MyBatis底层原理(小白版本)
!特别声明!:这篇文章只是单纯用来应对面试,并不能用来当作深度解析的文章来看。本人才疏学浅,文章也可能有不对的地方,望指正。
此源码分析使用的是Java11
基本使用流程:
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);User userById = mapper.getUserById(1);
我们在使用 mybatis时,基本使用用法如上所示
我们一步一步的来看
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
这一步,不做细讲,就是简单的将我们的xml配置文件转化为输入流对象。
第一步
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
这一步,我们调用了 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象的build()方法。进入源码分析
1.1 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象的build()方法源码分析
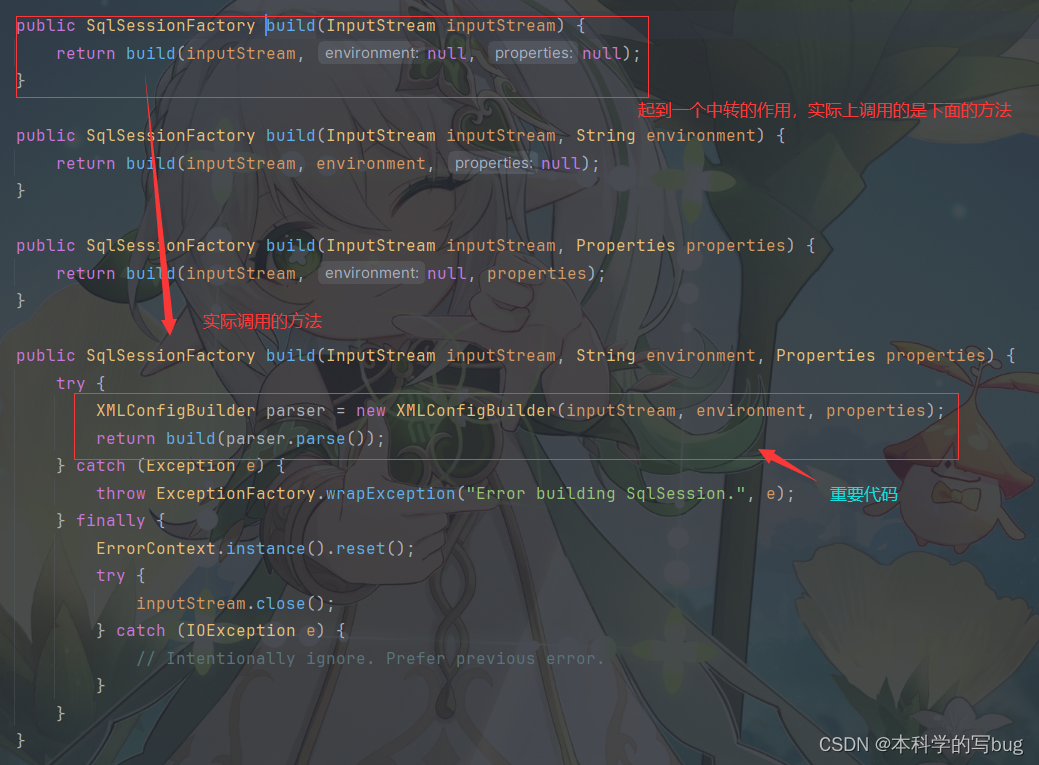
我们首先进入 第一条语句的源码
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
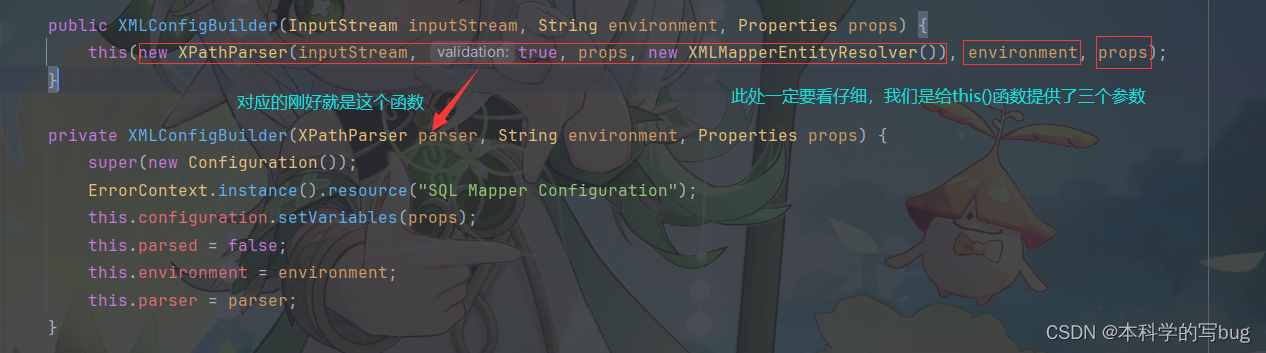
1.2 XMLConfigBuilder()函数源码分析
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {super(new Configuration());ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");this.configuration.setVariables(props);this.parsed = false;this.environment = environment;this.parser = parser;}
这个函数大致作用就是 构建了一个Configuration对象,然后给XMLConfigBuilder对象的属性赋值
(注意:Configuration对象类似于单例模式,就是整个Mybatis中只有一个Configuration对象。,这个对象很重要)
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
这条语句就到这里结束,就是创建了 一个 XMLConfigBuilder 类的实例,并给属性赋值,同时创建了一个 Configuration对象
接着我们分析第二条语句
return build(parser.parse());
里面先是 调用了 第一条语句创建的对象的parse()方法,我们进入源码进行分析
1.3 parser.parse()源码分析
public Configuration parse() {if (parsed) {throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");}parsed = true;parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));return configuration;}
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
我们可以看到其实整个 parse()函数就调用了这一个方法。
我们给parseConfiguration()提供的参数是一个 Xnode对象,对应的是我们配置文件中的一级标签 <configuration>。我们的配置文件大概构造如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--核心配置文件-->
<configuration>......<environments default="development">......</environments><mappers>......</mappers>
</configuration>
我们继续进入源码
1.4 parseConfiguration()源码分析
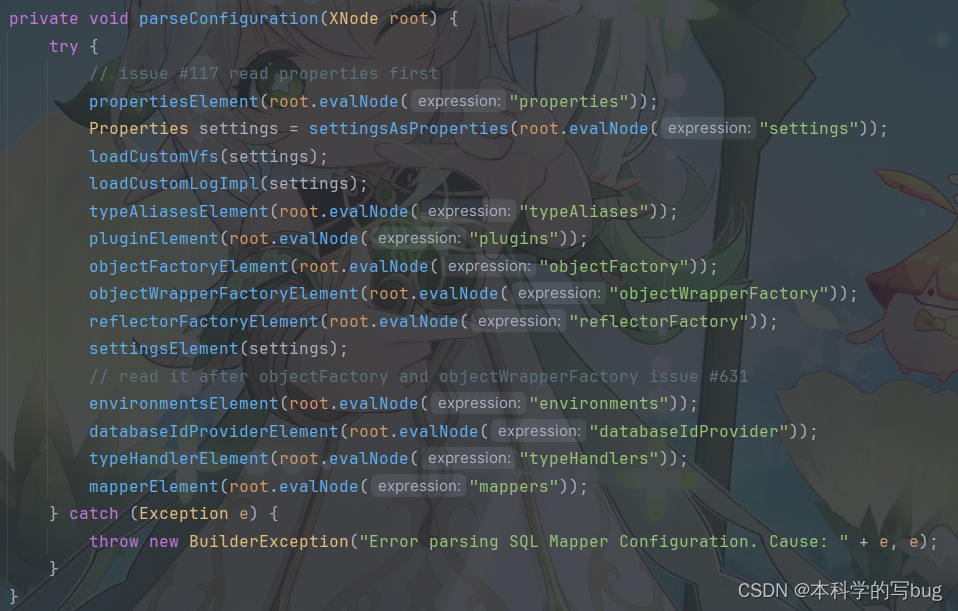
我们可以看到,我们提供的 root 参数就是 <configuration>的节点对象。然后这个parseConfiguration()函数对 配置文件中 <configuration>标签下的二级标签进行了一些操作,进行了哪些操作呢?我们随便进入一个源码进行查看,此处以 <properties>标签为例,我们进入propertiesElement()函数的源码
1.5 propertiesElement()源码分析
<properties resource="db.properties"><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="111111"/></properties>
xml文件中的一种用法,此处仅为了方便理解下面的代码
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {if (context != null) {//此处创建了一个 Properties 类的对象。//我们知道 在 mybatis的配置文件中,可以通过 <properties>文件引入别的文件:例如数据库Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();//我们看一下 context对象有没有这两种属性String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");//全都为 null 说明没有引入别的文件if (resource != null && url != null) {throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");}//否则的话,把引入的文件的内容 交给 defaults 对象 (大致这样理解就行)if (resource != null) {defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));} else if (url != null) {defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));}//我们在解析创建XMLConfigBuilder对象的时候创建了 一个 configuration对象Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();//看看 configu中是否已经存在别的引文的文件//如果有,把内容也交给 defaults 对象if (vars != null) {defaults.putAll(vars);}//用 defaults 再去更新 parse和configuration对象中的对应属性parser.setVariables(defaults);configuration.setVariables(defaults);}}
总的来说propertiesElement()函数的工作就是 解析配置文件中的<properties>标签的信息,生成相应的对象,更新 configuration对象的相应属性。
那么其他的函数操作应该作用基本相似,解析相应的标签的内容,将内容赋值给 configuration对象的对应属性。
别的标签的具体实现我们就不再深入去看了,但是有一个我们还是需要去看 <mapper>标签。
这个标签可谓是 配置文件的核心了。
我们去看一下
1.6 mapperElement(XNode parent)源码分析
在看源码前,我们需要知道一件事情
mapper映射的几种方式
<--! 1使用类路径 -->
<mappers><mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/><mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/><mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
<--! 2使用绝对url路径 -->
<mappers><mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/><mapper url="file:///var/mappers/BlogMapper.xml"/><mapper url="file:///var/mappers/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
<--! 3使用java类名 -->
<mappers><mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/><mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.BlogMapper"/><mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.PostMapper"/>
</mappers><--! 4自动扫描包下所有映射器 -->
<mappers><package name="org.mybatis.builder"/>
</mappers>
我们紧接着看源码
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {//可以没有 mappers 标签if (parent != null) {// child 就是 mappers 下的 mapper 标签for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {//如果有 package 属性,说明 用是是自动扫描if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");//把相应的属性值 交给 configuration 对象即可configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);} else {String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");//<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());mapperParser.parse();} else //<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/>if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());mapperParser.parse();} else //<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.PostMapper"/>if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);} else { // 都没有就抛出异常throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");}}}}}
其实这个函数也是用来解析<mappers>标签的,不过就是根据不同的映射方式,进行不同的方法解析。至于具体干了什么,此处不去探究(主要是因为我菜,看不懂)
至此 , parse()的作用我们有了一个大致的了解,就是将配置文件中的各种标签的信息都解析到 configuration 对象中, 并且返回configuration对象
public Configuration parse() {if (parsed) {throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");}parsed = true;parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));return configuration;}
return build(parser.parse());
这句代码中外层还有一个 build()函数,我们看一下这个函数干啥了。源码就一句
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);}
根据 parser.parse()返回的configuration创建一个 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 对象。具体怎么创建的我们不去探究(菜,懂?)
至此。我们的第一大步到此结束
小结:
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
这一步,就是解析我们的xml配置文件,并且将解析的内容赋值给 一个 configuration 对象。同时,使用这个 configuration 对象,创建一个 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 对象。
此行代码可以这样理解
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new DefaultSqlSessionFactory();
第二步
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
通过第一步 , 我们知道 sqlSessionFactory这个对象是 DefaultSqlSessionFactory类的实例,所以我们去 DefaultSqlSessionFactory类中去探究一下 openSession()具体做了什么。
2.1 sqlSessionFactory.openSession() 源码分析
//直接调用的是这个
@Overridepublic SqlSession openSession() {return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);}
//间接调用这个
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {Transaction tx = null;try {//从 configuration 中 获得 environment 标签下的信息//在 mybatis的配置文件中,environment 标签 存放的都是一些数据库的信息final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();//创建一个事务工厂final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);//创建一个事务对象,工厂模式tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);// 创建一个执行器final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);//返回 一个 DefaultSqlSession 对象return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);} catch (Exception e) {closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();}}
源码比较简单,本质就是返回了一个 DefaultSqlSession类的实例对象。
这个对象有两个比较重要的属性(DefaultSqlSession类的源码中就有,直接可以看到的)
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
那么
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
就可以理解为
SqlSession sqlSession = new DefaultSqlSession();
小结:
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
主要工作就是创建一个 DefaultSqlSession实例对象,赋值给 sqlSession。
此处我们稍微看下 executor的构建源码(可跳过)
2.2 configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType)源码解析(可跳过)
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;Executor executor;//第一步,确实executor的类型//SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCHif (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);} else {executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);}//是否有二级缓存if (cacheEnabled) {executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);}//是否有插件植入executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);return executor;}
大概了解即可,不必深究(我也不会,主打就是一个菜)
第三步
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
我们的 sqlSession是DefaultSqlSession类的实例,我们直接去看 DefaultSqlSession类的getMapper()方法
@Overridepublic <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {return configuration.getMapper(type, this);}
他是调用了 configuration对象的getMapper()。我们继续深入
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);}
configuration对象又调用的 mapperRegistry对象的getMapper()方法。我们继续深入。
3.1 mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession)源码分析
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//一个 mapper代理工厂final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");}try {return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);} catch (Exception e) {throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);}}
看到Proxy这个单词有没有很熟悉,代理
getMapper()的返回值我们可以大胆猜测是一个代理对象。而这个对象代理的就是 sqlSession
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
至于是不是,我们进入源码分析
3.2 mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession) 源码分析
为了区分,我们假设上面的函数为newInstance1,下面的为newInstance2。
直接调用newInstance2,间接调用 newInstance1
//这是间接调用的函数
// newInstance1
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);}
// newInstance2
// 这是直接调用的函数public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);return newInstance(mapperProxy);}
其实,看到这里,我们就可以结束第三步了
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
第三步就是得到了 sqlSession的代理对象。
第四步
User userById = mapper.getUserById(1);
让我们的代理对象去执行函数。实际上是我们的真实对象去执行其对应的函数(动态代理的知识)。
具体实现就在代理对象的 invoke()函数中。
在第三步中,我们源码进行到了这一步。我们获得了代理对象。
//这是间接调用的函数
// newInstance1
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);}
// newInstance2
// 这是直接调用的函数public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);return newInstance(mapperProxy);}
newProxyInstance()的基本形式如下
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h)
我们进行对比一下 newInstance1,可以看出
mapperProxy对象占据了InvocationHandler h对象的位置。那么我们可以大胆猜测,mapperProxy对象的类一定是实现了 InvocationHandler的接口的,并且重写了一个很重要的 invoke()函数
我们进入 new MapperProxy()进行分析。
4.1 new MapperProxy()源码分析
事实证明,我们的猜测完全正确。
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {}
然后我们看一下重写的invoke()方法
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {//一些默认的方法if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);} else {//自定义的方法(我只是这样理解,至于是不是,我不确定)return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}}
我们看一下 cachedInvoker(method).invoke()的源码
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {try {// A workaround for https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-8161372// It should be removed once the fix is backported to Java 8 or// MyBatis drops Java 8 support. See gh-1929MapperMethodInvoker invoker = methodCache.get(method);if (invoker != null) {return invoker;}return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {if (m.isDefault()) {try {if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));} else {return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));}} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException| NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}} else {return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));}});} catch (RuntimeException re) {Throwable cause = re.getCause();throw cause == null ? re : cause;}}
是不是看不懂,我也看不懂。但是有一个跟 sqlSession相关的
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
就是这一句(这只是我找的一个借口)(其实我也不知道为啥用这一句,我们就直接看,别管为啥了,),那我们进入 MapperMethod类的源码看看吧。
private final SqlCommand command;
private final MethodSignature method;public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
MapperMethod类中有两个属性,我们分别进入源码看看两个对象中存放的是什么。
4.2 new SqlCommand()源码分析
public static class SqlCommand {//两个属性private final String name; // sql对应的namespace+id private final SqlCommandType type; // sql 语句的类型。public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {//代理对象执行的方法名 final String methodName = method.getName();final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();//我们先去这个函数看看具体做了什么。//源码在下面一点点MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,configuration);if (ms == null) {if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {name = null;type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;} else {throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);}} else {//获得 sql标签的 id 和 sql 标签的类型(select 啥啥的)。name = ms.getId();type = ms.getSqlCommandType();if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);}}}
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName,Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {//这就是经常提到的 namespace+id 可以唯一确定一个 sql 语句//这个方法就是 将 namespace+id 作为一个 key 去获得一个 ,appedStatement对象// Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements; 这是configuration对象中的一个属性 String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {return null;}//这个我看不懂for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,declaringClass, configuration);if (ms != null) {return ms;}}}return null;}
}
看不懂没关系,只要记住 command中存放的是 sql 语句的 id 以及 类型即可。
new MethodSignature 的源码我们就不看了,method对象存放的是sql语句的返回值类型以及参数
我们赶紧回到 MapperMethod类的源码来,不要过多去纠结 SqlCommand类和 MethodSignature的源码了。我们知道里面主要有啥就行了。
private final SqlCommand command;
private final MethodSignature method;public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
此处先停止。我们先回到 MapperProxy的invoke()方法。我们必须要明白,我们第四步是要搞清楚到底是执行了哪个方法
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {//一些默认的方法if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);} else {//自定义的方法(我只是这样理解,至于是不是,我不确定)return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}}
cachedInvoker(method)是一个方法的返回对象。
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
这个方法的返回对象是 PlainMethodInvoker 类型的
那么
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
//就相当于
return new PlainMethodInvoker().invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
//就相当于最终我们返回的是 PlainMethodInvoker 对象的 invoke()函数的返回值我们进入PlainMethodInvoker类的源码去看一下
4.3 PlainMethodInvoker类源码分析
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {super();this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}}
看看我们发现了什么
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}
最终返回的结果居然是 mapperMethod.execute()函数的返回值。
我们进入 mapperMethod.execute()源码中看看~
4.4 mapperMethod.execute()源码分析
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;//根据 comman的type属性,确实我们的sql类型switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}case UPDATE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));break;}case DELETE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));break;}case SELECT:if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);result = null;} else if (method.returnsMany()) {result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsMap()) {result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);} else {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);if (method.returnsOptional()&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {result = Optional.ofNullable(result);}}break;case FLUSH:result = sqlSession.flushStatements();break;default:throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());}if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");}return result;}
我你们可以在上面源码中看到很多这样的代码!
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
我们发现 我们 的返回结果又变成了 sqlSession执行相应函数的返回结果。还记的我们前面提到的吗? sqlSession是 DefaultSqlSession类的实例。我们去DefaultSqlSession类中去找这些方法!!
以 sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)为例
进入源码分析
4.5 sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)源码分析
@Overridepublic int update(String statement, Object parameter) {try {dirty = true;MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));} catch (Exception e) {throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();}}
我们发现 sqlSession.update()的本质是交给 exectuor 去执行。至于执行器怎么去执行的,我们就不再探究了!(我不会)。到此第四步其实已经执行完了。可能有点乱,我们来小结一下。
小结:
User userById = mapper.getUserById(1);
我们知道, mapper.getUserById(1)回去执行对应 mapper.xml文件中对应的sql语句。第四步的原理解析实际上就是解析二者是怎么匹配的。
我们知道 代理对象执行方法时,其实执行的是 invoke() 方法。
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {//一些默认的方法if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);} else {//自定义的方法(我只是这样理解,至于是不是,我不确定)return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}}
下面我们用个流程图去说明,就不再看源码了。
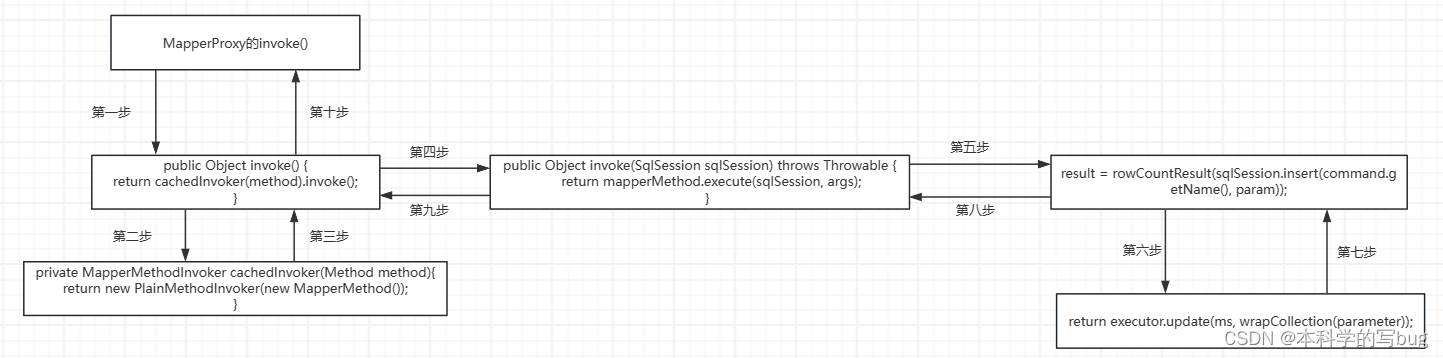
简单概括! 代理对象调用方法的过程底层是 :通过 mapperMethod对象的属性(command和method) ,匹配 sqlSession对象应该执行的函数。 同时 sqlSession将具体的实现交给 执行器 executor去执行。
这一步的口述我也很难用文字去表述清楚。大家多看几遍应该能理解。
分析就到这里啦,exectuor的底层就不再分析了,我也不会。
至于 mappedStatement 是从哪来的 大家可以看一下这篇文章 点击这里
相关文章:

MyBatis底层原理(小白版本)
!特别声明!:这篇文章只是单纯用来应对面试,并不能用来当作深度解析的文章来看。本人才疏学浅,文章也可能有不对的地方,望指正。 此源码分析使用的是Java11 基本使用流程: String resource &q…...
水经微图Web版从入门到精通
我们在《47GB水经微图从入门到精通视频教程》和《163M水经微图从入门到精通文档教程》中,为大家分享了水经微图PC版的教程。 这里,我们再为大家分享水经微图Web版的文档教程。 水经微图Web版教程 水经微图Web版的教程,主要包括基础名词、…...
IntelliJ IDEA 2023 最新版如何试用?IntelliJ IDEA 2023最新版试用方法及验证ja-netfilter配置成功提示
🌷🍁 博主猫头虎 带您 Go to New World.✨🍁 🦄 博客首页——猫头虎的博客🎐 🐳《面试题大全专栏》 文章图文并茂🦕生动形象🦖简单易学!欢迎大家来踩踩~🌺 &a…...

LeetCode541. Reverse String II
文章目录 一、题目二、题解 一、题目 541. Reverse String II Given a string s and an integer k, reverse the first k characters for every 2k characters counting from the start of the string. If there are fewer than k characters left, reverse all of them. If…...
ios原生分享
什么是 ios 系统的原生分享呢,如下图所示 具体使用系统UIActivityViewController,完整代码如下: -(void)shareAny:(NSString *)text url:(NSString *)_url imagePath:(NSString *)_imagePath {NSLog("shareAny, text:%, url:%, imagePa…...

【Ubuntu】安装chrome之后无法启动
【Ubuntu】安装chrome之后无法启动 文章目录 【Ubuntu】安装chrome之后无法启动1. 问题描述2.解决方法Reference 1. 问题描述 命令行运行 google-chrome报错 [5901:5901:0610/183033:ERROR:process_singleton_linux.cc(309)] 其他计算机 (money-Latitude-E5430-non-vPro) 的…...

顺序栈练习
顺序栈练习 相关内容: 1.判断顺序栈栈满的两种方式 2.一张图理解栈顶指针加加减减的问题 3.栈的顺序存储结构(顺序栈) //顺序栈的初始化、判空、入栈、出栈、读取栈顶元素 //顺序栈的结构:数组、栈顶指针(本质是下标) #include&…...

安全与HTTP协议:为何明文传输数据成为争议焦点?
🎬 江城开朗的豌豆:个人主页 🔥 个人专栏 :《 VUE 》 《 javaScript 》 📝 个人网站 :《 江城开朗的豌豆🫛 》 ⛺️ 生活的理想,就是为了理想的生活 ! 目录 ⭐ 专栏简介 📘 文章引言 一、H…...
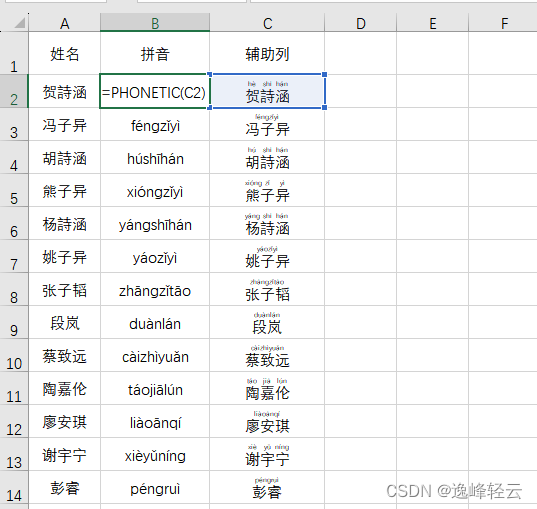
【笔记】excel怎么把汉字转换成拼音
1、准备好excel文件,复制需要转拼音列。 2、打开一个空白Word文档,并粘贴刚才复制的内容; 3、全选Word文档中刚粘贴的内容,点击「开始」选项卡「字体」命令组下的「拼音指南」,调出拼音指南对话框; 4、全…...

opencv官网文档学习
文章最后有一些图片资源 1.图像处理基本使用 import cv2# 读取图像 image cv2.imread("images/1.png", cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) print("image:",image)# 显示图像 namedWindow cv2.namedWindow("images/1.png") cv2.imshow("images/1.pn…...
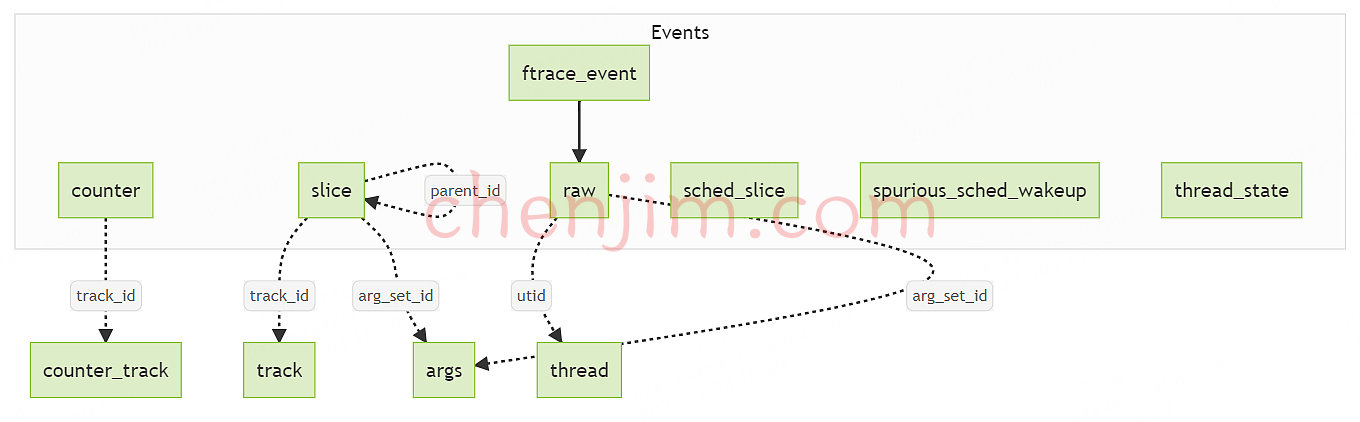
Android性能优化--Perfetto用SQL性能分析
Android性能优化–Perfetto用SQL性能分析 文章目录 Android性能优化--Perfetto用SQL性能分析介绍Perfetto SQL 基础使用 Perfetto SQL 进行性能分析总结 本文首发地址 https://blog.csdn.net/CSqingchen/article/details/134167741 最新更新地址 https://gitee.com/chenjim/che…...

NLP之Bert实现文本分类
文章目录 1. 代码展示2. 整体流程介绍3. 代码解读4. 报错解决4.1 解决思路4.2 解决方法 5. Bert介绍5.1 什么是BertBERT简介:BERT的核心思想:BERT的预训练策略:BERT的应用:为什么BERT如此受欢迎?总结: 1. 代…...
Pytorch从零开始实战08
Pytorch从零开始实战——YOLOv5-C3模块实现 本系列来源于365天深度学习训练营 原作者K同学 文章目录 Pytorch从零开始实战——YOLOv5-C3模块实现环境准备数据集模型选择开始训练可视化模型预测总结 环境准备 本文基于Jupyter notebook,使用Python3.8,…...
docker部署Jenkins(Jenkins+Gitlab+Maven实现CI/CD)
GitLab介绍 GitLab是一个用于仓库管理系统的开源项目,使用Git作为代码管理工具,并在此基础上搭建起来的Web服务,可通过Web界面进行访问公开的或者私人项目。它拥有与Github类似的功能,能够浏览源代码,管理缺陷和注释。…...
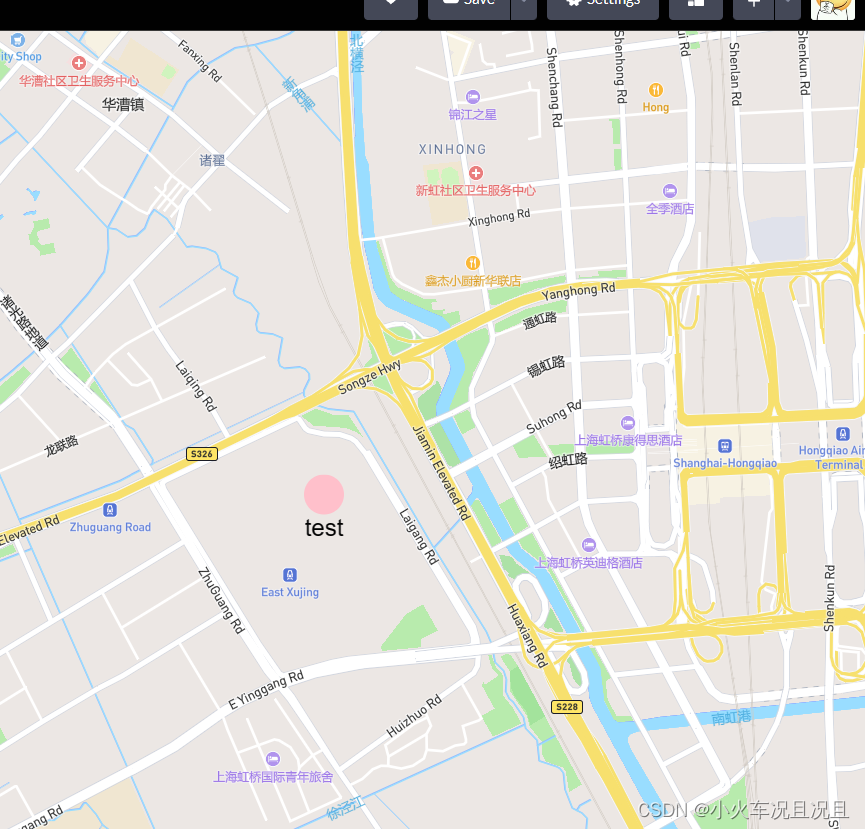
mapbox使用marker创建html点位信息
mapbox使用marker创建html点位信息 codePen地址 mapboxgl.accessToken "pk.eyJ1IjoibGl1emhhbzI1ODAiLCJhIjoiY2xmcnV5c2NtMDd4eDNvbmxsbHEwYTMwbCJ9.T0QCxGEJsLWC9ncE1B1rRw"; const center [121.29786, 31.19365]; const map new mapboxgl.Map({container: &quo…...
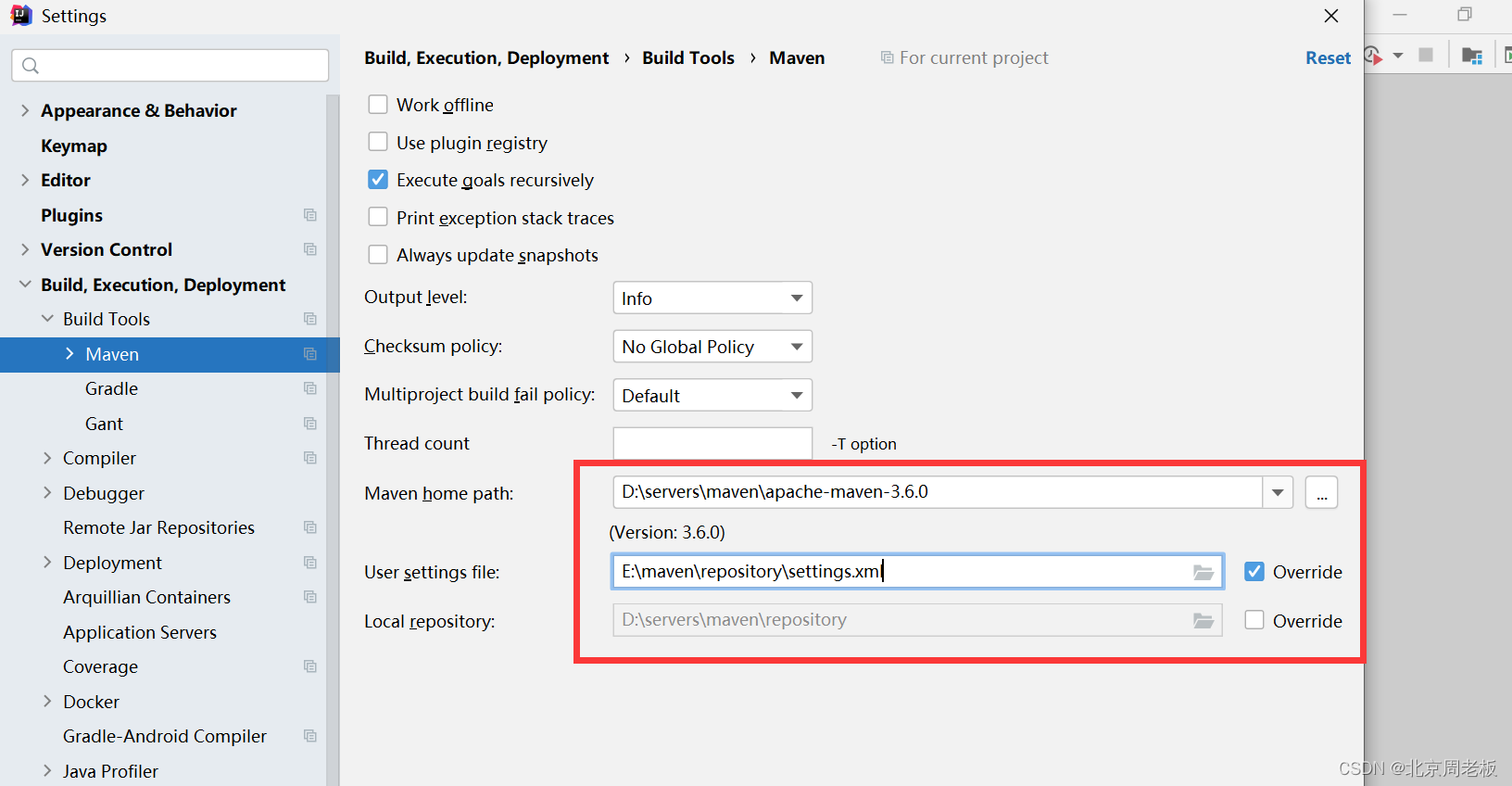
项目构建工具maven的基本配置
👑 博主简介:知名开发工程师 👣 出没地点:北京 💊 2023年目标:成为一个大佬 ——————————————————————————————————————————— 版权声明:本文为原创文…...

超详细docker学习笔记
关于docker 一、基本概念什么是docker?docker组件:我们能用docker做什么Docker与配置管理:Docker的技术组件Docker资源Docker与虚拟机对比 二、安装docker三、镜像命令启动命令帮助命令列出本地主机上的镜像在远程仓库中搜索镜像查看占据的空间删除镜像…...
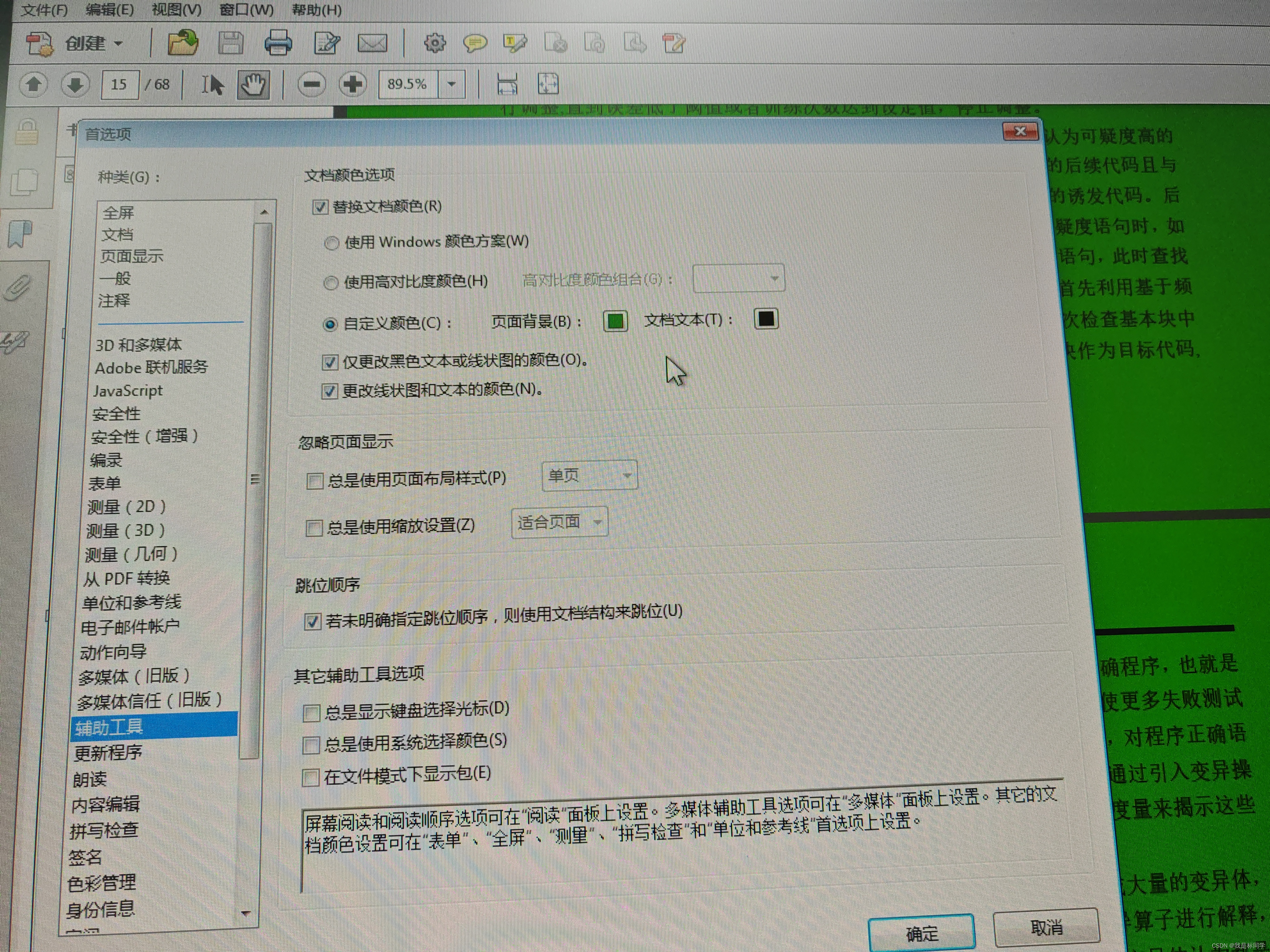
Adobe acrobat 11.0版本 pdf阅读器修改背景颜色方法
打开菜单栏,编辑,首选项,选择辅助工具项,页面中 勾选 替换文档颜色,页面背景自己选择一个颜色,然后确定,即可!...
HCIA数据通信——路由协议
数据通信——网络层(OSPF基础特性)_咕噜跳的博客-CSDN博客 数据通信——网络层(RIP与BGP)_咕噜跳的博客-CSDN博客 上述是之前写的理论知识部分,懒得在实验中再次提及了。这次做RIP协议以及OSPF协议。不过RIP协议不常用…...

十种常见典型算法
什么是算法? 简而言之,任何定义明确的计算步骤都可称为算法,接受一个或一组值为输入,输出一个或一组值。(来源:homas H. Cormen, Chales E. Leiserson 《算法导论第3版》) 可以这样理…...
:OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下))
脑机新手指南(八):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下)
一、数据处理与分析实战 (一)实时滤波与参数调整 基础滤波操作 60Hz 工频滤波:勾选界面右侧 “60Hz” 复选框,可有效抑制电网干扰(适用于北美地区,欧洲用户可调整为 50Hz)。 平滑处理&…...
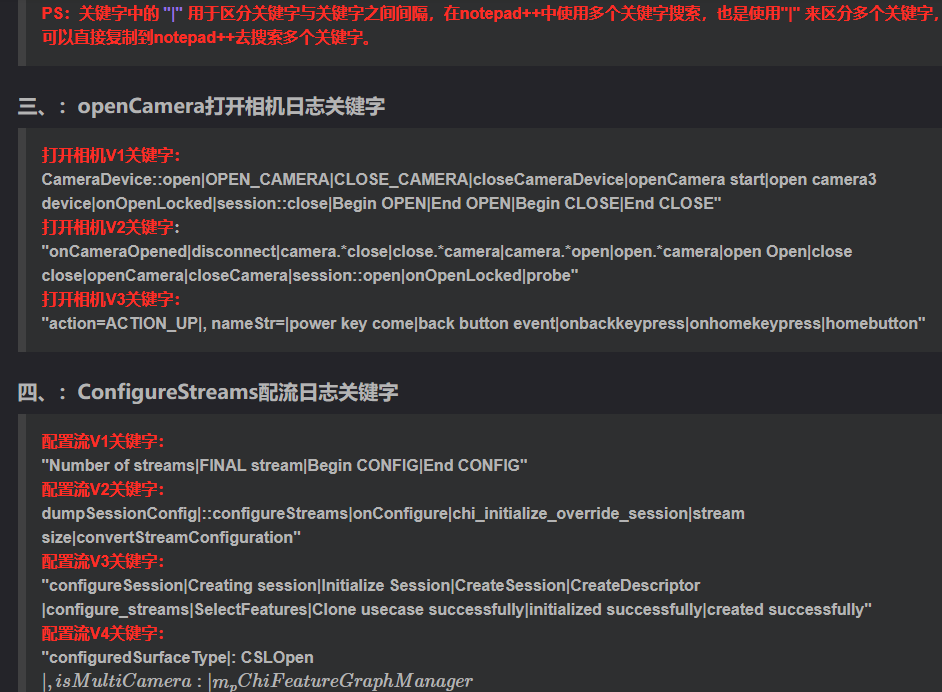
相机Camera日志实例分析之二:相机Camx【专业模式开启直方图拍照】单帧流程日志详解
【关注我,后续持续新增专题博文,谢谢!!!】 上一篇我们讲了: 这一篇我们开始讲: 目录 一、场景操作步骤 二、日志基础关键字分级如下 三、场景日志如下: 一、场景操作步骤 操作步…...

数据链路层的主要功能是什么
数据链路层(OSI模型第2层)的核心功能是在相邻网络节点(如交换机、主机)间提供可靠的数据帧传输服务,主要职责包括: 🔑 核心功能详解: 帧封装与解封装 封装: 将网络层下发…...

python如何将word的doc另存为docx
将 DOCX 文件另存为 DOCX 格式(Python 实现) 在 Python 中,你可以使用 python-docx 库来操作 Word 文档。不过需要注意的是,.doc 是旧的 Word 格式,而 .docx 是新的基于 XML 的格式。python-docx 只能处理 .docx 格式…...
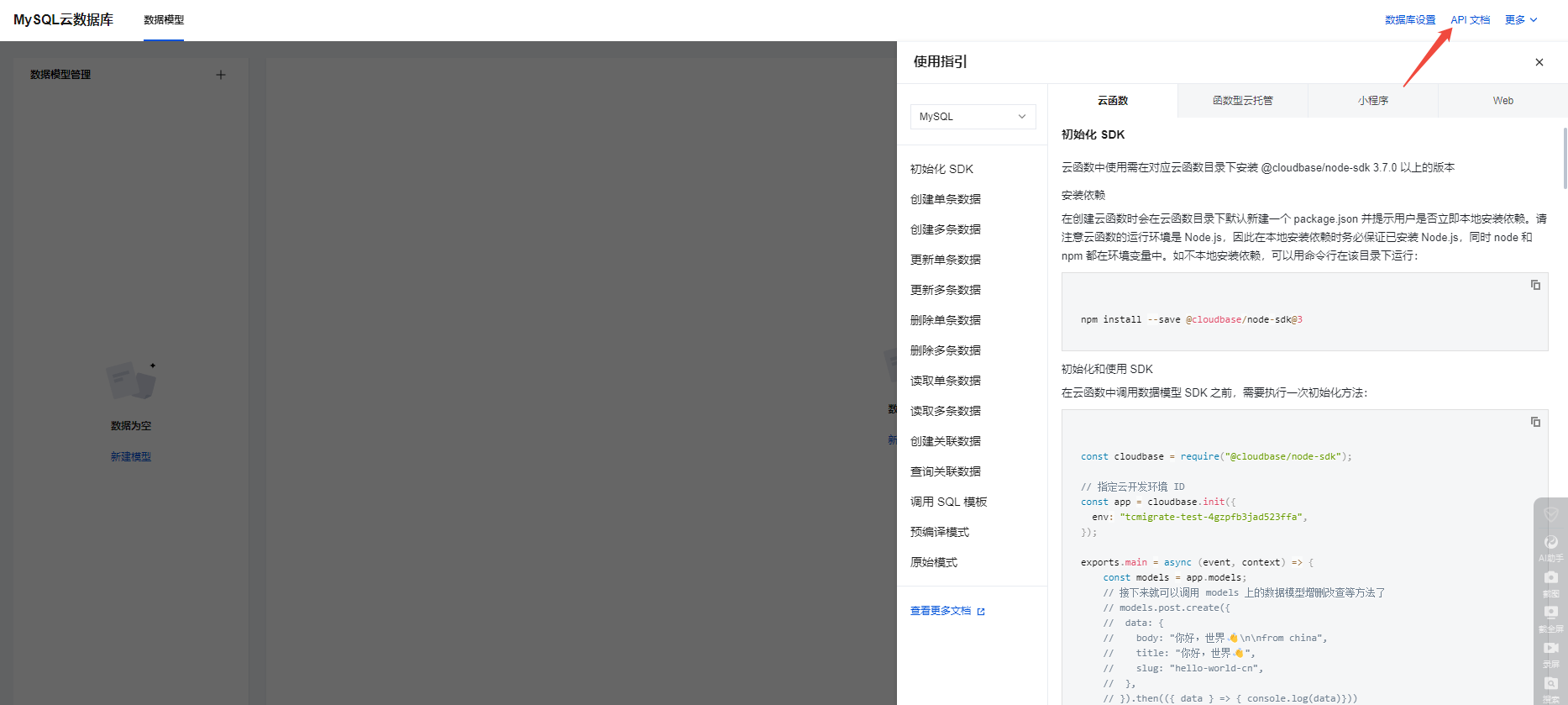
微信小程序云开发平台MySQL的连接方式
注:微信小程序云开发平台指的是腾讯云开发 先给结论:微信小程序云开发平台的MySQL,无法通过获取数据库连接信息的方式进行连接,连接只能通过云开发的SDK连接,具体要参考官方文档: 为什么? 因为…...
中的KV缓存压缩与动态稀疏注意力机制设计)
大语言模型(LLM)中的KV缓存压缩与动态稀疏注意力机制设计
随着大语言模型(LLM)参数规模的增长,推理阶段的内存占用和计算复杂度成为核心挑战。传统注意力机制的计算复杂度随序列长度呈二次方增长,而KV缓存的内存消耗可能高达数十GB(例如Llama2-7B处理100K token时需50GB内存&a…...
初探Service服务发现机制
1.Service简介 Service是将运行在一组Pod上的应用程序发布为网络服务的抽象方法。 主要功能:服务发现和负载均衡。 Service类型的包括ClusterIP类型、NodePort类型、LoadBalancer类型、ExternalName类型 2.Endpoints简介 Endpoints是一种Kubernetes资源…...
VM虚拟机网络配置(ubuntu24桥接模式):配置静态IP
编辑-虚拟网络编辑器-更改设置 选择桥接模式,然后找到相应的网卡(可以查看自己本机的网络连接) windows连接的网络点击查看属性 编辑虚拟机设置更改网络配置,选择刚才配置的桥接模式 静态ip设置: 我用的ubuntu24桌…...
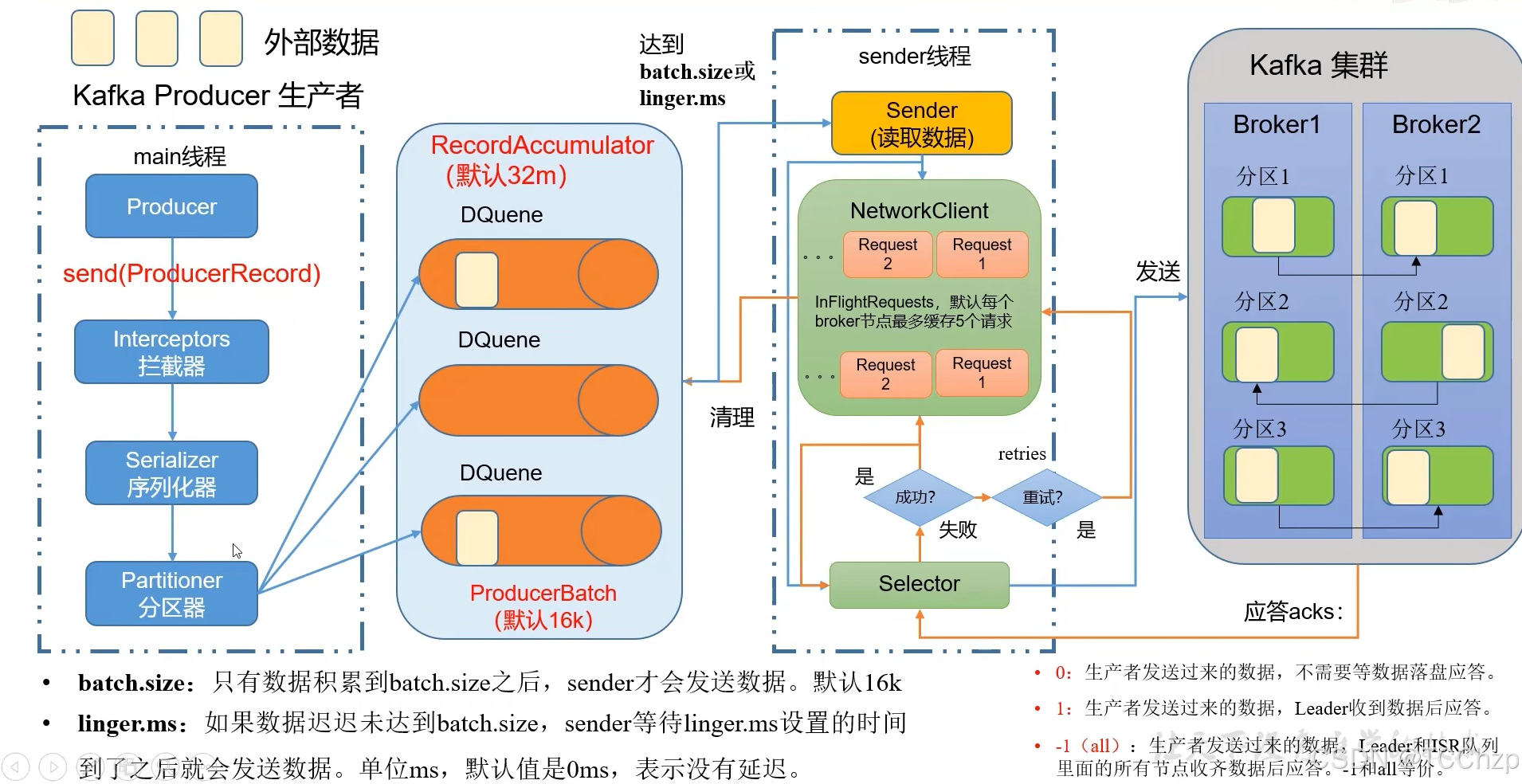
Kafka入门-生产者
生产者 生产者发送流程: 延迟时间为0ms时,也就意味着每当有数据就会直接发送 异步发送API 异步发送和同步发送的不同在于:异步发送不需要等待结果,同步发送必须等待结果才能进行下一步发送。 普通异步发送 首先导入所需的k…...

PostgreSQL——环境搭建
一、Linux # 安装 PostgreSQL 15 仓库 sudo dnf install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-$(rpm -E %{rhel})-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm# 安装之前先确认是否已经存在PostgreSQL rpm -qa | grep postgres# 如果存在࿰…...
