Linux学习笔记-芯片性能检测
文章目录
- 概述
- Dhrystone(单核性能测试工具)
- 简介:
- 源码下载:
- 源码编译:
- 使用及输出结果
- coremark(多核性能测试工具)
- 简介:
- 源码下载:
- 源码编译:
- 使用及输出结果:
- stream(DDR内存带宽测试工具)
- 简介:
- 源码下载:
- 源码编译:
- 使用及输出结果:
概述
本文描述linux系统下的芯片性能检测工具
Dhrystone(单核性能测试工具)
简介:
Dhrystone是测量处理器运算能力的最常见基准程序之一,常用于处理器的整型运算性能的测量。Dhrystone的计量单位为每秒计算多少次Dhrystone程序,后来把在VAX-11/780机器上的测试结果1757 Dhrystones/s定义为1 Dhrystone MIPS(百万条指令每秒,MIPS是Million Instructions Per Second的缩写)。
部分芯片测试结果参考网站:http://www.roylongbottom.org.uk/dhrystone results.htm
源码下载:
源码下载地址:http://www.roylongbottom.org.uk/classic_benchmarks.tar.gz
源码编译:
下载完源码后进行解压
tar -vxf classic_benchmarks.tar.gz
解压完成后进入文件夹,文件夹内容如下:
bin32:已经编译好的32位的工具bin64:已经编译好的64位工具source_code:源码目录--> common_32bit:通用的32位测试代码-->common_64bin:通用的64位测试代码-->dhrystone1:一代测试源码-->dhrystone2:二代测试源码-->linpack:浮点性能评估-->livermore_loops:其他工具-->whetstone:浮点性能测试程序README:说明文档
在解压的根目录创建一个存放编译的输出的文件夹,并进入文件夹
mkdir ./arm_build
cd ./arm_build
将相关的源码(cpuidc64.c、cpuidh.h、dhry.h、dhry_1.c 、dhry_2.c)拷贝到arm_build文件夹中
cp -rf ../source_code/common_64bit/cpuidc64.c ./
cp -rf ../source_code/common_64bit/cpuidh.h ./
cp -rf ../source_code/dhrystone2/dhry.h ./
cp -rf ../source_code/dhrystone2/dhry_1.c ./
cp -rf ../source_code/dhrystone2/dhry_2.c ./
拷贝完成后,创建makefile文件进行编译(这个makefile写了两种编译方式:gcc和arm64的交叉编译,根据需要选择屏蔽那个build_cc)
# build_cc=gcc
build_cc=/opt/rv3399/gcc-linaro-7.5.0-2019.12-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-linux-gnu-gccmain:*.o${build_cc} -o dhry2_64 *.o${build_cc} -O2 -o dhry22_64 *.o${build_cc} -O3 -o dhry23_64 *.o*.o:*.c${build_cc} -g -c *.cclean:rm -f *.o dhry2_64 dhry22_64 dhry23_64
添加完成makefile后,直接执行make是编译不通过的,还需要修改一下源码
需要修改 cpuidh.h,在文件末尾的 #endif 前面加上对应函数的声明
int getDetails();
void start_time();
void end_time();
需要修改 cpuidc64.c,屏蔽掉其中3个函数(_cpuida() 、_calculateMHz() 这两个是汇编函数,写在/source_code/common_64bit/cpuida64.asm中,但因为编译不过,所以屏蔽掉),修改如下:
// _cpuida();
// _calculateMHz();
// pagesize = getpagesize();pagesize = 0;
这些源码中,_cpuida() 、_calculateMHz() 这两个是汇编函数,但是交叉编译编译汇编源码不通过,导致只能屏蔽掉对应的汇编源码
gcc编译汇编源码
nasm -f elf64 cpuida64.asm
交叉编译器编译汇编源码
/opt/rv3399/gcc-linaro-7.5.0-2019.12-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-linux-gnu-as -f cpuida64.asm
以上两个编译汇编源码都会生成.o文件
修改完后执行编译
make clean
make
编译过程会有一些警告,不过也能正常编译出可执行文件:dhry2_64(无优化等级)、dhry22_64(优化等级2)、dhry23_64(优化等级3)
这3个可执行文件分别代表不同的优化等级,在Dhrystone中有大量的字符串复制语句,因此一个优化性能好的编译器能够在去掉循环的情形下通过一连串字的移动替代对字符串的复制,由此会出现优化等级越高,性能指标越好的情况。
使用及输出结果
直接执行可执行文件(dhry2_64),如果是交叉编译的,则只需要拷贝可执行文件(dhry2_64)到板子里面直接执行即可
输出结果如下:
root@ubuntu:~/classic_benchmarks/arm_build$ ./dhry2_64 ####################################################getDetails and MHzAssembler CPUID and RDTSC CPU , Features Code 00000000, Model Code 00000000Measured - Minimum -2147483648 MHz, Maximum 0 MHzLinux Functionsget_nprocs() - CPUs 2, Configured CPUs 2get_phys_pages() and size - RAM Size 0.00 GB, Page Size 0 Bytesuname() - Linux, ubuntu, 4.15.0-142-generic#146~16.04.1-Ubuntu SMP Tue Apr 13 09:27:15 UTC 2021, x86_64##########################################Dhrystone Benchmark, Version 2.1 (Language: C or C++)Optimisation Opt 3 64 Bit
Register option not selected10000 runs 0.00 seconds 100000 runs 0.01 seconds 1000000 runs 0.06 seconds 2000000 runs 0.15 seconds 4000000 runs 0.28 seconds 8000000 runs 0.53 seconds 16000000 runs 1.05 seconds 32000000 runs 2.10 seconds Final values (* implementation-dependent):Int_Glob: O.K. 5 Bool_Glob: O.K. 1
Ch_1_Glob: O.K. A Ch_2_Glob: O.K. B
Arr_1_Glob[8]: O.K. 7 Arr_2_Glob8/7: O.K. 32000010
Ptr_Glob-> Ptr_Comp: * 25137728Discr: O.K. 0 Enum_Comp: O.K. 2Int_Comp: O.K. 17 Str_Comp: O.K. DHRYSTONE PROGRAM, SOME STRING
Next_Ptr_Glob-> Ptr_Comp: * 25137728 same as aboveDiscr: O.K. 0 Enum_Comp: O.K. 1Int_Comp: O.K. 18 Str_Comp: O.K. DHRYSTONE PROGRAM, SOME STRING
Int_1_Loc: O.K. 5 Int_2_Loc: O.K. 13
Int_3_Loc: O.K. 7 Enum_Loc: O.K. 1
Str_1_Loc: O.K. DHRYSTONE PROGRAM, 1'ST STRING
Str_2_Loc: O.K. DHRYSTONE PROGRAM, 2'ND STRINGMicroseconds for one run through Dhrystone: 0.07
Dhrystones per Second: 15248279
VAX MIPS rating = 8678.59 Press Enter输出完结果后,按回车键可以退出界面,其中“15248279”表示单核的性能测试结果
Dhrystones per Second: 15248279
coremark(多核性能测试工具)
简介:
CoreMark是一个简单而复杂的基准测试,专门用于测试处理器核心的功能。运行CoreMark产生一个单数字分数(每秒钟能够执行的迭代次数(Iterations per Second,即CoreMarks),迭代次数越高,性能越好),允许用户快速比较处理器。
官网地址:https://www.eembc.org/coremark/index.php
一些芯片的性能参数参考列表:https://www.eembc.org/coremark/scores.php
源码下载:
源码下载地址:https://github.com/eembc/coremark
源码编译:
进入源码根目录后,执行编译命令
gcc编译:
# 先清除编译参数
make clean
# 重新编译
make
生成coremark.exe的可执行文件,这个可执行文件是可以直接在linux下运行的,查看编译出来的文件是否符合编译平台
root@ubuntu:~/app/coremark-main$ file ./coremark.exe
./coremark.exe: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=dd83f1651bf5fa4b513c4bc077146c2d1add2287, not stripped
可以看到是x86-64平台的,直接运行可执行文件coremark.exe即可
交叉编译器编译:
# 先清除编译参数
make clean
# 重新编译
make CC=aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc CXX=aarch64-linux-gnu-g++
生成coremark.exe的可执行文件,这个可执行文件是可以直接在linux下运行的,查看交叉编译出来的文件是否符合交叉编译的平台
root@ubuntu:~/app/coremark-main$ file ./coremark.exe
./coremark.exe: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, ARM aarch64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-linux-aarch64.so.1, for GNU/Linux 3.7.0, BuildID[sha1]=e60d55afe73eb5ddb2158e1a6a77b33130719b6b, not stripped
可以看到是“ARM aarch64”平台的,将该可执行文件coremark.exe复制到板子中直接运行即可
使用及输出结果:
直接运行可执行文件(执行后需要等一会才会输出结果)
./coremark.exe
运行结果
root@ubuntu:~/app/coremark-main$ ./coremark.exe
2K performance run parameters for coremark.
CoreMark Size : 666
Total ticks : 16466
Total time (secs): 16.466000
Iterations/Sec : 18219.361108
Iterations : 300000
Compiler version : GCC5.4.0 20160609
Compiler flags : -O2 -DPERFORMANCE_RUN=1 -lrt
Memory location : Please put data memory location here(e.g. code in flash, data on heap etc)
seedcrc : 0xe9f5
[0]crclist : 0xe714
[0]crcmatrix : 0x1fd7
[0]crcstate : 0x8e3a
[0]crcfinal : 0xcc42
Correct operation validated. See README.md for run and reporting rules.
CoreMark 1.0 : 18219.361108 / GCC5.4.0 20160609 -O2 -DPERFORMANCE_RUN=1 -lrt / Heap
可以看到总共迭代了300000次,共耗时16.466s,每秒的迭代次数为18219.361108次,可以通过这个迭代次数来评估出cpu的处理能力
stream(DDR内存带宽测试工具)
简介:
STREAM: Sustainable Memory Bandwidth in High Performance Computers(高性能计算机的可持续内存带宽),这是一个内存带宽测试的工具,主要是以四个方面反映测试结果:
copy(复制操作,2次访问内存(1读1写)):从内存单元中读取一个数,并复制到其他内存单元中;scale(乘法操作,2次访问内存(1读1写)):从内存单元中读取一个数,与常数相乘,得到的记过存到其他内存单元;Add(加法操作,3次访问内存(2读1写)):从两个内存单元中分别读取两个数,将其进行加法操作后,得到的结果写入另一个内存单元中;Triad(综合操作,3次访问内存(2读1写)):先从内存中读取一个数,与一个常数相乘得到一个乘积,然后从另一个内存单元中读取一个数与刚才乘积结果相加,得到的结果写入内存;
测试结果一般的规律是Add > Triad > Copy > Scale;
单核Stream测试,影响的因素除了内存控制器能力外,还有Core的ROB、Load/Store对其影响,因此不是单纯的内存带宽性能测试
多核Stream测试,通过多核同时发出大量内存访问请求,能够更加饱和地访问内存,从而测试到内存带宽的极限性能
官网地址:https://www.cs.virginia.edu/stream/
源码下载:
有C语言版本和Fortran语言版本,都需要自己下载源码后编译成可执行文件,再运行可编译出来的可执行文件输出测试结果;
官网源码地址(C语言版本):https://www.cs.virginia.edu/stream/FTP/Code/stream.c
官网源码地址(Fortran语言版本):https://www.cs.virginia.edu/stream/FTP/Code/stream.f
以下是C语言版本的源码:
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Program: STREAM */
/* Revision: $Id: stream.c,v 5.10 2013/01/17 16:01:06 mccalpin Exp mccalpin $ */
/* Original code developed by John D. McCalpin */
/* Programmers: John D. McCalpin */
/* Joe R. Zagar */
/* */
/* This program measures memory transfer rates in MB/s for simple */
/* computational kernels coded in C. */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Copyright 1991-2013: John D. McCalpin */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* License: */
/* 1. You are free to use this program and/or to redistribute */
/* this program. */
/* 2. You are free to modify this program for your own use, */
/* including commercial use, subject to the publication */
/* restrictions in item 3. */
/* 3. You are free to publish results obtained from running this */
/* program, or from works that you derive from this program, */
/* with the following limitations: */
/* 3a. In order to be referred to as "STREAM benchmark results", */
/* published results must be in conformance to the STREAM */
/* Run Rules, (briefly reviewed below) published at */
/* http://www.cs.virginia.edu/stream/ref.html */
/* and incorporated herein by reference. */
/* As the copyright holder, John McCalpin retains the */
/* right to determine conformity with the Run Rules. */
/* 3b. Results based on modified source code or on runs not in */
/* accordance with the STREAM Run Rules must be clearly */
/* labelled whenever they are published. Examples of */
/* proper labelling include: */
/* "tuned STREAM benchmark results" */
/* "based on a variant of the STREAM benchmark code" */
/* Other comparable, clear, and reasonable labelling is */
/* acceptable. */
/* 3c. Submission of results to the STREAM benchmark web site */
/* is encouraged, but not required. */
/* 4. Use of this program or creation of derived works based on this */
/* program constitutes acceptance of these licensing restrictions. */
/* 5. Absolutely no warranty is expressed or implied. */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
# include <stdio.h>
# include <unistd.h>
# include <math.h>
# include <float.h>
# include <limits.h>
# include <sys/time.h>/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------* INSTRUCTIONS:** 1) STREAM requires different amounts of memory to run on different* systems, depending on both the system cache size(s) and the* granularity of the system timer.* You should adjust the value of 'STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE' (below)* to meet *both* of the following criteria:* (a) Each array must be at least 4 times the size of the* available cache memory. I don't worry about the difference* between 10^6 and 2^20, so in practice the minimum array size* is about 3.8 times the cache size.* Example 1: One Xeon E3 with 8 MB L3 cache* STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE should be >= 4 million, giving* an array size of 30.5 MB and a total memory requirement* of 91.5 MB. * Example 2: Two Xeon E5's with 20 MB L3 cache each (using OpenMP)* STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE should be >= 20 million, giving* an array size of 153 MB and a total memory requirement* of 458 MB. * (b) The size should be large enough so that the 'timing calibration'* output by the program is at least 20 clock-ticks. * Example: most versions of Windows have a 10 millisecond timer* granularity. 20 "ticks" at 10 ms/tic is 200 milliseconds.* If the chip is capable of 10 GB/s, it moves 2 GB in 200 msec.* This means the each array must be at least 1 GB, or 128M elements.** Version 5.10 increases the default array size from 2 million* elements to 10 million elements in response to the increasing* size of L3 caches. The new default size is large enough for caches* up to 20 MB. * Version 5.10 changes the loop index variables from "register int"* to "ssize_t", which allows array indices >2^32 (4 billion)* on properly configured 64-bit systems. Additional compiler options* (such as "-mcmodel=medium") may be required for large memory runs.** Array size can be set at compile time without modifying the source* code for the (many) compilers that support preprocessor definitions* on the compile line. E.g.,* gcc -O -DSTREAM_ARRAY_SIZE=100000000 stream.c -o stream.100M* will override the default size of 10M with a new size of 100M elements* per array.*/
#ifndef STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE
# define STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE 10000000
#endif/* 2) STREAM runs each kernel "NTIMES" times and reports the *best* result* for any iteration after the first, therefore the minimum value* for NTIMES is 2.* There are no rules on maximum allowable values for NTIMES, but* values larger than the default are unlikely to noticeably* increase the reported performance.* NTIMES can also be set on the compile line without changing the source* code using, for example, "-DNTIMES=7".*/
#ifdef NTIMES
#if NTIMES<=1
# define NTIMES 10
#endif
#endif
#ifndef NTIMES
# define NTIMES 10
#endif/* Users are allowed to modify the "OFFSET" variable, which *may* change the* relative alignment of the arrays (though compilers may change the * effective offset by making the arrays non-contiguous on some systems). * Use of non-zero values for OFFSET can be especially helpful if the* STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE is set to a value close to a large power of 2.* OFFSET can also be set on the compile line without changing the source* code using, for example, "-DOFFSET=56".*/
#ifndef OFFSET
# define OFFSET 0
#endif/** 3) Compile the code with optimization. Many compilers generate* unreasonably bad code before the optimizer tightens things up. * If the results are unreasonably good, on the other hand, the* optimizer might be too smart for me!** For a simple single-core version, try compiling with:* cc -O stream.c -o stream* This is known to work on many, many systems....** To use multiple cores, you need to tell the compiler to obey the OpenMP* directives in the code. This varies by compiler, but a common example is* gcc -O -fopenmp stream.c -o stream_omp* The environment variable OMP_NUM_THREADS allows runtime control of the * number of threads/cores used when the resulting "stream_omp" program* is executed.** To run with single-precision variables and arithmetic, simply add* -DSTREAM_TYPE=float* to the compile line.* Note that this changes the minimum array sizes required --- see (1) above.** The preprocessor directive "TUNED" does not do much -- it simply causes the * code to call separate functions to execute each kernel. Trivial versions* of these functions are provided, but they are *not* tuned -- they just * provide predefined interfaces to be replaced with tuned code.*** 4) Optional: Mail the results to mccalpin@cs.virginia.edu* Be sure to include info that will help me understand:* a) the computer hardware configuration (e.g., processor model, memory type)* b) the compiler name/version and compilation flags* c) any run-time information (such as OMP_NUM_THREADS)* d) all of the output from the test case.** Thanks!**-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/# define HLINE "-------------------------------------------------------------\n"# ifndef MIN
# define MIN(x,y) ((x)<(y)?(x):(y))
# endif
# ifndef MAX
# define MAX(x,y) ((x)>(y)?(x):(y))
# endif#ifndef STREAM_TYPE
#define STREAM_TYPE double
#endifstatic STREAM_TYPE a[STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE+OFFSET],b[STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE+OFFSET],c[STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE+OFFSET];static double avgtime[4] = {0}, maxtime[4] = {0},mintime[4] = {FLT_MAX,FLT_MAX,FLT_MAX,FLT_MAX};static char *label[4] = {"Copy: ", "Scale: ","Add: ", "Triad: "};static double bytes[4] = {2 * sizeof(STREAM_TYPE) * STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE,2 * sizeof(STREAM_TYPE) * STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE,3 * sizeof(STREAM_TYPE) * STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE,3 * sizeof(STREAM_TYPE) * STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE};extern double mysecond();
extern void checkSTREAMresults();
#ifdef TUNED
extern void tuned_STREAM_Copy();
extern void tuned_STREAM_Scale(STREAM_TYPE scalar);
extern void tuned_STREAM_Add();
extern void tuned_STREAM_Triad(STREAM_TYPE scalar);
#endif
#ifdef _OPENMP
extern int omp_get_num_threads();
#endif
int
main(){int quantum, checktick();int BytesPerWord;int k;ssize_t j;STREAM_TYPE scalar;double t, times[4][NTIMES];/* --- SETUP --- determine precision and check timing --- */printf(HLINE);printf("STREAM version $Revision: 5.10 $\n");printf(HLINE);BytesPerWord = sizeof(STREAM_TYPE);printf("This system uses %d bytes per array element.\n",BytesPerWord);printf(HLINE);
#ifdef Nprintf("***** WARNING: ******\n");printf(" It appears that you set the preprocessor variable N when compiling this code.\n");printf(" This version of the code uses the preprocesor variable STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE to control the array size\n");printf(" Reverting to default value of STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE=%llu\n",(unsigned long long) STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE);printf("***** WARNING: ******\n");
#endifprintf("Array size = %llu (elements), Offset = %d (elements)\n" , (unsigned long long) STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE, OFFSET);printf("Memory per array = %.1f MiB (= %.1f GiB).\n", BytesPerWord * ( (double) STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE / 1024.0/1024.0),BytesPerWord * ( (double) STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE / 1024.0/1024.0/1024.0));printf("Total memory required = %.1f MiB (= %.1f GiB).\n",(3.0 * BytesPerWord) * ( (double) STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE / 1024.0/1024.),(3.0 * BytesPerWord) * ( (double) STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE / 1024.0/1024./1024.));printf("Each kernel will be executed %d times.\n", NTIMES);printf(" The *best* time for each kernel (excluding the first iteration)\n"); printf(" will be used to compute the reported bandwidth.\n");#ifdef _OPENMPprintf(HLINE);
#pragma omp parallel {
#pragma omp master{k = omp_get_num_threads();printf ("Number of Threads requested = %i\n",k);}}
#endif#ifdef _OPENMPk = 0;
#pragma omp parallel
#pragma omp atomic k++;printf ("Number of Threads counted = %i\n",k);
#endif/* Get initial value for system clock. */
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++) {a[j] = 1.0;b[j] = 2.0;c[j] = 0.0;}printf(HLINE);if ( (quantum = checktick()) >= 1) printf("Your clock granularity/precision appears to be ""%d microseconds.\n", quantum);else {printf("Your clock granularity appears to be ""less than one microsecond.\n");quantum = 1;}t = mysecond();
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j = 0; j < STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)a[j] = 2.0E0 * a[j];t = 1.0E6 * (mysecond() - t);printf("Each test below will take on the order"" of %d microseconds.\n", (int) t );printf(" (= %d clock ticks)\n", (int) (t/quantum) );printf("Increase the size of the arrays if this shows that\n");printf("you are not getting at least 20 clock ticks per test.\n");printf(HLINE);printf("WARNING -- The above is only a rough guideline.\n");printf("For best results, please be sure you know the\n");printf("precision of your system timer.\n");printf(HLINE);/* --- MAIN LOOP --- repeat test cases NTIMES times --- */scalar = 3.0;for (k=0; k<NTIMES; k++){times[0][k] = mysecond();
#ifdef TUNEDtuned_STREAM_Copy();
#else
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)c[j] = a[j];
#endiftimes[0][k] = mysecond() - times[0][k];times[1][k] = mysecond();
#ifdef TUNEDtuned_STREAM_Scale(scalar);
#else
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)b[j] = scalar*c[j];
#endiftimes[1][k] = mysecond() - times[1][k];times[2][k] = mysecond();
#ifdef TUNEDtuned_STREAM_Add();
#else
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)c[j] = a[j]+b[j];
#endiftimes[2][k] = mysecond() - times[2][k];times[3][k] = mysecond();
#ifdef TUNEDtuned_STREAM_Triad(scalar);
#else
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)a[j] = b[j]+scalar*c[j];
#endiftimes[3][k] = mysecond() - times[3][k];}/* --- SUMMARY --- */for (k=1; k<NTIMES; k++) /* note -- skip first iteration */{for (j=0; j<4; j++){avgtime[j] = avgtime[j] + times[j][k];mintime[j] = MIN(mintime[j], times[j][k]);maxtime[j] = MAX(maxtime[j], times[j][k]);}}printf("Function Best Rate MB/s Avg time Min time Max time\n");for (j=0; j<4; j++) {avgtime[j] = avgtime[j]/(double)(NTIMES-1);printf("%s%12.1f %11.6f %11.6f %11.6f\n", label[j],1.0E-06 * bytes[j]/mintime[j],avgtime[j],mintime[j],maxtime[j]);}printf(HLINE);/* --- Check Results --- */checkSTREAMresults();printf(HLINE);return 0;
}# define M 20int
checktick(){int i, minDelta, Delta;double t1, t2, timesfound[M];/* Collect a sequence of M unique time values from the system. */for (i = 0; i < M; i++) {t1 = mysecond();while( ((t2=mysecond()) - t1) < 1.0E-6 );timesfound[i] = t1 = t2;}/** Determine the minimum difference between these M values.* This result will be our estimate (in microseconds) for the* clock granularity.*/minDelta = 1000000;for (i = 1; i < M; i++) {Delta = (int)( 1.0E6 * (timesfound[i]-timesfound[i-1]));minDelta = MIN(minDelta, MAX(Delta,0));}return(minDelta);}/* A gettimeofday routine to give access to the wallclock timer on most UNIX-like systems. */#include <sys/time.h>double mysecond()
{struct timeval tp;struct timezone tzp;int i;i = gettimeofday(&tp,&tzp);return ( (double) tp.tv_sec + (double) tp.tv_usec * 1.e-6 );
}#ifndef abs
#define abs(a) ((a) >= 0 ? (a) : -(a))
#endif
void checkSTREAMresults ()
{STREAM_TYPE aj,bj,cj,scalar;STREAM_TYPE aSumErr,bSumErr,cSumErr;STREAM_TYPE aAvgErr,bAvgErr,cAvgErr;double epsilon;ssize_t j;int k,ierr,err;/* reproduce initialization */aj = 1.0;bj = 2.0;cj = 0.0;/* a[] is modified during timing check */aj = 2.0E0 * aj;/* now execute timing loop */scalar = 3.0;for (k=0; k<NTIMES; k++){cj = aj;bj = scalar*cj;cj = aj+bj;aj = bj+scalar*cj;}/* accumulate deltas between observed and expected results */aSumErr = 0.0;bSumErr = 0.0;cSumErr = 0.0;for (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++) {aSumErr += abs(a[j] - aj);bSumErr += abs(b[j] - bj);cSumErr += abs(c[j] - cj);// if (j == 417) printf("Index 417: c[j]: %f, cj: %f\n",c[j],cj); // MCCALPIN}aAvgErr = aSumErr / (STREAM_TYPE) STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE;bAvgErr = bSumErr / (STREAM_TYPE) STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE;cAvgErr = cSumErr / (STREAM_TYPE) STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE;if (sizeof(STREAM_TYPE) == 4) {epsilon = 1.e-6;}else if (sizeof(STREAM_TYPE) == 8) {epsilon = 1.e-13;}else {printf("WEIRD: sizeof(STREAM_TYPE) = %lu\n",sizeof(STREAM_TYPE));epsilon = 1.e-6;}err = 0;if (abs(aAvgErr/aj) > epsilon) {err++;printf ("Failed Validation on array a[], AvgRelAbsErr > epsilon (%e)\n",epsilon);printf (" Expected Value: %e, AvgAbsErr: %e, AvgRelAbsErr: %e\n",aj,aAvgErr,abs(aAvgErr)/aj);ierr = 0;for (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++) {if (abs(a[j]/aj-1.0) > epsilon) {ierr++;
#ifdef VERBOSEif (ierr < 10) {printf(" array a: index: %ld, expected: %e, observed: %e, relative error: %e\n",j,aj,a[j],abs((aj-a[j])/aAvgErr));}
#endif}}printf(" For array a[], %d errors were found.\n",ierr);}if (abs(bAvgErr/bj) > epsilon) {err++;printf ("Failed Validation on array b[], AvgRelAbsErr > epsilon (%e)\n",epsilon);printf (" Expected Value: %e, AvgAbsErr: %e, AvgRelAbsErr: %e\n",bj,bAvgErr,abs(bAvgErr)/bj);printf (" AvgRelAbsErr > Epsilon (%e)\n",epsilon);ierr = 0;for (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++) {if (abs(b[j]/bj-1.0) > epsilon) {ierr++;
#ifdef VERBOSEif (ierr < 10) {printf(" array b: index: %ld, expected: %e, observed: %e, relative error: %e\n",j,bj,b[j],abs((bj-b[j])/bAvgErr));}
#endif}}printf(" For array b[], %d errors were found.\n",ierr);}if (abs(cAvgErr/cj) > epsilon) {err++;printf ("Failed Validation on array c[], AvgRelAbsErr > epsilon (%e)\n",epsilon);printf (" Expected Value: %e, AvgAbsErr: %e, AvgRelAbsErr: %e\n",cj,cAvgErr,abs(cAvgErr)/cj);printf (" AvgRelAbsErr > Epsilon (%e)\n",epsilon);ierr = 0;for (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++) {if (abs(c[j]/cj-1.0) > epsilon) {ierr++;
#ifdef VERBOSEif (ierr < 10) {printf(" array c: index: %ld, expected: %e, observed: %e, relative error: %e\n",j,cj,c[j],abs((cj-c[j])/cAvgErr));}
#endif}}printf(" For array c[], %d errors were found.\n",ierr);}if (err == 0) {printf ("Solution Validates: avg error less than %e on all three arrays\n",epsilon);}
#ifdef VERBOSEprintf ("Results Validation Verbose Results: \n");printf (" Expected a(1), b(1), c(1): %f %f %f \n",aj,bj,cj);printf (" Observed a(1), b(1), c(1): %f %f %f \n",a[1],b[1],c[1]);printf (" Rel Errors on a, b, c: %e %e %e \n",abs(aAvgErr/aj),abs(bAvgErr/bj),abs(cAvgErr/cj));
#endif
}#ifdef TUNED
/* stubs for "tuned" versions of the kernels */
void tuned_STREAM_Copy()
{ssize_t j;
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)c[j] = a[j];
}void tuned_STREAM_Scale(STREAM_TYPE scalar)
{ssize_t j;
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)b[j] = scalar*c[j];
}void tuned_STREAM_Add()
{ssize_t j;
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)c[j] = a[j]+b[j];
}void tuned_STREAM_Triad(STREAM_TYPE scalar)
{ssize_t j;
#pragma omp parallel forfor (j=0; j<STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE; j++)a[j] = b[j]+scalar*c[j];
}
/* end of stubs for the "tuned" versions of the kernels */
#endif
源码编译:
可以使用gcc直接编译,如果需要移植到其他平台可以使用交叉编译
gcc编译(带编译参数):
gcc -O3 -mtune=native -march=native -fopenmp -DSTREAM_ARRAY_SIZE=200000000 -DNTIMES=100 stream.c -o stream
gcc编译(默认参数):
gcc stream.c -o stream
交叉编译器编译(默认参数):
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc stream.c -o stream
编译参数说明:
-O3 :指定最高编译优化级别,如-O0,-O1,-O2,-O3-fopenmp:启用OpenMP,适应多处理器环境,更能得到内存带宽实际最大值。开启后,程序默认运行线程为CPU线程数-DN=2000000(部分版本是-DSTREAM_ARRAY_SIZE=200000000):指定测试数组a[]、b[]、c[]的大小(Array size)
该值对测试结果影响较大(5.9版本默认值2000000,。若stream.c为5.10版本,参数名变为-DSTREAM_ARRAY_SIZE,默认值10000000);
注意:必须设置测试数组大小远大于CPU 最高级缓存(一般为L3 Cache)的大小,否则就是测试CPU缓存的吞吐性能,而非内存吞吐性能;
推荐计算公式:{最高级缓存X MB}×1024×1024×4.1×CPU路数/8,结果取整数;
公式说明:由于stream.c源码推荐设置至少4倍最高级缓存,且STREAM_ARRAY_SIZE为double类型=8 Byte。所以公式为:最高级缓存(单位:Byte)×4.1倍×CPU路数/8;
eg:测试机器是双路CPU,最高级缓存32MB,则计算值为32×1024×1024×4.1×2/8≈34393292-DNTIMES=10:执行的次数,并从这些结果中选最优值-mtune=native -march=native:针对CPU指令的优化-mcmodel=medium:当单个Memory Array Size 大于2GB时需要设置此参数;
新的gcc已经不支持‘-mcmodel=medium’参数了,可以改为“-mcmodel=large”、“-mcmodel=small”、“-mcmodel=tiny”-DOFFSET=4096:数组的偏移,一般可以不定义
使用及输出结果:
设置运行时的进程数(可设可不设)
# export OMP_NUM_THREADS=x x为自定义的要使用的处理器数量
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=8
直接运行编译出来的stream
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=8
./stream
编译及运行结果
root@ubuntu:~/app/stream_ddr$ gcc stream.c -o stream
root@ubuntu:~/app/stream_ddr$ export OMP_NUM_THREADS=8
root@ubuntu:~/app/stream_ddr$ ./stream
-------------------------------------------------------------
STREAM version $Revision: 5.10 $
-------------------------------------------------------------
This system uses 8 bytes per array element.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Array size = 10000000 (elements), Offset = 0 (elements)
Memory per array = 76.3 MiB (= 0.1 GiB).
Total memory required = 228.9 MiB (= 0.2 GiB).
Each kernel will be executed 10 times.The *best* time for each kernel (excluding the first iteration)will be used to compute the reported bandwidth.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Your clock granularity/precision appears to be 1 microseconds.
Each test below will take on the order of 20046 microseconds.(= 20046 clock ticks)
Increase the size of the arrays if this shows that
you are not getting at least 20 clock ticks per test.
-------------------------------------------------------------
WARNING -- The above is only a rough guideline.
For best results, please be sure you know the
precision of your system timer.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Function Best Rate MB/s Avg time Min time Max time
Copy: 7940.8 0.020932 0.020149 0.023032
Scale: 9247.6 0.018226 0.017302 0.019239
Add: 10917.1 0.022417 0.021984 0.023661
Triad: 10522.6 0.023232 0.022808 0.023928
-------------------------------------------------------------
Solution Validates: avg error less than 1.000000e-13 on all three arrays
-------------------------------------------------------------
在下面可以看到输出Copy、Scale、Add、Triad的数据读写速度及时间
-------------------------------------------------------------
Function Best Rate MB/s Avg time Min time Max time
Copy: 7940.8 0.020932 0.020149 0.023032
Scale: 9247.6 0.018226 0.017302 0.019239
Add: 10917.1 0.022417 0.021984 0.023661
Triad: 10522.6 0.023232 0.022808 0.023928
-------------------------------------------------------------
免责声明:本文内容含网络参考、作者编写等,内容版权归原作者所有,未经允许,禁止转载。如涉及作品版权问题,请与我们联系,我们将根据您提供的版权证明材料确认版权并支付稿酬或者删除内容。
相关文章:

Linux学习笔记-芯片性能检测
文章目录 概述Dhrystone(单核性能测试工具)简介:源码下载:源码编译:使用及输出结果 coremark(多核性能测试工具)简介:源码下载:源码编译:使用及输出结果&…...
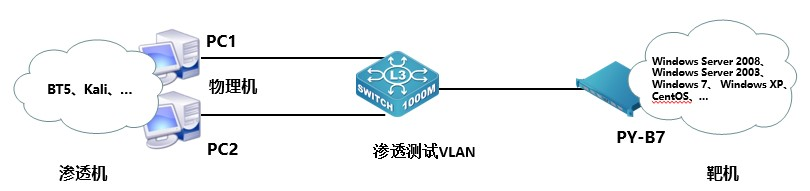
2023年网络安全比赛--综合渗透测试②(超详细)
一、竞赛时间 180分钟 共计3小时 二、竞赛阶段 竞赛阶段 任务阶段 竞赛任务 竞赛时间 分值 1.通过 PC 中的渗透测试平台 Kali 对服务器场景进行渗透测试,将扫描开放的所有端口当作flag提交(例:21,22,23); 2.通过 PC 中的渗透测试平台 Kali 对服务器场景进行渗透测试,将初…...

关于8位图像buffer显示到picturebox上
最终版本: void showbuffer2pictmod4(byte[] buffer, int ww, int hh, PictureBox destImg) { int mod ww % 4;//解决四位对齐问题20150716 int temproiw ww (4 - mod) % 4;//其实这都是和显示相关,处理图像其实不必…...
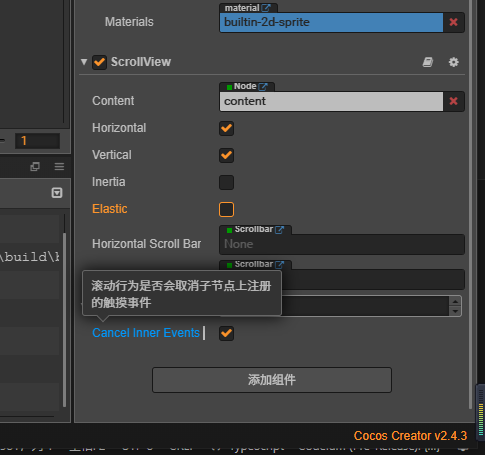
cocos游戏引擎制作的滚动框地图防止误点操作的简单方法
本篇文章主要讲解,使用cocos creator 来解决在我们日常滚动框开发中,滚动和触摸存在冲突的情况,导致的误触行为的解决办法。 日期:2023年11月25日 具体事项 说明:在我们滚动滚动框时,会出现误点的情况&…...

vue 使用vuex中的data数据引用问题
先上代码: this.userRoleInfo2 this.$store.state.userInfo this.userRoleInfo2.name 111 this.userRoleInfo2.orgName 222 this.userRoleInfo2.orgId 4444问题描述: 博主,定义了一个变量userRoleInfo2来接收了 从vuex中获取了userInfo…...

日志配置的一些思考
日志配置的一些思考 背景说明基础配置抽取子服务扩展配置 背景 基本所有的系统都需要完善的日志配置, 这里是一些常用的配置. 但是没有本地验证, 只能提供一份配置思路. 说明 不可直接用, 会报错, 提供一种配置思路. 不可直接用, 会报错, 提供一种配置思路. 不可直接用, 会报…...

阶梯排列硬币
题意: 你总共有 n 枚硬币,并计划将它们按阶梯状排列。对于一个由 k 行组成的阶梯,其第 i 行必须正好有 i 枚硬币。阶梯的最后一行 可能 是不完整的。 给你一个数字 n ,计算并返回可形成 完整阶梯行 的总行数。 示例 1ÿ…...

HarmonyOS应用开发者高级认证【题库答案】
HarmonyOS应用开发者基础认证【题库答案】 一、判断题 云函数打包完成后,需要到AppGallery Connect创建对应函数的触发器才可以在端侧中调用(错)在column和Row容器组件中,aligntems用于设置子组件在主轴方向上的对齐格式…...

【解答】关于Linux内核的一些疑问
GNU计划是什么 GNU计划是由理查德斯托曼在1983年9月27日公开发起的自由软件集体协作计划,其目标是创建一套完全自由的操作系统GNU。这个操作系统的内容软件完全以GPL方式发布,意味着用户拥有运行、复制、分发、学习、修改和改进该软件的自由。 GNU的命名…...
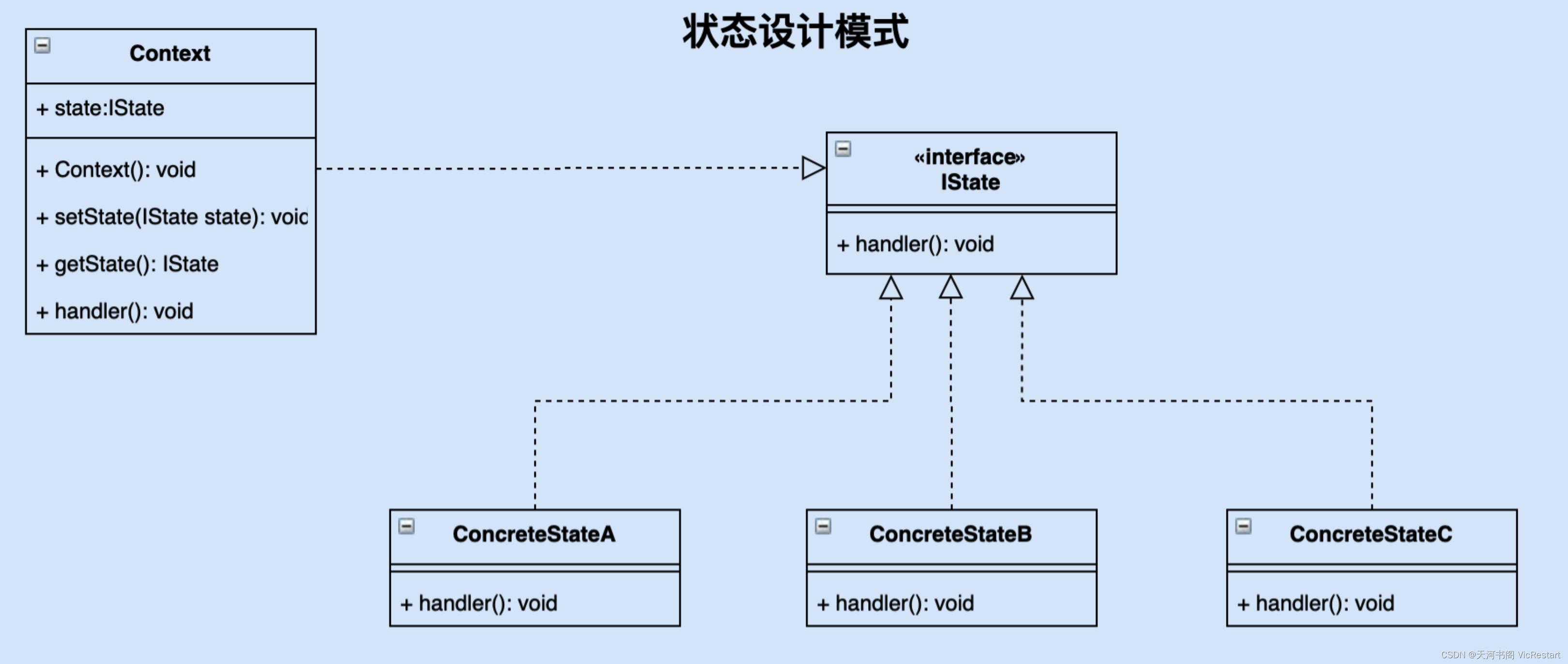
状态设计模式是什么?什么是 State 状态设计模式?Python 状态设计模式示例代码
什么是 State 状态设计模式? 状态设计模式是一种行为型设计模式,它允许一个对象在其内部状态发生改变时改变其行为,使其看起来好像改变了其类。状态模式主要解决的问题是:当一个对象的行为取决于它的状态,并且在运行时…...
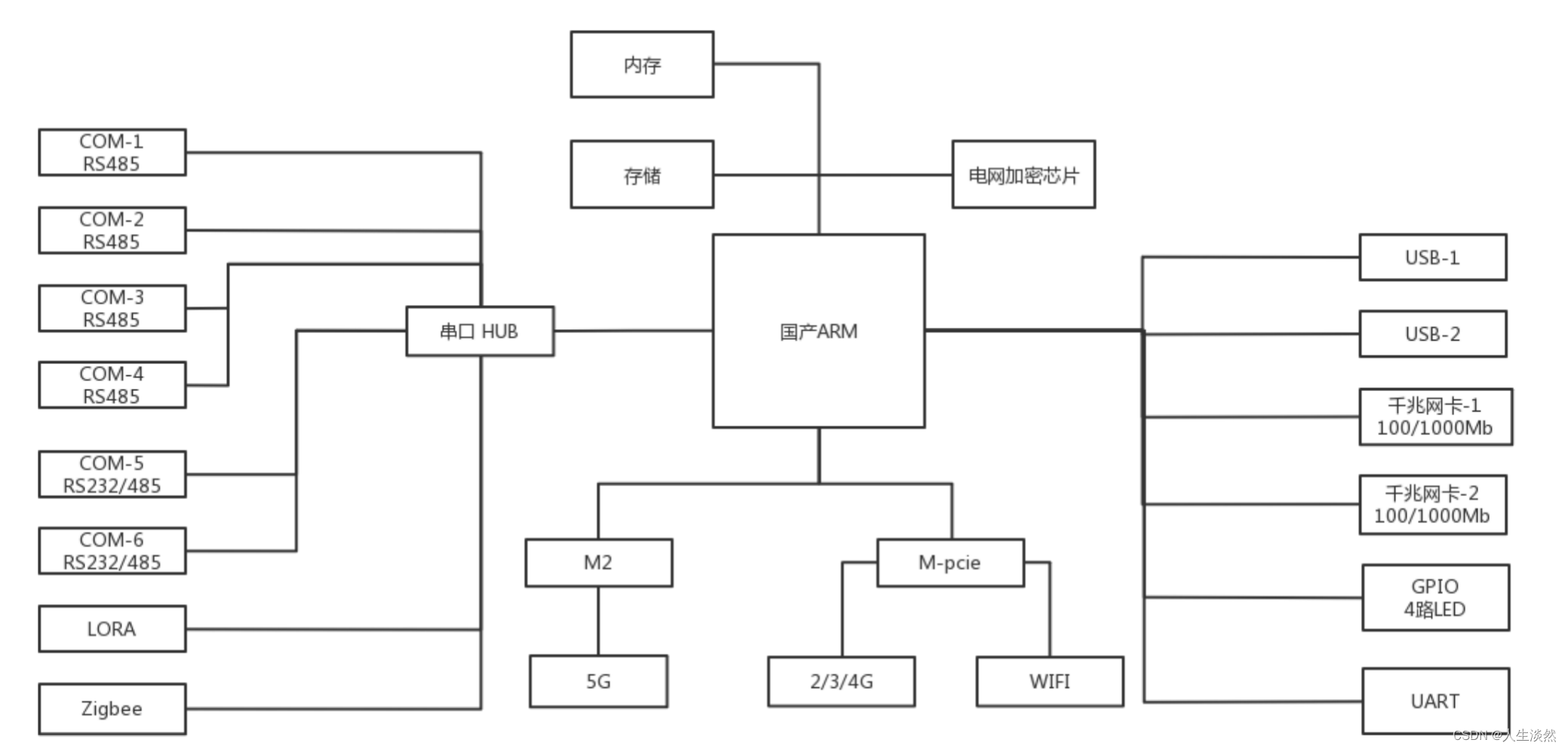
电力感知边缘计算技术网关产品设计方案-硬件方案
网关硬件架构设计图: 1.配置方案 配置差异 A类网关 B类网关 CPU...

【线性代数与矩阵论】坐标变换与相似矩阵
坐标变换与相似矩阵 2023年11月4日 #algebra 文章目录 坐标变换与相似矩阵1. 基变换与坐标变换2. 相似变换下链 1. 基变换与坐标变换 坐标变换与基变换都要通过过渡矩阵 A A A 来实现。设有一向量 f ⃗ \vec f f , x x x 是在基 α \alpha α 下该向量的坐标…...

C语言编译过程再解析
多年以前,分析过编译过程,并写了一篇博客,现在对编译过程有了更广阔的认识,记录在此 编译过程 中的 链接与 编译 编译过程分为1. 预处理2. 编译3. 汇编4. 链接其中有 2个过程比较特殊,1. 编译2. 链接对于C程序来说,链接分为提前链接(静态链接)对应下图第1行运行时链接(动态链…...
GeoTrust证书
GeoTrust证书的特点与优势: 1,广泛的浏览器兼容性: GeoTrust证书得到了各大主流浏览器的广泛支持,确保您的网站能够在用户使用的任何浏览器上获得正常的安全连接。 2,强大的加密技术: GeoTrust采用先进的…...
肾合胶囊 | 冬不养肾春易病,若出现了这六大表现,小心是肾虚!
冬季作为一年中最寒冷的季节,自然万物皆静谧闭藏,而肾具有潜藏、封藏、闭藏精气的特点,是封藏之本,肾的脏腑特性与冬季相通应,所以在冬季更应该重视养肾。 而现在正值初冬,正是开始养肾的最佳时间。此时培…...

IDEA中常用快捷键
整理了一些IDEA开发常用的快捷键: 快捷键组合实现效果psvm Tab键 / main Tab键public static void main(String[] args)sout Tab键System.out.println()Ctrl X删除当前行Ctrl D复制当前行AltInsert(或右键Generate)生成代码(如get,set方法,构造函数等)CtrlAltT…...

注解之@Configuration、@Bean、@Component
目录 前言 Component:通用的注解! Bean 引入第三方的类 Configuration 前言 首先:我们先简单描述一下这三个的作用 Component注解表明一个类会作为组件类,并告知Spring要为这个类创建bean。 Bean注解告诉Spring这个方法将会…...

【Web安全】sql注入绕过技法
sql注入绕过技法 1. 注释符号绕过 原理:SQL注释符号(如--, /* */)可以用来忽略查询的一部分,特别是在注入点之后的部分。这对于绕过需要闭合的查询或移除查询余下部分的情况特别有用。 -- 注释内容 # 注释内容 /*注释内容*/ ;2…...
Axios使用方式
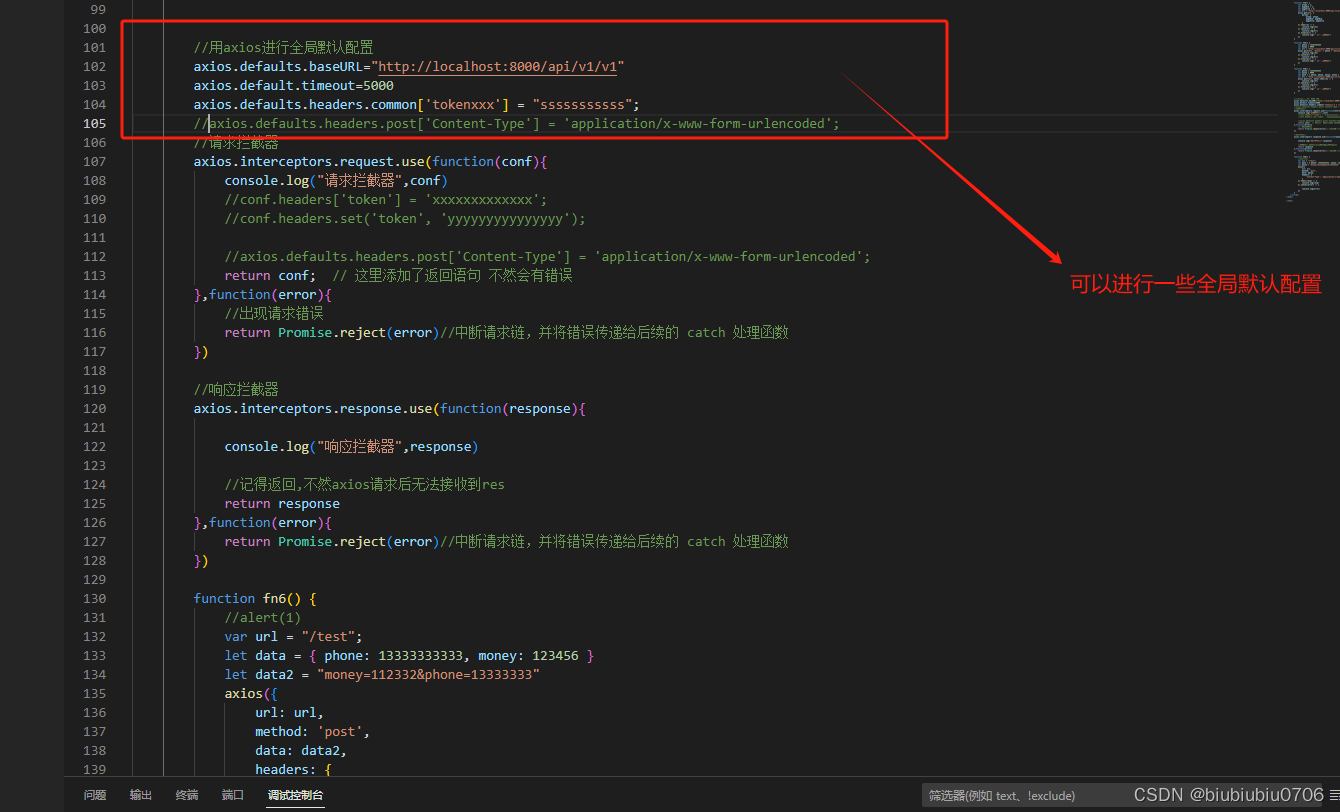
ajax是JQUERY封装的XMLHttprequest用来发送http请求 Axios简单点说它就是一个js库,支持ajax请求,发送axios请求功能更加丰富,丰富在哪不知道 1.npm使用方式 vue项目中 npm install axios 2.cdn方式 <script src"https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js">…...

kotlin 内置函数对数组进行各种操作
以下是一些常见的用法示例: plus() 函数将两个数组合并成一个数组。plus() 函数是 Kotlin 标准库中的一个扩展函数,可以用于合并两个同类型的数组。 fun main() {val array1 arrayOf(1, 2, 3)val array2 arrayOf(4, 5, 6)val mergedArray array1.plu…...

mongodb源码分析session执行handleRequest命令find过程
mongo/transport/service_state_machine.cpp已经分析startSession创建ASIOSession过程,并且验证connection是否超过限制ASIOSession和connection是循环接受客户端命令,把数据流转换成Message,状态转变流程是:State::Created 》 St…...

Qt Widget类解析与代码注释
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget) {ui->setupUi(this); }Widget::~Widget() {delete ui; }//解释这串代码,写上注释 当然可以!这段代码是 Qt …...

376. Wiggle Subsequence
376. Wiggle Subsequence 代码 class Solution { public:int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int>& nums) {int n nums.size();int res 1;int prediff 0;int curdiff 0;for(int i 0;i < n-1;i){curdiff nums[i1] - nums[i];if( (prediff > 0 && curdif…...
剑指offer20_链表中环的入口节点
链表中环的入口节点 给定一个链表,若其中包含环,则输出环的入口节点。 若其中不包含环,则输出null。 数据范围 节点 val 值取值范围 [ 1 , 1000 ] [1,1000] [1,1000]。 节点 val 值各不相同。 链表长度 [ 0 , 500 ] [0,500] [0,500]。 …...
)
postgresql|数据库|只读用户的创建和删除(备忘)
CREATE USER read_only WITH PASSWORD 密码 -- 连接到xxx数据库 \c xxx -- 授予对xxx数据库的只读权限 GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE xxx TO read_only; GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO read_only; GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO read_only; GRANT EXECUTE O…...

laravel8+vue3.0+element-plus搭建方法
创建 laravel8 项目 composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel8 8.* 安装 laravel/ui composer require laravel/ui 修改 package.json 文件 "devDependencies": {"vue/compiler-sfc": "^3.0.7","axios": …...

使用Matplotlib创建炫酷的3D散点图:数据可视化的新维度
文章目录 基础实现代码代码解析进阶技巧1. 自定义点的大小和颜色2. 添加图例和样式美化3. 真实数据应用示例实用技巧与注意事项完整示例(带样式)应用场景在数据科学和可视化领域,三维图形能为我们提供更丰富的数据洞察。本文将手把手教你如何使用Python的Matplotlib库创建引…...
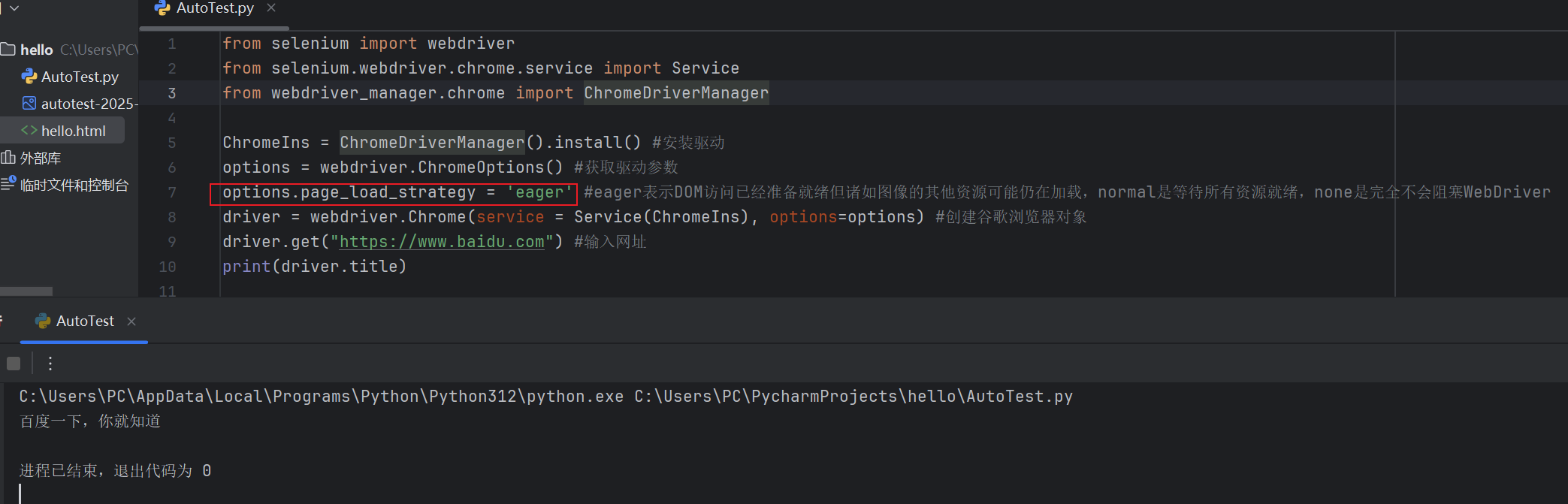
Selenium常用函数介绍
目录 一,元素定位 1.1 cssSeector 1.2 xpath 二,操作测试对象 三,窗口 3.1 案例 3.2 窗口切换 3.3 窗口大小 3.4 屏幕截图 3.5 关闭窗口 四,弹窗 五,等待 六,导航 七,文件上传 …...

Docker拉取MySQL后数据库连接失败的解决方案
在使用Docker部署MySQL时,拉取并启动容器后,有时可能会遇到数据库连接失败的问题。这种问题可能由多种原因导致,包括配置错误、网络设置问题、权限问题等。本文将分析可能的原因,并提供解决方案。 一、确认MySQL容器的运行状态 …...

用鸿蒙HarmonyOS5实现中国象棋小游戏的过程
下面是一个基于鸿蒙OS (HarmonyOS) 的中国象棋小游戏的实现代码。这个实现使用Java语言和鸿蒙的Ability框架。 1. 项目结构 /src/main/java/com/example/chinesechess/├── MainAbilitySlice.java // 主界面逻辑├── ChessView.java // 游戏视图和逻辑├──…...
