【OpenCV实现图像:用OpenCV图像处理技巧之巧用直方图】
文章目录
- 概要
- 前置条件
- 统计数据分析
- 直方图均衡化原理
- 小结
概要
图像处理是计算机视觉领域中的重要组成部分,而直方图在图像处理中扮演着关键的角色。如何巧妙地运用OpenCV库中的图像处理技巧,特别是直方图相关的方法,来提高图像质量、改善细节以及调整曝光。
通过对图像的直方图进行分析和调整,能够优化图像的对比度、亮度和色彩平衡,从而使图像更具可视化效果。
直方图是一种统计图,用于表示图像中像素灰度级别的分布情况。在OpenCV中,可以使用直方图来了解图像的整体亮度分布,从而为后续处理提供基础。
OpenCV库中的函数,如cv2.calcHist和cv2.equalizeHist等,对图像的直方图进行均衡化。直方图均衡化是一种有效的方法,通过重新分配像素的强度值,使图像的亮度分布更均匀,提高图像的对比度和细节。
直方图匹配的应用,通过将目标图像的直方图调整到参考图像的直方图,实现两者之间的色彩一致性。这在图像配准和合成中有广泛的应用,提高了图像处理的精度和效果。
在低光照条件下拍摄图像的处理技巧。通过分析图像的直方图,可以采取针对性的方法,提高低光照图像中物体的可见性,改善图像的细节,并校正曝光过度或曝光不足的问题。
前置条件
一般来说,通过合理利用一些直方图的技巧,可以用于提高低光照拍摄图像中物体的可见性,改善图像的细节,以及校正曝光过度或曝光不足的图像。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
from skimage.exposure import histogram, cumulative_distribution
from skimage import filters
from skimage.color import rgb2hsv, rgb2gray, rgb2yuv
from skimage import color, exposure, transform
from skimage.exposure import histogram, cumulative_distributionfrom skimage.io import imread# Load the image & remove the alpha or opacity channel (transparency)
dark_image = imread('img.png')[:,:,:3]# Visualize the image
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.title('Original Image: Plasma Ball')
plt.imshow(dark_image)
plt.show()
上述图像是在光照不足下进行拍摄的,接着我们就来通过控制直方图,来改善我们的视觉效果。
统计数据分析
使用以下代码:
def calc_color_overcast(image):# Calculate color overcast for each channelred_channel = image[:, :, 0]green_channel = image[:, :, 1]blue_channel = image[:, :, 2]# Create a dataframe to store the resultschannel_stats = pd.DataFrame(columns=['Mean', 'Std', 'Min', 'Median', 'P_80', 'P_90', 'P_99', 'Max'])# Compute and store the statistics for each color channelfor channel, name in zip([red_channel, green_channel, blue_channel], ['Red', 'Green', 'Blue']):mean = np.mean(channel)std = np.std(channel)minimum = np.min(channel)median = np.median(channel)p_80 = np.percentile(channel, 80)p_90 = np.percentile(channel, 90)p_99 = np.percentile(channel, 99)maximum = np.max(channel)channel_stats.loc[name] = [mean, std, minimum, median, p_80, p_90, p_99, maximum]return channel_stats
完整代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
from skimage.exposure import histogram, cumulative_distribution
from skimage import filters
from skimage.color import rgb2hsv, rgb2gray, rgb2yuv
from skimage import color, exposure, transform
from skimage.exposure import histogram, cumulative_distribution
import pandas as pdfrom skimage.io import imread# Load the image & remove the alpha or opacity channel (transparency)
dark_image = imread('img.png')[:,:,:3]# Visualize the image
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.title('Original Image: Plasma Ball')
plt.imshow(dark_image)
plt.show()def calc_color_overcast(image):# Calculate color overcast for each channelred_channel = image[:, :, 0]green_channel = image[:, :, 1]blue_channel = image[:, :, 2]# Create a dataframe to store the resultschannel_stats = pd.DataFrame(columns=['Mean', 'Std', 'Min', 'Median','P_80', 'P_90', 'P_99', 'Max'])# Compute and store the statistics for each color channelfor channel, name in zip([red_channel, green_channel, blue_channel],['Red', 'Green', 'Blue']):mean = np.mean(channel)std = np.std(channel)minimum = np.min(channel)median = np.median(channel)p_80 = np.percentile(channel, 80)p_90 = np.percentile(channel, 90)p_99 = np.percentile(channel, 99)maximum = np.max(channel)channel_stats.loc[name] = [mean, std, minimum, median, p_80, p_90, p_99, maximum]return channel_stats
# 调用函数并传入图像
result_stats = calc_color_overcast(dark_image)# 打印结果
print(result_stats)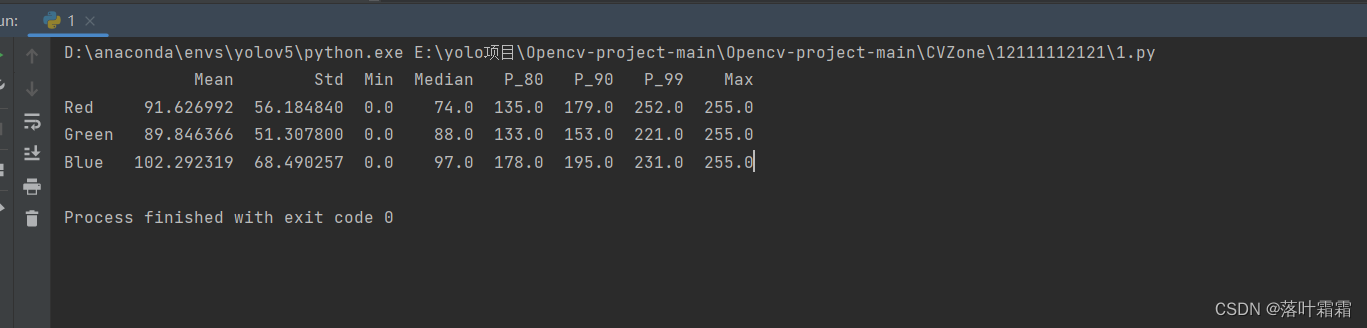
进而我们可以使用以下代码,来生成上述图像的直方图分布:
# Histogram plot
dark_image_intensity = img_as_ubyte(rgb2gray(dark_image))
freq, bins = histogram(dark_image_intensity)
plt.step(bins, freq*1.0/freq.sum())
plt.xlabel('intensity value')
plt.ylabel('fraction of pixels');
plt.show() # 添加这一行以显示直方图
得到直方图可视化效果如下:
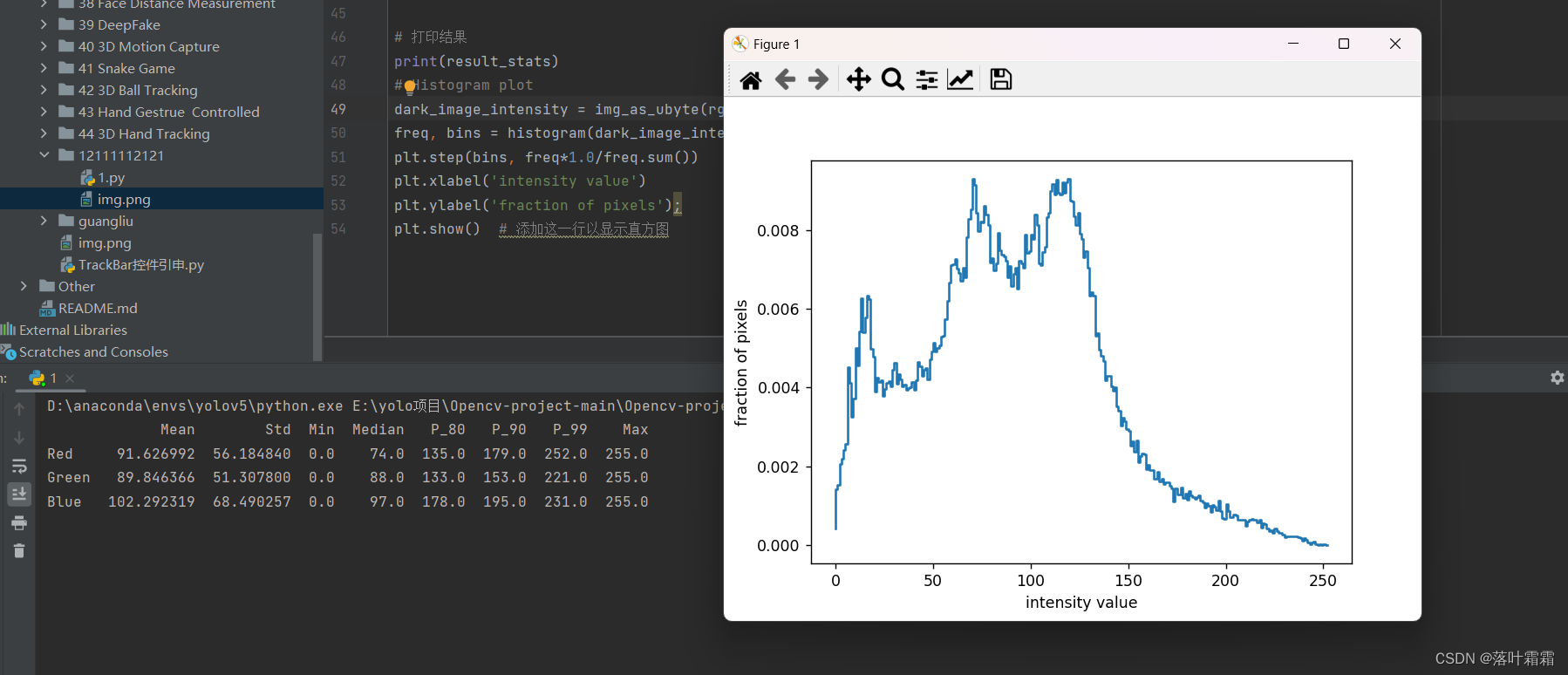
通过直方图的观察,可以注意到图像的像素平均强度似乎非常低,这进一步证实了图像的整体暗淡和曝光不足的情况。直方图展示了图像中像素强度值的分布情况,而大多数像素具有较低的强度值。这是有道理的,因为低像素强度值意味着图像中的大多数像素非常暗或呈现黑色。这样的观察有助于定量了解图像的亮度分布,为进一步的图像增强和调整提供了重要的线索。
直方图均衡化原理
直方图均衡化的基本原理是通过线性化图像的累积分布函数(CDF)来提高图像的对比度。实现这一目标的方法是将图像中每个像素的强度值映射到一个新的值,使得新的强度分布更加均匀。
可以通过以下几个步骤实现CDF的线性化:
将图像转换为灰度图:
如果图像不是灰度图,代码会将其转换为灰度图。这是因为直方图均衡化主要应用于灰度图。
计算累积分布函数(CDF):
通过计算图像像素的强度值的累积分布函数,可以了解每个强度值在图像中出现的累积频率。
绘制实际和目标CDF:
使用蓝色实线表示实际的CDF,使用红色实线表示目标CDF。目标CDF是一个线性分布,通过均匀分布来提高对比度。
绘制示例查找表:
绘制一个示例查找表,展示了像素强度值从原始值映射到目标值的过程。
自定义绘图:
对绘图进行自定义,包括设置坐标轴范围、标签和标题等。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.color import rgb2hsv, rgb2gray, rgb2yuv
from skimage.exposure import histogram, cumulative_distribution
import pandas as pd
from skimage import img_as_ubyte
from skimage.io import imread# Load the image & remove the alpha or opacity channel (transparency)
dark_image = imread('img.png')[:,:,:3]# Visualize the image
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.title('Original Image: Plasma Ball')
plt.imshow(dark_image)
plt.show()def calc_color_overcast(image):# Calculate color overcast for each channelred_channel = image[:, :, 0]green_channel = image[:, :, 1]blue_channel = image[:, :, 2]# Create a dataframe to store the resultschannel_stats = pd.DataFrame(columns=['Mean', 'Std', 'Min', 'Median','P_80', 'P_90', 'P_99', 'Max'])# Compute and store the statistics for each color channelfor channel, name in zip([red_channel, green_channel, blue_channel],['Red', 'Green', 'Blue']):mean = np.mean(channel)std = np.std(channel)minimum = np.min(channel)median = np.median(channel)p_80 = np.percentile(channel, 80)p_90 = np.percentile(channel, 90)p_99 = np.percentile(channel, 99)maximum = np.max(channel)channel_stats.loc[name] = [mean, std, minimum, median, p_80, p_90, p_99, maximum]return channel_statsdef plot_cdf(image):# Convert the image to grayscale if neededif len(image.shape) == 3:image = rgb2gray(image[:, :, :3])# Compute the cumulative distribution functionintensity = np.round(image * 255).astype(np.uint8)freq, bins = cumulative_distribution(intensity)# Plot the actual and target CDFstarget_bins = np.arange(256)target_freq = np.linspace(0, 1, len(target_bins))plt.step(bins, freq, c='b', label='Actual CDF')plt.plot(target_bins, target_freq, c='r', label='Target CDF')# Plot an example lookupexample_intensity = 50example_target = np.interp(freq[example_intensity], target_freq, target_bins)plt.plot([example_intensity, example_intensity, target_bins[-11], target_bins[-11]],[0, freq[example_intensity], freq[example_intensity], 0],'k--',label=f'Example lookup ({example_intensity} -> {example_target:.0f})')# Customize the plotplt.legend()plt.xlim(0, 255)plt.ylim(0, 1)plt.xlabel('Intensity Values')plt.ylabel('Cumulative Fraction of Pixels')plt.title('Cumulative Distribution Function')return freq, bins, target_freq, target_bins
# 调用函数并传入图像
result_stats = calc_color_overcast(dark_image)# 打印结果
print(result_stats)
# Histogram plot
# Histogram plot
dark_image_intensity = img_as_ubyte(rgb2gray(dark_image))
freq, bins = histogram(dark_image_intensity)
plt.step(bins, freq*1.0/freq.sum())
plt.xlabel('intensity value')
plt.ylabel('fraction of pixels')
plt.show() # 添加这一行以显示直方图# 调用 plot_cdf 函数并传入图像
plot_cdf(dark_image)
plt.show() # 添加这一行以显示CDF图形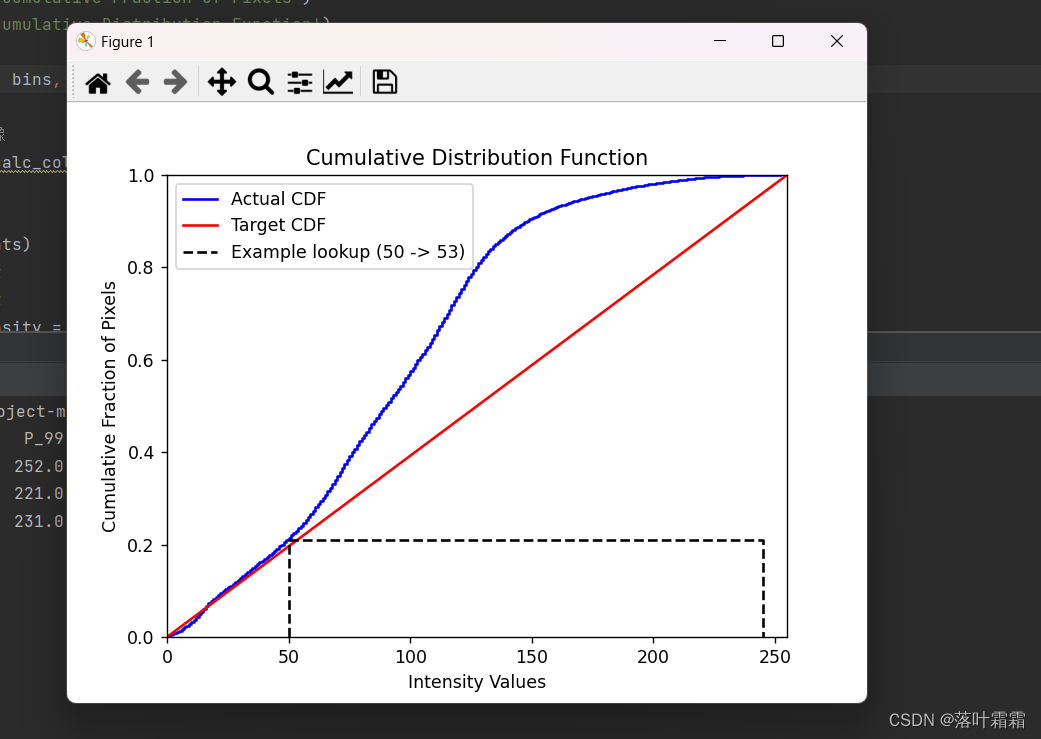
直方图均衡化实现结果:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
from skimage.exposure import histogram, cumulative_distribution, equalize_hist
from skimage import img_as_ubyte
from skimage.io import imread# Load the image & remove the alpha or opacity channel (transparency)
dark_image = imread('img.png')[:,:,:3]# Visualize the original image
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.title('Original Image: Plasma Ball')
plt.imshow(dark_image)
plt.show()# Convert the image to grayscale
gray_image = rgb2gray(dark_image)# Apply histogram equalization
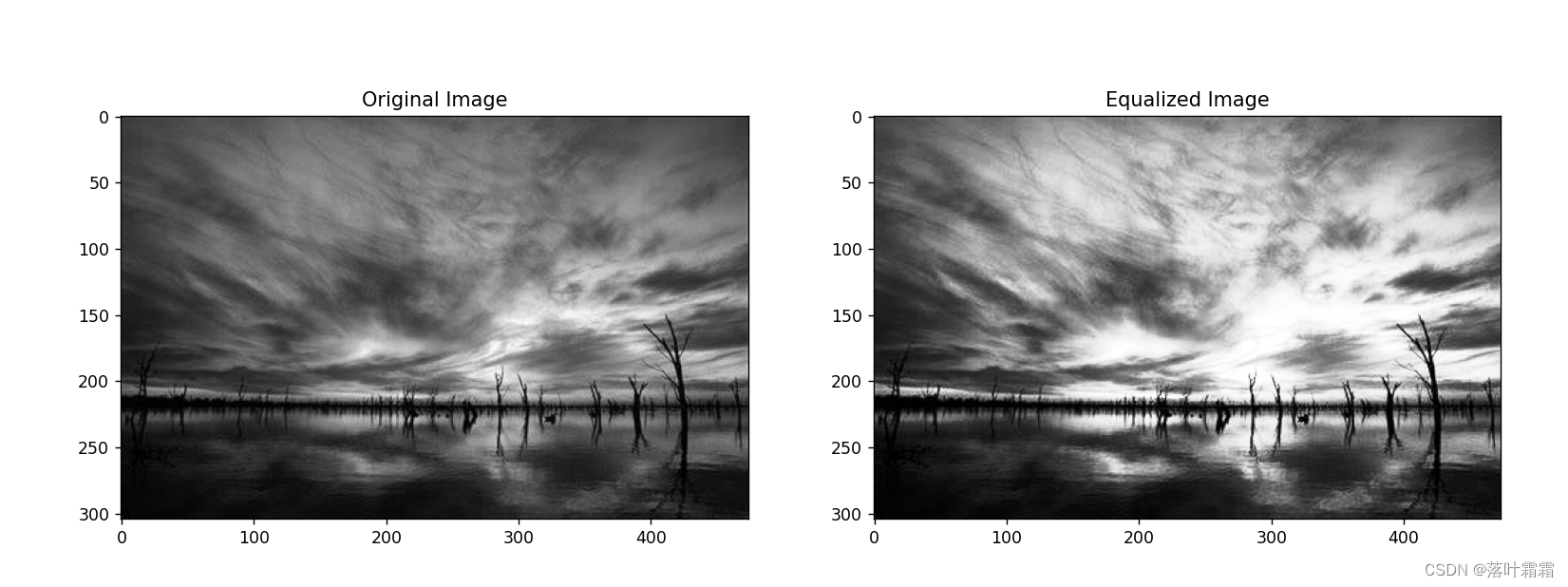
equalized_image = equalize_hist(gray_image)# Display the original and equalized images
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 7))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.title('Original Image')
plt.imshow(gray_image, cmap='gray')plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.title('Equalized Image')
plt.imshow(equalized_image, cmap='gray')plt.show()
扩展:
上面展示了最基本的直方图操作类型,接着让我们尝试不同类型的CDF技术,看看哪种技术适合给定的图像
# Linear
target_bins = np.arange(256)
# Sigmoid
def sigmoid_cdf(x, a=1):return (1 + np.tanh(a * x)) / 2
# Exponential
def exponential_cdf(x, alpha=1):return 1 - np.exp(-alpha * x)# Power
def power_law_cdf(x, alpha=1):return x ** alpha
# Other techniques:
def adaptive_histogram_equalization(image, clip_limit=0.03, tile_size=(8, 8)):clahe = exposure.equalize_adapthist(image, clip_limit=clip_limit, nbins=256, kernel_size=(tile_size[0], tile_size[1]))return clahe
def gamma_correction(image, gamma=1.0):corrected_image = exposure.adjust_gamma(image, gamma)return corrected_image
def contrast_stretching_percentile(image, lower_percentile=5, upper_percentile=95):in_range = tuple(np.percentile(image, (lower_percentile, upper_percentile)))stretched_image = exposure.rescale_intensity(image, in_range)return stretched_imagedef unsharp_masking(image, radius=5, amount=1.0):blurred_image = filters.gaussian(image, sigma=radius, multichannel=True)sharpened_image = (image + (image - blurred_image) * amount).clip(0, 1)return sharpened_imagedef equalize_hist_rgb(image):equalized_image = exposure.equalize_hist(image)return equalized_imagedef equalize_hist_hsv(image):hsv_image = color.rgb2hsv(image[:,:,:3])hsv_image[:, :, 2] = exposure.equalize_hist(hsv_image[:, :, 2])hsv_adjusted = color.hsv2rgb(hsv_image)return hsv_adjusteddef equalize_hist_yuv(image):yuv_image = color.rgb2yuv(image[:,:,:3])yuv_image[:, :, 0] = exposure.equalize_hist(yuv_image[:, :, 0])yuv_adjusted = color.yuv2rgb(yuv_image)return yuv_adjusted
使用代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.io import imread
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
from skimage.exposure import histogram, cumulative_distribution
from skimage import exposure, color, filters# Load the image & remove the alpha or opacity channel (transparency)
dark_image = imread('img.png')[:, :, :3]# Visualize the original image
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.title('Original Image: Plasma Ball')
plt.imshow(dark_image)
plt.show()# Linear
target_bins = np.arange(256)
# Sigmoid
def sigmoid_cdf(x, a=1):return (1 + np.tanh(a * x)) / 2
# Exponential
def exponential_cdf(x, alpha=1):return 1 - np.exp(-alpha * x)# Power
def power_law_cdf(x, alpha=1):return x ** alpha
# Other techniques:
def adaptive_histogram_equalization(image, clip_limit=0.03, tile_size=(8, 8)):clahe = exposure.equalize_adapthist(image, clip_limit=clip_limit, nbins=256, kernel_size=(tile_size[0], tile_size[1]))return clahe
def gamma_correction(image, gamma=1.0):corrected_image = exposure.adjust_gamma(image, gamma)return corrected_image
def contrast_stretching_percentile(image, lower_percentile=5, upper_percentile=95):in_range = tuple(np.percentile(image, (lower_percentile, upper_percentile)))stretched_image = exposure.rescale_intensity(image, in_range)return stretched_imagedef unsharp_masking(image, radius=5, amount=1.0):blurred_image = filters.gaussian(image, sigma=radius, multichannel=True)sharpened_image = (image + (image - blurred_image) * amount).clip(0, 1)return sharpened_imagedef equalize_hist_rgb(image):equalized_image = exposure.equalize_hist(image)return equalized_imagedef equalize_hist_hsv(image):hsv_image = color.rgb2hsv(image[:,:,:3])hsv_image[:, :, 2] = exposure.equalize_hist(hsv_image[:, :, 2])hsv_adjusted = color.hsv2rgb(hsv_image)return hsv_adjusteddef equalize_hist_yuv(image):yuv_image = color.rgb2yuv(image[:,:,:3])yuv_image[:, :, 0] = exposure.equalize_hist(yuv_image[:, :, 0])yuv_adjusted = color.yuv2rgb(yuv_image)return yuv_adjusted
def apply_cdf(image, cdf_function, *args, **kwargs):# Convert the image to grayscalegray_image = rgb2gray(image)# Calculate the cumulative distribution function (CDF)intensity = np.round(gray_image * 255).astype(np.uint8)cdf_values, bins = cumulative_distribution(intensity)# Apply the specified CDF functiontransformed_cdf = cdf_function(cdf_values, *args, **kwargs)# Map the CDF values back to intensity valuestransformed_intensity = np.interp(intensity, cdf_values, transformed_cdf)# Rescale the intensity values to [0, 1]transformed_intensity = transformed_intensity / 255.0# Apply the transformation to the original imagetransformed_image = image.copy()for i in range(3):transformed_image[:, :, i] = transformed_intensityreturn transformed_image# Apply and visualize different CDF techniques
linear_image = apply_cdf(dark_image, lambda x: x)
sigmoid_image = apply_cdf(dark_image, sigmoid_cdf, a=1)
exponential_image = apply_cdf(dark_image, exponential_cdf, alpha=1)
power_law_image = apply_cdf(dark_image, power_law_cdf, alpha=1)
adaptive_hist_eq_image = adaptive_histogram_equalization(dark_image)
gamma_correction_image = gamma_correction(dark_image, gamma=1.5)
contrast_stretch_image = contrast_stretching_percentile(dark_image)
unsharp_mask_image = unsharp_masking(dark_image)
equalized_hist_rgb_image = equalize_hist_rgb(dark_image)
equalized_hist_hsv_image = equalize_hist_hsv(dark_image)
equalized_hist_yuv_image = equalize_hist_yuv(dark_image)# Visualize the results
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15))
plt.subplot(4, 4, 1), plt.imshow(linear_image), plt.title('Linear CDF')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 2), plt.imshow(sigmoid_image), plt.title('Sigmoid CDF')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 3), plt.imshow(exponential_image), plt.title('Exponential CDF')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 4), plt.imshow(power_law_image), plt.title('Power Law CDF')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 5), plt.imshow(adaptive_hist_eq_image), plt.title('Adaptive Histogram Equalization')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 6), plt.imshow(gamma_correction_image), plt.title('Gamma Correction')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 7), plt.imshow(contrast_stretch_image), plt.title('Contrast Stretching')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 8), plt.imshow(unsharp_mask_image), plt.title('Unsharp Masking')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 9), plt.imshow(equalized_hist_rgb_image), plt.title('Equalized Histogram (RGB)')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 10), plt.imshow(equalized_hist_hsv_image), plt.title('Equalized Histogram (HSV)')
plt.subplot(4, 4, 11), plt.imshow(equalized_hist_yuv_image), plt.title('Equalized Histogram (YUV)')plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()输出结果:

小结
有多种方法和技术可用于改善RGB图像的可视效果,但其中许多方法都需要手动调整参数。上述输出展示了使用不同直方图操作生成的亮度校正效果。通过观察,发现HSV调整、指数变换、对比度拉伸和unsharp masking的效果都是令人满意的。
HSV调整:
HSV调整涉及将RGB图像转换为HSV颜色空间并修改强度分量。这种技术似乎在提高图像可视化效果方面取得了令人满意的结果。
指数变换:
指数变换用于根据指数函数调整像素强度。这种方法在提高图像整体亮度和视觉吸引力方面表现出色。
对比度拉伸:
对比度拉伸旨在通过拉伸指定百分位范围内的强度值来增强图像对比度。结果表明,这种技术有效地提高了图像的视觉质量。
Unsharp Masking:
Unsharp masking涉及通过减去模糊版本来创建图像的锐化版本。应用unsharp masking似乎增强了图像的细节和边缘
相关文章:

【OpenCV实现图像:用OpenCV图像处理技巧之巧用直方图】
文章目录 概要前置条件统计数据分析直方图均衡化原理小结 概要 图像处理是计算机视觉领域中的重要组成部分,而直方图在图像处理中扮演着关键的角色。如何巧妙地运用OpenCV库中的图像处理技巧,特别是直方图相关的方法,来提高图像质量、改善细…...

【Android】画面卡顿优化列表流畅度四之Glide几个常用参数设置
好像是一年前快两年了,笔者解析过glide的源码,也是因为觉得自己熟悉一些,也就没太关注过项目里glide的具体使用对当前业务的影响;主要是自负,还有就是真没有碰到过这样的数据加载情况。暴露了经验还是不太足够 有兴趣的…...

js控制手机蓝牙
要使用JavaScript控制手机蓝牙,您需要使用Web Bluetooth API。这是一种新的Web API,可以让Web应用程序访问和控制蓝牙设备。 以下是一些步骤,以便您开始使用Web Bluetooth API: 检查浏览器支持:首先,您需要…...
“)
C++11 原始字符串字面量R“()“
原始字符串字面量(Raw String Literals) R"()"是C11引入的一项特性,它允许创建不需要转义字符的字符串字面量。字符串中包含特殊字符、换行符和其他转义字符时,不需要反斜杠转义它们。 原始(Raw):不用使用反…...

【Vue原理解析】之虚拟DOM
Vue.js是一款流行的JavaScript框架,它采用了虚拟DOM(Virtual DOM)的概念来提高性能和开发效率。虚拟DOM是Vue.js的核心之一,它通过在内存中构建一个轻量级的DOM树来代替直接操作真实的DOM,从而减少了对真实DOM的操作次…...
HCIE-灾备技术和安全服务
灾备技术 灾备包含两个概念:容灾、备份 备份是为了保证数据的完整性,数据不丢失。全量备份、增量备份,备份数据还原。 容灾是为了保证业务的连续性,尽可能不断业务。 快照:保存的不是底层块数据,保存的是逻…...

【图论实战】Boost学习 01:基本操作
文章目录 头文件图的构建图的可视化基本操作 头文件 #include <boost/graph/adjacency_list.hpp> #include <boost/graph/graphviz.hpp> #include <boost/graph/properties.hpp> #include <boost/property_map/property_map.hpp> #include <boost/…...
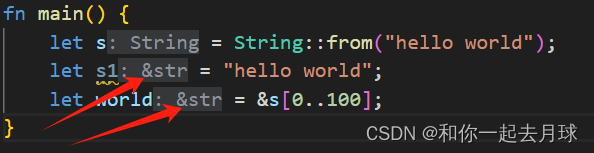
Rust 中的引用与借用
目录 1、引用与借用 1.1 可变引用 1.2 悬垂引用 1.3 引用的规则 2、slice 类型 2.1 字符串字面量其实就是一个slice 2.2 总结 1、引用与借用 在之前我们将String 类型的值返回给调用函数,这样会导致这个String会被移动到函数中,这样在原来的作用域…...
Azure 机器学习:在 Azure 机器学习中使用 Azure OpenAI 模型
目录 一、环境准备二、Azure 机器学习中的 OpenAI 模型是什么?三、在机器学习中访问 Azure OpenAI 模型连接到 Azure OpenAI部署 Azure OpenAI 模型 四、使用自己的训练数据微调 Azure OpenAI 模型使用工作室微调微调设置训练数据自定义微调参数部署微调的模型 使用…...
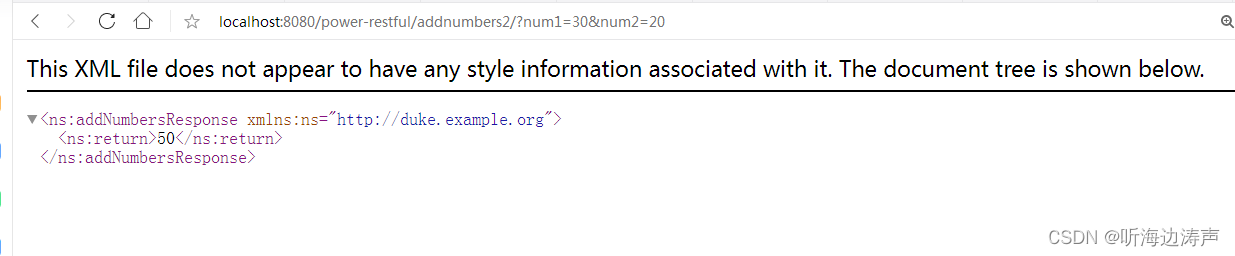
XML Web 服务 Eclipse实现中的sun-jaxws.xml文件
说明 在sun-jaxws.xml文件,可以配置endpoint、handler-chain等内容。在这个文件中配置的内容会覆盖在Java代码中使用注解属性配置的的内容。 这个文件根据自己的项目内容修改完成以后,作为web应用的一部分部署到web容器中(放到web应用的WEB…...

16.1 二次根式 教学设计及课堂检测设计
课堂检测如下:...

Android数据流的狂欢:Channel与Flow
在 Android 应用程序的开发中,处理异步数据流是一个常见的需求。为了更好地应对这些需求,Kotlin 协程引入了 Channel 和 Flow,它们提供了强大的工具来处理数据流,实现生产者-消费者模式,以及构建响应式应用程序。 本文…...

Java 单元测试最佳实践:如何充分利用测试自动化
单元测试是众所周知的做法,但还有很大的改进空间!在这篇文章中,我们讨论最有效的单元测试最佳实践,包括在此过程中最大化自动化工具的方法。我们还将讨论代码覆盖率、模拟依赖关系和整体测试策略。 什么是单元测试? 单…...
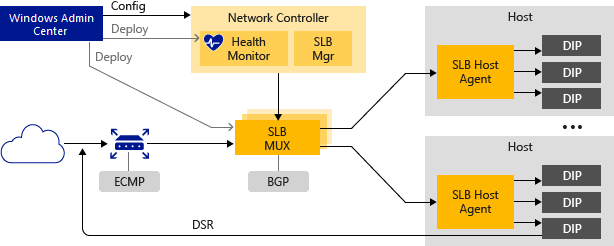
windows系统用于 SDN 的软件负载均衡器 (SLB)
适用于:Azure Stack HCI 版本 22H2 和 21H2;Windows Server 2022、Windows Server 2019、Windows Server 2016 软件负载均衡器包括哪些内容? 软件负载均衡器提供以下功能: 适用于北/南和东/西 TCP/UDP 流量的第 4 层 (L4) 负载均…...
漏洞复现--IP-guard flexpaper RCE
免责声明: 文章中涉及的漏洞均已修复,敏感信息均已做打码处理,文章仅做经验分享用途,切勿当真,未授权的攻击属于非法行为!文章中敏感信息均已做多层打马处理。传播、利用本文章所提供的信息而造成的任何直…...
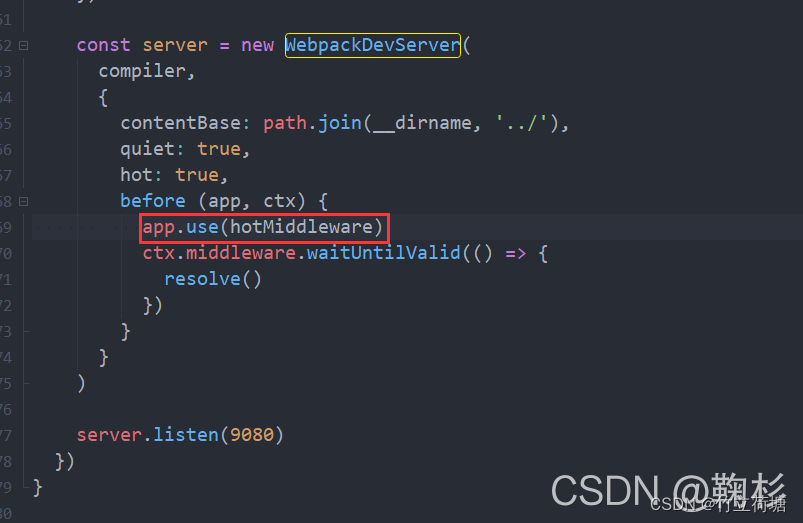
Electron-vue出现GET http://localhost:9080/__webpack_hmr net::ERR_ABORTED解决方案
GET http://localhost:9080/__webpack_hmr net::ERR_ABORTED解决方案 使用版本解决方案解决总结 使用版本 以下是我解决此问题时使用的electron和vue等的一些版本信息 【附】经过测试 electron 的版本为 13.1.4 时也能解决 解决方案 将项目下的 .electron-vue/dev-runner.js…...

Linux---(六)自动化构建工具 make/Makefile
文章目录 一、make/Makefile二、快速查看(1)建立Makefile文件(2)编辑Makefile文件(3)解释(4)效果展示 三、背后的基本知识、原理(1)如何清理对应的临时文件呢…...

谷歌:编写干净的代码以减少认知负荷
您是否曾经阅读过代码却发现很难理解?您可能正在经历认知负荷! 认知负荷是指完成一项任务所需的脑力劳动量。阅读代码时,您必须记住变量值、条件逻辑、循环索引、数据结构状态和接口契约等信息。随着代码变得更加复杂,认知负荷也…...
微信小程序display常用属性和子元素排列方式介绍
wxss中display常用显示属性与css一致,介绍如下: 针对元素本身显示的属性: displayblock,元素显示换行displayinline,元素显示换行,但不可设置固定的宽度和高度,也不可设置上下方向的margin和p…...
设计模式—结构型模式之代理模式
设计模式—结构型模式之代理模式 代理模式(Proxy Pattern) ,给某一个对象提供一个代理,并由代理对象控制对原对象的引用,对象结构型模式。 静态代理 比如我们有一个直播平台,提供了直播功能,但是如果不进行美颜,可能就比较冷清…...

[2025CVPR]DeepVideo-R1:基于难度感知回归GRPO的视频强化微调框架详解
突破视频大语言模型推理瓶颈,在多个视频基准上实现SOTA性能 一、核心问题与创新亮点 1.1 GRPO在视频任务中的两大挑战 安全措施依赖问题 GRPO使用min和clip函数限制策略更新幅度,导致: 梯度抑制:当新旧策略差异过大时梯度消失收敛困难:策略无法充分优化# 传统GRPO的梯…...

安宝特方案丨XRSOP人员作业标准化管理平台:AR智慧点检验收套件
在选煤厂、化工厂、钢铁厂等过程生产型企业,其生产设备的运行效率和非计划停机对工业制造效益有较大影响。 随着企业自动化和智能化建设的推进,需提前预防假检、错检、漏检,推动智慧生产运维系统数据的流动和现场赋能应用。同时,…...

关于iview组件中使用 table , 绑定序号分页后序号从1开始的解决方案
问题描述:iview使用table 中type: "index",分页之后 ,索引还是从1开始,试过绑定后台返回数据的id, 这种方法可行,就是后台返回数据的每个页面id都不完全是按照从1开始的升序,因此百度了下,找到了…...
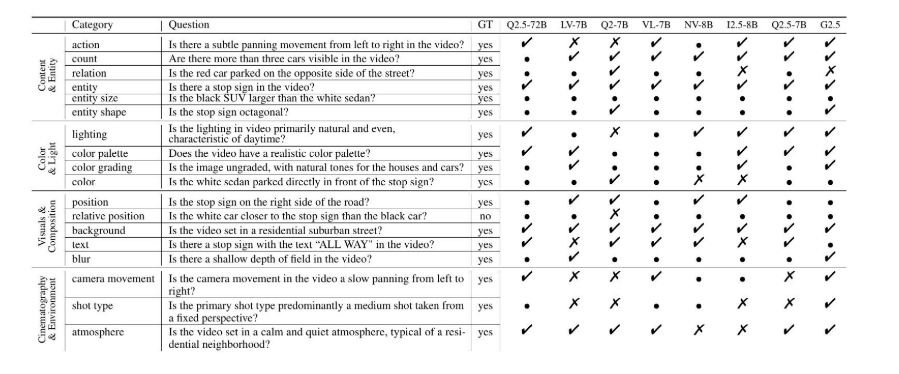
视频字幕质量评估的大规模细粒度基准
大家读完觉得有帮助记得关注和点赞!!! 摘要 视频字幕在文本到视频生成任务中起着至关重要的作用,因为它们的质量直接影响所生成视频的语义连贯性和视觉保真度。尽管大型视觉-语言模型(VLMs)在字幕生成方面…...

【android bluetooth 框架分析 04】【bt-framework 层详解 1】【BluetoothProperties介绍】
1. BluetoothProperties介绍 libsysprop/srcs/android/sysprop/BluetoothProperties.sysprop BluetoothProperties.sysprop 是 Android AOSP 中的一种 系统属性定义文件(System Property Definition File),用于声明和管理 Bluetooth 模块相…...

uniapp中使用aixos 报错
问题: 在uniapp中使用aixos,运行后报如下错误: AxiosError: There is no suitable adapter to dispatch the request since : - adapter xhr is not supported by the environment - adapter http is not available in the build 解决方案&…...

智能分布式爬虫的数据处理流水线优化:基于深度强化学习的数据质量控制
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,数据已成为企业和研究机构的核心资产。智能分布式爬虫作为高效的数据采集工具,在大规模数据获取中发挥着关键作用。然而,传统的数据处理流水线在面对复杂多变的网络环境和海量异构数据时,常出现数据质…...

return this;返回的是谁
一个审批系统的示例来演示责任链模式的实现。假设公司需要处理不同金额的采购申请,不同级别的经理有不同的审批权限: // 抽象处理者:审批者 abstract class Approver {protected Approver successor; // 下一个处理者// 设置下一个处理者pub…...

Caliper 配置文件解析:fisco-bcos.json
config.yaml 文件 config.yaml 是 Caliper 的主配置文件,通常包含以下内容: test:name: fisco-bcos-test # 测试名称description: Performance test of FISCO-BCOS # 测试描述workers:type: local # 工作进程类型number: 5 # 工作进程数量monitor:type: - docker- pro…...
论文阅读笔记——Muffin: Testing Deep Learning Libraries via Neural Architecture Fuzzing
Muffin 论文 现有方法 CRADLE 和 LEMON,依赖模型推理阶段输出进行差分测试,但在训练阶段是不可行的,因为训练阶段直到最后才有固定输出,中间过程是不断变化的。API 库覆盖低,因为各个 API 都是在各种具体场景下使用。…...
