关于opencv的contourArea计算方法
cv::contourArea计算的轮廓面积并不等于轮廓点计数,原因是cv::contourArea是基于Green公式计算
老外的讨论 github
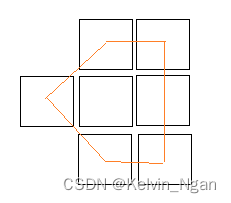
举一个直观的例子,图中有7个像素,橙色为轮廓点连线,按照contourArea的定义,轮廓的面积为橙色所包围的区域=3
以下代码基于opencv4.8.0
cv::contourArea源码位于.\sources\modules\imgproc\src\shapedescr.cpp
// area of a whole sequence
double cv::contourArea( InputArray _contour, bool oriented )
{CV_INSTRUMENT_REGION();Mat contour = _contour.getMat();int npoints = contour.checkVector(2);int depth = contour.depth();CV_Assert(npoints >= 0 && (depth == CV_32F || depth == CV_32S));if( npoints == 0 )return 0.;double a00 = 0;bool is_float = depth == CV_32F;const Point* ptsi = contour.ptr<Point>();const Point2f* ptsf = contour.ptr<Point2f>();Point2f prev = is_float ? ptsf[npoints-1] : Point2f((float)ptsi[npoints-1].x, (float)ptsi[npoints-1].y);for( int i = 0; i < npoints; i++ ){Point2f p = is_float ? ptsf[i] : Point2f((float)ptsi[i].x, (float)ptsi[i].y);a00 += (double)prev.x * p.y - (double)prev.y * p.x;prev = p;}a00 *= 0.5;if( !oriented )a00 = fabs(a00);return a00;
}
如果计算面积需要考虑轮廓点本身,可以通过cv::drawContoursI填充轮廓获得mask图像后统计非零点个数
cv::drawContours源码位于.\sources\modules\imgproc\src\drawing.cpp,主要包括两步:收集边缘cv::CollectPolyEdges和填充边缘cv::FillEdgeCollection,How does the drawContours function work in OpenCV when a contour is filled?
struct PolyEdge
{PolyEdge() : y0(0), y1(0), x(0), dx(0), next(0) {}//PolyEdge(int _y0, int _y1, int _x, int _dx) : y0(_y0), y1(_y1), x(_x), dx(_dx) {}int y0, y1;int64 x, dx;PolyEdge *next;
};static void
CollectPolyEdges( Mat& img, const Point2l* v, int count, std::vector<PolyEdge>& edges,const void* color, int line_type, int shift, Point offset )
{int i, delta = offset.y + ((1 << shift) >> 1);Point2l pt0 = v[count-1], pt1;pt0.x = (pt0.x + offset.x) << (XY_SHIFT - shift);pt0.y = (pt0.y + delta) >> shift;edges.reserve( edges.size() + count );for( i = 0; i < count; i++, pt0 = pt1 ){Point2l t0, t1;PolyEdge edge;pt1 = v[i];pt1.x = (pt1.x + offset.x) << (XY_SHIFT - shift);pt1.y = (pt1.y + delta) >> shift;Point2l pt0c(pt0), pt1c(pt1);if (line_type < cv::LINE_AA){t0.y = pt0.y; t1.y = pt1.y;t0.x = (pt0.x + (XY_ONE >> 1)) >> XY_SHIFT;t1.x = (pt1.x + (XY_ONE >> 1)) >> XY_SHIFT;Line(img, t0, t1, color, line_type);// use clipped endpoints to create a more accurate PolyEdgeif ((unsigned)t0.x >= (unsigned)(img.cols) ||(unsigned)t1.x >= (unsigned)(img.cols) ||(unsigned)t0.y >= (unsigned)(img.rows) ||(unsigned)t1.y >= (unsigned)(img.rows)){clipLine(img.size(), t0, t1);if (t0.y != t1.y){pt0c.y = t0.y; pt1c.y = t1.y;pt0c.x = (int64)(t0.x) << XY_SHIFT;pt1c.x = (int64)(t1.x) << XY_SHIFT;}}else{pt0c.x += XY_ONE >> 1;pt1c.x += XY_ONE >> 1;}}else{t0.x = pt0.x; t1.x = pt1.x;t0.y = pt0.y << XY_SHIFT;t1.y = pt1.y << XY_SHIFT;LineAA(img, t0, t1, color);}if (pt0.y == pt1.y)continue;edge.dx = (pt1c.x - pt0c.x) / (pt1c.y - pt0c.y);if (pt0.y < pt1.y){edge.y0 = (int)(pt0.y);edge.y1 = (int)(pt1.y);edge.x = pt0c.x + (pt0.y - pt0c.y) * edge.dx; // correct starting point for clipped lines}else{edge.y0 = (int)(pt1.y);edge.y1 = (int)(pt0.y);edge.x = pt1c.x + (pt1.y - pt1c.y) * edge.dx; // correct starting point for clipped lines}edges.push_back(edge);}
}struct CmpEdges
{bool operator ()(const PolyEdge& e1, const PolyEdge& e2){return e1.y0 - e2.y0 ? e1.y0 < e2.y0 :e1.x - e2.x ? e1.x < e2.x : e1.dx < e2.dx;}
};static void
FillEdgeCollection( Mat& img, std::vector<PolyEdge>& edges, const void* color, int line_type)
{PolyEdge tmp;int i, y, total = (int)edges.size();Size size = img.size();PolyEdge* e;int y_max = INT_MIN, y_min = INT_MAX;int64 x_max = 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF, x_min = 0x7FFFFFFFFFFFFFFF;int pix_size = (int)img.elemSize();int delta;if (line_type < CV_AA)delta = 0;elsedelta = XY_ONE - 1;if( total < 2 )return;for( i = 0; i < total; i++ ){PolyEdge& e1 = edges[i];CV_Assert( e1.y0 < e1.y1 );// Determine x-coordinate of the end of the edge.// (This is not necessary x-coordinate of any vertex in the array.)int64 x1 = e1.x + (e1.y1 - e1.y0) * e1.dx;y_min = std::min( y_min, e1.y0 );y_max = std::max( y_max, e1.y1 );x_min = std::min( x_min, e1.x );x_max = std::max( x_max, e1.x );x_min = std::min( x_min, x1 );x_max = std::max( x_max, x1 );}if( y_max < 0 || y_min >= size.height || x_max < 0 || x_min >= ((int64)size.width<<XY_SHIFT) )return;std::sort( edges.begin(), edges.end(), CmpEdges() );// start drawingtmp.y0 = INT_MAX;edges.push_back(tmp); // after this point we do not add// any elements to edges, thus we can use pointersi = 0;tmp.next = 0;e = &edges[i];y_max = MIN( y_max, size.height );for( y = e->y0; y < y_max; y++ ){PolyEdge *last, *prelast, *keep_prelast;int draw = 0;int clipline = y < 0;prelast = &tmp;last = tmp.next;while( last || e->y0 == y ){if( last && last->y1 == y ){// exclude edge if y reaches its lower pointprelast->next = last->next;last = last->next;continue;}keep_prelast = prelast;if( last && (e->y0 > y || last->x < e->x) ){// go to the next edge in active listprelast = last;last = last->next;}else if( i < total ){// insert new edge into active list if y reaches its upper pointprelast->next = e;e->next = last;prelast = e;e = &edges[++i];}elsebreak;if( draw ){if( !clipline ){// convert x's from fixed-point to image coordinatesuchar *timg = img.ptr(y);int x1, x2;if (keep_prelast->x > prelast->x){x1 = (int)((prelast->x + delta) >> XY_SHIFT);x2 = (int)(keep_prelast->x >> XY_SHIFT);}else{x1 = (int)((keep_prelast->x + delta) >> XY_SHIFT);x2 = (int)(prelast->x >> XY_SHIFT);}// clip and draw the lineif( x1 < size.width && x2 >= 0 ){if( x1 < 0 )x1 = 0;if( x2 >= size.width )x2 = size.width - 1;ICV_HLINE( timg, x1, x2, color, pix_size );}}keep_prelast->x += keep_prelast->dx;prelast->x += prelast->dx;}draw ^= 1;}// sort edges (using bubble sort)keep_prelast = 0;do{prelast = &tmp;last = tmp.next;PolyEdge *last_exchange = 0;while( last != keep_prelast && last->next != 0 ){PolyEdge *te = last->next;// swap edgesif( last->x > te->x ){prelast->next = te;last->next = te->next;te->next = last;prelast = te;last_exchange = prelast;}else{prelast = last;last = te;}}if (last_exchange == NULL)break;keep_prelast = last_exchange;} while( keep_prelast != tmp.next && keep_prelast != &tmp );}
}其中填充算法为scan-line polygon filling algorithm,下面转载该文
Polygon Filling? How do you do that?
In order to fill a polygon, we do not want to have to determine the type of polygon that we are filling. The easiest way to avoid this situation is to use an algorithm that works for all three types of polygons. Since both convex and concave polygons are subsets of the complex type, using an algorithm that will work for complex polygon filling should be sufficient for all three types. The scan-line polygon fill algorithm, which employs the odd/even parity concept previously discussed, works for complex polygon filling.
Reminder: The basic concept of the scan-line algorithm is to draw points from edges of odd parity to even parity on each scan-line.
What is a scan-line? A scan-line is a line of constant y value, i.e., y=c, where c lies within our drawing region, e.g., the window on our computer screen.
The scan-line algorithm is outlined next.
When filling a polygon, you will most likely just have a set of vertices, indicating the x and y Cartesian coordinates of each vertex of the polygon. The following steps should be taken to turn your set of vertices into a filled polygon.
1.Initializing All of the Edges:
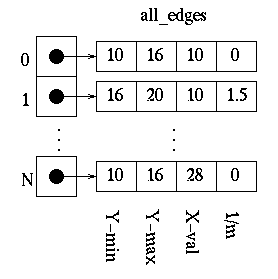
The first thing that needs to be done is determine how the polygon’s vertices are related. The all_edges table will hold this information.
Each adjacent set of vertices (the first and second, second and third, …, last and first) defines an edge. For each edge, the following information needs to be kept in a table:
缩进 1.The minimum y value of the two vertices.
缩进 2.The maximum y value of the two vertices.
缩进 3.The x value associated with the minimum y value.
缩进 4.The slope of the edge.
The slope of the edge can be calculated from the formula for a line:
y = mx + b;
where m = slope, b = y-intercept,
y0 = maximum y value,
y1 = minimum y value,
x0 = maximum x value,
x1 = minimum x value
The formula for the slope is as follows:
m = (y0 - y1) / (x0 - x1).
For example, the edge values may be kept as follows, where N is equal to the total number of edges - 1 and each index into the all_edges array contains a pointer to the array of edge values.
2.Initializing the Global Edge Table:
The global edge table will be used to keep track of the edges that are still needed to complete the polygon. Since we will fill the edges from bottom to top and left to right. To do this, the global edge table table should be inserted with edges grouped by increasing minimum y values. Edges with the same minimum y values are sorted on minimum x values as follows:
缩进 1.Place the first edge with a slope that is not equal to zero in the global edge table.
缩进 2.If the slope of the edge is zero, do not add that edge to the global edge table.
缩进 3.For every other edge, start at index 0 and increase the index to the global edge table once each time the current edge’s y value is greater than that of the edge at the current index in the global edge table.
Next, Increase the index to the global edge table once each time the current edge’s x value is greater than and the y value is less than or equal to that of the edge at the current index in the global edge table.
If the index, at any time, is equal to the number of edges currently in the global edge table, do not increase the index.
Place the edge information for minimum y value, maximum y value, x value, and 1/m in the global edge table at the index.
The global edge table should now contain all of the edge information necessary to fill the polygon in order of increasing minimum y and x values.
3.Initializing Parity
The initial parity is even since no edges have been crossed yet.
4.Initializing the Scan-Line
The initial scan-line is equal to the lowest y value for all of the global edges. Since the global edge table is sorted, the scan-line is the minimum y value of the first entry in this table.
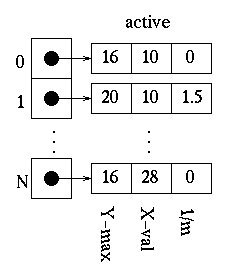
5.Initializing the Active Edge Table
The active edge table will be used to keep track of the edges that are intersected by the current scan-line. This should also contain ordered edges. This is initially set up as follows:
Since the global edge table is ordered on minimum y and x values, search, in order, through the global edge table and, for each edge found having a minimum y value equal to the current scan-line, append the edge information for the maximum y value, x value, and 1/m to the active edge table. Do this until an edge is found with a minimum y value greater than the scan line value. The active edge table will now contain ordered edges of those edges that are being filled as such:
6.Filling the Polygon
Filling the polygon involves deciding whether or not to draw pixels, adding to and removing edges from the active edge table, and updating x values for the next scan-line.
Starting with the initial scan-line, until the active edge table is empty, do the following:
缩进 1.Draw all pixels from the x value of odd to the x value of even parity edge pairs.
缩进 2.Increase the scan-line by 1.
缩进 3.Remove any edges from the active edge table for which the maximum y value is equal to the scan_line.
缩进 4.Update the x value for for each edge in the active edge table using the formula x1 = x0 + 1/m. (This is based on the line formula and the fact that the next scan-line equals the old scan-line plus one.)
缩进 5.Remove any edges from the global edge table for which the minimum y value is equal to the scan-line and place them in the active edge table.
缩进 6.Reorder the edges in the active edge table according to increasing x value. This is done in case edges have crossed.
相关文章:

关于opencv的contourArea计算方法
cv::contourArea计算的轮廓面积并不等于轮廓点计数,原因是cv::contourArea是基于Green公式计算 老外的讨论 github 举一个直观的例子,图中有7个像素,橙色为轮廓点连线,按照contourArea的定义,轮廓的面积为橙色所包围…...
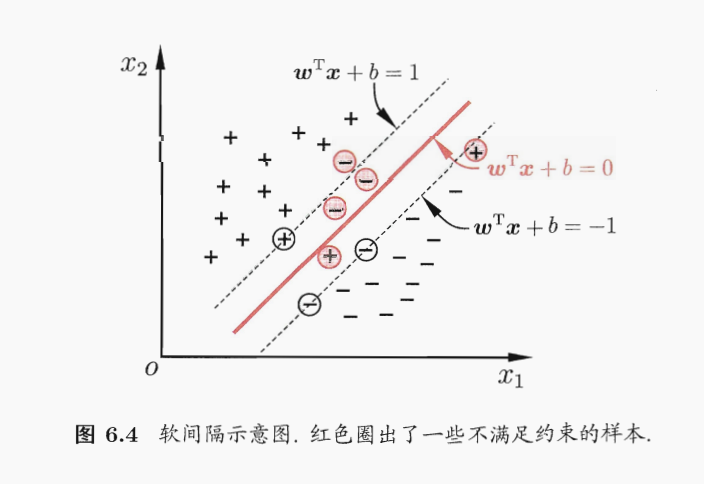
《机器学习》第6章 支持向量机
文章目录 6.1 间隔与支持向量6.2 对偶问题6.3 核函数支持向量展式核函数 6.4 软间隔与正则化6.5 支持向量回归6.6 核方法6.7 阅读材料 6.1 间隔与支持向量 分类学习最基本的想法就是基于训练集D在样本空间中找到一个划分超平面,将不同类别的样本分开.但能将训练样本分开的划分…...
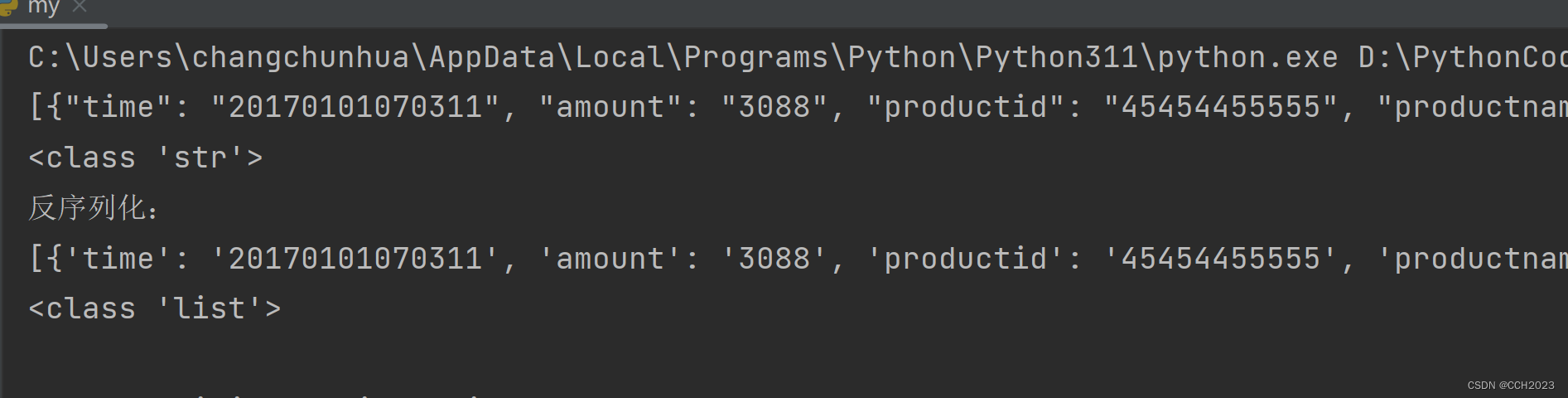
Python学习基础笔记七十七——json序列化
客户端和服务端之间需要交换数据才能完成各种功能。 假设 服务端程序都是用Python语言开发的话,那么 服务端从数据库中获取的最近的交易列表,可能就是像下面这样的一个Python列表对象: historyTransactions [{time : 20170101070311, #…...

【C++】C++11新特性
文章目录 一、C发展简介二、C11简介三、列表初始化1.统一使用{}初始化2.initializer_list类 四、变量的类型推导1.auto2.decltype3.nullptr 五、范围for循环六、STL中一些变化七、final与override八、新的类功能1.新增默认成员函数2.成员变量的缺省值3.default 和 delete4.fina…...
使用 PyAudio、语音识别、pyttsx3 和 SerpApi 构建简单的基于 CLI 的语音助手
德米特里祖布☀️ 一、介绍 正如您从标题中看到的,这是一个演示项目,显示了一个非常基本的语音助手脚本,可以根据 Google 搜索结果在终端中回答您的问题。 您可以在 GitHub 存储库中找到完整代码:dimitryzub/serpapi-demo-project…...

C++11——多线程
目录 一.thread类的简单介绍 二.线程函数参数 三.原子性操作库(atomic) 四.lock_guard与unique_lock 1.lock_guard 2.unique_lock 五.条件变量 一.thread类的简单介绍 在C11之前,涉及到多线程问题,都是和平台相关的,比如windows和linu…...
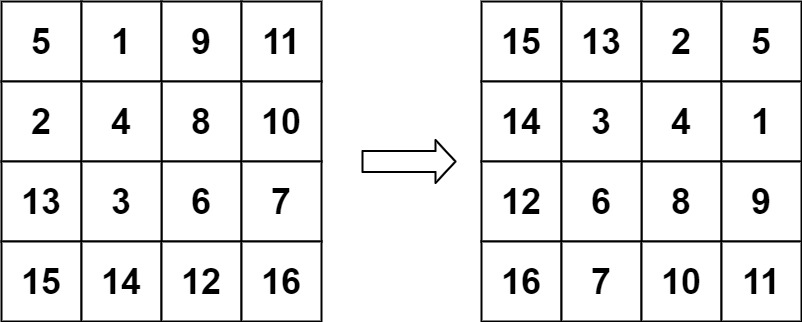
力扣每日一题48:旋转图像
题目描述: 给定一个 n n 的二维矩阵 matrix 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。 你必须在 原地 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要 使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。 示例 1: 输入:matrix [[1,2,3],…...
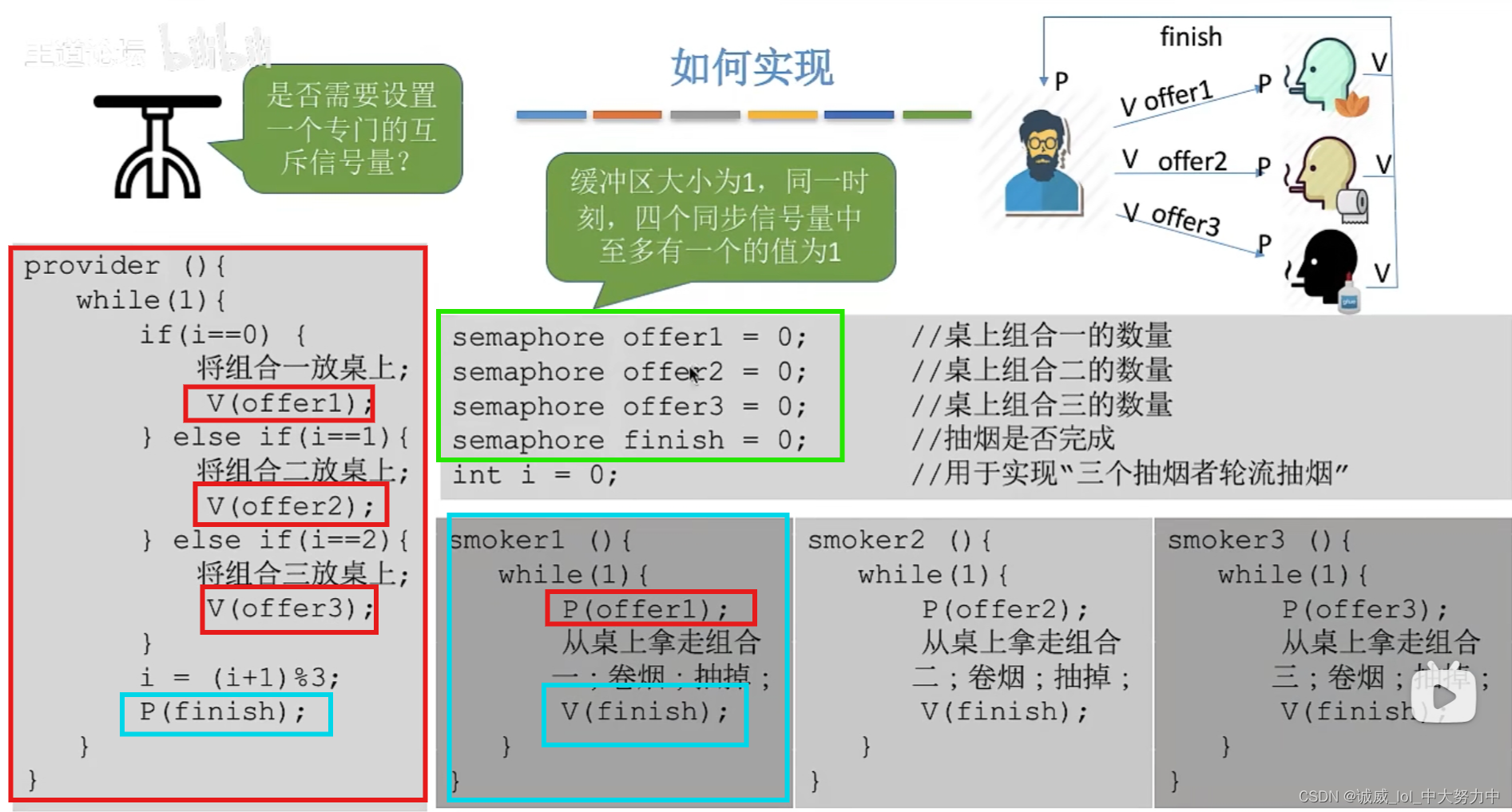
操作系统——吸烟者问题(王道视频p34、课本ch6)
1.问题分析:这个问题可以看作是 可以生产多种产品的 单生产者-多消费者问题 2.代码——这里就是由于同步信号量的初值都是1,所以没有使用mutex互斥信号, 总共4个同步信号量,其中一个是 finish信号量...
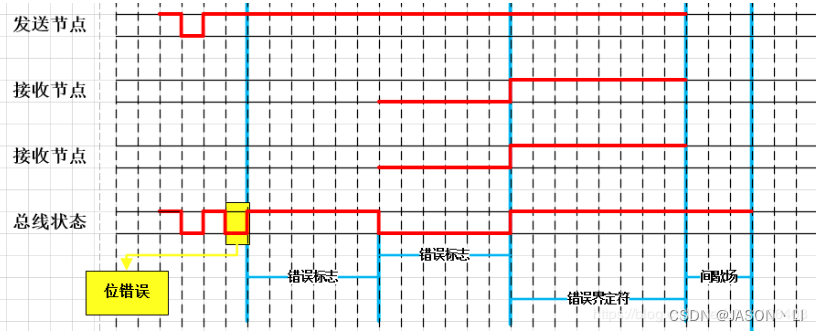
通讯协议学习之路:CAN协议理论
通讯协议之路主要分为两部分,第一部分从理论上面讲解各类协议的通讯原理以及通讯格式,第二部分从具体运用上讲解各类通讯协议的具体应用方法。 后续文章会同时发表在个人博客(jason1016.club)、CSDN;视频会发布在bilibili(UID:399951374) 序、…...
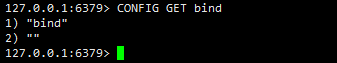
Redis常用配置详解
目录 一、Redis查看当前配置命令二、Redis基本配置三、RDB全量持久化配置(默认开启)四、AOF增量持久化配置五、Redis key过期监听配置六、Redis内存淘汰策略七、总结 一、Redis查看当前配置命令 # Redis查看当前全部配置信息 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG…...

卷积神经网络CNN学习笔记-MaxPool2D函数解析
目录 1.函数签名:2.学习中的疑问3.代码 1.函数签名: torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size, strideNone, padding0, dilation1, return_indicesFalse, ceil_modeFalse) 2.学习中的疑问 Q:使用MaxPool2D池化时,当卷积核移动到某位置,该卷积核覆盖区域超过了输入尺寸时,MaxPool2D会…...

基于图像字典学习的去噪技术研究与实践
图像去噪是计算机视觉领域的一个重要研究方向,其目标是从受到噪声干扰的图像中恢复出干净的原始图像。字典学习是一种常用的图像去噪方法,它通过学习图像的稀疏表示字典,从而实现对图像的去噪处理。本文将详细介绍基于字典学习的图像去噪技术…...
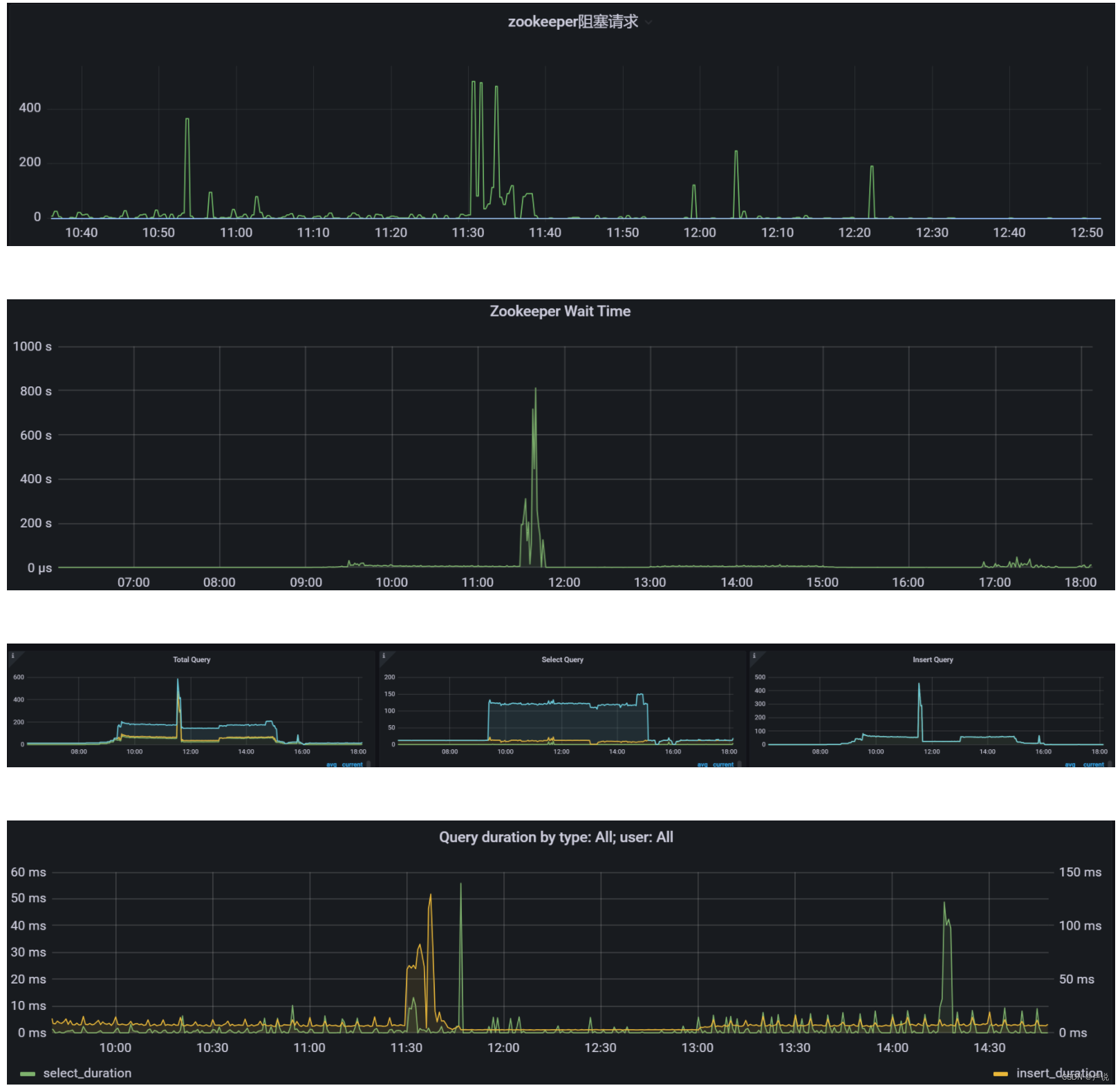
记一次Clickhouse 复制表同步延迟排查
现象 数据从集群中一个节点写入之后,其他两个节点无法及时查询到数据,等了几分钟。因为我们ck集群是读写分离架构,也就是一个节点写数据,其他节点供读取。 排查思路 从业务得知,数据更新时间点为:11:30。…...

Maven的详细安装步骤说明
Step 1: 下载Maven 首先,您需要从Maven官方网站(https://maven.apache.org/)下载Maven的最新版本。在下载页面上,找到与您操作系统对应的二进制文件(通常是.zip或.tar.gz格式),下载到本地。 St…...
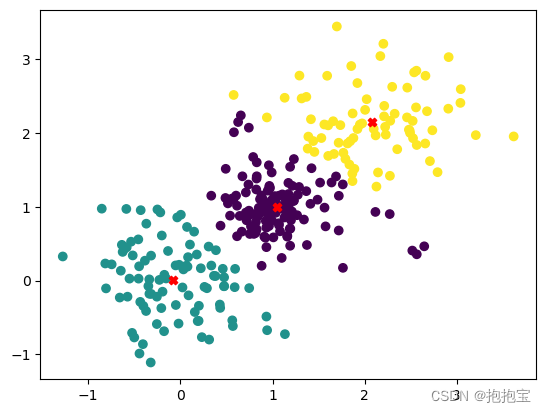
金融机器学习方法:K-均值算法
目录 1.算法介绍 2.算法原理 3.python实现示例 1.算法介绍 K均值聚类算法是机器学习和数据分析中常用的无监督学习方法之一,主要用于数据的分类。它的目标是将数据划分为几个独特的、互不重叠的子集或“集群”,以使得同一集群内的数据点彼此相似&…...

移远通信携手MIKROE推出搭载LC29H系列模组的Click boards开发板,为物联网应用带来高精定位服务
近日,移远通信与MikroElektronika(以下简称“MIKROE”)展开合作,基于移远LC29H系列模组推出了多款支持实时动态载波相位差分技术(RTK)和惯性导航(DR)技术的Click Boards™ 开发板&am…...
Spring Cloud 之 Sentinel简介与GATEWAY整合实现
简介 随着微服务的流行,服务和服务之间的稳定性变得越来越重要。Sentinel 是面向分布式服务架构的流量控制组件,主要以流量为切入点,从限流、流量整形、熔断降级、系统负载保护、热点防护等多个维度来帮助开发者保障微服务的稳定性。 熔断 …...

搭建网站七牛云CDN加速配置
打开七牛云后台;添加域名; 添加需要加速的域名,比如我添加的是motoshare.cn 源站配置,这里要用IP地址,访问的目录下面要有能访问测试的文件,尽量不要用源站域名,这个只能用加速二级域名&#x…...

算法|每日一题|做菜顺序|贪心
1402. 做菜顺序 原题地址: 力扣每日一题:做菜顺序 一个厨师收集了他 n 道菜的满意程度 satisfaction ,这个厨师做出每道菜的时间都是 1 单位时间。 一道菜的 「 like-time 系数 」定义为烹饪这道菜结束的时间(包含之前每道菜所花…...
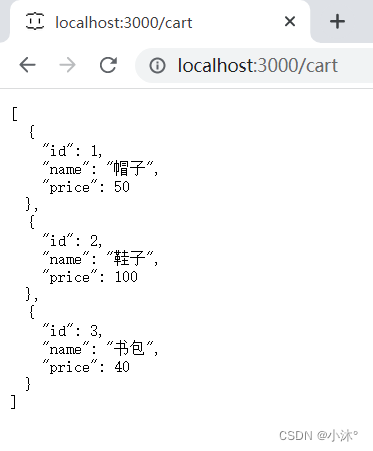
json-server工具准备后端接口服务环境
1.安装全局工具json-server(全局工具仅需要安装一次) 官网:json-server - npm 点击Getting started可以查看使用方法 在终端中输入yarn global add json-server或npm i json-server -g 如果输入json-server -v报错 再输入npm install -g j…...

利用最小二乘法找圆心和半径
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <Eigen/Dense> // 需安装Eigen库用于矩阵运算 // 定义点结构 struct Point { double x, y; Point(double x_, double y_) : x(x_), y(y_) {} }; // 最小二乘法求圆心和半径 …...
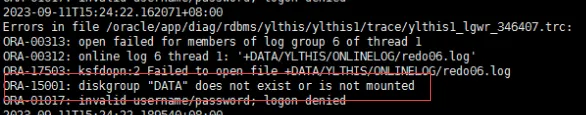
19c补丁后oracle属主变化,导致不能识别磁盘组
补丁后服务器重启,数据库再次无法启动 ORA01017: invalid username/password; logon denied Oracle 19c 在打上 19.23 或以上补丁版本后,存在与用户组权限相关的问题。具体表现为,Oracle 实例的运行用户(oracle)和集…...
label-studio的使用教程(导入本地路径)
文章目录 1. 准备环境2. 脚本启动2.1 Windows2.2 Linux 3. 安装label-studio机器学习后端3.1 pip安装(推荐)3.2 GitHub仓库安装 4. 后端配置4.1 yolo环境4.2 引入后端模型4.3 修改脚本4.4 启动后端 5. 标注工程5.1 创建工程5.2 配置图片路径5.3 配置工程类型标签5.4 配置模型5.…...
无法与IP建立连接,未能下载VSCode服务器
如题,在远程连接服务器的时候突然遇到了这个提示。 查阅了一圈,发现是VSCode版本自动更新惹的祸!!! 在VSCode的帮助->关于这里发现前几天VSCode自动更新了,我的版本号变成了1.100.3 才导致了远程连接出…...

抖音增长新引擎:品融电商,一站式全案代运营领跑者
抖音增长新引擎:品融电商,一站式全案代运营领跑者 在抖音这个日活超7亿的流量汪洋中,品牌如何破浪前行?自建团队成本高、效果难控;碎片化运营又难成合力——这正是许多企业面临的增长困局。品融电商以「抖音全案代运营…...

Nuxt.js 中的路由配置详解
Nuxt.js 通过其内置的路由系统简化了应用的路由配置,使得开发者可以轻松地管理页面导航和 URL 结构。路由配置主要涉及页面组件的组织、动态路由的设置以及路由元信息的配置。 自动路由生成 Nuxt.js 会根据 pages 目录下的文件结构自动生成路由配置。每个文件都会对…...
如何将联系人从 iPhone 转移到 Android
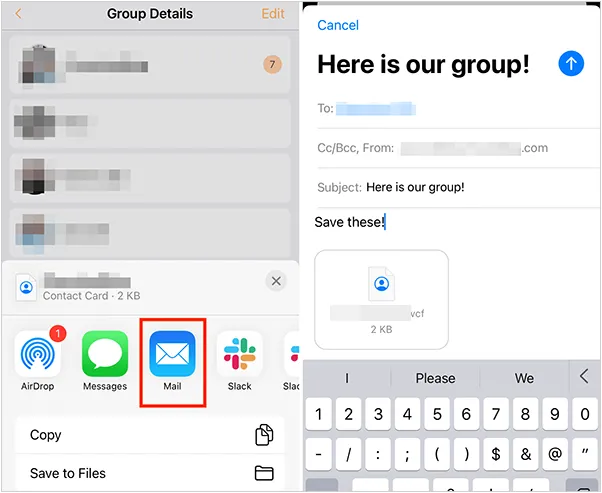
从 iPhone 换到 Android 手机时,你可能需要保留重要的数据,例如通讯录。好在,将通讯录从 iPhone 转移到 Android 手机非常简单,你可以从本文中学习 6 种可靠的方法,确保随时保持连接,不错过任何信息。 第 1…...

【Go】3、Go语言进阶与依赖管理
前言 本系列文章参考自稀土掘金上的 【字节内部课】公开课,做自我学习总结整理。 Go语言并发编程 Go语言原生支持并发编程,它的核心机制是 Goroutine 协程、Channel 通道,并基于CSP(Communicating Sequential Processes࿰…...

CMake控制VS2022项目文件分组
我们可以通过 CMake 控制源文件的组织结构,使它们在 VS 解决方案资源管理器中以“组”(Filter)的形式进行分类展示。 🎯 目标 通过 CMake 脚本将 .cpp、.h 等源文件分组显示在 Visual Studio 2022 的解决方案资源管理器中。 ✅ 支持的方法汇总(共4种) 方法描述是否推荐…...
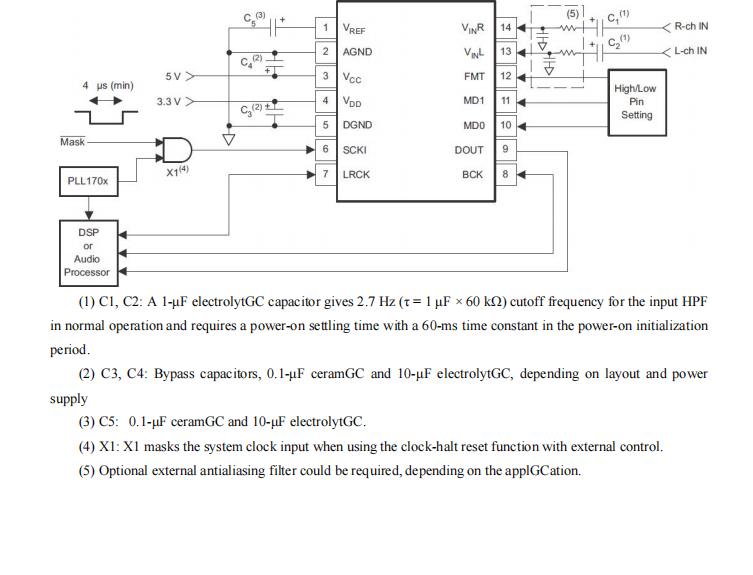
GC1808高性能24位立体声音频ADC芯片解析
1. 芯片概述 GC1808是一款24位立体声音频模数转换器(ADC),支持8kHz~96kHz采样率,集成Δ-Σ调制器、数字抗混叠滤波器和高通滤波器,适用于高保真音频采集场景。 2. 核心特性 高精度:24位分辨率,…...
