有了Future为什么还要CompletableFuture?
文章目录
- Future 接口理论知识复习
- Future 接口概述
- 场景描述
- 小结
- Future 接口常用实现类 FutureTask 异步任务
- Future 的作用
- Futrue 编码测试
- 优缺点分析
- 优点
- 缺点
- 小结
- 面对一些复杂的任务
- 对于简单的业务场景使用 Future 接口完全 OK
- 回调通知
- 创建异步任务
- 多个任务前后依赖可以组合
- 对计算速度选最快
- CompletableFuture 应运而生
- CompletableFuture 对 Future 的改进
- CompletableFuture 为什么会出现?
- CompletableFuture 与 CompletionStage 源码
- 类继承架构
- 接口 CompletionStage
- 类 CompletionFuture
- 核心的四个静态方法,创建一个异步任务
- runAsync 方法---无返回值
- supplyAsync 方法---有返回值
- 关于参数 Executor 说明
- 减少阻塞和轮询
- CompletableFuture 的优点
- 电商网站比价需求案例
- 函数式编程已经主流
- Lambda 表达式+Stream 流式应用+Chain 链式调用+Java8 函数式编程
- Runnable
- Function
- Consumer
- Supplier
- Summer
- 先说说 join 和 get 的对比
- 大厂业务需求说明
- Java8 函数式编程在 Case 中的应用
- 方案一,step by step
- 方案二,asyncExecutor
- 效果比较
- CompletableFuture 的常用方法
- 获得结果和触发计算
- get()
- get(long time,TimeUnit unit)
- join()
- getNow(String valueIfAbsent)
- complete(T value)
- 对计算结果进行处理
- thenApply
- handle
- Summary
- 对计算结果进行消费
- demo
- 补充
- CompletableFuture 和线程池说明
- 对计算速度进行选用
- 对计算结果进行合并
Future 接口理论知识复习
Future 接口概述
- Future 接口(FutureTask 实现类)定义了异步任务执行的一些方法
- 获取异步任务执行的结果
- 取消异步任务执行
- 判断任务是否被取消,
- 判断任务执行是否完毕等
场景描述
- 主线程让一个子线程去执行任务,子线程可能比较耗时,如果没有实现异步任务执行,主线程只能一直等待
- Future 接口支持了异步任务执行之后,子线程开始执行任务的同时,主线程继续执行自身任务,等到主线程或者子线程任务完成之后,主线程才会获取子线程任务执行结果
- 上课买水案例…
小结
Future 接口可为主线程开启一个分支任务,专门为主线程处理耗时和废力的复杂业务
Future 接口常用实现类 FutureTask 异步任务
- Future 接口是 Java5 新增的一个接口,提供了一种异步并行计算的功能
- 若主线程需要执行一些很耗时的计算任务,可以通过 future 把该任务放到异步线程中去执行
- 主线程继续处理其他任务或者先行结束,再通过 Future 获取计算结果
Future 的作用
- 异步多线程任务执行且返回有结果,三个特点
- 多线程
- 有返回
- 异步任务
- 为什么是 Future?

Futrue 编码测试
public class CompletableFutureDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new MyThread());Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask, "t1");t1.start();System.out.println(futureTask.get());}
}class MyThread implements Callable<String> {@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {System.out.println("-----come in call() ");return "hello Callable";}
}

优缺点分析
优点
- futrue+线程池异步多线程任务配合,能显著提高代码的执行效率
- 串型执行
//3个任务,目前只有一个线程main来处理,请问耗时多少?long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//暂停毫秒try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("----costTime: " + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t -----end");

- 使用 futureTask+线程池异步多线程任务
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();FutureTask<String> futureTask1 = new FutureTask<String>(() -> {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "task1 over";});threadPool.submit(futureTask1);FutureTask<String> futureTask2 = new FutureTask<String>(() -> {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "task2 over";});threadPool.submit(futureTask2);System.out.println(futureTask1.get());System.out.println(futureTask2.get());try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("----costTime: " + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t -----end");threadPool.shutdown();
缺点
- get 的获取容易阻塞
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<String>(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t -----come in");try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "task over";});Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask, "t1");t1.start();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t ----忙其它任务了");System.out.println(futureTask.get());

- get容易导致阻塞,一般建议放在程序后面,一旦调用不见不散,非要等到结果才会离开,不管你是否计算完成,容易程序堵塞。
System.out.println(futureTask.get());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t ----忙其它任务了");

- 假如我不愿意等待很长时间,我希望过时不候,可以自动离开.
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t ----忙其它任务了");System.out.println(futureTask.get(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
- 超过 3 秒结束线程抛出 TimeOutException

- 轮询耗费 CPU
while (true) {if (futureTask.isDone()) {//futureTask执行完成System.out.println(futureTask.get());break;} else {//暂停毫秒,未完成,持续等待try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火");}}

小结
- get(),一旦调用 get 方法求结果,如果计算没有完成,容易导致线程阻塞
- isDone()轮询
- 轮询的方式会消耗无谓的 CPU 资源,而且也不见得能及时得到计算结果
- 如果想要异步获取,通常都会以轮询的方式去获取结果,尽量不使用阻塞
- Future 对于结果的获取不是很友好,只能通过阻塞或轮询的方式得到结果
面对一些复杂的任务
对于简单的业务场景使用 Future 接口完全 OK
回调通知
- 应对 Future 的完成时间,完成之后发起回调通知
- 通过轮询方式去判断任务是否完成,非常不优雅,也占用 CPU
创建异步任务
- Future+线程池配合
多个任务前后依赖可以组合
- 若想将多个异步任务的计算结果组合起来,则后一个异步任务的计算结果,需要前一个异步任务的值
- 将两个或多个异步计算合成一个异步计算,这几个异步计算,互相独立,同时后面这个又依赖于前一个处理的结果
对计算速度选最快
- 当 Future 集合中某个任务最快结束时,返回结果,返回第一名处理结果
CompletableFuture 应运而生
- 使用 Future 接口提供的 API,处理不够优雅

- CompletableFuture 以声明式方式优雅的处理这些需求同时规避 Future 自身获取计算结果的弊端
CompletableFuture 对 Future 的改进
CompletableFuture 为什么会出现?
- get()方法在 Future 计算完成之前会一直处于阻塞状态下
- isDone()方法容易耗费 CPU 资源
- 对于真正在异步处理中我们希望可以通过传入回调函数,在 Future 结束时自动回调该函数,这样就不需要等待结果
- 阻塞的方式和异步编程的设计理念相违背,而轮询的方式会耗费无谓的 CPU 资源
- 因此,JDK8 设计出 CompletableFuture
- CompletableFuture 提供了一种与观察者模式类似的机制,可以让任务执行完成后通知监听的一方
- CompletableFuture 提供了一种与观察者模式类似的机制,可以让任务执行完成后通知监听的一方
CompletableFuture 与 CompletionStage 源码
类继承架构
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T>{}

接口 CompletionStage
- CompletionStage 代表异步计算过程中的某个阶段,一个阶段完成以后会触发另一个阶段(类似于 Linux 管道分隔符传参数)
- 一个阶段的计算执行可以是一个 Function,Consumer 或者 Runnable
//示例如下
stage
.thenApply(x->square(x))
.thenAccept(x->System.out.print(x))
.thenRun(()->System.out.println())
- 一个阶段的执行可能被单个阶段的完成触发,也可能有多个阶段一起触发
类 CompletionFuture
- Java8 中,CompletableFuture 提供了非常强大的 Future 的扩展功能,简化异步编程的复杂性,并且提供了函数式编程的能力,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,提供了转化和组合 CompletionFuture 的方法
- 它可能代表了一个明确完成 Future,也可能代表一个完成阶段 CompletionStage,它支持在计算完成之后触发一些函数或执行某些动作
- 实现了 Future 和 CompletionStage 接口
核心的四个静态方法,创建一个异步任务
- 为什么要不用 new CompletionFuture()方式创建异步任务

- API 中说明通过 new CompletionFuture()方式会创建一个不完备的 CompletionFuture,官方也不推荐使用该方式
runAsync 方法—无返回值
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)- 使用默认的 ForkJoinPool 线程池
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});System.out.println(completableFuture.get());

public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor)- 使用定义的线程池对象
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}},threadPool);System.out.println(completableFuture.get());threadPool.shutdown();

supplyAsync 方法—有返回值
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hello supplyAsync";});System.out.println(completableFuture.get());

public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,Executor executor)
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hello supplyAsync";},threadPool);System.out.println(completableFuture.get());threadPool.shutdown();

关于参数 Executor 说明
- 没有指定 Executor 的方法,直接默认使用 ForkJoinPool.commonPool()作为线程池,作为它的线程池执行异步代码
- 若指定线程池,则使用自定义或者特别定义的线程池执行异步代码
减少阻塞和轮询
- 从 Java8 开始引入了 CompletableFuture,它是 Future 的功能增强版,减少阻塞和轮询,
- 可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动回调对象的回调方法
- 使用 CompletableFuture 实现 Future 的功能
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----come in");int result = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("-----1秒钟后出结果:" + result);return result;});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程先去忙其它任务");System.out.println(completableFuture.get());

- CompletableFuture.supplyAsync()完成异步编程返回结果
try {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----come in");int result = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("-----1秒钟后出结果:" + result);return result;}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {//v为上述计算完成的result,e为异常if (e == null) { //没有异常System.out.println("-----计算完成,更新系统UpdateValue:" + v);}}).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("异常情况:" + e.getCause() + "\t" + e.getMessage());return null;});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程先去忙其它任务");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {threadPool.shutdown();}

- 解释下为什么默认线程池关闭,自定义线程池记得关闭?
- 用户线程中,程序执行完成需要 1 秒钟,main 线程执行太快,在 ForkJoinPool 线程池中若发现 main 线程执行完成则会关闭线程池
- 解决方法
- 将 main 线程延迟 1 秒,在用户线程的 try/catch/finally 代码之后添加睡眠代码
//主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:暂停3秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}

- 或是使用定义的线程对象,或是自定义线程对象
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);try {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----come in");int result = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("-----1秒钟后出结果:" + result);return result;},threadPool).whenComplete((v, e) -> {if (e == null) {System.out.println("-----计算完成,更新系统UpdateValue:" + v);}}).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("异常情况:" + e.getCause() + "\t" + e.getMessage());return null;});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程先去忙其它任务");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {threadPool.shutdown();}

- 编写异常代码测试


CompletableFuture 的优点
- 异步任务结束时,会自动调用对象的方法
- 主线程设置好回调之后,不在关系异步任务的执行,异步任务之间可以顺序进行
- 异步任务出错时,会自动调用某个对象的方法
try {//调用异步任务,传入线程池对象asyncTask(threadPool);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程先去忙其它任务");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {threadPool.shutdown();}//...主线程void asyncTask(ExecutorService threadPool) {//...业务的逻辑return result;}, threadPool).whenComplete((v, e) -> {//回调接口callInterface(v, e);}).exceptionally(e -> {//异常接口e.printStackTrace();exceptionHandel(e);return null;});}
电商网站比价需求案例
函数式编程已经主流
- 大厂面试题

Lambda 表达式+Stream 流式应用+Chain 链式调用+Java8 函数式编程
Runnable
- 无参数,无返回值
package java.lang;@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {public abstract void run();
}
Function
- Function<T,R>接受一个参数,并且有返回值
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {R apply(T t);
}
Consumer
- Consumer 接受一个参数,没有返回值
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> {void accept(T t);
}
- BiConsumer<T,U>接受两个参数,没有返回值
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BiConsumer<T, U> {void accept(T t, U u);
}
- 在回调 CompletableFuture.whenComplete 方法中进行调用

Supplier
- 供给型函数式接口,没有参数,有一个返回值
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {/*** Gets a result.** @return a result*/T get();
}
Summer

先说说 join 和 get 的对比
- get 在程序编译时会检查异常,join 在程序编译时不会检查异常,此外于 get 基本等价
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "join and get";});System.out.println(supplyAsync.join());

- 说说你过去工作中的项目亮点!!!(面试必备)
大厂业务需求说明
- 切记,先完成功能再到性能的逐步迭代
- 电商网站比价需求分析
案例说明:电商比价需求,模拟如下情况:1. 需求:1.1 同一款产品,同时搜索出同款产品在各大电商平台的售价;1.2 同一款产品,同时搜索出本产品在同一个电商平台下,各个入驻卖家售价是多少2. 输出:出来结果希望是同款产品的在不同地方的价格清单列表,返回一个List<String>《mysql》 in jd price is 88.05《mysql》 in dangdang price is 86.11《mysql》 in taobao price is 90.433. 解决方案,对别同一个商品在各个平台上的价格,要求获得一个清单列表3.1. step by step,按部就班查完jd,查taobao,查完taobao查天猫.....3.2. all in ,使用多线程,异步任务执行同时查询多个平台4. 技术要求3.1 函数式编程3.2 链式编程3.3 Stream流式计算
Java8 函数式编程在 Case 中的应用
- 创建资源
- 电商网站类
//电商网站类
class NetMall {/*** 电商网站名 jd,pdd taobao...*/@Getterprivate String netMallName;/*** 构造方法* @param netMallName*/public NetMall(String netMallName) {this.netMallName = netMallName;}/*** 售价* @param productName* @return*/public double calcPrice(String productName) {try {//查询需要1秒钟TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//模拟价格return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() * 2 + productName.charAt(0);}
}
- 查询电商网站
static List<NetMall> list = Arrays.asList(new NetMall("jd"),new NetMall("dangdang"),new NetMall("taobao"),new NetMall("pdd"),new NetMall("tmall"));
方案一,step by step
- 使用流式计算,查询返回结果
/*** step by step 一家家搜查* List<NetMall> ----->map------> List<String>** @param list* @param productName* @return*/public static List<String> getPrice(List<NetMall> list, String productName) {//《mysql》 in taobao price is 90.43return list.stream()//流式计算.map(netMall -> //映射为map集合//字符串格式化String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f",netMall.getNetMallName(),netMall.calcPrice(productName))).collect(Collectors.toList());}- 测试计算结果
public static void main(String[] args) {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();List<String> list1 = getPrice(list, "mysql");for (String element : list1) {System.out.println(element);}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("----costTime: " + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");}

方案二,asyncExecutor
- 基于CompletableFuture.supplyAsync
/*** List<NetMall> ----->List<CompletableFuture<String>>------> List<String>** @param list* @param productName* @return*/public static List<String> getPriceByCompletableFuture(List<NetMall> list, String productName) {return list.stream().map(netMall ->CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f",netMall.getNetMallName(),netMall.calcPrice(productName)))).collect(Collectors.toList()).stream().map(s -> s.join()).collect(Collectors.toList());}- 两次流式映射

public static void main(String[] args) {long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();List<String> list2 = getPriceByCompletableFuture(list, "mysql");for (String element : list2) {System.out.println(element);}long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("----costTime: " + (endTime2 - startTime2) + " 毫秒");
}
效果比较

CompletableFuture 的常用方法
获得结果和触发计算

get()
/*** 获得结果和触发计算** @throws InterruptedException* @throws ExecutionException*/private static void group1() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "abc";});System.out.println(completableFuture.get());}

get(long time,TimeUnit unit)
System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS));

join()
System.out.println(completableFuture.join());

getNow(String valueIfAbsent)
System.out.println(completableFuture.getNow("xxx"));

- 源码解读
- 当调用 getNow 时,计算完成,获取计算结果
- 当调用 getNow 时,计算未完成,返回备选值(valueIfabsent)

- 异步任务执行 1s,主线程 2s,在 ,异步任务在 2s 内执行完成,返回结果给 getNow
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "abc";});//暂停几秒钟线程try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }System.out.println(completableFuture.getNow("xxx"));

complete(T value)
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {//暂停几秒钟线程try {//执行2sTimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "abc";});//执行1stry { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }System.out.println(completableFuture.complete("completeValue") + "\t" + completableFuture.join());

- 源码说明

- 主线程调用异步任务时
- 计算未完成,返回 true,同时将 value 作为 result 给到主线程
- 计算完成,返回 false,同时将异步任务的计算结果给到主线程
- 将异步任务与主线程的睡眠时间互换,得到以下结果

对计算结果进行处理
- 此处 supplyAsync 若不使用指定线程池,主线程执行完会直接结束 jvm
thenApply
- 计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化
- demo
private static void thenApply1(ExecutorService threadPool) {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("111");return 1;}, threadPool).thenApply(f -> {System.out.println("222");return f + 2;}).thenApply(f -> {System.out.println("333");return f;}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {if (e == null) {System.out.println("----计算结果: " + v);}}).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println(e.getMessage());return null;});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----主线程先去忙其它任务");threadPool.shutdown();}

- f=1+2=3
- 异常处理
- 计算过程中出现异常,thenApply(),会直接终止计算


handle
- 计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化
- demo
private static void handle1(ExecutorService threadPool) {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("111");return 1;}, threadPool).handle((f, e) -> {System.out.println("222");return f + 2;}).handle((f, e) -> {System.out.println("333");return f + 3;}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {if (e == null) {System.out.println("----计算结果: " + v);}}).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println(e.getMessage());return null;});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----主线程先去忙其它任务");threadPool.shutdown();}

- 异常处理
- 有异常时,跳过异常代码,带着异常参数继续执行后续代码


Summary

对计算结果进行消费
- 接受任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果
demo
- 源码解读

- 调用了 Consumer 接口,传入参数无返回值
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return 1;}).thenApply(f ->{return f + 2;}).thenApply(f ->{return f + 3;}).thenAccept(System.out::println);}

补充

- thenRun 不调用前置计算的结果

- thenAccpet 获取前置计算结果,最终不返回记过,consumer 直接消费

- thenApply,获取前置计算结果,最终返回所有计算结果

CompletableFuture 和线程池说明
- 以 thenRun 和 thenRunAsync 为例
public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);try {CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("1号任务" + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName());return "abcd";}, threadPool).thenRunAsync(() -> {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("2号任务" + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName());}).thenRun(() -> {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("3号任务" + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName());}).thenRun(() -> {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("4号任务" + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName());});System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {threadPool.shutdown();}}

- 将所有的方法都统一为 thenRun

- 将入口睡眠代码注释

- 结论
- 没有传入自定义线程池,都默认使用 ForkJoinPool
- 传入一个指定线程池之后
- 执行第一个任务时,传入指定线程池
- 调用 thenRun 方法执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务和第二个任务共用同一个线程池
- 调用 thenRunAsync 执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务用指定线程池,第二个任务用 ForkJoinPool
- 执行第一个任务时,传入指定线程池
- 有可能处理太快,系统优化切换原则直接使用 main 线程处理
- 其它 thenAccept 与 thenAccpetAsync,thenApply 和 thenApplyAsync 等,之间的区别亦是同理
- 源码解读


- 调用 thenXxxxAsync 方法默认都会调用一个 ForkJoinPool.commonPool()
对计算速度进行选用
- 谁快用谁
- applyToEither
public static void main(String[] args) {//开启两个异步任务CompletableFuture<String> playA = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("A come in");try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "playA";});CompletableFuture<String> playB = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("B come in");try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "playB";});//比较两个异步任务,返回率先完成计算的异步任务的结果CompletableFuture<String> result = playA.applyToEither(playB, f -> {return f + " is winer";});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "-----: " + result.join());}


对计算结果进行合并
- 两个 CompletionStage 任务都完成后,最终能把两个任务的结果一起交给 thenCombine 进行处理
- 先完成的先等待,所有分支完成后执行 thenCombine
- 拆分方式
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t ---启动");//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 10;});CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t ---启动");//暂停几秒钟线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 20;});CompletableFuture<Integer> result = completableFuture1.thenCombine(completableFuture2, (x, y) -> {System.out.println("-----开始两个结果合并");return x + y;});System.out.println(result.join());}

- 函数式接口方式
private static void interfaceChain() {ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCombineResult = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t"+"come in 1");return 10;}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t"+"come in 2");return 20;}),(x,y)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t"+"x + y = a =" +(x+y));return x + y ;}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t"+"come in 3");return 30;}),(a,b)->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t"+"a + b = " +(a+b));return a+b;});System.out.println("---主线程结束,END");System.out.println(thenCombineResult.join());}


相关文章:

有了Future为什么还要CompletableFuture?
文章目录 Future 接口理论知识复习Future 接口概述场景描述小结 Future 接口常用实现类 FutureTask 异步任务Future 的作用Futrue 编码测试优缺点分析优点缺点小结 面对一些复杂的任务对于简单的业务场景使用 Future 接口完全 OK回调通知创建异步任务多个任务前后依赖可以组合对…...
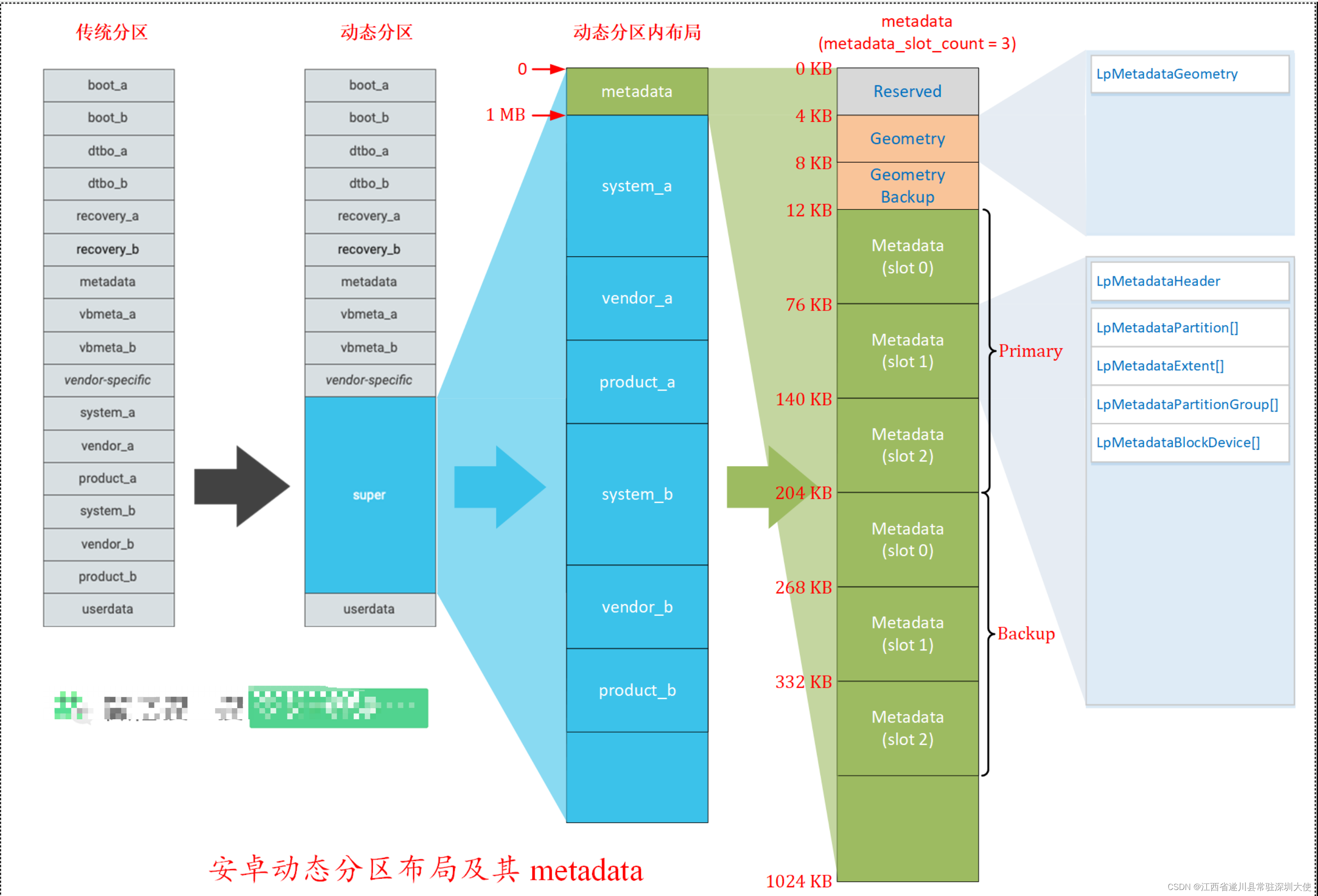
Android super.img解包和打包指南(含工具下载lpunpack、lpmake、lpdump)
本文所有命令均需要在linux 上执行 一、解包 1、将Android sparse image格式的super.img转成二进制文件 $ sudo apt install android-sdk-libsparse-utils $ simg2img super.img super.img.bin 2、下载工具lpunpack 和lpmake、lpdump 以及其依赖库 下载地址:https://downl…...
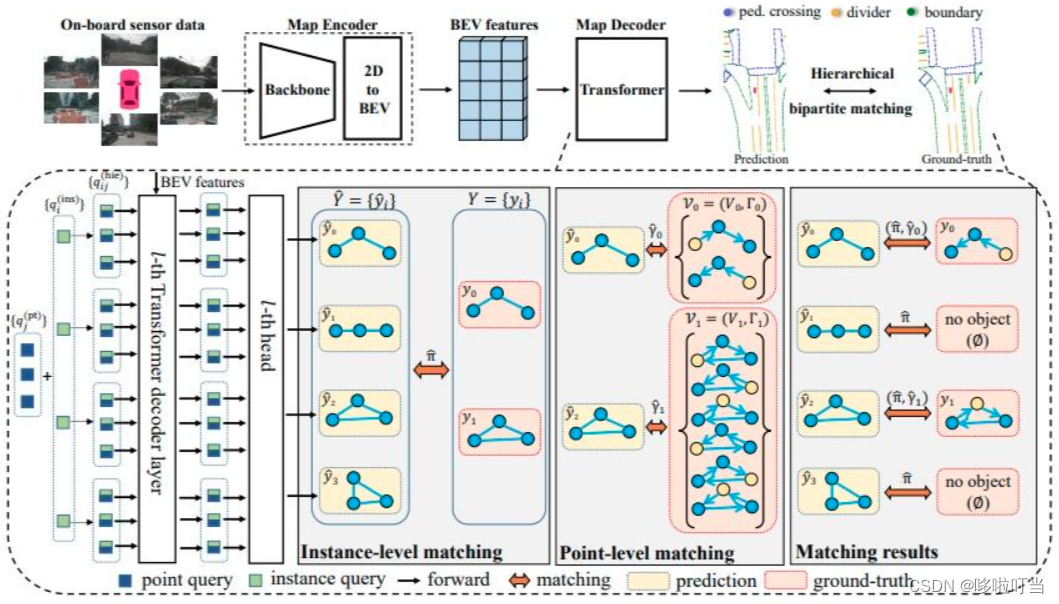
端到端实现高精地图重建(TopoNet解读和横评)
论文出处 [2304.05277] Graph-based Topology Reasoning for Driving Scenes (arxiv.org)https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.05277 TopoNet TopoNet的目标是从车辆上安装的多视角摄像头获取图像,感知实体并推理出驾驶场景的拓扑关系,实现端到端预测…...

系统架构20 - 统一建模语言UML(上)
统一建模语言 组成要素事物关系 在目前的软件开发方法中,面向对象的方法占据着主导地位。面向对象方法的主导地位也决定着软件开发过程模型化技术的发展,面向对象的建模技术方法也就成为主导的方法。 公认的面向对象建模语言出现于20世纪70年代中期。从1…...
数据库学习笔记2024/2/4
随笔 1. 为什么学? 认识数据,熟悉数据,掌握数据。 进企业必备技能。 2. 怎么学? 1、MySQL数据库就是存储和管理数据的一个大型软件,这个软件有一个专门的语言叫SQL,主要学的是SQL语言,但想要达到企业用人标准,就还得学会熟练使用MySQL这个软件。 2、学习分三阶段: 一. …...
Apache POI 处理excel文件 记录用法
Apache POI 写excel public static void write() throws IOException {//再内存中创建了一个Excel文件XSSFWorkbook excel new XSSFWorkbook();//创建一个sheet页XSSFSheet sheet excel.createSheet("info");//这里创建行对象,这里的rownum 是从0开始的,类似于数…...
Transformer实战-系列教程2:Transformer算法解读2
🚩🚩🚩Transformer实战-系列教程总目录 有任何问题欢迎在下面留言 Transformer实战-系列教程1:Transformer算法解读1 Transformer实战-系列教程2:Transformer算法解读2 5、Multi-head机制 在4中我们的输入是X&#x…...
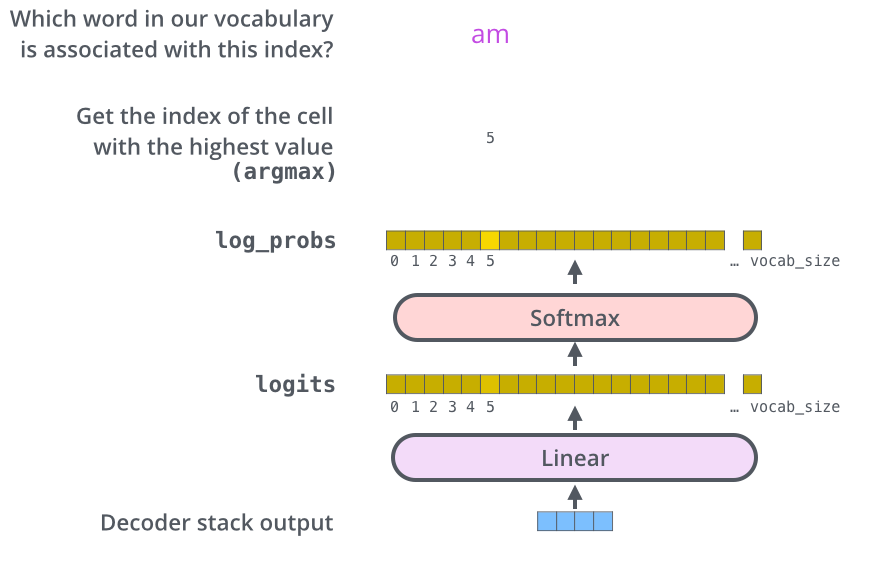
python_蓝桥杯刷题记录_笔记_全AC代码_入门3
前言 记录我的解法以及笔记思路,谢谢观看。 题单目录 1.P2141 [NOIP2014 普及组] 珠心算测验 2.P1567 统计天数 3.P1055 [NOIP2008 普及组] ISBN 号码 4.P1200 [USACO1.1] 你的飞碟在这儿 Your Ride Is Here 5.P1308 [NOIP2011 普及组] 统计单词数 6.P1047 […...
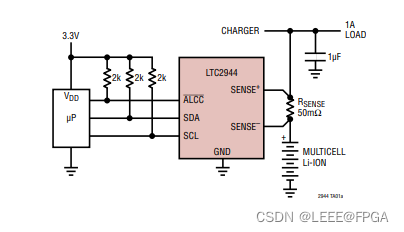
STM32 IIC电量计LTC2944
1 描述 LTC2944 可在便携式产品应用中测量电池充电状态、电池电压、电池电流及其自身温度。宽输入电压范围允许使用高达 60V 的多节电池。精密库仑反向积分电流通过电池正极端子与负载或充电器之间的检测电阻器。 电压、电流和温度由内部 14 位无延迟 ΔΣ™ ADC 测量。测量结…...

Linux 链接 GitHub 出现 Connection timed out
问题 安装GIT并完成公钥验证:Linux 系统拉取 Github项目 [rootxxx devtools]# ssh -T gitgithub.com ssh: connect to host github.com port 22: Connection timed out解决方案 进入在存放公钥私钥id_rsa.pub文件里,新建/修改config文本 [rootxxx my…...
vulnhub靶场之Thales
一.环境搭建 1.靶场描述 Description : Open your eyes and change your perspective includes 2 flags:user.txt and root.txt. Telegram: machineboy141 (for any hint) This works better with VIrtualBox rathe than VMware 2.靶场地址 https://www.vulnhub.com/entry/t…...
Qt之使用Qt内置图标
一效果 二.原理 Qt内置图标封装在QStyle中,共七十多个图标,可以直接拿来用,能应付不少简单程序需求,不用自己去找图标并添加到资源文件了。 下面是内置图标的枚举定义: enum StandardPixmap {SP_TitleBarMenuButton,SP_TitleBarMinButton,SP_TitleBarMaxButton,SP_T…...

《计算机网络简易速速上手小册》第10章:未来网络技术趋势(2024 最新版)
文章目录 10.1 边缘计算与网络设计 - 未来网络的速度与激情10.1.1 基础知识10.1.2 重点案例:使用 Python 实现边缘计算的实时视频分析准备工作Python 脚本示例 10.1.3 拓展案例1:智能交通系统Python 脚本示例 - 边缘计算设备上的交通流量分析 10.1.4 拓展…...
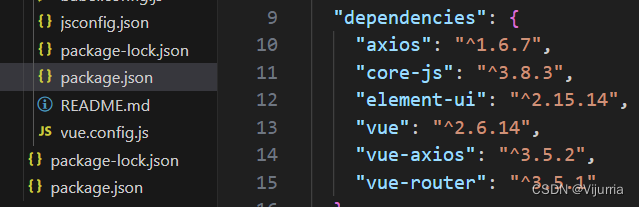
Vue引入Axios
1.命令安装axios和vue-axios npm install axios --save npm install vue-axios --save 2.package.json查看版本 3.在main.js中引用 import axios from axios; import VueAxios from vue-axios; Vue.use(VueAxios,axios) 4.如何使用 (初始化方法) 将下列代…...

【git 本地管理版本及与github合并】 Init Push Pull操作解决方案
文章目录 创建本地仓库,并与远程仓库链接更新本地仓库并使用Push推送到远程仓库 1. 几种基础命令介绍:2. git push操作流程 .gitignore删除本地仓库,断开本地与远程的链接设置用于提交commit的用户名,邮箱,以便githu…...

JavaSE-项目小结-IP归属地查询(本地IP地址库)
一、项目介绍 1. 背景 IP地址是网络通信中的重要标识,通过分析IP地址的归属地信息,可以帮助我们了解访问来源、用户行为和网络安全等关键信息。例如应用于网站访问日志分析:通过分析访问日志中的IP地址,了解网站访问者的地理位置分…...
使用最大边界相关算法处理文章自动摘要
一、需求背景 对于博客或者文章来说,摘要是普遍性的需求。但是我们不可能让作者自己手动填写摘要或者直接暴力截取文章的部分段落作为摘要,这样既不符合逻辑又不具有代表性,那么,是否有相关的算法或者数学理论能够完成这个需求呢&…...
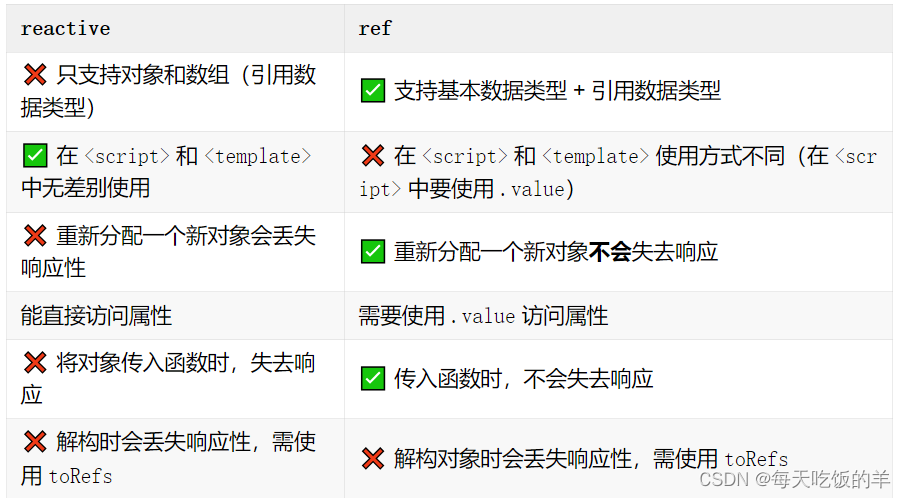
ref和reactive, toRefs的使用
看尤雨溪说:为什么Vue3 中应该使用 Ref 而不是 Reactive? toRefs import { ref, toRefs } from vue;// 定义一个响应式对象 const state ref({count: 0,name: Vue });// 使用toRefs转换为响应式引用对象 const reactiveState toRefs(state);// 现在你…...
从源代码看Chrome 版本号
一直以来都是用Chrome 浏览器,但是看到Chrome 点分4 组数据的表达方式,总是感觉怪怪的,遂深入源代码了解她的版本号具体表示的内容 chrome 浏览器中显示的版本号 源代码中的版本号标识 版本号文件位于 chrome/VERSION , 看到源代…...

Vue 图片加载失败处理
Vue 图片加载失败处理 很多人会使用 error 方法在图片加载 失败时替换img.src 的方式 但是这种方式在默认图片加载失败时,error会出现死循环,所以我使用了error v-if的方式。 <template><div><!-- 正常时显示 --><img v-if&quo…...
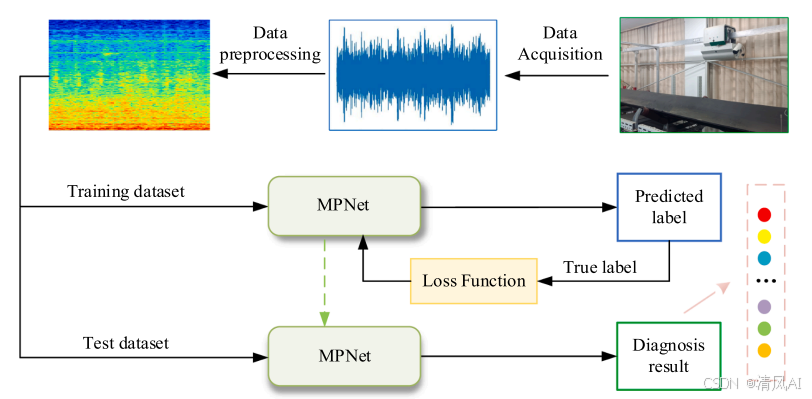
MPNet:旋转机械轻量化故障诊断模型详解python代码复现
目录 一、问题背景与挑战 二、MPNet核心架构 2.1 多分支特征融合模块(MBFM) 2.2 残差注意力金字塔模块(RAPM) 2.2.1 空间金字塔注意力(SPA) 2.2.2 金字塔残差块(PRBlock) 2.3 分类器设计 三、关键技术突破 3.1 多尺度特征融合 3.2 轻量化设计策略 3.3 抗噪声…...

conda相比python好处
Conda 作为 Python 的环境和包管理工具,相比原生 Python 生态(如 pip 虚拟环境)有许多独特优势,尤其在多项目管理、依赖处理和跨平台兼容性等方面表现更优。以下是 Conda 的核心好处: 一、一站式环境管理:…...

【网络】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iftop
在Linux系统中,iftop是网络管理的得力助手,能实时监控网络流量、连接情况等,帮助排查网络异常。接下来从多方面详细介绍它。 目录 【网络】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iftop工具概述安装方式核心功能基础用法进阶操作实战案例面试题场景生产场景…...
docker详细操作--未完待续
docker介绍 docker官网: Docker:加速容器应用程序开发 harbor官网:Harbor - Harbor 中文 使用docker加速器: Docker镜像极速下载服务 - 毫秒镜像 是什么 Docker 是一种开源的容器化平台,用于将应用程序及其依赖项(如库、运行时环…...

JVM垃圾回收机制全解析
Java虚拟机(JVM)中的垃圾收集器(Garbage Collector,简称GC)是用于自动管理内存的机制。它负责识别和清除不再被程序使用的对象,从而释放内存空间,避免内存泄漏和内存溢出等问题。垃圾收集器在Ja…...

【配置 YOLOX 用于按目录分类的图片数据集】
现在的图标点选越来越多,如何一步解决,采用 YOLOX 目标检测模式则可以轻松解决 要在 YOLOX 中使用按目录分类的图片数据集(每个目录代表一个类别,目录下是该类别的所有图片),你需要进行以下配置步骤&#x…...
微信小程序云开发平台MySQL的连接方式
注:微信小程序云开发平台指的是腾讯云开发 先给结论:微信小程序云开发平台的MySQL,无法通过获取数据库连接信息的方式进行连接,连接只能通过云开发的SDK连接,具体要参考官方文档: 为什么? 因为…...
Springboot社区养老保险系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,社区养老保险系统小程序被用户普遍使用,为方…...

Python ROS2【机器人中间件框架】 简介
销量过万TEEIS德国护膝夏天用薄款 优惠券冠生园 百花蜂蜜428g 挤压瓶纯蜂蜜巨奇严选 鞋子除臭剂360ml 多芬身体磨砂膏280g健70%-75%酒精消毒棉片湿巾1418cm 80片/袋3袋大包清洁食品用消毒 优惠券AIMORNY52朵红玫瑰永生香皂花同城配送非鲜花七夕情人节生日礼物送女友 热卖妙洁棉…...
C++:多态机制详解
目录 一. 多态的概念 1.静态多态(编译时多态) 二.动态多态的定义及实现 1.多态的构成条件 2.虚函数 3.虚函数的重写/覆盖 4.虚函数重写的一些其他问题 1).协变 2).析构函数的重写 5.override 和 final关键字 1&#…...
