【 K8s 源码之调度学习】Pod 间亲和性和反亲和性的源码分析
查看案例
| 字段 | 含义 | |
|---|---|---|
| podAffinity | Pod 间的亲和性定义 | |
| podAntiAffinity | Pod 间的反亲和性定义 | |
| requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution | 硬性要求,必须满足条件,保证分散部署的效果最好使用用此方式 | |
| preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution | 软性要求,可以不完全满足,即有可能同一node上可以跑多个副本 | |
| requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution | labelSelector | |
| topologyKey | ||
| preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution | weight | |
| podAffinityTerm | labelSelector | |
| topologyKey | ||
| topologyKey | 可以理解为 Node 的 Label,具有相同的 Label 的 Node,视为同一拓扑 | |
| 如三个节点打上 Label : - Node1 —— zone:beijing - Node2 —— zone:shanghai - Node3 —— zone:beijing 那么 Node1 和 Node3 为同一拓扑,Node2 为另一拓扑 | ||
| topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname 上面为常见的配置,可以通过 kubectl get nodes --show-labels看到节点上的 Lable,就具有此 kubernetes.io/hostname Label因此就是将每个节点,作为一个独立的拓扑 |
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: test-pod
spec:affinity:# 首先根据 labelSelector 选择具有 service.cpaas.io/name: deployment-nginx Label 的 所有 Pod# 接下来根据 podAffinity 亲和性,将此 pod 调度到与选中 Pod 中具有 topologyKey 的 Node 上podAffinity:requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:- labelSelector:matchLabels:service.cpaas.io/name: deployment-nginxtopologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname- labelSelector:matchLabels:service.cpaas.io/name: deployment-busyboxtopologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname# 首先根据 labelSelector 选择具有 key 为 a ,value为 b 或 c 的 Label 的 Pod# 接下来根据 podAntiAffinity,将此 pod 调度到与选中 Pod 中都不相同的 Node 上,该节点需要具有 topologyKey labelpodAntiAffinity:preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:- weight: 100podAffinityTerm:labelSelector:matchExpressions:- key: aoperator: Invalues: ["b", "c"]topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostnamecontainers:- name: test-podimage: nginx:1.18代码分析
代码路径:pkg/scheduler/framework/plugins/interpodaffinity

首先根据调度器框架,观察源码,可以看出实现了一下四个接口:
- PreFilter
- Filter
- PreScore
- Score
首先明确几点
- 该插件是考虑 Pod 间的亲和性和反亲和性(就是新Pod 和 现存 Pod 的关系)
- 但最终结果是将 Pod 调度到合适的 Node 上(因此要记录 Node 的信息)
1 | PreFilter
此步骤作用:
- 梳理出【现存哪些 Pod】 讨厌【新 Pod】,记录【满足条件的现存 Pod】 对应 Node 信息为 existingPodAntiAffinityMap
- 梳理出【新 Pod】喜欢【哪些现存Pod】,记录【满足条件的现存 Pod】 对应 Node 信息为 incomingPodAffinityMap
- 梳理出【新 Pod】讨厌【哪些现存Pod】,记录【满足条件的现存 Pod】 对应 Node 信息为 incomingPodAntiAffinityMap
所以可以小总结一下
- existingPodAntiAffinityMap 和 incomingPodAntiAffinityMap 这些记录的节点,新 Pod 不喜欢
- incomingPodAffinityMap 记录的节点,Pod 喜欢
问题 —— 为什么不梳理 【现存哪些 Pod】 喜欢【新 Pod】?
- 因为现在是调度【新 Pod】,只要不被讨厌,不影响【现存 Pod 】就行,因此只需要可能会影响的【现存 Pod】
注意上面所说的【条件】—— 指的是【硬性要求 requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution 】 —— 因此才考虑这么详细
// 这里只截取了 PreFilter 部分重要函数
// pkg/scheduler/framework/plugins/interpodaffinity/filtering.go// 考虑现存 Pod 的 反亲和性 anti-affinity
// 简单理解:就是用现存 Pod 的 anti-affinity Terms 配置,要求 NewPod,记录下满足的 Node,说明这些节点不能调度(因为现存 Pod 排斥新 Pod)
// 这里的 anti-affinity Terms 是指 requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution 定义的硬性要求
// 问题:为什么不考虑现存 Pod 的亲和性? —— 因为现存 Pod 的亲和性(是亲和他之前 Pod),在其调度的时候早已考虑,现在只需要考虑其反感的
// 代码级理解:
// 1. 遍历所有具有 anti-affinity 现存 Pod
// 2. 若即将调度的 NewPod 满足该 Pod 的 anti-affnity Terms,
// 3. 就记录到 existingPodAntiAffinityMap 中,key 为该 Pod 所在的 node 信息(topologyKey、topologyValue),value 为满足的 Terms 次数
// 例如 map{(hostname:node01):1}
// existingPodAntiAffinityMap will be used later for efficient check on existing pods' anti-affinity
existingPodAntiAffinityMap := getTPMapMatchingExistingAntiAffinity(pod, nodesWithRequiredAntiAffinityPods)// 考虑新 NewPod 的亲和性和反亲和性
// 简单理解: 就是用 NewPod 的 anti-affinity 和 affinity Terms 配置,要求现存的 Pod,记录下满足的 Node
// incomingPodAffinityMap will be used later for efficient check on incoming pod's affinity
// incomingPodAntiAffinityMap will be used later for efficient check on incoming pod's anti-affinity
incomingPodAffinityMap, incomingPodAntiAffinityMap := getTPMapMatchingIncomingAffinityAntiAffinity(podInfo, allNodes)
2 | Filter
- *framework.CycleState 将上面统计的信息传递过来
- 现在的工作就是:
- 传来了一个 Node 信息
- 判断该 Node 与上面的 existingPodAntiAffinityMap、incomingPodAntiAffinityMap 、incomingPodAffinityMap 的关系
- 若该 Node 满足条件,那么可以进入到下面的【打分阶段】
// pkg/scheduler/framework/plugins/interpodaffinity/filtering.go
func (pl *InterPodAffinity) Filter(ctx context.Context, cycleState *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo) *framework.Status {if nodeInfo.Node() == nil {return framework.NewStatus(framework.Error, "node not found")}state, err := getPreFilterState(cycleState)if err != nil {return framework.NewStatus(framework.Error, err.Error())}if !satisfyPodAffinity(state, nodeInfo) {return framework.NewStatus(framework.UnschedulableAndUnresolvable, ErrReasonAffinityNotMatch, ErrReasonAffinityRulesNotMatch)}if !satisfyPodAntiAffinity(state, nodeInfo) {return framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable, ErrReasonAffinityNotMatch, ErrReasonAntiAffinityRulesNotMatch)}if !satisfyExistingPodsAntiAffinity(state, nodeInfo) {return framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable, ErrReasonAffinityNotMatch, ErrReasonExistingAntiAffinityRulesNotMatch)}return nil
}
3 | PreScore
这部分主要看 processExistingPod 函数
- 可以看出根据【现存 Pod】 和【新 Pod】的【软性要求preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution】,对节点进行打分
// pkg/scheduler/framework/plugins/interpodaffinity/scoring.go
// PreScore builds and writes cycle state used by Score and NormalizeScore.
func (pl *InterPodAffinity) PreScore(pCtx context.Context,cycleState *framework.CycleState,pod *v1.Pod,nodes []*v1.Node,
) *framework.Status {// ... ...topoScores := make([]scoreMap, len(allNodes))index := int32(-1)processNode := func(i int) {nodeInfo := allNodes[i]if nodeInfo.Node() == nil {return}// Unless the pod being scheduled has affinity terms, we only// need to process pods with affinity in the node.podsToProcess := nodeInfo.PodsWithAffinityif hasAffinityConstraints || hasAntiAffinityConstraints {// We need to process all the pods.podsToProcess = nodeInfo.Pods}topoScore := make(scoreMap)for _, existingPod := range podsToProcess {pl.processExistingPod(state, existingPod, nodeInfo, pod, topoScore)}if len(topoScore) > 0 {topoScores[atomic.AddInt32(&index, 1)] = topoScore}}parallelize.Until(context.Background(), len(allNodes), processNode)for i := 0; i <= int(index); i++ {state.topologyScore.append(topoScores[i])}cycleState.Write(preScoreStateKey, state)return nil
}func (pl *InterPodAffinity) processExistingPod(state *preScoreState,existingPod *framework.PodInfo,existingPodNodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo,incomingPod *v1.Pod,topoScore scoreMap,
) {existingPodNode := existingPodNodeInfo.Node()// For every soft pod affinity term of <pod>, if <existingPod> matches the term,// increment <p.counts> for every node in the cluster with the same <term.TopologyKey>// value as that of <existingPods>`s node by the term`s weight.topoScore.processTerms(state.podInfo.PreferredAffinityTerms, existingPod.Pod, existingPodNode, 1)// For every soft pod anti-affinity term of <pod>, if <existingPod> matches the term,// decrement <p.counts> for every node in the cluster with the same <term.TopologyKey>// value as that of <existingPod>`s node by the term`s weight.topoScore.processTerms(state.podInfo.PreferredAntiAffinityTerms, existingPod.Pod, existingPodNode, -1)// For every hard pod affinity term of <existingPod>, if <pod> matches the term,// increment <p.counts> for every node in the cluster with the same <term.TopologyKey>// value as that of <existingPod>'s node by the constant <args.hardPodAffinityWeight>if pl.args.HardPodAffinityWeight > 0 {for _, term := range existingPod.RequiredAffinityTerms {t := framework.WeightedAffinityTerm{AffinityTerm: term, Weight: pl.args.HardPodAffinityWeight}topoScore.processTerm(&t, incomingPod, existingPodNode, 1)}}// For every soft pod affinity term of <existingPod>, if <pod> matches the term,// increment <p.counts> for every node in the cluster with the same <term.TopologyKey>// value as that of <existingPod>'s node by the term's weight.topoScore.processTerms(existingPod.PreferredAffinityTerms, incomingPod, existingPodNode, 1)// For every soft pod anti-affinity term of <existingPod>, if <pod> matches the term,// decrement <pm.counts> for every node in the cluster with the same <term.TopologyKey>// value as that of <existingPod>'s node by the term's weight.topoScore.processTerms(existingPod.PreferredAntiAffinityTerms, incomingPod, existingPodNode, -1)
}
4 | Score
这部分就是,将节点的得分进行累计计算,返回此符合条件的节点的得分数
- 注意,所有符合条件都会调用此函数,得到自己对应的分数
// pkg/scheduler/framework/plugins/interpodaffinity/scoring.go
// Score invoked at the Score extension point.
// The "score" returned in this function is the sum of weights got from cycleState which have its topologyKey matching with the node's labels.
// it is normalized later.
// Note: the returned "score" is positive for pod-affinity, and negative for pod-antiaffinity.
func (pl *InterPodAffinity) Score(ctx context.Context, cycleState *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *framework.Status) {nodeInfo, err := pl.sharedLister.NodeInfos().Get(nodeName)if err != nil || nodeInfo.Node() == nil {return 0, framework.NewStatus(framework.Error, fmt.Sprintf("getting node %q from Snapshot: %v, node is nil: %v", nodeName, err, nodeInfo.Node() == nil))}node := nodeInfo.Node()s, err := getPreScoreState(cycleState)if err != nil {return 0, framework.NewStatus(framework.Error, err.Error())}var score int64for tpKey, tpValues := range s.topologyScore {if v, exist := node.Labels[tpKey]; exist {score += tpValues[v]}}return score, nil
}
相关文章:

【 K8s 源码之调度学习】Pod 间亲和性和反亲和性的源码分析
查看案例 字段含义podAffinityPod 间的亲和性定义podAntiAffinityPod 间的反亲和性定义requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution硬性要求,必须满足条件,保证分散部署的效果最好使用用此方式preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution软性…...

计及绿证交易及碳排放的含智能楼宇微网优化调度(Matlab代码实现)
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥 🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。 ⛳️座右铭&a…...
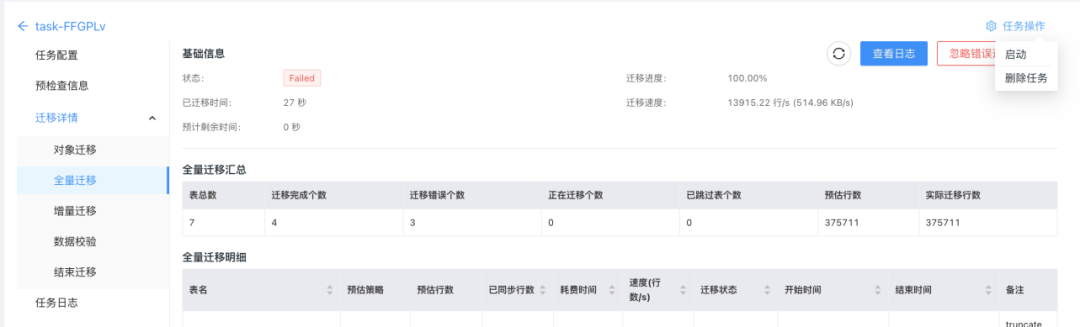
场景扩展,体验升级 | DBMotion新增无公网数据库迁移、支持监控报警等多项功能
丝滑的零停机数据库在线迁移工具——DBMotion,又双叒叕发新版:新增的网关、数据源功能,让你无公网IP的数据库也可以迁移;新增的监控功能,让你对迁移性能一目了然;新增的报警功能,让你及时获得同…...
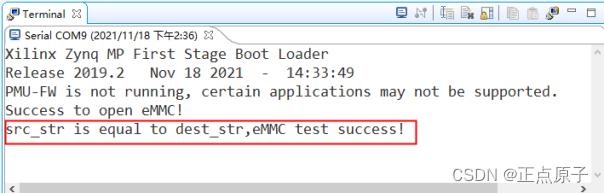
【正点原子FPGA连载】第十五章eMMC读写测试实验 摘自【正点原子】DFZU2EG_4EV MPSoC之嵌入式Vitis开发指南
1)实验平台:正点原子MPSoC开发板 2)平台购买地址:https://detail.tmall.com/item.htm?id692450874670 3)全套实验源码手册视频下载地址: http://www.openedv.com/thread-340252-1-1.html 第十五章eMMC读写…...
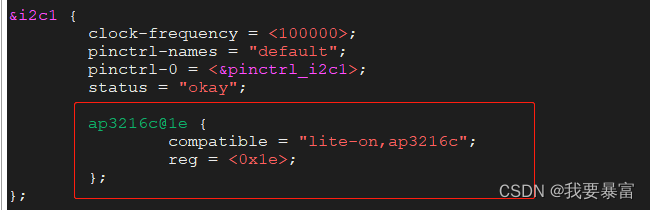
i2c子系统
i2c 硬件协议 Linux 应用层读写i2c 数据 在Linux系统上,不仅可以在内核中使用 i2c 总线发送、接收数据,同时也支持应用层使用i2c 总线发送、接收。 如果在内核中使能了drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c 配置,内核就会为每一个i2c 控制器生成一个/dev/…...

【K3s】第17篇 Helm版本和支持的Kubernetes版本对照表
目录 Helm版本和支持的Kubernetes版本对照表 Helm版本和支持的Kubernetes版本对照表 描述了在Helm和Kubernetes之间支持的最大版本偏差。 Helm的版本用 x.y.z 描述,x是主版本,y是次版本,z是补丁版本。 当一个Helm的新版本发布时࿰…...
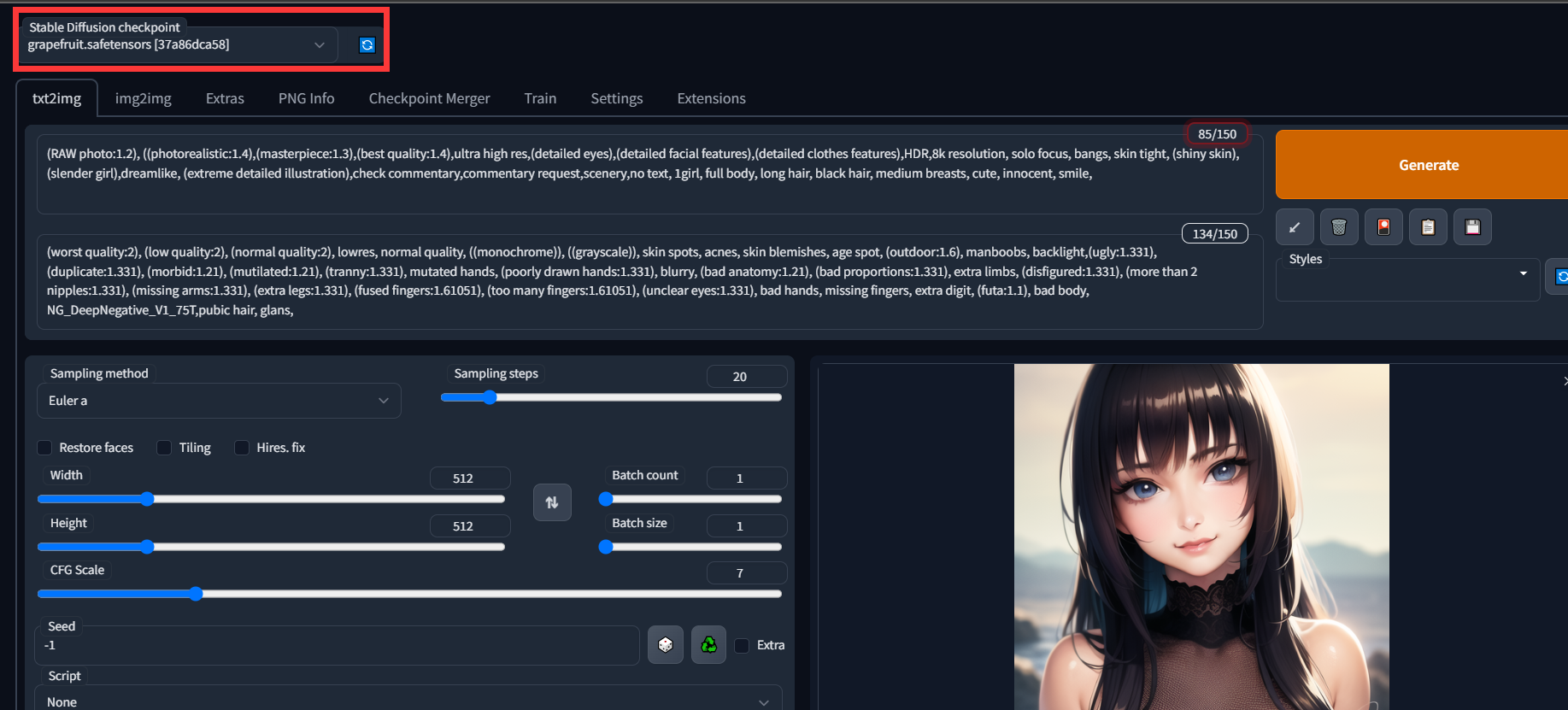
如何自己搭建一个ai画图系统? 从0开始云服务器部署novelai
如何自己搭建一个ai画图系统? 从0开始云服务器部署novelai 上面两张图都是通过ai生成的,是不是有以假乱真的感觉。 本教程提供的是自己搭建一个可以外网访问的ai系统的方法,需要采购gpu服务器(后续会出白嫖的方式)&…...

SpringSecurity过滤请求导致的系统bug
背景 今天开发一个新的会员管理系统,继承了SpringSecurity的,用以控制权限。结果无论怎么配置,都会报错:An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext 这句话的意思很明确:指的就是在SecurityCon…...

css\js\vue知识点
1.css3新特性 css3新特性 1)选择器 2)阴影 3)形状转换(2D <-> 3D) 4)变形 5)动画(过渡动画、帧动画) 6)边框 7)多重背景 8)反…...

在vue项目中使用video.js实现视频播放和视频进度条打点
一、用video.js实现视频播放 1、安装video.js插件 // 安装video.js插件 npm install video.js -S // 如果需要播放rtmp直播流,需安装一下插件 npm install videojs-flash -S 2、在组件代码里使用 <template><div data-vjs-player><video ref&quo…...

【代码训练营】day41 | 01背包问题 416. 分割等和子集
所用代码 java 01背包理论 背包最大重量为:4 重量价值物品0115物品1320物品2430 暴力:O(2^n) 动态规划: 1、二维dp数组 dp[i] [j] dp数组含义:[0, i]物品,任取放进容量为j的背包里的最大价值 递推公式:…...
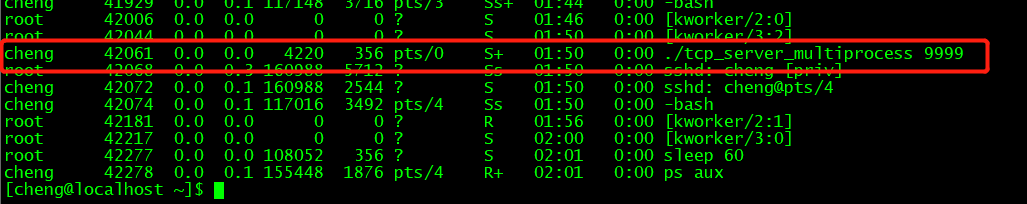
linux网络编程-多进程实现TCP并发服务器
服务端流程步骤socket函数创建监听套接字lfdbind函数将监听套接字绑定ip和端口listen函数设置服务器为被动监听状态,同时创建一条未完成连接队列(没走完tcp三次握手流程的连接),和一条已完成连接队列(已完成tcp三次握手…...
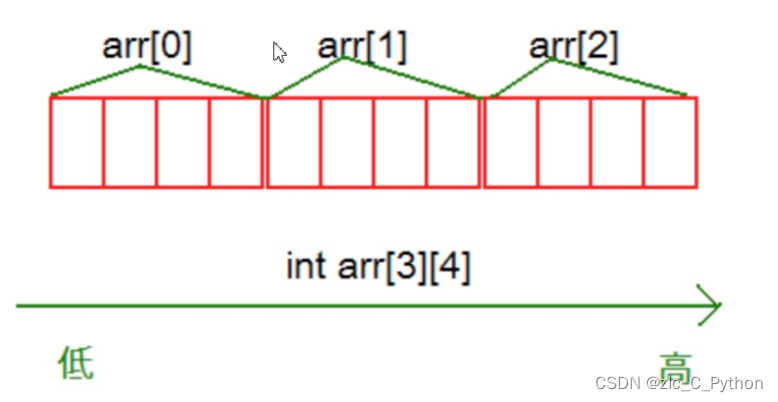
C语言的学习小结——数组
一、一维数组的创建与初始化 1、格式: type_t arr_name[const_n];//type_t 是指数组的元素类型 //const_n 是一个常量表达式,用来指定数组的大小 注: 数组是使用下标来访问的,下标从0开始。 数组的大小可以通过计算得到&…...
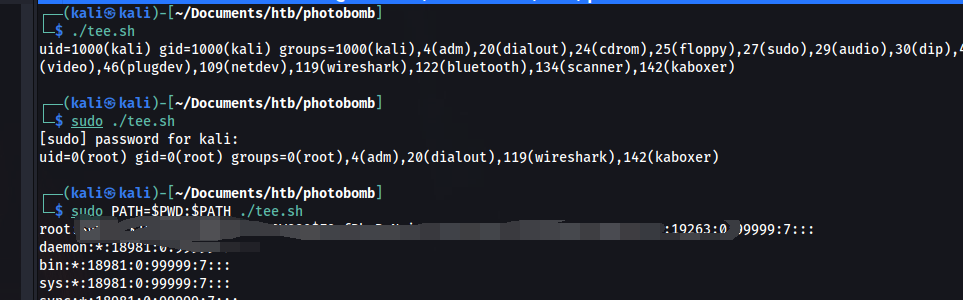
HTB-Photobomb
HTB-Photobomb信息收集开机提权对于问题的思考信息收集 端口扫描 目标首页 有一个http Authorization 目录扫描 在查看源码的时候发现了一个js文件。 并且发现了访问不存在的目录会出现错误提示。 通过搜索得知 Sinatra 是一个基于 Ruby 语言的 DSL(领域…...
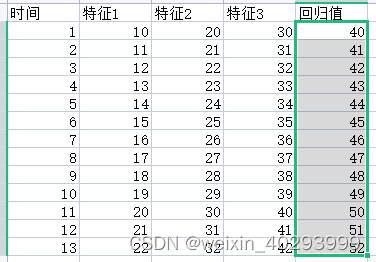
【LSTM】2 多因素单步骤预测
基于时间序列的预测,一定要明白它的原理,不是工作原理,而是工程落地原因。 基于时间序列,以已知回归未知----这两句话是分量很重的。 多因素单步单输出组合 时间序列:t1 是 特征 1,2,3 预测t2 的回归值41 多因素单步多…...

ChatGPT从下游应用“火”到了上游芯片厂,国内谁将受益?
因库存陷入低迷周期的半导体市场近日因ChatGPT的火热而重新受到外界关注。 原文链接:ChatGPT从下游应用“火”到了上游芯片厂,国内谁将受益? 由于ChatGPT属于生成式AI,被誉为“AI芯片”第一股的英伟达应声而涨。2月13日收盘&#…...

算法单调栈—Java版
单调栈 概念:维护栈中元素的单调性,单调增或者单调减。 什么时候用? 要寻找任一个元素的右边或者左边第一个比自己大或者小的元素的位置。单调栈的本质是空间换时间,在遍历的过程中需要用一个栈来记录右边第一个比当前元素高的元…...

在Linux中进行rocketmq及rocketmq控制台安装与配置
rocketmq下载安装的版本:rocketmq-rocketmq-all-5.0.0.tar.gz rocketmq控制台下载安装的版本:rocketmq-externals-rocketmq-console-1.0.0.tar.gz rocketmq安装 第一步,下载server-jre-8u202-linux-x64.tar.gz安装包。 登录网址ÿ…...

2023年全国最新食品安全管理员精选真题及答案4
百分百题库提供食品安全管理员考试试题、食品安全员考试预测题、食品安全管理员考试真题、食品安全员证考试题库等,提供在线做题刷题,在线模拟考试,助你考试轻松过关。 31.国家对食品添加剂生产实行____制度。 A.产品注册 B.产品备案 C.登…...

es-07脚本查询
脚本查询 概念 Scripting是Elasticsearch支持的一种专门用于复杂场景下支持自定义编程的强大的脚本功能,ES支持多种脚本语言,如painless,其语法类似于Java,也有注释、关键字、类型、变量、函数等,其就要相对于其他脚本高出几倍的性…...

智慧医疗能源事业线深度画像分析(上)
引言 医疗行业作为现代社会的关键基础设施,其能源消耗与环境影响正日益受到关注。随着全球"双碳"目标的推进和可持续发展理念的深入,智慧医疗能源事业线应运而生,致力于通过创新技术与管理方案,重构医疗领域的能源使用模式。这一事业线融合了能源管理、可持续发…...

黑马Mybatis
Mybatis 表现层:页面展示 业务层:逻辑处理 持久层:持久数据化保存 在这里插入图片描述 Mybatis快速入门 
12.找到字符串中所有字母异位词
🧠 题目解析 题目描述: 给定两个字符串 s 和 p,找出 s 中所有 p 的字母异位词的起始索引。 返回的答案以数组形式表示。 字母异位词定义: 若两个字符串包含的字符种类和出现次数完全相同,顺序无所谓,则互为…...

汇编常见指令
汇编常见指令 一、数据传送指令 指令功能示例说明MOV数据传送MOV EAX, 10将立即数 10 送入 EAXMOV [EBX], EAX将 EAX 值存入 EBX 指向的内存LEA加载有效地址LEA EAX, [EBX4]将 EBX4 的地址存入 EAX(不访问内存)XCHG交换数据XCHG EAX, EBX交换 EAX 和 EB…...

06 Deep learning神经网络编程基础 激活函数 --吴恩达
深度学习激活函数详解 一、核心作用 引入非线性:使神经网络可学习复杂模式控制输出范围:如Sigmoid将输出限制在(0,1)梯度传递:影响反向传播的稳定性二、常见类型及数学表达 Sigmoid σ ( x ) = 1 1 +...

Java多线程实现之Thread类深度解析
Java多线程实现之Thread类深度解析 一、多线程基础概念1.1 什么是线程1.2 多线程的优势1.3 Java多线程模型 二、Thread类的基本结构与构造函数2.1 Thread类的继承关系2.2 构造函数 三、创建和启动线程3.1 继承Thread类创建线程3.2 实现Runnable接口创建线程 四、Thread类的核心…...
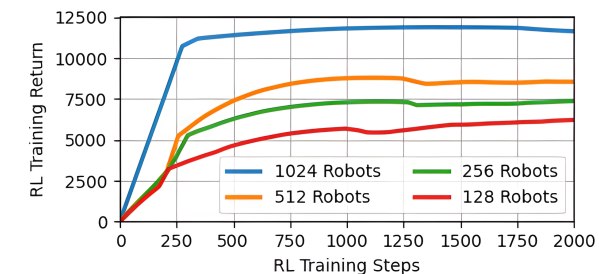
【VLNs篇】07:NavRL—在动态环境中学习安全飞行
项目内容论文标题NavRL: 在动态环境中学习安全飞行 (NavRL: Learning Safe Flight in Dynamic Environments)核心问题解决无人机在包含静态和动态障碍物的复杂环境中进行安全、高效自主导航的挑战,克服传统方法和现有强化学习方法的局限性。核心算法基于近端策略优化…...
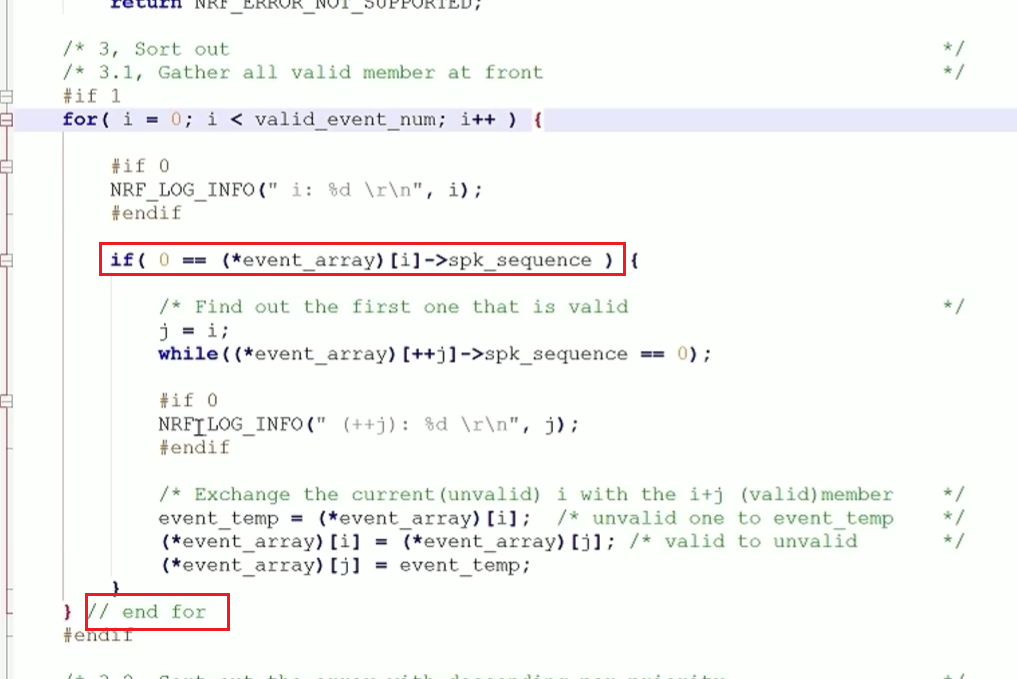
代码规范和架构【立芯理论一】(2025.06.08)
1、代码规范的目标 代码简洁精炼、美观,可持续性好高效率高复用,可移植性好高内聚,低耦合没有冗余规范性,代码有规可循,可以看出自己当时的思考过程特殊排版,特殊语法,特殊指令,必须…...
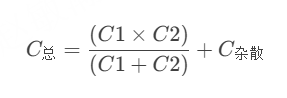
STM32---外部32.768K晶振(LSE)无法起振问题
晶振是否起振主要就检查两个1、晶振与MCU是否兼容;2、晶振的负载电容是否匹配 目录 一、判断晶振与MCU是否兼容 二、判断负载电容是否匹配 1. 晶振负载电容(CL)与匹配电容(CL1、CL2)的关系 2. 如何选择 CL1 和 CL…...
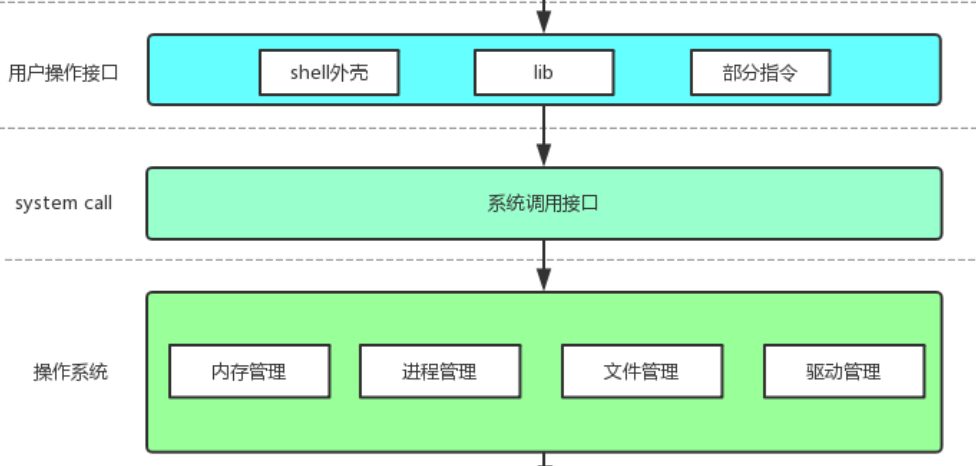
【Linux手册】探秘系统世界:从用户交互到硬件底层的全链路工作之旅
目录 前言 操作系统与驱动程序 是什么,为什么 怎么做 system call 用户操作接口 总结 前言 日常生活中,我们在使用电子设备时,我们所输入执行的每一条指令最终大多都会作用到硬件上,比如下载一款软件最终会下载到硬盘上&am…...
