[算法沉淀记录] 排序算法 —— 冒泡排序
排序算法 —— 冒泡排序
基本概念
冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法。它重复地遍历要排序的列表,一次比较两个元素,并交换它们的位置,如果它们不是按照升序排列的。这步遍历是重复进行的,直到没有再需要交换,也就是说该列表已经排序完成。该算法为交换排序之一。
算法步骤
- 比较相邻的元素。如果第一个比第二个大,就交换它们两个。
- 对每一对相邻元素作同样的工作,从开始第一对到结尾的最后一对。这步做完后,最后的元素会是最大的数。
- 针对所有的元素重复以上的步骤,除了最后一个。
- 重复步骤1~3,直到排序完成。
时间复杂度
冒泡排序算法的运行时间与输入数据有关。最佳情况下,数据已经排序,算法仅需一次遍历即可完成。在最坏情况下,数据是完全逆序的,需要 n-1 次遍历和 n-1 次比较。因此,其时间复杂度为 O(n^2)。
最好的时间复杂度
当列表已经排序时,冒泡排序的最佳时间复杂度为 O(n)。在最坏情况下,当列表反转时,时间复杂度为 O(n^2)。
最坏的时间复杂度
当列表反转时,冒泡排序的最坏时间复杂度为 O(n^2)。
平均时间复杂度
冒泡排序的平均时间复杂度为 O(n^2)。
空间复杂度
冒泡排序的空间复杂度为 O(1),它只使用了两个附加变量。
稳定性
冒泡排序是一种稳定的排序算法,因为它不会改变相等元素的顺序。
优缺点
冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法,但它也有其优缺点。它的优点是它的实现非常简单,并且对于小数据集来说,它的性能很好。然而,它的缺点是它对于大型数据集来说非常慢,并且它需要额外的空间来存储临时变量。因此,它最适合用于小数据集的排序。
优点
- 实现简单
- 对于小数据集来说,它的性能很好
- 它是一个稳定的排序算法,不会改变具有相等键的元素的相对顺序。
- 原地排序,不需要额外的内存。
缺点
- 对于大型数据集来说,它的性能很慢
- 它需要额外的空间来存储临时变量
应用场景
冒泡排序是一种基础的排序算法,由于其算法简单,因此常用于教学排序算法的入门。在实际应用中,由于其平均和最坏情况下的时间复杂度都是O(n^2),所以它并不适合处理大数据集。然而,冒泡排序在特定情况下仍然有其适用场景:
- 小型数据集:当数据量较小,特别是数据规模在几十到几百之间时,冒泡排序可以很快完成任务,因为其常数因子较小。
- 部分已排序的数组:如果数组已经部分排序,冒泡排序可以很快地将剩下的元素排到正确的位置,因为它在每一轮排序后至少会将一个元素放到最终位置。
- 几乎已排序的数组:对于几乎已经排序好的数组,冒泡排序的时间复杂度可以接近O(n),因为在这种情况下,内部循环的提前终止特性会发挥作用。
- 内存使用限制:冒泡排序是原地排序算法,除了交换元素时需要的常数额外空间,不需要额外的存储空间,这在有严格内存使用限制的环境下是一个优点。
- 实现简单:在一些简单的应用场景中,如嵌入式系统或教学示例中,可能会优先选择冒泡排序,因为它的实现代码简单,易于理解和维护。
- 稳定排序:冒泡排序是一个稳定的排序算法,如果需要保持相等元素的相对顺序不变,冒泡排序可以满足这一需求。
- 教学演示:在计算机科学教育中,冒泡排序经常被用来教授排序算法的基本概念,如比较和交换操作。
尽管冒泡排序在上述场景中有其应用,但在大多数需要高性能排序的应用中,更高效的算法如快速排序、归并排序或堆排序通常是更好的选择。
代码实现
下面是一个简单的python的案例:
def bubble_sort(arr):n = len(arr)for i in range(n):for j in range(0, n-i-1):if arr[j] > arr[j+1]:arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]return arr
接下来是一个C++代码案例:
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) {for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) {if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) {int temp = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j+1];arr[j+1] = temp;}}}
}
下面是一个 C++ 模板的代码案例:
template <typename T>
void bubbleSort(T arr[], int n)
{// Loop through the array n-1 timesfor (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){// Loop through the array n-i-1 timesfor (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++){// If the element at index j is greater than the element at index j+1, swap themif (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);}}}
}
完整 C++ 代码
下面是一个完整的C++代码案例:
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include <string>using namespace std;template <typename T>
void bubbleSort(T arr[], int n)
{// Loop through the array n-1 timesfor (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){// Loop through the array n-i-1 timesfor (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++){// If the element at index j is greater than the element at index j+1, swap themif (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);}}}
}class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age, int score){this->name = name;this->age = age;this->socre = score;}// Override the operator> for other function to use.bool operator>(const Person &other) const{// Compare the socre of two Person objects.return this->socre > other.socre;}// Override the operator< for other function to use.bool operator<(const Person &other) const{// Compare the socre of two Person objects.return this->socre < other.socre;}// Override the operator== for other function to use.bool operator==(const Person &other) const{// Compare the socre, age and name of two Person objects.return this->socre == other.socre &&this->age == other.age &&this->name == other.name;}// Override the operator!= for other function to use.bool operator!=(const Person &other) const{// Compare the socre, age and name of two Person objects.return this->socre != other.socre ||this->age != other.age ||this->name != other.name;}// Now there are some get parameters function for this calss:const string &getName() const { return this->name; }int getAge() const { return this->age; }int getSocre() const { return this->socre; }private:string name;int age;int socre;
};// This is a unit test function for Person class.
void testPerson()
{Person person1("Alice", 20, 90);Person person2("Bob", 21, 80);Person person3("Charlie", 22, 85);// Test operator>assert(person1 > person2);assert(!(person1 > person3));// Test operator<assert(person2 < person1);assert(!(person3 < person1));// Test operator==assert(person1 == person1);assert(!(person1 == person2));// Test operator!=assert(person1 != person2);assert(!(person1 != person1));
}int main()
{// Declare an array of integersint arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};// Calculate the size of the arrayint n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<int>(arr, n);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){cout << arr[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of floatsdouble arr2[] = {64.5, 34.2, 25.1, 12.6, 22.8, 11.9, 90.0};// Calculate the size of the arrayint n2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<double>(arr2, n2);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++){cout << arr2[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of characterschar arr3[] = {'g', 'e', 'k', 'i', 't', 'c', 'h'};// Calculate the size of the arrayint n3 = sizeof(arr3) / sizeof(arr3[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<char>(arr3, n3);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n3; i++){cout << arr3[i] << " ";}cout << endl;testPerson();// Now I want to write some Person class's bubble sort examples in here:// Declare an array of Person objectsPerson arr4[] = {Person("John", 25, 90), Person("Alice", 30, 85), Person("Bob", 20, 78), Person("Eve", 22, 89)}; // This is a dummy Person class, you need to implement it properly.// Calculate the size of the arrayint n4 = sizeof(arr4) / sizeof(arr4[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<Person>(arr4, n4);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n4; i++){const auto& person = arr4[i];cout << person.getName() << " " << person.getAge() << " " << person.getSocre() << endl;}cout << endl;// Declare an array of Person pointersPerson *arr5[4];arr5[0] = new Person("John", 25, 90);arr5[1] = new Person("Alice", 30, 85);arr5[2] = new Person("Bob", 20, 78);arr5[3] = new Person("Eve", 22, 89);// Calculate the size of the arrayint n5 = sizeof(arr5) / sizeof(arr5[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<Person *>(arr5, n5);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n5; i++){const auto& person = arr5[i];cout << person->getName() << " " << person->getAge() << " " << person->getSocre() << endl;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
这段代码在最开始定义了一个模板函数bubbleSort,用于对不同类型的数据(如整数、浮点数和字符)进行冒泡排序。然后,定义了一个名为Person的类,该类具有name、age和score属性,并重载了>、<、==和!=运算符,以便在排序时比较Person对象。
接下来,定义了一个名为testPerson的函数,用于测试Person类。在这个函数中,创建了一些Person对象,并测试了重载的运算符。
在main函数中,首先对整数、浮点数和字符类型的数组进行冒泡排序,然后测试Person类。最后,对Person对象的数组和Person指针的数组进行冒泡排序,并输出排序后的结果。
综上所述,这段代码演示了如何使用冒泡排序算法对不同类型的数据进行排序,并展示了如何使用Person类进行排序。
扩展阅读
优化时间复杂度和空间复杂度的思路
冒泡排序的时间复杂度和空间复杂度优化通常涉及以下几个方面:
- 提前终止:在冒泡排序的过程中,如果在某一趟遍历中没有发生任何元素的交换,那么可以认为数组已经排序完成,可以提前终止排序过程。这种优化可以将最好情况下的时间复杂度从O(n^2)降低到O(n)。
- 双向冒泡(鸡尾酒排序):传统的冒泡排序每次只将最大的元素移动到数组的一端,而双向冒泡排序则是在每趟遍历中同时将最大元素和最小元素移动到数组的两端。这样可以在一定程度上减少排序所需的趟数。
- 梳排序(Comb Sort):梳排序是冒泡排序的一种改进,它通过设置一个逐渐减小的“间隔”(也称为“梳子”)来比较和交换元素。开始时,间隔较大,可以快速将大距离的元素移动到正确位置,随着排序的进行,间隔逐渐减小,最终变为1,这时数组几乎已经排序完成,进行最后一轮冒泡排序。梳排序的平均时间复杂度接近O(n2/2p),其中p是梳子间隔减小的速度。
- 泡沫优化:在冒泡排序中,每一趟遍历后,最后一个交换的位置之后的元素在下一趟遍历中不再需要比较,因为这部分的元素已经是排序好的。记录这个位置,下一趟遍历只需要遍历到这个位置即可。
- 差值交换:在冒泡排序中,如果使用差值交换代替传统的交换方式,可以减少交换操作的次数。差值交换是指只在需要交换的元素之间记录差值,而不是实际交换它们的位置。
常见的变种算法
历史上常用的冒泡排序变种包括:
- 经典冒泡排序:最基本的冒泡排序,每次遍历将最大的元素移动到数组的末尾。
- 鸡尾酒排序:也称为双向冒泡排序,每次遍历同时将最大元素移动到数组的一端,最小元素移动到另一端。
- 梳排序(Comb Sort):通过逐渐减小的间隔来比较和交换元素,最后进行一次冒泡排序来修正剩余的元素顺序。
- 奇偶排序:在冒泡排序的基础上,交替进行奇数索引和偶数索引的元素比较和交换。
- 混沌冒泡排序:引入随机性,每次随机选择两个元素进行比较和交换,用于某些特定场景下的排序。
需要注意的是,尽管这些优化可以在某些情况下提高冒泡排序的性能,但它们通常不能改变冒泡排序最坏情况下的时间复杂度O(n^2)。因此,对于大规模数据集的排序,更高效的算法如快速排序、归并排序或堆排序通常是更好的选择。
鸡尾酒排序(双向冒泡排序)
鸡尾酒排序(Cocktail Sort)也被称为双向冒泡排序或鸡尾酒搅拌排序,它是一种改进的冒泡排序算法。与传统的冒泡排序不同,鸡尾酒排序在每趟遍历中会同时将最大元素和最小元素移动到数组的两端,而不是只将最大元素移动到一端。这样可以在一定程度上减少排序所需的趟数。
算法步骤
算法步骤如下:
- 初始化:设置两个指针,一个指向数组的开始(left),另一个指向数组的末尾(right)。设置一个标志变量,用于检测在上一趟遍历中是否发生了元素交换。
- 正向遍历:从left开始,到right结束,比较相邻元素,如果它们的顺序错误,则交换它们。这一步将最大的元素移动到数组的末尾。
- 反向遍历:将right指针减一,从right开始,到left结束,比较相邻元素,如果它们的顺序错误,则交换它们。这一步将最小的元素移动到数组的开头。
- 重复步骤2和3:重复步骤2和3,直到在一次完整的正向遍历和反向遍历中都没有发生元素交换,这时数组已经排序完成。
- 结束:当left >= right时,排序结束。
伪代码描述
鸡尾酒排序的伪代码如下:
procedure cocktailSort(arr: list of sortable items)n = length(arr)swapped = truestart = 0end = n - 1while (swapped == true)// 设置交换标志为falseswapped = false// 正向遍历for i = start to end - 1if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1])swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1])// 发生了交换,设置交换标志为trueswapped = true// 如果没有发生交换,数组已经排序完成if (swapped == false)break// 将end指针减一end = end - 1// 设置交换标志为falseswapped = false// 反向遍历for i = end - 1 downto startif (arr[i] > arr[i + 1])swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1])// 发生了交换,设置交换标志为trueswapped = true// 将start指针加一start = start + 1// 结束循环
end procedure
C++ 模板代码
下面是使用C++模板实现的鸡尾酒排序:
template<typename T>
void cocktailSort(std::vector<T>& arr) {bool swapped = true;int start = 0;int end = arr.size() - 1;while (swapped) {// 设置交换标志为falseswapped = false;// 正向遍历for (int i = start; i < end; ++i) {if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {std::swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);// 发生了交换,设置交换标志为trueswapped = true;}}// 如果没有发生交换,数组已经排序完成if (!swapped) {break;}// 将end指针减一--end;// 设置交换标志为falseswapped = false;// 反向遍历for (int i = end - 1; i >= start; --i) {if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {std::swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);// 发生了交换,设置交换标志为trueswapped = true;}}// 将start指针加一++start;}
}
梳排序(Comb Sort)
梳排序(Comb Sort)是一种由Wlodzimierz Dobosiewicz于1980年发明,由Tim Peter于1989年发表的排序算法。它是冒泡排序的一种改进算法,旨在减少其所需的交换次数。梳排序通过比较相隔一定“间隔”(也称为“梳子”)的元素来工作,逐渐减小这个间隔,最终进行一次冒泡排序来修正剩余的元素顺序。
算法步骤
算法步骤如下:
- 初始化间隔:开始时,间隔设置为数组长度除以1.3(这个值是经验值,也可以使用其他系数),向下取整。这个间隔会随着排序的进行而逐渐减小。
- 缩减间隔:在每趟排序之后,间隔会按照某个系数(通常也是1.3)减小,直到间隔变为1。
- 排序:对于当前的间隔,比较相隔该间隔的元素,如果它们的顺序错误,则交换它们。这个过程类似于冒泡排序,但是比较的元素间隔更大。
- 重复步骤2和3:重复步骤2和3,直到间隔减小到1。这时,数组应该已经基本有序。
- 最终冒泡排序:进行一次传统的冒泡排序,确保数组完全有序。
伪代码描述
梳排序的伪代码如下:
procedure combSort(arr: list of sortable items)n = length(arr)gap = nshrink = 1.3swapped = falsewhile gap > 1 or swapped// 设置间隔gap = floor(gap / shrink)if gap < 1gap = 1swapped = false// 对于当前的间隔,进行排序for i = 0 to n - gap - 1if arr[i] > arr[i + gap]swap(arr[i], arr[i + gap])swapped = true// 最终进行一次冒泡排序for i = 0 to n - 2if arr[i] > arr[i + 1]swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1])
end procedure
C++ 模板代码
下面是使用C++模板实现的梳排序:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath> // 用于计算地板除法
template<typename T>
void combSort(std::vector<T>& arr) {int n = arr.size();int gap = n;bool swapped = false;const double shrink = 1.3;while (gap > 1 || swapped) {// 设置间隔gap = static_cast<int>(floor(gap / shrink));if (gap < 1) {gap = 1;}swapped = false;// 对于当前的间隔,进行排序for (int i = 0; i < n - gap; ++i) {if (arr[i] > arr[i + gap]) {std::swap(arr[i], arr[i + gap]);swapped = true;}}}// 最终进行一次冒泡排序for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {std::swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);}}
}
混沌冒泡排序
混沌冒泡排序(Chaotic Bubble Sort)是一种基于冒泡排序的变体,它在比较和交换元素时引入了混沌理论的原理。混沌理论是一种研究在确定性系统中出现的看似随机或复杂行为的方法。在混沌冒泡排序中,混沌序列用于决定哪些元素进行比较和交换,而不是按照固定的顺序。
算法步骤
算法步骤如下:
- 生成混沌序列:首先,需要生成一个混沌序列,这个序列的长度与待排序数组的长度相同。混沌序列中的每个元素都是数组索引的一个排列,确保每个索引都会被访问到。
- 排序过程:使用生成的混沌序列进行排序。对于混沌序列中的每一对索引,比较对应的数组元素,如果它们的顺序错误,则交换它们。
- 重复排序:重复步骤2,直到没有更多的元素需要交换,即数组已经排序完成。
伪代码描述
混沌冒泡排序的伪代码如下:
procedure chaoticBubbleSort(arr: list of sortable items)n = length(arr)// 生成混沌序列chaoticSequence = generateChaoticSequence(n)// 初始化交换标志swapped = truewhile swapped// 设置交换标志为falseswapped = false// 使用混沌序列进行排序for i = 1 to n - 1// 获取混沌序列中的索引index1 = chaoticSequence[i]index2 = chaoticSequence[i + 1]// 比较并交换元素if arr[index1] > arr[index2]swap(arr[index1], arr[index2])// 发生了交换,设置交换标志为trueswapped = trueend while
end procedure
C++模板实现
下面是使用C++模板实现的混沌冒泡排序:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib> // 用于生成随机数
template<typename T>
void chaoticBubbleSort(std::vector<T>& arr) {int n = arr.size();std::vector<int> chaoticSequence(n);bool swapped = true;// 生成混沌序列for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {chaoticSequence[i] = i;}// 混沌打乱序列for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {std::swap(chaoticSequence[i], chaoticSequence[rand() % n]);}while (swapped) {swapped = false;// 使用混沌序列进行排序for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {// 获取混沌序列中的索引int index1 = chaoticSequence[i];int index2 = chaoticSequence[i + 1];// 比较并交换元素if (arr[index1] > arr[index2]) {std::swap(arr[index1], arr[index2]);swapped = true;}}}
}
这段代码定义了一个模板函数chaoticBubbleSort,它可以接受任何类型的可排序元素数组。在main函数中,我们创建了一个整数向量并使用chaoticBubbleSort进行排序,然后打印排序后的结果。请注意,这个实现使用了std::rand()来生成混沌序列,这并不是真正的混沌序列生成方法,而是一种简单的随机化方法。在实际应用中,可能需要使用更复杂的混沌映射函数来生成混沌序列。
奇偶排序
奇偶排序(Odd-Even Sort),也称为奇偶换位排序,是一种基于比较的排序算法,它是冒泡排序的一种变体。在奇偶排序中,排序过程分为两个阶段:奇数阶段和偶数阶段。在奇数阶段,比较所有奇数索引的元素对;在偶数阶段,比较所有偶数索引的元素对。这样交替进行,直到数组完全排序。
算法步骤
算法步骤如下:
- 初始化:设置一个标记变量,用于检测在上一轮排序中是否发生了元素交换。
- 奇数阶段:比较所有奇数索引的元素对(索引为1, 2, 3, …),如果它们的顺序错误,则交换它们。
- 偶数阶段:比较所有偶数索引的元素对(索引为0, 2, 4, …),如果它们的顺序错误,则交换它们。
- 重复步骤2和3:重复步骤2和3,直到在一次完整的奇数阶段和偶数阶段中都没有发生元素交换,这时数组已经排序完成。
伪代码描述
奇偶排序的伪代码如下:
procedure oddEvenSort(arr: list of sortable items)n = length(arr)swapped = truewhile swappedswapped = false// 奇数阶段for i = 1 to n - 2 by 2if arr[i] > arr[i + 1]swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1])swapped = true// 偶数阶段for i = 0 to n - 2 by 2if arr[i] > arr[i + 1]swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1])swapped = trueend while
end procedure
C++模板代码实现
下面是使用C++模板实现的奇偶排序:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
template<typename T>
void oddEvenSort(std::vector<T>& arr) {bool swapped = true;int n = arr.size();while (swapped) {swapped = false;// 奇数阶段for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i += 2) {if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {std::swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);swapped = true;}}// 偶数阶段for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i += 2) {if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {std::swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);swapped = true;}}}
}
带扩展阅读的完整C++代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>using namespace std;template <typename T>
void bubbleSort(T arr[], int n)
{// Loop through the array n-1 timesfor (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){// Loop through the array n-i-1 timesfor (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++){// If the element at index j is greater than the element at index j+1, swap themif (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);}}}
}class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age, int score){this->name = name;this->age = age;this->socre = score;}// Override the operator> for other function to use.bool operator>(const Person &other) const{// Compare the socre of two Person objects.return this->socre > other.socre;}// Override the operator< for other function to use.bool operator<(const Person &other) const{// Compare the socre of two Person objects.return this->socre < other.socre;}// Override the operator== for other function to use.bool operator==(const Person &other) const{// Compare the socre, age and name of two Person objects.return this->socre == other.socre &&this->age == other.age &&this->name == other.name;}// Override the operator!= for other function to use.bool operator!=(const Person &other) const{// Compare the socre, age and name of two Person objects.return this->socre != other.socre ||this->age != other.age ||this->name != other.name;}// Now there are some get parameters function for this calss:const string &getName() const { return this->name; }int getAge() const { return this->age; }int getSocre() const { return this->socre; }private:string name;int age;int socre;
};// This is a unit test function for Person class.
void testPerson()
{Person person1("Alice", 20, 90);Person person2("Bob", 21, 80);Person person3("Charlie", 22, 85);// Test operator>assert(person1 > person2);assert(!(person1 > person3));// Test operator<assert(person2 < person1);assert(!(person3 < person1));// Test operator==assert(person1 == person1);assert(!(person1 == person2));// Test operator!=assert(person1 != person2);assert(!(person1 != person1));
}template <typename T>
void cocktailSort(vector<T> &arr)
{// Initialize swapped to true to enter loopbool swapped = true;// Initialize start and end indicesint start = 0;int end = arr.size() - 1;// Loop until all swaps are donewhile (swapped){// Reset swapped to falseswapped = false;// Loop through all elements in arrayfor (int i = start; i < end; ++i){// If element is greater than next element, swap themif (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]){swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);swapped = true;}}// If no swaps, then array is sortedif (!swapped){break;}// Decrement end index--end;// Reset swapped to falseswapped = false;// Loop through all elements in arrayfor (int i = end - 1; i >= start; --i){// If element is greater than next element, swap themif (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]){swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);swapped = true;}}// Increment start index++start;}
}template <typename T>
void combSort(vector<T> &arr)
{// n is the size of the arrayint n = arr.size();// gap is the gap between elementsint gap = n;// swapped is a flag to check if any elements have been swappedbool swapped = false;// the constant value of the gap is 1.3const double shrink = 1.3;// while the gap is greater than 1 or swapped is truewhile (gap > 1 || swapped){// gap is the new gapgap = static_cast<int>(floor(gap / shrink));// if the gap is less than 1, set it to 1if (gap < 1){gap = 1;}// set swapped to falseswapped = false;// loop through the arrayfor (int i = 0; i < n - gap; ++i){// if the current element is greater than the next elementif (arr[i] > arr[i + gap]){// swap themswap(arr[i], arr[i + gap]);// set swapped to trueswapped = true;}}}// loop through the arrayfor (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i){// if the current element is greater than the next elementif (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]){// swap themswap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);}}
}template <typename T>
void chaoticBubbleSort(vector<T> &arr)
{// n is the size of the arrayint n = arr.size();// create a vector to store the chaotic sequencevector<int> chaoticSequence(n);// set swapped to true to start the loopbool swapped = true;// fill the chaotic sequence with the indices of the arrayfor (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){chaoticSequence[i] = i;}// shuffle the chaotic sequencefor (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){swap(chaoticSequence[i], chaoticSequence[rand() % n]);}// start the bubble sort loopwhile (swapped){swapped = false;// loop through the array and compare each element to the one after itfor (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i){// store the indices of the elementsint index1 = chaoticSequence[i];int index2 = chaoticSequence[i + 1];// if the element at the first index is greater than the one after itif (arr[index1] > arr[index2]){// swap themswap(arr[index1], arr[index2]);// set swapped to true to start the next loopswapped = true;}}}
}template <typename T>
void oddEvenSort(vector<T> &arr)
{bool swapped = true;int n = arr.size();while (swapped){swapped = false;for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i += 2){if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]){swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);swapped = true;}}for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i += 2){if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]){swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);swapped = true;}}}
}void bubbleSortTestCase()
{// Declare an array of integersint arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};// Calculate the size of the arrayint n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<int>(arr, n);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){cout << arr[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of floatsdouble arr2[] = {64.5, 34.2, 25.1, 12.6, 22.8, 11.9, 90.0};// Calculate the size of the arrayint n2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<double>(arr2, n2);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++){cout << arr2[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of characterschar arr3[] = {'g', 'e', 'k', 'i', 't', 'c', 'h'};// Calculate the size of the arrayint n3 = sizeof(arr3) / sizeof(arr3[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<char>(arr3, n3);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n3; i++){cout << arr3[i] << " ";}cout << endl;testPerson();// Now I want to write some Person class's bubble sort examples in here:// Declare an array of Person objectsPerson arr4[] = {Person("John", 25, 90), Person("Alice", 30, 85), Person("Bob", 20, 78), Person("Eve", 22, 89)}; // This is a dummy Person class, you need to implement it properly.// Calculate the size of the arrayint n4 = sizeof(arr4) / sizeof(arr4[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<Person>(arr4, n4);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n4; i++){const auto &person = arr4[i];cout << person.getName() << " " << person.getAge() << " " << person.getSocre() << endl;}cout << endl;// Declare an array of Person pointersPerson *arr5[4];arr5[0] = new Person("John", 25, 90);arr5[1] = new Person("Alice", 30, 85);arr5[2] = new Person("Bob", 20, 78);arr5[3] = new Person("Eve", 22, 89);// Calculate the size of the arrayint n5 = sizeof(arr5) / sizeof(arr5[0]);// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraybubbleSort<Person *>(arr5, n5);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < n5; i++){const auto &person = arr5[i];cout << person->getName() << " " << person->getAge() << " " << person->getSocre() << endl;}cout << endl;
}void cocktailSortTestCase()
{// Declare an array of integersvector<int> arr = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraycocktailSort<int>(arr);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++){cout << arr[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of floatsvector<double> arr2 = {64.5, 34.2, 25.1, 12.6, 22.8, 11.9, 90.0};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraycocktailSort<double>(arr2);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr2.size(); i++){cout << arr2[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of charactersvector<char> arr3 = {'g', 'e', 'k', 'i', 't', 'c', 'h'};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraycocktailSort<char>(arr3);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr3.size(); i++){cout << arr3[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Now I want to write some Person class's bubble sort examples in here:// Declare an array of Person objectsvector<Person> arr4 = {Person("John", 25, 90), Person("Alice", 30, 85), Person("Bob", 20, 78), Person("Eve", 22, 89)}; // This is a dummy Person class, you need to implement it properly.// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraycocktailSort<Person>(arr4);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr4.size(); i++){const auto &person = arr4[i];cout << person.getName() << " " << person.getAge() << " " << person.getSocre() << endl;}cout << endl;
}void combSortTestCase()
{// Declare an array of integersvector<int> arr = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraycombSort<int>(arr);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++){cout << arr[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of floatsvector<double> arr2 = {64.5, 34.2, 25.1, 12.6, 22.8, 11.9, 90.0};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraycombSort<double>(arr2);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr2.size(); i++){cout << arr2[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of charactersvector<char> arr3 = {'g', 'e', 'k', 'i', 't', 'c', 'h'};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraycombSort<char>(arr3);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr3.size(); i++){cout << arr3[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Now I want to write some Person class's bubble sort examples in here:// Declare an array of Person objectsvector<Person> arr4 = {Person("John", 25, 90), Person("Alice", 30, 85), Person("Bob", 20, 78), Person("Eve", 22, 89)}; // This is a dummy Person class, you need to implement it properly.// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraycombSort<Person>(arr4);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr4.size(); i++){const auto &person = arr4[i];cout << person.getName() << " " << person.getAge() << " " << person.getSocre() << endl;}cout << endl;
}void chaoticButtleSortTestCase()
{// Declare an array of integersvector<int> arr = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraychaoticBubbleSort<int>(arr);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++){cout << arr[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of floatsvector<double> arr2 = {64.5, 34.2, 25.1, 12.6, 22.8, 11.9, 90.0};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraychaoticBubbleSort<double>(arr2);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr2.size(); i++){cout << arr2[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of charactersvector<char> arr3 = {'g', 'e', 'k', 'i', 't', 'c', 'h'};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraychaoticBubbleSort<char>(arr3);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr3.size(); i++){cout << arr3[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Now I want to write some Person class's bubble sort examples in here:// Declare an array of Person objectsvector<Person> arr4 = {Person("John", 25, 90), Person("Alice", 30, 85), Person("Bob", 20, 78), Person("Eve", 22, 89)}; // This is a dummy Person class, you need to implement it properly.// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arraychaoticBubbleSort<Person>(arr4);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr4.size(); i++){const auto &person = arr4[i];cout << person.getName() << " " << person.getAge() << " " << person.getSocre() << endl;}cout << endl;
}void oddEvenSortTestCase()
{// Declare an array of integersvector<int> arr = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arrayoddEvenSort<int>(arr);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++){cout << arr[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of floatsvector<double> arr2 = {64.5, 34.2, 25.1, 12.6, 22.8, 11.9, 90.0};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arrayoddEvenSort<double>(arr2);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr2.size(); i++){cout << arr2[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Declare an array of charactersvector<char> arr3 = {'g', 'e', 'k', 'i', 't', 'c', 'h'};// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arrayoddEvenSort<char>(arr3);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr3.size(); i++){cout << arr3[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// Now I want to write some Person class's bubble sort examples in here:// Declare an array of Person objectsvector<Person> arr4 = {Person("John", 25, 90), Person("Alice", 30, 85), Person("Bob", 20, 78), Person("Eve", 22, 89)}; // This is a dummy Person class, you need to implement it properly.// Call the bubbleSort function to sort the arrayoddEvenSort<Person>(arr4);// Print the sorted arraycout << "Sorted array: \n";for (int i = 0; i < arr4.size(); i++){const auto &person = arr4[i];cout << person.getName() << " " << person.getAge() << " " << person.getSocre() << endl;}cout << endl;
}int main()
{testPerson();bubbleSortTestCase();cocktailSortTestCase();combSortTestCase();chaoticButtleSortTestCase();oddEvenSortTestCase();return 0;
}个人格言
追寻与内心共鸣的生活,未来会逐渐揭晓答案。
Pursue the life that resonates with your heart, and the future will gradually reveal the answer.

相关文章:

[算法沉淀记录] 排序算法 —— 冒泡排序
排序算法 —— 冒泡排序 基本概念 冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法。它重复地遍历要排序的列表,一次比较两个元素,并交换它们的位置,如果它们不是按照升序排列的。这步遍历是重复进行的,直到没有再需要交换,也就是说该…...
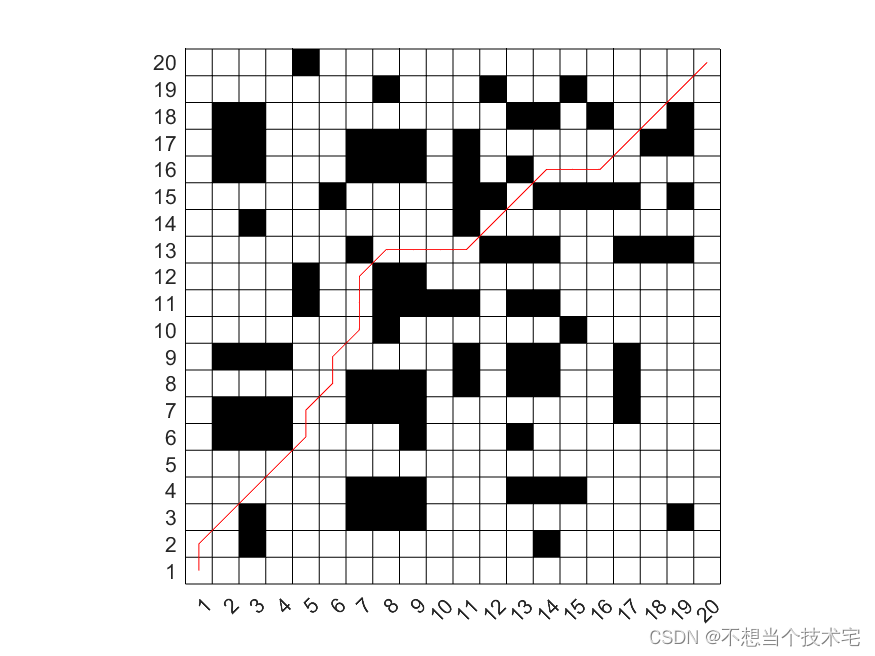
【机器人最短路径规划问题(栅格地图)】基于遗传算法求解
基于遗传算法求解机器人最短路径规划问题(栅格地图)的仿真结果 仿真结果: 路径长度的变化曲线: 遗传算法优化后的机器人避障路径:...

如何做代币分析:以 TRX 币为例
作者:lesleyfootprint.network 编译:cicifootprint.network 数据源:TRX 代币仪表板 (仅包括以太坊数据) 在加密货币和数字资产领域,代币分析起着至关重要的作用。代币分析指的是深入研究与代币相关的数据…...

关于地址引用与值引用的坑
List<UserInfo> userInfoList new List<UserInfo>(); List<UserInfo> userInfoList_new new List<UserInfo>(userInfoList);userInfoList_new 与userInfoList 指的是相同的内存吗? 答: 在C#中,userInfoList_new …...

初谈软件工程(一)
我就读于兰州交通大学的软件工程专业。虽然在全国众多的985、211高校中,兰州交通大学可能并不显眼,似乎未能跻身这些所谓的“顶尖”行列就意味着不被认可。然而,在甘肃省的教育领域中,它无疑是一座璀璨的明珠,名列前茅…...

自动化开展思路
自动化开展思路 本人在公司一直从事自动化测试推进工作,最近在好友的邀请下去其就职的公司分享如何开展自动化测试! 希望能帮其解决如下几个痛点: 1.上线周期长; 2.测试时间紧张,上线信心不足,测试覆盖…...
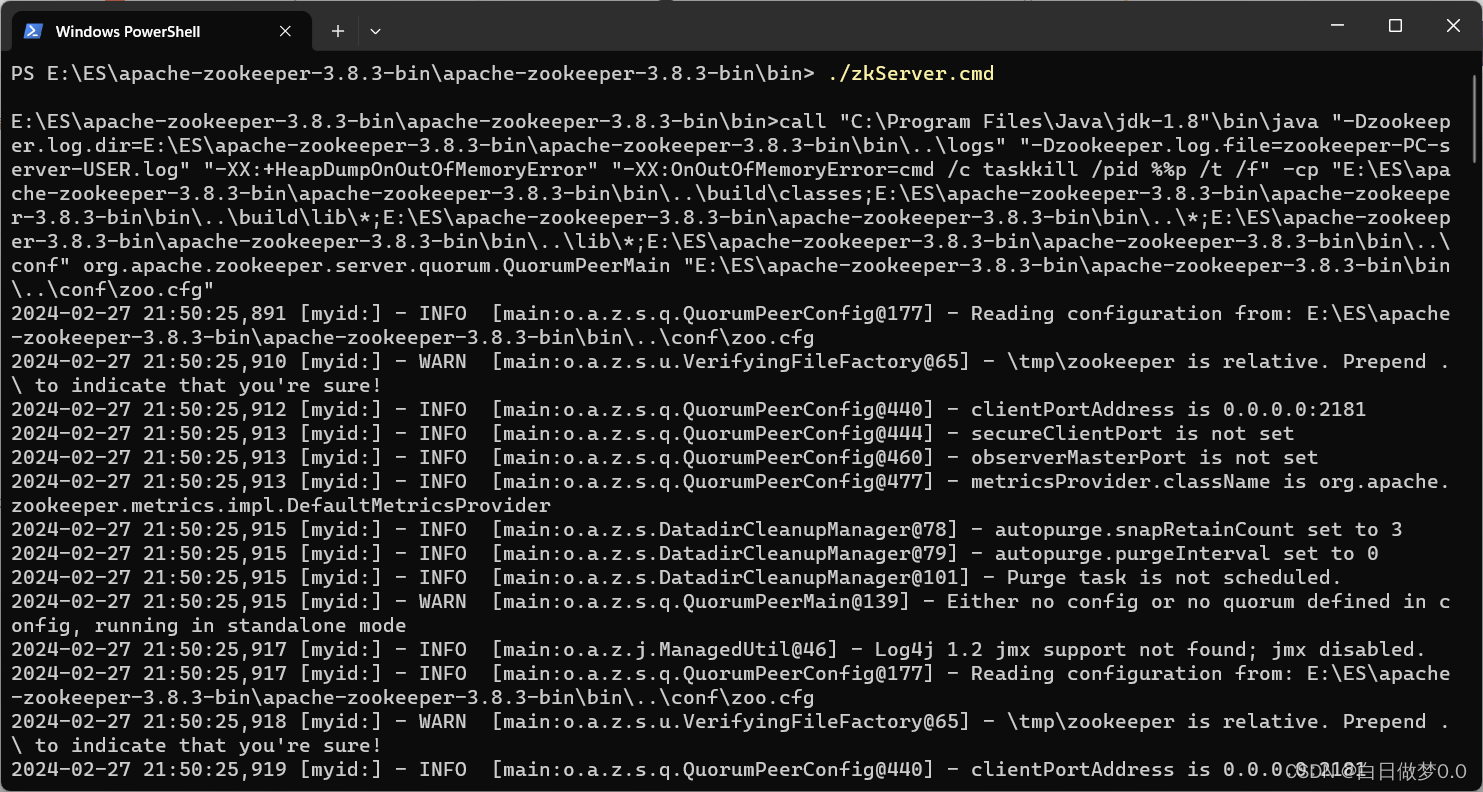
安装使用zookeeper
先去官网下载zookeeper:Apache ZooKeeper 直接进入bin目录,使用powerShell打开。 输入: ./zkServer.cmd 命令,启动zookeeper。 zookeeper一般需要配合Dubbo一起使用,作为注册中心使用,可以参考另一篇博客…...
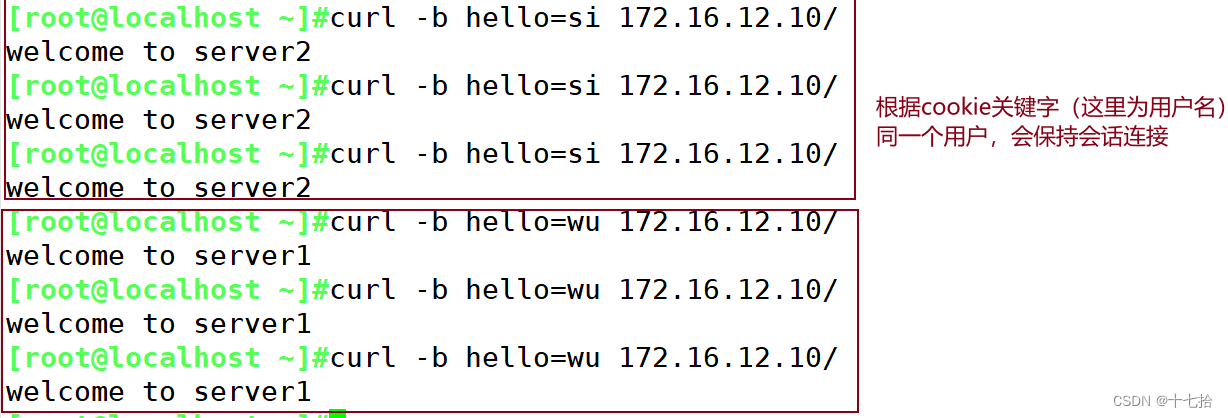
nginx实现http反向代理及负载均衡
目录 一、代理概述 1、代理概念 1.1 正向代理(Forward Proxy) 1.2 反向代理(Reverse Proxy) 1.3 正向代理与反向代理的区别 2、同构代理与异构代理 2.1 同构代理 2.2 异构代理 2.3 同构代理与异构代理的区别 二、四层代…...

vue组件中data为什么必须是一个函数
查看本专栏目录 关于作者 还是大剑师兰特:曾是美国某知名大学计算机专业研究生,现为航空航海领域高级前端工程师;CSDN知名博主,GIS领域优质创作者,深耕openlayers、leaflet、mapbox、cesium,canvas&#x…...

科技论文编写思路
科技论文编写思路 1.基本框架2.课题可行性评估1.研究目标和意义2.研究方法和技术3.可行性和可操作性4.风险和不确定性5.经济性和资源投入6.成果预期和评估 3.写作思路4.利用AI读论文5.实验流程 1.基本框架 IntroductionRelated worksMethodExperiment and analysisDiscussionC…...
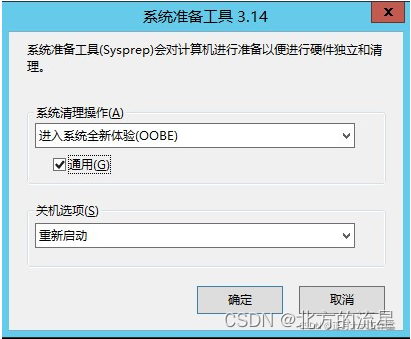
Windows虚拟机克隆后修改SID
在日常使用VMware Workstation我们经常会去克隆一些Windows操作系统的虚拟机,克隆的虚拟机和源虚拟机的系统安全标识符(Security Identifiers,SID)相同,SID是标识用户、组和计算机账户的唯一的号码。 如果两台虚拟机都…...

前端架构: 脚手架工具rxjs的快速上手应用
rxjs rxjs 是一个异步的库和Promise是非常的相似 文档:https://www.npmjs.com/package/rxjs Weekly Downloads 44,474,389 (动态数据) 说明这个库也是非常的流行 安装 $ npm i -S rxjs 使用 import { range, filter, map } from rxjs;range(1, 200).pipe(filte…...
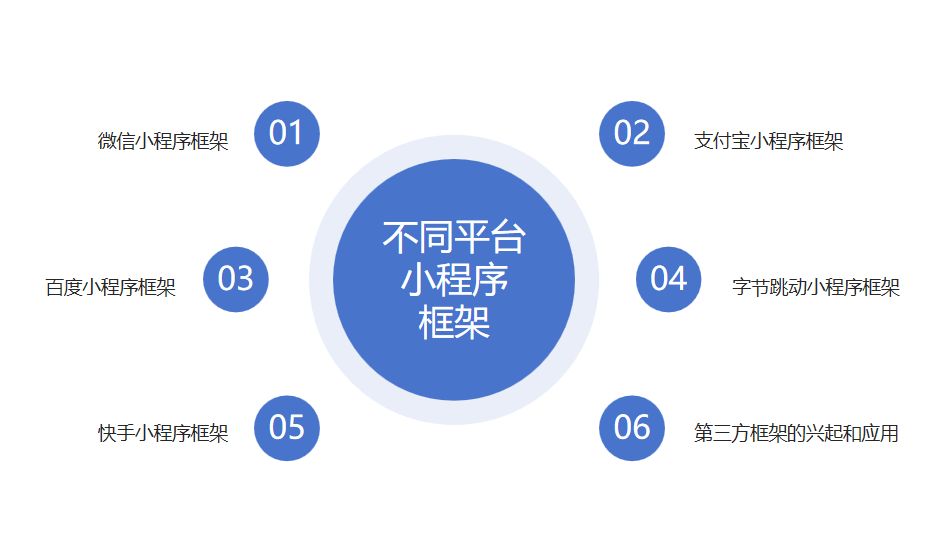
小程序框架(概念、工作原理、发展及应用)
引言 移动应用的普及使得用户对于轻量级、即时可用的应用程序需求越来越迫切。在这个背景下,小程序应运而生,成为一种无需下载安装、即点即用的应用形式,为用户提供了更便捷的体验。小程序的快速发展离不开强大的开发支持,而小程…...

音视频数字化(数字与模拟-电影)
针对电视屏幕,电影被称为“大荧幕”,也是娱乐行业的顶尖产业。作为一项综合艺术,从被发明至今,近200年的发展史中,无人可以替代,并始终走在时代的前列。 电影回放的原理就是“视觉残留”,也就是快速移过眼前的画面,会在人的大脑中残留短暂的时间,随着画面不断地移过,…...

在 Ubuntu 中, 使用 fsck 命令来修复磁盘文件系统
在 Ubuntu 中,可以使用 fsck 命令来修复磁盘文件系统。fsck 是用于检查和修复文件系统的工具。 使用 fsck 命令修复磁盘文件系统的步骤如下: 首先,您需要在命令行终端窗口中以 root 用户身份登录。 使用 fdisk -l 命令列出所有磁盘设备。 …...

LED电子显示屏连接方式解析
LED电子显示屏作为现代化数字展示设备的重要组成部分,其连接方式对于显示效果和稳定性至关重要。正确选择和实施连接方式不仅可以确保LED显示屏系统的正常运行,还可以提高其可靠性和持久性。本文将介绍LED电子显示屏常见的连接方式,以帮助读者…...
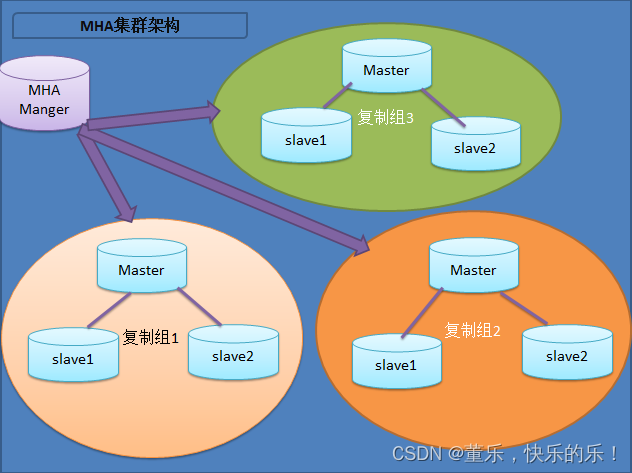
Mysql运维篇(五) 部署MHA--主机环境配置
一路走来,所有遇到的人,帮助过我的、伤害过我的都是朋友,没有一个是敌人。如有侵权,请留言,我及时删除! 大佬博文 https://www.cnblogs.com/gomysql/p/3675429.html MySQL 高可用(MHA&#x…...
)
Offer必备算法09_分治快排_四道力扣OJ(快排三路划分)
目录 分治快排算法原理 ①力扣75. 颜色分类 解析代码 ②力扣912. 排序数组 解析代码 ③力扣215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 解析代码 ④力扣LCR 159. 库存管理 III(剑指 Offer . 最小的k个数) 解析代码 本篇完。 分治快排算法原理 分治就是分而治…...
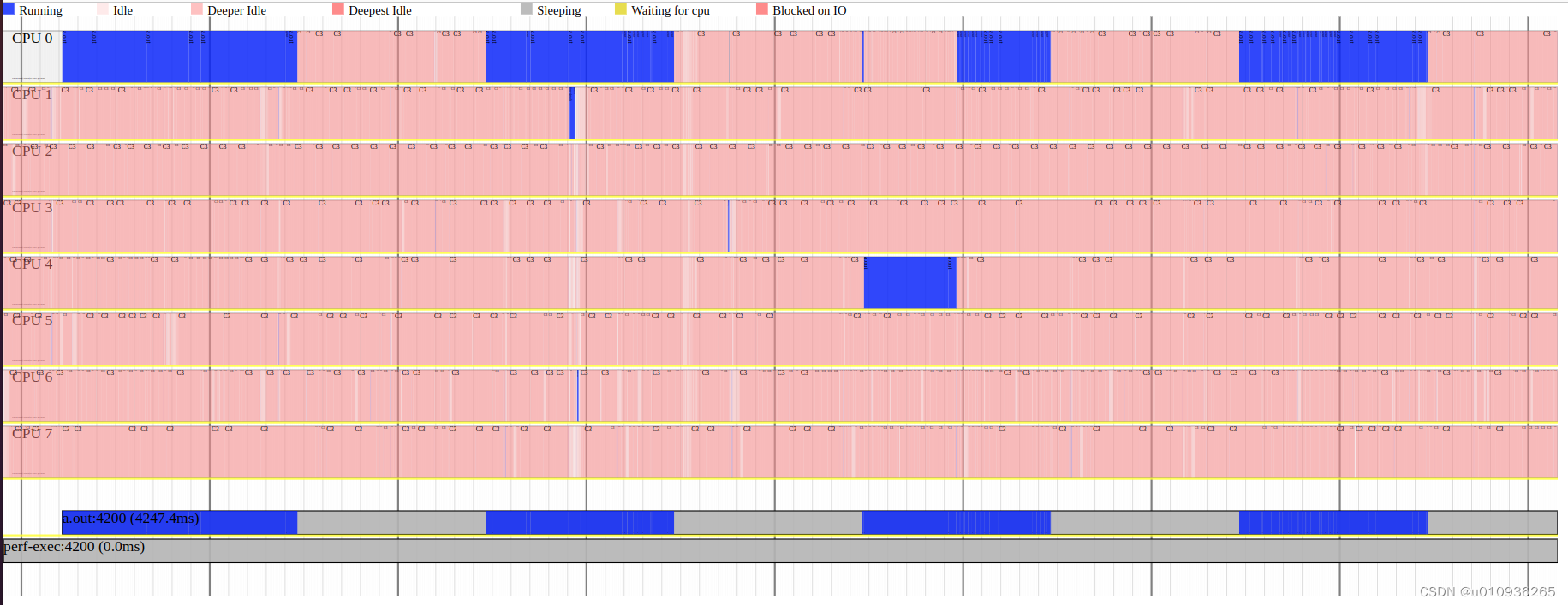
Linux下性能分析的可视化图表工具
1 sar 和sadf 1.1 简介 sar命令可以记录系统下的常见活动信息,例如CPU使用率、网络统计数据、Block I/O数据、内存使用情况 等。 sar命令的“-o [file_name]”参数可以将系统活动数据记录到file_name文件,然后通过sadf来解析,sadf命令的“-g…...

泽攸科技JS系列高精度台阶仪在半导体领域的应用
泽攸科技JS系列高精度台阶仪是一款先进的自主研发的国产台阶仪,采用了先进的扫描探针技术。通过扫描探针在样品表面上进行微观测量,台阶仪能够准确获取表面形貌信息。其工作原理基于探针与样品表面的相互作用力,通过测量探针的微小位移&#…...
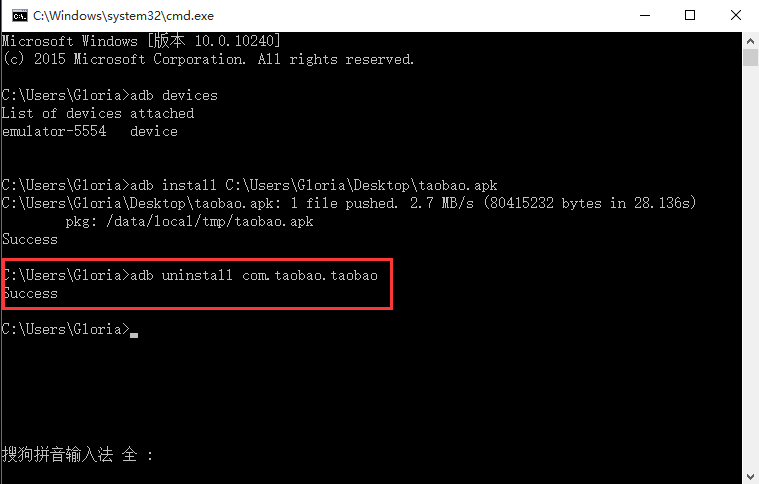
Appium+python自动化(十六)- ADB命令
简介 Android 调试桥(adb)是多种用途的工具,该工具可以帮助你你管理设备或模拟器 的状态。 adb ( Android Debug Bridge)是一个通用命令行工具,其允许您与模拟器实例或连接的 Android 设备进行通信。它可为各种设备操作提供便利,如安装和调试…...

Swift 协议扩展精进之路:解决 CoreData 托管实体子类的类型不匹配问题(下)
概述 在 Swift 开发语言中,各位秃头小码农们可以充分利用语法本身所带来的便利去劈荆斩棘。我们还可以恣意利用泛型、协议关联类型和协议扩展来进一步简化和优化我们复杂的代码需求。 不过,在涉及到多个子类派生于基类进行多态模拟的场景下,…...
渗透实战PortSwigger靶场-XSS Lab 14:大多数标签和属性被阻止
<script>标签被拦截 我们需要把全部可用的 tag 和 event 进行暴力破解 XSS cheat sheet: https://portswigger.net/web-security/cross-site-scripting/cheat-sheet 通过爆破发现body可以用 再把全部 events 放进去爆破 这些 event 全部可用 <body onres…...

多模态商品数据接口:融合图像、语音与文字的下一代商品详情体验
一、多模态商品数据接口的技术架构 (一)多模态数据融合引擎 跨模态语义对齐 通过Transformer架构实现图像、语音、文字的语义关联。例如,当用户上传一张“蓝色连衣裙”的图片时,接口可自动提取图像中的颜色(RGB值&…...
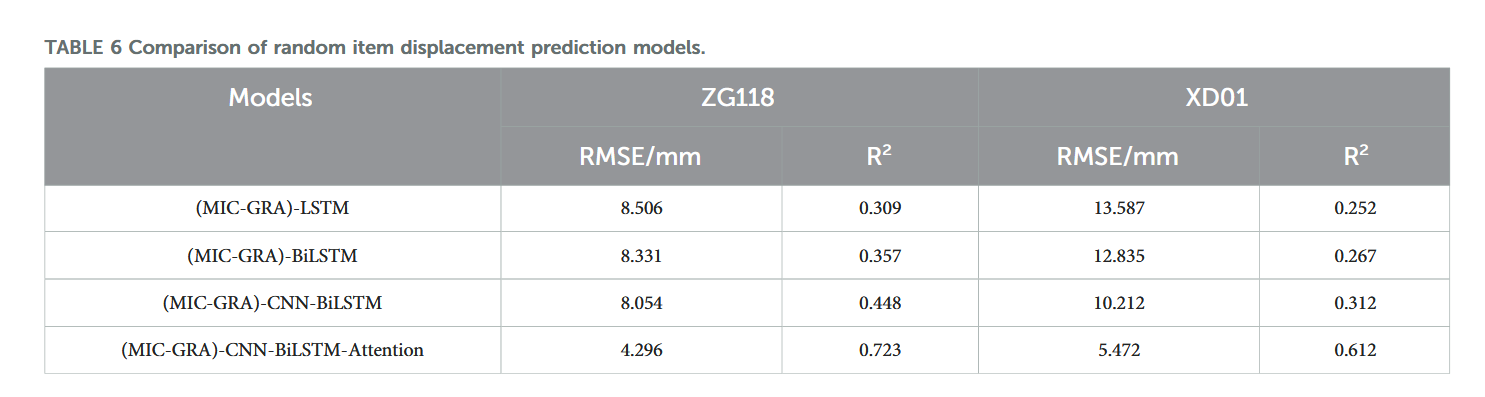
【论文阅读28】-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention-(2024)
本文把滑坡位移序列拆开、筛优质因子,再用 CNN-BiLSTM-Attention 来动态预测每个子序列,最后重构出总位移,预测效果超越传统模型。 文章目录 1 引言2 方法2.1 位移时间序列加性模型2.2 变分模态分解 (VMD) 具体步骤2.3.1 样本熵(S…...

稳定币的深度剖析与展望
一、引言 在当今数字化浪潮席卷全球的时代,加密货币作为一种新兴的金融现象,正以前所未有的速度改变着我们对传统货币和金融体系的认知。然而,加密货币市场的高度波动性却成为了其广泛应用和普及的一大障碍。在这样的背景下,稳定…...

《C++ 模板》
目录 函数模板 类模板 非类型模板参数 模板特化 函数模板特化 类模板的特化 模板,就像一个模具,里面可以将不同类型的材料做成一个形状,其分为函数模板和类模板。 函数模板 函数模板可以简化函数重载的代码。格式:templa…...

[免费]微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端+Vue管理端)【论文+源码+SQL脚本】
大家好,我是java1234_小锋老师,看到一个不错的微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端)【论文源码SQL脚本】,分享下哈。 项目视频演示 【免费】微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端) Java毕业设计_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 项…...

Kafka主题运维全指南:从基础配置到故障处理
#作者:张桐瑞 文章目录 主题日常管理1. 修改主题分区。2. 修改主题级别参数。3. 变更副本数。4. 修改主题限速。5.主题分区迁移。6. 常见主题错误处理常见错误1:主题删除失败。常见错误2:__consumer_offsets占用太多的磁盘。 主题日常管理 …...

Kubernetes 网络模型深度解析:Pod IP 与 Service 的负载均衡机制,Service到底是什么?
Pod IP 的本质与特性 Pod IP 的定位 纯端点地址:Pod IP 是分配给 Pod 网络命名空间的真实 IP 地址(如 10.244.1.2)无特殊名称:在 Kubernetes 中,它通常被称为 “Pod IP” 或 “容器 IP”生命周期:与 Pod …...
