Qt隐式共享浅析
一、什么是隐式共享
Qt 的隐式共享(implicit sharing)机制是一种设计模式,用于在进行数据拷贝时提高效率和减少内存占用。
在 Qt 中,许多类(如 QString、QList 等)都使用了隐式共享机制。这意味着当这些类的实例被拷贝时,实际上并不会立即进行数据的深拷贝,而是共享同一份数据。只有在其中一个实例发生修改时,才会进行实际的数据复制,以确保数据的独立性,即Copy-On-Write。
隐式共享机制通过引用计数(reference counting)来实现。每个共享的实例都包含一个引用计数,用于记录当前有多少个实例共享同一份数据。当一个实例被拷贝时,引用计数会增加;当一个实例被销毁时,引用计数会减少。只有当引用计数为 1 时,才会进行实际的数据复制。
这种设计模式可以提高程序的性能和内存利用率,特别是在处理大量数据拷贝的情况下。同时,开发者也无需过多关注数据的共享和拷贝,从而简化了程序的设计和实现。
总之,Qt 的隐式共享机制是一种高效的数据共享和拷贝方式,它通过引用计数来实现数据的延迟复制,从而提高了程序的性能和内存利用率。
二、隐式共享代码示例
下面是一个简单的例子,展示了QString如何使用隐式共享:
#include <QString>
#include <QDebug>int main() {QString str1 = "Hello, Qt!";QString str2 = str1; // 这里并没有发生真正的数据复制,str1和str2共享同一份数据,拷贝赋值使用的是浅拷贝的方式qDebug() << str1; // 输出 "Hello, Qt!"qDebug() << str2; // 输出 "Hello, Qt!"str2[0] = 'h'; // 在这里,由于str2要修改数据,所以发生了真正的数据复制,str1和str2不再共享数据qDebug() << str1; // 输出 "Hello, Qt!"qDebug() << str2; // 输出 "hello, Qt!"return 0;
}
在上述代码中,当我们创建str2并将其初始化为str1时,并没有发生真正的数据复制,str1和str2实际上是共享同一份数据的。只有当我们试图修改str2的数据时,才会发生真正的数据复制,这就是所谓的写时复制。
这种技术的优点是可以大大减少不必要的数据复制,从而提高程序的性能。但是,它也有一些缺点,例如在多线程环境中可能需要额外的同步操作,以防止数据竞争。
在Qt的源码中,这种技术的实现主要依赖于引用计数和深拷贝。每个可以共享数据的对象都有一个引用计数,当引用计数为1时,表示只有一个对象在使用这份数据,可以直接修改。当引用计数大于1时,表示有多个对象在共享这份数据,如果有一个对象要修改数据,就需要先进行深拷贝,然后再修改新的数据,这样就不会影响到其他对象。
三、自定义一个使用隐式共享技术的数据类型
在Qt中,你可以通过使用QSharedData和QSharedDataPointer类来实现隐式共享(也称为写时复制)。
以下是一个简单的例子,定义了一个自定义的数据类型MyData,它使用了隐式共享技术:
#include <QSharedData>
#include <QSharedDataPointer>class MyData : public QSharedData {
public:MyData() : x(0), y(0) {}MyData(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {}int x, y;
};class MySharedType {
public:MySharedType() : data(new MyData) {}MySharedType(int x, int y) : data(new MyData(x, y)) {}MySharedType(const MySharedType &other) : data(other.data) {}MySharedType &operator=(const MySharedType &other) {if (this != &other)data = other.data;return *this;}int x() const { return data->x; }int y() const { return data->y; }void setX(int x) { if (data->x != x) detach(); data->x = x; }void setY(int y) { if (data->y != y) detach(); data->y = y; }private:void detach() { if (data->ref != 1) data = new MyData(*data); }QSharedDataPointer<MyData> data;
};
在这个例子中,MyData类是实际存储数据的类,它继承自QSharedData。MySharedType类是用户使用的类,它包含一个QSharedDataPointer,指向MyData实例。当需要修改数据时,detach方法会被调用,如果有多个MySharedType实例共享同一个MyData实例,那么detach方法会创建一个新的MyData实例,以实现写时复制。
顺便看看 QSharedData 和QSharedDataPointer 的源码实现:
#ifndef QSHAREDDATA_H
#define QSHAREDDATA_H#include <QtCore/qglobal.h>
#include <QtCore/qatomic.h>
#if QT_DEPRECATED_SINCE(5, 6)
#include <QtCore/qhash.h>
#endif
#include <QtCore/qhashfunctions.h>QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACEtemplate <class T> class QSharedDataPointer;class
#if QT_VERSION < QT_VERSION_CHECK(6, 0, 0)
Q_CORE_EXPORT
#endif
QSharedData
{
public:mutable QAtomicInt ref; /// 原子计算inline QSharedData() noexcept : ref(0) { }inline QSharedData(const QSharedData &) noexcept : ref(0) { }// using the assignment operator would lead to corruption in the ref-countingQSharedData &operator=(const QSharedData &) = delete;~QSharedData() = default;
};template <class T> class QSharedDataPointer
{
public:typedef T Type;typedef T *pointer;/***************************************************//// 分离数据inline void detach() { if (d && d->ref.loadRelaxed() != 1) detach_helper(); }/***************************************************/inline T &operator*() { detach(); return *d; }inline const T &operator*() const { return *d; }inline T *operator->() { detach(); return d; }inline const T *operator->() const { return d; }inline operator T *() { detach(); return d; }inline operator const T *() const { return d; }inline T *data() { detach(); return d; }inline const T *data() const { return d; }inline const T *constData() const { return d; }inline bool operator==(const QSharedDataPointer<T> &other) const { return d == other.d; }inline bool operator!=(const QSharedDataPointer<T> &other) const { return d != other.d; }inline QSharedDataPointer() { d = nullptr; }inline ~QSharedDataPointer() { if (d && !d->ref.deref()) delete d; }explicit QSharedDataPointer(T *data) noexcept;inline QSharedDataPointer(const QSharedDataPointer<T> &o) : d(o.d) { if (d) d->ref.ref(); }inline QSharedDataPointer<T> & operator=(const QSharedDataPointer<T> &o) {if (o.d != d) {if (o.d)o.d->ref.ref();T *old = d;d = o.d;if (old && !old->ref.deref())delete old;}return *this;}inline QSharedDataPointer &operator=(T *o) {if (o != d) {if (o)o->ref.ref();T *old = d;d = o;if (old && !old->ref.deref())delete old;}return *this;}QSharedDataPointer(QSharedDataPointer &&o) noexcept : d(o.d) { o.d = nullptr; }inline QSharedDataPointer<T> &operator=(QSharedDataPointer<T> &&other) noexcept{QSharedDataPointer moved(std::move(other));swap(moved);return *this;}inline bool operator!() const { return !d; }inline void swap(QSharedDataPointer &other) noexcept{ qSwap(d, other.d); }protected:T *clone();private:void detach_helper();T *d;
};template <class T> inline bool operator==(std::nullptr_t p1, const QSharedDataPointer<T> &p2)
{Q_UNUSED(p1);return !p2;
}template <class T> inline bool operator==(const QSharedDataPointer<T> &p1, std::nullptr_t p2)
{Q_UNUSED(p2);return !p1;
}template <class T> class QExplicitlySharedDataPointer
{
public:typedef T Type;typedef T *pointer;inline T &operator*() const { return *d; }inline T *operator->() { return d; }inline T *operator->() const { return d; }inline T *data() const { return d; }inline const T *constData() const { return d; }inline T *take() { T *x = d; d = nullptr; return x; }inline void detach() { if (d && d->ref.loadRelaxed() != 1) detach_helper(); }inline void reset(){if(d && !d->ref.deref())delete d;d = nullptr;}inline operator bool () const { return d != nullptr; }inline bool operator==(const QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &other) const { return d == other.d; }inline bool operator!=(const QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &other) const { return d != other.d; }inline bool operator==(const T *ptr) const { return d == ptr; }inline bool operator!=(const T *ptr) const { return d != ptr; }inline QExplicitlySharedDataPointer() { d = nullptr; }inline ~QExplicitlySharedDataPointer() { if (d && !d->ref.deref()) delete d; }explicit QExplicitlySharedDataPointer(T *data) noexcept;inline QExplicitlySharedDataPointer(const QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &o) : d(o.d) { if (d) d->ref.ref(); }template<class X>inline QExplicitlySharedDataPointer(const QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<X> &o)
#ifdef QT_ENABLE_QEXPLICITLYSHAREDDATAPOINTER_STATICCAST: d(static_cast<T *>(o.data()))
#else: d(o.data())
#endif{if(d)d->ref.ref();}inline QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> & operator=(const QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &o) {if (o.d != d) {if (o.d)o.d->ref.ref();T *old = d;d = o.d;if (old && !old->ref.deref())delete old;}return *this;}inline QExplicitlySharedDataPointer &operator=(T *o) {if (o != d) {if (o)o->ref.ref();T *old = d;d = o;if (old && !old->ref.deref())delete old;}return *this;}inline QExplicitlySharedDataPointer(QExplicitlySharedDataPointer &&o) noexcept : d(o.d) { o.d = nullptr; }inline QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &operator=(QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &&other) noexcept{QExplicitlySharedDataPointer moved(std::move(other));swap(moved);return *this;}inline bool operator!() const { return !d; }inline void swap(QExplicitlySharedDataPointer &other) noexcept{ qSwap(d, other.d); }protected:T *clone();private:void detach_helper();T *d;
};template <class T>
Q_INLINE_TEMPLATE QSharedDataPointer<T>::QSharedDataPointer(T *adata) noexcept: d(adata)
{ if (d) d->ref.ref(); }template <class T>
Q_INLINE_TEMPLATE T *QSharedDataPointer<T>::clone()
{return new T(*d);
}template <class T>
Q_OUTOFLINE_TEMPLATE void QSharedDataPointer<T>::detach_helper()
{T *x = clone();x->ref.ref();if (!d->ref.deref())delete d;d = x;
}template <class T>
Q_INLINE_TEMPLATE T *QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T>::clone()
{return new T(*d);
}template <class T>
Q_OUTOFLINE_TEMPLATE void QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T>::detach_helper()
{T *x = clone();x->ref.ref();if (!d->ref.deref())delete d;d = x;
}template <class T>
Q_INLINE_TEMPLATE QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T>::QExplicitlySharedDataPointer(T *adata) noexcept: d(adata)
{ if (d) d->ref.ref(); }template <class T> inline bool operator==(std::nullptr_t p1, const QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &p2)
{Q_UNUSED(p1);return !p2;
}template <class T> inline bool operator==(const QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &p1, std::nullptr_t p2)
{Q_UNUSED(p2);return !p1;
}template <class T>
Q_INLINE_TEMPLATE void swap(QSharedDataPointer<T> &p1, QSharedDataPointer<T> &p2)
{ p1.swap(p2); }template <class T>
Q_INLINE_TEMPLATE void swap(QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &p1, QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &p2)
{ p1.swap(p2); }template <class T>
Q_INLINE_TEMPLATE uint qHash(const QSharedDataPointer<T> &ptr, uint seed = 0) noexcept
{return qHash(ptr.data(), seed);
}
template <class T>
Q_INLINE_TEMPLATE uint qHash(const QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T> &ptr, uint seed = 0) noexcept
{return qHash(ptr.data(), seed);
}template<typename T> Q_DECLARE_TYPEINFO_BODY(QSharedDataPointer<T>, Q_MOVABLE_TYPE);
template<typename T> Q_DECLARE_TYPEINFO_BODY(QExplicitlySharedDataPointer<T>, Q_MOVABLE_TYPE);QT_END_NAMESPACE#endif // QSHAREDDATA_H相关文章:

Qt隐式共享浅析
一、什么是隐式共享 Qt 的隐式共享(implicit sharing)机制是一种设计模式,用于在进行数据拷贝时提高效率和减少内存占用。 在 Qt 中,许多类(如 QString、QList 等)都使用了隐式共享机制。这意味着当这些类…...

2023年我国网络安全法律法规一览
2023 年,是我国网络安全和数据安全领域法制建设持续发展的一年。政府进一步加大网络安全法规的制定和实施力度,不断强化数据安全和关键信息基础设施的保护,中央政府、国务院、中央网信办、工信部及各地方政府部门在《关键信息基础设施安全保护…...
Qt/QML编程学习之心得:一个音频播放器的实现(29)
在window下,打开音乐播放器,然后打开一个.mp3文件,就可以实现播放了,那么在Qt/QML中如何实现呢?首先所有的设计都是基于音乐播放器的,嵌入式linux下同样也有音乐播放器,比如mplayer。其调用方法…...
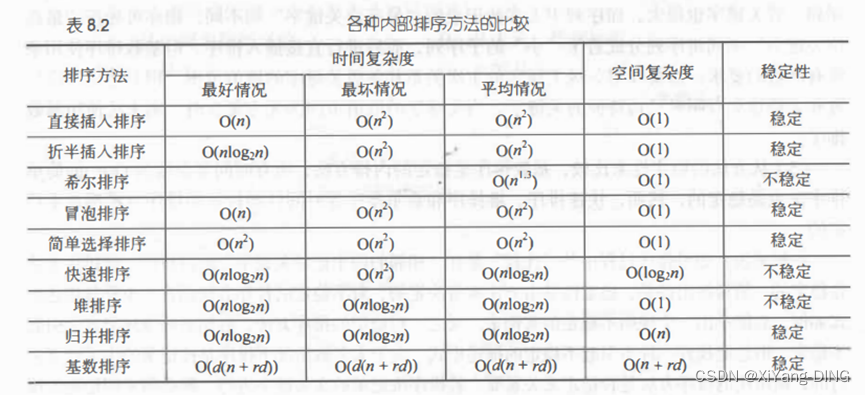
【数据结构】数据结构中应用题大全(完结)
自己在学习过程中总结了DS中几乎所有的应用题,可以用于速通期末考/考研/各种考试。很多方法来源于B站大佬,底层原理本文不做过多介绍,建议自己研究。例题大部分选自紫皮严书。pdf版在主页资源 一、递归时间/空间分析 1.时间复杂度的分析 设…...
WPF常用控件-Window
常用属性 这里重点记录一些关键且容易忘记的属性,那些很常用的如Title啥的就不在这里一一说明了。 任务栏按钮 ShowInTaskbar:是否在任务栏中显示应用按钮,默认为True。 层级 Topmost:应用是否始终在所有应用的最上层&#x…...

计算机网络——实验七
使用socket实现一个基于C/S架构的通信程序 (1)客户端发送给服务器请求,发送表征身份的用户名和密码("admin","123456"); (2)服务器根据客户端发来的信息验证身份,如果验证…...

数据分析基础之《pandas(1)—pandas介绍》
一、pandas介绍 1、2008年Wes McKinney(韦斯麦金尼)开发出的库 2、专门用于数据分析的开源python库 3、以numpy为基础,借力numpy模块在计算方面性能高的优势 4、基于matplotlib能够简便的画图 5、独特的数据结构 6、也是三个单词组合而…...

LLM_InterLM-Demo学习
reference Github: https://github.com/InternLM/tutorial/blob/main/helloworld/hello_world.md 1- 环境配置 之前都是用科学上网在huggingFace进行的模型下载,同时还需要进行一些配置 import os os.environ[CURL_CA_BUNDLE] 在本次的学习中发现可以设置镜像或…...

倍思科技红海突围要义:紧随新趋势,“实用而美”理念从一而终
移动数码周边市场始终不缺热度。 销售端是业绩的节节高升,如在2023年京东双十一,移动数码周边产品销售成果丰硕,根据京东战报,大功率充电器成交额同比提升 200%,65W以上移动电源成交额同比提升 150%,自带线…...
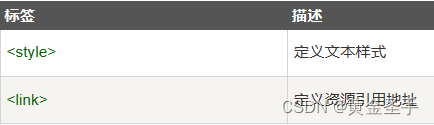
十、HTML 样式- CSS
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) 用于渲染HTML元素标签的样式。 一、实例 1、HTML使用样式 本例演示如何使用添加到 <head> 部分的样式信息对 HTML 进行格式化。 <!DOCTYPE html> <html><head><meta charset"utf-8"><title>HTM…...

Spring的mybatis整合
mybatis整合 主要是处理dao包下的接口和xml文件,以及service下的类和接口 第一步 在resource目录下创建mybatis-config.xml文件【注意点:mybatis-config.xml文件下通常都是写别名、和mappers】 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"U…...
React 入门 - 01
本章内容 目录 1. 简介1.1 初始 React1.2 React 相关技术点1.3 React.js vs Vue.js 2. React 开发环境准备2.1 关于脚手架工具2.2 create-react-app 构建一个 React 项目工程 1. 简介 1.1 初始 React React JS 是 Facebook 在 2013年5月开源的一款前端框架,其带来…...
Windows Server 2019 Standard 和 Datacenter 版本差异比较
文章目录 正式版本的通用功能差异锁定和限制差异服务器角色差异可用功能差异Windows 2019 ISO下载推荐阅读 在测试hyper-V的过程中,计划安装一个Windows 2019的OS,顺便了解Windows Server 2019 的 Standard 和 Datacenter 版本有哪些差异?我们…...

计算机网络的交通灯:停止-等待协议
停止-等待协议是一种在计算机网络通信中常用的协议,用于在数据传输过程中进行流量控制。它的核心思想是在发送端发送数据后,等待接收端的确认信号,确保数据的可靠传输。本文将深入探讨停止-等待协议的原理、优缺点以及在实际应用中的局限性。…...
命令行模式的rancher如何安装?
在学习kubectl操作的时候,发现rancher也有命令行模式,学习整理记录此文。 说明 rancher 命令是 Rancher 平台提供的命令行工具,用于管理 Rancher 平台及其服务。 前提 已经参照前文安装过了rancher环境了,拥有了自己的k8s集群…...

苍穹外卖Day01——总结1
总结1 1. 软件开发整体介绍1.1 软件开发流程1.2 角色分工1.3 软件环境 2. 苍穹外卖项目介绍2.1 项目介绍2.2 技术选项 3. Swagger4. 补充内容(待解决...) 1. 软件开发整体介绍 1.1 软件开发流程 1.2 角色分工 从角色分工里面就可以查看自己以后从事哪一…...
)
Java 基础(二)
数组 数组就是一个容器,用来存一批同类型的数据 数组关键要素:定义及初始化、元素访问和元素遍历 1.静态初始化数组 // 完整格式 数据类型[] 数组名 new 数据类型[]{元素1,元素2 ,元素3… };// 简化格式数据类型[] 数组名 …...
BERT 模型是什么
科学突破很少发生在真空中。相反,它们往往是建立在积累的人类知识之上的阶梯的倒数第二步。要了解 ChatGPT 和 Google Bart 等大型语言模型 (LLM) 的成功,我们需要回到过去并谈论 BERT。 BERT 由 Google 研究人员于 2018 年开发&…...

Elasticsearch中object类型与nested类型以及数组之间的区别
一、区别: 0、一般情况下用object 类型来查es中为json对象的字段数据,用nested来查es中为JsonArray数组类型的字段数据。 1、默认情况下ES会把JSON对象直接映射为object类型,只有手动设置才会映射为nested类型 2、object类型可以直接使用普…...

办公文档,私人专用
一、安装Minio 1.1、创建文件夹,并在指定文件夹中下载minio文件 cd /opt mkdir minio cd minio touch minio.log wget https://dl.minio.io/server/minio/release/linux-amd64/minio1.2、赋予minio文件执行权限 chmod 777 minio1.3、启动minio ./minio server /…...
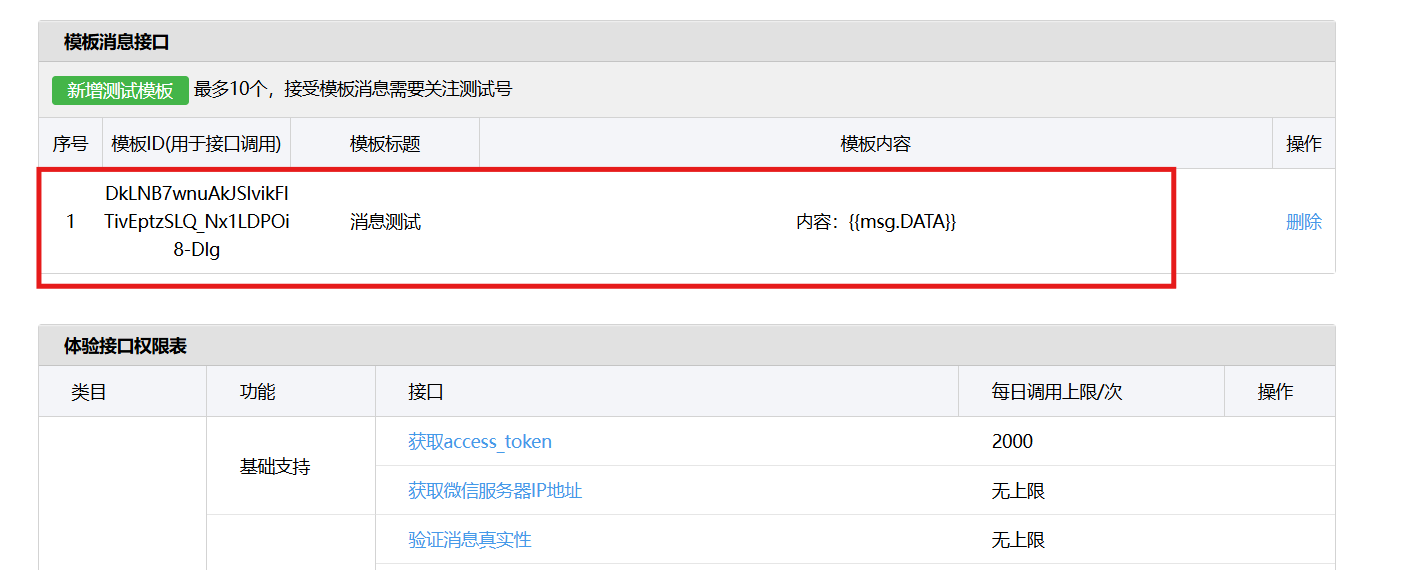
测试微信模版消息推送
进入“开发接口管理”--“公众平台测试账号”,无需申请公众账号、可在测试账号中体验并测试微信公众平台所有高级接口。 获取access_token: 自定义模版消息: 关注测试号:扫二维码关注测试号。 发送模版消息: import requests da…...
大数据学习栈记——Neo4j的安装与使用
本文介绍图数据库Neofj的安装与使用,操作系统:Ubuntu24.04,Neofj版本:2025.04.0。 Apt安装 Neofj可以进行官网安装:Neo4j Deployment Center - Graph Database & Analytics 我这里安装是添加软件源的方法 最新版…...

边缘计算医疗风险自查APP开发方案
核心目标:在便携设备(智能手表/家用检测仪)部署轻量化疾病预测模型,实现低延迟、隐私安全的实时健康风险评估。 一、技术架构设计 #mermaid-svg-iuNaeeLK2YoFKfao {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg…...
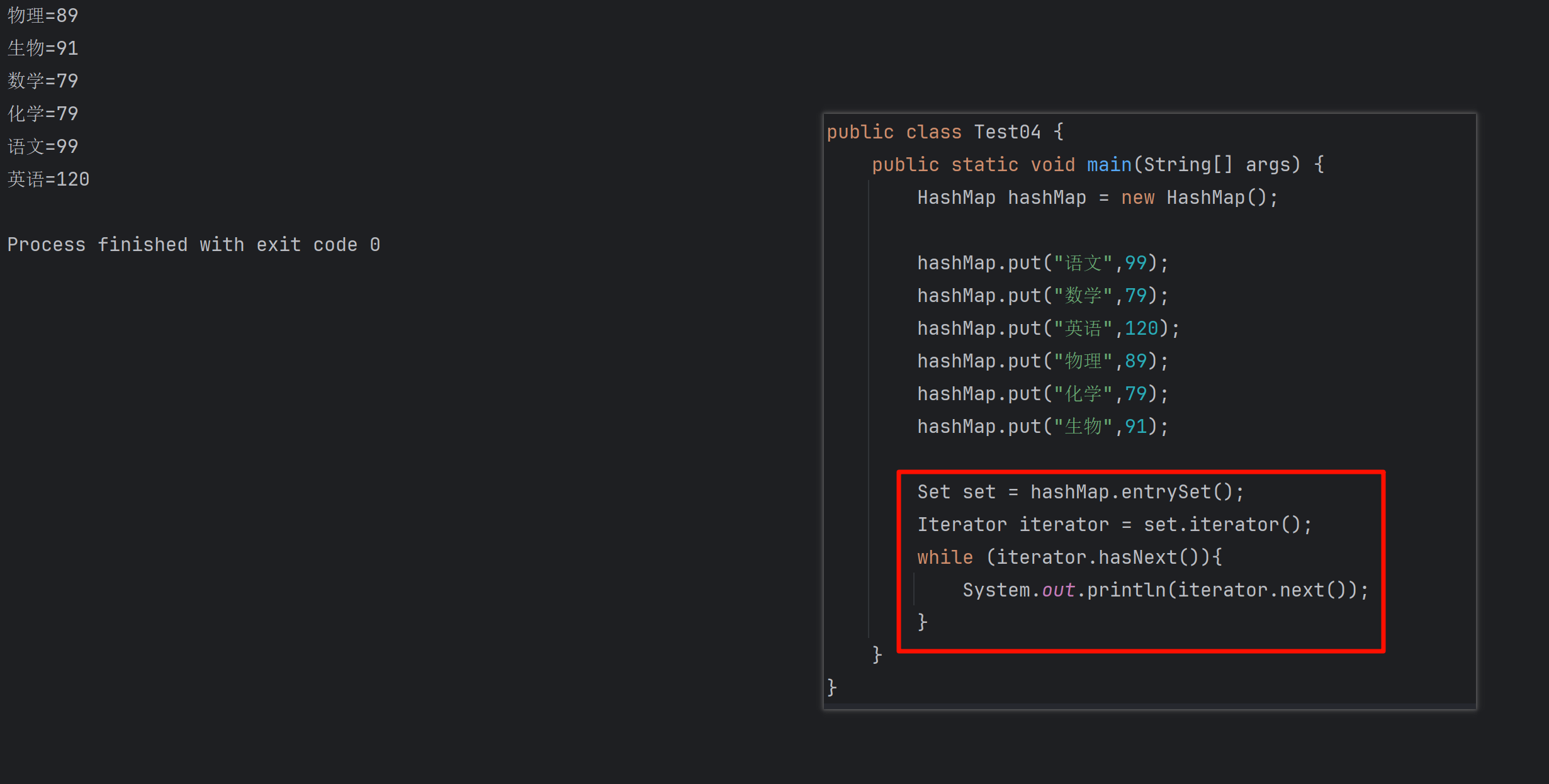
遍历 Map 类型集合的方法汇总
1 方法一 先用方法 keySet() 获取集合中的所有键。再通过 gey(key) 方法用对应键获取值 import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Set;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap hashMap new HashMap();hashMap.put("语文",99);has…...

django filter 统计数量 按属性去重
在Django中,如果你想要根据某个属性对查询集进行去重并统计数量,你可以使用values()方法配合annotate()方法来实现。这里有两种常见的方法来完成这个需求: 方法1:使用annotate()和Count 假设你有一个模型Item,并且你想…...
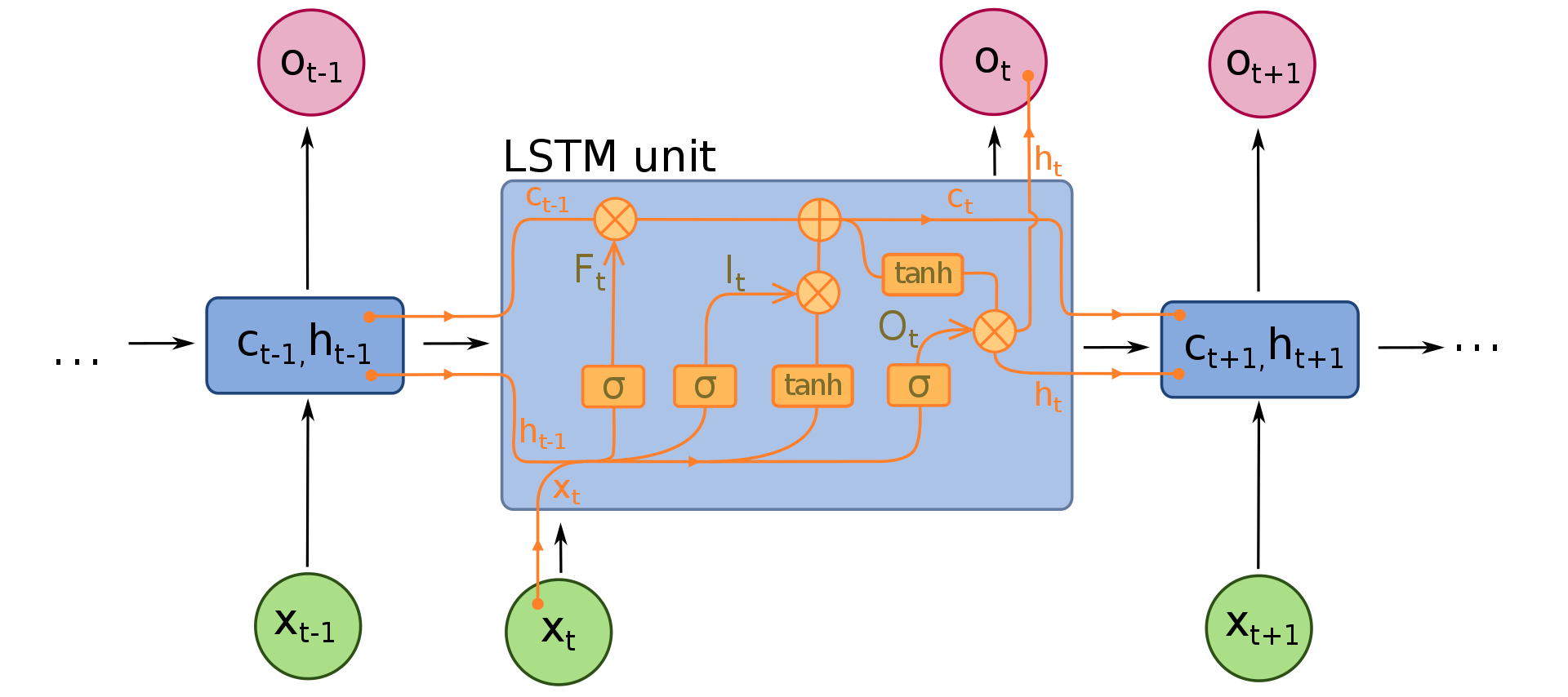
NLP学习路线图(二十三):长短期记忆网络(LSTM)
在自然语言处理(NLP)领域,我们时刻面临着处理序列数据的核心挑战。无论是理解句子的结构、分析文本的情感,还是实现语言的翻译,都需要模型能够捕捉词语之间依时序产生的复杂依赖关系。传统的神经网络结构在处理这种序列依赖时显得力不从心,而循环神经网络(RNN) 曾被视为…...
嵌入式学习笔记DAY33(网络编程——TCP)
一、网络架构 C/S (client/server 客户端/服务器):由客户端和服务器端两个部分组成。客户端通常是用户使用的应用程序,负责提供用户界面和交互逻辑 ,接收用户输入,向服务器发送请求,并展示服务…...
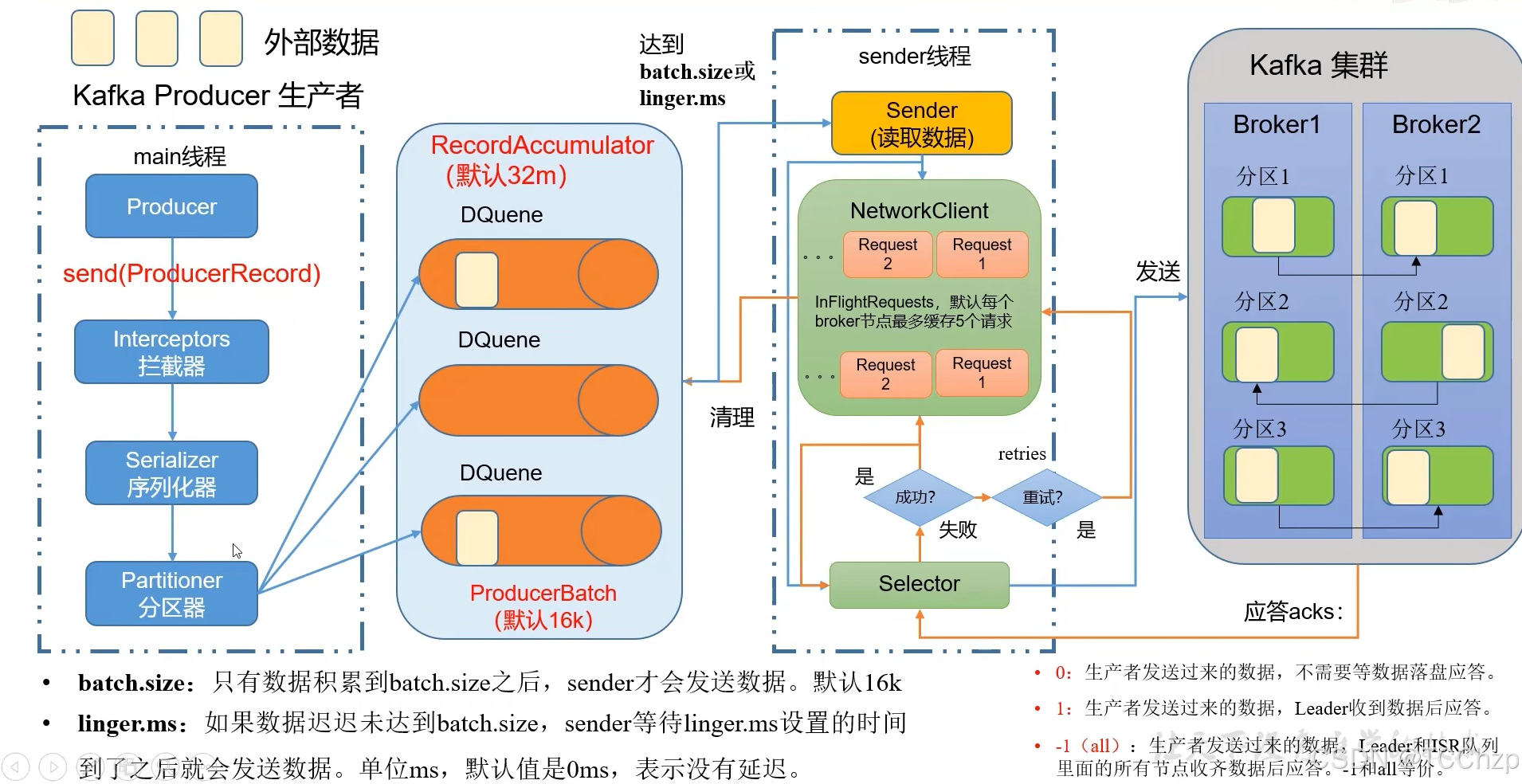
Kafka入门-生产者
生产者 生产者发送流程: 延迟时间为0ms时,也就意味着每当有数据就会直接发送 异步发送API 异步发送和同步发送的不同在于:异步发送不需要等待结果,同步发送必须等待结果才能进行下一步发送。 普通异步发送 首先导入所需的k…...

JS手写代码篇----使用Promise封装AJAX请求
15、使用Promise封装AJAX请求 promise就有reject和resolve了,就不必写成功和失败的回调函数了 const BASEURL ./手写ajax/test.jsonfunction promiseAjax() {return new Promise((resolve, reject) > {const xhr new XMLHttpRequest();xhr.open("get&quo…...
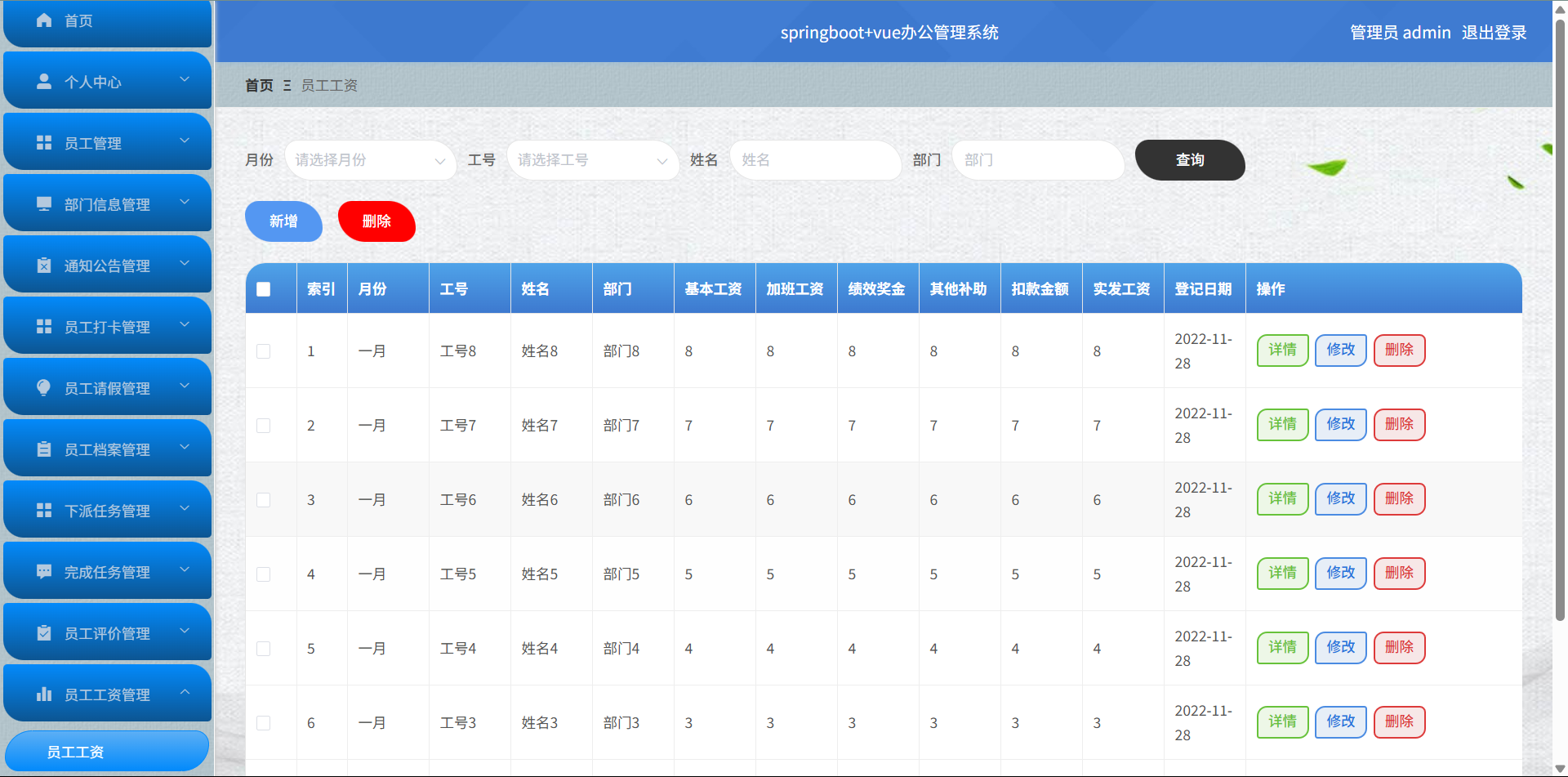
基于Springboot+Vue的办公管理系统
角色: 管理员、员工 技术: 后端: SpringBoot, Vue2, MySQL, Mybatis-Plus 前端: Vue2, Element-UI, Axios, Echarts, Vue-Router 核心功能: 该办公管理系统是一个综合性的企业内部管理平台,旨在提升企业运营效率和员工管理水…...
