FFmpeg-基础组件-AVFrame
本章主要介绍FFmpeg基础组件AVFrame.
文章目录
- 1.结构体成员
- 2.成员函数
- AVFrame Host内存的获取 av_frame_get_buffer
- AVFrame device内存获取av_hwframe_get_buffer()
1.结构体成员
我们把所有的代码先粘贴上来,在后边一个一个解释。
typedef struct AVFrame {
#define AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS 8/*** pointer to the picture/channel planes.* This might be different from the first allocated byte. For video,* it could even point to the end of the image data.** All pointers in data and extended_data must point into one of the* AVBufferRef in buf or extended_buf.** Some decoders access areas outside 0,0 - width,height, please* see avcodec_align_dimensions2(). Some filters and swscale can read* up to 16 bytes beyond the planes, if these filters are to be used,* then 16 extra bytes must be allocated.** NOTE: Pointers not needed by the format MUST be set to NULL.** @attention In case of video, the data[] pointers can point to the* end of image data in order to reverse line order, when used in* combination with negative values in the linesize[] array.*/uint8_t *data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS];/*** For video, a positive or negative value, which is typically indicating* the size in bytes of each picture line, but it can also be:* - the negative byte size of lines for vertical flipping* (with data[n] pointing to the end of the data* - a positive or negative multiple of the byte size as for accessing* even and odd fields of a frame (possibly flipped)** For audio, only linesize[0] may be set. For planar audio, each channel* plane must be the same size.** For video the linesizes should be multiples of the CPUs alignment* preference, this is 16 or 32 for modern desktop CPUs.* Some code requires such alignment other code can be slower without* correct alignment, for yet other it makes no difference.** @note The linesize may be larger than the size of usable data -- there* may be extra padding present for performance reasons.** @attention In case of video, line size values can be negative to achieve* a vertically inverted iteration over image lines.*/int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS];/*** pointers to the data planes/channels.** For video, this should simply point to data[].** For planar audio, each channel has a separate data pointer, and* linesize[0] contains the size of each channel buffer.* For packed audio, there is just one data pointer, and linesize[0]* contains the total size of the buffer for all channels.** Note: Both data and extended_data should always be set in a valid frame,* but for planar audio with more channels that can fit in data,* extended_data must be used in order to access all channels.*/uint8_t **extended_data;/*** @name Video dimensions* Video frames only. The coded dimensions (in pixels) of the video frame,* i.e. the size of the rectangle that contains some well-defined values.** @note The part of the frame intended for display/presentation is further* restricted by the @ref cropping "Cropping rectangle".* @{*/int width, height;/*** @}*//*** number of audio samples (per channel) described by this frame*/int nb_samples;/*** format of the frame, -1 if unknown or unset* Values correspond to enum AVPixelFormat for video frames,* enum AVSampleFormat for audio)*/int format;/*** 1 -> keyframe, 0-> not*/int key_frame;/*** Picture type of the frame.*/enum AVPictureType pict_type;/*** Sample aspect ratio for the video frame, 0/1 if unknown/unspecified.*/AVRational sample_aspect_ratio;/*** Presentation timestamp in time_base units (time when frame should be shown to user).*/int64_t pts;/*** DTS copied from the AVPacket that triggered returning this frame. (if frame threading isn't used)* This is also the Presentation time of this AVFrame calculated from* only AVPacket.dts values without pts values.*/int64_t pkt_dts;/*** Time base for the timestamps in this frame.* In the future, this field may be set on frames output by decoders or* filters, but its value will be by default ignored on input to encoders* or filters.*/AVRational time_base;/*** picture number in bitstream order*/int coded_picture_number;/*** picture number in display order*/int display_picture_number;/*** quality (between 1 (good) and FF_LAMBDA_MAX (bad))*/int quality;/*** for some private data of the user*/void *opaque;/*** When decoding, this signals how much the picture must be delayed.* extra_delay = repeat_pict / (2*fps)*/int repeat_pict;/*** The content of the picture is interlaced.*/int interlaced_frame;/*** If the content is interlaced, is top field displayed first.*/int top_field_first;/*** Tell user application that palette has changed from previous frame.*/int palette_has_changed;/*** reordered opaque 64 bits (generally an integer or a double precision float* PTS but can be anything).* The user sets AVCodecContext.reordered_opaque to represent the input at* that time,* the decoder reorders values as needed and sets AVFrame.reordered_opaque* to exactly one of the values provided by the user through AVCodecContext.reordered_opaque*/int64_t reordered_opaque;/*** Sample rate of the audio data.*/int sample_rate;/*** Channel layout of the audio data.*/uint64_t channel_layout;/*** AVBuffer references backing the data for this frame. All the pointers in* data and extended_data must point inside one of the buffers in buf or* extended_buf. This array must be filled contiguously -- if buf[i] is* non-NULL then buf[j] must also be non-NULL for all j < i.** There may be at most one AVBuffer per data plane, so for video this array* always contains all the references. For planar audio with more than* AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS channels, there may be more buffers than can fit in* this array. Then the extra AVBufferRef pointers are stored in the* extended_buf array.*/AVBufferRef *buf[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS];/*** For planar audio which requires more than AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS* AVBufferRef pointers, this array will hold all the references which* cannot fit into AVFrame.buf.** Note that this is different from AVFrame.extended_data, which always* contains all the pointers. This array only contains the extra pointers,* which cannot fit into AVFrame.buf.** This array is always allocated using av_malloc() by whoever constructs* the frame. It is freed in av_frame_unref().*/AVBufferRef **extended_buf;/*** Number of elements in extended_buf.*/int nb_extended_buf;AVFrameSideData **side_data;int nb_side_data;/*** @defgroup lavu_frame_flags AV_FRAME_FLAGS* @ingroup lavu_frame* Flags describing additional frame properties.** @{*//*** The frame data may be corrupted, e.g. due to decoding errors.*/
#define AV_FRAME_FLAG_CORRUPT (1 << 0)
/*** A flag to mark the frames which need to be decoded, but shouldn't be output.*/
#define AV_FRAME_FLAG_DISCARD (1 << 2)
/*** @}*//*** Frame flags, a combination of @ref lavu_frame_flags*/int flags;/*** MPEG vs JPEG YUV range.* - encoding: Set by user* - decoding: Set by libavcodec*/enum AVColorRange color_range;enum AVColorPrimaries color_primaries;enum AVColorTransferCharacteristic color_trc;/*** YUV colorspace type.* - encoding: Set by user* - decoding: Set by libavcodec*/enum AVColorSpace colorspace;enum AVChromaLocation chroma_location;/*** frame timestamp estimated using various heuristics, in stream time base* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by libavcodec, read by user.*/int64_t best_effort_timestamp;/*** reordered pos from the last AVPacket that has been input into the decoder* - encoding: unused* - decoding: Read by user.*/int64_t pkt_pos;/*** duration of the corresponding packet, expressed in* AVStream->time_base units, 0 if unknown.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: Read by user.*/int64_t pkt_duration;/*** metadata.* - encoding: Set by user.* - decoding: Set by libavcodec.*/AVDictionary *metadata;/*** decode error flags of the frame, set to a combination of* FF_DECODE_ERROR_xxx flags if the decoder produced a frame, but there* were errors during the decoding.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by libavcodec, read by user.*/int decode_error_flags;
#define FF_DECODE_ERROR_INVALID_BITSTREAM 1
#define FF_DECODE_ERROR_MISSING_REFERENCE 2
#define FF_DECODE_ERROR_CONCEALMENT_ACTIVE 4
#define FF_DECODE_ERROR_DECODE_SLICES 8/*** number of audio channels, only used for audio.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: Read by user.*/int channels;/*** size of the corresponding packet containing the compressed* frame.* It is set to a negative value if unknown.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by libavcodec, read by user.*/int pkt_size;/*** For hwaccel-format frames, this should be a reference to the* AVHWFramesContext describing the frame.*/AVBufferRef *hw_frames_ctx;/*** AVBufferRef for free use by the API user. FFmpeg will never check the* contents of the buffer ref. FFmpeg calls av_buffer_unref() on it when* the frame is unreferenced. av_frame_copy_props() calls create a new* reference with av_buffer_ref() for the target frame's opaque_ref field.** This is unrelated to the opaque field, although it serves a similar* purpose.*/AVBufferRef *opaque_ref;/*** @anchor cropping* @name Cropping* Video frames only. The number of pixels to discard from the the* top/bottom/left/right border of the frame to obtain the sub-rectangle of* the frame intended for presentation.* @{*/size_t crop_top;size_t crop_bottom;size_t crop_left;size_t crop_right;/*** @}*//*** AVBufferRef for internal use by a single libav* library.* Must not be used to transfer data between libraries.* Has to be NULL when ownership of the frame leaves the respective library.** Code outside the FFmpeg libs should never check or change the contents of the buffer ref.** FFmpeg calls av_buffer_unref() on it when the frame is unreferenced.* av_frame_copy_props() calls create a new reference with av_buffer_ref()* for the target frame's private_ref field.*/AVBufferRef *private_ref;
} AVFrame;
AVFrame中核心成员,我们常用的就是下面几个
typedef struct AVFrame {
...uint8_t *data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS];uint8_t **extended_data;uint8_t **extended_data;int width, height;int format;int key_frame;int64_t pts;int64_t pkt_dts;AVRational time_base;AVBufferRef *buf[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS];
...
}
这个结构体主要保存解码后的YUV数据,特别注意的是AVBufferRef *buf[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS];这个成员,因为它用来进行分配内存的释放。
其实在很多地方用到了AVBufferRef ,原理就是其中内部使用了一个引用,当引用为1的时候,就把内部指向的memory释放掉。
/*** A reference counted buffer type. It is opaque and is meant to be used through* references (AVBufferRef).*/
typedef struct AVBuffer AVBuffer;/*** A reference to a data buffer.** The size of this struct is not a part of the public ABI and it is not meant* to be allocated directly.*/
typedef struct AVBufferRef {AVBuffer *buffer;/*** The data buffer. It is considered writable if and only if* this is the only reference to the buffer, in which case* av_buffer_is_writable() returns 1.*/uint8_t *data;/*** Size of data in bytes.*/size_t size;
} AVBufferRef;
其中data就是yuv数据,size就是数据大小,我们看到里面的AVBuffer ,其详细结构如下,其中refcount就是引用数量,free就是释放函数
struct AVBuffer {uint8_t *data; /**< data described by this buffer */size_t size; /**< size of data in bytes *//*** number of existing AVBufferRef instances referring to this buffer*/atomic_uint refcount;/*** a callback for freeing the data*/void (*free)(void *opaque, uint8_t *data);/*** an opaque pointer, to be used by the freeing callback*/void *opaque;/*** A combination of AV_BUFFER_FLAG_**/int flags;/*** A combination of BUFFER_FLAG_**/int flags_internal;
};
关于这一块智能引用,其提供了一些函数族
/*** Allocate an AVBuffer of the given size using av_malloc().** @return an AVBufferRef of given size or NULL when out of memory*/
AVBufferRef *av_buffer_alloc(size_t size);/*** Same as av_buffer_alloc(), except the returned buffer will be initialized* to zero.*/
AVBufferRef *av_buffer_allocz(size_t size);
/*** Create an AVBuffer from an existing array.** If this function is successful, data is owned by the AVBuffer. The caller may* only access data through the returned AVBufferRef and references derived from* it.* If this function fails, data is left untouched.* @param data data array* @param size size of data in bytes* @param free a callback for freeing this buffer's data* @param opaque parameter to be got for processing or passed to free* @param flags a combination of AV_BUFFER_FLAG_*** @return an AVBufferRef referring to data on success, NULL on failure.*/
AVBufferRef *av_buffer_create(uint8_t *data, size_t size,void (*free)(void *opaque, uint8_t *data),void *opaque, int flags);
/*** Default free callback, which calls av_free() on the buffer data.* This function is meant to be passed to av_buffer_create(), not called* directly.*/
void av_buffer_default_free(void *opaque, uint8_t *data);
/*** Create a new reference to an AVBuffer.** @return a new AVBufferRef referring to the same AVBuffer as buf or NULL on* failure.*/
AVBufferRef *av_buffer_ref(const AVBufferRef *buf);/*** Free a given reference and automatically free the buffer if there are no more* references to it.** @param buf the reference to be freed. The pointer is set to NULL on return.*/
void av_buffer_unref(AVBufferRef **buf);/*** @return 1 if the caller may write to the data referred to by buf (which is* true if and only if buf is the only reference to the underlying AVBuffer).* Return 0 otherwise.* A positive answer is valid until av_buffer_ref() is called on buf.*/
int av_buffer_is_writable(const AVBufferRef *buf);/*** @return the opaque parameter set by av_buffer_create.*/
void *av_buffer_get_opaque(const AVBufferRef *buf);int av_buffer_get_ref_count(const AVBufferRef *buf);
这些函数族用户是用不到的,一般在ffmpeg内部模块中使用到。比如AVFrame函数族中。
其余根据字面意思很好理解。其中linesize表示每个plane的步长。
比如YUV420的数,其数据长度大小为:
if (frame->pixel_format == TOPSCODEC_PIX_FMT_I420 ||frame->pixel_format == TOPSCODEC_PIX_FMT_NV12 ||frame->pixel_format == TOPSCODEC_PIX_FMT_NV21 ||frame->pixel_format == TOPSCODEC_PIX_FMT_P010 ||frame->pixel_format == TOPSCODEC_PIX_FMT_P010LE) {int Y = frame->linesize[0] * frame->height;int U = frame->linesize[1] * ((frame->height + 1) / 2);int V = frame->linesize[2] * ((frame->height + 1) / 2);}
也就是说yuv数据的宽度是多大。
其实这个并不用手工来计算,ffmpeg框架提供了专用的函数来处理:
int av_image_fill_plane_sizes(size_t sizes[4], enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt,int height, const ptrdiff_t linesizes[4])
这个函数用来计算每个plane的长度是多少,通过传入参数我们很容易看到height.原理和我们上面一样。
下面这个函数比较特殊,可以计算linesizes,也就是每个通道的stride.
int av_image_fill_linesizes(int linesizes[4], enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width)这个函数专门通过width和pix_fmt来计算linesizes[4],这样就不用我们通过手动来去计算了。
还有另外一个函数用来计算每个planes数据长度
该类函数族ffmpeg提供了很多,具体在imgutils.h中
/*** Compute the size of an image line with format pix_fmt and width* width for the plane plane.** @return the computed size in bytes*/
int av_image_get_linesize(enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width, int plane);
/*** Fill plane linesizes for an image with pixel format pix_fmt and* width width.** @param linesizes array to be filled with the linesize for each plane* @return >= 0 in case of success, a negative error code otherwise*/
int av_image_fill_linesizes(int linesizes[4], enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width);
/*** Fill plane sizes for an image with pixel format pix_fmt and height height.** @param size the array to be filled with the size of each image plane* @param linesizes the array containing the linesize for each* plane, should be filled by av_image_fill_linesizes()* @return >= 0 in case of success, a negative error code otherwise** @note The linesize parameters have the type ptrdiff_t here, while they are* int for av_image_fill_linesizes().*/
int av_image_fill_plane_sizes(size_t size[4], enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt,int height, const ptrdiff_t linesizes[4]);
/*** Fill plane data pointers for an image with pixel format pix_fmt and* height height.** @param data pointers array to be filled with the pointer for each image plane* @param ptr the pointer to a buffer which will contain the image* @param linesizes the array containing the linesize for each* plane, should be filled by av_image_fill_linesizes()* @return the size in bytes required for the image buffer, a negative* error code in case of failure*/
int av_image_fill_pointers(uint8_t *data[4], enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int height,uint8_t *ptr, const int linesizes[4]);
/*** Allocate an image with size w and h and pixel format pix_fmt, and* fill pointers and linesizes accordingly.* The allocated image buffer has to be freed by using* av_freep(&pointers[0]).** @param align the value to use for buffer size alignment* @return the size in bytes required for the image buffer, a negative* error code in case of failure*/
int av_image_alloc(uint8_t *pointers[4], int linesizes[4],int w, int h, enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int align);
/*** Copy image plane from src to dst.* That is, copy "height" number of lines of "bytewidth" bytes each.* The first byte of each successive line is separated by *_linesize* bytes.** bytewidth must be contained by both absolute values of dst_linesize* and src_linesize, otherwise the function behavior is undefined.** @param dst_linesize linesize for the image plane in dst* @param src_linesize linesize for the image plane in src*/
void av_image_copy_plane(uint8_t *dst, int dst_linesize,const uint8_t *src, int src_linesize,int bytewidth, int height);
/*** Copy image in src_data to dst_data.** @param dst_linesizes linesizes for the image in dst_data* @param src_linesizes linesizes for the image in src_data*/
void av_image_copy(uint8_t *dst_data[4], int dst_linesizes[4],const uint8_t *src_data[4], const int src_linesizes[4],enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width, int height);
/*** Setup the data pointers and linesizes based on the specified image* parameters and the provided array.** The fields of the given image are filled in by using the src* address which points to the image data buffer. Depending on the* specified pixel format, one or multiple image data pointers and* line sizes will be set. If a planar format is specified, several* pointers will be set pointing to the different picture planes and* the line sizes of the different planes will be stored in the* lines_sizes array. Call with src == NULL to get the required* size for the src buffer.** To allocate the buffer and fill in the dst_data and dst_linesize in* one call, use av_image_alloc().** @param dst_data data pointers to be filled in* @param dst_linesize linesizes for the image in dst_data to be filled in* @param src buffer which will contain or contains the actual image data, can be NULL* @param pix_fmt the pixel format of the image* @param width the width of the image in pixels* @param height the height of the image in pixels* @param align the value used in src for linesize alignment* @return the size in bytes required for src, a negative error code* in case of failure*/
int av_image_fill_arrays(uint8_t *dst_data[4], int dst_linesize[4],const uint8_t *src,enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width, int height, int align);
/*** Return the size in bytes of the amount of data required to store an* image with the given parameters.** @param pix_fmt the pixel format of the image* @param width the width of the image in pixels* @param height the height of the image in pixels* @param align the assumed linesize alignment* @return the buffer size in bytes, a negative error code in case of failure*/
int av_image_get_buffer_size(enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width, int height, int align);
/*** Copy image data from an image into a buffer.** av_image_get_buffer_size() can be used to compute the required size* for the buffer to fill.** @param dst a buffer into which picture data will be copied* @param dst_size the size in bytes of dst* @param src_data pointers containing the source image data* @param src_linesize linesizes for the image in src_data* @param pix_fmt the pixel format of the source image* @param width the width of the source image in pixels* @param height the height of the source image in pixels* @param align the assumed linesize alignment for dst* @return the number of bytes written to dst, or a negative value* (error code) on error*/
int av_image_copy_to_buffer(uint8_t *dst, int dst_size,const uint8_t * const src_data[4], const int src_linesize[4],enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width, int height, int align);
/*** Check if the given dimension of an image is valid, meaning that all* bytes of the image can be addressed with a signed int.** @param w the width of the picture* @param h the height of the picture* @param log_offset the offset to sum to the log level for logging with log_ctx* @param log_ctx the parent logging context, it may be NULL* @return >= 0 if valid, a negative error code otherwise*/
int av_image_check_size(unsigned int w, unsigned int h, int log_offset, void *log_ctx);
/*** Check if the given dimension of an image is valid, meaning that all* bytes of a plane of an image with the specified pix_fmt can be addressed* with a signed int.** @param w the width of the picture* @param h the height of the picture* @param max_pixels the maximum number of pixels the user wants to accept* @param pix_fmt the pixel format, can be AV_PIX_FMT_NONE if unknown.* @param log_offset the offset to sum to the log level for logging with log_ctx* @param log_ctx the parent logging context, it may be NULL* @return >= 0 if valid, a negative error code otherwise*/
int av_image_check_size2(unsigned int w, unsigned int h, int64_t max_pixels, enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int log_offset, void *log_ctx);2.成员函数
const char *av_get_colorspace_name(enum AVColorSpace val);
AVFrame *av_frame_alloc(void);
void av_frame_free(AVFrame **frame);
int av_frame_ref(AVFrame *dst, const AVFrame *src);
AVFrame *av_frame_clone(const AVFrame *src);
void av_frame_move_ref(AVFrame *dst, AVFrame *src);
int av_frame_get_buffer(AVFrame *frame, int align);
int av_frame_is_writable(AVFrame *frame);
int av_frame_make_writable(AVFrame *frame);
int av_frame_copy(AVFrame *dst, const AVFrame *src);
int av_frame_copy_props(AVFrame *dst, const AVFrame *src);
AVFrameSideData *av_frame_new_side_data(AVFrame *frame,enum AVFrameSideDataType type,size_t size);
AVFrameSideData *av_frame_new_side_data_from_buf(AVFrame *frame,enum AVFrameSideDataType type,AVBufferRef *buf);
void av_frame_remove_side_data(AVFrame *frame, enum AVFrameSideDataType type);
const char *av_frame_side_data_name(enum AVFrameSideDataType type);
上面函数核心就是操作AVFrame。
AVFrame Host内存的获取 av_frame_get_buffer
ffmpeg提供了一个比较特殊的接口
/*** Allocate new buffer(s) for audio or video data.** The following fields must be set on frame before calling this function:* - format (pixel format for video, sample format for audio)* - width and height for video* - nb_samples and channel_layout for audio** This function will fill AVFrame.data and AVFrame.buf arrays and, if* necessary, allocate and fill AVFrame.extended_data and AVFrame.extended_buf.* For planar formats, one buffer will be allocated for each plane.** @warning: if frame already has been allocated, calling this function will* leak memory. In addition, undefined behavior can occur in certain* cases.** @param frame frame in which to store the new buffers.* @param align Required buffer size alignment. If equal to 0, alignment will be* chosen automatically for the current CPU. It is highly* recommended to pass 0 here unless you know what you are doing.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on error.*/
int av_frame_get_buffer(AVFrame *frame, int align)
这个函数是用来从ffmpeg内存池中为frame中获取buf,从上面的注释可以看到,如果想要获取buf,必须要设置
/** The following fields must be set on frame before calling this function:* - format (pixel format for video, sample format for audio)* - width and height for video* - nb_samples and channel_layout for audio* /
查看详细的函数代码:
int av_frame_get_buffer(AVFrame *frame, int align)
{if (frame->format < 0)return AVERROR(EINVAL);if (frame->width > 0 && frame->height > 0)return get_video_buffer(frame, align);else if (frame->nb_samples > 0 && (frame->channel_layout || frame->channels > 0))return get_audio_buffer(frame, align);return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
详细的调用流程如下:
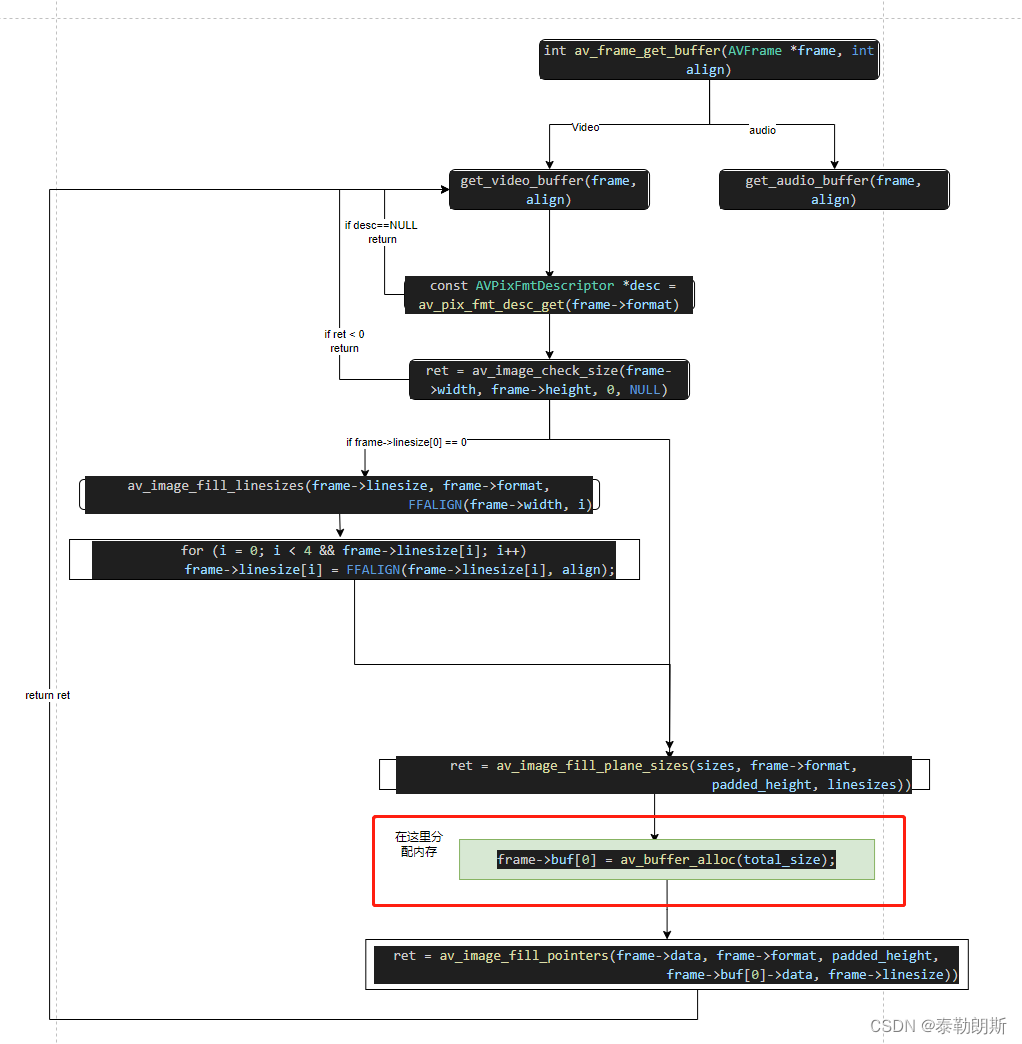
AVFrame device内存获取av_hwframe_get_buffer()
既然有host的内存获取,那么就有device内存的获取
/*** Allocate a new frame attached to the given AVHWFramesContext.** @param hwframe_ctx a reference to an AVHWFramesContext* @param frame an empty (freshly allocated or unreffed) frame to be filled with* newly allocated buffers.* @param flags currently unused, should be set to zero* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR code on failure*/
int av_hwframe_get_buffer(AVBufferRef *hwframe_ctx, AVFrame *frame, int flags);
其调用流程如下,注意分支代码,这里是继承了父类后,通过mmap去map到父类的内存上去。
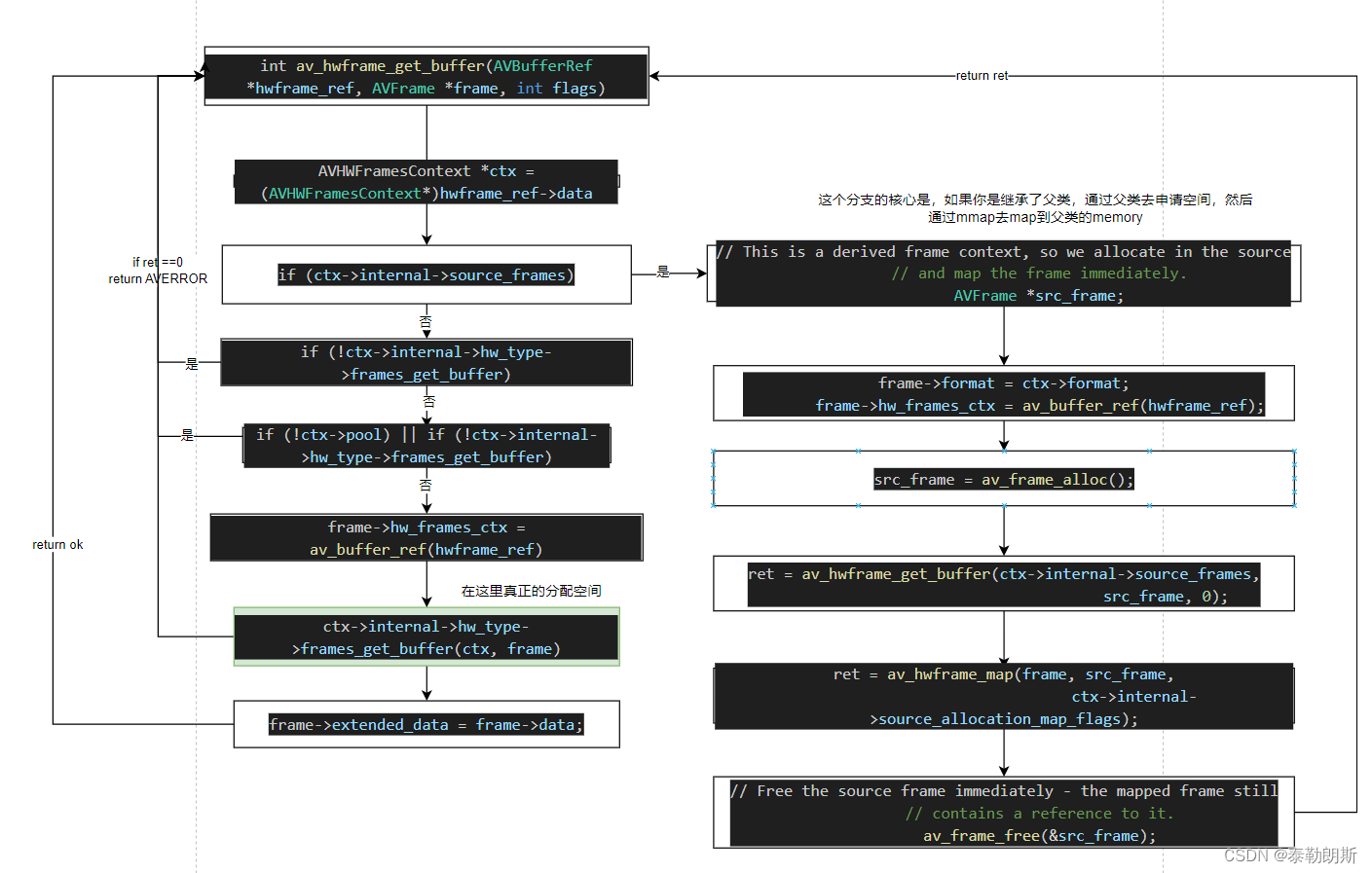
相关文章:

FFmpeg-基础组件-AVFrame
本章主要介绍FFmpeg基础组件AVFrame. 文章目录 1.结构体成员2.成员函数AVFrame Host内存的获取 av_frame_get_bufferAVFrame device内存获取av_hwframe_get_buffer() 1.结构体成员 我们把所有的代码先粘贴上来,在后边一个一个解释。 typede…...
Vue 组件传参 emit
emit 属性:用于创建自定义事件,接收子组件传递过来的数据。 注意:如果自定义事件的名称,和原生事件的名称一样,那么只会触发自定义事件。 setup 语法糖写法请见:《Vue3 子传父 组件传参 defineEmits》 语…...

Makefile基本指令
语法规则 目标 ... : 依赖 ...命令1命令2. . .1、目标即要生成的文件。如果目标文件的更新时间晚于依赖文件更新时间,则说明依赖文件没有改动,目标文件不需要重新编译。否则会进行重新编译并更新目标文件。 2、默认情况下Makefile的第一个目标为终极目…...

爬取图片python代码
在百度上爬取图片 pic_baidu.py import re import requests from urllib import error from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import os num 0 numPicture 0 file List []def Find(url, A):global Listprint(正在检测图片总数,请稍等.....)t 0i 1s 0while t <…...
Android通过listview实现输入框自定义提示栏(代替AutoCompleteTextView自动完成文本框)
效果图 背景 本人因为一些需求初次接触android,需要实现一个类似android自带的AutoCompleteTextView(自动完成文本框),但和其不同的是通过后端接口直接筛选数据(自己的分词处理规则),然后返回前…...

DA-AD试验
/********************************************************************************** * * * 1.通过本例程了解并掌握AD-DA转换芯片的基本原理和使用 * * …...
Leetcode—896.单调数列【简单】
2023每日刷题(五十九) Leetcode—896.单调数列 实现代码 class Solution { public:bool isMonotonic(vector<int>& nums) {int up 0;int down 0;if(nums.size() 1) {return true;}for(int i 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i) {if(nums[i] …...

vue2生命周期
vue2生命周期 在进行组件化项目开发的时候都会存在一个组件的生命周期概念,像Vue、React、小程序等等,无一例外,而通常情况组件的生命周期主要分成三个阶段,包括:创建、更新以及销毁阶段。 Vue的生命周期钩子函数主要包…...

【Flink on k8s】 -- flink kubernetes operator 1.7.0 发布
目录 前言 重大特性 1、自动伸缩 2、版本支持 3、savepoint 触发改进 4、jdk 支持 前言 Flink 官方博客于 2023-11-22 发布了 flink kubernetes operator 1.7.0 发布的消息。这个版本对自动缩放进行了大量的改进,包括与 Kubernetes 的完全分离,以便…...
三次握手实现的补充)
Java网络编程,对使用UDP实现TCP(一)三次握手实现的补充
修改片段1 在第一次握手时,由《TCP/IP详解》卷二中对tcp计时器的描述中,我们可知连接的建立是需要进行判断,如果客户端发送了SYN连接请求,服务端没有在有限时间内进行恢复,就会取消本次连接。 我们使用 setSoTimeout…...

Redis 的常见使用场景
01 缓存 作为 Key-Value 形态的内存数据库,Redis 最先会被想到的应用场景便是作为数据缓存。而使用 Redis 缓存数据非常简单,只需要通过 string 类型将序列化后的对象存起来即可,不过也有一些需要注意的地方: 必须保证不同对象的…...
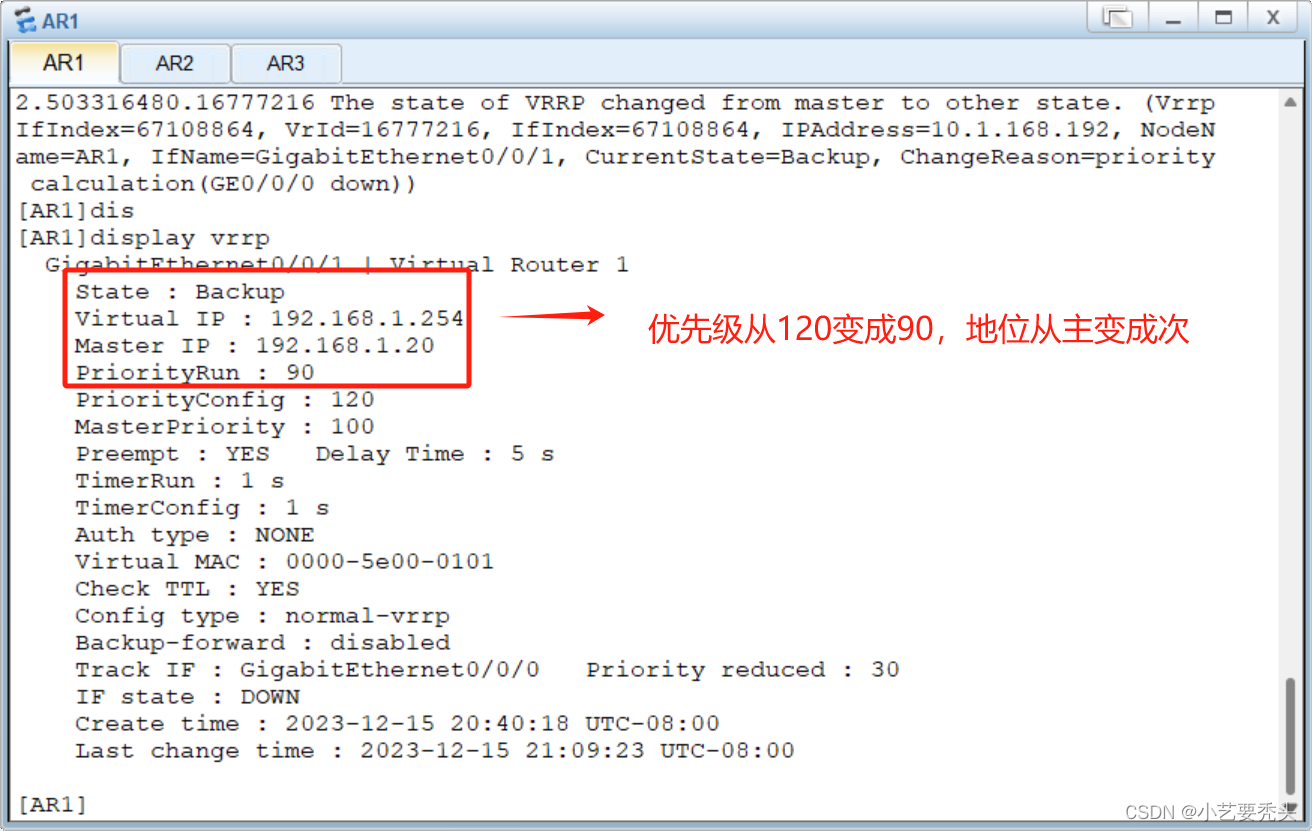
VRRP协议详解
目录 一、基础概念 1、概念 2、VRRP的基本结构 状态机 二、VRRP主备备份工作过程 1、备份工作过程 2、VRRP的负载分担工作 三、实验 一、基础概念 1、概念 VRRP能够在不改变组网的情况下,将多台路由器虚拟成一个虚拟路由器,通过配置虚拟路由器的I…...

Linux 常用命令----mktemp 命令
文章目录 基本用法实例演示高级用法注意事项 mktemp 命令用于创建一个临时文件或目录,这在需要处理临时数据或进行安全性测试时非常有用。使用 mktemp 可以保证文件名的唯一性,避免因文件名冲突而导致的问题。 基本用法 创建临时文件: 命令 mktemp 默认…...
基于ssm服装定制系统源码和论文
idea 数据库mysql5.7 数据库链接工具:navcat,小海豚等 环境: jdk8 tomcat8.5 开发技术 ssm 基于ssm服装定制系统源码和论文751 1.1项目研究的背景 困扰管理层的许多问题当中,服装定制将是广大用户们不可忽视的一块。但是管理好服装定制又面临很多麻…...
【AI】如何准备mac开发vue项目的环境
为了在Mac上开发Vue项目,你需要准备一些工具和环境。以下是主要的步骤: 安装Node.js和npm: Vue.js是一个基于JavaScript的框架,因此你需要Node.js环境。访问Node.js官网下载并安装Node.js,这也会自动安装npm࿰…...

BERT大模型:英语NLP的里程碑
BERT的诞生与重要性 BERT(Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)大模型标志着自然语言处理(NLP)领域的一个重要转折点。作为首个利用掩蔽语言模型(MLM)在英语语言上进行预训练的模型&…...

JVM的类的生命周期
目录 前言 1. 加载(Loading): 2. 验证(Verification): 3. 准备(Preparation): 4. 解析(Resolution): 5. 初始化(Ini…...
)
uni-app获取response header响应头(h5/app/小程序三端)
h5、app获取方式:getResponseHeader(key) 示例:参考:HTML5 API Reference // 创建xhr实例: // #ifdef APP-VUE let xhr new plus.net.XMLHttpRequest(); // #endif // #ifdef H5 let xhr new window.XMLHttpRequest(); // #en…...
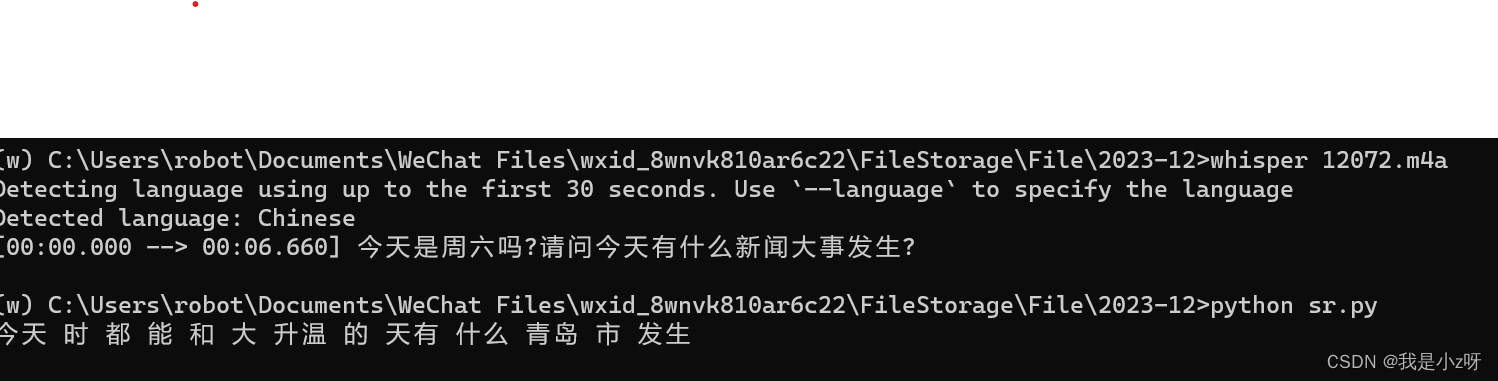
本地部署语音转文字(whisper,SpeechRecognition)
本地部署语音转文字 1.whisper1.首先安装Chocolatey2.安装3.使用 2.SpeechRecognition1.环境2.中文包3.格式转化4.运行 3.效果 1.whisper 1.首先安装Chocolatey https://github.com/openai/whisper 以管理员身份运行PowerShell Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -…...

js new 原理
mdn new new 调用函数时,该函数将被用作构造函数 类只能用 new 运算符实例化 不使用 new 调用一个类将抛出 TypeError。 过程 new Foo(…) 执行时: 创建一个空的简单 JavaScript 对象。 为方便起见,我们称之为 newInstance。 如果构造函数…...

Vue记事本应用实现教程
文章目录 1. 项目介绍2. 开发环境准备3. 设计应用界面4. 创建Vue实例和数据模型5. 实现记事本功能5.1 添加新记事项5.2 删除记事项5.3 清空所有记事 6. 添加样式7. 功能扩展:显示创建时间8. 功能扩展:记事项搜索9. 完整代码10. Vue知识点解析10.1 数据绑…...
基于uniapp+WebSocket实现聊天对话、消息监听、消息推送、聊天室等功能,多端兼容
基于 UniApp + WebSocket实现多端兼容的实时通讯系统,涵盖WebSocket连接建立、消息收发机制、多端兼容性配置、消息实时监听等功能,适配微信小程序、H5、Android、iOS等终端 目录 技术选型分析WebSocket协议优势UniApp跨平台特性WebSocket 基础实现连接管理消息收发连接…...

Qt Widget类解析与代码注释
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget) {ui->setupUi(this); }Widget::~Widget() {delete ui; }//解释这串代码,写上注释 当然可以!这段代码是 Qt …...

oracle与MySQL数据库之间数据同步的技术要点
Oracle与MySQL数据库之间的数据同步是一个涉及多个技术要点的复杂任务。由于Oracle和MySQL的架构差异,它们的数据同步要求既要保持数据的准确性和一致性,又要处理好性能问题。以下是一些主要的技术要点: 数据结构差异 数据类型差异ÿ…...

三体问题详解
从物理学角度,三体问题之所以不稳定,是因为三个天体在万有引力作用下相互作用,形成一个非线性耦合系统。我们可以从牛顿经典力学出发,列出具体的运动方程,并说明为何这个系统本质上是混沌的,无法得到一般解…...

【C语言练习】080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作
080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作 080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作使用原生APIODBC接口第三方库ORM框架文件模拟1. 安装SQLite2. 示例代码:使用SQLite创建数据库、表和插入数据3. 编译和运行4. 示例运行输出:5. 注意事项6. 总结080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作 在…...
企业如何增强终端安全?
在数字化转型加速的今天,企业的业务运行越来越依赖于终端设备。从员工的笔记本电脑、智能手机,到工厂里的物联网设备、智能传感器,这些终端构成了企业与外部世界连接的 “神经末梢”。然而,随着远程办公的常态化和设备接入的爆炸式…...
相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?)
Redis的发布订阅模式与专业的 MQ(如 Kafka, RabbitMQ)相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?
Redis 的发布订阅(Pub/Sub)模式与专业的 MQ(Message Queue)如 Kafka、RabbitMQ 进行比较,核心的权衡点在于:简单与速度 vs. 可靠与功能。 下面我们详细展开对比。 Redis Pub/Sub 的核心特点 它是一个发后…...
push [特殊字符] present
push 🆚 present 前言present和dismiss特点代码演示 push和pop特点代码演示 前言 在 iOS 开发中,push 和 present 是两种不同的视图控制器切换方式,它们有着显著的区别。 present和dismiss 特点 在当前控制器上方新建视图层级需要手动调用…...
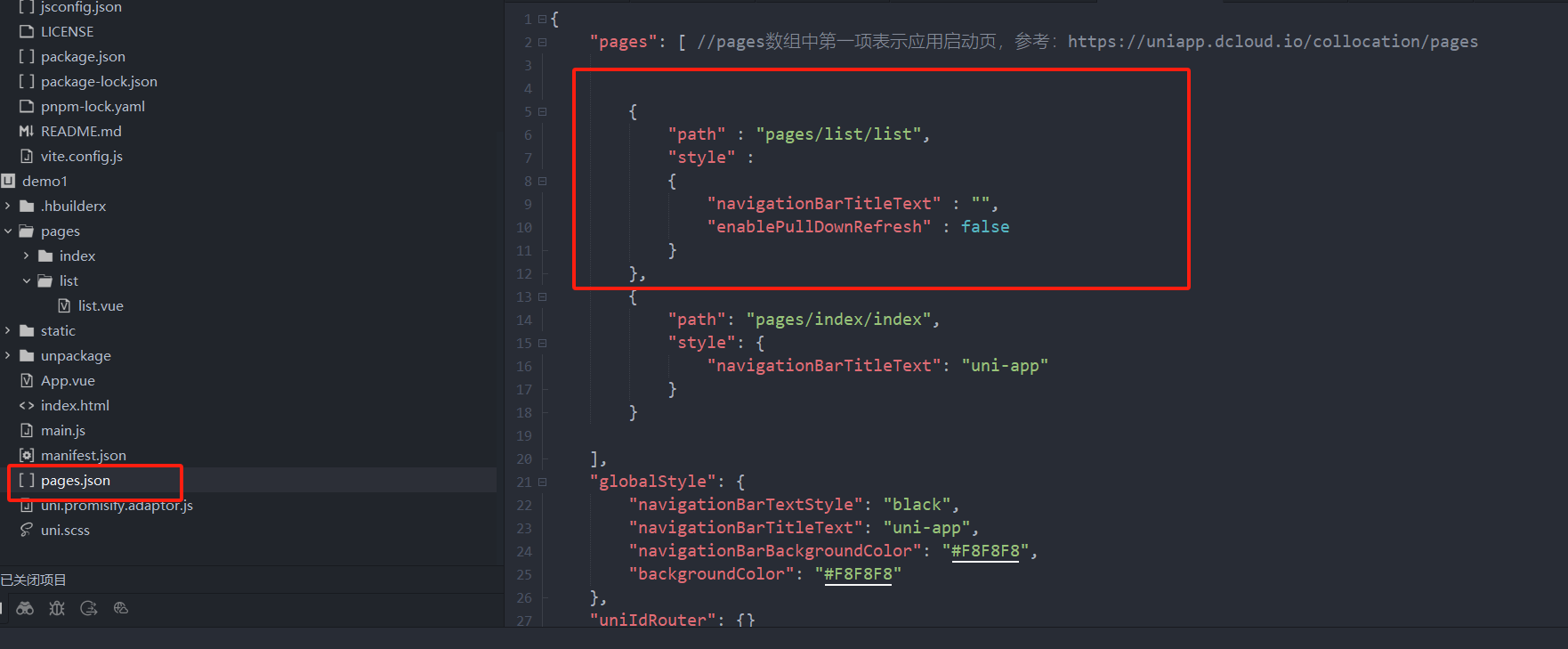
uniapp 小程序 学习(一)
利用Hbuilder 创建项目 运行到内置浏览器看效果 下载微信小程序 安装到Hbuilder 下载地址 :开发者工具默认安装 设置服务端口号 在Hbuilder中设置微信小程序 配置 找到运行设置,将微信开发者工具放入到Hbuilder中, 打开后出现 如下 bug 解…...
