【数据结构】数组和字符串(十三):链式字符串的基本操作(串长统计、查找、复制、插入、删除、串拼接)
文章目录
- 4.3 字符串
- 4.3.1 字符串的定义与存储
- 4.3.2 字符串的基本操作(链式存储)
- 1. 结构体
- 2. 初始化
- 3. 判空
- 4. 串尾添加
- 5. 打印
- 6. 串长统计
- 7. 查找
- 8. 复制
- 9. 插入
- 10. 删除
- 11. 串拼接
- 12. 销毁
- 13. 主函数
- 14. 代码整合
4.3 字符串
字符串(String)是由零个或多个字符(char)顺序排列组成的有限序列,简称为串。例如 “good morning”就是由12个字符构成的一个字符串。一般把字符串记作:
S = ′ ′ a 0 a 1 … a n − 1 ′ ′ S=''a_{0} a_{1}…a_{n-1}'' S=′′a0a1…an−1′′
其中S是串名,引号中的字符序列是串值。字符个数是串的长度,长度为0的串被称为空串,因为它不包含任何字符。需要注意的是,空格字符(" ")并不是空串,因为它包含一个字符——空格。
若把某个串称为主串,则主串中任意个连续的字符组成的子序列被称为子串。子串在主串中第一次出现时,其首字符在主串中的序号被称为该子串在主串中的位置。
关于字符串的基础知识亦可参考前文:
【重拾C语言】六、批量数据组织(三)数组初值;字符串、字符数组、字符串数组;类型定义 typedef
【重拾C语言】七、指针(三)指针与字符串(字符串与字符串数组;指针与字符串的遍历、拷贝、比较;反转字符串)
4.3.1 字符串的定义与存储
字符串在许多非数值计算问题中扮演着重要的角色,并在模式匹配、程序编译和数据处理等领域得到广泛应用。在高级程序设计语言中,字符串通常被定义为以特殊字符’\0’(称为空字符或字符串结束符)结尾的字符序列。这个约定使得在处理字符串时可以方便地确定字符串的结束位置。关于字符串的存储方式,主要有两种常见的方式:
-
顺序存储:字符串的字符按照顺序依次存储在连续的内存空间中。这种方式使得字符串的访问和操作效率较高,可以通过索引直接访问任意位置的字符。在顺序存储方式中,字符串的长度可以通过计算字符个数或者遇到’\0’结束符来确定。
-
链式存储:字符串的字符通过链表的方式进行存储。每个节点包含一个字符和指向下一个节点的指针。链式存储方式可以动态地分配内存,适用于长度可变的字符串。但是相比于顺序存储,链式存储方式需要更多的内存空间,并且访问字符需要遍历链表。
选择何种存储方式取决于具体的应用场景和需求。顺序存储适合于需要频繁访问和操作字符串的情况,而链式存储适合于长度可变的字符串或者对内存空间要求较高的情况。具体C语言实现可参照前文:
【数据结构】数组和字符串(十一):字符串的定义与存储(顺序存储、链式存储及其C语言实现)
4.3.2 字符串的基本操作(链式存储)
- 串长统计返回串s的长度;
- 串定位返回字符或子串在母串s中首次出现的位置的指针;
- 串复制将一个串s2复制到另一个串s1中;
- 串插入在指定位置后面插入字符串;
- 串删除是删除一个子串;
- 串拼接将串s2拼接到串s1的尾部;
- ……
【数据结构】线性表(二)单链表及其基本操作(创建、插入、删除、修改、遍历打印)
1. 结构体
typedef struct Node {char data;struct Node* next;
} Node;typedef struct {Node* head;Node* tail;
} LinkedList;Node:表示链表的节点,包含一个字符数据和一个指向下一个节点的指针。LinkedList:表示链表,包含链表的头节点和尾节点。
2. 初始化
initLinkedList函数:用于初始化链表,将头节点和尾节点都设置为NULL。
void initLinkedList(LinkedList* list) {list->head = NULL;list->tail = NULL;
}3. 判空
isEmpty函数:判断链表是否为空,即头节点是否为NULL。
bool isEmpty(const LinkedList* list) {return list->head == NULL;
}4. 串尾添加
append函数:向链表末尾添加一个字符节点。
void append(LinkedList* list, char data) {Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = data;newNode->next = NULL;if (isEmpty(list)) {list->head = newNode;list->tail = newNode;} else {list->tail->next = newNode;list->tail = newNode;}
}- 如果链表为空,即头节点为
NULL,则将新节点设置为头节点和尾节点。 - 如果链表不为空,即头节点不为
NULL,则将新节点链接到尾节点的后面,并将尾节点更新为新节点。
5. 打印
display函数:遍历链表并打印出所有字符节点的数据。
void display(const LinkedList* list) {Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {printf("%c", current->data);current = current->next;}printf("\n");
}- 函数接受一个指向
LinkedList结构体的指针作为参数,然后从头节点开始遍历链表,打印每个节点的数据。
6. 串长统计
length函数:计算链表的长度,即字符节点的个数。
int length(const LinkedList* list) {int count = 0;Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {count++;current = current->next;}return count;
}- 函数接受一个指向
LinkedList结构体的指针作为参数,然后从头节点开始遍历链表,每遍历一个节点,计数器加1,最后返回计数器的值。
7. 查找
search函数:在链表中搜索目标字符串。
int search(const LinkedList* list, const char* target) {int targetLength = strlen(target);int listLength = length(list);if (targetLength > listLength) {printf("Error: Target string is longer than the source string.\n");return -1;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (current->data == target[0]) {Node* temp = current;int i = 0;while (temp != NULL && temp->data == target[i]) {temp = temp->next;i++;if (i == targetLength) {return index;}}}current = current->next;index++;}printf("Error: Target string not found in the source string.\n");return -1;
}- 首先比较目标字符串的长度和链表的长度,如果目标字符串比链表长,说明无法找到目标字符串,函数返回错误。
- 然后从头节点开始遍历链表,找到第一个与目标字符串首字符相同的节点,
- 然后从该节点开始逐个比较字符,直到找到完全匹配的目标字符串或链表遍历结束。
- 如果找到目标字符串,函数返回目标字符串在链表中的起始位置的索引;
- 如果未找到目标字符串,函数返回错误。
8. 复制
copy函数:将源链表中的字符复制到目标链表中。
bool copy(LinkedList* dest, const LinkedList* src) {Node* current = src->head;while (current != NULL) {append(dest, current->data);current = current->next;}return true;
}- 函数接受两个指向
LinkedList结构体的指针,分别表示源链表和目标链表。 - 通过遍历源链表的每个节点,创建一个新节点并将数据复制过去,然后将新节点添加到目标链表的末尾。
9. 插入
insert函数:在链表的指定位置插入一个字符串。
bool insert(LinkedList* list, const char* insertStr, int pos) {int listLength = length(list);int insertStrLength = strlen(insertStr);if (pos < 0 || pos > listLength) {printf("Error: Invalid insertion position.\n");return false;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (index == pos) {for (int i = 0; i < insertStrLength; i++) {Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = insertStr[i];newNode->next = current->next;current->next = newNode;current = newNode;}return true;}current = current->next;index++;}return false;
}- 首先判断插入位置是否合法,即索引是否在有效范围内。然后遍历链表找到插入位置的节点,然后逐个创建新节点并插入到链表中。
10. 删除
delete函数:从链表中删除指定位置和长度的字符。
bool delete(LinkedList* list, int pos, int len) {int listLength = length(list);if (pos < 0 || pos >= listLength) {printf("Error: Invalid deletion position.\n");return false;}if (pos + len > listLength) {printf("Error: Deletion length exceeds the length of the string.\n");return false;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (index == pos) {Node* prev = current;Node* temp = current;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {temp = temp->next;free(prev);prev = temp;}current->next = temp;return true;}current = current->next;index++;}return false;
}- 首先判断删除位置是否合法,然后找到删除位置的节点,逐个删除指定长度的节点。
11. 串拼接
concat函数:将第二个链表中的字符追加到第一个链表的末尾。的末尾。
bool concat(LinkedList* list1, const LinkedList* list2) {Node* current = list2->head;while (current != NULL) {append(list1, current->data);current = current->next;}return true;
}- 遍历第二个链表的每个节点,将节点的数据追加到第一个链表。
12. 销毁
destroy函数:释放链表占用的内存。遍历链表的每个节点,释放节点的内存,并将头节点和尾节点设置为NULL。
void destroy(LinkedList* list) {Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {Node* temp = current;current = current->next;free(temp);}list->head = NULL;list->tail = NULL;
}
- 函数遍历链表的每个节点,释放节点的内存,并将头节点和尾节点设置为
NULL。
13. 主函数
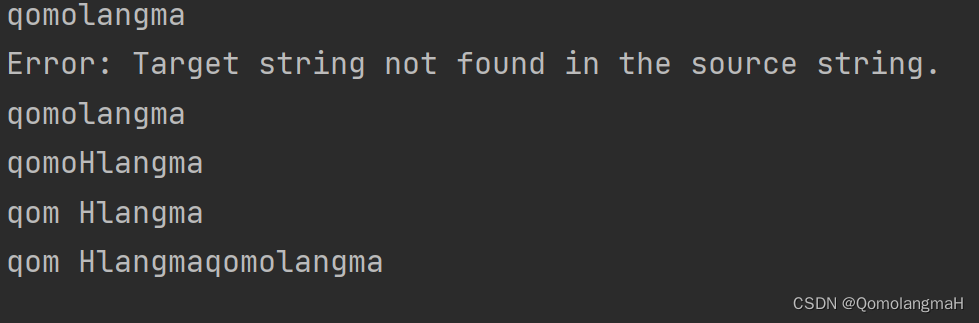
int main() {LinkedList S;initLinkedList(&S);const char target[] = "H";LinkedList copyStr;initLinkedList(©Str);const char insertStr[] = "H";int pos = 3;append(&S, 'q');append(&S, 'o');append(&S, 'm');append(&S, 'o');append(&S, 'l');append(&S, 'a');append(&S, 'n');append(&S, 'g');append(&S, 'm');append(&S, 'a');display(&S);int searchIndex = search(&S, target);if (searchIndex != -1) {printf("Target string found at index: %d\n", searchIndex);}copy(©Str, &S);display(©Str);insert(&S, insertStr, pos);display(&S);delete(&S, pos, strlen(insertStr));display(&S);concat(&S, ©Str);display(&S);destroy(&S);destroy(©Str);return 0;
}
14. 代码整合
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>typedef struct Node {char data;struct Node* next;
} Node;typedef struct {Node* head;Node* tail;
} LinkedList;void initLinkedList(LinkedList* list) {list->head = NULL;list->tail = NULL;
}bool isEmpty(const LinkedList* list) {return list->head == NULL;
}void append(LinkedList* list, char data) {Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = data;newNode->next = NULL;if (isEmpty(list)) {list->head = newNode;list->tail = newNode;} else {list->tail->next = newNode;list->tail = newNode;}
}void display(const LinkedList* list) {Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {printf("%c", current->data);current = current->next;}printf("\n");
}int length(const LinkedList* list) {int count = 0;Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {count++;current = current->next;}return count;
}int search(const LinkedList* list, const char* target) {int targetLength = strlen(target);int listLength = length(list);if (targetLength > listLength) {printf("Error: Target string is longer than the source string.\n");return -1;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (current->data == target[0]) {Node* temp = current;int i = 0;while (temp != NULL && temp->data == target[i]) {temp = temp->next;i++;if (i == targetLength) {return index;}}}current = current->next;index++;}printf("Error: Target string not found in the source string.\n");return -1;
}bool copy(LinkedList* dest, const LinkedList* src) {Node* current = src->head;while (current != NULL) {append(dest, current->data);current = current->next;}return true;
}bool insert(LinkedList* list, const char* insertStr, int pos) {int listLength = length(list);int insertStrLength = strlen(insertStr);if (pos < 0 || pos > listLength) {printf("Error: Invalid insertion position.\n");return false;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (index == pos) {for (int i = 0; i < insertStrLength; i++) {Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = insertStr[i];newNode->next = current->next;current->next = newNode;current = newNode;}return true;}current = current->next;index++;}return false;
}bool delete(LinkedList* list, int pos, int len) {int listLength = length(list);if (pos < 0 || pos >= listLength) {printf("Error: Invalid deletion position.\n");return false;}if (pos + len > listLength) {printf("Error: Deletion length exceeds the length of the string.\n");return false;}Node* current = list->head;int index = 0;while (current != NULL) {if (index == pos) {Node* prev = current;Node* temp = current;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {temp = temp->next;free(prev);prev = temp;}current->next = temp;return true;}current = current->next;index++;}return false;
}bool concat(LinkedList* list1, const LinkedList* list2) {Node* current = list2->head;while (current != NULL) {append(list1, current->data);current = current->next;}return true;
}void destroy(LinkedList* list) {Node* current = list->head;while (current != NULL) {Node* temp = current;current = current->next;free(temp);}list->head = NULL;list->tail = NULL;
}int main() {LinkedList S;initLinkedList(&S);const char target[] = "H";LinkedList copyStr;initLinkedList(©Str);const char insertStr[] = "H";int pos = 3;append(&S, 'q');append(&S, 'o');append(&S, 'm');append(&S, 'o');append(&S, 'l');append(&S, 'a');append(&S, 'n');append(&S, 'g');append(&S, 'm');append(&S, 'a');display(&S);int searchIndex = search(&S, target);if (searchIndex != -1) {printf("Target string found at index: %d\n", searchIndex);}copy(©Str, &S);display(©Str);insert(&S, insertStr, pos);display(&S);delete(&S, pos, strlen(insertStr));display(&S);concat(&S, ©Str);display(&S);destroy(&S);destroy(©Str);return 0;
}相关文章:

【数据结构】数组和字符串(十三):链式字符串的基本操作(串长统计、查找、复制、插入、删除、串拼接)
文章目录 4.3 字符串4.3.1 字符串的定义与存储4.3.2 字符串的基本操作(链式存储)1. 结构体2. 初始化3. 判空4. 串尾添加5. 打印6. 串长统计7. 查找8. 复制9. 插入10. 删除11. 串拼接12. 销毁13. 主函数14. 代码整合 4.3 字符串 字符串(String)是由零个或…...

Python3 获取当前服务器公网 IP 地址
有同学问我如何使用 Python 获取服务器公网的 IP 地址呢?我测试几个发现,方法有很多,好用的就发现一种,即直接使用 Python 自带的 socket 包。 代码示例: # 获取主机 IP dgram socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socke…...

EAS查前5分钟到现在的组织变动数据
select * from T_ORG_Admin where ( (FCREATETIME between ( sysdate-(1/24/60)*8) and sysdate ) or (FLASTUPDATETIME between ( sysdate-(1/24/60)*8) and sysdate ) ) -- FLASTUPDATETIME < sysdate-(1/24/60)*10 --FNUMBER 110112...

uni-app——如何阻止事件冒泡
引言 在开发移动应用程序时,我们经常需要处理用户交互事件。然而,有时候这些事件会冒泡,导致意外的行为和不良用户体验。在本文中,我们将探讨如何使用UniApp框架来阻止事件冒泡,并提供一些示例代码来帮助您理解如何实…...
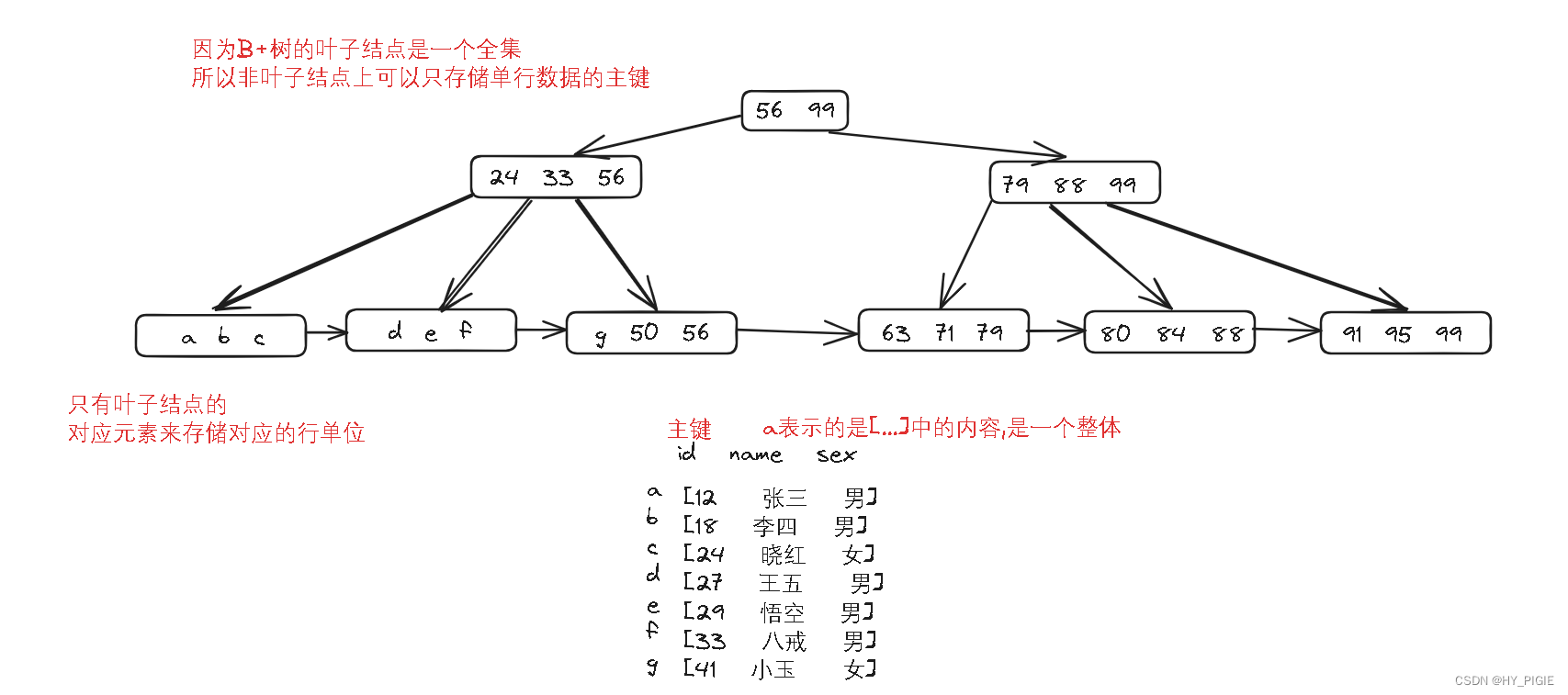
[MySQL]索引
目录 概念解释 作用/优点 缺点 适用场景 索引的创建,删除与查看 系统对索引的自动创建 索引建立的时机 索引存储的数据结构 选择B树的原因 B树的原理 查询流程 优点 B树 与B树的区别 优点 概念解释 索引就像是一本字典的目录,我们可以根据目录快速定位到我们想…...
什么是AUTOSAR ComStack,AUTOSAR架构中,CAN通信堆栈CAN Communication Stack介绍
AUTOSAR(Automotive Open System Architecture)ComStack指的是AUTOSAR架构中的通信堆栈。在AUTOSAR体系结构中,ComStack是指用于不同软件组件(如应用软件、基础软件等)之间进行通信的一组协议和服务。 在AUTOSAR架构中…...

黄金期货与黄金现货的区别
黄金期货与黄金现货是有区别的,比如在交易机制方面,黄金期货有具体的交割日,合约到期就必须交割,否则会被强行平仓或以实物进行交割,而在保证金不足时也会被强行平仓;而现货黄金就没有交割限制,…...
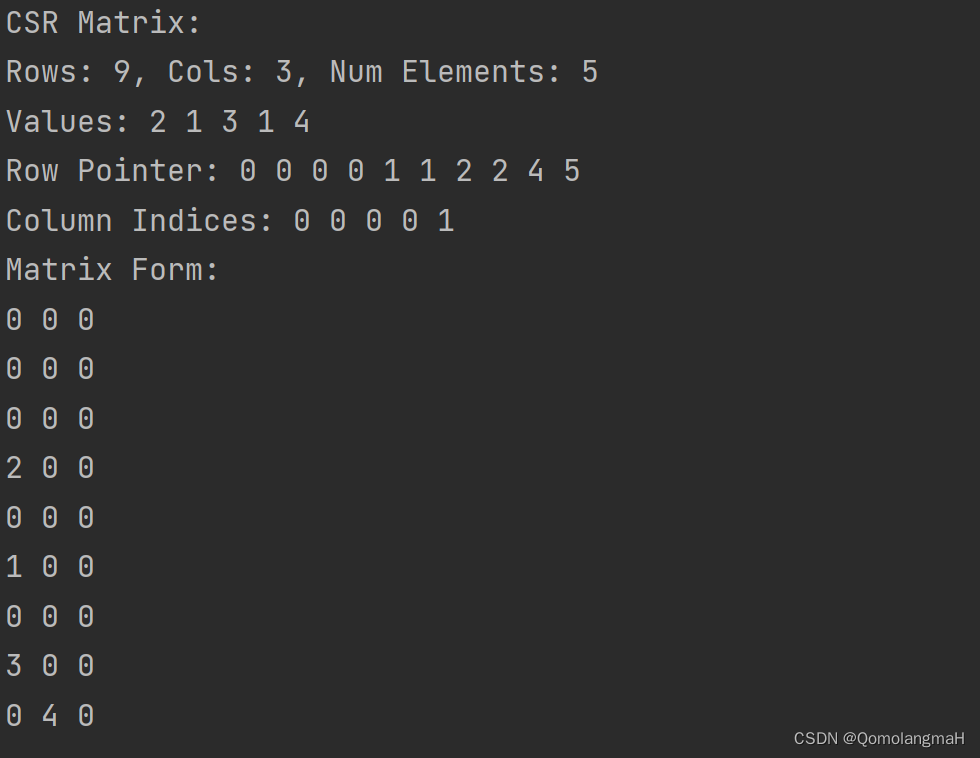
【数据结构】数组和字符串(五):特殊矩阵的压缩存储:稀疏矩阵——压缩稀疏行(CSR)
文章目录 4.2.1 矩阵的数组表示4.2.2 特殊矩阵的压缩存储a. 对角矩阵的压缩存储b~c. 三角、对称矩阵的压缩存储d. 稀疏矩阵的压缩存储——三元组表e. 压缩稀疏行(Compressed Sparse Row,CSR)矩阵结构体创建CSR矩阵元素设置初始化打印矩阵销毁…...
springboot整合postgresql
使用docker安装postgres 简单起见,这里用docker来安装postgresql docker pull postgresdocker run --name postgres \-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD123456 \-p 5432:5432 \-v /usr/local/docker/postgresql/data:/var/lib/postgresql/data \-d postgrespostgres客户端 pg…...

C#__委托delegate
委托存储的是函数的引用(把某个函数赋值给一个委托类型的变量,这样的话这个变量就可以当成这个函数来进行使用了) 委托类型跟整型类型、浮点型类型一样,也是一种类型,是一种存储函数引用的类型 using System.Reflec…...

Jupyter Notebook的安装方法以及生成ipykernel
1. 安装Python和pip Jupyter Notebook是基于Python的,因此首先需要在电脑上安装Python和pip。可以通过访问Python官网(Welcome to Python.org)下载安装包进行安装。在安装Python的过程中,会提示是否安装pip,选择安装即可。 2. 安装Jupyter …...
测试员如何快速复现bug?一款合适的视频录制软件了解一下
你是不是还在为描述缺陷复现步骤而苦恼?你是不是还在为寻找一款合适的视屏录制软件而挣扎?那么,你应该好好看看这篇小文章。 作为测试人员,撰写测试用例、提交测试缺陷是基本工作。但往往我们会遇到:开发人员无法根据…...

论文-分布式-并发控制-并发控制问题的解决方案
目录 参考文献 问题 解法与证明 易读版本 参考文献 Dijkstra于1965年发表文章Solution of a Problem in Concurrent Programming Control,引出并发系统下的互斥(mutual exclusion)问题,自此开辟了分布式计算领域Dijkstra在文中给出了基于共享存储原子…...
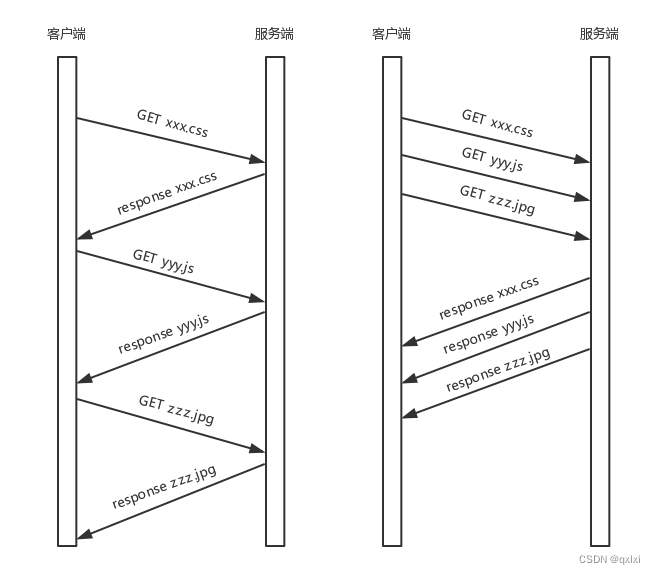
【网络协议】聊聊http协议
当我们输入www.baidu.com的时候,其实是先将baidu.com的域名进行DNS解析,转换成对应的ip地址,然后开始进行基于TCP构建三次握手的连接,目前使用的是1.1 默认是开启了keep-Alive。可以在多次请求中进行连接复用。 HTTP 请求的构建…...
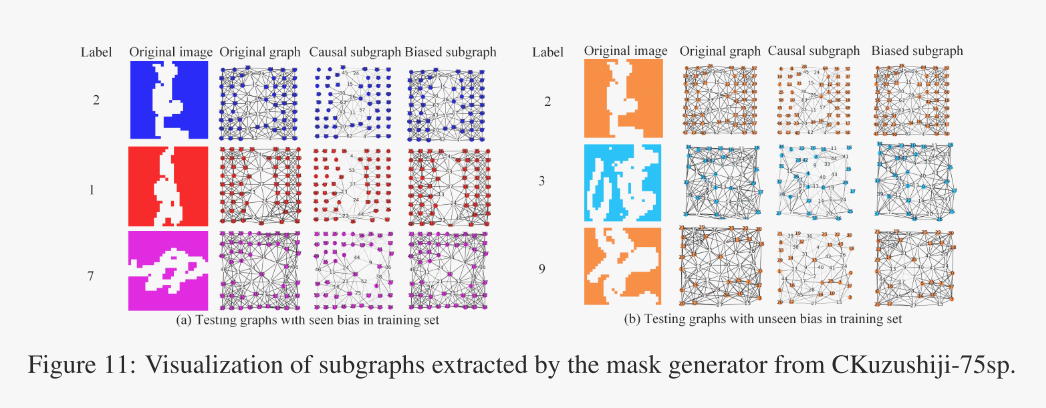

图神经网络论文笔记(一)——北邮:基于学习解纠缠因果子结构的图神经网络去偏
作者 :范少华 研究方向 :图神经网络 论文标题 :基于学习解纠缠因果子结构的图神经网络去偏 论文链接 :https://arxiv.org/pdf/2209.14107.pdf https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2209.14107 大多数图神经网络(GNNs)通…...

java初始化list的几种方式
在Java中初始化List有以下几种常见的方式: 使用Arrays.asList()静态方法: List<Integer> list1 Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);使用List接口的实现类ArrayList的构造函数: List<String> list2 new ArrayList<>();使用Collections.singletonList() String obj…...
Linux:文件操作
目录 一、关于文件 1、文件类的系统接口 2、文件的含义 二、文件操作 1、C语言文件相关接口 2、系统接口 open close write read 三、文件描述符 关于fd fd的分配规则 输出重定向示例 输入重定向示例 追加重定向示例 dup2函数 缓冲区 stdout与stderr perror…...
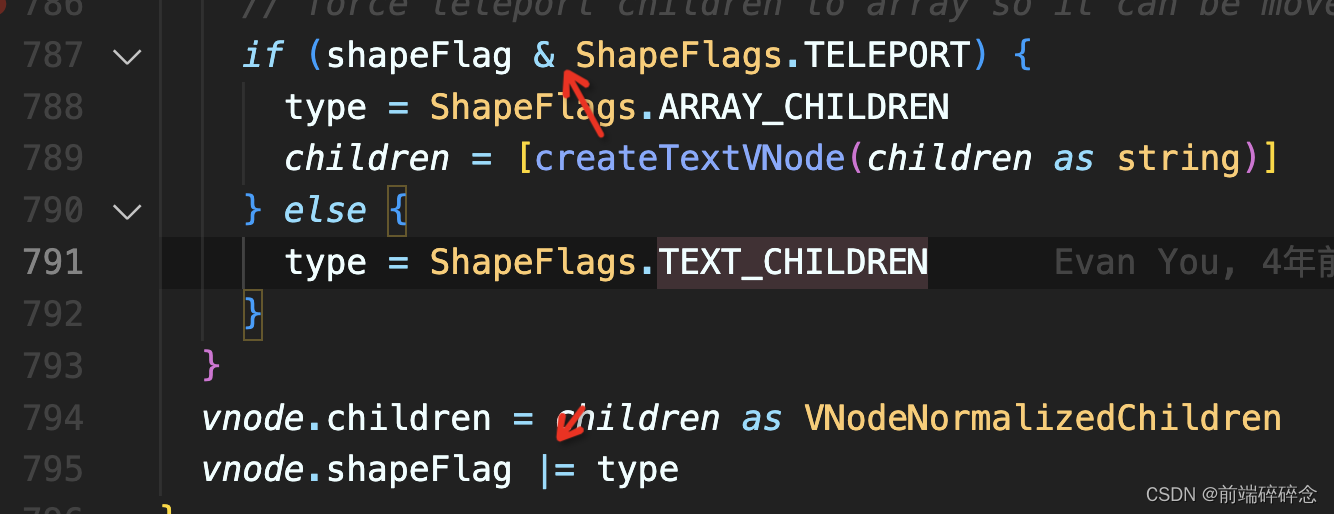
vue源码笔记之——运行时runtime
源码中的位运算 按位于 运算 if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TELEPORT) {解释:如果shapFlag本身值为8,type为1的话,那么转换为二进制(js都是32位)那就是 shapFlag:00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000 …...
)
MySQL数据库干货_09—— MySQL中的外键约束(Foreign Key)
外键约束(Foreign Key) 添加外键约束 使用DDL语句添加外键约束 ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD CONSTRAINT 约束名 FOREIGN KEY( 列 名 ) REFERENCES 参照的表名(参照的列名);示例一: 创建 departments 表包含 department_id 、department_name ,location_id。…...
springboot配置https
SSL : secure socket layer 是一种加密协议,SSL主要用于保护数据在 客户端和服务器之间的传输,,防止未经授权的访问和窃取敏感信息 在腾讯云申请ssl证书 申请了之后在我的域名中,,解析 解析了之后&…...
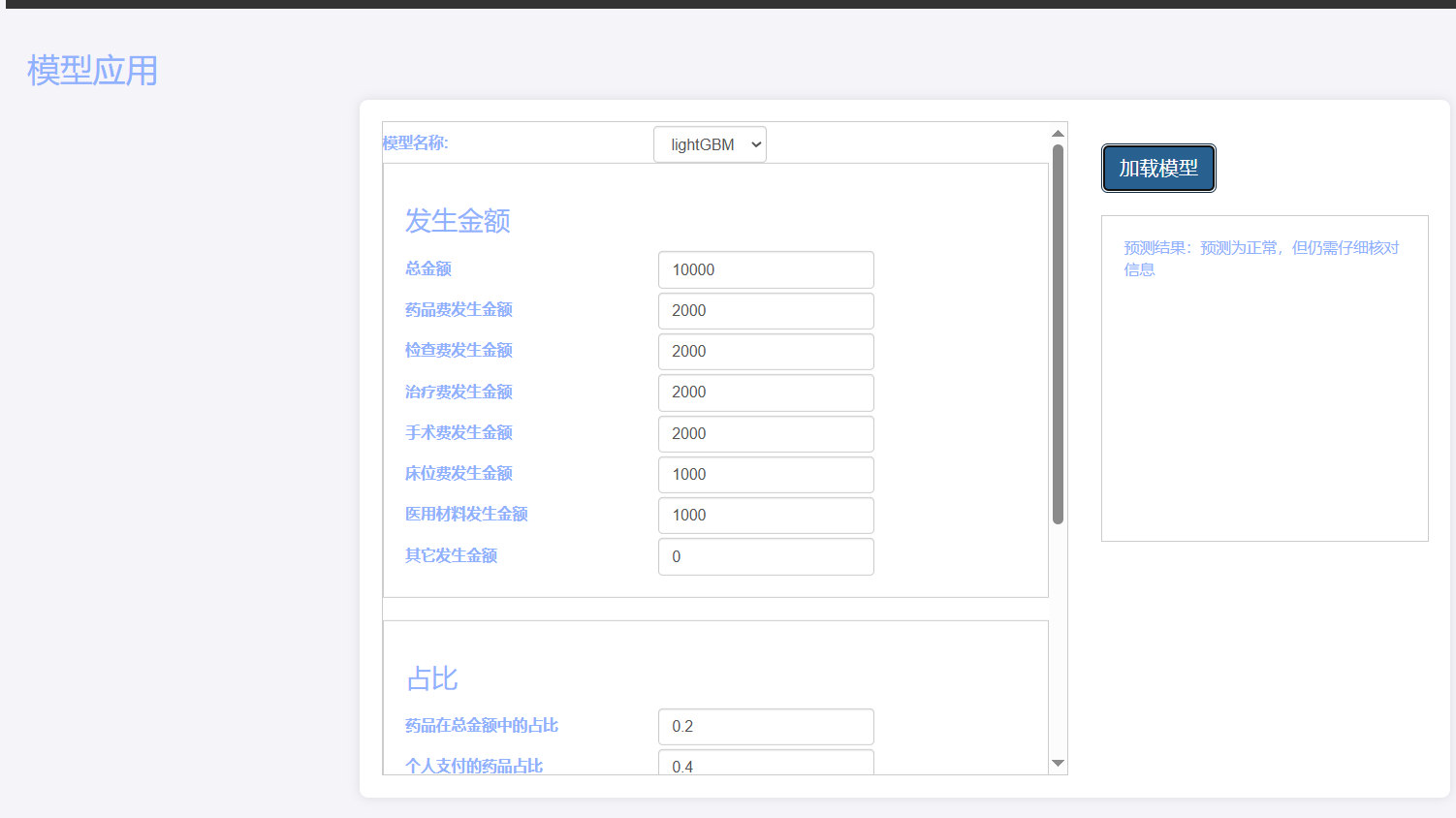
基于Flask实现的医疗保险欺诈识别监测模型
基于Flask实现的医疗保险欺诈识别监测模型 项目截图 项目简介 社会医疗保险是国家通过立法形式强制实施,由雇主和个人按一定比例缴纳保险费,建立社会医疗保险基金,支付雇员医疗费用的一种医疗保险制度, 它是促进社会文明和进步的…...
-----深度优先搜索(DFS)实现)
c++ 面试题(1)-----深度优先搜索(DFS)实现
操作系统:ubuntu22.04 IDE:Visual Studio Code 编程语言:C11 题目描述 地上有一个 m 行 n 列的方格,从坐标 [0,0] 起始。一个机器人可以从某一格移动到上下左右四个格子,但不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 k 的格子。 例…...
从零开始打造 OpenSTLinux 6.6 Yocto 系统(基于STM32CubeMX)(九)
设备树移植 和uboot设备树修改的内容同步到kernel将设备树stm32mp157d-stm32mp157daa1-mx.dts复制到内核源码目录下 源码修改及编译 修改arch/arm/boot/dts/st/Makefile,新增设备树编译 stm32mp157f-ev1-m4-examples.dtb \stm32mp157d-stm32mp157daa1-mx.dtb修改…...

解决本地部署 SmolVLM2 大语言模型运行 flash-attn 报错
出现的问题 安装 flash-attn 会一直卡在 build 那一步或者运行报错 解决办法 是因为你安装的 flash-attn 版本没有对应上,所以报错,到 https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases 下载对应版本,cu、torch、cp 的版本一定要对…...

Java 二维码
Java 二维码 **技术:**谷歌 ZXing 实现 首先添加依赖 <!-- 二维码依赖 --><dependency><groupId>com.google.zxing</groupId><artifactId>core</artifactId><version>3.5.1</version></dependency><de…...

AirSim/Cosys-AirSim 游戏开发(四)外部固定位置监控相机
这个博客介绍了如何通过 settings.json 文件添加一个无人机外的 固定位置监控相机,因为在使用过程中发现 Airsim 对外部监控相机的描述模糊,而 Cosys-Airsim 在官方文档中没有提供外部监控相机设置,最后在源码示例中找到了,所以感…...

vulnyx Blogger writeup
信息收集 arp-scan nmap 获取userFlag 上web看看 一个默认的页面,gobuster扫一下目录 可以看到扫出的目录中得到了一个有价值的目录/wordpress,说明目标所使用的cms是wordpress,访问http://192.168.43.213/wordpress/然后查看源码能看到 这…...
并发编程 - go版
1.并发编程基础概念 进程和线程 A. 进程是程序在操作系统中的一次执行过程,系统进行资源分配和调度的一个独立单位。B. 线程是进程的一个执行实体,是CPU调度和分派的基本单位,它是比进程更小的能独立运行的基本单位。C.一个进程可以创建和撤销多个线程;同一个进程中…...

uniapp 字符包含的相关方法
在uniapp中,如果你想检查一个字符串是否包含另一个子字符串,你可以使用JavaScript中的includes()方法或者indexOf()方法。这两种方法都可以达到目的,但它们在处理方式和返回值上有所不同。 使用includes()方法 includes()方法用于判断一个字…...

Proxmox Mail Gateway安装指南:从零开始配置高效邮件过滤系统
💝💝💝欢迎莅临我的博客,很高兴能够在这里和您见面!希望您在这里可以感受到一份轻松愉快的氛围,不仅可以获得有趣的内容和知识,也可以畅所欲言、分享您的想法和见解。 推荐:「storms…...
