C++从入门到精通 第十六章(STL常用算法)
写在前面:
- 本系列专栏主要介绍C++的相关知识,思路以下面的参考链接教程为主,大部分笔记也出自该教程,笔者的原创部分主要在示例代码的注释部分。
- 除了参考下面的链接教程以外,笔者还参考了其它的一些C++教材(比如计算机二级教材和C语言教材),笔者认为重要的部分大多都会用粗体标注(未被标注出的部分可能全是重点,可根据相关部分的示例代码量和注释量判断,或者根据实际经验判断)。
- 如有错漏欢迎指出。
参考教程:黑马程序员匠心之作|C++教程从0到1入门编程,学习编程不再难_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
一、概述
算法主要是由头文件<algorithm> <functional> <numeric>组成:
(1)<algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较、交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等。
(2)<numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数。
(3)<functional>定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象。
二、常用遍历算法
1、算法简介
for_each //遍历容器
transform //将容器中的元素搬运到另一个容器中
2、for_each
for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func); //遍历容器
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// _func——函数或者函数对象
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;void print01(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}
class print02
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);cout << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}3、transform
transform(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, _func);
// beg1——源容器开始迭代器
// end1——源容器结束迭代器
// beg2——目标容器开始迭代器
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;class Transform
{
public:int operator()(int v){return v; //可以对v做运算,比如v+100}
};
class Print
{
public:void operator()(int v){cout << v << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>vTarget;vTarget.resize(v.size()); //目标容器需要提前开辟空间transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), Transform());for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), Print());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}三、常用查找算法
1、算法简介
find //查找元素
find_if //按条件查找元素
adjacent_find //查找相邻重复元素
binary_search //二分查找法
count //统计元素个数
count_if //按条件统计元素个数
//_func 函数或者函数对象
2、find
(1)功能描述:查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到则返回结束迭代器end()。
(2)函数原型:
find(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// value——查找的元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string>void test01()
{vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i + 1);}//查找容器中是否有 5 这个元素vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到:" << *it << endl;}
}class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//重载==bool operator==(const Person& p){if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}return false;}
public:string m_Name;int m_Age;
};void test02()
{vector<Person> v;//创建数据Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), p2);if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age << endl;}
}int main() {test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}3、find_if
(1)功能描述:按条件查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置。
(2)函数原型:
find_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// _Pred——函数或者谓词(返回bool类型的仿函数)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class GreaterFive
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 5;}
};void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>::iterator it;it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到大于5的数" << endl;}else{cout << *it << endl;}
}class Person
{
public:int m_Age;string m_Name;Person(int age, string name){this->m_Age = age;this->m_Name = name;}
};
class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(Person &p){return p.m_Age > 20;}
};
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1(10 ,"aaa");Person p2(20 ,"bbb");Person p3(30 ,"ccc");Person p4(40 ,"ddd");v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);vector<Person>::iterator it;it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到年龄大于20的人" << endl;}else{cout << "找到力" << endl;}
}int main() {test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}4、adjacent_find
(1)功能描述:查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器。
(2)函数原型:
adjacent_find(iterator beg, iterator end);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(0);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(0);vector<int>::iterator it;it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());if (it == v.end()){cout << "未找到相邻重复元素" << endl;}else{cout << "找到相邻重复元素" << *it << endl;}
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}5、binary_search
(1)功能描述:查找指定元素是否存在,查到就返回true,否则返回false。
(2)函数原型:
bool binary_search(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// value——查找的元素
// 注意: 虽然它查找效率高,但是在无序序列中不可用
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void test01()
{vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i); //如果容器不是有序的序列,那么返回的结果可能会不准确}bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9);if (ret){cout << "找到元素9" << endl;}else{cout << "未找到元素9" << endl;}
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}6、count
(1)功能描述:统计元素个数(统计元素出现次数)。
(2)函数原型:
count(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// value——统计的元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(4);cout << "4元素个数为" << count(v.begin(), v.end(), 4) << endl;
}class Person
{
public:int m_Age;int m_Age2;Person(int a1, int a2){m_Age = a1;m_Age2 = a2;}bool operator==(const Person &p){if (m_Age2 == p.m_Age2){return true;}else{return false;}}
};
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1(1, 10);Person p2(1, 10);Person p3(2, 10);Person p4(1, 20);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);cout << "与p1同Age2的人数为" << count(v.begin(), v.end(), p1)-1 << endl;
}int main()
{test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}7、count_if
(1)功能描述:按条件统计元素个数(元素出现次数)。
(2)函数原型:
count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// _Pred——谓词
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>class Greater4
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 4;}
};
void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(4);cout << "大于4的元素个数为" << count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater4()) << endl;
}class Person
{
public:int m_Age;int m_Age2;Person(int a1, int a2){m_Age = a1;m_Age2 = a2;}bool operator==(const Person &p){if (p.m_Age2 == m_Age2){return true;}return false;}
};
class Greater15
{
public:bool operator()(const Person &p){return p.m_Age2 > 15;}
};
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1(1, 10);Person p2(1, 10);Person p3(2, 30);Person p4(1, 20);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);cout << "Age2>15的人数为" << count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater15()) << endl;
}int main()
{test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}四、常用排序算法
1、算法简介
sort //对容器内元素进行排序
random_shuffle //洗牌,指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
merge //容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
reverse //反转指定范围的元素
2、sort
(1)功能描述:对容器内元素进行排序。
(2)函数原型:
sort(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// _Pred——谓词
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(4);sort(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;sort(v.begin(), v.end(),greater<int>()); //改成降序for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}3、random_shuffle
(1)功能描述:洗牌,指定范围内的元素随机调整次序。
(2)函数原型:
random_shuffle(iterator beg, iterator end);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<ctime>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(6);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(4);sort(v.begin(), v.end()); //升序排列for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end()); //打乱for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));test01();system("pause");return 0;
}4、merge
(1)功能描述:两个容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中(两个容器必须是有序的)。
(2)函数原型:
merge(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// begx——容器x的开始迭代器
// endx——容器x的结束迭代器
// dest——目标容器的开始迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 1);}vector<int>v3;v3.resize(v.size() + v2.size()); //提前给目标容器分配空间merge(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}5、reverse
(1)功能描述:将容器内指定范围的元素进行反转。
(2)函数原型:
reverse(iterator beg, iterator end);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(40);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;reverse(v.begin(), v.end()); //首尾对调(反转)for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}五、常用拷贝和替换算法
1、算法简介
copy //容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中
replace //将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素
replace_if //容器内指定范围满足条件的元素替换为新元素
swap //互换两个容器的元素
2、copy
(1)功能描述:容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中。
(2)函数原型:
copy(iterator beg, iterator end, iterator dest);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// dest——目标容器的起始迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(40);vector<int>v2;v2.resize(v.size());copy(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin());for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}3、replace
(1)功能描述:将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素。
(2)函数原型:
replace(iterator beg, iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// oldvalue——旧元素
// newvalue——新元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(20);replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 20, 60);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}4、replace_if
(1)功能描述:将区间内满足条件的元素,替换成指定元素。
(2)函数原型:
replace_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _pred, newvalue);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// _pred——谓词
// newvalue——新元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}class Greater25
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 25; //大于25的元素全部替换为60}
};
void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(20);replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater25(), 60);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}5、swap
(1)功能描述:互换两个容器的元素(交换的容器元素类型要相同)。
(2)函数原型:
swap(container c1, container c2);
// c1——容器1
// c2——容器2
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 100);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;cout << "-----------------------" << endl;v.swap(v2);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}六、常用算术生成算法
1、算法简介
算术生成算法属于小型算法,使用时包含的头文件为 <numeric>。
accumulate //计算容器元素累计总和
fill //向容器中添加元素
2、accumulate
(1)功能描述:计算区间内容器元素累计总和。
(2)函数原型:
accumulate(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// value——起始值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<numeric>void test01()
{vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++){v.push_back(i);}cout << accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 1000) << endl; //1000 + 容器v中元素的总和
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}3、fill
(1)功能描述:向容器中填充指定的元素。
(2)函数原型:
fill(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// beg——开始迭代器
// end——结束迭代器
// value——填充值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<numeric>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.resize(10);fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}七、常用集合算法
1、算法简介
set_intersection //求两个容器的交集
set_union //求两个容器的并集
set_difference //求两个容器的差集
2、set_intersection
(1)功能描述:求两个容器的交集(两个集合必须是有序序列),返回值是交集中最后一个元素的位置。
(2)函数原型:
set_intersection(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// begx——容器x的开始迭代器
// endx——容器x的结束迭代器
// dest——目标容器的开始迭代器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<numeric>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i); //0-9v2.push_back(i + 5); //5-14}vector<int> v3;v3.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());for_each(v3.begin(), itEnd, myPrint); //输出的是交集cout << endl;for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), myPrint); //给v3开辟空间时可能会有多余cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}3、set_union
(1)功能描述:求两个集合的并集(两个集合必须是有序序列),返回值是并集中最后一个元素的位置。
(2)函数原型:
set_union(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// begx——容器x的开始迭代器
// endx——容器x的结束迭代器
// dest——目标容器的开始迭代器
//目标容器需要开辟的空间大小为两个容器空间的相加结果
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<numeric>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i); //0-9v2.push_back(i + 5); //5-14}vector<int> v3;v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());for_each(v3.begin(), itEnd, myPrint); //输出的是并集cout << endl;for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), myPrint); //给v3开辟空间时可能会有多余cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}4、set_difference
(1)功能描述:求两个集合的差集(两个集合必须是有序序列),返回值是差集中最后一个元素的位置。
(2)函数原型:
set_difference(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// begx——容器x的开始迭代器
// endx——容器x的结束迭代器
// dest——目标容器的开始迭代器
//目标容器需要开辟的空间大小为两个容器空间的较大值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 5);}vector<int> vTarget;//取两个里面较大的值给目标容器开辟空间vTarget.resize(max(v1.size(), v2.size()));//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址cout << "v1与v2的差集为: " << endl;vector<int>::iterator itEnd =set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;cout << "v2与v1的差集为: " << endl;itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}相关文章:
)
C++从入门到精通 第十六章(STL常用算法)
写在前面: 本系列专栏主要介绍C的相关知识,思路以下面的参考链接教程为主,大部分笔记也出自该教程,笔者的原创部分主要在示例代码的注释部分。除了参考下面的链接教程以外,笔者还参考了其它的一些C教材(比…...
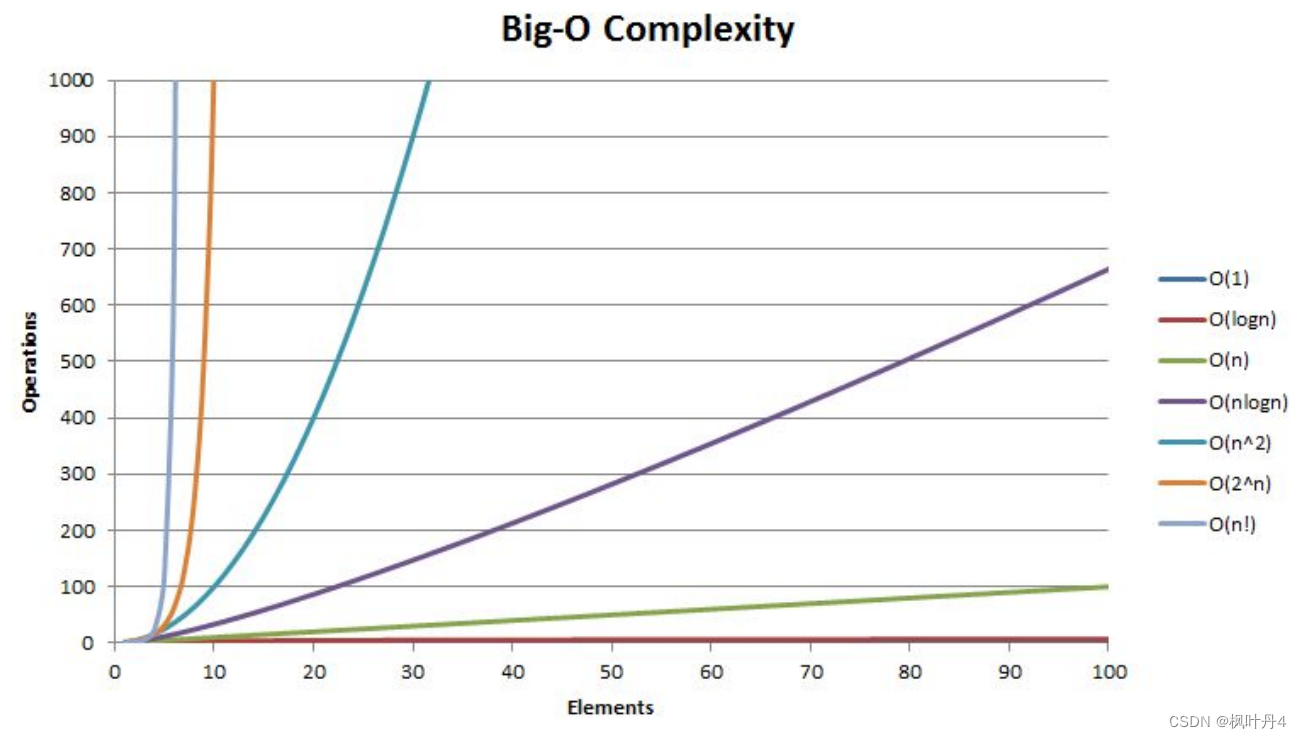
【海贼王的数据航海:利用数据结构成为数据海洋的霸主】时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度
目录 1 -> 算法效率 1.1 -> 如何衡量一个算法的好坏? 1.2 -> 算法的复杂度 2 -> 时间复杂度 2.1 -> 时间复杂度的概念 2.2 -> 大O的渐进表示法 2.3 -> 常见时间复杂度计算 3 -> 空间复杂度 4 -> 常见复杂度对比 1 -> 算法效…...

OpenTiny Vue 组件库适配微前端可能遇到的4个问题
本文由体验技术团队 TinyVue 项目成员岑灌铭同学创作。 前言 微前端是一种多个团队通过独立发布功能的方式来共同构建现代化 web 应用的技术手段及方法策略,每个应用可以选择不同的技术栈,独立开发、独立部署。 TinyVue组件库的跨技术栈能力与微前端十…...
jmeter 命令行启动 动态参数化
[Jmeter命令行参数] 一、在linux中,使用非gui的方式执行jmeter。若需更改参数,必须先编辑jmx文件,找到对应的变量进行修改,比较麻烦。因此,可以参数化一些常用的变量,直接在Jmeter命令行进行设置 二、参数…...

C++跨模块释放内存
linux一个进程只有一个堆,不要考虑这些问题,但是windows一个进程可能有多个堆,要在对应的堆上释放。 一, MT改MD 一个进程的地址空间是由一个可执行模块和多个DLL模块构成的,这些模块中,有些可能会链接到…...

jQuery浅析
jQuery 是一个快速、简洁的 JavaScript 库,旨在简化 HTML 文档遍历、事件处理、动画以及 Ajax 交互等功能。由 John Resig 在2006年创建,它极大地简化了JavaScript开发人员在处理网页文档、选择DOM元素以及执行各种效果和功能时的工作。 核心特性&#x…...
)
分班问题 、幼儿园分班(C语言)
题目 幼儿园两个班的小朋友排队时混在了一起,每个小朋友都知道自己跟前面一个小朋友是不是同班,请你帮忙把同班的小朋友找出来 小朋友的编号为整数,与前面一个小朋友同班用Y表示,不同班用N表示 输入 输入为空格分开的小朋友编号…...

QT 如何让多语言翻译变得简单,提高效率?
一.QT多语言如何翻译的? 在QT的多语言翻译过程中,分为两个步骤:第一步生成ts文件,第二步将ts文件翻译为qm文件。如果我们在需要多语言的情况下,qml经常使用qstr或者qwidget中使用tr等等,遍布许多个文件夹,在需要更新新的翻译时会很麻烦。整个工程收索并修改,效率十分低…...

线性代数:线性方程组解的结构
目录 齐次/非齐次方程组的解 Ax 0 的解的性质 定理 Ax b 的解的性质 相关证明 例1 例2 例3 齐次/非齐次方程组的解 Ax 0 的解的性质 定理 Ax b 的解的性质 相关证明 例1 例2 例3...

mysql之CRUD常见函数union查询
select select * from c insert 字段设置自增后,当我们指定增加一条数据后,往后增加的数据都会在该条数据后进行递增,但是可以认为的指定增加某条id不存在的数据 insert into c values(7,‘政治’) insert into c(c2) values(‘历史1’),(…...

开窗函数实践-实现两行记录之间计算时间差
一、需求背景 基于保密要求,不放原始表,新建测试表用来演示 insert into TEST0221 (采血人, 采血时间, 条码号, 病人ID) values (张三, to_date(21-02-2024 12:00:00, dd-mm-yyyy hh24:mi:ss), 2024001, 0001);insert into TEST0221 (采血人, 采血时间…...

String字符串的常见方法总结
目录 一、int length():返回字符串的长度 二、char charAt(int index):返回某索引处的字符 三、boolean isEmpty():判断字符串是否为空 四、String toUpperCase():将字符转换成大写 五、String toLowerCase():将字符转换成小写 六、String trim():去除首尾空白…...
Listen / Notify与事务的联动机制)
Postgresql源码(122)Listen / Notify与事务的联动机制
前言 Notify和Listen是Postgresql提供的不同会话间异步消息通信功能,例子: LISTEN virtual; NOTIFY virtual; Asynchronous notification "virtual" received from server process with PID 8448. NOTIFY virtual, This is the payload; Asy…...
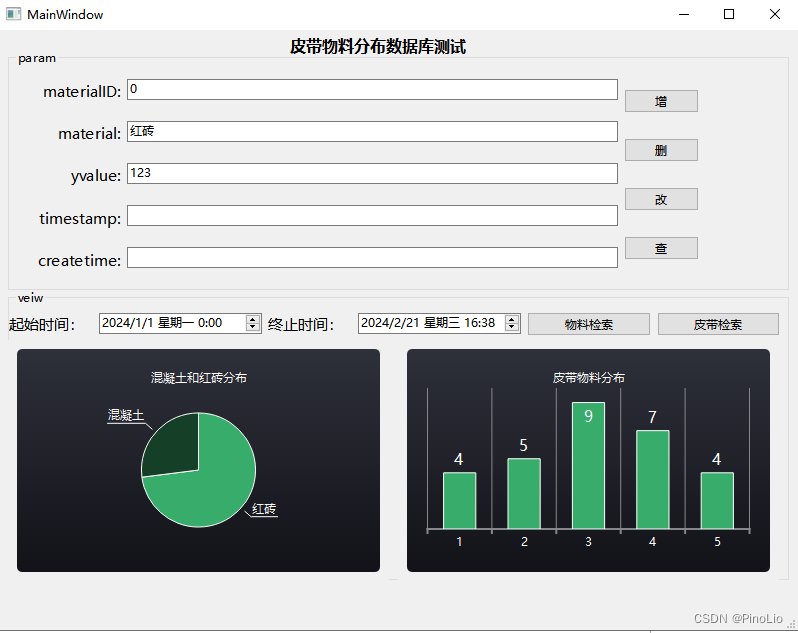
QT 数据库的增加操作和画图 Win
第一步、先配置CMakeLists.txt 在CMakeLists.txt中添加 find_package(Qt6 REQUIRED COMPONENTS Sql) find_package(Qt6 REQUIRED COMPONENTS Charts)target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE Qt6::Sql) target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE Qt6::Charts)避…...

【JS逆向学习】同花顺(q.10jqka)补环境
逆向目标 目标网址:https://q.10jqka.com.cn/ 目标接口: https://q.10jqka.com.cn/index/index/board/all/field/zdf/order/desc/page/3/ajax/1/ 目标参数:cookie 逆向过程 老规矩,先分析网络请求,发现是 cookie 加…...
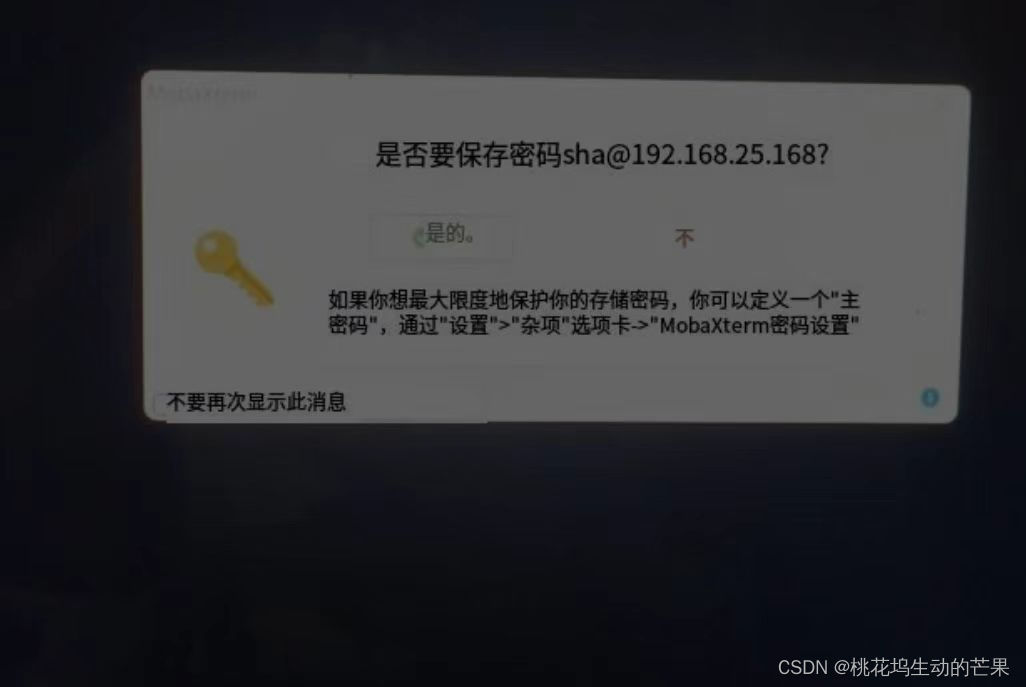
解决MobaXterm网络错误连接超时问题
报错页面: 报错原因: ①网络断开了 ②网络端口,端口号改变 解决办法: ①重新连接网络按R ②固定端口号 第一步:编辑------>虚拟机网络编辑器(我的Linux在虚拟机里) 第二步:用…...

突发!AI独角兽「竹间智能」被曝停工停产6个月
大家好我是二狗。 今天早上起来刷朋友圈,看到一张截图——AI创企竹间智能,宣称因为公司所处的经营环境艰难,部分部门和岗位将从即日起停工停产6个月。 图源:(企服科学) 下面是文字版: 由于公司…...

Qt应用软件【协议篇】GPIO控制LED灯
GPIO简介 GPIO(General Purpose Input/Output,通用输入输出)是一种通用的端口定义,在各种计算机、嵌入式系统和微控制器中广泛应用。通过GPIO,计算机或微控制器可以与外部世界进行交互,例如读取传感器数据或控制外部设备(如LED灯、电机等)。 GPIO的应用场景 按钮和开…...
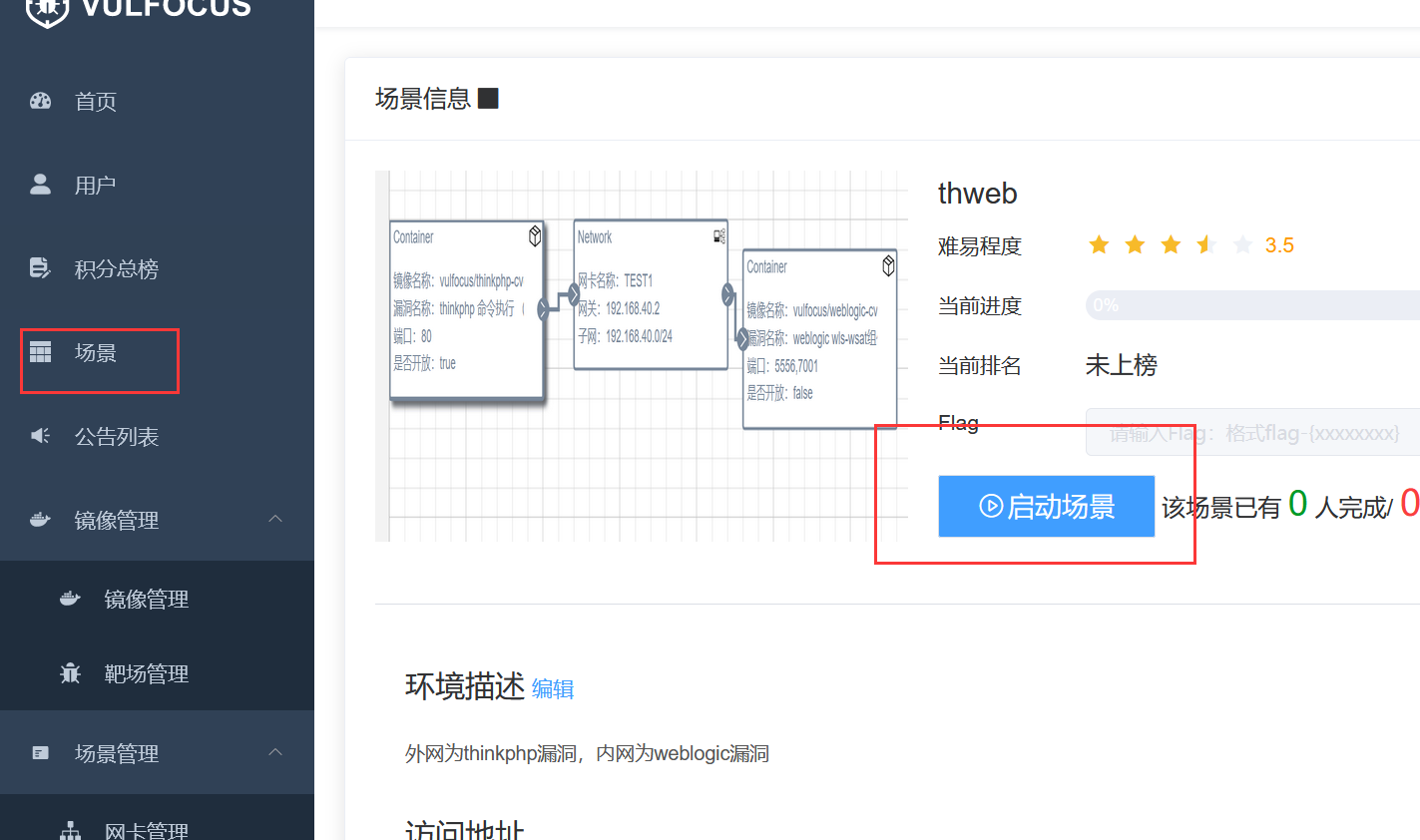
vulfocus靶场搭建
vulfocus靶场搭建 什么是vulfocus搭建教程靶场配置场景靶场编排靶场优化 什么是vulfocus Vulfocus 是一个漏洞集成平台,将漏洞环境 docker 镜像,放入即可使用,开箱即用,我们可以通过搭建该靶场,简单方便地复现一些框架…...

Swift基础知识:30.Swift访问控制
在 Swift 中,访问控制(Access Control)是一种用于限制代码模块对其他代码模块的访问权限的机制。通过访问控制,可以控制代码中各个部分的可见性和可访问性,以便于提高代码的安全性、可维护性和可复用性。 访问级别 S…...
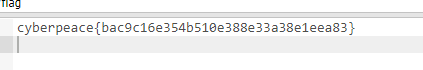
XCTF-web-easyupload
试了试php,php7,pht,phtml等,都没有用 尝试.user.ini 抓包修改将.user.ini修改为jpg图片 在上传一个123.jpg 用蚁剑连接,得到flag...

【杂谈】-递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战
递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战 文章目录 递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战1、自我改进型人工智能的崛起2、人工智能如何挑战人类监管?3、确保人工智能受控的策略4、人类在人工智能发展中的角色5、平衡自主性与控制力6、总结与…...
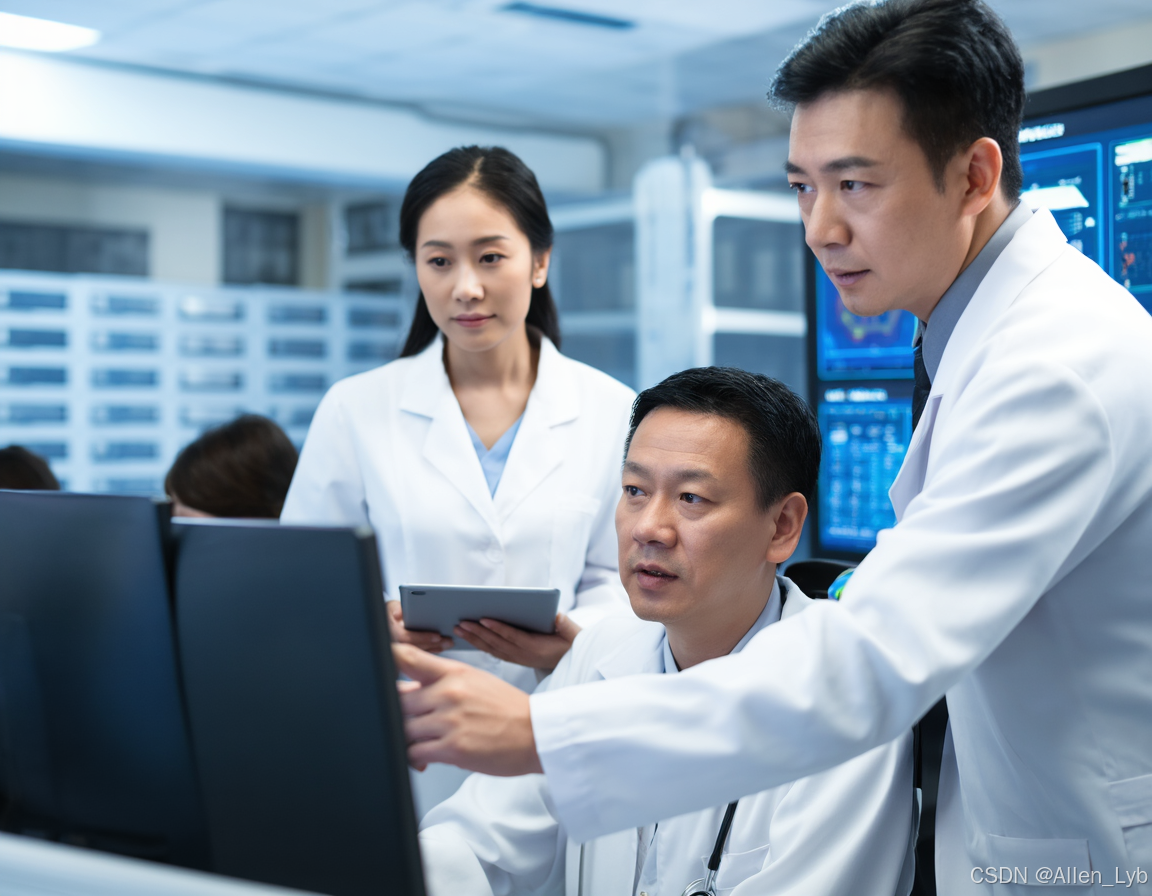

智慧医疗能源事业线深度画像分析(上)
引言 医疗行业作为现代社会的关键基础设施,其能源消耗与环境影响正日益受到关注。随着全球"双碳"目标的推进和可持续发展理念的深入,智慧医疗能源事业线应运而生,致力于通过创新技术与管理方案,重构医疗领域的能源使用模式。这一事业线融合了能源管理、可持续发…...
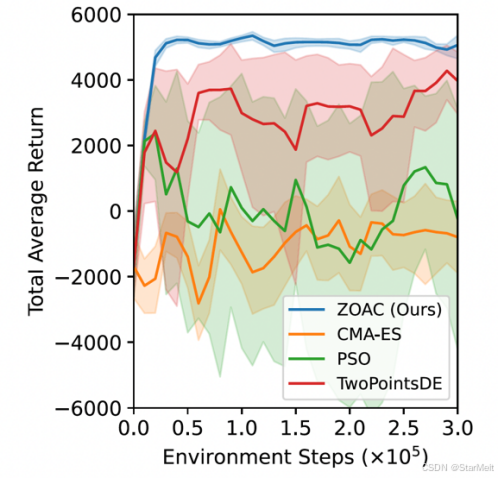
突破不可导策略的训练难题:零阶优化与强化学习的深度嵌合
强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)是工业领域智能控制的重要方法。它的基本原理是将最优控制问题建模为马尔可夫决策过程,然后使用强化学习的Actor-Critic机制(中文译作“知行互动”机制),逐步迭代求解…...

【Java学习笔记】Arrays类
Arrays 类 1. 导入包:import java.util.Arrays 2. 常用方法一览表 方法描述Arrays.toString()返回数组的字符串形式Arrays.sort()排序(自然排序和定制排序)Arrays.binarySearch()通过二分搜索法进行查找(前提:数组是…...
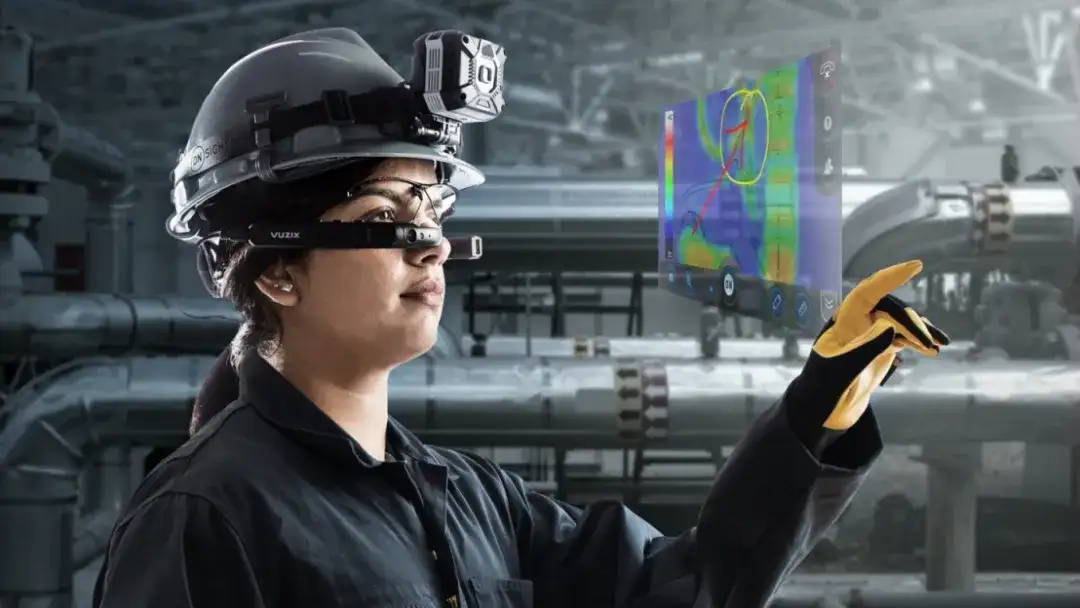

安宝特方案丨XRSOP人员作业标准化管理平台:AR智慧点检验收套件
在选煤厂、化工厂、钢铁厂等过程生产型企业,其生产设备的运行效率和非计划停机对工业制造效益有较大影响。 随着企业自动化和智能化建设的推进,需提前预防假检、错检、漏检,推动智慧生产运维系统数据的流动和现场赋能应用。同时,…...
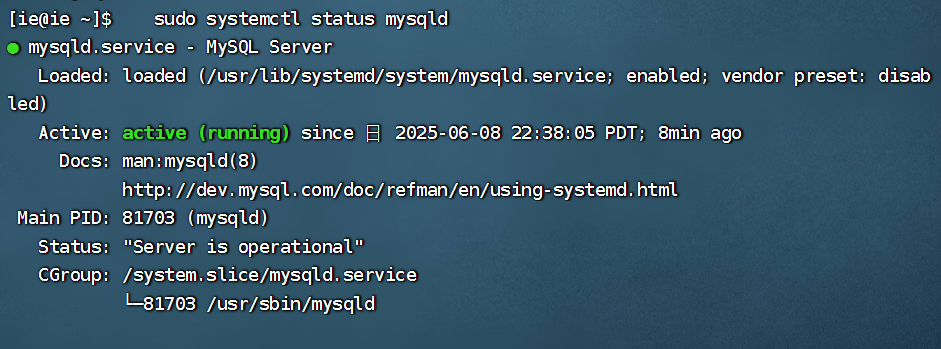
项目部署到Linux上时遇到的错误(Redis,MySQL,无法正确连接,地址占用问题)
Redis无法正确连接 在运行jar包时出现了这样的错误 查询得知问题核心在于Redis连接失败,具体原因是客户端发送了密码认证请求,但Redis服务器未设置密码 1.为Redis设置密码(匹配客户端配置) 步骤: 1).修…...
AI书签管理工具开发全记录(十九):嵌入资源处理
1.前言 📝 在上一篇文章中,我们完成了书签的导入导出功能。本篇文章我们研究如何处理嵌入资源,方便后续将资源打包到一个可执行文件中。 2.embed介绍 🎯 Go 1.16 引入了革命性的 embed 包,彻底改变了静态资源管理的…...
使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台
🎯 使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台 📌 项目背景 随着大语言模型(LLM)的广泛应用,开发者常面临多个挑战: 各大模型(OpenAI、Claude、Gemini、Ollama)接口风格不统一;缺乏一个统一平台进行模型调用与测试;本地模型 Ollama 的集成与前…...
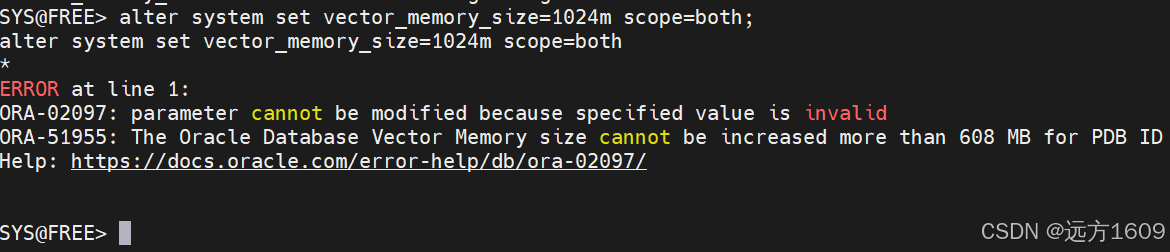
10-Oracle 23 ai Vector Search 概述和参数
一、Oracle AI Vector Search 概述 企业和个人都在尝试各种AI,使用客户端或是内部自己搭建集成大模型的终端,加速与大型语言模型(LLM)的结合,同时使用检索增强生成(Retrieval Augmented Generation &#…...
