容器库(5)-std::list
std::forward_list是可以从任何位置快速插入和移除元素的容器,不支持快速随机访问,支持正向和反向的迭代。
本文章的代码库:
https://gitee.com/gamestorm577/CppStd
成员函数
构造、析构和赋值
构造函数
可以用元素、元素列表、迭代器或者另一个list来构造list。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::vector<float> vec{1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f};
std::list<float> l1(5, 1.1f);
std::list<float> l2(5);
std::list<float> l3(vec.begin(), vec.end());
std::list<float> l4(l1);
std::list<float> tmp(l1);
std::list<float> l5(std::move(tmp));
std::list<float> l6{11.1f, 12.1, 13.1f};print_func(l1);
print_func(l2);
print_func(l3);
print_func(l4);
print_func(l5);
print_func(l6);输出结果:
1.1 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.1
0 0 0 0 0
1.1 2.1 3.1
1.1 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.1
1.1 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.1
11.1 12.1 13.1 析构函数
list析构时,会按照正向顺序依次删除元素。代码示例:
struct MyStruct
{MyStruct(int i): Index(i){}~MyStruct(){std::cout << "destruct, Index = " << Index << std::endl;}int Index = 0;
};std::list<MyStruct> l;
l.emplace_front(1);
l.emplace_front(3);
l.emplace_front(5);输出结果:
destruct, Index = 5
destruct, Index = 3
destruct, Index = 1赋值函数
可以用元素列表或者另一个list赋值给forward_list。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::list<float> tmp = {1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f};
std::list<float> l1;
std::list<float> l2;l1 = tmp;
l2 = {2.1f, 2.2f, 2.3f, 2.4f};
print_func(l1);
print_func(l2);输出结果:
1.1 2.1 3.1
2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 assign
将值赋值给forward_list,可以是元素、元素列表或者迭代器。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::vector<float> vec(10, 1.2f);
std::list<float> l;l.assign(5, 1.2);
print_func(l);
l.assign(vec.begin(), vec.end());
print_func(l);
l.assign({1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f});
print_func(l);输出结果:
1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2
1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2
1.1 2.1 3.1 元素访问
front
返回首个元素的引用。示例代码:
std::list<float> l = {1.f, 2.f, 3.f};
l.front() = 4.1f;
std::cout << "l front is: " << l.front() << std::endl;输出结果:
l front is: 4.1back
返回最后一个元素的引用。示例代码:
std::list<float> l = {1.f, 2.f, 3.f};
l.back() = 24.1f;
std::cout << "l back is: " << l.back() << std::endl;输出结果:
l back is: 24.1迭代器
接口begin、cbegin指向list起始的迭代器,end、cend指向末尾的迭代器。rbegin、crbegin指向起始的逆向迭代器,rend、crend指向末尾的逆向迭代器。代码示例:
std::list<float> l = {1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f};
for (auto iter = l.rbegin(); iter != l.rend(); ++iter)
{*iter += 27.f;
}for (auto iter = l.crbegin(); iter != l.crend(); ++iter)
{std::cout << "num is: " << *iter << std::endl;
}输出结果:
num is: 30.1
num is: 29.1
num is: 28.1容量
empty
检查list是否为空。示例代码:
std::list<float> l1 = {1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f};
std::list<float> l2;
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "l1 empty: " << l1.empty() << std::endl;
std::cout << "l2 empty: " << l2.empty() << std::endl;输出结果:
l1 empty: false
l2 empty: truesize
获取list元素的个数。代码示例:
std::list<float> l1 = {1.1f, 2.1f, 3.1f};
std::list<float> l2;
std::cout << "l1 size = " << l1.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "l2 size = " << l2.size() << std::endl;输出结果:
l1 size = 3
l2 size = 0max_size
返回可以容纳的最大元素个数。代码示例:
struct MyStruct
{double num1;double num2;double num3;double num4;
};std::list<float> l1;
std::list<double> l2;
std::list<MyStruct> l3;
std::cout << "l1 max size = " << l1.max_size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "l2 max size = " << l2.max_size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "l3 max size = " << l3.max_size() << std::endl;输出结果:
l1 max size = 768614336404564650
l2 max size = 768614336404564650
l3 max size = 384307168202282325修改器
clear
清除所有的元素。代码示例:
std::list<float> l(3, 1.f);
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "l empty: " << l.empty() << std::endl;
l.clear();
std::cout << "l empty: " << l.empty() << std::endl;输出结果:
l empty: false
l empty: trueinsert
在指定的位置插入元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::vector<float> vec{40.1f, 40.2f};std::list<float> l = {1.1f, 1.2f, 1.3f};
print_func(l);
l.insert(l.begin(), 15.7f);
print_func(l);
l.insert(std::next(l.begin(), 2), 3, 27.9f);
print_func(l);
l.insert(std::next(l.begin(), 1), vec.begin(), vec.end());
print_func(l);
l.insert(std::next(l.begin(), 1), {70.5f, 75.5f, 71.5f});
print_func(l);输出结果:
1.1 1.2 1.3
15.7 1.1 1.2 1.3
15.7 1.1 27.9 27.9 27.9 1.2 1.3
15.7 40.1 40.2 1.1 27.9 27.9 27.9 1.2 1.3
15.7 70.5 75.5 71.5 40.1 40.2 1.1 27.9 27.9 27.9 1.2 1.3 emplace
在指定位置一个元素。代码示例:
struct MyStruct
{MyStruct(float num1, int num2){std::cout << "construct " << num1 << " " << num2 << std::endl;}
};std::list<MyStruct> f;
f.emplace(f.begin(), 5.5f, 20);输出结果:
construct 5.5 20erase
删除指定位置的元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::list<float> l = {1.1f, 1.2f, 1.3f, 1.5f, 1.6f, 1.7f, 1.8f};
print_func(l);
l.erase(std::next(l.begin(), 1));
print_func(l);
l.erase(std::next(l.begin(), 1), std::next(l.begin(), 5));
print_func(l);输出结果:
1.1 1.2 1.3 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8
1.1 1.3 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8
1.1 1.8 push_back
将元素添加到末尾。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::list<float> l = {1.1f, 1.2f};
l.push_back(1.3f);
l.push_back(1.4f);
print_func(l);输出结果:
1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 emplace_back
在列表末尾构造一个元素。代码示例:
struct MyStruct
{MyStruct(float num1, int num2){std::cout << "construct " << num1 << " " << num2 << std::endl;}
};std::list<MyStruct> l;
l.emplace_back(1.5f, 17);
l.emplace_back(2.3f, 4);输出结果:
construct 1.5 17
construct 2.3 4pop_back
移除末尾的元素。代码示例:
std::list<float> l = {1.1f, 1.2f, 1.3f};
std::cout << "l back is: " << l.back() << std::endl;
l.pop_back();
std::cout << "l back is: " << l.back() << std::endl;输出结果:
l back is: 1.3
l back is: 1.2push_front
将元素添加到起始位置。代码示例:
std::list<float> l = {1.1f, 1.2f, 1.3f};
std::cout << "l front is: " << l.front() << std::endl;
l.push_front(17.7f);
std::cout << "l front is: " << l.front() << std::endl;输出结果:
l front is: 1.1
l front is: 17.7emplace_front
在列表起始位置构造一个元素。代码示例:
struct MyStruct
{MyStruct(float num1, int num2){std::cout << "construct " << num1 << " " << num2 << std::endl;}
};std::list<MyStruct> l;
l.emplace_front(2.7f, 17);
l.emplace_front(15.1f, 13);输出结果:
construct 2.7 17
construct 15.1 13pop_front
移除列表的首个元素。代码示例:
std::list<float> l = {1.1f, 1.2f, 1.3f};
std::cout << "l front is: " << l.front() << std::endl;
l.pop_front();
std::cout << "l front is: " << l.front() << std::endl;输出结果:
l front is: 1.1
l front is: 1.2resize
重新设置元素的个数。代码示例:
std::list<float> l = {1.1f, 1.2f, 1.3f};
std::cout << "l size is: " << l.size() << std::endl;
l.resize(2);
std::cout << "l size is: " << l.size() << std::endl;
l.resize(20);
std::cout << "l size is: " << l.size() << std::endl;输出结果:
l size is: 3
l size is: 2
l size is: 20swap
交换两个列表的元素内容。代码示例:
std::list<float> l1 = {1.1f, 1.2f, 1.3f};
std::list<float> l2 = {2.1f, 2.2f};
l1.swap(l2);
std::cout << "l1 size = " << l1.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "l2 size = " << l2.size() << std::endl;输出结果:
l1 size = 2
l2 size = 3操作
sort
对元素进行排序。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::list<int> l = {7, 17, 5, 47, 25};
print_func(l);l.sort();
print_func(l);l.sort([](int a, int b){return a > b;});
print_func(l);输出结果:
7 17 5 47 25
5 7 17 25 47
47 25 17 7 5 merge
合并两个有序的列表。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};{std::list<int> l1 = {1, 5, 7, 19};std::list<int> l2 = {2, 3, 14, 15};l1.merge(l2);print_func(l1);
}{std::list<int> l1 = {1, 5, 7, 19};std::list<int> l2 = {2, 3, 14, 15};l1.merge(l2,[](int a, int b){return a > b;});print_func(l1);
}输出结果:
1 2 3 5 7 14 15 19
2 3 14 15 1 5 7 19 splice
将另一个列表中的一些元素移动到this列表指定的位置。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](std::string tag, const std::list<float>& list)
{std::cout << tag;for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};{std::list<float> l1 = {1.5f, 5.5f, 7.5f, 19.5f};std::list<float> l2 = {2.4f, 3.4f, 14.4f, 15.4f};l1.splice(l1.begin(), l2);print_func("l1 = ", l1);print_func("l2 = ", l2);
}{std::list<float> l1 = {1.5f, 5.5f, 7.5f, 19.5f};std::list<float> l2 = {2.4f, 3.4f, 14.4f, 15.4f};l1.splice(std::next(l1.begin(), 2), l2, std::next(l2.begin(), 1));print_func("l1 = ", l1);print_func("l2 = ", l2);
}{std::list<float> l1 = {1.5f, 5.5f, 7.5f, 19.5f};std::list<float> l2 = {2.4f, 3.4f, 14.4f, 15.4f};l1.splice(l1.begin(), l2, l2.begin(), std::next(l2.begin(), 2));print_func("l1 = ", l1);print_func("l2 = ", l2);
}输出结果:
l1 = 2.4 3.4 14.4 15.4 1.5 5.5 7.5 19.5
l2 =
l1 = 1.5 5.5 3.4 7.5 19.5
l2 = 2.4 14.4 15.4
l1 = 2.4 3.4 1.5 5.5 7.5 19.5
l2 = 14.4 15.4 remove、remove_if
remove移除等于指定值的元素。remove_if移除满足指定要求的元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::list<int> l = {5, 9, 17, 27, 15, 5, 5};
print_func(l);l.remove(5);
print_func(l);l.remove_if([](int n){return n > 15;});
print_func(l);输出结果:
5 9 17 27 15 5 5
9 17 27 15
9 15 reverse
反转元素的顺序。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<float>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::list<float> l = {1.1f, 3.1f, 19.1f, 7.1f};
print_func(l);
l.reverse();
print_func(l);输出结果:
1.1 3.1 19.1 7.1
7.1 19.1 3.1 1.1 unique
删除连续的重复元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::list<int> l = {1, 3, 3, 17, 7, 3, 17, 17, 19, 1, 3, 1};
print_func(l);
l.unique();
print_func(l);输出结果:
1 3 3 17 7 3 17 17 19 1 3 1
1 3 17 7 3 17 19 1 3 1 非成员函数
比较运算符
operator==,!=,<,<=,>,>=用于比较两个forward_list。代码示例:
std::list<int> l1 = {1, 2, 3, 4};
std::list<int> l2 = {1, 5};
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << "l1 == l2: " << (l1 == l2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "l1 != l2: " << (l1 != l2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "l1 < l2: " << (l1 < l2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "l1 <= l2: " << (l1 <= l2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "l1 > l2: " << (l1 > l2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "l1 >= l2: " << (l1 >= l2) << std::endl;输出结果:
l1 == l2: false
l1 != l2: true
l1 < l2: true
l1 <= l2: true
l1 > l2: false
l1 >= l2: falseswap
交换两个列表的元素内容。示例代码:
std::list<float> l1 = {1.5f, 2.5f};
std::list<float> l2 = {17.1f, 15.1f, 27.1f};
std::swap(l1, l2);
std::cout << "l1 front is: " << l1.front() << std::endl;
std::cout << "l2 front is: " << l2.front() << std::endl;输出结果:
l1 front is: 17.1
l2 front is: 1.5erase、erase_if
erase删除等于指定值的元素,erase_if删除满足条件的元素。代码示例:
auto print_func = [](const std::list<int>& list)
{for (auto i : list){std::cout << i << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
};std::list<int> l = {5, 7, 17, 29, 7, 7, 35};
print_func(l);std::erase(l, 7);
print_func(l);std::erase_if(l,[](int a){return a > 17;});
print_func(l);输出结果:
5 7 17 29 7 7 35
5 17 29 35
5 17 相关文章:
-std::list)
容器库(5)-std::list
std::forward_list是可以从任何位置快速插入和移除元素的容器,不支持快速随机访问,支持正向和反向的迭代。 本文章的代码库: https://gitee.com/gamestorm577/CppStd 成员函数 构造、析构和赋值 构造函数 可以用元素、元素列表、迭代器…...

配置VMware实现从服务器到虚拟机的一键启动脚本
正文共:1666 字 15 图,预估阅读时间:2 分钟 首先祝大家新年快乐!略备薄礼,18000个红包封面来讨个开年好彩头! 虽然之前将服务器放到了公网(成本增加了100块,内网服务器上公网解决方案…...
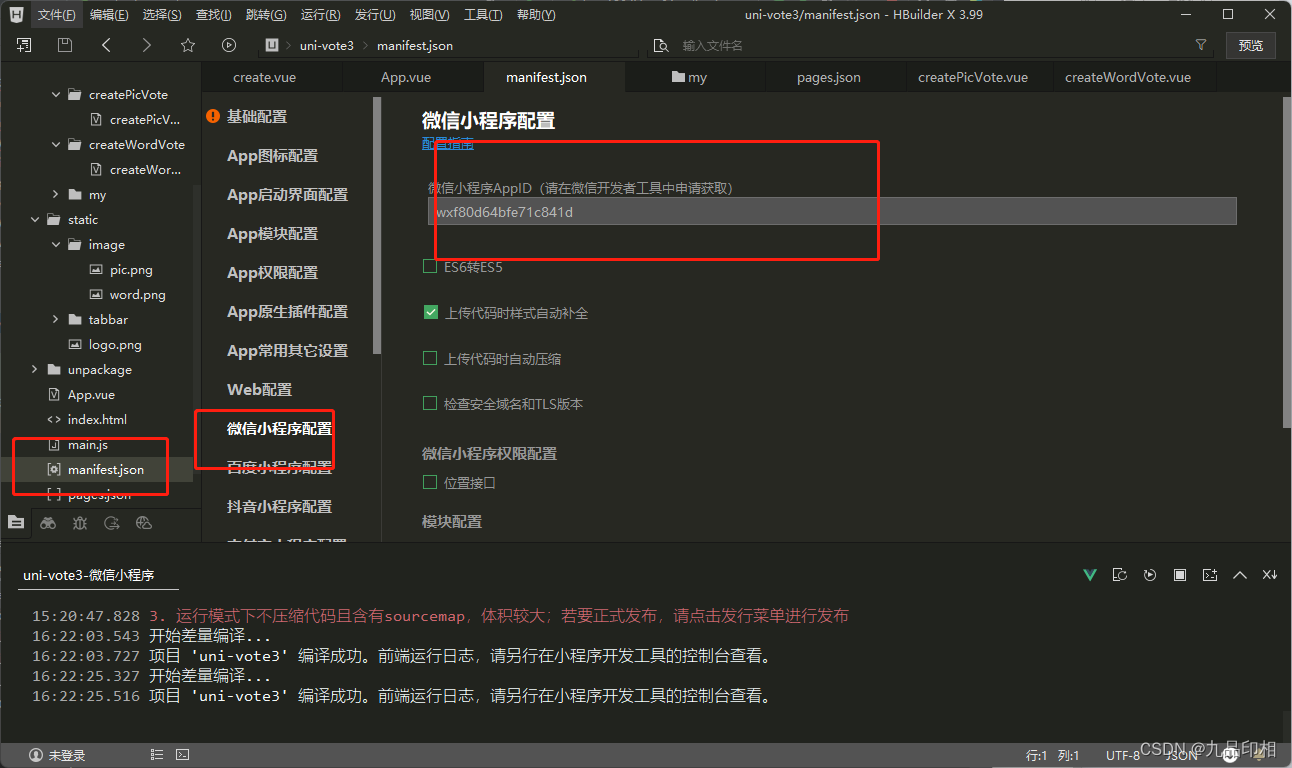
第5讲小程序微信用户登录实现
小程序微信用户登录实现 小程序登录和jwt,httpclient工具类详细介绍可以看下小锋老师的 小程序电商系统课程:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1kP4y1F7tU application.yml加上小程序登录需要的参数,小伙伴们可以登录小程序后台管理&#…...
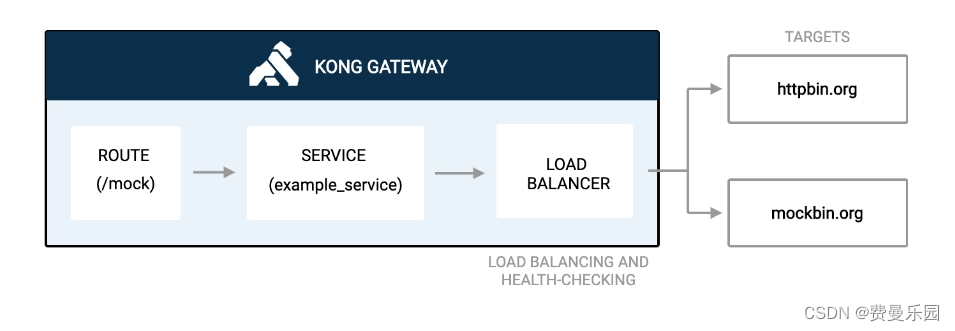
Kong 负载均衡
负载均衡是一种将API请求流量分发到多个上游服务的方法。负载均衡可以提高整个系统的响应速度,通过防止单个资源过载而减少故障。 在以下示例中,您将使用部署在两台不同服务器或上游目标上的应用程序。Kong网关需要在这两台服务器之间进行负载均衡&…...
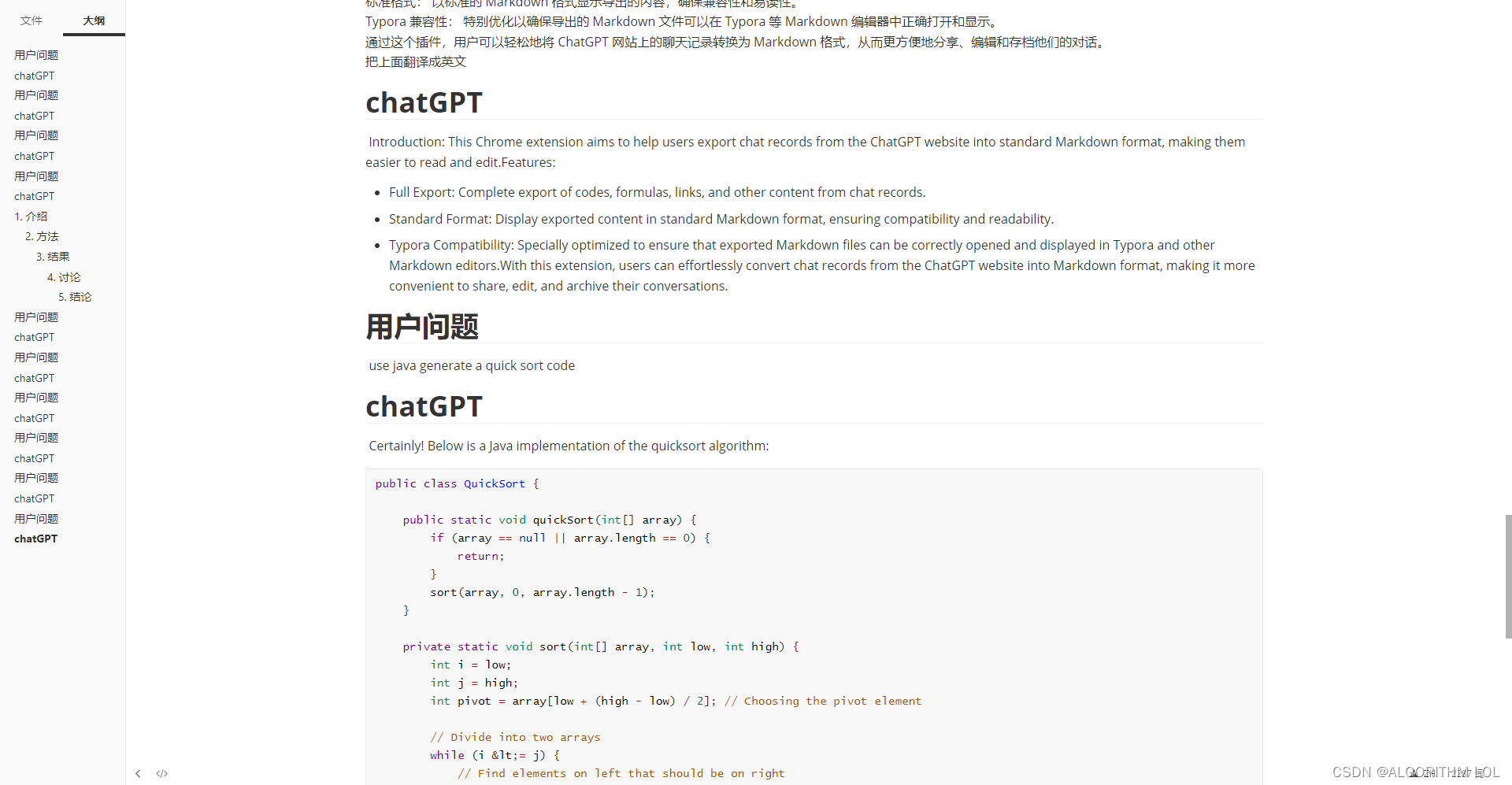
基于Chrome插件的Chatgpt对话无损导出markdown格式(Typora完美显示)
Google插件名称为:ChatGPT to MarkDown plus, 下载地址为ChatGPT to MarkDown plus使用方法:见GitHub主页或插件介绍页面https://github.com/thisisbaiy/ChatGPT-To-Markdown-google-plugin/tree/main 我将源代码上传至了GitHub,欢迎star, Is…...

react函数组件中使用context
效果 1.在父组件中创建一个createcontext并将他导出 import React, { createContext } from react import Bpp from ./Bpp import Cpp from ./Cpp export let MyContext createContext(我是组件B) export let Ccontext createContext(我是组件C)export default function App…...
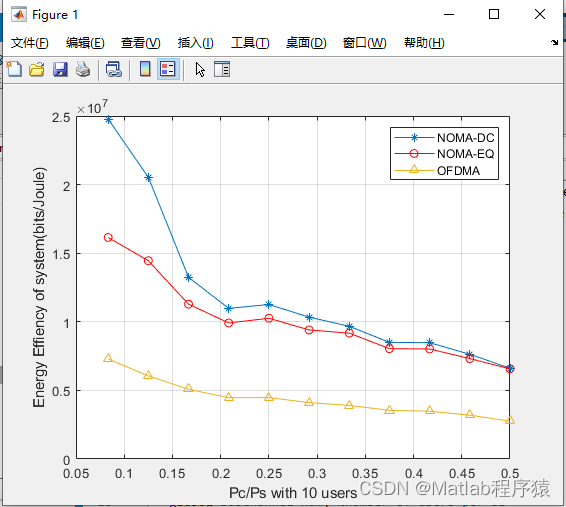
【MATLAB源码-第137期】基于matlab的NOMA系统和OFDMA系统对比仿真。
操作环境: MATLAB 2022a 1、算法描述 NOMA(非正交多址)和OFDMA(正交频分多址)是两种流行的无线通信技术,广泛应用于现代移动通信系统中,如4G、5G和未来的6G网络。它们的设计目标是提高频谱效…...

【FPGA Verilog】各种加法器Verilog
1bit半加器adder设计实例 module adder(cout,sum,a,b); output cout; output sum; input a,b; wire cout,sum; assign {cout,sum}ab; endmodule 解释说明 (1)assign {cout,sum}ab 是连续性赋值 对于线网wire进行赋值,必须以assign或者dea…...
)
【MySQL】-21 MySQL综合-7(MySQL主键+MySQL外检约束+MySQL唯一约束+MySQL检查约束)
MySQL主键MySQL外检约束MySQL唯一约束MySQL检查约束 MySQL主键选取设置主键约束的字段在创建表时设置主键约束在创建表时设置复合主键在修改表时添加主键约束 MySQL外键约束选取设置 MySQL 外键约束的字段在创建表时设置外键约束在修改表时添加外键约束删除外键约束 MySQL唯一约…...
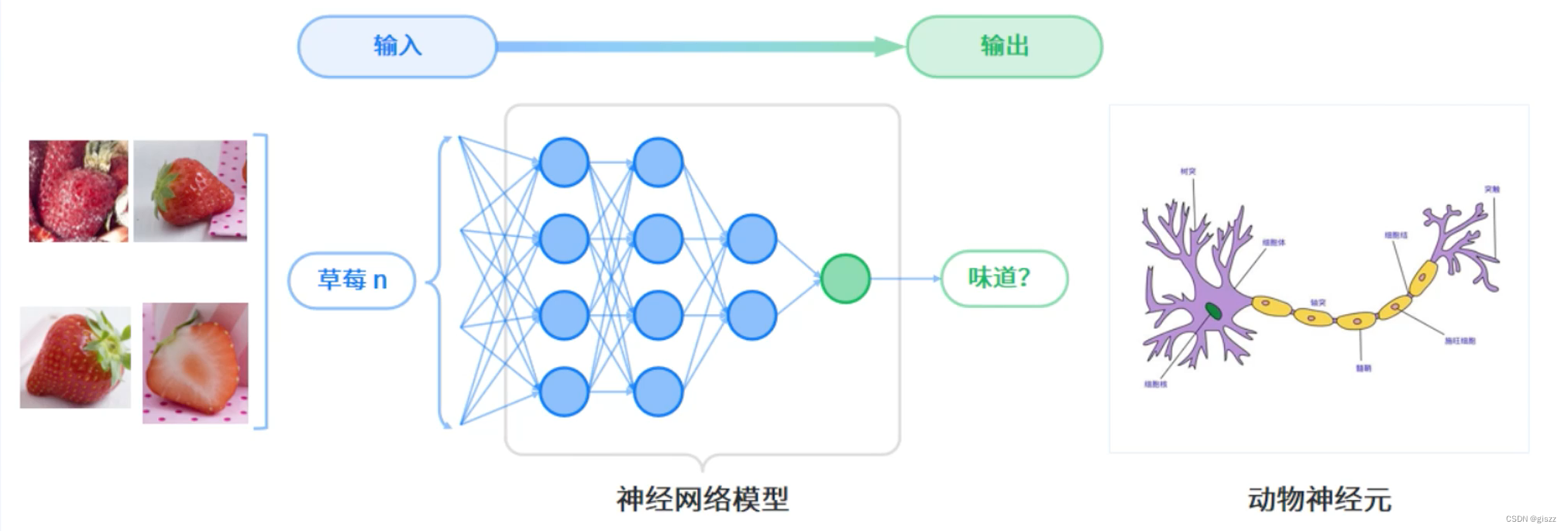
【大厂AI课学习笔记】【1.6 人工智能基础知识】(3)神经网络
深度学习是机器学习中一种基于对数据进行表征学习的算法。观测值(例如一幅草莓照片)可以使用 多种方式来表示,如每个像素强度值的向量,或者更抽象地表示成一系列边、特定形状的区域等。 深度学习的最主要特征是使用神经网络作为计算模型。神经网络模型 …...
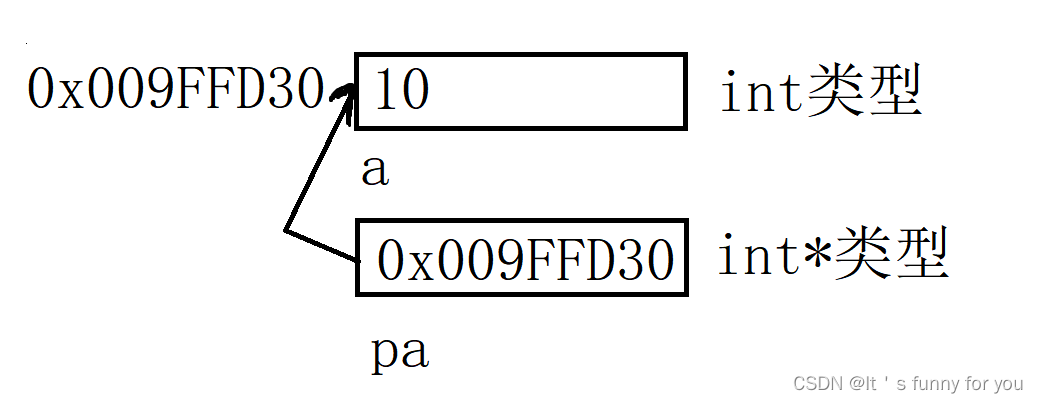
指针的基本含义及其用法
1.前言 在学习C语言的时候,我们会经常接触一个概念,指针和地址,关于这两个概念很多人并不能理解地十分透彻,接下来我将详细介绍一下这两者的概念 2.地址 我们知道计算机的上CPU(中央处理器)在处理数据的时…...

黄金交易策略(Nerve Nnife.mql4):趋势做单
完整EA:Nerve Knife.ex4黄金交易策略_黄金趋势ea-CSDN博客 当大小趋势相同行情走向也相同,就会开仓做顺势单,并会顺势追单,以达到快速止盈平仓的效果。大趋势追求稳定,小趋势追求敏捷,行情走向比小趋势更敏…...
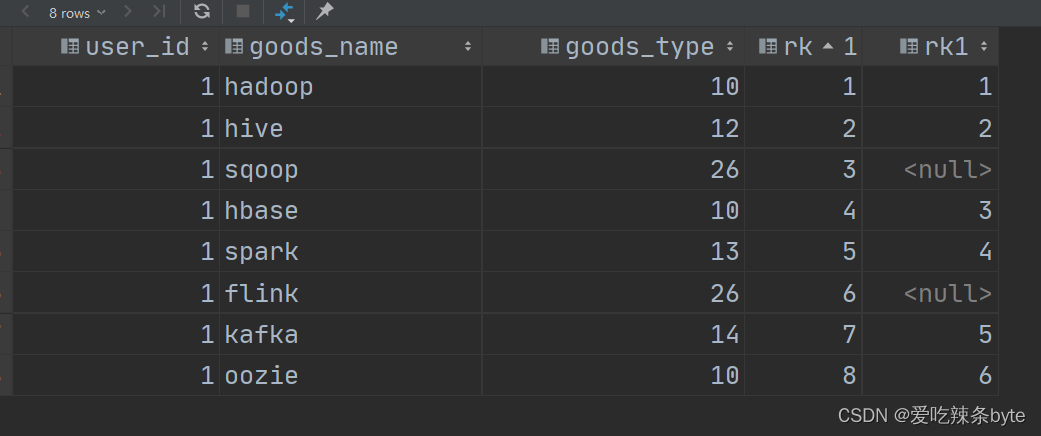
HiveSQL——条件判断语句嵌套windows子句的应用
注:参考文章: SQL条件判断语句嵌套window子句的应用【易错点】--HiveSql面试题25_sql剁成嵌套判断-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读920次,点赞4次,收藏4次。0 需求分析需求:表如下user_idgood_namegoods_typerk1hadoop1011hive1…...

ClickHouse--01--简介
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 1. ClickHouse 简介官网: [https://clickhouse.com/docs/zh](https://clickhouse.com/docs/zh) 1.1 大数据处理场景1.2 什么是 ClickHouse1.3 OLAP 场景…...

【Django-ninja】在django ninja中处理异常
1. 直接抛内置异常 Django ninja内置了一些常用异常类。 from ninja.errors import HttpErrorapi.get("/some/resource") def some_operation(request):if True:raise HttpError(503, "Service Unavailable. Please retry later.")2. 覆写异常类 可以覆…...
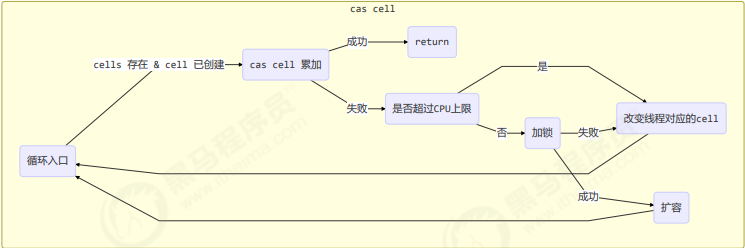
【并发编程】原子累加器
📝个人主页:五敷有你 🔥系列专栏:并发编程 ⛺️稳重求进,晒太阳 JDK8之后有专门做累加的类,效率比自己做快数倍以上 累加器性能比较 参数是方法 // supplier 提供者 无中生有 ()->结果// func…...
Java 基于微信小程序的电子商城购物系统
博主介绍:✌程序员徐师兄、7年大厂程序员经历。全网粉丝12W、csdn博客专家、掘金/华为云/阿里云/InfoQ等平台优质作者、专注于Java技术领域和毕业项目实战✌ 🍅文末获取源码联系🍅 👇🏻 精彩专栏推荐订阅👇…...

Git Push -f 命令详解
直接看原文: Git Push -f 命令详解 - 玩转Linux - SegmentFault 思否 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- git push -f 这个命令的作用是将自己本地仓库的代码直接推送至仓…...

【LeetCode每日一题】前缀和的例题1248. 统计「优美子数组」974. 和可被 K 整除的子数组
leetcode 724. 寻找数组的中心索引 题目描述 给定一个整数类型的数组 nums,请编写一个能够返回数组 “中心索引” 的方法。 我们是这样定义数组 中心索引 的:数组中心索引的左侧所有元素相加的和等于右侧所有元素相加的和。 如果数组不存在中心索引&…...

备战蓝桥杯---数学基础3
本专题主要围绕同余来讲: 下面介绍一下基本概念与定理: 下面给出解这方程的一个例子: 下面是用代码实现扩展欧几里得算法: #include<bits/stdc.h> using namespace std; int gcd(int a,int b,int &x,int &y){if(b…...
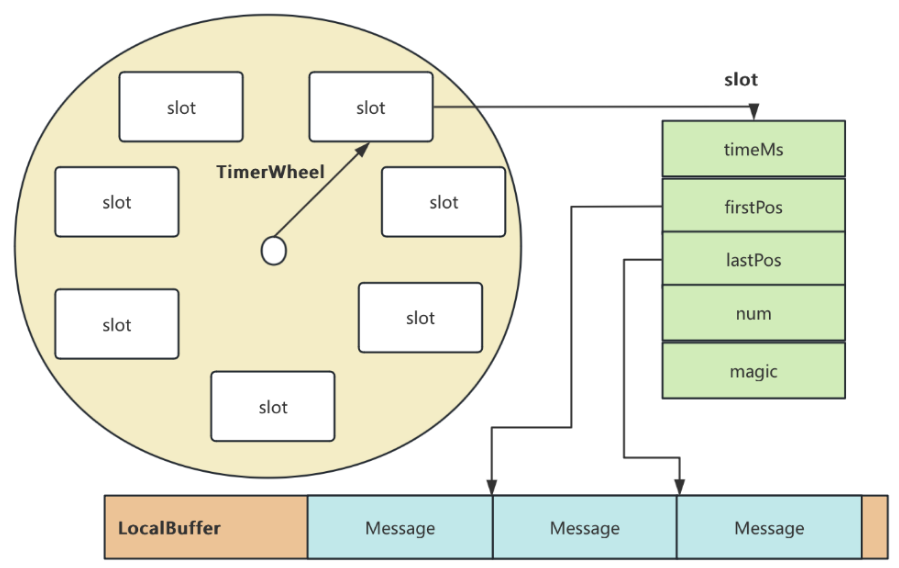
RocketMQ延迟消息机制
两种延迟消息 RocketMQ中提供了两种延迟消息机制 指定固定的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个MessageDelayLevel参数,对应18个预设的延迟级别指定时间点的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个DeliverTimeMS指定一个Long类型表示的具体时间点。到了时间点后…...
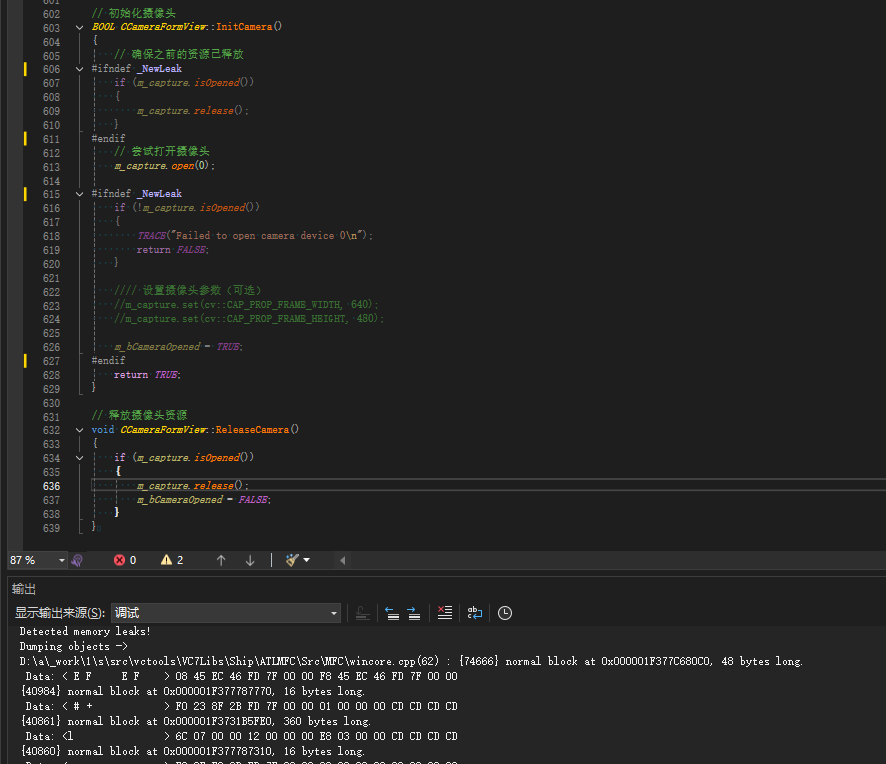
MFC内存泄露
1、泄露代码示例 void X::SetApplicationBtn() {CMFCRibbonApplicationButton* pBtn GetApplicationButton();// 获取 Ribbon Bar 指针// 创建自定义按钮CCustomRibbonAppButton* pCustomButton new CCustomRibbonAppButton();pCustomButton->SetImage(IDB_BITMAP_Jdp26)…...

mongodb源码分析session执行handleRequest命令find过程
mongo/transport/service_state_machine.cpp已经分析startSession创建ASIOSession过程,并且验证connection是否超过限制ASIOSession和connection是循环接受客户端命令,把数据流转换成Message,状态转变流程是:State::Created 》 St…...
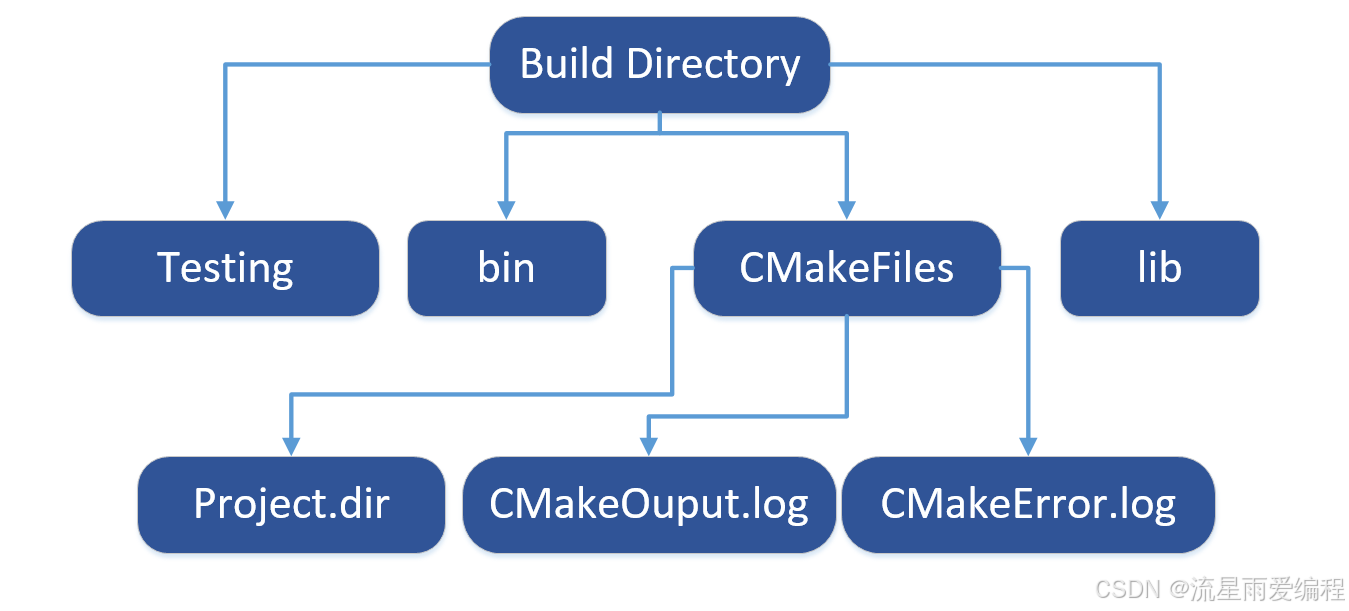
CMake基础:构建流程详解
目录 1.CMake构建过程的基本流程 2.CMake构建的具体步骤 2.1.创建构建目录 2.2.使用 CMake 生成构建文件 2.3.编译和构建 2.4.清理构建文件 2.5.重新配置和构建 3.跨平台构建示例 4.工具链与交叉编译 5.CMake构建后的项目结构解析 5.1.CMake构建后的目录结构 5.2.构…...

FastAPI 教程:从入门到实践
FastAPI 是一个现代、快速(高性能)的 Web 框架,用于构建 API,支持 Python 3.6。它基于标准 Python 类型提示,易于学习且功能强大。以下是一个完整的 FastAPI 入门教程,涵盖从环境搭建到创建并运行一个简单的…...

STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解
STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解 前言如何确定定时器挂载在哪条时钟线上配置及使用方法参数配置PrescalerCounter ModeCounter Periodauto-reload preloadTrigger Event Selection 中断配置生成的代码及使用方法初始化代码基本定时器触发DCA或者ADC的代码讲解中断代码定时启动…...

江苏艾立泰跨国资源接力:废料变黄金的绿色供应链革命
在华东塑料包装行业面临限塑令深度调整的背景下,江苏艾立泰以一场跨国资源接力的创新实践,重新定义了绿色供应链的边界。 跨国回收网络:废料变黄金的全球棋局 艾立泰在欧洲、东南亚建立再生塑料回收点,将海外废弃包装箱通过标准…...

linux 错误码总结
1,错误码的概念与作用 在Linux系统中,错误码是系统调用或库函数在执行失败时返回的特定数值,用于指示具体的错误类型。这些错误码通过全局变量errno来存储和传递,errno由操作系统维护,保存最近一次发生的错误信息。值得注意的是,errno的值在每次系统调用或函数调用失败时…...
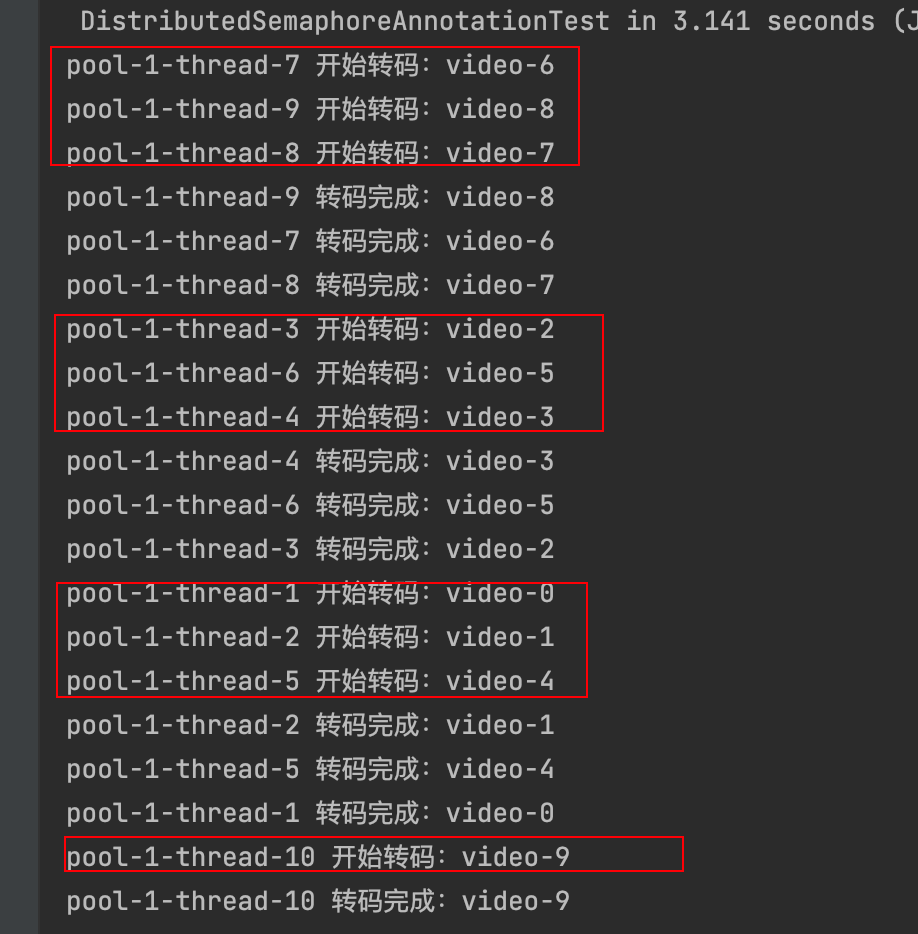
令牌桶 滑动窗口->限流 分布式信号量->限并发的原理 lua脚本分析介绍
文章目录 前言限流限制并发的实际理解限流令牌桶代码实现结果分析令牌桶lua的模拟实现原理总结: 滑动窗口代码实现结果分析lua脚本原理解析 限并发分布式信号量代码实现结果分析lua脚本实现原理 双注解去实现限流 并发结果分析: 实际业务去理解体会统一注…...

华硕a豆14 Air香氛版,美学与科技的馨香融合
在快节奏的现代生活中,我们渴望一个能激发创想、愉悦感官的工作与生活伙伴,它不仅是冰冷的科技工具,更能触动我们内心深处的细腻情感。正是在这样的期许下,华硕a豆14 Air香氛版翩然而至,它以一种前所未有的方式&#x…...
