C++:关于模拟实现vector和list中迭代器模块的理解
文章目录
- list和vector的迭代器对比
- list的实现过程
- 完整代码
本篇是关于vector和list的模拟实现中,关于迭代器模块的更进一步理解,以及在前文的基础上增加对于反向迭代器的实现和库函数的对比等
本篇是写于前面模拟实现的一段时间后,重新回头看迭代器的实现,尤其是在模板角度对list中迭代器封装的部分进行解析,希望可以对迭代器的封装实现有更深层次的理解,同时将与库内的实现做对比进行优化处理
list和vector的迭代器对比
list和vector的迭代器实现是不一样的,在vector中的迭代器就是一个原生指针,因此在实现的时候也就是用的原生指针即可,但是对于list来说不能这样,list的迭代器中例如++和--这样的操作,是不能和vector中的原生指针一样直接去实现的,而是需要用next或者是prior来模拟这个过程,还有例如*和->这样的访问数据的模式,因此在list的迭代器实现中是使用了封装来进行实现的
STL中有六大组件,其中迭代器算其中一个,那么也就意味着迭代器具有通用的功能,例如下面的代码,在使用构造函数时可以使用迭代器进行构造,而这个构造的过程使用的迭代器对于各种容器来说都是通用的:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v1{ 1,2,3,4,5,3,2,2 };vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());list<int> l1(v1.begin(), v1.end());return 0;
}
那么就意味着,在实现迭代器的过程中也是就可以根据迭代器来进行不同容器间的构造
list的实现过程
首先,在list的实现过程中要有下面几个部分组成:list中包含的节点,list的迭代器访问,list的节点之间的关系
那么首先就是list中节点的定义,用到了模板,现在再对该部分进行解析,其实就是在创建的时候可以根据需要的内容开辟出对应的节点类型
template<class T>
struct list_node
{T _data;list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node(const T& x = T()):_data(x), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}
};
有了节点信息,就可以对list做一些基础的操作,例如头插头删,尾插尾删等操作,但对于insert和erase这些操作还不能够实现,因此就要实现迭代器模块的内容
不管是对于vector还是list,迭代器的本质就是用一个原生指针去进行访问等等,但是list和vector不同的是,list的存储地址并不是连续的,因此在访问的过程中就需要对迭代器进行一定程度的封装,例如在++或者--的操作符上可以进行一些体现,因此list迭代器的实现是需要进行单独的封装的
// 定义正向迭代器
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class __list_iterator
{
public:typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> self;__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self& operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator !=(const self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator ==(const self& s){return _node == s._node;}Node* _node;
};
上面的片段对list进行了一些封装,实现了它的一些基础功能,从代码中也能看出来,迭代器的本质确确实实就是指针,用指针来进行一系列的操作,对下面这几个片段单独进行解析:
Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}
这是对于迭代器中解引用的运算符重载,这里使用的是&_node->_data的写法,看似很怪,但是实际上这里的函数调用过程应该是这样

也就是说,这里对于->进行运算符重载后,还需要进行解引用,这个运算符重载函数返回的是一个指针,而这个指针还要继续进行解引用才能得到用户想要得到的值,编译器在这里进行了特殊处理,两个->使得可读性下降,因此将两个->进行了一定程度的合并,只需要一个->就可以实现解引用的目的
其次是对模板的使用部分
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> self;
这里在最开始定义的时候,就定义了数据类型,引用和指针三种模板参数,借助这个参数就可以用模板将复杂的内容实现简单化,只需要一份代码,模板就可以直接实例化出用户在调用的时候需要的代码,在进行封装const迭代器的时候,只需要提供的参数改为const版本就可以实现目的,很便捷
这样就实现了正向迭代器的普通版本,而对于const迭代器的版本也只需要进行不同的模板参数就可以实例化出const版本的迭代器
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
有了迭代器,在实现链表的各种函数功能就更加方便,例如可以实现erase和insert的操作,实现了这两个函数,在进行头插头删,尾插尾删的时候就更加方便,只需要进行原地的调用即可
// Modifiersvoid push_front(const T& val){//Node* newnode = new Node;//newnode->_data = val;//newnode->_next = _head->_next;//_head->_next->_prev = newnode;//_head->_next = newnode;//newnode->_prev = _head;//_size++;insert(begin(), val);}void pop_front(){//Node* delnode = _head->_next;//_head->_next = _head->_next->_next;//_head->_next->_prev = _head;//delete delnode;//delnode = nullptr;//_size--;erase(begin());}void push_back(const T& val){//Node* newnode = new Node;//newnode->_data = val;//newnode->_prev = _head->_prev;//_head->_prev->_next = newnode;//newnode->_next = _head;//_head->_prev = newnode;//_size++;insert(end(), val);}void pop_back(){//Node* delnode = _head->_prev;//delnode->_prev->_next = _head;//_head->_prev = delnode->_prev;//delete delnode;//delnode = nullptr;//_size--;erase(--end());}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(val);_size++;prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = nullptr;_size--;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;return iterator(next);}
那么上面是对前面已经有过的内容进行的重新温故,但是上面的代码其实是没有实现反向迭代器的,而在STL的库中,反向迭代器的定义和正向迭代器其实并不相同,它是直接借助正向迭代器对反向迭代器进行适配,有些类似于用vector,list或者deque对栈和队列进行的适配,也体现了封装和代码复用
template<class Iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>
class ReverseIterator
{
public:typedef ReverseIterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self;ReverseIterator(Iterator it):_it(it){}Self& operator++(){--_it;return *this;}Ref operator*(){return *_it;}Ptr operator->(){return _it.operator->();}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _it != s._it;}
private:Iterator _it;
};
上面的代码就是对于反向迭代器的封装,从中可以看出反向迭代器是使用了正向迭代器的,并且在它的基础上进行的修改,因此这个反向迭代器是可以适配于vector也可以适配于list的
整体来说,对于反向迭代器就是用正向迭代器进行适配出来的,体现了模板的好处
完整代码
#pragma oncenamespace mylist
{// 定义节点内容template <class T>struct list_node{list_node(const T& x = T()):_data(x), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}T _data;list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;};// 定义正向迭代器template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>class __list_iterator{public:typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> self;__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self& operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator !=(const self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator ==(const self& s){return _node == s._node;}Node* _node;};// 定义反向迭代器template<class Iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>class reverse_iterator{typedef reverse_iterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> self;public:reverse_iterator(Iterator it):_it(it){}self& operator++(){_it--;return *this;}self& operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_it--;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_it++;return *this;}self& operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_it++;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){Iterator cur = _it;return *(--cur);}Ptr operator->(){return &(operator*());}bool operator !=(const self& s){return _it != s._it;}bool operator ==(const self& s){return _it == s._it;}Iterator _it;};// 定义链表template <class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;typedef reverse_iterator<iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;//typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;// Constructorlist(){empty_init();}list(const list<T>& lt){for (auto x : lt){push_back(x);}}list(iterator begin, iterator end){empty_init();while (begin != end){push_back(begin._node->_data);begin++;}}//list(reverse_iterator rbegin, reverse_iterator rend)//{// empty_init();// while (rbegin != rend)// {// push_back(rbegin._node->_data);// rbegin++;// }//}// Destructor~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}// Operator=list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& lt){swap(lt);return *this;}// Iteratorsiterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return reverse_iterator(end());}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(begin());}//const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const//{// return const_reverse_iterator(end());//}//const_reverse_iterator rend() const//{// return const_reverse_iterator(begin());//}// Capacitybool empty(){return _size == 0;}size_t size(){return _size;}// Element accessT& front(){return begin()._node->_data;}T& back(){return (--end())._node->_data;}// Modifiersvoid push_front(const T& val){//Node* newnode = new Node;//newnode->_data = val;//newnode->_next = _head->_next;//_head->_next->_prev = newnode;//_head->_next = newnode;//newnode->_prev = _head;//_size++;insert(begin(), val);}void pop_front(){//Node* delnode = _head->_next;//_head->_next = _head->_next->_next;//_head->_next->_prev = _head;//delete delnode;//delnode = nullptr;//_size--;erase(begin());}void push_back(const T& val){//Node* newnode = new Node;//newnode->_data = val;//newnode->_prev = _head->_prev;//_head->_prev->_next = newnode;//newnode->_next = _head;//_head->_prev = newnode;//_size++;insert(end(), val);}void pop_back(){//Node* delnode = _head->_prev;//delnode->_prev->_next = _head;//_head->_prev = delnode->_prev;//delete delnode;//delnode = nullptr;//_size--;erase(--end());}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(val);_size++;prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = nullptr;_size--;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;return iterator(next);}void swap(const list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}void clear(){Node* cur = _head->_next;while (cur != _head){Node* next = cur->_next;delete(cur);cur = next;}_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_head->_data = T();_size = 0;}void Print(){Node* cur = _head->_next;while (cur != _head){cout << cur->_data << "->";cur = cur->_next;}cout << "null" << endl;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};void test_iterator(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);cout << "iterator constructor:";list<int> lt1(lt.begin(), lt.end());lt1.Print();cout << "front():" << lt.front() << endl;cout << "back():" << lt.back() << endl;mylist::__list_iterator<int, int&, int*> it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){std::cout << *it << " ";it++;}cout << endl;}void test_clear(){list<int> lt1;cout << "push_back:" << endl;lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(2);lt1.push_back(3);lt1.push_back(4);lt1.Print();lt1.clear();lt1.push_back(5);lt1.push_back(6);lt1.push_back(7);lt1.push_back(8);lt1.Print();}void test_push_pop(){list<int> lt1;cout << "push_back:" << endl;lt1.push_back(1);lt1.push_back(2);lt1.push_back(3);lt1.push_back(4);lt1.Print();cout << "pop_back:" << endl;lt1.pop_back();lt1.Print();list<int> lt2;cout << "push_front:" << endl;lt2.push_front(1);lt2.push_front(2);lt2.push_front(3);lt2.push_front(4);lt2.Print();cout << "pop_front:" << endl;lt2.pop_front();lt2.Print();}void test_reverse_iterator(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);cout << "iterator constructor:";//list<int> lt1(lt.rbegin(), lt.rend());//lt1.Print();cout << "front():" << lt.front() << endl;cout << "back():" << lt.back() << endl;mylist::list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = lt.rbegin();while (rit != lt.rend()){std::cout << *rit << " ";rit++;}cout << endl;}void test(){test_reverse_iterator();//test_push_pop();//test_clear();}
}
相关文章:

C++:关于模拟实现vector和list中迭代器模块的理解
文章目录 list和vector的迭代器对比list的实现过程完整代码 本篇是关于vector和list的模拟实现中,关于迭代器模块的更进一步理解,以及在前文的基础上增加对于反向迭代器的实现和库函数的对比等 本篇是写于前面模拟实现的一段时间后,重新回头…...
HTML 笔记 表格
1 表格基本语法 tr:table row th:table head 2 表格属性 2.1 基本属性 表格的基本属性是指表格的行、列和单元格但并不是每个表格的单元格大小都是统一的,所以需要设计者通过一些属性参数来修改表格的样子,让它们可以更更多样…...

3.1 C/C++ 使用字符与指针
C/C语言是一种通用的编程语言,具有高效、灵活和可移植等特点。C语言主要用于系统编程,如操作系统、编译器、数据库等;C语言是C语言的扩展,增加了面向对象编程的特性,适用于大型软件系统、图形用户界面、嵌入式系统等。…...

[代码学习]einsum详解
einsum详解 该函数用于对一组输入 Tensor 进行 Einstein 求和,该函数目前仅适用于paddle的动态图。 Einstein 求和是一种采用 Einstein 标记法描述的 Tensor 求和,输入单个或多个 Tensor,输出单个 Tensor。 paddle.einsum(equation, *opera…...

女性必看——“黄体破裂”到底有多可怕?
前几天的亚运会上发生了这样一件事: 雅思敏(化名)是一名国外皮划艇运动员,在亚运会上奋力完成皮划艇比赛后,突然开始 剧烈腹痛、面色苍白,大汗淋漓,经过进一步检查,确诊卵巢黄体破裂…...
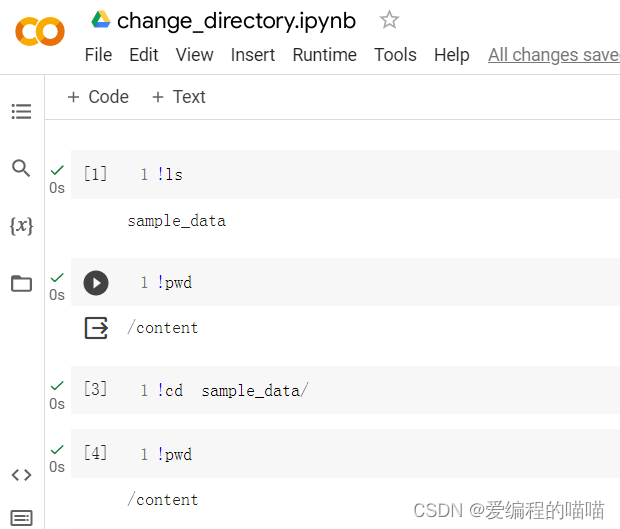
colab切换目录的解决方案
大家好,我是爱编程的喵喵。双985硕士毕业,现担任全栈工程师一职,热衷于将数据思维应用到工作与生活中。从事机器学习以及相关的前后端开发工作。曾在阿里云、科大讯飞、CCF等比赛获得多次Top名次。现为CSDN博客专家、人工智能领域优质创作者。喜欢通过博客创作的方式对所学的…...
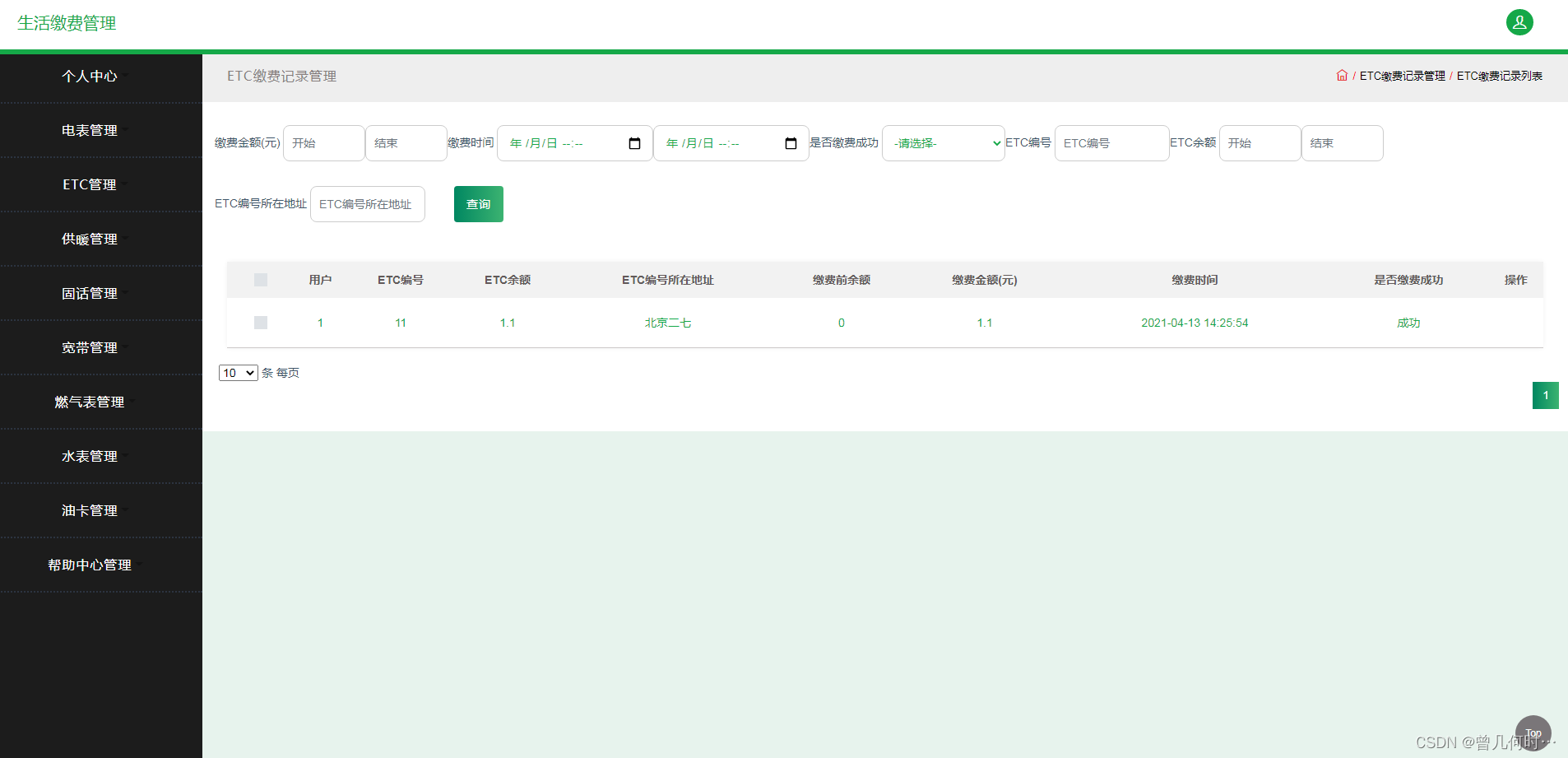
基于SSM的生活缴费系统的设计与实现
末尾获取源码 开发语言:Java Java开发工具:JDK1.8 后端框架:SSM 前端:采用JSP技术开发 数据库:MySQL5.7和Navicat管理工具结合 服务器:Tomcat8.5 开发软件:IDEA / Eclipse 是否Maven项目&#x…...

【WebLogic】WebLogic 2023年7月补丁导致JVM崩溃的解决方案
受影响版本: Oracle WebLogic 12c(12.2.1.4.0)Oracle WebLogic 14c(14.1.1.0.0) 问题描述: Oracle官方在2023年7月发布的最新版本的OPatch(13.9.4.2.13)存在一个新出现的Bug&#…...

简单OpenSL ES学习
初识OpenSL ES OpenSL ESObjects和Interfaces 所有的Object在OpenSl里面我们拿到的都是一个SLObjectItf:SLObjectItf_创建引擎创建过程要设计得这么麻烦?(object的生命周期)这么多参数,参数类型这么多学习障碍太大&…...
)
Linux网络编程- struct packet_mreq setsockopt()
struct packet_mreq struct packet_mreq 是一个数据结构,用于 Linux 中的原始数据包套接字,当我们想改变套接字的行为以接收特定类型的数据包时,它与 setsockopt() 函数配合使用。 下面是 struct packet_mreq 的定义: struct p…...
C++学习day4
作业: 1> 思维导图 2> 整理代码 1. 拷贝赋值函数课上代码 //拷贝赋值函数课上代码 #include<iostream> using namespace std;//创建类 class Stu { private://私有的string name;int socer;int *age;//此处注意用到指针类型 public://共有的//无参构…...
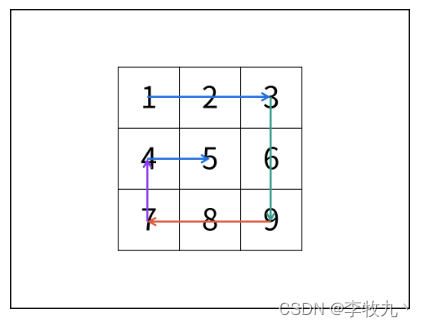
从零学算法54
54.给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。 螺旋遍历:从左上角开始,按照 向右、向下、向左、向上 的顺序 依次 提取元素,然后再进入内部一层重复相同的步骤,直到…...
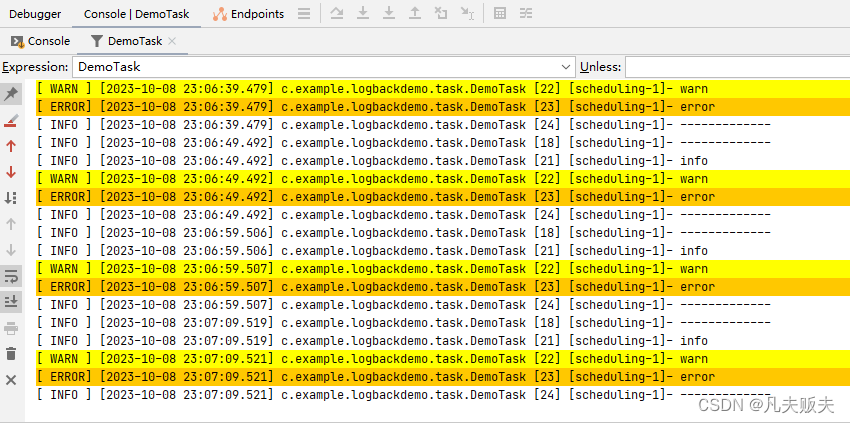
Logback日志框架使用详解以及如何Springboot快速集成
Logback简介 日志系统是用于记录程序的运行过程中产生的运行信息、异常信息等,一般有8个级别,从低到高为All < Trace < Debug < Info < Warn < Error < Fatal < OFF off 最高等级,用于关闭所有日志记录fatal 指出每个…...

Nginx概念
Nginx概念 Nginx 是一款面向性能设计的 HTTP 服务器,相较于 Apache、lighttpd 具有占有内存少,稳定性高等优势,同时也是一个非常高效的反向代理、负载平衡服务器 nginx使用的是反应器模式,主事件循环等待操作系统发出准备事件的信…...
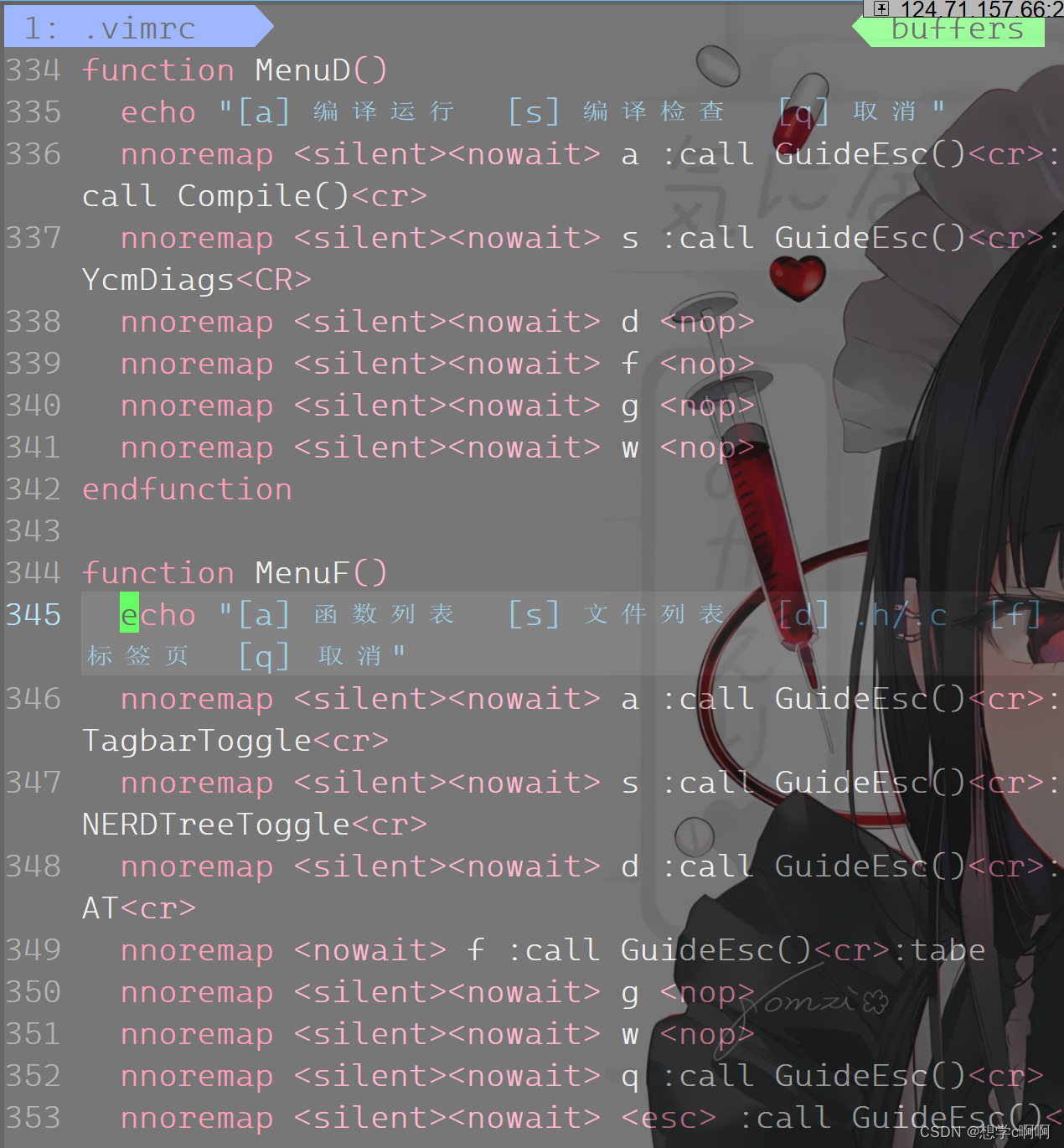
vim基础指令(自用)
这个是自己随便写的,类似于笔记 vim 多模式编辑器 查看指令: gg: 定位光标到最开始行 shift(按)g 定位到最结尾行 nshift(按)g 定位到任意行 shift$ 定位到本行结尾 0 定位到本行开头 w:跨单词移动 h.j.k,l: 左下上右 …...
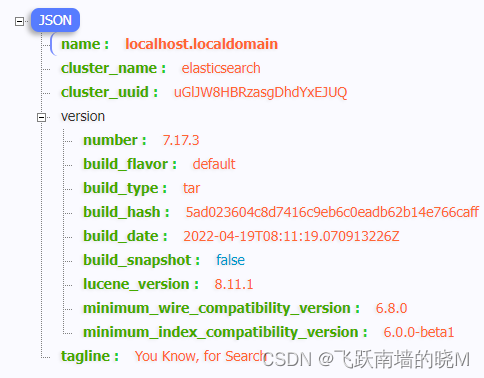
【centos7安装ElasticSearch】
概述 最近工作中有用到ES ,当然少不了自己装一个服务器捣鼓。本文的ElasticSearch 的版本: 7.17.3 一、下载 ElasticSearch 点此下载 下载完成后上传至 Linux 服务器,本文演示放在: /root/ 下,进行解压࿱…...

ElementPlus Switch 开关基础使用
昨天开发用到开关组件 后台返回字段是 can_write 默认是0 or 1 但是Switch 组件绑定的默认值默认是 true or false 直接绑定会导致默认是关闭状态 在页面一加载 值发生变化时 会自己调用 查了文档 需要使用 active-value 和 inactive-value 来指定绑定的数据类型 …...

Spring Boot:自定义注解--annotation
目录 自定义注解的定义和作用范围如何创建自定义注解创建注解接口 如何使用自定义注解进行数据验证创建注解处理器控制器中使用注解 如何为字段添加注解 自定义注解的定义和作用范围 自定义注解可以作用在类、方法、属性、参数、异常、字段或其他注解上。 如何创建自定义注解…...

WIFI频段
问题: 5ghzwifi频段带宽怎么选 智造喵回答: 选择5GHz WiFi频段的带宽取决于你的网络需求和设备兼容性。通常有两种可选的带宽:20MHz和40MHz。 20MHz带宽:这是较为常见的 WiFi 频段带宽设置。它提供较好的穿墙能力和信号稳定性…...

Java的引用详解与示例
引用的作用 在Java中,引用(Reference)是一种重要的概念,它们用于管理对象的生命周期、内存分配和垃圾回收。引用的作用包括以下几个方面: 内存管理:引用帮助Java虚拟机(JVM)管理内存…...
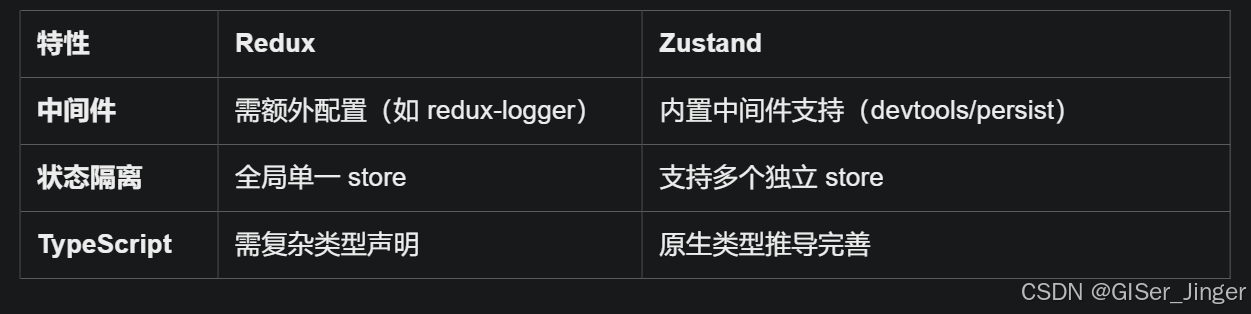
Zustand 状态管理库:极简而强大的解决方案
Zustand 是一个轻量级、快速和可扩展的状态管理库,特别适合 React 应用。它以简洁的 API 和高效的性能解决了 Redux 等状态管理方案中的繁琐问题。 核心优势对比 基本使用指南 1. 创建 Store // store.js import create from zustandconst useStore create((set)…...

mongodb源码分析session执行handleRequest命令find过程
mongo/transport/service_state_machine.cpp已经分析startSession创建ASIOSession过程,并且验证connection是否超过限制ASIOSession和connection是循环接受客户端命令,把数据流转换成Message,状态转变流程是:State::Created 》 St…...

《Playwright:微软的自动化测试工具详解》
Playwright 简介:声明内容来自网络,将内容拼接整理出来的文档 Playwright 是微软开发的自动化测试工具,支持 Chrome、Firefox、Safari 等主流浏览器,提供多语言 API(Python、JavaScript、Java、.NET)。它的特点包括&a…...

条件运算符
C中的三目运算符(也称条件运算符,英文:ternary operator)是一种简洁的条件选择语句,语法如下: 条件表达式 ? 表达式1 : 表达式2• 如果“条件表达式”为true,则整个表达式的结果为“表达式1”…...
Cinnamon修改面板小工具图标
Cinnamon开始菜单-CSDN博客 设置模块都是做好的,比GNOME简单得多! 在 applet.js 里增加 const Settings imports.ui.settings;this.settings new Settings.AppletSettings(this, HTYMenusonichy, instance_id); this.settings.bind(menu-icon, menu…...

汇编常见指令
汇编常见指令 一、数据传送指令 指令功能示例说明MOV数据传送MOV EAX, 10将立即数 10 送入 EAXMOV [EBX], EAX将 EAX 值存入 EBX 指向的内存LEA加载有效地址LEA EAX, [EBX4]将 EBX4 的地址存入 EAX(不访问内存)XCHG交换数据XCHG EAX, EBX交换 EAX 和 EB…...
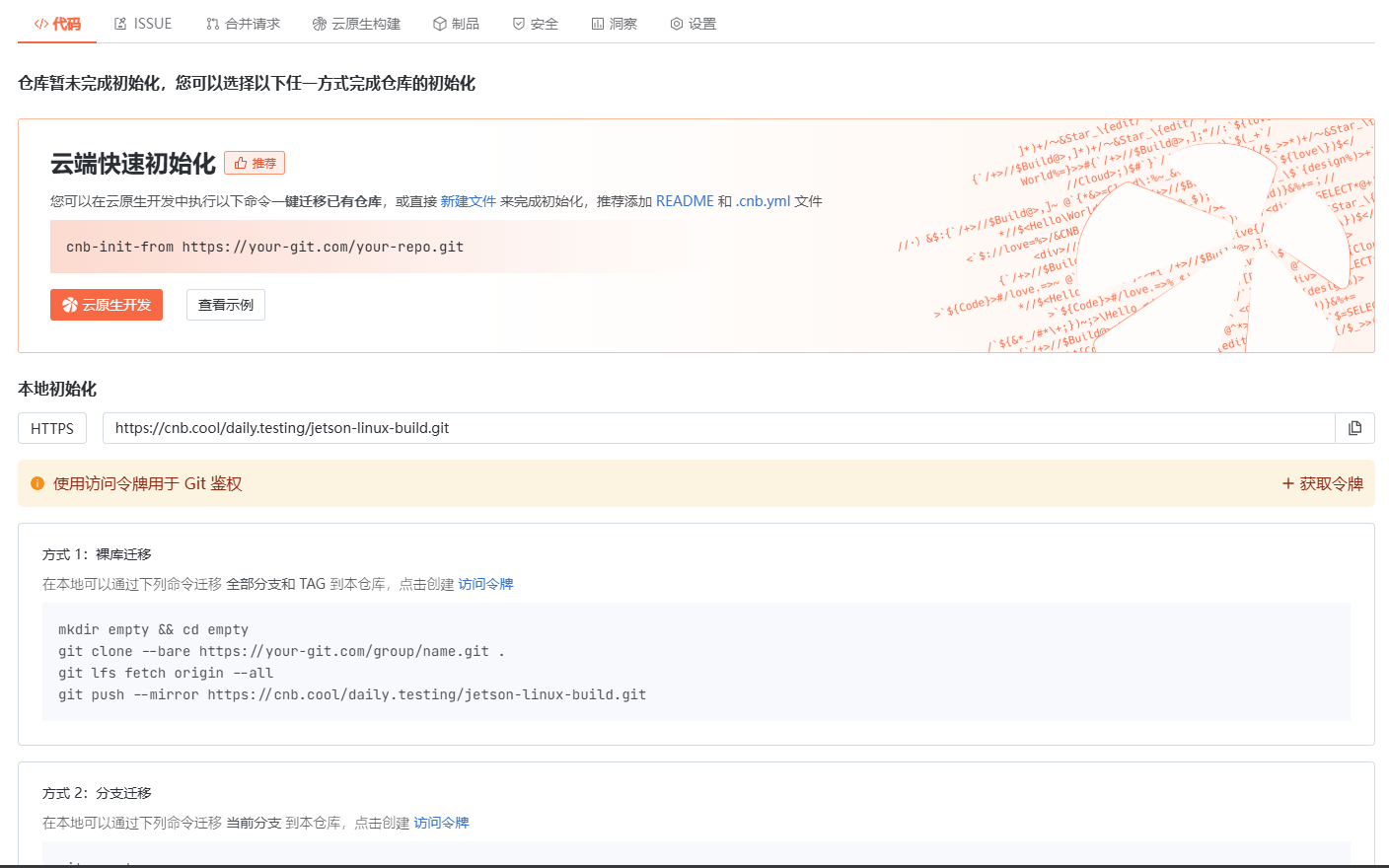
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境 引言 临时运维一个古董项目,无文档,无环境,无交接人,俗称三无。 运行设备的环境老,本地环境版本高,ssh不过去。正好最近对 腾讯出品的云原生 cnb 感兴趣&…...
安装docker)
Linux离线(zip方式)安装docker
目录 基础信息操作系统信息docker信息 安装实例安装步骤示例 遇到的问题问题1:修改默认工作路径启动失败问题2 找不到对应组 基础信息 操作系统信息 OS版本:CentOS 7 64位 内核版本:3.10.0 相关命令: uname -rcat /etc/os-rele…...

Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析
Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析 一、第一轮提问(基础概念问题) 1. 请解释Spring框架的核心容器是什么?它在Spring中起到什么作用? Spring框架的核心容器是IoC容器&#…...
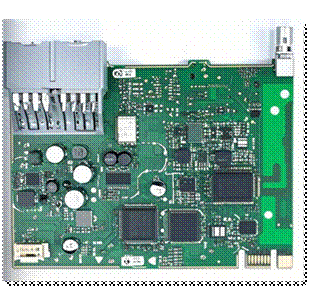
NXP S32K146 T-Box 携手 SD NAND(贴片式TF卡):驱动汽车智能革新的黄金组合
在汽车智能化的汹涌浪潮中,车辆不再仅仅是传统的交通工具,而是逐步演变为高度智能的移动终端。这一转变的核心支撑,来自于车内关键技术的深度融合与协同创新。车载远程信息处理盒(T-Box)方案:NXP S32K146 与…...
