深入浅出 Linux 中的 ARM IOMMU SMMU I
Linux 系统下的 SMMU 介绍
在计算机系统架构中,与传统的用于 CPU 访问内存的管理的 MMU 类似,IOMMU (Input Output Memory Management Unit) 将来自系统 I/O 设备的 DMA 请求传递到系统互连之前,它会先转换请求的地址,并对系统 I/O 设备的内存访问事务进行管理和限制。IOMMU 将设备可见的虚拟地址 (IOVA) 映射到物理内存地址。不同的硬件体系结构有不同的 IOMMU 实现,ARM 平台的 IOMMU 是 SMMU (System Memory Management)。
SMMU 只为来自系统 I/O 设备的内存访问事务提供转换服务,而不为到系统 I/O 设备的事务提供转换服务。从系统或 CPU 到系统 I/O 设备的事务由其它方式管理,例如 MMU。下图展示了 SMMU 在系统中的角色。

来自系统 I/O 设备的内存访问事务指系统 I/O 设备对内存的读写,到系统 I/O 设备的事务通常指 CPU 访问系统 I/O 设备内部映射到物理内存地址空间的存储器或寄存器。关于 SMMU 更详细的介绍,可以参考 IOMMU和Arm SMMU介绍 及 SMMU 软件指南。关于 SMMU 的寄存器、数据结构和行为的详细描述,可以参考 ARM 系统内存管理单元架构规范版本 3。关于 SMMU 的具体实现,可以参考相关实现的文档,如 MMU-600 的 Arm CoreLink MMU-600 系统内存管理单元技术参考手册 和 MMU-700 的 Arm® CoreLink™ MMU-700 系统内存管理单元技术参考手册。
SMMU 通过 StreamID 等区分不同的系统 I/O 设备,系统 I/O 设备在通过 SMMU 访问内存时,需要将 StreamID 等信息带给 SMMU。从系统 I/O 设备的角度来看,包含 SMMU 的系统更精细的结构如下图:

系统 I/O 设备通过 DMA 访问内存,DMA 请求发出后,在送到 SMMU 和系统互联之前,先要经过一个称为 DAA (对于其它实现,可能是其它设备) 的设备,DAA 做第一次地址转换,之后将内存访问请求信息,包括配置的 StreamID 等送进 SMMU,以做进一步的处理。
在 Linux 系统中,要为某个系统 I/O 设备开启 SMMU,一般要经过如下步骤:
- SMMU 驱动程序的初始化。这主要包括读取 dts 文件中的,SMMU 设备节点,探测 SMMU 的硬件设备特性,初始化全局资源及数据结构,如命令队列、事件队列、中断,和流表等,并将 SMMU 设备注册进 Linux 内核的 IOMMU 子系统。
- 系统 I/O 设备探测、发现,并和驱动程序绑定初始化的过程中,设备和 IOMMU 的绑定。对于使用 DMA 来访问内存的设备,这一般通过调用
of_dma_configure()/of_dma_configure_id()函数完成。设备探测、发现,并和驱动程序绑定初始化的过程,需要访问设备树 dts 文件里,设备节点定义中与 IOMMU 配置相关的字段。如在 arch/arm64/boot/dts/renesas/r8a77961.dtsi 文件中:
iommus = <&ipmmu_vc0 19>;
- 系统 I/O 设备驱动程序关于 IOMMU 的配置。这部分通常因具体的硬件系统实现而异。这主要包括调用
dma_coerce_mask_and_coherent()/dma_set_mask_and_coherent()函数将 DMA 掩码和一致性 DMA 掩码设置为相同的值,以及配置类似前面提到的 DAA 之类的设备。 - 系统 I/O 设备驱动程序分配内存。系统 I/O 设备驱动程序通过
dma_alloc_coherent()等接口分配内存,这个过程除了分配内存外,还会通过 SMMU 设备驱动程序的操作函数,创建地址转换表,并完成 SMMU CD 等数据结构的设置。在 Linux 内核中,不同的子系统实际调用的分配 DMA 内存的方法不同,但最终都需要调用dma_alloc_coherent()函数,这样分配的内存,在通过 DMA 访问时,才会经过 SMMU。 - 访问分配的内存。通过
dma_alloc_coherent()函数分配到的内存,其地址可以提供给系统 I/O 设备的 DMA 配置相关逻辑,后续系统 I/O 设备通过 DMA 访问内存,将经过 SMMU 完成地址转换。通过 DMA 访问内存时,将经过 SMMU 的地址转换。
SMMU 的地址转换借助于相关的数据结构完成,这主要包括流表及其流表项 STE,上下文描述符表及其表项 CD,和地址转换表及其表项。STE 存储流的上下文信息,每个 STE 64 字节。CD 存储了与第 1 阶段转换有关的所有设置,每个 CD 64 字节。地址转换表用于描述虚拟地址和物理内存地址之间的映射关系。流表的结构可以分为 线性流表 和 2 级流表 两种。线性流表结构如下图:

2 级流表示例结构如下图:

上下文描述符表的结构可以分为 单个 CD,单级 CD 表 和 2 级 CD 表 三种情况。单个 CD 示例结构如下图:

单级 CD 表示例结构如下图:

2 级 CD 表示例结构如下图:

SMMU 在做地址转换时,根据 SMMU 的流表基址寄存器找到流表,通过 StreamID 在流表中找到 STE。之后根据 STE 的配置和 SubstreamID/PASID,找到上下文描述符表及对应的 CD。再根据 CD 中的信息找到地址转换表,并通过地址转换表完成最终的地址转换。
Linux 内核的 IOMMU 子系统相关源码位于 drivers/iommu,ARM SMMU 驱动实现位于 drivers/iommu/arm/arm-smmu-v3。在 Linux 内核的 SMMU 驱动实现中,做地址转换所用到的数据结构,在上面提到的不同步骤中创建:
- 流表在 SMMU 驱动程序的初始化过程中创建。如果流表的结构为线性流表,则线性流表中所有的 STE 都被配置为旁路 SMMU,即对应的流不做 SMMU 地址转换;如果流表的结构为 2 级流表,则流表中为无效的 L1 流表描述符。
- 系统 I/O 设备发现、探测,并和驱动程序绑定初始化的过程中,设备和 IOMMU 绑定时,创建上下文描述符表。如果流表的结构为 2 级流表,这个过程会先创建第 2 级流表,第 2 级流表中的 STE 都被配置为旁路 SMMU。创建上下文描述符表时,同样分是否需要 2 级上下文描述符表来执行。上下文描述符表创建之后,其地址被写入 STE。
- 系统 I/O 设备驱动程序分配内存的过程中创建地址转换表。这个过程中,SMMU 驱动程序的回调会被调用,以将地址转换表的地址放进 CD 中。
Linux 内核中 SMMU 的数据结构
Linux 内核的 IOMMU 子系统用 struct iommu_device 结构体表示一个 IOMMU 硬件设备实例,并用 struct iommu_ops 结构体描述 IOMMU 硬件设备实例支持的操作和能力,这两个结构体定义 (位于 include/linux/iommu.h 文件中) 如下:
/*** struct iommu_ops - iommu ops and capabilities* @capable: check capability* @domain_alloc: allocate iommu domain* @domain_free: free iommu domain* @attach_dev: attach device to an iommu domain* @detach_dev: detach device from an iommu domain* @map: map a physically contiguous memory region to an iommu domain* @unmap: unmap a physically contiguous memory region from an iommu domain* @flush_iotlb_all: Synchronously flush all hardware TLBs for this domain* @iotlb_sync_map: Sync mappings created recently using @map to the hardware* @iotlb_sync: Flush all queued ranges from the hardware TLBs and empty flush* queue* @iova_to_phys: translate iova to physical address* @probe_device: Add device to iommu driver handling* @release_device: Remove device from iommu driver handling* @probe_finalize: Do final setup work after the device is added to an IOMMU* group and attached to the groups domain* @device_group: find iommu group for a particular device* @domain_get_attr: Query domain attributes* @domain_set_attr: Change domain attributes* @support_dirty_log: Check whether domain supports dirty log tracking* @switch_dirty_log: Perform actions to start|stop dirty log tracking* @sync_dirty_log: Sync dirty log from IOMMU into a dirty bitmap* @clear_dirty_log: Clear dirty log of IOMMU by a mask bitmap* @get_resv_regions: Request list of reserved regions for a device* @put_resv_regions: Free list of reserved regions for a device* @apply_resv_region: Temporary helper call-back for iova reserved ranges* @domain_window_enable: Configure and enable a particular window for a domain* @domain_window_disable: Disable a particular window for a domain* @of_xlate: add OF master IDs to iommu grouping* @is_attach_deferred: Check if domain attach should be deferred from iommu* driver init to device driver init (default no)* @dev_has/enable/disable_feat: per device entries to check/enable/disable* iommu specific features.* @dev_feat_enabled: check enabled feature* @aux_attach/detach_dev: aux-domain specific attach/detach entries.* @aux_get_pasid: get the pasid given an aux-domain* @sva_bind: Bind process address space to device* @sva_unbind: Unbind process address space from device* @sva_get_pasid: Get PASID associated to a SVA handle* @page_response: handle page request response* @cache_invalidate: invalidate translation caches* @sva_bind_gpasid: bind guest pasid and mm* @sva_unbind_gpasid: unbind guest pasid and mm* @def_domain_type: device default domain type, return value:* - IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY: must use an identity domain* - IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA: must use a dma domain* - 0: use the default setting* @attach_pasid_table: attach a pasid table* @detach_pasid_table: detach the pasid table* @pgsize_bitmap: bitmap of all possible supported page sizes* @owner: Driver module providing these ops*/
struct iommu_ops {bool (*capable)(enum iommu_cap);/* Domain allocation and freeing by the iommu driver */struct iommu_domain *(*domain_alloc)(unsigned iommu_domain_type);void (*domain_free)(struct iommu_domain *);int (*attach_dev)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev);void (*detach_dev)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev);int (*map)(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova,phys_addr_t paddr, size_t size, int prot, gfp_t gfp);size_t (*unmap)(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova,size_t size, struct iommu_iotlb_gather *iotlb_gather);void (*flush_iotlb_all)(struct iommu_domain *domain);void (*iotlb_sync_map)(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova,size_t size);void (*iotlb_sync)(struct iommu_domain *domain,struct iommu_iotlb_gather *iotlb_gather);phys_addr_t (*iova_to_phys)(struct iommu_domain *domain, dma_addr_t iova);struct iommu_device *(*probe_device)(struct device *dev);void (*release_device)(struct device *dev);void (*probe_finalize)(struct device *dev);struct iommu_group *(*device_group)(struct device *dev);int (*domain_get_attr)(struct iommu_domain *domain,enum iommu_attr attr, void *data);int (*domain_set_attr)(struct iommu_domain *domain,enum iommu_attr attr, void *data);/** Track dirty log. Note: Don't concurrently call these interfaces with* other ops that access underlying page table.*/bool (*support_dirty_log)(struct iommu_domain *domain);int (*switch_dirty_log)(struct iommu_domain *domain, bool enable,unsigned long iova, size_t size, int prot);int (*sync_dirty_log)(struct iommu_domain *domain,unsigned long iova, size_t size,unsigned long *bitmap, unsigned long base_iova,unsigned long bitmap_pgshift);int (*clear_dirty_log)(struct iommu_domain *domain,unsigned long iova, size_t size,unsigned long *bitmap, unsigned long base_iova,unsigned long bitmap_pgshift);/* Request/Free a list of reserved regions for a device */void (*get_resv_regions)(struct device *dev, struct list_head *list);void (*put_resv_regions)(struct device *dev, struct list_head *list);void (*apply_resv_region)(struct device *dev,struct iommu_domain *domain,struct iommu_resv_region *region);/* Window handling functions */int (*domain_window_enable)(struct iommu_domain *domain, u32 wnd_nr,phys_addr_t paddr, u64 size, int prot);void (*domain_window_disable)(struct iommu_domain *domain, u32 wnd_nr);int (*of_xlate)(struct device *dev, struct of_phandle_args *args);bool (*is_attach_deferred)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev);/* Per device IOMMU features */bool (*dev_has_feat)(struct device *dev, enum iommu_dev_features f);bool (*dev_feat_enabled)(struct device *dev, enum iommu_dev_features f);int (*dev_enable_feat)(struct device *dev, enum iommu_dev_features f);int (*dev_disable_feat)(struct device *dev, enum iommu_dev_features f);/* Aux-domain specific attach/detach entries */int (*aux_attach_dev)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev);void (*aux_detach_dev)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev);int (*aux_get_pasid)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev);struct iommu_sva *(*sva_bind)(struct device *dev, struct mm_struct *mm,void *drvdata);void (*sva_unbind)(struct iommu_sva *handle);u32 (*sva_get_pasid)(struct iommu_sva *handle);int (*page_response)(struct device *dev,struct iommu_fault_event *evt,struct iommu_page_response *msg);int (*cache_invalidate)(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev,struct iommu_cache_invalidate_info *inv_info);int (*sva_bind_gpasid)(struct iommu_domain *domain,struct device *dev, struct iommu_gpasid_bind_data *data);int (*sva_unbind_gpasid)(struct device *dev, u32 pasid);int (*attach_pasid_table)(struct iommu_domain *domain,struct iommu_pasid_table_config *cfg);void (*detach_pasid_table)(struct iommu_domain *domain);int (*def_domain_type)(struct device *dev);int (*dev_get_config)(struct device *dev, int type, void *data);int (*dev_set_config)(struct device *dev, int type, void *data);unsigned long pgsize_bitmap;struct module *owner;
};/*** struct iommu_device - IOMMU core representation of one IOMMU hardware* instance* @list: Used by the iommu-core to keep a list of registered iommus* @ops: iommu-ops for talking to this iommu* @dev: struct device for sysfs handling*/
struct iommu_device {struct list_head list;const struct iommu_ops *ops;struct fwnode_handle *fwnode;struct device *dev;
};
SMMU 驱动程序创建 struct iommu_device 和 struct iommu_ops 结构体的实例并注册进 IOMMU 子系统中。
Linux 内核的 IOMMU 子系统用 struct dev_iommu 结构体表示一个连接到 IOMMU 的系统 I/O 设备,用 struct iommu_fwspec 表示系统 I/O 设备连接的 IOMMU 设备,这几个结构体定义 (位于 include/linux/iommu.h 文件中) 如下:
struct fwnode_handle {struct fwnode_handle *secondary;const struct fwnode_operations *ops;struct device *dev;
};. . . . . .
/*** struct dev_iommu - Collection of per-device IOMMU data** @fault_param: IOMMU detected device fault reporting data* @iopf_param: I/O Page Fault queue and data* @fwspec: IOMMU fwspec data* @iommu_dev: IOMMU device this device is linked to* @priv: IOMMU Driver private data** TODO: migrate other per device data pointers under iommu_dev_data, e.g.* struct iommu_group *iommu_group;*/
struct dev_iommu {struct mutex lock;struct iommu_fault_param *fault_param;struct iopf_device_param *iopf_param;struct iommu_fwspec *fwspec;struct iommu_device *iommu_dev;void *priv;
};. . . . . .
/*** struct iommu_fwspec - per-device IOMMU instance data* @ops: ops for this device's IOMMU* @iommu_fwnode: firmware handle for this device's IOMMU* @iommu_priv: IOMMU driver private data for this device* @num_ids: number of associated device IDs* @ids: IDs which this device may present to the IOMMU*/
struct iommu_fwspec {const struct iommu_ops *ops;struct fwnode_handle *iommu_fwnode;u32 flags;unsigned int num_ids;u32 ids[];
};
在 IOMMU 中,每一个 domain 即代表一个 IOMMU 映射地址空间,即一个 page table。一个 group 逻辑上是需要与 domain 进行绑定的,即一个 group 中的所有设备都位于一个 domain 中。在 Linux 内核的 IOMMU 子系统中,domain 由 struct iommu_domain 结构体表示,这个结构体定义 (位于 include/linux/iommu.h 文件中) 如下:
struct iommu_domain {unsigned type;const struct iommu_ops *ops;unsigned long pgsize_bitmap; /* Bitmap of page sizes in use */iommu_fault_handler_t handler;void *handler_token;struct iommu_domain_geometry geometry;void *iova_cookie;struct mutex switch_log_lock;
};
Linux 内核的 IOMMU 子系统用 struct iommu_group 结构体表示位于同一个 domain 的设备组,并用 struct group_device 结构体表示设备组中的一个设备。这两个结构体定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
struct iommu_group {struct kobject kobj;struct kobject *devices_kobj;struct list_head devices;struct mutex mutex;struct blocking_notifier_head notifier;void *iommu_data;void (*iommu_data_release)(void *iommu_data);char *name;int id;struct iommu_domain *default_domain;struct iommu_domain *domain;struct list_head entry;
};struct group_device {struct list_head list;struct device *dev;char *name;
};
以面向对象的编程方法来看,可以认为在 ARM SMMUv3 驱动程序中,struct iommu_device 和 struct iommu_domain 结构体有其特定的实现,即 struct arm_smmu_device 和 struct arm_smmu_domain 结构体继承了 struct iommu_device 和 struct iommu_domain 结构体,这两个结构体定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/arm/arm-smmu-v3/arm-smmu-v3.h 文件中) 如下:
/* An SMMUv3 instance */
struct arm_smmu_device {struct device *dev;void __iomem *base;void __iomem *page1;#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_STRTAB (1 << 0)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_CDTAB (1 << 1)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TT_LE (1 << 2)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TT_BE (1 << 3)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_PRI (1 << 4)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_ATS (1 << 5)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_SEV (1 << 6)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_MSI (1 << 7)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_COHERENCY (1 << 8)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TRANS_S1 (1 << 9)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TRANS_S2 (1 << 10)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_STALLS (1 << 11)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HYP (1 << 12)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_STALL_FORCE (1 << 13)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_VAX (1 << 14)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_RANGE_INV (1 << 15)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_BTM (1 << 16)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_SVA (1 << 17)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_E2H (1 << 18)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HA (1 << 19)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HD (1 << 20)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_BBML1 (1 << 21)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_BBML2 (1 << 22)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_ECMDQ (1 << 23)
#define ARM_SMMU_FEAT_MPAM (1 << 24)u32 features;#define ARM_SMMU_OPT_SKIP_PREFETCH (1 << 0)
#define ARM_SMMU_OPT_PAGE0_REGS_ONLY (1 << 1)
#define ARM_SMMU_OPT_MSIPOLL (1 << 2)u32 options;union {u32 nr_ecmdq;u32 ecmdq_enabled;};struct arm_smmu_ecmdq *__percpu *ecmdq;struct arm_smmu_cmdq cmdq;struct arm_smmu_evtq evtq;struct arm_smmu_priq priq;int gerr_irq;int combined_irq;unsigned long ias; /* IPA */unsigned long oas; /* PA */unsigned long pgsize_bitmap;#define ARM_SMMU_MAX_ASIDS (1 << 16)unsigned int asid_bits;#define ARM_SMMU_MAX_VMIDS (1 << 16)unsigned int vmid_bits;DECLARE_BITMAP(vmid_map, ARM_SMMU_MAX_VMIDS);unsigned int ssid_bits;unsigned int sid_bits;struct arm_smmu_strtab_cfg strtab_cfg;/* IOMMU core code handle */struct iommu_device iommu;struct rb_root streams;struct mutex streams_mutex;unsigned int mpam_partid_max;unsigned int mpam_pmg_max;bool bypass;
};. . . . . .
struct arm_smmu_domain {struct arm_smmu_device *smmu;struct mutex init_mutex; /* Protects smmu pointer */struct io_pgtable_ops *pgtbl_ops;bool stall_enabled;bool non_strict;atomic_t nr_ats_masters;enum arm_smmu_domain_stage stage;union {struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg s1_cfg;struct arm_smmu_s2_cfg s2_cfg;};struct iommu_domain domain;/* Unused in aux domains */struct list_head devices;spinlock_t devices_lock;struct list_head mmu_notifiers;/* Auxiliary domain stuff */struct arm_smmu_domain *parent;ioasid_t ssid;unsigned long aux_nr_devs;
};
在 ARM SMMUv3 驱动程序中,用 struct arm_smmu_master 结构体描述连接到 SMMU 的系统 I/O 设备的 SMMU 私有数据,这个结构体定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/arm/arm-smmu-v3/arm-smmu-v3.h 文件中) 如下:
struct arm_smmu_stream {u32 id;struct arm_smmu_master *master;struct rb_node node;
};/* SMMU private data for each master */
struct arm_smmu_master {struct arm_smmu_device *smmu;struct device *dev;struct arm_smmu_domain *domain;struct list_head domain_head;struct arm_smmu_stream *streams;unsigned int num_streams;bool ats_enabled;bool stall_enabled;bool pri_supported;bool prg_resp_needs_ssid;bool sva_enabled;bool iopf_enabled;bool auxd_enabled;struct list_head bonds;unsigned int ssid_bits;
};
以面向对象的编程方法来看,可以认为 struct arm_smmu_master 结构体继承了 struct dev_iommu 结构体。
Linux 内核中 SMMU 的数据结构大体有如下的结构关系:

上面这些数据结构,基本上都包含指向 struct device 对象的指针,struct device 则包含指向几个关键 IOMMU 对象的指针。struct device 对象是各个部分的中介者,相关的各个子系统多通过 struct device 对象找到它需要的操作或数据。struct device 结构体中与 IOMMU 相关的字段主要有如下这些:
struct device {
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_OPSconst struct dma_map_ops *dma_ops;
#endif. . . . . .
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_DECLARE_COHERENTstruct dma_coherent_mem *dma_mem; /* internal for coherent memoverride */
#endif. . . . . .struct iommu_group *iommu_group;struct dev_iommu *iommu;. . . . . .
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_DEVICE) || \defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_CPU) || \defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_CPU_ALL)bool dma_coherent:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_OPS_BYPASSbool dma_ops_bypass : 1;
#endif
};
除了 IOMMU 子系统的这些数据结构外,在更底层的 SMMU 驱动程序实现中,还定义了许多特定于硬件的数据结构,如:
- 命令队列项
struct arm_smmu_cmdq_ent, - 命令队列
struct arm_smmu_cmdq, - 扩展命令队列
struct arm_smmu_ecmdq, - 事件队列
struct arm_smmu_evtq, - PRI 队列
struct arm_smmu_priq, - 2 级流表中的 L1 流表描述符
struct arm_smmu_strtab_l1_desc, - 上下文描述符
struct arm_smmu_ctx_desc - 2 级上下文描述符表中的 L1 表描述符
struct arm_smmu_l1_ctx_desc - 上下文描述符配置
struct arm_smmu_ctx_desc_cfg - 第 1 阶段转换配置
struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg - 第 2 阶段转换配置
struct arm_smmu_s2_cfg - 流表配置
struct arm_smmu_strtab_cfg
特定于硬件的这些数据结构基本上与 ARM 官方的硬件说明文档 SMMU 软件指南 和 ARM 系统内存管理单元架构规范版本 3 中提到的数据结构严格的一一对应。
SMMU 相关的操作及过程,和对 SMMU 的访问,基于上面这些数据结构实现,这种实现的分层结构大体如下图所示:

系统 I/O 设备发现、探测,并和驱动程序绑定初始化的过程及系统 I/O 设备驱动程序通常调用平台设备子系统和 DMA 子系统提供的接口,如平台设备子系统的 of_dma_configure()/of_dma_configure_id() 和 DMA 子系统的 dma_alloc_coherent() 函数,这些函数的实现中,借助于更底层的模块完成。
SMMUv3 设备驱动程序的初始化
Linux 内核启动早期,会执行 IOMMU 初始化,这主要是执行 iommu_init() 函数,它创建并添加 iommu_groups kset,这个函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static int __init iommu_init(void)
{iommu_group_kset = kset_create_and_add("iommu_groups",NULL, kernel_kobj);BUG_ON(!iommu_group_kset);iommu_debugfs_setup();return 0;
}
core_initcall(iommu_init);
Linux 内核启动时,可以传入一些配置 IOMMU 的命令行参数,这包括用于配置默认 domain 类型的 iommu.passthrough、用于配置 DMA setup 的 iommu.strict 和用于配置等待挂起的页请求的页相应的超时时间的 iommu.prq_timeout。Linux 内核启动早期,会初始化 IOMMU 子系统,如果没有通过 Linux 内核的命令行参数配置 IOMMU,则会设置默认的 domain 类型,相关代码 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static unsigned int iommu_def_domain_type __read_mostly;
static bool iommu_dma_strict __read_mostly;
static u32 iommu_cmd_line __read_mostly;/** Timeout to wait for page response of a pending page request. This is* intended as a basic safety net in case a pending page request is not* responded for an exceptionally long time. Device may also implement* its own protection mechanism against this exception.* Units are in jiffies with a range between 1 - 100 seconds equivalent.* Default to 10 seconds.* Setting 0 means no timeout tracking.*/
#define IOMMU_PAGE_RESPONSE_MAX_TIMEOUT (HZ * 100)
#define IOMMU_PAGE_RESPONSE_DEF_TIMEOUT (HZ * 10)
static unsigned long prq_timeout = IOMMU_PAGE_RESPONSE_DEF_TIMEOUT;. . . . . .
#define IOMMU_CMD_LINE_DMA_API BIT(0)static void iommu_set_cmd_line_dma_api(void)
{iommu_cmd_line |= IOMMU_CMD_LINE_DMA_API;
}static bool iommu_cmd_line_dma_api(void)
{return !!(iommu_cmd_line & IOMMU_CMD_LINE_DMA_API);
}. . . . . .
/** Use a function instead of an array here because the domain-type is a* bit-field, so an array would waste memory.*/
static const char *iommu_domain_type_str(unsigned int t)
{switch (t) {case IOMMU_DOMAIN_BLOCKED:return "Blocked";case IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY:return "Passthrough";case IOMMU_DOMAIN_UNMANAGED:return "Unmanaged";case IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA:return "Translated";default:return "Unknown";}
}static int __init iommu_subsys_init(void)
{bool cmd_line = iommu_cmd_line_dma_api();if (!cmd_line) {if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IOMMU_DEFAULT_PASSTHROUGH))iommu_set_default_passthrough(false);elseiommu_set_default_translated(false);if (iommu_default_passthrough() && mem_encrypt_active()) {pr_info("Memory encryption detected - Disabling default IOMMU Passthrough\n");iommu_set_default_translated(false);}}pr_info("Default domain type: %s %s\n",iommu_domain_type_str(iommu_def_domain_type),cmd_line ? "(set via kernel command line)" : "");return 0;
}
subsys_initcall(iommu_subsys_init);. . . . . .
static int __init iommu_set_def_domain_type(char *str)
{bool pt;int ret;ret = kstrtobool(str, &pt);if (ret)return ret;if (pt)iommu_set_default_passthrough(true);elseiommu_set_default_translated(true);return 0;
}
early_param("iommu.passthrough", iommu_set_def_domain_type);static int __init iommu_dma_setup(char *str)
{return kstrtobool(str, &iommu_dma_strict);
}
early_param("iommu.strict", iommu_dma_setup);static int __init iommu_set_prq_timeout(char *str)
{int ret;unsigned long timeout;if (!str)return -EINVAL;ret = kstrtoul(str, 10, &timeout);if (ret)return ret;timeout = timeout * HZ;if (timeout > IOMMU_PAGE_RESPONSE_MAX_TIMEOUT)return -EINVAL;prq_timeout = timeout;return 0;
}
early_param("iommu.prq_timeout", iommu_set_prq_timeout);. . . . . .
void iommu_set_default_passthrough(bool cmd_line)
{if (cmd_line)iommu_set_cmd_line_dma_api();iommu_def_domain_type = IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY;
}void iommu_set_default_translated(bool cmd_line)
{if (cmd_line)iommu_set_cmd_line_dma_api();iommu_def_domain_type = IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA;
}
core_initcall 的函数比 subsys_initcall 的函数执行地更早。
IOMMU 子系统初始化之后,就轮到 SMMU 设备驱动程序上场了。SMMUv3 本身是一个平台设备,其硬件设备信息,包括寄存器映射地址范围,中断号等使用的资源,在设备树 dts/dtsi 文件中描述。SMMUv3 设备在设备树文件中的示例设备节点 (位于 arch/arm64/boot/dts/arm/fvp-base-revc.dts 文件中) 如下:
smmu: iommu@2b400000 {compatible = "arm,smmu-v3";reg = <0x0 0x2b400000 0x0 0x100000>;interrupts = <GIC_SPI 74 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING>,<GIC_SPI 79 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING>,<GIC_SPI 75 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING>,<GIC_SPI 77 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING>;interrupt-names = "eventq", "gerror", "priq", "cmdq-sync";dma-coherent;#iommu-cells = <1>;msi-parent = <&its 0x10000>;};
SMMUv3 设备驱动程序加载的入口为 arm_smmu_device_probe() 函数,这个函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/arm/arm-smmu-v3/arm-smmu-v3.c 文件中) 如下:
static struct arm_smmu_option_prop arm_smmu_options[] = {{ ARM_SMMU_OPT_SKIP_PREFETCH, "hisilicon,broken-prefetch-cmd" },{ ARM_SMMU_OPT_PAGE0_REGS_ONLY, "cavium,cn9900-broken-page1-regspace"},{ 0, NULL},
};static void parse_driver_options(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{int i = 0;do {if (of_property_read_bool(smmu->dev->of_node,arm_smmu_options[i].prop)) {smmu->options |= arm_smmu_options[i].opt;dev_notice(smmu->dev, "option %s\n",arm_smmu_options[i].prop);}} while (arm_smmu_options[++i].opt);
}. . . . . .
static int arm_smmu_device_dt_probe(struct platform_device *pdev,struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;u32 cells;int ret = -EINVAL;if (of_property_read_u32(dev->of_node, "#iommu-cells", &cells))dev_err(dev, "missing #iommu-cells property\n");else if (cells != 1)dev_err(dev, "invalid #iommu-cells value (%d)\n", cells);elseret = 0;parse_driver_options(smmu);if (of_dma_is_coherent(dev->of_node))smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_COHERENCY;return ret;
}static unsigned long arm_smmu_resource_size(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{if (smmu->options & ARM_SMMU_OPT_PAGE0_REGS_ONLY)return SZ_64K;elsereturn SZ_128K;
}. . . . . .
static void __iomem *arm_smmu_ioremap(struct device *dev, resource_size_t start,resource_size_t size)
{struct resource res = DEFINE_RES_MEM(start, size);return devm_ioremap_resource(dev, &res);
}. . . . . .
static int arm_smmu_device_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{int irq, ret;struct resource *res;resource_size_t ioaddr;struct arm_smmu_device *smmu;struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;smmu = devm_kzalloc(dev, sizeof(*smmu), GFP_KERNEL);if (!smmu) {dev_err(dev, "failed to allocate arm_smmu_device\n");return -ENOMEM;}smmu->dev = dev;if (dev->of_node) {ret = arm_smmu_device_dt_probe(pdev, smmu);} else {ret = arm_smmu_device_acpi_probe(pdev, smmu);if (ret == -ENODEV)return ret;}/* Set bypass mode according to firmware probing result */smmu->bypass = !!ret;/* Base address */res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);if (!res)return -EINVAL;if (resource_size(res) < arm_smmu_resource_size(smmu)) {dev_err(dev, "MMIO region too small (%pr)\n", res);return -EINVAL;}ioaddr = res->start;/** Don't map the IMPLEMENTATION DEFINED regions, since they may contain* the PMCG registers which are reserved by the PMU driver.*/smmu->base = arm_smmu_ioremap(dev, ioaddr, ARM_SMMU_REG_SZ);if (IS_ERR(smmu->base))return PTR_ERR(smmu->base);if (arm_smmu_resource_size(smmu) > SZ_64K) {smmu->page1 = arm_smmu_ioremap(dev, ioaddr + SZ_64K,ARM_SMMU_REG_SZ);if (IS_ERR(smmu->page1))return PTR_ERR(smmu->page1);} else {smmu->page1 = smmu->base;}/* Interrupt lines */irq = platform_get_irq_byname_optional(pdev, "combined");if (irq > 0)smmu->combined_irq = irq;else {irq = platform_get_irq_byname_optional(pdev, "eventq");if (irq > 0)smmu->evtq.q.irq = irq;irq = platform_get_irq_byname_optional(pdev, "priq");if (irq > 0)smmu->priq.q.irq = irq;irq = platform_get_irq_byname_optional(pdev, "gerror");if (irq > 0)smmu->gerr_irq = irq;}/* Probe the h/w */ret = arm_smmu_device_hw_probe(smmu);if (ret)return ret;/* Initialise in-memory data structures */ret = arm_smmu_init_structures(smmu);if (ret)return ret;/* Record our private device structure */platform_set_drvdata(pdev, smmu);/* Reset the device */ret = arm_smmu_device_reset(smmu, false);if (ret)return ret;/* And we're up. Go go go! */ret = iommu_device_sysfs_add(&smmu->iommu, dev, NULL,"smmu3.%pa", &ioaddr);if (ret)return ret;iommu_device_set_ops(&smmu->iommu, &arm_smmu_ops);iommu_device_set_fwnode(&smmu->iommu, dev->fwnode);ret = iommu_device_register(&smmu->iommu);if (ret) {dev_err(dev, "Failed to register iommu\n");return ret;}return arm_smmu_set_bus_ops(&arm_smmu_ops);
}
arm_smmu_device_probe() 函数主要做了如下几件事情:
- 分配
struct arm_smmu_device对象,这个对象用来在 IOMMU 子系统中描述 SMMUv3 设备。 - 获取设备树文件
dts/dtsi中的 SMMUv3 设备节点中包含的信息,和引用的资源,这主要包括:- 关于 SMMUv3 设备的信息,如
iommu-cells,其值必须为 1;options,如是否只有寄存器页 0 等;SMMU 是否支持 coherent,这主要由设备树文件中的设备节点的dma-coherent属性表示; - SMMUv3 设备的寄存器映射,
arm_smmu_device_probe()函数会根据 options 的值检查寄存器映射的范围大小是否与预期匹配,并重映射 SMMUv3 设备的寄存器映射; - SMMUv3 设备引用的中断资源,包括用于命令队列、事件队列和全局错误的中断资源。
- 关于 SMMUv3 设备的信息,如
- 探测 SMMUv3 设备的硬件特性,这主要按照 ARM 系统内存管理单元架构规范版本 3 中定义的寄存器 SMMU_IDR0、SMMU_IDR1、SMMU_IDR3、和 SMMU_IDR5 (另外一些用于提供信息的只读寄存器包含的信息和 SMMUv3 硬件设备的特性关系不大,SMMU_IDR2 包含 SMMU 为非安全编程接口实现的特性相关的信息,SMMU_IDR4 是一个 SMMU 实现定义的寄存器,SMMU_IIDR 寄存器包含 SMMU 的实现和实现者的信息,以及由实现定义的支持的架构版本信息,SMMU_AIDR 寄存器包含 SMMU 实现遵从的 SMMU 架构版本号信息) 的各个字段,确认实际的 SMMUv3 硬件设备支持的特性,这主要通过调用
arm_smmu_device_hw_probe()函数完成。 - 初始化数据结构,这主要包括几个队列和流表,队列包括命令队列、事件队列和 PRIQ 队列。对于流表的初始化,分两种情况,如果流表的结构为线性流表,则线性流表中所有的 STE 都被配置为旁路 SMMU;如果流表的结构为 2 级流表,则流表中为无效的 L1 流表描述符,这主要通过调用
arm_smmu_init_structures()函数完成。 - 在设备结构
struct platform_device对象的私有字段中记录struct arm_smmu_device对象。 - 复位 SMMUv3 设备,这主要包括通过 SMMU_CR0 等寄存器复位硬件设备,设置流表基址寄存器等;以及设置中断,包括向系统请求中断及注册中断处理程序;初始化数据结构在内存中建立各个数据结构,复位 SMMUv3 设备则将各个数据结构的基地址和各种配置写进对应的设备寄存器中,这主要通过调用
arm_smmu_device_reset()函数完成。 - 将 SMMUv3 设备注册到 IOMMU 子系统,这包括为
struct iommu_device设置struct iommu_ops和struct fwnode_handle,并将struct iommu_device对象注册进 IOMMU 子系统。struct fwnode_handle用于匹配 SMMUv3 设备和系统 I/O 设备,这主要通过调用iommu_device_register()函数完成。 - 为各个总线类型设置
struct iommu_ops,SMMUv3 设备驱动程序和要使用 IOMMU 的系统 I/O 设备的加载顺序可能是不确定的;正常情况下,应该是 SMMUv3 设备驱动程序先加载,要使用 IOMMU 的系统 I/O 设备后加载;这里会处理使用 IOMMU 的系统 I/O 设备先于 SMMUv3 设备驱动程序加载的情况,这主要通过调用arm_smmu_set_bus_ops()函数完成。
探测 SMMUv3 设备的硬件特性
arm_smmu_device_probe() 函数调用 arm_smmu_device_hw_probe() 函数探测 SMMUv3 设备的硬件特性,后者定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/arm/arm-smmu-v3/arm-smmu-v3.c 文件中) 如下:
static int arm_smmu_ecmdq_probe(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{int ret, cpu;u32 i, nump, numq, gap;u32 reg, shift_increment;u64 addr, smmu_dma_base;void __iomem *cp_regs, *cp_base;/* IDR6 */reg = readl_relaxed(smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_IDR6);smmu_reg_dump(smmu);nump = 1 << FIELD_GET(IDR6_LOG2NUMP, reg);numq = 1 << FIELD_GET(IDR6_LOG2NUMQ, reg);smmu->nr_ecmdq = nump * numq;gap = ECMDQ_CP_RRESET_SIZE >> FIELD_GET(IDR6_LOG2NUMQ, reg);smmu_dma_base = (vmalloc_to_pfn(smmu->base) << PAGE_SHIFT);cp_regs = ioremap(smmu_dma_base + ARM_SMMU_ECMDQ_CP_BASE, PAGE_SIZE);if (!cp_regs)return -ENOMEM;for (i = 0; i < nump; i++) {u64 val, pre_addr;val = readq_relaxed(cp_regs + 32 * i);if (!(val & ECMDQ_CP_PRESET)) {iounmap(cp_regs);dev_err(smmu->dev, "ecmdq control page %u is memory mode\n", i);return -EFAULT;}if (i && ((val & ECMDQ_CP_ADDR) != (pre_addr + ECMDQ_CP_RRESET_SIZE))) {iounmap(cp_regs);dev_err(smmu->dev, "ecmdq_cp memory region is not contiguous\n");return -EFAULT;}pre_addr = val & ECMDQ_CP_ADDR;}addr = readl_relaxed(cp_regs) & ECMDQ_CP_ADDR;iounmap(cp_regs);cp_base = devm_ioremap(smmu->dev, smmu_dma_base + addr, ECMDQ_CP_RRESET_SIZE * nump);if (!cp_base)return -ENOMEM;smmu->ecmdq = devm_alloc_percpu(smmu->dev, struct arm_smmu_ecmdq *);if (!smmu->ecmdq)return -ENOMEM;ret = arm_smmu_ecmdq_layout(smmu);if (ret)return ret;shift_increment = order_base_2(num_possible_cpus() / smmu->nr_ecmdq);addr = 0;for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {struct arm_smmu_ecmdq *ecmdq;struct arm_smmu_queue *q;ecmdq = *per_cpu_ptr(smmu->ecmdq, cpu);q = &ecmdq->cmdq.q;/** The boot option "maxcpus=" can limit the number of online* CPUs. The CPUs that are not selected are not showed in* cpumask_of_node(node), their 'ecmdq' may be NULL.** (q->ecmdq_prod & ECMDQ_PROD_EN) indicates that the ECMDQ is* shared by multiple cores and has been initialized.*/if (!ecmdq || (q->ecmdq_prod & ECMDQ_PROD_EN))continue;ecmdq->base = cp_base + addr;q->llq.max_n_shift = ECMDQ_MAX_SZ_SHIFT + shift_increment;ret = arm_smmu_init_one_queue(smmu, q, ecmdq->base, ARM_SMMU_ECMDQ_PROD,ARM_SMMU_ECMDQ_CONS, CMDQ_ENT_DWORDS, "ecmdq");if (ret)return ret;q->ecmdq_prod = ECMDQ_PROD_EN;rwlock_init(&q->ecmdq_lock);ret = arm_smmu_ecmdq_init(&ecmdq->cmdq);if (ret) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "ecmdq[%d] init failed\n", i);return ret;}addr += gap;}return 0;
}static void arm_smmu_get_httu(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, u32 reg)
{u32 fw_features = smmu->features & (ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HA | ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HD);u32 features = 0;switch (FIELD_GET(IDR0_HTTU, reg)) {case IDR0_HTTU_ACCESS_DIRTY:features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HD;fallthrough;case IDR0_HTTU_ACCESS:features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HA;}if (smmu->dev->of_node)smmu->features |= features;else if (features != fw_features)/* ACPI IORT sets the HTTU bits */dev_warn(smmu->dev,"IDR0.HTTU overridden by FW configuration (0x%x)\n",fw_features);
}static int arm_smmu_device_hw_probe(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{u32 reg;bool coherent = smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_COHERENCY;bool vhe = cpus_have_cap(ARM64_HAS_VIRT_HOST_EXTN);/* IDR0 */reg = readl_relaxed(smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_IDR0);/* 2-level structures */if (FIELD_GET(IDR0_ST_LVL, reg) == IDR0_ST_LVL_2LVL)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_STRTAB;if (reg & IDR0_CD2L)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_CDTAB;/** Translation table endianness.* We currently require the same endianness as the CPU, but this* could be changed later by adding a new IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK.*/switch (FIELD_GET(IDR0_TTENDIAN, reg)) {case IDR0_TTENDIAN_MIXED:smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TT_LE | ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TT_BE;break;
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIANcase IDR0_TTENDIAN_BE:smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TT_BE;break;
#elsecase IDR0_TTENDIAN_LE:smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TT_LE;break;
#endifdefault:dev_err(smmu->dev, "unknown/unsupported TT endianness!\n");return -ENXIO;}/* Boolean feature flags */if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_PCI_PRI) && reg & IDR0_PRI)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_PRI;if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_PCI_ATS) && reg & IDR0_ATS)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_ATS;if (reg & IDR0_SEV)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_SEV;if (reg & IDR0_MSI) {smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_MSI;if (coherent && !disable_msipolling)smmu->options |= ARM_SMMU_OPT_MSIPOLL;}if (reg & IDR0_HYP) {smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HYP;if (vhe)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_E2H;}arm_smmu_get_httu(smmu, reg);/** If the CPU is using VHE, but the SMMU doesn't support it, the SMMU* will create TLB entries for NH-EL1 world and will miss the* broadcasted TLB invalidations that target EL2-E2H world. Don't enable* BTM in that case.*/if (reg & IDR0_BTM && (!vhe || reg & IDR0_HYP))smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_BTM;/** The coherency feature as set by FW is used in preference to the ID* register, but warn on mismatch.*/if (!!(reg & IDR0_COHACC) != coherent)dev_warn(smmu->dev, "IDR0.COHACC overridden by FW configuration (%s)\n",coherent ? "true" : "false");switch (FIELD_GET(IDR0_STALL_MODEL, reg)) {case IDR0_STALL_MODEL_FORCE:smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_STALL_FORCE;fallthrough;case IDR0_STALL_MODEL_STALL:smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_STALLS;}if (reg & IDR0_S1P)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TRANS_S1;if (reg & IDR0_S2P)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TRANS_S2;if (!(reg & (IDR0_S1P | IDR0_S2P))) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "no translation support!\n");return -ENXIO;}/* We only support the AArch64 table format at present */switch (FIELD_GET(IDR0_TTF, reg)) {case IDR0_TTF_AARCH32_64:smmu->ias = 40;fallthrough;case IDR0_TTF_AARCH64:break;default:dev_err(smmu->dev, "AArch64 table format not supported!\n");return -ENXIO;}/* ASID/VMID sizes */smmu->asid_bits = reg & IDR0_ASID16 ? 16 : 8;smmu->vmid_bits = reg & IDR0_VMID16 ? 16 : 8;/* IDR1 */reg = readl_relaxed(smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_IDR1);if (reg & (IDR1_TABLES_PRESET | IDR1_QUEUES_PRESET | IDR1_REL)) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "embedded implementation not supported\n");return -ENXIO;}if (reg & IDR1_ECMDQ)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_ECMDQ;/* Queue sizes, capped to ensure natural alignment */smmu->cmdq.q.llq.max_n_shift = min_t(u32, CMDQ_MAX_SZ_SHIFT,FIELD_GET(IDR1_CMDQS, reg));if (smmu->cmdq.q.llq.max_n_shift <= ilog2(CMDQ_BATCH_ENTRIES)) {/** We don't support splitting up batches, so one batch of* commands plus an extra sync needs to fit inside the command* queue. There's also no way we can handle the weird alignment* restrictions on the base pointer for a unit-length queue.*/dev_err(smmu->dev, "command queue size <= %d entries not supported\n",CMDQ_BATCH_ENTRIES);return -ENXIO;}smmu->evtq.q.llq.max_n_shift = min_t(u32, EVTQ_MAX_SZ_SHIFT,FIELD_GET(IDR1_EVTQS, reg));smmu->priq.q.llq.max_n_shift = min_t(u32, PRIQ_MAX_SZ_SHIFT,FIELD_GET(IDR1_PRIQS, reg));/* SID/SSID sizes */smmu->ssid_bits = FIELD_GET(IDR1_SSIDSIZE, reg);smmu->sid_bits = FIELD_GET(IDR1_SIDSIZE, reg);/** If the SMMU supports fewer bits than would fill a single L2 stream* table, use a linear table instead.*/if (smmu->sid_bits <= STRTAB_SPLIT)smmu->features &= ~ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_STRTAB;/* IDR3 */reg = readl_relaxed(smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_IDR3);switch (FIELD_GET(IDR3_BBML, reg)) {case IDR3_BBML0:break;case IDR3_BBML1:smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_BBML1;break;case IDR3_BBML2:smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_BBML2;break;default:dev_err(smmu->dev, "unknown/unsupported BBM behavior level\n");return -ENXIO;}if (FIELD_GET(IDR3_RIL, reg))smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_RANGE_INV;if (reg & IDR3_MPAM) {reg = readl_relaxed(smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_MPAMIDR);smmu->mpam_partid_max = FIELD_GET(MPAMIDR_PARTID_MAX, reg);smmu->mpam_pmg_max = FIELD_GET(MPAMIDR_PMG_MAX, reg);if (smmu->mpam_partid_max || smmu->mpam_pmg_max)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_MPAM;}/* IDR5 */reg = readl_relaxed(smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_IDR5);/* Maximum number of outstanding stalls */smmu->evtq.max_stalls = FIELD_GET(IDR5_STALL_MAX, reg);/* Page sizes */if (reg & IDR5_GRAN64K)smmu->pgsize_bitmap |= SZ_64K | SZ_512M;if (reg & IDR5_GRAN16K)smmu->pgsize_bitmap |= SZ_16K | SZ_32M;if (reg & IDR5_GRAN4K)smmu->pgsize_bitmap |= SZ_4K | SZ_2M | SZ_1G;/* Input address size */if (FIELD_GET(IDR5_VAX, reg) == IDR5_VAX_52_BIT)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_VAX;/* Output address size */switch (FIELD_GET(IDR5_OAS, reg)) {case IDR5_OAS_32_BIT:smmu->oas = 32;break;case IDR5_OAS_36_BIT:smmu->oas = 36;break;case IDR5_OAS_40_BIT:smmu->oas = 40;break;case IDR5_OAS_42_BIT:smmu->oas = 42;break;case IDR5_OAS_44_BIT:smmu->oas = 44;break;case IDR5_OAS_52_BIT:smmu->oas = 52;smmu->pgsize_bitmap |= 1ULL << 42; /* 4TB */break;default:dev_info(smmu->dev,"unknown output address size. Truncating to 48-bit\n");fallthrough;case IDR5_OAS_48_BIT:smmu->oas = 48;}if (arm_smmu_ops.pgsize_bitmap == -1UL)arm_smmu_ops.pgsize_bitmap = smmu->pgsize_bitmap;elsearm_smmu_ops.pgsize_bitmap |= smmu->pgsize_bitmap;/* Set the DMA mask for our table walker */if (dma_set_mask_and_coherent(smmu->dev, DMA_BIT_MASK(smmu->oas)))dev_warn(smmu->dev,"failed to set DMA mask for table walker\n");smmu->ias = max(smmu->ias, smmu->oas);if (arm_smmu_sva_supported(smmu))smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_SVA;dev_info(smmu->dev, "ias %lu-bit, oas %lu-bit (features 0x%08x)\n",smmu->ias, smmu->oas, smmu->features);if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_ECMDQ) {int err;err = arm_smmu_ecmdq_probe(smmu);if (err) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "suppress ecmdq feature, errno=%d\n", err);smmu->ecmdq_enabled = 0;}}return 0;
}
在 struct arm_smmu_device 结构体中,SMMUv3 驱动程序用一个 32 位的值来描述支持的硬件特性,其中每个特性用一位来表示。函数 arm_smmu_device_hw_probe() 通过读取 SMMU 的寄存器获取 SMMU 的硬件特性。
SMMU_IDR0 寄存器:
- 是否支持两级流表
- 是否支持两级上下文描述符 (CD) 表
- 支持的转换表的字节序
- 是否支持 PRI
- 是否支持 ATS
- 是否支持 SEV
- 是否支持 MSI
- 是否支持 HYP
- HTTU 特性
- 是否支持 BTM
- 是否支持 COHACC
- 是否支持 STALL
- 是否支持第 1 阶段转换
- 是否支持第 2 阶段转换
- IAS (输入地址大小) 的值
- ASID bits
- VMID bits
SMMU_IDR1 寄存器 (部分字段被忽略,如 ATTR_TYPE_OVR 和 ATTR_PERMS_OVR):
- 流表基地址和流表配置是否固定
- 命令队列、事件队列和 PRI 队列基址是否固定
- 基址固定时,基址寄存器包含的是绝对地址还是相对地址,SMMUv3 设备驱动程序要求流表基地址和流表配置不固定,命令队列、事件队列和 PRI 队列基址不固定
- 是否支持扩展的命令队列
- 命令队列、事件队列和 PRI 队列的大小
- StreamID SID 的大小
- SubstreamID SSID 的大小
SMMU_IDR3 寄存器 (部分字段被忽略):
- 支持的 BBML
- 是否支持 RIL
- 是否支持 MPAM,支持 MPAM 时,还会读取 MPAM 的寄存器获得更多信息
SMMU_IDR5 寄存器:
- SMMU 和系统支持的未完成停滞事务的最大数目。
- 支持的页大小
- 虚拟地址扩展 VAX,即支持的虚拟地址大小
- 输出地址大小 OAS
此外,arm_smmu_device_hw_probe() 函数还会探测是否支持 SVA,当前面检测到支持扩展的命令队列时,还会读取 ARM_SMMU_IDR6 寄存器检测 ECMDQ 的特性。
arm_smmu_device_hw_probe() 函数按照 ARM 系统内存管理单元架构规范版本 3 中定义的寄存器各个字段的含义执行。
初始化数据结构
初始化数据结构主要通过调用 arm_smmu_init_structures() 函数完成,这个函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/arm/arm-smmu-v3/arm-smmu-v3.c 文件中) 如下:
/* Stream table manipulation functions */
static void
arm_smmu_write_strtab_l1_desc(__le64 *dst, struct arm_smmu_strtab_l1_desc *desc)
{u64 val = 0;val |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_L1_DESC_SPAN, desc->span);val |= desc->l2ptr_dma & STRTAB_L1_DESC_L2PTR_MASK;/* See comment in arm_smmu_write_ctx_desc() */WRITE_ONCE(*dst, cpu_to_le64(val));
}static void arm_smmu_sync_ste_for_sid(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, u32 sid)
{struct arm_smmu_cmdq_ent cmd = {.opcode = CMDQ_OP_CFGI_STE,.cfgi = {.sid = sid,.leaf = true,},};arm_smmu_cmdq_issue_cmd_with_sync(smmu, &cmd);
}static void arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent(struct arm_smmu_master *master, u32 sid,__le64 *dst)
{/** This is hideously complicated, but we only really care about* three cases at the moment:** 1. Invalid (all zero) -> bypass/fault (init)* 2. Bypass/fault -> translation/bypass (attach)* 3. Translation/bypass -> bypass/fault (detach)** Given that we can't update the STE atomically and the SMMU* doesn't read the thing in a defined order, that leaves us* with the following maintenance requirements:** 1. Update Config, return (init time STEs aren't live)* 2. Write everything apart from dword 0, sync, write dword 0, sync* 3. Update Config, sync*/u64 val = le64_to_cpu(dst[0]);bool ste_live = false;struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = NULL;struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg *s1_cfg = NULL;struct arm_smmu_s2_cfg *s2_cfg = NULL;struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain = NULL;struct arm_smmu_cmdq_ent prefetch_cmd = {.opcode = CMDQ_OP_PREFETCH_CFG,.prefetch = {.sid = sid,},};if (master) {smmu_domain = master->domain;smmu = master->smmu;}if (smmu_domain) {switch (smmu_domain->stage) {case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S1:s1_cfg = &smmu_domain->s1_cfg;break;case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S2:case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_NESTED:s2_cfg = &smmu_domain->s2_cfg;break;default:break;}}if (val & STRTAB_STE_0_V) {switch (FIELD_GET(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, val)) {case STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_BYPASS:break;case STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_S1_TRANS:case STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_S2_TRANS:ste_live = true;break;case STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_ABORT:BUG_ON(!disable_bypass);break;default:BUG(); /* STE corruption */}}/* Nuke the existing STE_0 value, as we're going to rewrite it */val = STRTAB_STE_0_V;/* Bypass/fault */if (!smmu_domain || !(s1_cfg || s2_cfg)) {if (!smmu_domain && disable_bypass)val |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_ABORT);elseval |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_BYPASS);dst[0] = cpu_to_le64(val);dst[1] = cpu_to_le64(FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_SHCFG,STRTAB_STE_1_SHCFG_INCOMING));dst[2] = 0; /* Nuke the VMID *//** The SMMU can perform negative caching, so we must sync* the STE regardless of whether the old value was live.*/if (smmu)arm_smmu_sync_ste_for_sid(smmu, sid);return;}if (s1_cfg) {u64 strw = smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_E2H ?STRTAB_STE_1_STRW_EL2 : STRTAB_STE_1_STRW_NSEL1;BUG_ON(ste_live);dst[1] = cpu_to_le64(FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_S1DSS, STRTAB_STE_1_S1DSS_SSID0) |FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_S1CIR, STRTAB_STE_1_S1C_CACHE_WBRA) |FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_S1COR, STRTAB_STE_1_S1C_CACHE_WBRA) |FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_S1CSH, ARM_SMMU_SH_ISH) |FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_STRW, strw));if (master->prg_resp_needs_ssid)dst[1] |= cpu_to_le64(STRTAB_STE_1_PPAR);if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_STALLS &&!master->stall_enabled)dst[1] |= cpu_to_le64(STRTAB_STE_1_S1STALLD);val |= (s1_cfg->cdcfg.cdtab_dma & STRTAB_STE_0_S1CTXPTR_MASK) |FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_S1_TRANS) |FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_S1CDMAX, s1_cfg->s1cdmax) |FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_S1FMT, s1_cfg->s1fmt);}if (s2_cfg) {BUG_ON(ste_live);dst[2] = cpu_to_le64(FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_2_S2VMID, s2_cfg->vmid) |FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_2_VTCR, s2_cfg->vtcr) |
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIANSTRTAB_STE_2_S2ENDI |
#endifSTRTAB_STE_2_S2PTW | STRTAB_STE_2_S2AA64 |STRTAB_STE_2_S2R);dst[3] = cpu_to_le64(s2_cfg->vttbr & STRTAB_STE_3_S2TTB_MASK);val |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_S2_TRANS);}if (master->ats_enabled)dst[1] |= cpu_to_le64(FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_EATS,STRTAB_STE_1_EATS_TRANS));pr_info("arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent[%d], val[0]=0x%llx, val[1]=0x%llx, val[2]=0x%llx, val[3]=0x%llx\n",sid, val, dst[1], dst[2], dst[3]);arm_smmu_sync_ste_for_sid(smmu, sid);/* See comment in arm_smmu_write_ctx_desc() */WRITE_ONCE(dst[0], cpu_to_le64(val));arm_smmu_sync_ste_for_sid(smmu, sid);/* It's likely that we'll want to use the new STE soon */if (!(smmu->options & ARM_SMMU_OPT_SKIP_PREFETCH))arm_smmu_cmdq_issue_cmd(smmu, &prefetch_cmd);
}static void arm_smmu_init_bypass_stes(__le64 *strtab, unsigned int nent)
{unsigned int i;for (i = 0; i < nent; ++i) {arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent(NULL, -1, strtab);strtab += STRTAB_STE_DWORDS;}
}. . . . . .
/* Probing and initialisation functions */
static int arm_smmu_init_one_queue(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu,struct arm_smmu_queue *q,void __iomem *page,unsigned long prod_off,unsigned long cons_off,size_t dwords, const char *name)
{size_t qsz;do {qsz = ((1 << q->llq.max_n_shift) * dwords) << 3;q->base = dmam_alloc_coherent(smmu->dev, qsz, &q->base_dma,GFP_KERNEL);if (q->base || qsz < PAGE_SIZE)break;q->llq.max_n_shift--;} while (1);if (!q->base) {dev_err(smmu->dev,"failed to allocate queue (0x%zx bytes) for %s\n",qsz, name);return -ENOMEM;}if (!WARN_ON(q->base_dma & (qsz - 1))) {dev_info(smmu->dev, "allocated %u entries for %s\n",1 << q->llq.max_n_shift, name);}q->prod_reg = page + prod_off;q->cons_reg = page + cons_off;q->ent_dwords = dwords;q->q_base = Q_BASE_RWA;q->q_base |= q->base_dma & Q_BASE_ADDR_MASK;q->q_base |= FIELD_PREP(Q_BASE_LOG2SIZE, q->llq.max_n_shift);q->llq.prod = q->llq.cons = 0;return 0;
}static void arm_smmu_cmdq_free_bitmap(void *data)
{unsigned long *bitmap = data;bitmap_free(bitmap);
}static int arm_smmu_cmdq_init(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{int ret = 0;struct arm_smmu_cmdq *cmdq = &smmu->cmdq;unsigned int nents = 1 << cmdq->q.llq.max_n_shift;atomic_long_t *bitmap;cmdq->shared = 1;atomic_set(&cmdq->owner_prod, 0);atomic_set(&cmdq->lock, 0);bitmap = (atomic_long_t *)bitmap_zalloc(nents, GFP_KERNEL);if (!bitmap) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to allocate cmdq bitmap\n");ret = -ENOMEM;} else {cmdq->valid_map = bitmap;devm_add_action(smmu->dev, arm_smmu_cmdq_free_bitmap, bitmap);}return ret;
}static int arm_smmu_ecmdq_init(struct arm_smmu_cmdq *cmdq)
{unsigned int nents = 1 << cmdq->q.llq.max_n_shift;atomic_set(&cmdq->owner_prod, 0);atomic_set(&cmdq->lock, 0);cmdq->valid_map = (atomic_long_t *)bitmap_zalloc(nents, GFP_KERNEL);if (!cmdq->valid_map)return -ENOMEM;return 0;
}static int arm_smmu_init_queues(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{int ret;/* cmdq */ret = arm_smmu_init_one_queue(smmu, &smmu->cmdq.q, smmu->base,ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_PROD, ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_CONS,CMDQ_ENT_DWORDS, "cmdq");if (ret)return ret;ret = arm_smmu_cmdq_init(smmu);if (ret)return ret;/* evtq */ret = arm_smmu_init_one_queue(smmu, &smmu->evtq.q, smmu->page1,ARM_SMMU_EVTQ_PROD, ARM_SMMU_EVTQ_CONS,EVTQ_ENT_DWORDS, "evtq");if (ret)return ret;if ((smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_SVA) &&(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_STALLS)) {smmu->evtq.iopf = iopf_queue_alloc(dev_name(smmu->dev));if (!smmu->evtq.iopf)return -ENOMEM;}/* priq */if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_PRI))return 0;if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_SVA) {smmu->priq.iopf = iopf_queue_alloc(dev_name(smmu->dev));if (!smmu->priq.iopf)return -ENOMEM;}init_waitqueue_head(&smmu->priq.wq);smmu->priq.batch = 0;return arm_smmu_init_one_queue(smmu, &smmu->priq.q, smmu->page1,ARM_SMMU_PRIQ_PROD, ARM_SMMU_PRIQ_CONS,PRIQ_ENT_DWORDS, "priq");
}static int arm_smmu_init_l1_strtab(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{unsigned int i;struct arm_smmu_strtab_cfg *cfg = &smmu->strtab_cfg;size_t size = sizeof(*cfg->l1_desc) * cfg->num_l1_ents;void *strtab = smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab;cfg->l1_desc = devm_kzalloc(smmu->dev, size, GFP_KERNEL);if (!cfg->l1_desc) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to allocate l1 stream table desc\n");return -ENOMEM;}for (i = 0; i < cfg->num_l1_ents; ++i) {arm_smmu_write_strtab_l1_desc(strtab, &cfg->l1_desc[i]);strtab += STRTAB_L1_DESC_DWORDS << 3;}return 0;
}#ifdef CONFIG_SMMU_BYPASS_DEV
static void arm_smmu_install_bypass_ste_for_dev(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu,u32 sid)
{u64 val;__le64 *step = arm_smmu_get_step_for_sid(smmu, sid);if (!step)return;val = STRTAB_STE_0_V;val |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_BYPASS);step[0] = cpu_to_le64(val);step[1] = cpu_to_le64(FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_SHCFG,STRTAB_STE_1_SHCFG_INCOMING));step[2] = 0;
}static int arm_smmu_prepare_init_l2_strtab(struct device *dev, void *data)
{u32 sid;int ret;struct pci_dev *pdev;struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = (struct arm_smmu_device *)data;if (!arm_smmu_device_domain_type(dev))return 0;pdev = to_pci_dev(dev);sid = PCI_DEVID(pdev->bus->number, pdev->devfn);if (!arm_smmu_sid_in_range(smmu, sid))return -ERANGE;ret = arm_smmu_init_l2_strtab(smmu, sid);if (ret)return ret;arm_smmu_install_bypass_ste_for_dev(smmu, sid);return 0;
}
#endifstatic int arm_smmu_init_strtab_2lvl(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{void *strtab;u64 reg;u32 size, l1size;struct arm_smmu_strtab_cfg *cfg = &smmu->strtab_cfg;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMMU_BYPASS_DEVint ret;
#endif/* Calculate the L1 size, capped to the SIDSIZE. */size = STRTAB_L1_SZ_SHIFT - (ilog2(STRTAB_L1_DESC_DWORDS) + 3);size = min(size, smmu->sid_bits - STRTAB_SPLIT);cfg->num_l1_ents = 1 << size;size += STRTAB_SPLIT;if (size < smmu->sid_bits)dev_warn(smmu->dev,"2-level strtab only covers %u/%u bits of SID\n",size, smmu->sid_bits);l1size = cfg->num_l1_ents * (STRTAB_L1_DESC_DWORDS << 3);strtab = dmam_alloc_coherent(smmu->dev, l1size, &cfg->strtab_dma,GFP_KERNEL);if (!strtab) {dev_err(smmu->dev,"failed to allocate l1 stream table (%u bytes)\n",l1size);return -ENOMEM;}cfg->strtab = strtab;/* Configure strtab_base_cfg for 2 levels */reg = FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_FMT, STRTAB_BASE_CFG_FMT_2LVL);reg |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_LOG2SIZE, size);reg |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_SPLIT, STRTAB_SPLIT);cfg->strtab_base_cfg = reg;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMMU_BYPASS_DEVret = arm_smmu_init_l1_strtab(smmu);if (ret)return ret;if (smmu_bypass_devices_num) {ret = bus_for_each_dev(&pci_bus_type, NULL, (void *)smmu,arm_smmu_prepare_init_l2_strtab);}return ret;
#elsereturn arm_smmu_init_l1_strtab(smmu);
#endif
}static int arm_smmu_init_strtab_linear(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{void *strtab;u64 reg;u32 size;struct arm_smmu_strtab_cfg *cfg = &smmu->strtab_cfg;size = (1 << smmu->sid_bits) * (STRTAB_STE_DWORDS << 3);strtab = dmam_alloc_coherent(smmu->dev, size, &cfg->strtab_dma,GFP_KERNEL);if (!strtab) {dev_err(smmu->dev,"failed to allocate linear stream table (%u bytes)\n",size);return -ENOMEM;}cfg->strtab = strtab;cfg->num_l1_ents = 1 << smmu->sid_bits;/* Configure strtab_base_cfg for a linear table covering all SIDs */reg = FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_FMT, STRTAB_BASE_CFG_FMT_LINEAR);reg |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_LOG2SIZE, smmu->sid_bits);cfg->strtab_base_cfg = reg;arm_smmu_init_bypass_stes(strtab, cfg->num_l1_ents);return 0;
}static int arm_smmu_init_strtab(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{u64 reg;int ret;if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_STRTAB)ret = arm_smmu_init_strtab_2lvl(smmu);elseret = arm_smmu_init_strtab_linear(smmu);if (ret)return ret;/* Set the strtab base address */reg = smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab_dma & STRTAB_BASE_ADDR_MASK;reg |= STRTAB_BASE_RA;smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab_base = reg;/* Allocate the first VMID for stage-2 bypass STEs */set_bit(0, smmu->vmid_map);return 0;
}static int arm_smmu_init_structures(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{int ret;mutex_init(&smmu->streams_mutex);smmu->streams = RB_ROOT;ret = arm_smmu_init_queues(smmu);if (ret)return ret;return arm_smmu_init_strtab(smmu);
}
arm_smmu_init_structures() 函数初始化的数据结构,主要有命令队列和事件队列,当 SMMUv3 硬件设备支持 PRI 时,会初始化 PRI 队列,以及流表。
队列的初始化主要通过 arm_smmu_init_queues()/arm_smmu_init_one_queue() 函数完成,这个过程大体如下:
- 为队列分配内存,SMMU_IDR1 寄存器中有字段描述了支持的命令队列、事件队列和 PRIQ 队列的最大大小,这个大小的含义为,支持的队列中包含的项的最大个数以 2 为底的对数。在为队列分配内存时,会尝试从分配最大数量的内存开始,并逐渐减半,直到内存分配成功,或队列大小的字节数小于一个内存页,后一种情况也就意味着内存分配失败,此时将报错退出。
- 初始化队列的生产者和消费者寄存器地址,以及队列项以 64 位为单位的大小。
- 基于为队列分配的内存的地址,以及队列大小,构造队列基址寄存器的值,这个值将在后面被写入 SMMU_CMDQ_BASE、SMMU_EVENTQ_BASE 和 SMMU_PRIQ_BASE 等寄存器。
流表的初始化主要通过 arm_smmu_init_strtab() 及其调用的 arm_smmu_init_strtab_2lvl()/arm_smmu_init_strtab_linear() 等函数完成,这个过程大体如下:
- 如果 SMMUv3 硬件设备支持 2 级流表,则创建 2 级流表:
- SMMU_STRTAB_BASE_CFG 寄存器中有几个位可以用来配置使用多级流表时,StreamID 的分割点,即多少位用于索引第 1 级流表,多少位用于索引第 2 级流表,还有几个位可以用来配置 StreamID 的位长,另外从 SMMU_IDR1 寄存器中可以获得 SMMUv3 硬件设备支持的最长 StreamID 位长;
- SMMUv3 设备驱动程序取第 2 级流表位长为 STRTAB_SPLIT 位,即 8 位,并取第 1 级流表最大占用 1 MB 内存空间,以此计算第 1 级流表的位长,并计算第 1 级流表的项数,和所需的以字节为单位的内存空间;
- 为第 1 级流表分配内存;
- 初始化流表配置结构体
struct arm_smmu_strtab_cfg的流表基址,流表项个数,和流表配置值等字段,其中的流表配置值将在后面被写入 SMMU_STRTAB_BASE_CFG 寄存器; - 调用
arm_smmu_init_l1_strtab()函数初始化第 1 级流表,SMMUv3 设备驱动程序维护两个 L1 流表描述符表,一个主要由 SMMUv3 驱动程序访问,另一个给 SMMUv3 硬件访问,前者用struct arm_smmu_strtab_l1_desc结构体数组来表示,在arm_smmu_init_l1_strtab()函数中会创建struct arm_smmu_strtab_l1_desc结构体数组,并初始化为无效 L1 流表描述符,并将这些对象的内容写入第 1 级流表。
- SMMUv3 硬件设备不支持 2 级流表,创建线性流表:
- 根据前面从 SMMU_IDR1 寄存器中获得的 StreamID 的位长度,计算线性流表所需的内存空间以字节为单位的大小;
- 为线性流表分配内存;
- 初始化流表配置结构体
struct arm_smmu_strtab_cfg的流表基址,流表项个数,和流表配置值等字段,其中的流表配置值将在后面被写入 SMMU_STRTAB_BASE_CFG 寄存器; - 调用
arm_smmu_init_bypass_stes()函数,将线性流表中的所有 STE 初始化为旁路 SMMU。
- 基于在内存中创建的流表的基地址,构造流表基址寄存器的值,这个值将在后面被写入 SMMU_STRTAB_BASE 寄存器。
arm_smmu_init_structures() 函数按照 ARM 系统内存管理单元架构规范版本 3 中定义的数据结构及它们的关系执行。
复位 SMMUv3 设备
复位 SMMUv3 设备主要通过调用 arm_smmu_device_reset() 函数完成,这个函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/arm/arm-smmu-v3/arm-smmu-v3.c 文件中) 如下:
static int arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, u32 val,unsigned int reg_off, unsigned int ack_off)
{u32 reg;writel_relaxed(val, smmu->base + reg_off);return readl_relaxed_poll_timeout(smmu->base + ack_off, reg, reg == val,1, ARM_SMMU_POLL_TIMEOUT_US);
}/* GBPA is "special" */
static int arm_smmu_update_gbpa(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, u32 set, u32 clr)
{int ret;u32 reg, __iomem *gbpa = smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_GBPA;ret = readl_relaxed_poll_timeout(gbpa, reg, !(reg & GBPA_UPDATE),1, ARM_SMMU_POLL_TIMEOUT_US);if (ret)return ret;reg &= ~clr;reg |= set;writel_relaxed(reg | GBPA_UPDATE, gbpa);ret = readl_relaxed_poll_timeout(gbpa, reg, !(reg & GBPA_UPDATE),1, ARM_SMMU_POLL_TIMEOUT_US);if (ret)dev_err(smmu->dev, "GBPA not responding to update\n");return ret;
}static void arm_smmu_free_msis(void *data)
{struct device *dev = data;platform_msi_domain_free_irqs(dev);
}static void arm_smmu_write_msi_msg(struct msi_desc *desc, struct msi_msg *msg)
{phys_addr_t doorbell;struct device *dev = msi_desc_to_dev(desc);struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = dev_get_drvdata(dev);phys_addr_t *cfg = arm_smmu_msi_cfg[desc->platform.msi_index];doorbell = (((u64)msg->address_hi) << 32) | msg->address_lo;doorbell &= MSI_CFG0_ADDR_MASK;#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP/* Saves the msg (base addr of msi irq) and restores it during resume */desc->msg.address_lo = msg->address_lo;desc->msg.address_hi = msg->address_hi;desc->msg.data = msg->data;
#endifwriteq_relaxed(doorbell, smmu->base + cfg[0]);writel_relaxed(msg->data, smmu->base + cfg[1]);writel_relaxed(ARM_SMMU_MEMATTR_DEVICE_nGnRE, smmu->base + cfg[2]);
}static void arm_smmu_setup_msis(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{struct msi_desc *desc;int ret, nvec = ARM_SMMU_MAX_MSIS;struct device *dev = smmu->dev;/* Clear the MSI address regs */writeq_relaxed(0, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_GERROR_IRQ_CFG0);writeq_relaxed(0, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_EVTQ_IRQ_CFG0);if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_PRI)writeq_relaxed(0, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_PRIQ_IRQ_CFG0);elsenvec--;if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_MSI))return;if (!dev->msi_domain) {dev_info(smmu->dev, "msi_domain absent - falling back to wired irqs\n");return;}/* Allocate MSIs for evtq, gerror and priq. Ignore cmdq */ret = platform_msi_domain_alloc_irqs(dev, nvec, arm_smmu_write_msi_msg);if (ret) {dev_warn(dev, "failed to allocate MSIs - falling back to wired irqs\n");return;}for_each_msi_entry(desc, dev) {switch (desc->platform.msi_index) {case EVTQ_MSI_INDEX:smmu->evtq.q.irq = desc->irq;break;case GERROR_MSI_INDEX:smmu->gerr_irq = desc->irq;break;case PRIQ_MSI_INDEX:smmu->priq.q.irq = desc->irq;break;default: /* Unknown */continue;}}/* Add callback to free MSIs on teardown */devm_add_action(dev, arm_smmu_free_msis, dev);
}#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
static void arm_smmu_resume_msis(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{struct msi_desc *desc;struct device *dev = smmu->dev;for_each_msi_entry(desc, dev) {switch (desc->platform.msi_index) {case EVTQ_MSI_INDEX:case GERROR_MSI_INDEX:case PRIQ_MSI_INDEX: {phys_addr_t *cfg = arm_smmu_msi_cfg[desc->platform.msi_index];struct msi_msg *msg = &desc->msg;phys_addr_t doorbell = (((u64)msg->address_hi) << 32) | msg->address_lo;doorbell &= MSI_CFG0_ADDR_MASK;writeq_relaxed(doorbell, smmu->base + cfg[0]);writel_relaxed(msg->data, smmu->base + cfg[1]);writel_relaxed(ARM_SMMU_MEMATTR_DEVICE_nGnRE,smmu->base + cfg[2]);break;}default:continue;}}
}
#else
static void arm_smmu_resume_msis(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{
}
#endifstatic void arm_smmu_setup_unique_irqs(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, bool resume)
{int irq, ret;if (!resume)arm_smmu_setup_msis(smmu);else {/* The irq doesn't need to be re-requested during resume */arm_smmu_resume_msis(smmu);return;}/* Request interrupt lines */irq = smmu->evtq.q.irq;if (irq) {ret = devm_request_threaded_irq(smmu->dev, irq, NULL,arm_smmu_evtq_thread,IRQF_ONESHOT,"arm-smmu-v3-evtq", smmu);if (ret < 0)dev_warn(smmu->dev, "failed to enable evtq irq\n");} else {dev_warn(smmu->dev, "no evtq irq - events will not be reported!\n");}irq = smmu->gerr_irq;if (irq) {ret = devm_request_irq(smmu->dev, irq, arm_smmu_gerror_handler,0, "arm-smmu-v3-gerror", smmu);if (ret < 0)dev_warn(smmu->dev, "failed to enable gerror irq\n");} else {dev_warn(smmu->dev, "no gerr irq - errors will not be reported!\n");}if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_PRI) {irq = smmu->priq.q.irq;if (irq) {ret = devm_request_threaded_irq(smmu->dev, irq, NULL,arm_smmu_priq_thread,IRQF_ONESHOT,"arm-smmu-v3-priq",smmu);if (ret < 0)dev_warn(smmu->dev,"failed to enable priq irq\n");} else {dev_warn(smmu->dev, "no priq irq - PRI will be broken\n");}}
}static int arm_smmu_setup_irqs(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, bool resume)
{int ret, irq;u32 irqen_flags = IRQ_CTRL_EVTQ_IRQEN | IRQ_CTRL_GERROR_IRQEN;/* Disable IRQs first */ret = arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(smmu, 0, ARM_SMMU_IRQ_CTRL,ARM_SMMU_IRQ_CTRLACK);if (ret) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to disable irqs\n");return ret;}irq = smmu->combined_irq;if (irq) {/** Cavium ThunderX2 implementation doesn't support unique irq* lines. Use a single irq line for all the SMMUv3 interrupts.*/ret = devm_request_threaded_irq(smmu->dev, irq,arm_smmu_combined_irq_handler,arm_smmu_combined_irq_thread,IRQF_ONESHOT,"arm-smmu-v3-combined-irq", smmu);if (ret < 0)dev_warn(smmu->dev, "failed to enable combined irq\n");} elsearm_smmu_setup_unique_irqs(smmu, resume);if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_PRI)irqen_flags |= IRQ_CTRL_PRIQ_IRQEN;/* Enable interrupt generation on the SMMU */ret = arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(smmu, irqen_flags,ARM_SMMU_IRQ_CTRL, ARM_SMMU_IRQ_CTRLACK);if (ret)dev_warn(smmu->dev, "failed to enable irqs\n");return 0;
}static int arm_smmu_device_disable(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{int ret;ret = arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(smmu, 0, ARM_SMMU_CR0, ARM_SMMU_CR0ACK);if (ret)dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to clear cr0\n");return ret;
}static int arm_smmu_device_reset(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, bool resume)
{int i;int ret;u32 reg, enables;struct arm_smmu_cmdq_ent cmd;/* Clear CR0 and sync (disables SMMU and queue processing) */reg = readl_relaxed(smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_CR0);if (reg & CR0_SMMUEN) {dev_warn(smmu->dev, "SMMU currently enabled! Resetting...\n");WARN_ON(is_kdump_kernel() && !disable_bypass);arm_smmu_update_gbpa(smmu, GBPA_ABORT, 0);}ret = arm_smmu_device_disable(smmu);if (ret)return ret;/* CR1 (table and queue memory attributes) */reg = FIELD_PREP(CR1_TABLE_SH, ARM_SMMU_SH_ISH) |FIELD_PREP(CR1_TABLE_OC, CR1_CACHE_WB) |FIELD_PREP(CR1_TABLE_IC, CR1_CACHE_WB) |FIELD_PREP(CR1_QUEUE_SH, ARM_SMMU_SH_ISH) |FIELD_PREP(CR1_QUEUE_OC, CR1_CACHE_WB) |FIELD_PREP(CR1_QUEUE_IC, CR1_CACHE_WB);writel_relaxed(reg, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_CR1);/* CR2 (random crap) */reg = CR2_RECINVSID;if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_E2H)reg |= CR2_E2H;if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_BTM))reg |= CR2_PTM;writel_relaxed(reg, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_CR2);/* Stream table */writeq_relaxed(smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab_base,smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_STRTAB_BASE);writel_relaxed(smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab_base_cfg,smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_STRTAB_BASE_CFG);/* Command queue */writeq_relaxed(smmu->cmdq.q.q_base, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_BASE);writel_relaxed(smmu->cmdq.q.llq.prod, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_PROD);writel_relaxed(smmu->cmdq.q.llq.cons, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_CONS);for (i = 0; i < smmu->nr_ecmdq; i++) {struct arm_smmu_ecmdq *ecmdq;struct arm_smmu_queue *q;ecmdq = *per_cpu_ptr(smmu->ecmdq, i);q = &ecmdq->cmdq.q;if (WARN_ON(q->llq.prod != q->llq.cons)) {q->llq.prod = 0;q->llq.cons = 0;}writeq_relaxed(q->q_base, ecmdq->base + ARM_SMMU_ECMDQ_BASE);writel_relaxed(q->llq.prod, ecmdq->base + ARM_SMMU_ECMDQ_PROD);writel_relaxed(q->llq.cons, ecmdq->base + ARM_SMMU_ECMDQ_CONS);/* enable ecmdq */writel(ECMDQ_PROD_EN | q->llq.prod, q->prod_reg);ret = readl_relaxed_poll_timeout(q->cons_reg, reg, reg & ECMDQ_CONS_ENACK,1, ARM_SMMU_POLL_TIMEOUT_US);if (ret) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "ecmdq[%d] enable failed\n", i);smmu->ecmdq_enabled = 0;break;}}enables = CR0_CMDQEN;ret = arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(smmu, enables, ARM_SMMU_CR0,ARM_SMMU_CR0ACK);if (ret) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to enable command queue\n");return ret;}/* Invalidate any cached configuration */cmd.opcode = CMDQ_OP_CFGI_ALL;arm_smmu_cmdq_issue_cmd_with_sync(smmu, &cmd);/* Invalidate any stale TLB entries */if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HYP) {cmd.opcode = CMDQ_OP_TLBI_EL2_ALL;arm_smmu_cmdq_issue_cmd_with_sync(smmu, &cmd);}cmd.opcode = CMDQ_OP_TLBI_NSNH_ALL;arm_smmu_cmdq_issue_cmd_with_sync(smmu, &cmd);/* Event queue */writeq_relaxed(smmu->evtq.q.q_base, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_EVTQ_BASE);writel_relaxed(smmu->evtq.q.llq.prod, smmu->page1 + ARM_SMMU_EVTQ_PROD);writel_relaxed(smmu->evtq.q.llq.cons, smmu->page1 + ARM_SMMU_EVTQ_CONS);enables |= CR0_EVTQEN;ret = arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(smmu, enables, ARM_SMMU_CR0,ARM_SMMU_CR0ACK);if (ret) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to enable event queue\n");return ret;}/* PRI queue */if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_PRI) {writeq_relaxed(smmu->priq.q.q_base,smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_PRIQ_BASE);writel_relaxed(smmu->priq.q.llq.prod,smmu->page1 + ARM_SMMU_PRIQ_PROD);writel_relaxed(smmu->priq.q.llq.cons,smmu->page1 + ARM_SMMU_PRIQ_CONS);enables |= CR0_PRIQEN;ret = arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(smmu, enables, ARM_SMMU_CR0,ARM_SMMU_CR0ACK);if (ret) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to enable PRI queue\n");return ret;}}if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_ATS) {enables |= CR0_ATSCHK;ret = arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(smmu, enables, ARM_SMMU_CR0,ARM_SMMU_CR0ACK);if (ret) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to enable ATS check\n");return ret;}}ret = arm_smmu_setup_irqs(smmu, resume);if (ret) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to setup irqs\n");return ret;}if (is_kdump_kernel())enables &= ~(CR0_EVTQEN | CR0_PRIQEN);/* Enable the SMMU interface, or ensure bypass */if (!smmu->bypass || disable_bypass) {enables |= CR0_SMMUEN;} else {ret = arm_smmu_update_gbpa(smmu, 0, GBPA_ABORT);if (ret)return ret;}ret = arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(smmu, enables, ARM_SMMU_CR0,ARM_SMMU_CR0ACK);if (ret) {dev_err(smmu->dev, "failed to enable SMMU interface\n");return ret;}return 0;
}
复位 SMMUv3 设备完成硬件 SMMUv3 设备的使能,这个过程大体如下:
- 检查 SMMU_CR0 寄存器,如果 SMMU 已经使能,则更新 SMMU_GBPA 寄存器,停止所有传入的事务。
- 禁用 SMMU 设备的所有功能,包括命令队列、事件队列,和 PRI 队列 等,这里可以看到 SMMU 的一种独特的寄存器写入模式,SMMU_CR0 寄存器有一个对应的确认寄存器 SMMU_CR0ACK,当向 SMMU_CR0 寄存器写入的值确认生效时,SMMU_CR0ACK 寄存器对应的位会被更新,这里在写入 SMMU_CR0 寄存器时,会等待 SMMU_CR0ACK 寄存器对应位的更新,以确定写入生效,还有其它几个 SMMU 寄存器的写入模式与此类似。
- 写入SMMU_CR1 寄存器,配置表和队列的内存属性,流表、命令队列、事件队列和 PRI 队列等的可缓存性,可共享性。
- 写入SMMU_CR2 寄存器,配置 RECINVSID、E2H 和 BTM。
- 将前面在初始化数据结构中创建的流表基址配置,流表基址值写入对应的寄存器。
- 将前面在初始化数据结构中创建的命令队列基址值,命令队列生产者指针,命令队列消费者指针,扩展命令队列相关的配置写入对应的寄存器,并写入 SMMU_CR0 寄存器 启用命令队列。
- 向命令队列中发送几条命令,无效任何缓存配置,陈旧的 TLB 项等。
- 将前面在初始化数据结构中创建的事件队列基址值,事件队列生产者指针,事件队列消费者指针写入对应的寄存器,并写入 SMMU_CR0 寄存器 启用事件队列。
- SMMUv3 硬件设备支持 PRI 时,将前面在初始化数据结构中创建的 PRI 队列基址值,PRI 队列生产者指针,PRI 队列消费者指针写入对应的寄存器,并写入 SMMU_CR0 寄存器 启用 PRI 队列。
- 如果 SMMUv3 硬件设备支持 ATS 检查,则写入 SMMU_CR0 寄存器 启用 ATS 检查。
- 配置中断。
- 如果没有配置旁路 SMMU 或禁用 SMMU,则写入 SMMU_CR0 寄存器开启 SMMU。
设置中断的过程如下:
- 写入 SMMU_IRQ_CTRL 寄存器禁用中断。
- 如果配置了使用联合中断,则向系统申请中断资源,并注册中断处理程序。
- 没有使用联合中断:
- 配置 MSI;
- 为事件队列请求中断线,并注册中断处理程序;
- 为全局错误请求中断线,并注册中断处理程序;
- SMMUv3 硬件设备支持 PRI 时,为 PRI 队列请求中断线,并注册中断处理程序。
- 写入 SMMU_IRQ_CTRL 寄存器启用中断。
arm_smmu_device_reset() 函数复位 SMMUv3 设备,集中设置 SMMUv3 设备的各种寄存器,和流表,队列,及中断相关的各个寄存器,并在最后使能 SMMU 硬件设备。
将 SMMUv3 设备注册到 IOMMU 子系统
arm_smmu_device_probe() 函数调用 iommu_device_register() 函数将 SMMUv3 设备注册进 IOMMU 子系统,iommu_device_register() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static LIST_HEAD(iommu_device_list);
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(iommu_device_lock);. . . . . .
int iommu_device_register(struct iommu_device *iommu)
{spin_lock(&iommu_device_lock);list_add_tail(&iommu->list, &iommu_device_list);spin_unlock(&iommu_device_lock);return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_device_register);
IOMMU 子系统用一个链表来维护系统中的 IOMMU 设备,将 SMMUv3 设备注册进 IOMMU 子系统即将表示 SMMUv3 设备的 struct iommu_device 对象放进 IOMMU 子系统的 IOMMU 设备链表中。
为各个总线类型设置 IOMMU 回调
arm_smmu_device_probe() 函数调用 arm_smmu_set_bus_ops() 函数为各个支持的总线类型设置 IOMMU 回调,arm_smmu_set_bus_ops() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/arm/arm-smmu-v3/arm-smmu-v3.c 文件中) 如下:
static int arm_smmu_set_bus_ops(struct iommu_ops *ops)
{int err;#ifdef CONFIG_PCIif (pci_bus_type.iommu_ops != ops) {err = bus_set_iommu(&pci_bus_type, ops);if (err)return err;}
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM_AMBAif (amba_bustype.iommu_ops != ops) {err = bus_set_iommu(&amba_bustype, ops);if (err)goto err_reset_pci_ops;}
#endifif (platform_bus_type.iommu_ops != ops) {err = bus_set_iommu(&platform_bus_type, ops);if (err)goto err_reset_amba_ops;}return 0;err_reset_amba_ops:
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM_AMBAbus_set_iommu(&amba_bustype, NULL);
#endif
err_reset_pci_ops: __maybe_unused;
#ifdef CONFIG_PCIbus_set_iommu(&pci_bus_type, NULL);
#endifreturn err;
}
arm_smmu_set_bus_ops() 函数调用 bus_set_iommu() 函数为 platform_bus_type、pci_bus_type 和 amba_bustype 等设置 IOMMU 回调。bus_set_iommu() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static int probe_get_default_domain_type(struct device *dev, void *data)
{const struct iommu_ops *ops = dev->bus->iommu_ops;struct __group_domain_type *gtype = data;unsigned int type = 0;if (ops->def_domain_type)type = ops->def_domain_type(dev);if (type) {if (gtype->type && gtype->type != type) {dev_warn(dev, "Device needs domain type %s, but device %s in the same iommu group requires type %s - using default\n",iommu_domain_type_str(type),dev_name(gtype->dev),iommu_domain_type_str(gtype->type));gtype->type = 0;}if (!gtype->dev) {gtype->dev = dev;gtype->type = type;}}return 0;
}static void probe_alloc_default_domain(struct bus_type *bus,struct iommu_group *group)
{struct __group_domain_type gtype;memset(>ype, 0, sizeof(gtype));/* Ask for default domain requirements of all devices in the group */__iommu_group_for_each_dev(group, >ype,probe_get_default_domain_type);if (!gtype.type)gtype.type = iommu_def_domain_type;iommu_group_alloc_default_domain(bus, group, gtype.type);}static int iommu_group_do_dma_attach(struct device *dev, void *data)
{struct iommu_domain *domain = data;int ret = 0;if (!iommu_is_attach_deferred(domain, dev))ret = __iommu_attach_device(domain, dev);return ret;
}static int __iommu_group_dma_attach(struct iommu_group *group)
{return __iommu_group_for_each_dev(group, group->default_domain,iommu_group_do_dma_attach);
}static int iommu_group_do_probe_finalize(struct device *dev, void *data)
{struct iommu_domain *domain = data;if (domain->ops->probe_finalize)domain->ops->probe_finalize(dev);return 0;
}static void __iommu_group_dma_finalize(struct iommu_group *group)
{__iommu_group_for_each_dev(group, group->default_domain,iommu_group_do_probe_finalize);
}static void __iommu_group_dma_finalize(struct iommu_group *group)
{__iommu_group_for_each_dev(group, group->default_domain,iommu_group_do_probe_finalize);
}static int iommu_group_create_direct_mappings(struct iommu_group *group)
{return __iommu_group_for_each_dev(group, group,iommu_do_create_direct_mappings);
}static int probe_iommu_group(struct device *dev, void *data)
{struct list_head *group_list = data;struct iommu_group *group;int ret;/* Device is probed already if in a group */group = iommu_group_get(dev);if (group) {iommu_group_put(group);return 0;}ret = __iommu_probe_device(dev, group_list);if (ret == -ENODEV)ret = 0;return ret;
}static int remove_iommu_group(struct device *dev, void *data)
{iommu_release_device(dev);return 0;
}static int iommu_bus_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb,unsigned long action, void *data)
{unsigned long group_action = 0;struct device *dev = data;struct iommu_group *group;/** ADD/DEL call into iommu driver ops if provided, which may* result in ADD/DEL notifiers to group->notifier*/if (action == BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE) {int ret;ret = iommu_probe_device(dev);return (ret) ? NOTIFY_DONE : NOTIFY_OK;} else if (action == BUS_NOTIFY_REMOVED_DEVICE) {iommu_release_device(dev);return NOTIFY_OK;}/** Remaining BUS_NOTIFYs get filtered and republished to the* group, if anyone is listening*/group = iommu_group_get(dev);if (!group)return 0;switch (action) {case BUS_NOTIFY_BIND_DRIVER:group_action = IOMMU_GROUP_NOTIFY_BIND_DRIVER;break;case BUS_NOTIFY_BOUND_DRIVER:group_action = IOMMU_GROUP_NOTIFY_BOUND_DRIVER;break;case BUS_NOTIFY_UNBIND_DRIVER:group_action = IOMMU_GROUP_NOTIFY_UNBIND_DRIVER;break;case BUS_NOTIFY_UNBOUND_DRIVER:group_action = IOMMU_GROUP_NOTIFY_UNBOUND_DRIVER;break;}if (group_action)blocking_notifier_call_chain(&group->notifier,group_action, dev);iommu_group_put(group);return 0;
}. . . . . .
int bus_iommu_probe(struct bus_type *bus)
{struct iommu_group *group, *next;LIST_HEAD(group_list);int ret;/** This code-path does not allocate the default domain when* creating the iommu group, so do it after the groups are* created.*/ret = bus_for_each_dev(bus, NULL, &group_list, probe_iommu_group);if (ret)return ret;list_for_each_entry_safe(group, next, &group_list, entry) {/* Remove item from the list */list_del_init(&group->entry);mutex_lock(&group->mutex);/* Try to allocate default domain */probe_alloc_default_domain(bus, group);if (!group->default_domain) {mutex_unlock(&group->mutex);continue;}iommu_group_create_direct_mappings(group);ret = __iommu_group_dma_attach(group);mutex_unlock(&group->mutex);if (ret)break;__iommu_group_dma_finalize(group);}return ret;
}static int iommu_bus_init(struct bus_type *bus, const struct iommu_ops *ops)
{struct notifier_block *nb;int err;nb = kzalloc(sizeof(struct notifier_block), GFP_KERNEL);if (!nb)return -ENOMEM;nb->notifier_call = iommu_bus_notifier;err = bus_register_notifier(bus, nb);if (err)goto out_free;err = bus_iommu_probe(bus);if (err)goto out_err;return 0;out_err:/* Clean up */bus_for_each_dev(bus, NULL, NULL, remove_iommu_group);bus_unregister_notifier(bus, nb);out_free:kfree(nb);return err;
}/*** bus_set_iommu - set iommu-callbacks for the bus* @bus: bus.* @ops: the callbacks provided by the iommu-driver** This function is called by an iommu driver to set the iommu methods* used for a particular bus. Drivers for devices on that bus can use* the iommu-api after these ops are registered.* This special function is needed because IOMMUs are usually devices on* the bus itself, so the iommu drivers are not initialized when the bus* is set up. With this function the iommu-driver can set the iommu-ops* afterwards.*/
int bus_set_iommu(struct bus_type *bus, const struct iommu_ops *ops)
{int err;if (ops == NULL) {bus->iommu_ops = NULL;return 0;}if (bus->iommu_ops != NULL)return -EBUSY;bus->iommu_ops = ops;/* Do IOMMU specific setup for this bus-type */err = iommu_bus_init(bus, ops);if (err)bus->iommu_ops = NULL;return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(bus_set_iommu);
bus_set_iommu() 函数执行过程如下:
- 为总线设置 IOMMU 回调。
- 执行总线类型 IOMMU 特有的设置:
- 向总线注册一个回调,以便于在有新设备添加时得到通知;
- 探测已经添加到总线的设备。
探测已经添加到总线的设备的过程如下:
- 遍历总线上已经添加的所有设备,探测各个设备,如果设备连接到注册的 IOMMU 设备上,则获得设备的
iommu_group,这些iommu_group都被放进一个链表中。 - 遍历获得的
iommu_group,针对每个iommu_group:- 将
iommu_group移出链表; - 尝试分配默认的 domain,先确认默认的 domain 类型,然后分配 domain 对象,确认 domain 类型时,先尝试通过 SMMU 设备注册的回调
def_domain_type获取,失败时则取 IOMMO 子系统的默认 domain 类型; - 为各个设备创建直接映射;
- 为各个设备执行 attach;
- 为各个设备执行探测结束回调。
- 将
为各个总线类型设置 IOMMU 回调,处理了连接到 IOMMU 的系统 I/O 设备先于 IOMMU 设备探测的情况。
参考文档
IOMMU的现状和发展
IOMMU和Arm SMMU介绍
SMMU内核驱动分析
IOMMU/SMMUV3代码分析(5)IO设备与SMMU的关联2
相关文章:

深入浅出 Linux 中的 ARM IOMMU SMMU I
Linux 系统下的 SMMU 介绍 在计算机系统架构中,与传统的用于 CPU 访问内存的管理的 MMU 类似,IOMMU (Input Output Memory Management Unit) 将来自系统 I/O 设备的 DMA 请求传递到系统互连之前,它会先转换请求的地址,并对系统 I…...

关于sqlModel 实现查询表单入参空值和模糊匹配一次性查询
在处理表单提交后,后端 SQL 查询部分空值和部分模糊值时,可以使用 SQLModel 构建动态查询。你可以根据表单数据动态构建 SQL 查询,并且只添加那些非空的、有值的条件。 以下是一个示例,假设你有一个模型 Item: from …...
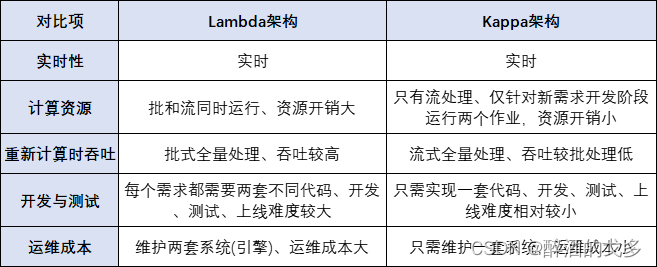
数据仓库架构之详解Kappa和Lambda
目录 一、前言 二、架构详解 1 Lambda 架构 1.1 Lambda 架构组成 1.2 Lambda 特点 1.3 Lambda 架构的优点 1.4 Lambda 架构的不足 2 Kappa 架构 2.1 Kappa 架构的核心组件 2.2 Kappa 架构优点 2.3 Kappa 架构的注意事项 三、区别对比 四、选择时考虑因素 一、前言 …...
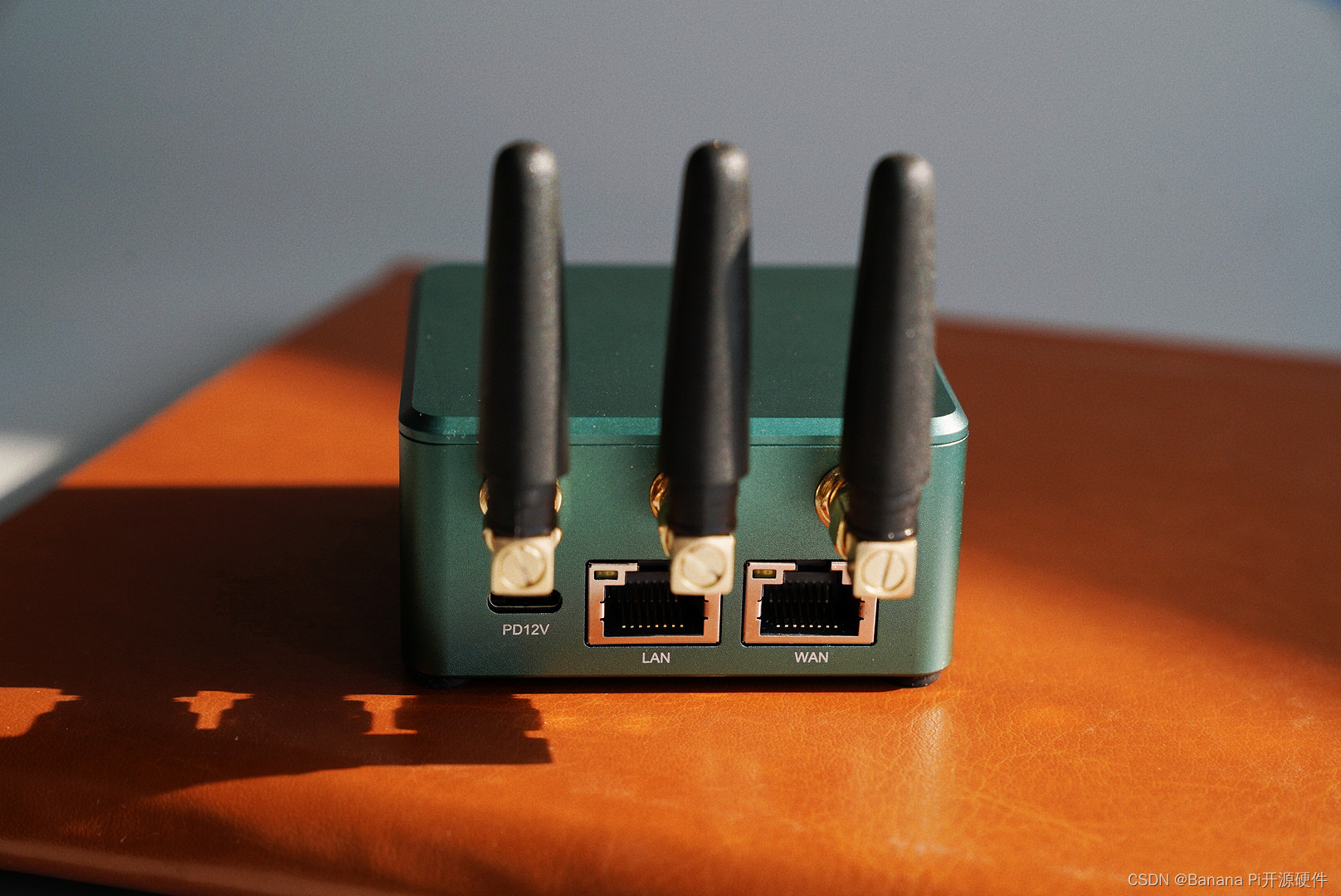

Banana Pi BPI-R3 Mini 开源路由器,也能拍出艺术美感
香蕉派BPI-R3 Mini路由器板开发板采用联发科MT7986A(Filogic 830)四核ARM A53芯片设计,板载2G DDR 内存,8G eMMC和128MB SPI NAND存储,是一款非常高性能的开源路由器开发板,支持Wi-Fi6 2.4G/5G(MT7976C)&am…...

Django高级之-分页器
目录 一、引入 二、分页推导 三、数据总页面获取 四、内置方法之divmod 五、终极大法 六、自定义分页器使用 【1】后端 【2】前端 一、引入 针对上一小节批量插入的数据 我们在前端展示的时候发现一个很严重的问题一页展示了所有的数据,数据量太大…...
Vue-报错No “exports“ main defined in xx
vue报错:No "exports" main defined in F:\wjh\vue#Practice\EasyQuestionnaire-web-master\EasyQuestionnaire-web-master\node_modules\babel\helper-compilation-targets\package.json 1.在文件中找到该路径的package.json文件, 2.按照提示…...

EL-input添加双击或者单击事件
#El-lement UI # 这个框架确实给我们带来了很多好处,最近一直忙于项目,没时间来写文章,最近有个问题困扰我很久,最终却很简单的解决了,记下来希望能帮助更多的人。 大家都知道el-input是无法直接添加click或者dblcli…...
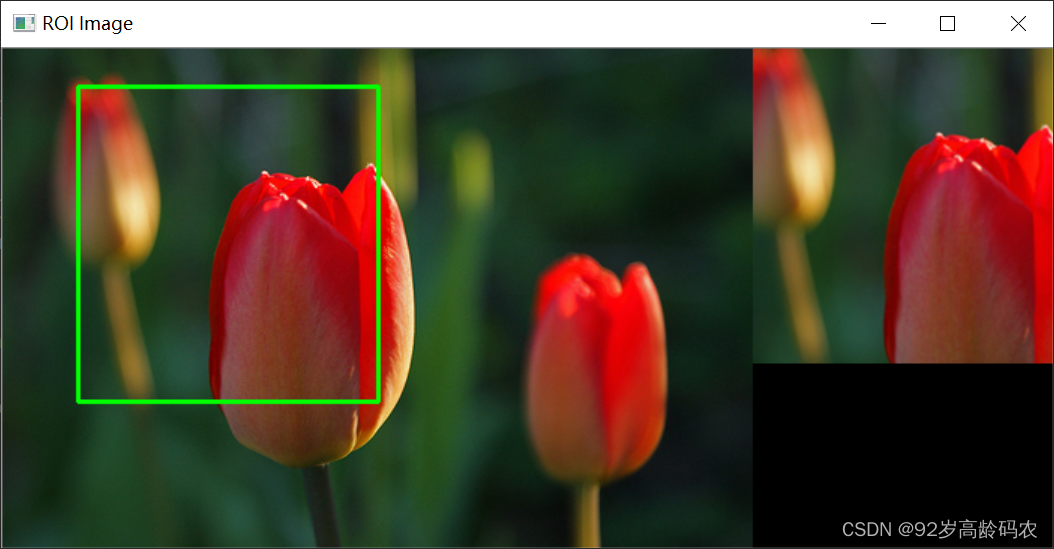
OpenCV快速入门:绘制图形、图像金字塔和感兴趣区域
文章目录 前言一、绘制图形1. 绘制直线2. 绘制圆3. 绘制矩形4. 绘制椭圆5. 绘制多边形6. 绘制文字7. 可选参数8. 手工绘制OpenCV的logo 二、图像金字塔1. 高斯金字塔2. 拉普拉斯金字塔 三、感兴趣区域(ROI)数组切片方式OpenCV截取方式 总结 前言 OpenCV…...
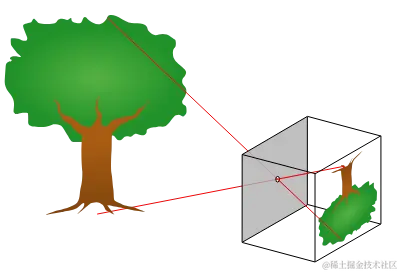
Three.js相机模拟
有没有想过如何在 3D Web 应用程序中模拟物理相机? 在这篇博文中,我将向你展示如何使用 Three.js和 OpenCV 来完成此操作。 我们将从模拟针孔相机模型开始,然后添加真实的镜头畸变。 具体来说,我们将仔细研究 OpenCV 的两个失真模型,并使用后处理着色器复制它们。 拥有逼…...
Verilog基础:仿真时x信号的产生和x信号对于各运算符的特性
相关阅读 Verilog基础https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45791458/category_12263729.html?spm1001.2014.3001.5482 信号爆x也许是所有IC人的噩梦,满屏的红色波形常让人头疼不已,但x信号的产生原因却常常只有几种,只要遵循一定的代码规范&#…...

穿越数据的迷宫-数据管理知识介绍
一、权威书籍介绍 《穿越数据的迷宫》 本书分12章重点阐述了数据管理的重要性,数据管理的挑战,DAMA的数据管理原则,数据伦理,数据治理,数据生命周期管理的规划和设计,数据赋能和数据维护,使用…...

3
目录 【任务 3】私有云运维开发[10 分] 【题目 1】Ansible 服务部署:部署 MariaDB 集群[2 分] 【题目 2】Ansible 服务部署:部署ELK 集群服务[2 分] 【题目 3】Python 运维开发:基于OpenStack Restful API 实现镜像上传[1 分] 【题目 4】Pyth…...

【python学习】基础篇-常用模块-multiprocessing模块:多进程
multiprocessing模块是Python标准库中用于实现多进程的模块,它提供了一些工具和类来创建和管理多个进程。 以下是multiprocessing模块的一些常用方法: Process()创建一个新的进程对象,需要传入一个函数作为该进程要执行的任务。 start()启动…...

JAVA SQL
-- /* */ -- 简单查询: -- 查询所有字段: select * from 表名 -- *:通配符,代表所有 select * from employees -- 查询部分字段: select 列名1,列名2,.. from 表名 -- 查询员工ID,员工姓名,员工的工资 select employee_id,salary,first_name from employees -- 查…...

[Linux] 进程入门
💻文章目录 📄前言计算机的结构体系与概念冯诺依曼体系结构操作系统概念目的与定位 进程概念描述进程-PCBtask_struct检查进程利用fork创建子进程 进程状态进程状态查看僵尸进程孤儿进程 📓总结 📄前言 作为一名程序员,…...
深入解析数据结构与算法之堆
文章目录 🥦引言:🥦什么是堆🥦大顶堆与小顶堆🧄大顶堆(Max Heap)🧄小顶堆(Min Heap) 🥦堆的表示🧄数组表示:🧄…...
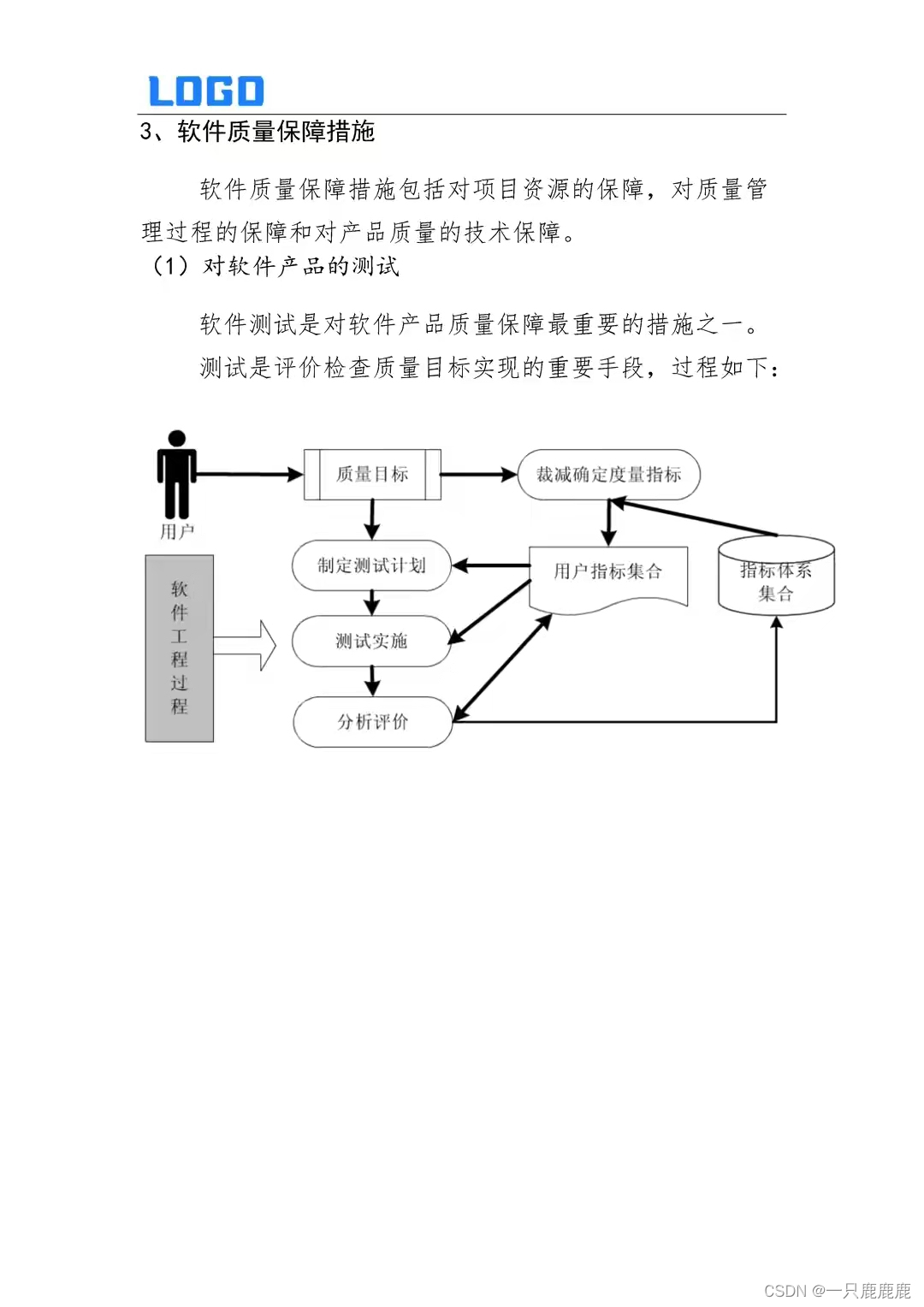
信息化项目质量保证措施
...
es的优势
系列文章目录 提示:这里可以添加系列文章的所有文章的目录,目录需要自己手动添加 例如:第一章 Python 机器学习入门之pandas的使用 提示:写完文章后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目…...
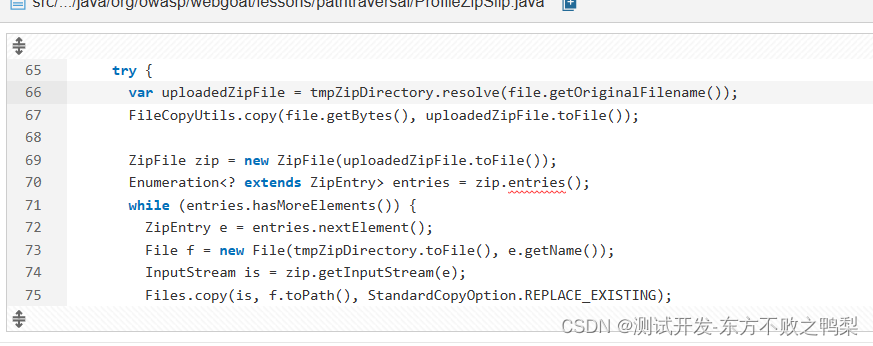
sonar对webgoat进行静态扫描
安装sonar并配置 docker安装sonarqube,sonarQube静态代码扫描 - Joson6350 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) 对webgoat进行sonar扫描 扫描结果 bugs Change this condition so that it does not always evaluate to "false" 意思是这里的else if语句不会执行…...

opencv-重点知识
OpenCV(Open Source Computer Vision Library)是一个开源的计算机视觉库,提供了大量用于图像处理和计算机视觉任务的工具和算法。以下是一些OpenCV中的重点知识: 图像加载与显示: 使用cv2.imread()加载图像。使用cv2.imshow()显示…...

生成xcframework
打包 XCFramework 的方法 XCFramework 是苹果推出的一种多平台二进制分发格式,可以包含多个架构和平台的代码。打包 XCFramework 通常用于分发库或框架。 使用 Xcode 命令行工具打包 通过 xcodebuild 命令可以打包 XCFramework。确保项目已经配置好需要支持的平台…...

ES6从入门到精通:前言
ES6简介 ES6(ECMAScript 2015)是JavaScript语言的重大更新,引入了许多新特性,包括语法糖、新数据类型、模块化支持等,显著提升了开发效率和代码可维护性。 核心知识点概览 变量声明 let 和 const 取代 var…...

MODBUS TCP转CANopen 技术赋能高效协同作业
在现代工业自动化领域,MODBUS TCP和CANopen两种通讯协议因其稳定性和高效性被广泛应用于各种设备和系统中。而随着科技的不断进步,这两种通讯协议也正在被逐步融合,形成了一种新型的通讯方式——开疆智能MODBUS TCP转CANopen网关KJ-TCPC-CANP…...

spring:实例工厂方法获取bean
spring处理使用静态工厂方法获取bean实例,也可以通过实例工厂方法获取bean实例。 实例工厂方法步骤如下: 定义实例工厂类(Java代码),定义实例工厂(xml),定义调用实例工厂ÿ…...

Ascend NPU上适配Step-Audio模型
1 概述 1.1 简述 Step-Audio 是业界首个集语音理解与生成控制一体化的产品级开源实时语音对话系统,支持多语言对话(如 中文,英文,日语),语音情感(如 开心,悲伤)&#x…...
Android 之 kotlin 语言学习笔记三(Kotlin-Java 互操作)
参考官方文档:https://developer.android.google.cn/kotlin/interop?hlzh-cn 一、Java(供 Kotlin 使用) 1、不得使用硬关键字 不要使用 Kotlin 的任何硬关键字作为方法的名称 或字段。允许使用 Kotlin 的软关键字、修饰符关键字和特殊标识…...

Python 训练营打卡 Day 47
注意力热力图可视化 在day 46代码的基础上,对比不同卷积层热力图可视化的结果 import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from torchvision import datasets, transforms from torch.utils.data import DataLoader import matplotlib.pypl…...
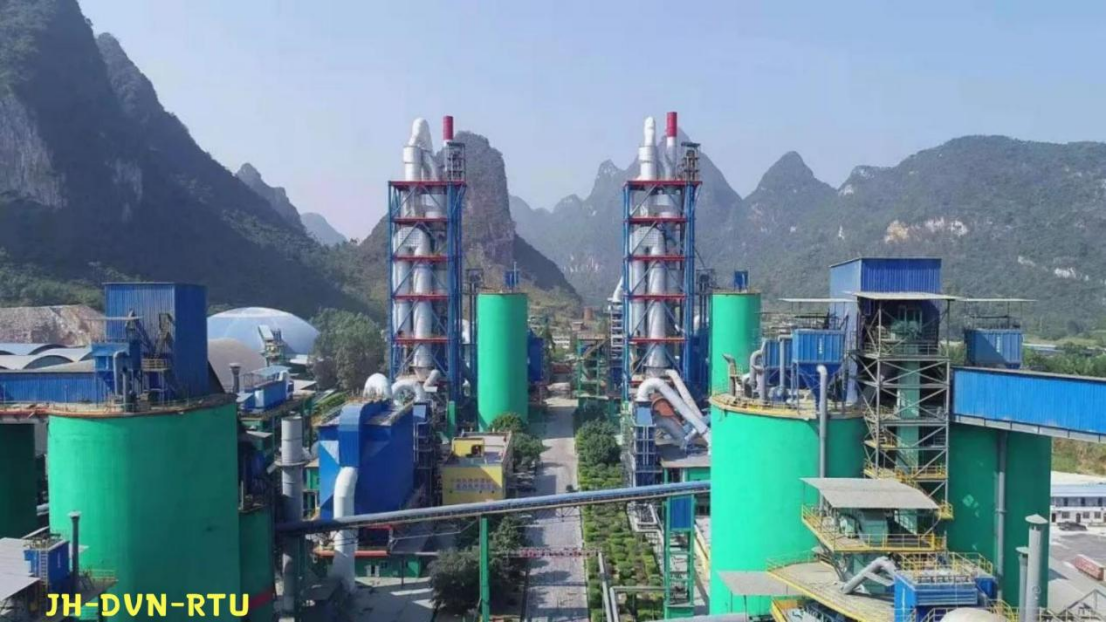

水泥厂自动化升级利器:Devicenet转Modbus rtu协议转换网关
在水泥厂的生产流程中,工业自动化网关起着至关重要的作用,尤其是JH-DVN-RTU疆鸿智能Devicenet转Modbus rtu协议转换网关,为水泥厂实现高效生产与精准控制提供了有力支持。 水泥厂设备众多,其中不少设备采用Devicenet协议。Devicen…...
 ----- Python的类与对象)
Python学习(8) ----- Python的类与对象
Python 中的类(Class)与对象(Object)是面向对象编程(OOP)的核心。我们可以通过“类是模板,对象是实例”来理解它们的关系。 🧱 一句话理解: 类就像“图纸”,对…...

游戏开发中常见的战斗数值英文缩写对照表
游戏开发中常见的战斗数值英文缩写对照表 基础属性(Basic Attributes) 缩写英文全称中文释义常见使用场景HPHit Points / Health Points生命值角色生存状态MPMana Points / Magic Points魔法值技能释放资源SPStamina Points体力值动作消耗资源APAction…...
