12.0 -h 254 -l 1 二、扫描其他端口。 1898 三、查看网站漏洞情况,典型的漏洞特征 Ac扫描漏洞情况,利用典型的漏洞。 四、开始getshell 1、启动M…...
)
笔记:VLAN及交换机处理详细教程(Tagged, UnTagged and Native VLANS Tutorial)
一、内容来源 本文是对下面这篇文章的总结,写的很全、很细致、干货满满,强力推荐: 《Tagged, UnTagged and Native VLANS Tutorial – A Quick Guide about What they Are?》 二、为什么引入VLAN? 早期设备间通过集线器&#x…...
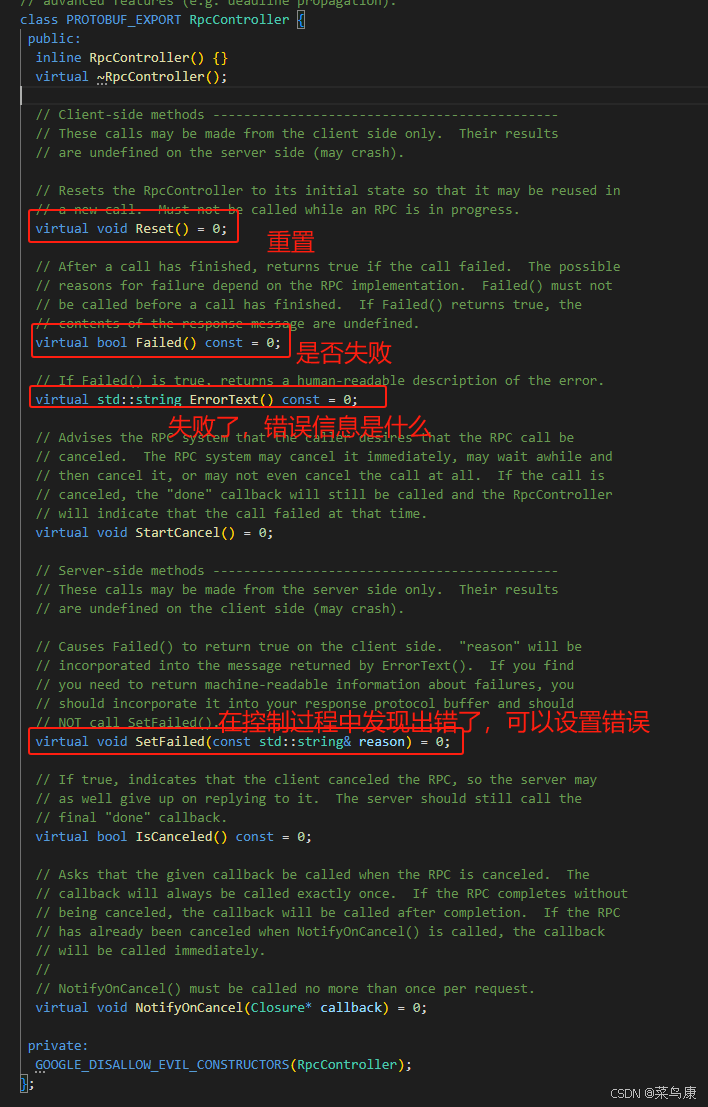
C++实现分布式网络通信框架RPC(3)--rpc调用端
目录 一、前言 二、UserServiceRpc_Stub 三、 CallMethod方法的重写 头文件 实现 四、rpc调用端的调用 实现 五、 google::protobuf::RpcController *controller 头文件 实现 六、总结 一、前言 在前边的文章中,我们已经大致实现了rpc服务端的各项功能代…...

从WWDC看苹果产品发展的规律
WWDC 是苹果公司一年一度面向全球开发者的盛会,其主题演讲展现了苹果在产品设计、技术路线、用户体验和生态系统构建上的核心理念与演进脉络。我们借助 ChatGPT Deep Research 工具,对过去十年 WWDC 主题演讲内容进行了系统化分析,形成了这份…...
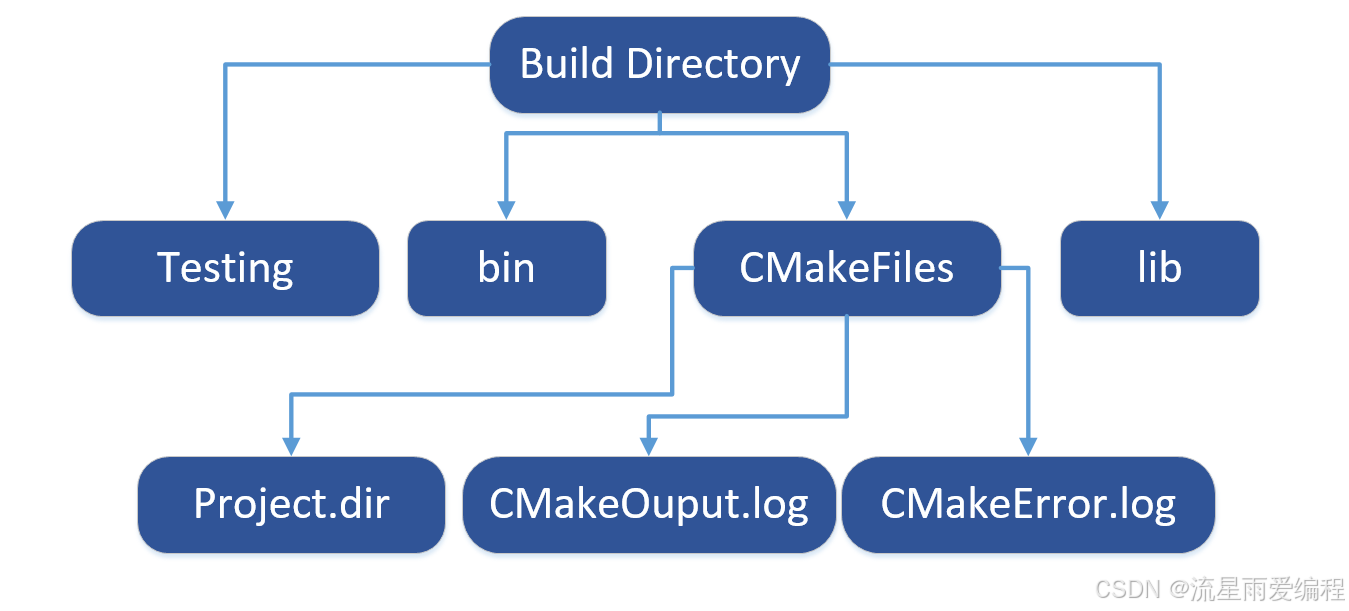
CMake基础:构建流程详解
目录 1.CMake构建过程的基本流程 2.CMake构建的具体步骤 2.1.创建构建目录 2.2.使用 CMake 生成构建文件 2.3.编译和构建 2.4.清理构建文件 2.5.重新配置和构建 3.跨平台构建示例 4.工具链与交叉编译 5.CMake构建后的项目结构解析 5.1.CMake构建后的目录结构 5.2.构…...
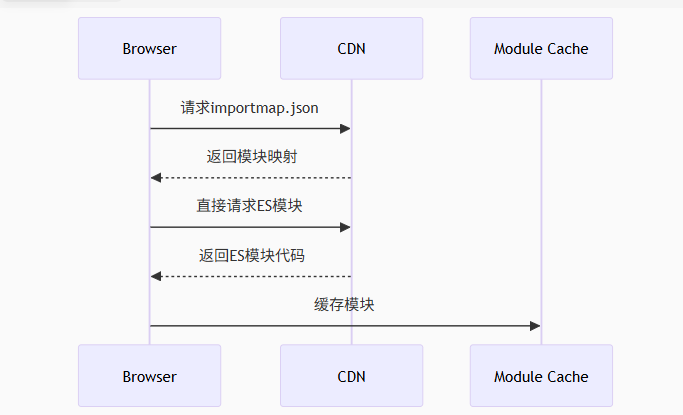
Module Federation 和 Native Federation 的比较
前言 Module Federation 是 Webpack 5 引入的微前端架构方案,允许不同独立构建的应用在运行时动态共享模块。 Native Federation 是 Angular 官方基于 Module Federation 理念实现的专为 Angular 优化的微前端方案。 概念解析 Module Federation (模块联邦) Modul…...

三体问题详解
从物理学角度,三体问题之所以不稳定,是因为三个天体在万有引力作用下相互作用,形成一个非线性耦合系统。我们可以从牛顿经典力学出发,列出具体的运动方程,并说明为何这个系统本质上是混沌的,无法得到一般解…...

安全突围:重塑内生安全体系:齐向东在2025年BCS大会的演讲
文章目录 前言第一部分:体系力量是突围之钥第一重困境是体系思想落地不畅。第二重困境是大小体系融合瓶颈。第三重困境是“小体系”运营梗阻。 第二部分:体系矛盾是突围之障一是数据孤岛的障碍。二是投入不足的障碍。三是新旧兼容难的障碍。 第三部分&am…...

git: early EOF
macOS报错: Initialized empty Git repository in /usr/local/Homebrew/Library/Taps/homebrew/homebrew-core/.git/ remote: Enumerating objects: 2691797, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (1760/1760), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (636/636…...

Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法
Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法 引言 在音频数据处理中,压缩算法是降低存储成本和传输效率的关键技术。Python作为一门灵活且功能强大的编程语言,提供了丰富的库和工具来实现音频数据的压缩与解压。本文将通过一个简单的音频数据压缩与解压算法…...

2025年- H71-Lc179--39.组合总和(回溯,组合)--Java版
1.题目描述 2.思路 当前的元素可以重复使用。 (1)确定回溯算法函数的参数和返回值(一般是void类型) (2)因为是用递归实现的,所以我们要确定终止条件 (3)单层搜索逻辑 二…...

21-Oracle 23 ai-Automatic SQL Plan Management(SPM)
小伙伴们,有没有迁移数据库完毕后或是突然某一天在同一个实例上同样的SQL, 性能不一样了、业务反馈卡顿、业务超时等各种匪夷所思的现状。 于是SPM定位开始,OCM考试中SPM必考。 其他的AWR、ASH、SQLHC、SQLT、SQL profile等换作下一个话题…...
