【C++】日期类的实现
在上篇博客中我们已经学习了C++中的运算符重载,我们说,操作符只能对于内置类型进行操作,对自定义类型我们需要自己定义函数去实现一系列的操作
那么这篇博客我们就专门把日期这个类单独拿出来写一下它都有哪些有意义的可以重载的运算符,这个函数我们要放到类里面为了访问私有的成员变量,但是函数声明和定义可以分到两个文件中写,只需要标识一下它属于哪个类就行。还有我们之前说过的一点,缺省参数只能声明给,定义不用给,因为编译器怕你给的不一样。
下面一个类当中首先是成员变量年月日我就不说了,下面是构造函数,我们就写一个全缺省的函数,默认不传参数年月日都是一,但是我们要判断传过来的数字是否合法,不合法要做出提醒,可以assert断言,也可以就打印一下。
//声明
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);
//定义
Date::Date(int year, int month , int day ) {_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (_year < 1 || _month < 1 || _month>12 || _day<1 || _day>GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) {cout << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日";cout << "日期非法" << endl;}
}
下面比较两个日期的大小和是否相等其实逻辑就比较简单了,写上一个后边的直接赋用就行
比如说
bool Date:: operator==(const Date& n) {return _year == n._year && _month == n._month && _day == n._day;
}bool Date::operator!=(const Date& n) {return !(*this == n);
}
写了等于那么不等于不就是它的相反嘛
下面的大于小于也是同理
bool Date:: operator<(const Date& n) {if (_year < n._year) {return true;}if (_year == n._year && _month < n._month) {return true;}if (_year == n._year && _month == n._month && _day < n._day) {return true;}return false;
}bool Date::operator<=(const Date& n) {return ((*this < n) || (*this == n));
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& n) {return !(*this <= n);
}bool Date:: operator>=(const Date& n) {//return *this > n || *this == n;return !(*this < n);
}
下面是加减运算,首先日期加日期是没有意义的,但是日期加减天数是有意义的,这个该如何去加减呢?我们可以先把天数加到年月日的日数上,如果合法就不用动了,如果多余本月的该有的天数就进位到月上。为了方便就得有一个得到该年该月的天数的一个函数
int Date :: GetMonthDay(int year, int month) {assert(year >= 1 && month >= 1 && month <= 12);int monthArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if ((month == 2) && (((year % 400) == 0) || ((year % 4) == 0 && (year % 100) != 0))) {return 29;}return monthArray[month];
}
下边就是日期加减一个天数
Date& Date:: operator+=(int day) {if (day < 0) {return *this -= (-day);}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) {_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13) {++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}Date Date:: operator+(int day) {Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;
}Date& Date:: operator-=(int day) {if (day < 0) {return *this += (-day);}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0) {--_month;if (_month == 0) {--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}Date Date:: operator-(int day) {Date tmp(*this);tmp -= day;return tmp;
}
我这里的加减是赋用的加等和减等,当然了我们也可以让加等和减等赋用加减,我们也来实现一下,然后看看这两种情况哪个好
Date Date:: operator+(int day) {Date tmp=*this;tmp._day += day;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month)) {tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);tmp._month++;if (tmp._month == 13) {++tmp._year;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;
}
Date& Date:: operator+=(int day) {*this = *this + day;return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day) {Date tmp(*this);tmp._day -= day;while (tmp._day <= 0) {--tmp._month;if (tmp._month == 0) {tmp._year--;tmp._month = 12;}tmp._day += GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);}return tmp;
}
Date& Date:: operator-=(int day) {*this = *this - day;return *this;
}
我们先看第一种情况,加等其实是不需要进行拷贝的,而加则需要拷贝两次。第二种情况,加要拷贝两次,而加等要拷贝三次,所以我们可以看出第一种情况更好一些
我们这里的加等还有一个问题,如果我们写的是加等一个负数或者说减等一个负数时就会有问题,这时就会有问题,我们只需要转到相反的就行了,就类似这样:
Date& Date:: operator-=(int day) {if (day < 0) {return *this -= (-day);}
下面就是++了,但是++有前置,有后置,这时我们就规定后置++要在形参上写上一个int,写别的不行
Date& Date::operator++() {*this += 1;return *this;
}Date Date:: operator++(int) {Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp;
}Date& Date::operator--() {*this -= 1;return *this;
}Date Date:: operator--(int) {Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;
}下面的日期减日期也是有意义的,就是相差的天数
简单的话就是从小的日期一直加直到大的日期,看一共加了多少回
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) {int flag = -1;Date min = *this;Date max = d;if (*this > d) {min = d;max = *this;flag = 1;}int n = 0;while (min < max) {++min;++n;}return n*flag;
}
要想效率更高些就要整年整年的加,后面的零碎的天数就从1月1日开始数,大的日期就加上,小的日期就减去
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) {int flag = 1;Date max = *this;Date min = d;if (*this < d) {max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}int n = 0;int y = min._year;while (y != max._year) {if (y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0 || y % 400 == 0) {n += 366;}else {n += 365;}y++;}int m1 = 1;int m2 = 1;while (m1 < max._month) {n += GetMonthDay(max._year, m1);m1++;}while (m2 < min._month) {n -= GetMonthDay(min._year, m2);m2++;}n = n + max._day - min._day;return n;
}
下面是Date.h中所有代码
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
class Date {
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print();int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);bool operator==(const Date& n);bool operator!=(const Date& n);bool operator<(const Date& n);bool operator<=(const Date& n);bool operator>(const Date& n);bool operator>=(const Date& n);Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day);Date& operator-=(int day);Date operator-(int day);Date& operator++();//前置++Date operator++(int);//后置++Date& operator--();Date operator--(int);int operator-(const Date& d);
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
Date.cpp文件中的代码
#include"Date.h"
Date::Date(int year, int month , int day ) {_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (_year < 1 || _month < 1 || _month>12 || _day<1 || _day>GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) {cout << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日";cout << "日期非法" << endl;}
}void Date::Print() {cout << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;
}int Date :: GetMonthDay(int year, int month) {assert(year >= 1 && month >= 1 && month <= 12);int monthArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if ((month == 2) && (((year % 400) == 0) || ((year % 4) == 0 && (year % 100) != 0))) {return 29;}return monthArray[month];
}bool Date:: operator==(const Date& n) {return _year == n._year && _month == n._month && _day == n._day;
}bool Date::operator!=(const Date& n) {return !(*this == n);
}bool Date:: operator<(const Date& n) {if (_year < n._year) {return true;}if (_year == n._year && _month < n._month) {return true;}if (_year == n._year && _month == n._month && _day < n._day) {return true;}return false;
}bool Date::operator<=(const Date& n) {return ((*this < n) || (*this == n));
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& n) {return !(*this <= n);
}bool Date:: operator>=(const Date& n) {//return *this > n || *this == n;return !(*this < n);
}Date& Date:: operator+=(int day) {if (day < 0) {return *this -= (-day);}if (day < 0) {return *this -= (-day);}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) {_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13) {++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}Date Date:: operator+(int day) {Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;
}Date& Date:: operator-=(int day) {if (day < 0) {return *this -= (-day);}if (day < 0) {return *this += (-day);}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0) {--_month;if (_month == 0) {--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}Date Date:: operator-(int day) {Date tmp(*this);tmp -= day;return tmp;
}Date& Date::operator++() {*this += 1;return *this;
}Date Date:: operator++(int) {Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp;
}Date& Date::operator--() {*this -= 1;return *this;
}Date Date:: operator--(int) {Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;
}//int Date::operator-(const Date& d) {
// int flag = -1;
// Date min = *this;
// Date max = d;
// if (*this > d) {
// min = d;
// max = *this;
// flag = 1;
// }
// int n = 0;
// while (min < max) {
// ++min;
// ++n;
// }
// return n*flag;
//}
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) {int flag = 1;Date max = *this;Date min = d;if (*this < d) {max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}int n = 0;int y = min._year;while (y != max._year) {if (y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0 || y % 400 == 0) {n += 366;}else {n += 365;}y++;}int m1 = 1;int m2 = 1;while (m1 < max._month) {n += GetMonthDay(max._year, m1);m1++;}while (m2 < min._month) {n -= GetMonthDay(min._year, m2);m2++;}n = n + max._day - min._day;return n;
}
相关文章:

【C++】日期类的实现
在上篇博客中我们已经学习了C中的运算符重载,我们说,操作符只能对于内置类型进行操作,对自定义类型我们需要自己定义函数去实现一系列的操作 那么这篇博客我们就专门把日期这个类单独拿出来写一下它都有哪些有意义的可以重载的运算符…...
带残差连接的ResNet18
目录 1 模型构建 1.1 残差单元 1.2 残差网络的整体结构 2 没有残差连接的ResNet18 2.1 模型训练 2.2 模型评价 3 带残差连接的ResNet18 3.1 模型训练 3.2 模型评价 4 与高层API实现版本的对比实验 总结 残差网络(Residual Network,ResNet)…...

【深入解析git和gdb:版本控制与调试利器的终极指南】
【本节目标】 1. 掌握简单gdb使用于调试 2. 学习 git 命令行的简单操作, 能够将代码上传到 Github 上 1.Linux调试器-gdb使用 1.1.背景 程序的发布方式有两种,debug模式和release模式release模式不可被调试,debug模式可被调试Linux gcc/g出来的二进制…...
CGAN原理讲解与源码
1.CGAN原理 生成器,输入的是c和z,z是随机噪声,c是条件,对应MNIST数据集,要求规定生成数字是几。 输出是生成的虚假图片。 生成器生成的图片被判别器认为是真实图片,那么标签就是1 其实判别器模型输出的是…...

C#实体类与XML互转以及List和DataTable转XML的使用
引言 在C#开发中,数据的存储和传输是非常常见的需求。使用XML作为数据格式有很多优点,例如可读性强、易于解析等。而实体类、List和DataTable是表示数据模型的常用方式。本文将介绍如何在C#中实现实体类、List和DataTable与XML之间的相互转换,…...

uniapp的vue3的模版的setup函数内使用uniapp内置方法
vue2使用方式直接在method同级使用就行,但是在vue3的setup函数内直接使用会报错,本人找了好久,发现vue3需要导入uniapp模块才能使用,具体如下 使用uniapp上拉加载更多方法 <script>import {onReachBottom} from dcloudio/uni-apponReachBottom(() > {console.log(&qu…...

UI自动化的基本知识
一、UI自动化测试介绍 1、什么是自动化测试 概念:由程序代替人工进行系统校验的过程 1.1自动化测试能解决的问题? 回归测试 (冒烟测试) 针对之前老的功能进行测试 通过自动化的代码来实现。 针对上一个版本的问题的回归 兼容性测试 web实例化不同的浏…...
python实现C++简易自动压行
突发奇想,想要将自己的c压行之后交上去。但是苦于手动压行效率太低,在网上搜索压行网站没有找到,突然发现压行不就是检查检查去个换行符吗。于是心血来潮,用python实现了一个简易压行程序。 首先,宏定义等带#的文件不…...
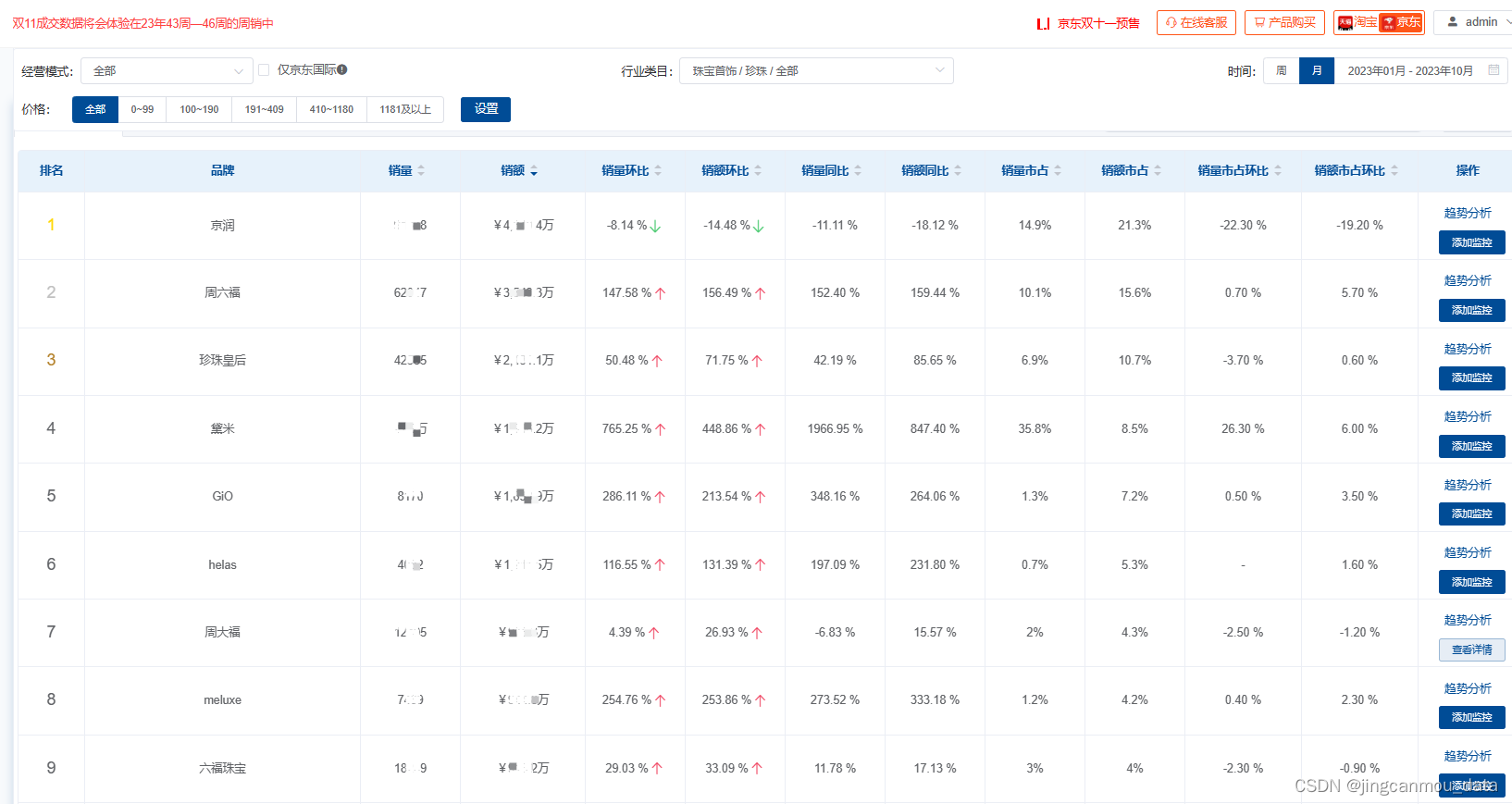
京东数据分析(京东大数据采集):2023年线上珍珠市场销售数据采集
在珠宝首饰市场,从黄金到钻石,如今年轻人的新风潮又转向了珍珠。珍珠热潮并非刚刚兴起,早在前两年,抖音、快手等短视频台的珍珠开蚌直播内容,就掀起了一波珍珠热潮。 此后,随着珍珠饰品被越来越多社交平台的…...
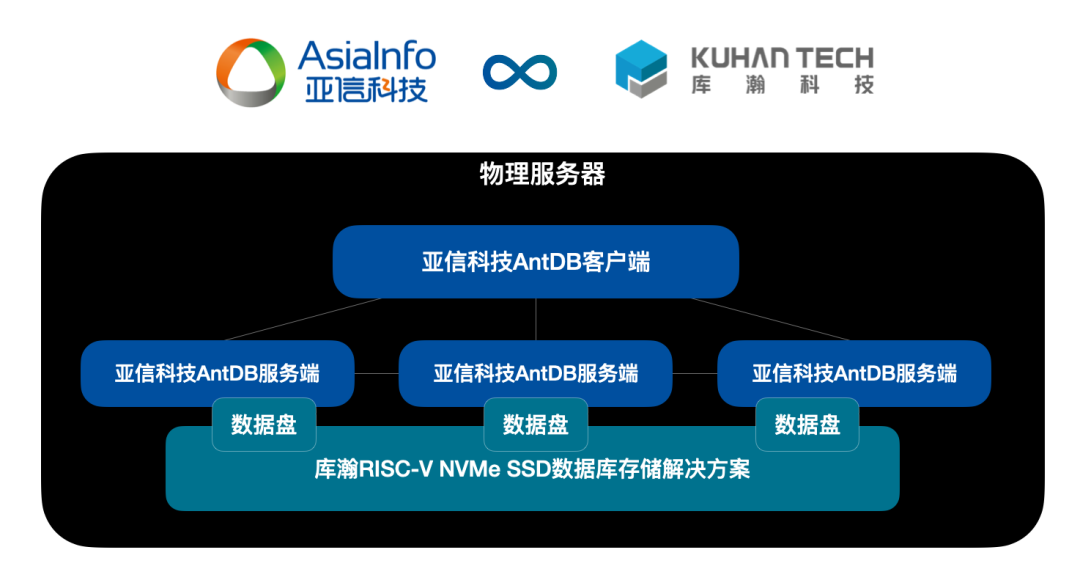
亚信科技AntDB数据库与库瀚存储方案完成兼容性互认证
近日,亚信科技AntDB数据库与苏州库瀚信息科技有限公司自主研发的RISC-V数据库存储解决方案进行了产品兼容测试。经过双方团队的严格测试,亚信科技AntDB数据库与库瀚数据库存储解决方案完全兼容、运行稳定。除高可用性测试外,双方进一步开展TP…...

现代C++之万能引用、完美转发、引用折叠
现代C之万能引用、完美转发、引用折叠 0.导语1.问题引入2.引入万能引用3.万能引用出现场合4.理解左值与右值4.1 精简版4.2 完整版4.3 生命周期延长4.4 生命周期延长应用5.区分万能引用6.表达式的左右值性与类型无关7.引用折叠和完美转发7.1 引用折叠之本质细节7.2 示例与使用7.…...
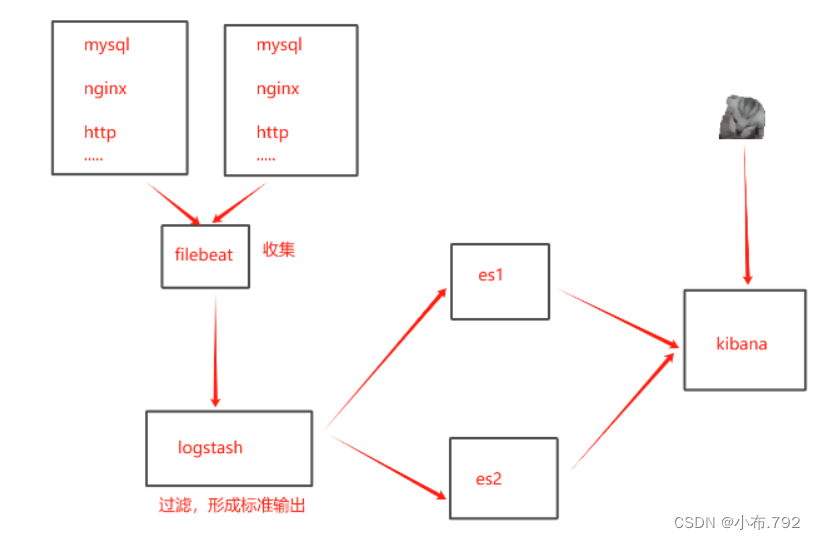
ELK日志收集系统-filbeat
filebeat日志收集工具 elk:filebeat日志收集工具和logstash相同 filebeat是一个轻量级的日志收集工具,所使用的系统资源比logstash部署和启动时使用的资源要小的多 filebeat可以运行在非Java环境,它可以代理logstash在非java环境上收集日志…...
Python小知识
个人学习笔记,用于记录使用过程中好用的技巧、好用的库。 1 小知识 1.1 相对路径 1.2 打包Exe文件 命令: pyinstaller -F main.py其中-F:覆盖之前打包的文件 mian.py:需要打包的Python文件 PS:使用pyinstaller 5.1…...
如何在Ubuntu系统上安装Redis
Redis的下载 Redis安装包分为windows版和Linux版当前示例中介绍的是Linux版本Linux的下载地址:Index of /releases/ (redis.io)本次下载的压缩包为:redis-6.2.14.tar.gzRedis的安装 将压缩包通过ssh远程工具上传到Linux服务器中解压压缩包 tar -zxvf red…...
Vue2问题:如何全局使用less和sass变量?
前端功能问题系列文章,点击上方合集↑ 序言 大家好,我是大澈! 本文约2400字,整篇阅读大约需要4分钟。 本文主要内容分三部分,如果您只需要解决问题,请阅读第一、二部分即可。如果您有更多时间ÿ…...
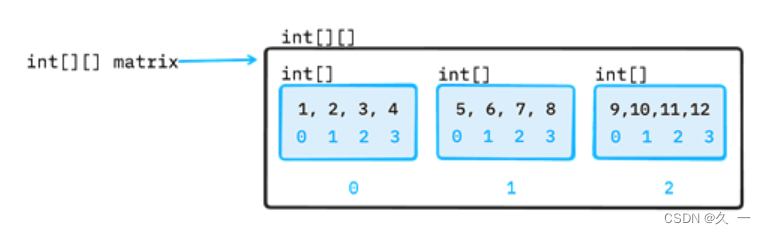
Java 基础学习(四)操作数组、软件开发管理
1 操作数组 1.1.1 System.arraycopy 方法用于数组复制 当需要将一个数组的元素复制到另一个数组中时,可以使用System.arraycopy方法。它提供了一种高效的方式来复制数组的内容,避免了逐个元素赋值的繁琐过程。相对于使用循环逐个元素赋值的方式&#x…...

git仓库如何撤销提交,恢复提交,重置版本命令
撤销提交: 要撤销最近一次提交(未推送到远程仓库),可以使用以下命令: git reset HEAD^该命令将会把最后一次提交的修改从当前主分支中移除,并将这些修改的状态保留在本地工作目录中。 如果想要取消所有的…...
Java 基础学习(三)循环流程控制与数组
1 循环流程控制 1.1 循环流程控制概述 1.1.1 什么是循环流程控制 当一个业务过程需要多次重复执行一个程序单元时,可以使用循环流程控制实现。 Java中包含3种循环结构: 1.2 for循环 1.2.1 for循环基础语法 for循环是最常用的循环流程控制ÿ…...

别太担心,人类只是把一小部分理性和感性放到了AI里
尽管人工智能(AI)在许多方面已经取得了重大进展,但它仍然无法完全复制人类的理性和感性。AI目前主要侧重于处理逻辑和分析任务,而人类则具有更复杂的思维能力和情感经验。 人类已经成功地将一些可以数据化和程序化的理性和感性特征…...
最新AIGC创作系统ChatGPT系统源码+DALL-E3文生图+图片上传对话识图/支持OpenAI-GPT全模型+国内AI全模型
一、AI创作系统 SparkAi创作系统是基于ChatGPT进行开发的Ai智能问答系统和Midjourney绘画系统,支持OpenAI-GPT全模型国内AI全模型。本期针对源码系统整体测试下来非常完美,可以说SparkAi是目前国内一款的ChatGPT对接OpenAI软件系统。那么如何搭建部署AI…...

Docker 离线安装指南
参考文章 1、确认操作系统类型及内核版本 Docker依赖于Linux内核的一些特性,不同版本的Docker对内核版本有不同要求。例如,Docker 17.06及之后的版本通常需要Linux内核3.10及以上版本,Docker17.09及更高版本对应Linux内核4.9.x及更高版本。…...
多模态2025:技术路线“神仙打架”,视频生成冲上云霄
文|魏琳华 编|王一粟 一场大会,聚集了中国多模态大模型的“半壁江山”。 智源大会2025为期两天的论坛中,汇集了学界、创业公司和大厂等三方的热门选手,关于多模态的集中讨论达到了前所未有的热度。其中,…...

黑马Mybatis
Mybatis 表现层:页面展示 业务层:逻辑处理 持久层:持久数据化保存 在这里插入图片描述 Mybatis快速入门 )
python爬虫:Newspaper3k 的详细使用(好用的新闻网站文章抓取和解析的Python库)
更多内容请见: 爬虫和逆向教程-专栏介绍和目录 文章目录 一、Newspaper3k 概述1.1 Newspaper3k 介绍1.2 主要功能1.3 典型应用场景1.4 安装二、基本用法2.2 提取单篇文章的内容2.2 处理多篇文档三、高级选项3.1 自定义配置3.2 分析文章情感四、实战案例4.1 构建新闻摘要聚合器…...
前端开发面试题总结-JavaScript篇(一)
文章目录 JavaScript高频问答一、作用域与闭包1.什么是闭包(Closure)?闭包有什么应用场景和潜在问题?2.解释 JavaScript 的作用域链(Scope Chain) 二、原型与继承3.原型链是什么?如何实现继承&a…...
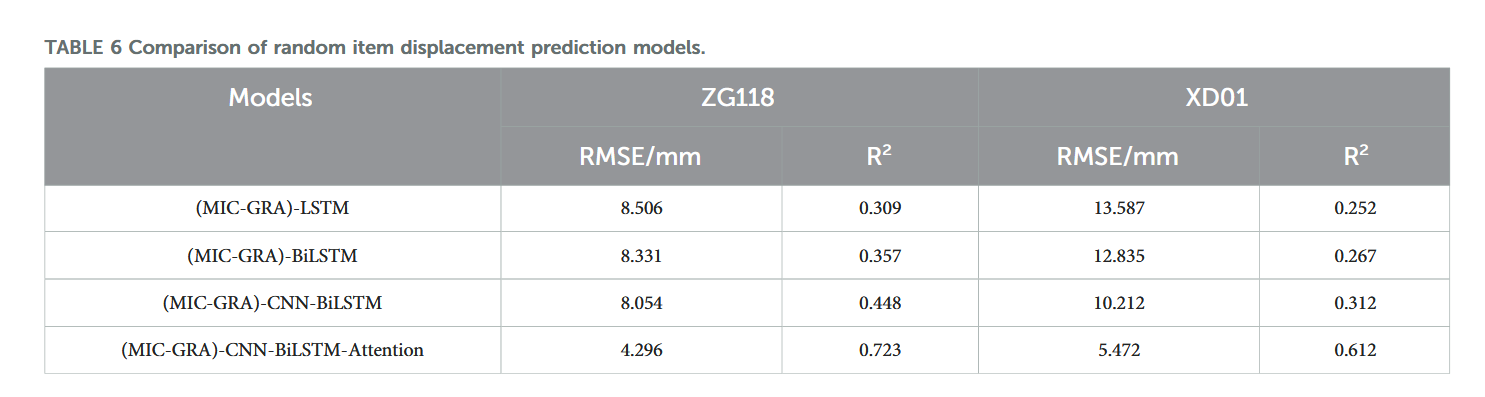
【论文阅读28】-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention-(2024)
本文把滑坡位移序列拆开、筛优质因子,再用 CNN-BiLSTM-Attention 来动态预测每个子序列,最后重构出总位移,预测效果超越传统模型。 文章目录 1 引言2 方法2.1 位移时间序列加性模型2.2 变分模态分解 (VMD) 具体步骤2.3.1 样本熵(S…...

Golang——6、指针和结构体
指针和结构体 1、指针1.1、指针地址和指针类型1.2、指针取值1.3、new和make 2、结构体2.1、type关键字的使用2.2、结构体的定义和初始化2.3、结构体方法和接收者2.4、给任意类型添加方法2.5、结构体的匿名字段2.6、嵌套结构体2.7、嵌套匿名结构体2.8、结构体的继承 3、结构体与…...

破解路内监管盲区:免布线低位视频桩重塑停车管理新标准
城市路内停车管理常因行道树遮挡、高位设备盲区等问题,导致车牌识别率低、逃费率高,传统模式在复杂路段束手无策。免布线低位视频桩凭借超低视角部署与智能算法,正成为破局关键。该设备安装于车位侧方0.5-0.7米高度,直接规避树枝遮…...
基础)
6个月Python学习计划 Day 16 - 面向对象编程(OOP)基础
第三周 Day 3 🎯 今日目标 理解类(class)和对象(object)的关系学会定义类的属性、方法和构造函数(init)掌握对象的创建与使用初识封装、继承和多态的基本概念(预告) &a…...

大模型真的像人一样“思考”和“理解”吗?
Yann LeCun 新研究的核心探讨:大语言模型(LLM)的“理解”和“思考”方式与人类认知的根本差异。 核心问题:大模型真的像人一样“思考”和“理解”吗? 人类的思考方式: 你的大脑是个超级整理师。面对海量信…...
