towr code阅读
1. Introduction
towr是非常优美的足式机器人规划代码,通过阅读towr重要的几个迭代版本的代码深入了解。
2 v0.1
第一代的版本,foot的位置是提前给定的,只对COG的trajectory进行优化。
2.1 cost
- 公式
仅仅只考虑加速度,
∫ 0 T x ¨ 2 ( t ) d t + v = q T G q + v \int_0^T \ddot{x}^2(t)dt+v=q^TGq+v ∫0Tx¨2(t)dt+v=qTGq+v
其中,
q = [ a b c d ] T q = \begin{bmatrix} a & b &c &d \end{bmatrix}^T q=[abcd]T

- 代码
// 使用六阶多项式进行表示,有XY两个维度,需要优化的参数数目,用std::vecXd 表示
int n_coeff = splines.size() * kCoeffCount * kDim2d;
// 1e-12 < EndFCost < 1e-8, 初始值要非零
cf->M = EandFCost * Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(cf->M.rows(), cf->M.cols()); // 初始化q和G的数据结构// 修改权重矩阵,将权重矩阵G进行分块,每一段占据一块,通过索引定位要对应的权重:X、Y、分段
for (const SplineInfo& s : splines) {std::array<double, 10> t_span = cache_exponents<10>(s.duration_);for (int dim = X; dim <= Y; dim++) {const int a = var_index(s.id_, dim, A);const int b = var_index(s.id_, dim, B);const int c = var_index(s.id_, dim, C);const int d = var_index(s.id_, dim, D);// for explanation of values see M.Kalakrishnan et al., page 248// "Learning, Planning and Control for Quadruped Robots over challenging// Terrain", IJRR, 2010// exact spline cf->M(a, a) = 400.0 / 7.0 * t_span[7] * weight[dim];}
}
//具体每块的权重
cf->M(a, a) = 400.0 / 7.0 * t_span[7] * weight[dim];
cf->M(a, b) = 40.0 * t_span[6] * weight[dim];
cf->M(a, c) = 120.0 / 5.0 * t_span[5] * weight[dim];
cf->M(a, d) = 10.0 * t_span[4] * weight[dim];
cf->M(b, b) = 144.0 / 5.0 * t_span[5] * weight[dim];
cf->M(b, c) = 18.0 * t_span[4] * weight[dim];
cf->M(b, d) = 8.0 * t_span[3] * weight[dim];
cf->M(c, c) = 12.0 * t_span[3] * weight[dim];
cf->M(c, d) = 6.0 * t_span[2] * weight[dim];
cf->M(d, d) = 4.0 * t_span[1] * weight[dim];// mirrow values over diagonal to fill bottom left triangle
for (int c = 0; c < cf->M.cols(); ++c)for (int r = c + 1; r < cf->M.rows(); ++r)cf->M(r, c) = cf->M(c, r);
总结:标准QP类型,不需要提供Hessian 矩阵
2.2 equality constraints
- Continuity and Goal Constraints
在QP问题上,表示为 M ∗ c o e f f + v = 0 M*coeff+v=0 M∗coeff+v=0

- 位置、速度和加速度的约束
M [ a b c d e f ] T + v = 0 M \begin{bmatrix} a & b & c & d & e & f \end{bmatrix}^T + v = 0 M[abcdef]T+v=0 - 初始和终止状态约束code
// 计算constraints的数目
int coeff = splines.size() * kCoeffCount * kDim2d; // total number of all spline coefficients
int constraints = 0;
constraints += 2*4; // init {x,y} * {pos, vel, acc, jerk}
constraints += 2*3; // end {x,y} * {pos, vel, acc, jerk}
constraints += (splines.size() - 1) * kDim2d * 4; // junctions {pos, vel, acc, jerk}
MatVecPtr ec(new MatVec(coeff, constraints, constraints));
// 满足初始状态
// positions at t = 0, M * V = cog
int f = var_index(0, dim, F);
ec->M(f, i) = 1.0; // 权重
ec->v(i++) = -start_cog(dim);
// velocity set to zero
int e = var_index(0, dim, E);
ec->M(e, i) = 1.0;
ec->v(i++) = -kVelStart(dim);
// acceleration set to zero
int d = var_index(0, dim, D);
ec->M(d, i) = 2.0;
ec->v(i++) = -kAccStart(dim);
// jerk set to zero
int c = var_index(0, dim, C);
ec->M(c, i) = 6.0;
ec->v(i++) = -kJerkStart(dim);
终止状态的约束
ec->M(last_spline + A, i) = t_duration[5];ec->M(last_spline + B, i) = t_duration[4];ec->M(last_spline + C, i) = t_duration[3];ec->M(last_spline + D, i) = t_duration[2];ec->M(last_spline + E, i) = t_duration[1];ec->M(last_spline + F, i) = 1;ec->v(i++) = -end_cog(dim);// velocityec->M(last_spline + A, i) = 5 * t_duration[4];ec->M(last_spline + B, i) = 4 * t_duration[3];ec->M(last_spline + C, i) = 3 * t_duration[2];ec->M(last_spline + D, i) = 2* t_duration[1];ec->M(last_spline + E, i) = 1;ec->v(i++) = -kVelEnd(dim); // accelerationsec->M(last_spline + A, i) = 20 * t_duration[3];ec->M(last_spline + B, i) = 12 * t_duration[2];ec->M(last_spline + C, i) = 6 * t_duration[1];ec->M(last_spline + D, i) = 2;
- 连接点约束
初始点t=0; t_end = t_duration

int curr_spline = var_index(s, dim, A);
int next_spline = var_index(s+1, dim, A);// position of current spline at t_duration
ec->M(curr_spline + A, i) = t_duration[5];
ec->M(curr_spline + B, i) = t_duration[4];
ec->M(curr_spline + C, i) = t_duration[3];
ec->M(curr_spline + D, i) = t_duration[2];
ec->M(curr_spline + E, i) = t_duration[1];
ec->M(curr_spline + F, i) = 1;
// ...minus position of next spline at t=0...
ec->M(next_spline + F, i) = -1.0;
// ...must be zero
ec->v(i++) = 0.0;// velocity
ec->M(curr_spline + A, i) = 5 * t_duration[4];
ec->M(curr_spline + B, i) = 4 * t_duration[3];
ec->M(curr_spline + C, i) = 3 * t_duration[2];
ec->M(curr_spline + D, i) = 2 * t_duration[1];
ec->M(curr_spline + E, i) = 1;
ec->M(next_spline + E, i) = -1.0;
ec->v(i++) = 0.0;// acceleration
ec->M(curr_spline + A, i) = 20 * t_duration[3];
ec->M(curr_spline + B, i) = 12 * t_duration[2];
ec->M(curr_spline + C, i) = 6 * t_duration[1];
ec->M(curr_spline + D, i) = 2;
ec->M(next_spline + D, i) = -2.0;
ec->v(i++) = 0.0;// jerk (derivative of acceleration)
ec->M(curr_spline + A, i) = 60 * t_duration[2];
ec->M(curr_spline + B, i) = 24 * t_duration[1];
ec->M(curr_spline + C, i) = 6;
ec->M(next_spline + C, i) = -6.0;
ec->v(i++) = 0.0;
2.3 inequality constraints
- 质心在zmp安全范围内
将四组其中三个脚组成边缘
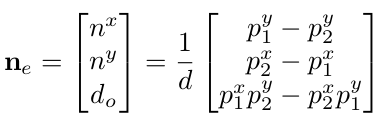
ZMP的作用位置
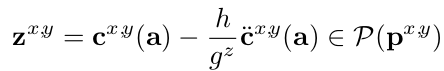
zmp到边缘的距离满足要求
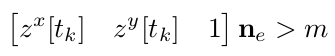
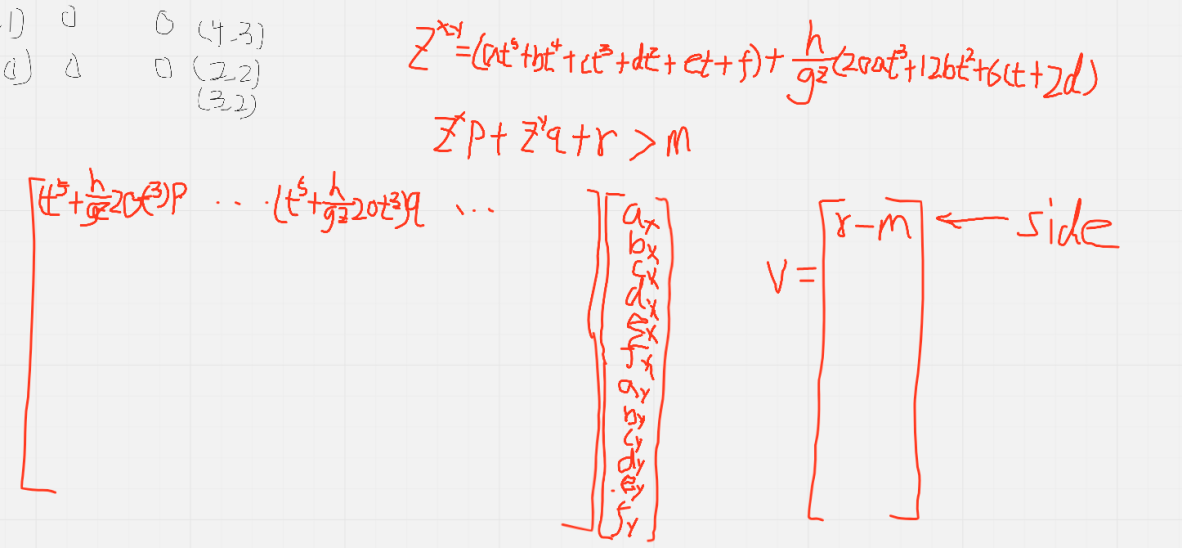
- code
// 优化参数
int coeff = splines.size() * kCoeffCount * kDim2d;// calculate number of inequality constraints
double t_total = 0.0;
for (const SplineInfo& s : splines) t_total += s.duration_;int points = ceil(t_total / kDt); // 离散化位置点
int constraints = points * 3; // 3 triangle side constraints per point,满足3个边缘要求
MatVecPtr ineq(new MatVec(coeff, constraints, constraints)); //不等式约束 Mq+v<=0// calculate zmp
for (double time(0.0); time < s.duration_; time += kDt) {std::array<double,6> t = cache_exponents<6>(time);// one constraint per line of support trianglefor (SuppTriangle::TrLine l: lines) {double z_acc = 0.0; // TODO: calculate z_acc based on foothold heightconst int x = var_index(s.id_, X, A);const int y = var_index(s.id_, Y, A);ineq->M(x + A, c) = l.coeff.p * (t[5] - h/(g+z_acc) * 20.0 * t[3]);ineq->M(x + B, c) = l.coeff.p * (t[4] - h/(g+z_acc) * 12.0 * t[2]);ineq->M(x + C, c) = l.coeff.p * (t[3] - h/(g+z_acc) * 6.0 * t[1]);ineq->M(x + D, c) = l.coeff.p * (t[2] - h/(g+z_acc) * 2.0);ineq->M(x + E, c) = l.coeff.p * t[1];ineq->M(x + F, c) = l.coeff.p * 1;ineq->M(y + A, c) = l.coeff.q * (t[5] - h/(g+z_acc) * 20.0 * t[3]);ineq->M(y + B, c) = l.coeff.q * (t[4] - h/(g+z_acc) * 12.0 * t[2]);ineq->M(y + C, c) = l.coeff.q * (t[3] - h/(g+z_acc) * 6.0 * t[1]);ineq->M(y + D, c) = l.coeff.q * (t[2] - h/(g+z_acc) * 2.0);ineq->M(y + E, c) = l.coeff.q * t[1];ineq->M(y + F, c) = l.coeff.q * 1;ineq->v[c] = l.coeff.r - l.s_margin;++c;2.4 参数配置
初始状态:
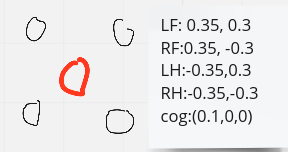
所有步态

步态的时序
注意交叉的时候需要留出时间给cog进行调整

DEBUG xpp.zmp.zmpoptimizer :
Spline: id= 0: duration=0.60 four_leg_supp=0 step=0
Spline: id= 1: duration=0.60 four_leg_supp=0 step=1
Spline: id= 2: duration=0.20 four_leg_supp=1 step=2
Spline: id= 3: duration=0.60 four_leg_supp=0 step=2
Spline: id= 4: duration=0.60 four_leg_supp=0 step=3
Spline: id= 5: duration=0.20 four_leg_supp=1 step=4
Spline: id= 6: duration=0.60 four_leg_supp=0 step=4
Spline: id= 7: duration=0.60 four_leg_supp=0 step=5
Spline: id= 8: duration=0.20 four_leg_supp=1 step=6
Spline: id= 9: duration=0.60 four_leg_supp=0 step=6
Spline: id= 10: duration=0.60 four_leg_supp=0 step=7
Spline: id= 11: duration=0.20 four_leg_supp=1 step=8
2.5 数据结构
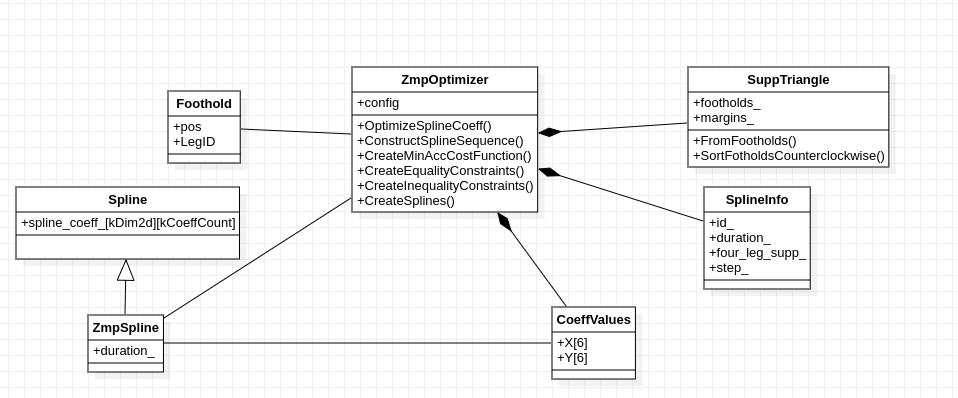
2.6 注意事项
在LH,LF,RH, RF, (LF,RH)切换的时候,机器人是四个腿全放在地面的,所以不会形成triangle
suppTriangles 的数量和splines的数量并不一致
SuppTriangles SuppTriangle::FromFootholds(LegDataMap<Foothold> stance,const Footholds& steps,const MarginValues& margins, LegDataMap<Foothold>& last_stance)
{SuppTriangles tr;ArrayF3 non_swing;for (std::size_t s=0; s<steps.size(); s++) {LegID swingleg = steps[s].leg;// extract the 3 non-swinglegs from stanceint i = 0;for (LegID l : LegIDArray) if (stance[l].leg != swingleg)non_swing[i++] = stance[l];tr.push_back(SuppTriangle(non_swing, margins));stance[swingleg] = steps[s]; // update current stance with last step}last_stance = stance;::xpp::utils::logger_helpers::print_triangles(tr, log_);::xpp::utils::logger_helpers::PrintTriaglesMatlabInfo(tr, log_matlab_);return tr;
}
但是在计算triangle的时候,这里没有考虑four-support的情况,four-support 不用考虑平衡
for (const SplineInfo& s : splines) {LOG4CXX_DEBUG(log_, "Calc inequality constaints of spline " << s.id_ << " of " << splines.size() << ", duration=" << std::setprecision(3) << s.duration_ << ", step=" << s.step_);// no constraints in 4ls phaseif (s.four_leg_supp_) continue;// TODO: insert support polygon constraints here instead of just // allowing the ZMP to be anywhere// cache lines of support triangle of current spline for efficiencySuppTriangle::TrLines3 lines = supp_triangles[s.step_].CalcLines(); // 仍然使用上一次swing的triangle
2.7 代码的技巧
3 v0.2
第二版中最主要的改变是将6阶spline中只优化其中四个参数,提高了运算速度。
3.1 优化器设置
所要优化的参数变量
3.1.1 cost
仍然采用二阶积分,计算cost.
for (const SplineInfo& s : spline_infos_) {std::array<double, 10> t_span = cache_exponents<10>(s.duration_);for (int dim = X; dim <= Y; dim++) {const int a = var_index(s.id_, dim, A);const int b = var_index(s.id_, dim, B);const int c = var_index(s.id_, dim, C);const int d = var_index(s.id_, dim, D);// for explanation of values see M.Kalakrishnan et al., page 248// "Learning, Planning and Control for Quadruped Robots over challenging// Terrain", IJRR, 2010// exact spline cf->M(a, a) = 400.0 / 7.0 * t_span[7] * weight[dim];cf->M(a, b) = 40.0 * t_span[6] * weight[dim];cf->M(a, c) = 120.0 / 5.0 * t_span[5] * weight[dim];cf->M(a, d) = 10.0 * t_span[4] * weight[dim];cf->M(b, b) = 144.0 / 5.0 * t_span[5] * weight[dim];cf->M(b, c) = 18.0 * t_span[4] * weight[dim];cf->M(b, d) = 8.0 * t_span[3] * weight[dim];cf->M(c, c) = 12.0 * t_span[3] * weight[dim];cf->M(c, d) = 6.0 * t_span[2] * weight[dim];cf->M(d, d) = 4.0 * t_span[1] * weight[dim]; // mirrow values over diagonal to fill bottom left trianglefor (int c = 0; c < cf->M.cols(); ++c) for (int r = c+1; r < cf->M.rows(); ++r)cf->M(r, c) = cf->M(c, r); }}
3.1.2 equality constraints
连接点只考虑加速度和速度
初始对应的速度和位置通过参数给定start_p 和start_v进行导入
constraints += kDim2d*2; // init {x,y} * {acc, jerk} pos, vel implied
constraints += kDim2d*3; // end {x,y} * {pos, vel, acc}
constraints += (spline_infos_.size()-1) * kDim2d * 2; // junctions {acc,jerk} since pos, vel implied
- 初始状态,不对初始位置速度进行限制了
f ( x ) = A t 5 + B t 4 + C t 3 + D t 2 + E t + F f(x)=At^5+Bt^4+Ct^3+Dt^2+Et+F f(x)=At5+Bt4+Ct3+Dt2+Et+F
只对加速度和jerk进行限制
[ 0 0 0 2.0 0 0 6 0 ] [ A B C D ] = [ 0 0 ] \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 0 & 0 & 2.0 \\ 0 & 0 & 6 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} A \\ B \\ C \\D \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} [0000062.00] ABCD =[00]
代码:
// acceleration set to zero
int d = var_index(0, dim, D);
ec->M(d, i) = 2.0;
ec->v(i++) = -kAccStart(dim);
// jerk set to zero
int c = var_index(0, dim, C);
ec->M(c, i) = 6.0;
ec->v(i++) = -kJerkStart(dim);
- 终止状态
var_index(int spline, int dim, int coeff) 对应结果
n = s p l i n e ∗ k D i m 2 d ∗ c o e f f + d i m ∗ c o e f f + c o e f f n = spline*kDim2d*coeff+dim*coeff+coeff n=spline∗kDim2d∗coeff+dim∗coeff+coeff
DescribeEByPrev的计算效果
E k = [ 5 t 0 4 4 t 0 3 3 t 0 2 2 t 0 . . . 5 t i 4 4 t i 3 3 t i 2 2 t i . . . 5 t n − 1 4 4 t n − 1 3 3 t n − 1 2 2 t n − 1 ] n o n d e p e n d e n t = s t a r t c o g v \begin{aligned} Ek & = \begin{bmatrix} 5t_0^4 & 4t_0^3 & 3t_0^2 & 2t_0 & ... & 5t_i^4 & 4t_i^3 & 3t_i^2 & 2t_i & ... & 5t_{n-1}^4 & 4t_{n-1}^3 & 3t_{n-1}^2 & 2t_{n-1} \end{bmatrix} \\ nondependent & = startcogv \end{aligned} Eknondependent=[5t044t033t022t0...5ti44ti33ti22ti...5tn−144tn−133tn−122tn−1]=startcogv
考虑到隐含关系
5 A i t i 4 + 4 B i t i 3 + 3 C i t i 2 + 2 D i t i + E i = E i + 1 C o e f f ∗ E k = ∑ i n − 1 E i + 1 − E i = E n − E 0 n o n d e p e n d e n t = E 0 C o e f f ∗ E k + n o n d e p e n d e n t = E n \begin{aligned} 5A_it_i^4+4B_it_i^3+3C_it_i^2+2D_it_i+E_i &=E_{i+1} \\ Coeff * Ek&=\sum_i^{n-1}E_{i+1}-E_{i}=E_n-E_0 \\ nondependent & = E_0 \\ Coeff*Ek+nondependent &=E_n \end{aligned} 5Aiti4+4Biti3+3Citi2+2Diti+EiCoeff∗EknondependentCoeff∗Ek+nondependent=Ei+1=i∑n−1Ei+1−Ei=En−E0=E0=En
DescribeFByPrev的计算效果
F k = [ 5 t 0 4 + ∑ 0 k 5 t 0 4 t i 4 t 0 3 + ∑ 0 k 4 t 0 3 t i . . . 3 t 0 2 + ∑ 0 k 3 t 0 2 t i 2 t 0 + ∑ 0 k 2 t 0 t i 5 t 1 4 + ∑ 1 k 5 t 1 4 t i 4 t 1 3 + ∑ 1 k 4 t 1 3 t i . . . 3 t 1 2 + ∑ 1 k 3 t 1 2 t i 2 t 1 + ∑ 1 k 2 t 1 t i ] n o n d e p e n d e n t = s t a r t c o g v ∗ ∑ t i + s t a r t c o g p \begin{aligned} Fk & = \begin{bmatrix} 5t_0^4+\sum_0^k5t_0^4t_i & 4t_0^3+ \sum_0^k4t_0^3t_i & ... & 3t_0^2+\sum_0^k3t_0^2t_i & 2t_0+ \sum_0^k2t_0t_i \\ 5t_1^4+\sum_1^k5t_1^4t_i & 4t_1^3+ \sum_1^k4t_1^3t_i & ... & 3t_1^2+\sum_1^k3t_1^2t_i & 2t_1+ \sum_1^k2t_1t_i \end{bmatrix} \\ nondependent & = startcogv * \sum t_i+startcogp \\ \end{aligned} Fknondependent=[5t04+∑0k5t04ti5t14+∑1k5t14ti4t03+∑0k4t03ti4t13+∑1k4t13ti......3t02+∑0k3t02ti3t12+∑1k3t12ti2t0+∑0k2t0ti2t1+∑1k2t1ti]=startcogv∗∑ti+startcogp
考虑到位置隐含关系
A i t i 5 + B i t i 4 + C i t i 3 + D i t i 2 + E i t i + F i = F i + 1 ∑ 0 i − 1 ( 5 A j t j 4 t i + 4 B j t j 3 t i + 3 D j t j 2 t i + 2 D j t j t i ) = ∑ 0 i − 1 ( E j + 1 − E j ) t i = ( E i − E 0 ) t i C o e f f ∗ F k = ∑ i n − 1 ( F i + 1 − F i − E i t i + E i t i − E 0 t i ) = F n − F 0 − E 0 t s u m n o n d e p e n d e n t = E 0 t s u m + F 0 C o e f f ∗ F k + n o n d e p e n d e n t = F n \begin{aligned} A_it_i^5+B_it_i^4+C_it_i^3+D_it_i^2+E_it_i+F_i &=F_{i+1} \\ \sum_0^{i-1}(5A_jt_j^4t_i+4B_jt_j^3t_i+3D_jt_j^2t_i+2D_jt_jt_i) & = \sum_0^{i-1}(E_{j+1}-E_j)t_i=(E_{i}-E_0)t_i \\ Coeff * Fk&=\sum_i^{n-1}(F_{i+1}-F_{i}-E_it_i+E_it_i-E_0t_i)=F_n-F_0-E_0t_{sum} \\ nondependent & = E_0t_{sum}+F_0 \\ Coeff * Fk+nondependent &=F_n \end{aligned} Aiti5+Biti4+Citi3+Diti2+Eiti+Fi0∑i−1(5Ajtj4ti+4Bjtj3ti+3Djtj2ti+2Djtjti)Coeff∗FknondependentCoeff∗Fk+nondependent=Fi+1=0∑i−1(Ej+1−Ej)ti=(Ei−E0)ti=i∑n−1(Fi+1−Fi−Eiti+Eiti−E0ti)=Fn−F0−E0tsum=E0tsum+F0=Fn
借助DescribeEByPrev和DescribeFByPrev,同样可以计算pos和velocity对应的数值
- 对于终止位置
( C o e f f ∗ E k + n o n d e p e n d e n t e ) ∗ t n + ( C o e f f ∗ F k + n o n d e p e n d e n t f ) + ( e n d P − E n t n − F n ) = = E n ∗ t n + F n + ( e n d P − E n t n − F n ) = e n d P \begin{aligned} (Coeff*Ek+nondependente)*t_n+ & \\(Coeff*Fk+nondependentf) +(end_P-E_nt_n-F_n)& = \\ & = E_n*t_n+ F_n+(end_P-E_nt_n-F_n) \\ & = end_P \end{aligned} (Coeff∗Ek+nondependente)∗tn+(Coeff∗Fk+nondependentf)+(endP−Entn−Fn)==En∗tn+Fn+(endP−Entn−Fn)=endP - 对于终止速度
( C o e f f ∗ E k + n o n d e p e n d e n t e ) + ( e n d V − E n ) = = E n + ( e n d v − E n ) = e n d V \begin{aligned} (Coeff*Ek+nondependente)+ & \\(end_V-E_n)& = \\ & = E_n+(end_v-E_n) \\ & = end_V \end{aligned} (Coeff∗Ek+nondependente)+(endV−En)==En+(endv−En)=endV - 对于加速度不需要借助DescribeFByPrev和DescribeEByPrev
// 2. Final conditions
int K = spline_infos_.back().id_; // id of last spline
int last_spline = var_index(K, dim, A);
std::array<double,6> t_duration = cache_exponents<6>(spline_infos_.back().duration_);// calculate e and f coefficients from previous values
Eigen::VectorXd Ek(coeff); Ek.setZero();
Eigen::VectorXd Fk(coeff); Fk.setZero();
double non_dependent_e, non_dependent_f;
DescribeEByPrev(K, dim, start_cog_v(dim), Ek, non_dependent_e);
DescribeFByPrev(K, dim, start_cog_v(dim), start_cog_p(dim), Fk, non_dependent_f);// position
ec->M(last_spline + A, i) = t_duration[5];
ec->M(last_spline + B, i) = t_duration[4];
ec->M(last_spline + C, i) = t_duration[3];
ec->M(last_spline + D, i) = t_duration[2];
ec->M.col(i) += Ek*t_duration[1];
ec->M.col(i) += Fk;ec->v(i) += non_dependent_e*t_duration[1] + non_dependent_f;
ec->v(i++) = -end_cog(dim);// velocity
ec->M(last_spline + A, i) = 5 * t_duration[4];
ec->M(last_spline + B, i) = 4 * t_duration[3];
ec->M(last_spline + C, i) = 3 * t_duration[2];
ec->M(last_spline + D, i) = 2* t_duration[1];
ec->M.col(i) += Ek;ec->v(i) += non_dependent_e;
ec->v(i++) += -kVelEnd(dim); // accelerations
ec->M(last_spline + A, i) = 20 * t_duration[3];
ec->M(last_spline + B, i) = 12 * t_duration[2];
ec->M(last_spline + C, i) = 6 * t_duration[1];
ec->M(last_spline + D, i) = 2;ec->v(i++) = -kAccEnd(dim);
- 连接点状态
连接点状态因为没有位置和速度约束和v0.1的一样
for (SplineInfoVec::size_type s = 0; s < spline_infos_.size() - 1; ++s)
{std::array<double,6> t_duration = cache_exponents<6>(spline_infos_.at(s).duration_);for (int dim = X; dim <= Y; dim++) {int curr_spline = var_index(s, dim, A);int next_spline = var_index(s + 1, dim, A);// accelerationec->M(curr_spline + A, i) = 20 * t_duration[3];ec->M(curr_spline + B, i) = 12 * t_duration[2];ec->M(curr_spline + C, i) = 6 * t_duration[1];ec->M(curr_spline + D, i) = 2;ec->M(next_spline + D, i) = -2.0;ec->v(i++) = 0.0;// jerk (derivative of acceleration)ec->M(curr_spline + A, i) = 60 * t_duration[2];ec->M(curr_spline + B, i) = 24 * t_duration[1];ec->M(curr_spline + C, i) = 6;ec->M(next_spline + C, i) = -6.0;ec->v(i++) = 0.0;}
}
3.1.3 inequality constraints
ZMP的作用位置
zmp到边缘的距离满足要求
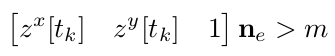
Z x ∗ l . p + Z y ∗ l q + r − m > 0 z = p o s t − E i ∗ t − F i + ( C o e f f ∗ E K + E 0 ) ∗ t + ( C o e f f ∗ F K + n o n d e F ) − h g z a c c ∗ a c c t \begin{aligned} Z_x*l.p+Z_y*l_q+r-m &>0 \\ z &= pos_t-E_i*t-F_i+(Coeff*EK+E_0)*t+ \\ &(Coeff*FK+nondeF)-\frac{h}{g_{zacc}}*acc_t \end{aligned} Zx∗l.p+Zy∗lq+r−mz>0=post−Ei∗t−Fi+(Coeff∗EK+E0)∗t+(Coeff∗FK+nondeF)−gzacch∗acct
for (double i=0; i < std::floor(s.duration_/kDt); ++i) {double time = i*kDt;std::array<double,6> t = cache_exponents<6>(time);// one constraint per line of support trianglefor (SuppTriangle::TrLine l: lines) {// the zero moment point must always lay on one side of triangle side:// p*x_zmp + q*y_zmp + r > stability_margin// with: x_zmp = x_pos - height/(g+z_acc) * x_acc// x_pos = at^5 + bt^4 + ct^3 + dt*2 + et + f// x_acc = 20at^3 + 12bt^2 + 6ct + 2ddouble z_acc = 0.0; // TODO: calculate z_acc based on foothold heightfor (int dim=X; dim<=Y; dim++) {double lc = (dim==X) ? l.coeff.p : l.coeff.q;// calculate e and f coefficients from previous valuesEigen::VectorXd Ek(coeff); Ek.setZero();Eigen::VectorXd Fk(coeff); Fk.setZero();double non_dependent_e, non_dependent_f;DescribeEByPrev(k, dim, start_cog_v(dim), Ek, non_dependent_e);DescribeFByPrev(k, dim, start_cog_v(dim), start_cog_p(dim), Fk, non_dependent_f);ineq->M(var_index(k,dim,A), c) = lc * (t[5] - h/(g+z_acc) * 20.0 * t[3]);ineq->M(var_index(k,dim,B), c) = lc * (t[4] - h/(g+z_acc) * 12.0 * t[2]);ineq->M(var_index(k,dim,C), c) = lc * (t[3] - h/(g+z_acc) * 6.0 * t[1]);ineq->M(var_index(k,dim,D), c) = lc * (t[2] - h/(g+z_acc) * 2.0);ineq->M.col(c) += lc * Ek*t[1];ineq->M.col(c) += lc * Fk;ineq->v[c] += lc *(non_dependent_e*t[0] + non_dependent_f);}ineq->v[c] += l.coeff.r - l.s_margin;++c;}
}
}
3.2 轨迹优化的流程
ConstructSplineSequence->optCeff->generateTraj
逻辑和之前一样,但是处理更加漂亮
double discretization_time = 0.1;
double swing_time = 0.6;
double stance_time = 0.2;
double t_stance_initial = 1.0; //sint step = 0;
unsigned int id = 0; // unique identifiers for each splineconst int kSplinesPer4ls = 1;
const int kSplinesPerStep = 1;// 人为的建立抬脚的step sequences:延长了初始和结束的时间1s
for (size_t i = 0; i < step_sequence.size(); ++i) {// 1. insert 4ls-phase when switching between disjoint support triangles// Attention: these 4ls-phases much coincide with the ones in the zmp optimizer if (i == 0) { // never insert 4ls-phase before first stepspline_infos_.push_back(SplineInfo(id++, t_stance_initial, true, step));} else {LegID swing_leg = step_sequence[i]; // 按照顺序进行抬腿LegID swing_leg_prev = step_sequence[i-1];if (SuppTriangle::Insert4LSPhase(swing_leg_prev, swing_leg)) {for (int s = 0; s < kSplinesPer4ls; s++) spline_infos_.push_back(SplineInfo(id++, t_stance/kSplinesPer4ls, true, step));}}// insert swing phase splinesfor (int s = 0; s < kSplinesPerStep; s++) spline_infos_.push_back(SplineInfo(id++, t_swing/kSplinesPerStep, false, step));// always have last 4ls spline for robot to move into center of feetif (i==step_sequence.size()-1) spline_infos_.push_back(SplineInfo(id++, t_stance_final, true, step));step++;
}
v0.3
v0.3 中添加了nlp形式,同时对qp形式的优化问题,进行了解耦。
相关文章:
towr code阅读
1. Introduction towr是非常优美的足式机器人规划代码,通过阅读towr重要的几个迭代版本的代码深入了解。 2 v0.1 第一代的版本,foot的位置是提前给定的,只对COG的trajectory进行优化。 2.1 cost 公式 仅仅只考虑加速度, ∫ …...

Channel扇出模式
文章目录 扇出模式reflectSelect 方式 扇出模式 有扇入模式,就有扇出模式,扇出模式是和扇入模式相反的。扇出模式只有一个输入源 Channel,有多个目标 Channel,扇出比就是 1 比目标 Channel 数的值,经常用在设计模式中…...

学者观察 | 联邦学习与区块链、大模型等新技术的融合与挑战-北京航空航天大学童咏昕
导语 当下,数据已成为经济社会发展中不可或缺的生产要素,正在发挥越来越大的价值。但是在数据使用过程中,由于隐私、合规或者无法完全信任合作方等原因,数据的拥有者并不希望彻底和他方共享数据。为解决原始数据自主可控与数据跨…...

ubuntu连接蓝牙耳机
本人也是经历了重重困难,特写此篇希望对读者能够带来帮助 1. 编辑 /etc/bluetooth/main.conf 文件,设定ControllerMode bredr 这一步使用vim编写完成后,保存退出的时候,会显示说没有修改权限,执行以下命令 sudo chm…...

长春理工大学漏洞报送证书
获取来源:edusrc(教育漏洞报告平台) url:主页 | 教育漏洞报告平台 兑换价格:10金币 获取条件:提交长春理工大学任意中危或以上级别漏洞...

Excel和Chatgpt是最好的组合。
内容来源:bitfool1 Excel和Chatgpt是最好的组合。 您可以轻松地自动化数据处理。 我向您展示如何在不打字公式的情况下将AI与Excel一起使用: 建立chatgpt 主要目的是使用Chatgpt自动编写Excel宏。 这消除了键入公式的需求,并让您在自然语言…...

Java用Jsoup库实现的多线程爬虫代码
因为没有提供具体的Python多线程跑数据的内容,所以我们将假设你想要爬取的网站是一个简单的URL。以下是一个基本的Java爬虫程序,使用了Jsoup库来解析HTML和爬虫ip信息。 import org.jsoup.Jsoup; import org.jsoup.nodes.Document; import org.jsoup.nod…...

layui控件开发,实现下拉搜索从数据库获取数据
1 标签部分使用带搜索的下拉框 <div class"layui-inline"><label class"layui-form-label">单位</label><div class"layui-input-inline"><select name"org" lay-search id"org_dwbh" lay-filt…...

让代码变美的第一天 - 观察者模式
文章目录 丑陋的模样变美步骤第一步 - 基本预期第二步 - 核心逻辑梳理第三步 - 重构重构1 - 消息定义重构2 - 消息订阅重构3 - 消息发布 高级用法按顺序订阅异步订阅多消息订阅 丑陋的模样 当我们开发一个功能,代码可能如下: private void test() {fun…...
微服务-网关设计
文章目录 引言I 网关部署java启动jar包II 其他服务部署细节2.1 服务端api 版本号III 网关常规设置3.1 外部请求系统服务都需要通过网关访问3.2 第三方平台回调校验文件的配置IV 微服务日志跟踪4.1 打印线程ID4.2 封装线程池任务执行器4.3 将自身MDC中的数据复制给子线程4.4 微服…...

WxJava使用lettuce的redis实现access_token的共享
使用WxJava微信开发时,调用接口获取access_token,如果多个服务部署,就需要使用到缓存来保存access_token以达到重复利用,WxJava 也提供了相关的实现类WxMaRedisConfigImpl,但是这个是基于jedis客户端的实现,…...

干货:如何运作一个全新品牌?
新品牌推广是真金白银的事儿,在你不了解情况的时候,最好以观察为主,不要不管三七二十一就动手。小马识途营销顾问建议创业者首先要找到自己的细分市场,按如下步骤去运作一个新品牌。 第一步、社群试水 先建立一个目标受众的社群&a…...
TCP/IP卷一详解第二章Internet地址结构概要
在这一章中介绍了Internet中使用的网络层地址(也就是IP地址),还有如何为Internet中的设备分配地址,以及各种类型的地址等等…… 一、IP地址的表示 为大家所常见的有IPV4地址和IPV6地址,但在IPV4地址中,通…...
小程序 打开方式 页面效果 表单页面 点击跳到详情页 图标 获取后台数据 进行页面渲染
请求地址:geecg-uniapp 同源策略 数据请求 获取后台数据 ui库安装 冲突解决(3)-CSDN博客 一.uniapp转小程序 (1) 运行微信开发工具 (2) 配置id 然后运行 打开小程序 路径 E:\通\uniapp-jeecg\unpackage\dist\d…...
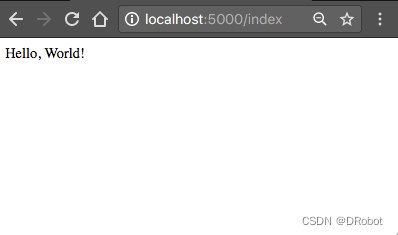
一个“Hello, World”Flask应用程序
如果您访问Flask网站,会看到一个非常简单的示例应用程序,只有5行代码。为了不重复那个简单的示例,我将向您展示一个稍微复杂一些的示例,它将为您编写大型应用程序提供一个良好的基础结构。 应用程序将存在于包中。在Python中&…...

计算机丢失mfc100.dll如何恢复,详细解析mfc100.dll文件丢失解决方法
在计算机使用过程中,我们可能会遇到一些错误提示,比如“mfc100.dll丢失”。这是因为动态链接库(DLL)文件是Windows操作系统的重要组成部分,它们包含了许多程序运行所需的函数和数据。当这些DLL文件丢失或损坏时&#x…...

分享一本让你真正理解深度学习的书
关注微信公众号:人工智能大讲堂,后台回复udl获取pdf文档。 今天要分享的书是Understanding Deep Learning,作者是西蒙普林斯,英国巴斯大学的荣誉教授,其个人学术能力相当强大,在AI领域有着深厚的学术造诣。…...
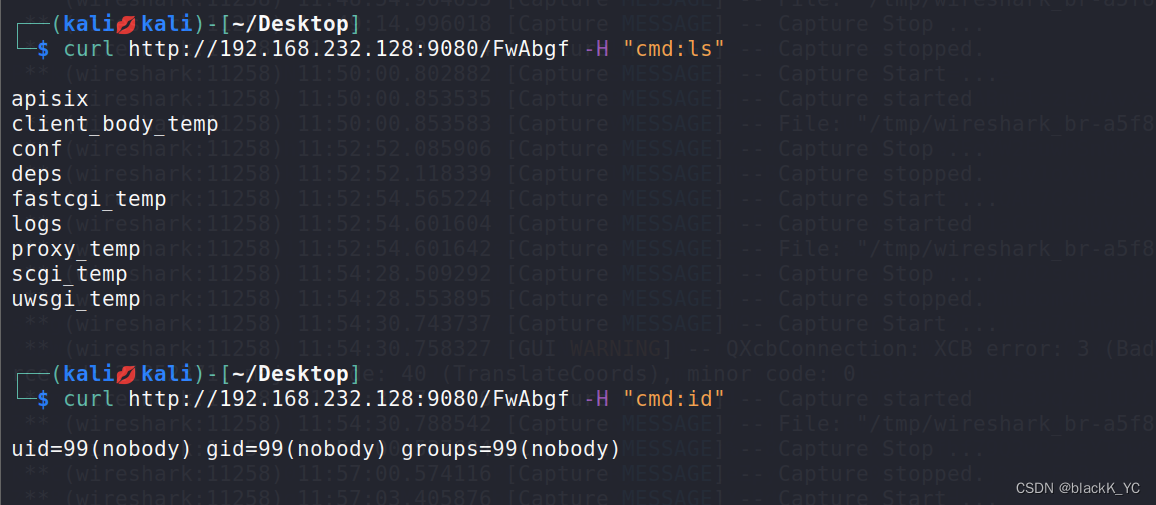
Apache APISIX Dashboard 未经认证访问导致 RCE(CVE-2021-45232)漏洞复现
漏洞描述 Apache APISIX 是一个动态、实时、高性能的 API 网关,而 Apache APISIX Dashboard 是一个简单易用的前端界面,用于管理 Apache APISIX。 在 2.10.1 之前的 Apache APISIX Dashboard 中,Manager API 使用了两个框架,并在…...

Git 安全警告修复手册:解决 `fatal: detected dubious ownership in repository at ` 问题 ️
🌷🍁 博主猫头虎 带您 Go to New World.✨🍁 🦄 博客首页——猫头虎的博客🎐 🐳《面试题大全专栏》 文章图文并茂🦕生动形象🦖简单易学!欢迎大家来踩踩~🌺 &a…...

【MySQL事务篇】多版本并发控制(MVCC)
多版本并发控制(MVCC) 文章目录 多版本并发控制(MVCC)1. 概述2. 快照读与当前读2.1 快照读2.2 当前读 3. MVCC实现原理之ReadView3.1 ReadView概述3.2 设计思路3.3 ReadView的规则3.4 MVCC整体操作流程 4. 举例说明4.1 READ COMMITTED隔离级别下4.2 REPEATABLE READ隔离级别下 …...
Vue2 第一节_Vue2上手_插值表达式{{}}_访问数据和修改数据_Vue开发者工具
文章目录 1.Vue2上手-如何创建一个Vue实例,进行初始化渲染2. 插值表达式{{}}3. 访问数据和修改数据4. vue响应式5. Vue开发者工具--方便调试 1.Vue2上手-如何创建一个Vue实例,进行初始化渲染 准备容器引包创建Vue实例 new Vue()指定配置项 ->渲染数据 准备一个容器,例如: …...
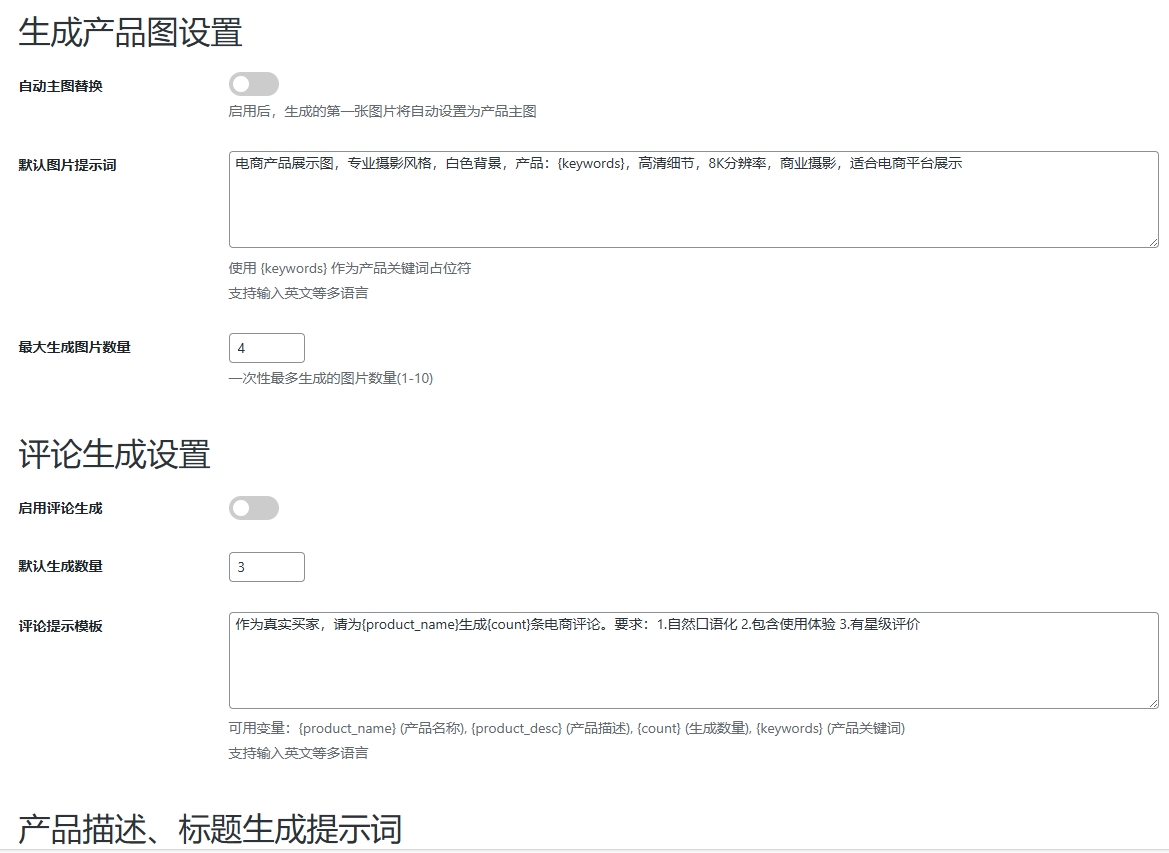
WordPress插件:AI多语言写作与智能配图、免费AI模型、SEO文章生成
厌倦手动写WordPress文章?AI自动生成,效率提升10倍! 支持多语言、自动配图、定时发布,让内容创作更轻松! AI内容生成 → 不想每天写文章?AI一键生成高质量内容!多语言支持 → 跨境电商必备&am…...

Caliper 配置文件解析:config.yaml
Caliper 是一个区块链性能基准测试工具,用于评估不同区块链平台的性能。下面我将详细解释你提供的 fisco-bcos.json 文件结构,并说明它与 config.yaml 文件的关系。 fisco-bcos.json 文件解析 这个文件是针对 FISCO-BCOS 区块链网络的 Caliper 配置文件,主要包含以下几个部…...
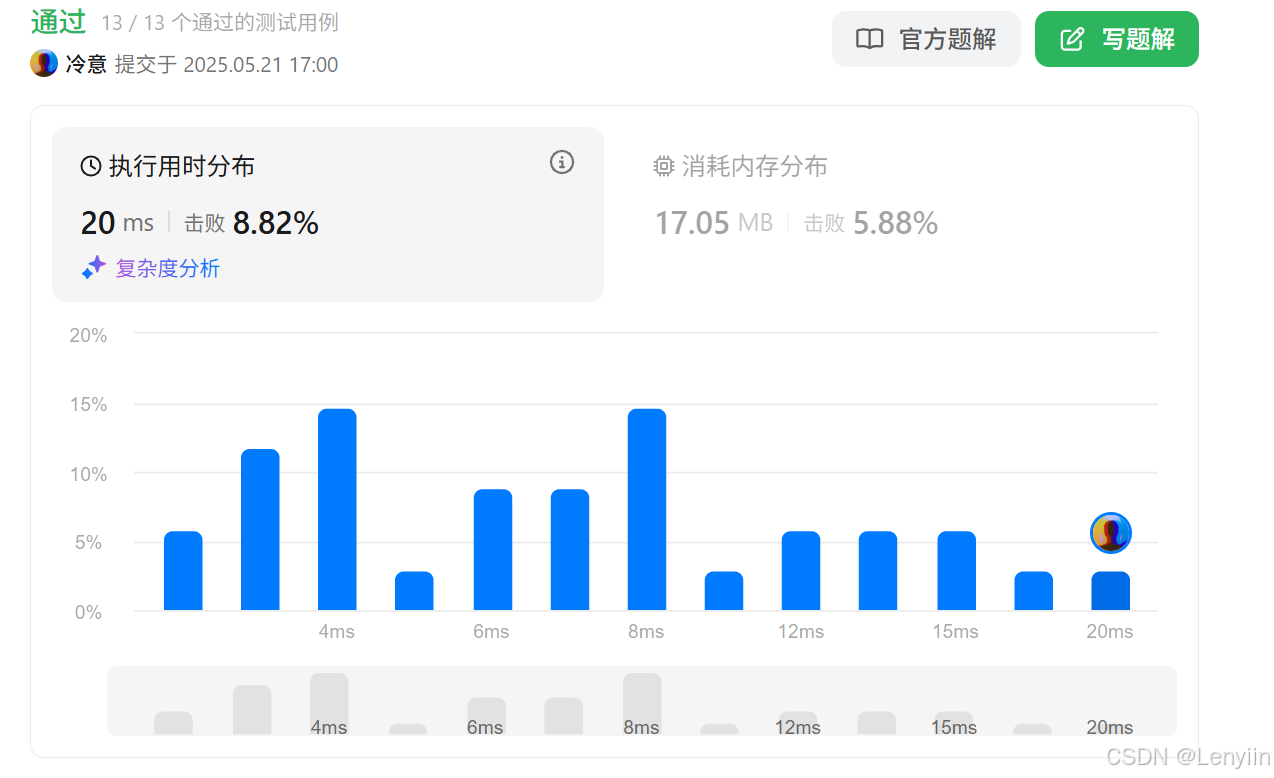
第 86 场周赛:矩阵中的幻方、钥匙和房间、将数组拆分成斐波那契序列、猜猜这个单词
Q1、[中等] 矩阵中的幻方 1、题目描述 3 x 3 的幻方是一个填充有 从 1 到 9 的不同数字的 3 x 3 矩阵,其中每行,每列以及两条对角线上的各数之和都相等。 给定一个由整数组成的row x col 的 grid,其中有多少个 3 3 的 “幻方” 子矩阵&am…...
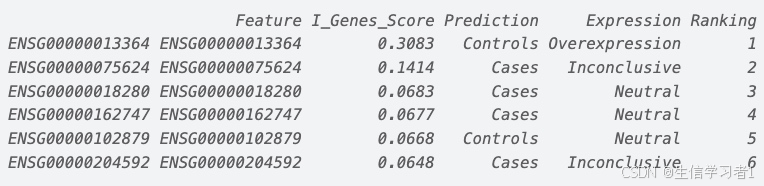
【数据分析】R版IntelliGenes用于生物标志物发现的可解释机器学习
禁止商业或二改转载,仅供自学使用,侵权必究,如需截取部分内容请后台联系作者! 文章目录 介绍流程步骤1. 输入数据2. 特征选择3. 模型训练4. I-Genes 评分计算5. 输出结果 IntelliGenesR 安装包1. 特征选择2. 模型训练和评估3. I-Genes 评分计…...

MySQL JOIN 表过多的优化思路
当 MySQL 查询涉及大量表 JOIN 时,性能会显著下降。以下是优化思路和简易实现方法: 一、核心优化思路 减少 JOIN 数量 数据冗余:添加必要的冗余字段(如订单表直接存储用户名)合并表:将频繁关联的小表合并成…...
)
GitHub 趋势日报 (2025年06月06日)
📊 由 TrendForge 系统生成 | 🌐 https://trendforge.devlive.org/ 🌐 本日报中的项目描述已自动翻译为中文 📈 今日获星趋势图 今日获星趋势图 590 cognee 551 onlook 399 project-based-learning 348 build-your-own-x 320 ne…...

在 Spring Boot 项目里,MYSQL中json类型字段使用
前言: 因为程序特殊需求导致,需要mysql数据库存储json类型数据,因此记录一下使用流程 1.java实体中新增字段 private List<User> users 2.增加mybatis-plus注解 TableField(typeHandler FastjsonTypeHandler.class) private Lis…...
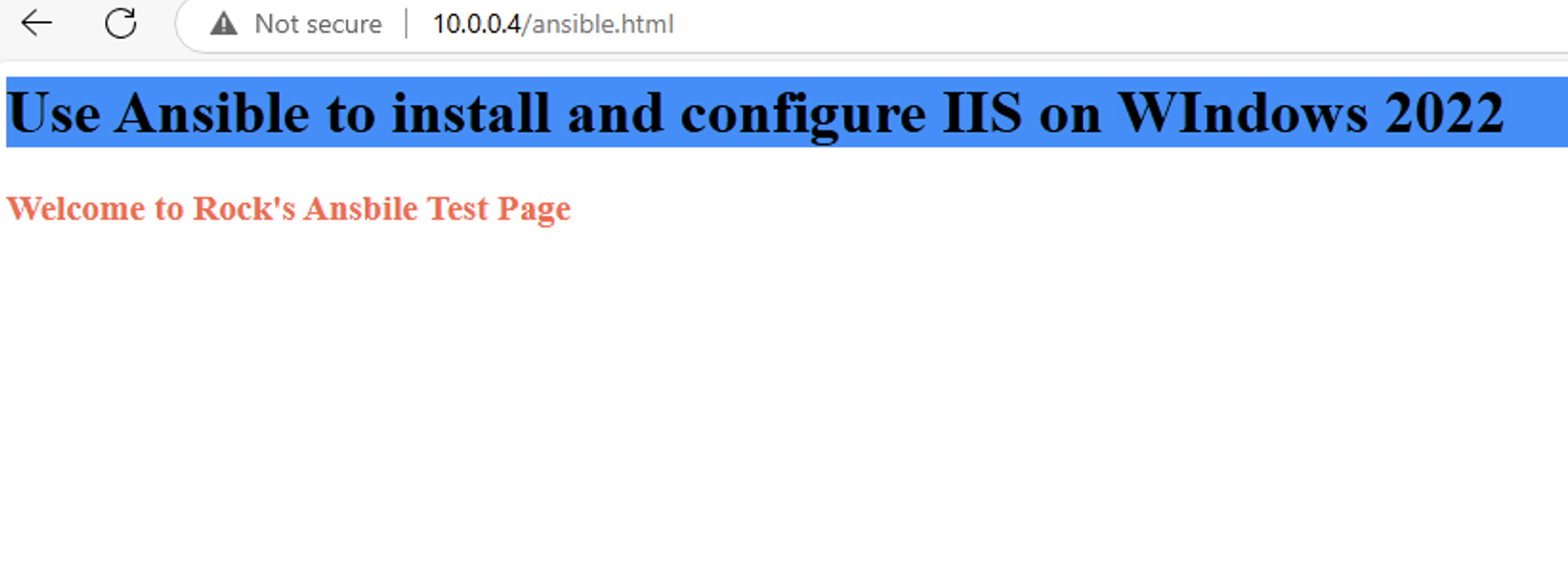
通过 Ansible 在 Windows 2022 上安装 IIS Web 服务器
拓扑结构 这是一个用于通过 Ansible 部署 IIS Web 服务器的实验室拓扑。 前提条件: 在被管理的节点上安装WinRm 准备一张自签名的证书 开放防火墙入站tcp 5985 5986端口 准备自签名证书 PS C:\Users\azureuser> $cert New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName &…...
)
Leetcode33( 搜索旋转排序数组)
题目表述 整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。 在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 < k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k1], …, nums[n-1], nums[0], nu…...
