List集合的Stream流式操作实现数据类型转换
问题现象:
最近在项目中,有一些逻辑想用List集合的Stream流式操作来快速实现,但由于之前没做好学习笔记和总结,导致一时间想不起来,只能用本方法来解决,如下:
可以看出来代码量是比较冗长的,于是就回顾了一下List集合的Stream流式操作的相关知识点;打算打一个代码优化!
问题分析:
由上图可以知道,我是想将集合list(List<Map<String, Object>> list )根据元素(Map<String, Object> map)中的key为"infoType"的字段值来作相关的业务逻辑,形成指定的集合(如:List<Map<String, Object>> baseInfoList等),然后再存到map集合(Map<String, Object> exportParams)中去。
根据这个思路其实就可以使用集合list中的Stream流式操作中的Collectors.groupingBy方法来解决了:
1、首先对集合list中使用Stream流式操作中的Collectors.groupingBy进行分组(分组依据是元素中的key:"infoType"),形成infoTypeListMap集合(Map<String, List<Map<String, Object>>> infoTypeListMap)。
2、遍历infoTypeListMap集合,然后将元素存入exportParams集合。
解决方法:
将上图的代码做如下修改即可:
exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.BASE_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.EDUCATION_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.TRAIN_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.WORK_EXPERIENCE_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.SALARY_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.FAMILY_CONTACT_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.LANGUAGE_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());Map<String, List<Map<String, Object>>> infoTypeListMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(map -> (String)map.get("infoType")));infoTypeListMap.entrySet().stream().forEach(entry->{String key = entry.getKey();List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = entry.getValue();exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(key+"_LIST"), mapList);});拓展:
文末有我写的测试代码,有助于理解,可直接搬运使用!
相信小伙伴们都见识到List集合的Stream流式操作的强大了吧,接下来,我就把List集合的Stream流式操作实现数据类型转换的常用方法记录并分享在此,以供自己和大家学习记忆。
1、Collectors.toList()
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());作用:可用于克隆/拷贝原list集合。作用相当于以下代码:
new ArrayList<>(list);
2、Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));作用:List<Object> 转为 ArrayList<Object> 。作用相当于以下代码:
new ArrayList<>(list);
3、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));作用:List<Object> 转为 LinkedList<Object> 。作用相当于以下代码:
new LinkedList<>(list);
4、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new));作用:List<Object> 转为 LinkedHashSet<Object>。作用相当于以下代码:
new LinkedHashSet<>(list);
5、Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
作用:List<Object> 转为 HashSet<Object> 。作用相当于以下代码:
new HashSet<>(list);
6、Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));作用:List<Object> 转为 TreeSet<Object>。
7、Collectors.partitioningBy
list.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.length() > 2));作用:List<Object> 转为 Map<Boolean, List<Object>>。
8、【重点】Collectors.groupingBy
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s));作用:List<Object> 转为 Map<Object, List<Object>>。
9、Collectors.collectingAndThen
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s));作用:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素形成的指定类型的结果集合后,再将结果集合做指定的结果集。如:List<Object> 转为 Map<Object, List<Object>> 再转为 Set<String>返回,如下:
list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s), Map::keySet));10、map
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s));作用:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性/字段,形成新的类型(指定属性/字段的数据类型)集合。如:List<Object> 转为 List<Integer>。
list.stream().map(String::length).collect(Collectors.toList());11、【重点】Collectors.toMap
作用:List<Object> 转为 Map<Object, Object>。
具有3个重载方法:
11.1、Collectors.toMap(key, value)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(str -> str, String::length));作用:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性/字段,形成新的类型(指定属性/字段的数据类型)集合。
参数说明:
key:指定元素对象的某个属性作为map结果集合的key值。
value:指定元素对象的某个属性作为map结果集合的value值。
缺点:当元素中存在重复的key时,会有如下报错:Duplicate key XX。
11.2、【重点】Collectors.toMap(key, value, distinctStrategy)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str, (length, str) -> str));作用:在11.1功能一致,多了一个第三参数,该参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免key重复报错问题。
参数说明:
distinctStrategy:去重逻辑,当遇到重复key时触发该逻辑。
11.3、【重点】Collectors.toMap(key, value, distinctStrategy, returnTypeSupplier)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str, (length, str) -> str, TreeMap::new));参数说明:
returnTypeSupplier:指定map结果集合的数据类型,通过查询源代码可知:当未指定该参数时,默认返回的是HashMap数据类型;如下:
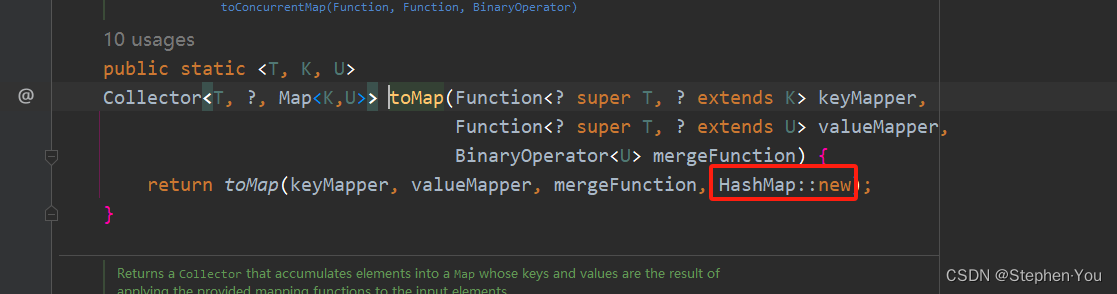
测试代码:
1、StreamStringListTransformTest 测试类:
测试List<String>集合的Stream流式操作,实现数据类型转换的功能:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;/*** Stream流的各种数据类型转换操作*/
public class StreamStringListTransformTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//List<String>集合原数据List<String> list = Arrays.asList("java", "python", "C#","php");//1、Collectors.toList()// List<String>克隆(代替流)List<String> listResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());listResult.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//2、Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new)// List<String> 转为 ArrayList<String>ArrayList<String> arrayList = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));arrayList.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//3、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)// List<String> 转为 LinkedList<String>List<String> linkedList = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));linkedList.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//4、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new)// List<String> 转为 LinkedHashSet<String>LinkedHashSet<String> linkedHashSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new));linkedHashSet.forEach(System.out::println);//LinkedHashSet是有序的System.out.println("--------------");//5、Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)// List<String> 转为 HashSet<String>HashSet<String> hashSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));hashSet.forEach(System.out::println);//HashSet是无序的(按hash逻辑自动排序)System.out.println("--------------");//6、Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new)// List<String> 转为 TreeSet<String>TreeSet<String> treeSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));treeSet.forEach(System.out::println);//TreeSet是按自然顺序自动排序System.out.println("--------------");//7、Collectors.partitioningBy:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素分成key为true或false的两组集合,形成的map集合// List<String> 转为 Map<Boolean, List<String>>Map<Boolean, List<String>> partitioningByMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.length() > 2));System.out.println(partitioningByMap.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//8、Collectors.groupingBy:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素分成key为元素本身的集合,形成的map集合//List<String> 转为 Map<String, List<String>>Map<String, List<String>> groupingByMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s));System.out.println(groupingByMap.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//9、Collectors.collectingAndThen:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素形成的指定类型的结果集合后,再将结果集合做指定的结果集//List<String> 转为 Map<String, List<String>> 再转为 Set<String>Set<String> collectingAndThen = list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s), Map::keySet));System.out.println(collectingAndThen.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//10、map:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性,形成新的指定集合//List<String> 转为 List<Integer>List<Integer> lengthList = list.stream().map(String::length).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(lengthList.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//11、Collectors.toMap:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性,组合成自定义类型的map结果集合//List<String> 转为 Map<Integer, String>//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>//注意:该函数有3个重载方法:// 11.1、2个参数(key,value):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key。// 第二个参数作为value。(缺点:当存在key重复的不同元素时,会有类似以下报错:Duplicate key 王五)// 11.2、3个参数(key,value,distinctStrategy):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key;// 第二个参数作为value;// 第三个参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免上面的key重复报错问题。// 11.2、3个参数(key,value,distinctStrategy,returnTypeSupplier):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key;// 第二个参数作为value;// 第三个参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免上面的key重复报错问题。// 第四个参数用于设置返回map的数据类型(如:TreeMap、ConcurrentHashMap等),默认是返回HashMap。List<String> strList = Arrays.asList("java", "python", "C#","php", "java");//List<String> 转为 Map<Integer, String>
// Map<Integer, String> strList1 = strList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str));//报错:Duplicate key java
// System.out.println(strList1.toString());
// System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>
// Map<String, Integer> strList2 = strList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(str -> str, String::length));//报错:Duplicate key 4
// System.out.println(strList2.toString());
// System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>Map<String, Integer> strList3 = strList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(str -> str, String::length, (first, second) -> second));System.out.println(strList3.toString());System.out.println("--------------");Map<String, Integer> list1 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(str -> str, String::length));System.out.println(list1.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>Map<Integer, String> list2 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str));System.out.println(list2.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>Map<Integer, String> list3 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str, (length, str) -> str));System.out.println(list3.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 TreeMap<String, Integer>TreeMap<Integer, String> list4 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str, (length, str) -> str, TreeMap::new));System.out.println(list4.toString());System.out.println("--------------");}
}2、Person实体类:
用于支持的测试:
public class Person {private String name;private Integer age;public Person() {}public Person(String name, Integer age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';}
}3、StreamObjectListTransformTest 测试类:
测试List<Object>集合的Stream流式操作,实现数据类型转换的功能:
import xxx.Person;//注意:修改为引用的Person实体类的文件路径import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;/*** Stream流的各种数据类型转换操作*/
public class StreamObjectListTransformTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//List<Object>集合原数据List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new Person("老六", 20));list.add(new Person("王五", 20));list.add(new Person("李四", 19));list.add(new Person("张三", 18));list.add(new Person("钱二", 17));list.add(new Person("赵一", 16));//1、Collectors.toList()// List<Object>克隆(代替流)List<Person> listResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());listResult.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//2、Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new)// List<Object> 转为 ArrayList<Object>ArrayList<Person> arrayList = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));arrayList.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//3、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)// List<Object> 转为 LinkedList<Object>List<Person> linkedList = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));linkedList.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//4、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new)// List<Object> 转为 LinkedHashSet<Object>LinkedHashSet<Person> linkedHashSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new));linkedHashSet.forEach(System.out::println);//LinkedHashSet是有序的System.out.println("--------------");//5、Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)// List<Object> 转为 HashSet<Object>HashSet<Person> hashSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));hashSet.forEach(System.out::println);//HashSet是无序的(按hash逻辑自动排序)System.out.println("--------------");// //6、Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new)
// // List<Object> 转为 TreeSet<Object>
// TreeSet<Person> treeSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));
// treeSet.forEach(System.out::println);
//TreeSet是按单一元素自然顺序自动排序,所以转换时会有类似以下报错:
// com.stephen.javademo.stream.bo.Person cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable
// System.out.println("--------------");//7、Collectors.partitioningBy:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素分成key为true或false的两组集合,形成的map集合// List<Object> 转为 Map<Boolean, List<Object>>Map<Boolean, List<Person>> partitioningByMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(person -> person.getAge() >= 18));System.out.println(partitioningByMap.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//8、Collectors.groupingBy:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素分成key为元素本身的集合,形成的map集合//List<Object> 转为 Map<String, List<Object>>Map<String, List<Person>> groupingByMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getName));System.out.println(groupingByMap.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//9、Collectors.collectingAndThen:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素形成的指定类型的结果集合后,再将结果集合做指定的结果集//List<Object> 转为 Map<String, List<Object>> 再转为 Set<String>Collection<List<Person>> collectingAndThen = list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getName), Map::values));System.out.println(collectingAndThen.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//10、map:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性,形成新的指定集合//List<Object> 转为 List<String>List<String> nameList = list.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(nameList.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Object> 转为 List<Integer>List<Integer> ageList = list.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(ageList.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Object> 转为 Set<Integer>Set<Integer> ageSet = list.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println(ageSet.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//11、Collectors.toMap:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性,组合成自定义类型的map结果集合//List<Object> 转为 Map<Object, Object>//注意:该函数有3个重载方法:// 11.1、2个参数(key,value):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key。// 第二个参数作为value。(缺点:当存在key重复的不同元素时,会有类似以下报错:Duplicate key 王五)// 11.2、3个参数(key,value,distinctStrategy):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key;// 第二个参数作为value;// 第三个参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免上面的key重复报错问题。// 11.2、3个参数(key,value,distinctStrategy,returnTypeSupplier):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key;// 第二个参数作为value;// 第三个参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免上面的key重复报错问题。// 第四个参数用于设置返回map的数据类型(如:TreeMap、ConcurrentHashMap等),默认是返回HashMap。//List<Person> 转为 Map<Integer, String>
// Map<Integer, String> personMap1 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName));//报错:Duplicate key 王五
// System.out.println(personMap1.toString());
// System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<String, Integer>Map<String, Integer> personMap2 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, Person::getAge));System.out.println(personMap2.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<String, Person>Map<String, Person> personMap3 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, person -> person));System.out.println(personMap3.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<Integer, String>Map<Integer, String> personMap4 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName, (preValue, nextValue) -> nextValue));//(preValue, nextValue) -> nextValue):key重复时,取后者System.out.println(personMap4.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<Integer, String>Map<Integer, String> personMap5 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName, (preValue, nextValue) -> preValue));//(preValue, nextValue) -> preValue):key重复时,取前者System.out.println(personMap5.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<Integer, String>Map<Integer, String> personMap6 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName, (preValue, nextValue) -> preValue+"、"+nextValue));//(preValue, nextValue) -> preValue+"、"+nextValue):key重复时,取两者拼接System.out.println(personMap6.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 TreeMap<Integer, String>TreeMap<Integer, String> personMap7 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName, (preValue, nextValue) -> preValue + "、" + nextValue, TreeMap::new));//(preValue, nextValue) -> preValue+"、"+nextValue):key重复时,取两者拼接System.out.println(personMap7.toString());System.out.println("--------------");}
}相关文章:

List集合的Stream流式操作实现数据类型转换
问题现象: 最近在项目中,有一些逻辑想用List集合的Stream流式操作来快速实现,但由于之前没做好学习笔记和总结,导致一时间想不起来,只能用本方法来解决,如下: 可以看出来代码量是比较冗长的&…...

Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTS下edge浏览器点击图标没反应
1.网上的解决方案 解决Ubuntu系统下启动root账户后Linux版本edge浏览器无法启动等 2.采用的解决方案 之前我一直是在官网下载 Microsoft Edge下载,安装,卸载,重装的stable版本,然后安装,始终没有效果。 最后利用Linux…...
php基础学习之错误处理(其一)
一,错误处理的概念 错误处理指的是系统(或者用户)在执行某些代码的时候,发现有错误,就会通过错误处理的形式告知程序员,俗称报错 二,错误分类 语法错误:书写的代码不符合 PHP 的语法规范,语法错…...

Nginx 解析漏洞复现
环境搭建 下载之后上传到虚拟机并解压 进入这个路径 (root?kali)-[~/vulhub-master/nginx/nginx_parsing_vulnerability]就能看到有docker-compose.yml 启动环境 正常显示 增加/.php后缀,被解析成PHP文件: 漏洞原因:开启了cgi.fix_pathin…...
JQMobile Loader Widget 遮罩层改造
最近在用jqmobile 做一个混合APP项目时候用到 jqmobile1.4.3提供的Loader Widget控件,但是这个控件本身是一个loading弹出层,这个弹出层弹出之后,用户还是可以去点击按钮,重复发送请求,为了防止重复提交,我想了两种办法, 1,在loading弹出层弹出之后,让按钮不可用.但是form表单…...
练习 2 Web [ACTF2020 新生赛]BackupFile 1
[ACTF2020 新生赛]BackupFile 1 Web常规题目 首先尝试查找常见的前端页面index.php之类的,没找到 题目有个“BackupFile”——备份文件 尝试用工具遍历查找相关的文件 御剑没扫出来,搜索搭建好dirsearch后,扫出来的index.php.bak 扫描工…...

【python】subprocess用法示例
当然,下面是一些使用 Python subprocess 模块的示例: 1. 运行命令并捕获输出 import subprocess # 运行 ls 命令并捕获输出 result subprocess.run([ls, -l], stdoutsubprocess.PIPE, stderrsubprocess.PIPE, textTrue) # 获取命令的输出和错误信息 o…...
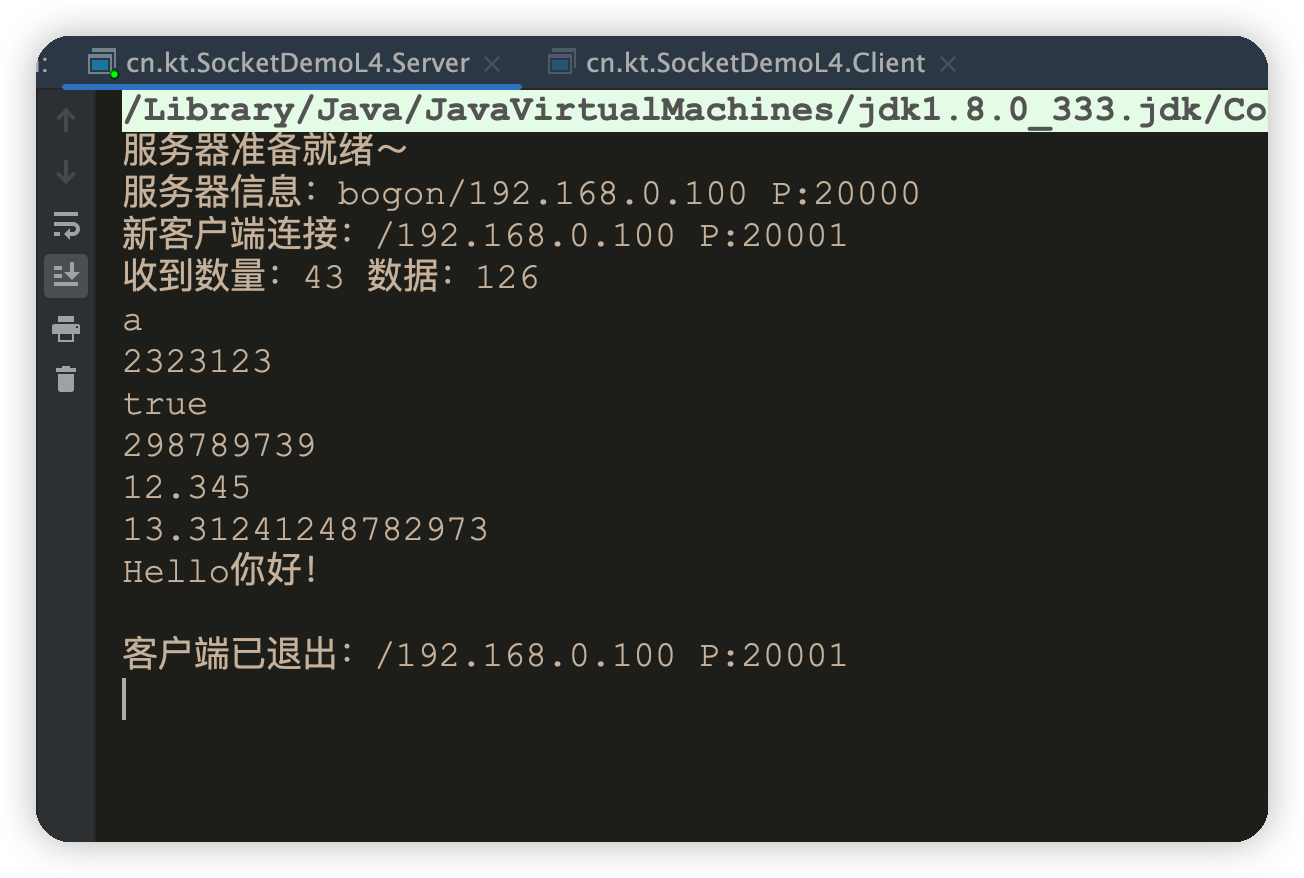
Socket网络编程(三)——TCP快速入门
目录 概述TCP连接可靠性1. 三次握手过程2. 四次挥手过程3. 为什么挥手需要四次? 传输可靠性TCP核心APITCP传输初始化配置&建立连接客户端创建Socket建立连接服务端创建ServerSocket监听连接ServerSocket 和 Socket的关系 Socket基本数据类型传输客户端数据传输服…...

皇冠测评:网络电视盒子哪个品牌好?电视盒子排行榜
欢迎各位来到我们的测评频道,本期我们要分享的产品是电视盒子,因很多网友留言不知道网络电视盒子哪个品牌好,我们通过为期一个月的测评后整理了电视盒子排行榜,想买电视盒子的可以看看下面这五款产品,它们各方面表现非…...
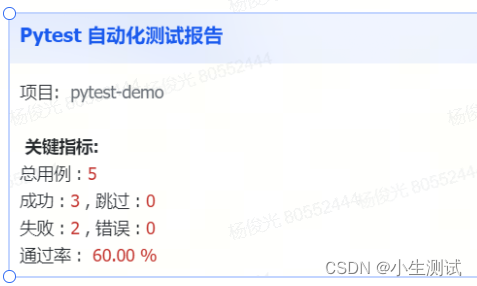
simple-pytest 框架使用指南
simple-pytest 框架使用指南 一、框架介绍简介框架理念:框架地址 二、实现功能三、目录结构四、依赖库五、启动方式六、使用教程1、快速开始1.1、创建用例:1.2、生成py文件1.3、运行脚本1.3.1 单个脚本运行1.3.2 全部运行 1.4 报告查看 2、功能介绍2.1、…...
React中使用useActive
1.引入 import { useActivate } from "react-activation";2.React Activation 在React中使用react-activation,其实就是类似于Vue中的keep-alive,实现数据的缓存; 源码: import { ReactNode, ReactNodeArray, Context, Component…...

ElasticSearch安装和kibana控制台安装
文章目录 简介ElasticSearch安装环境下载参数密码配置启动 kibana安装修改config/kibana.yml配置 简介 Elasticsearch 是一个分布式文档存储。Elasticsearch 是存储已序列化为 JSON 文档的复杂数据结构。当集群中有多个 Elasticsearch 节点时,存储的文档分布在整个…...

VSCode安装与使用详细教程
一、引言 简要介绍VSCode(Visual Studio Code)是什么,它的主要特点和用途,以及为什么选择VSCode作为代码编辑器。 二、下载与安装 访问VSCode官方网站下载页面。选择适合操作系统的版本(Windows、macOS、Linux&…...

土壤墒情监测站的工作原理
TH-TS600】土壤湿度监测系统是一种用于实时监测土壤湿度的设备系统,通过多个传感器和数据采集设备组合而成。该系统能够安装在农田、果园、草地等不同类型的土壤中,实时监测土壤的水分含量,并将数据传输到数据采集设备中进行记录和分析。 土…...

Flutter 多标签页显示 有关TabController需要知道的知识
背景 很多应用都需要导航栏加多个标签页的方式来构建一个多页显示逻辑,比如购物软件常有:已完成,已发货,待付款三个顶部导航按钮,点击则下面的页面显示不同属性的订单 正文 在flutter中,实现这样的功能需…...

【Elasticsearch专栏 16】深入探索:Elasticsearch的Master选举机制及其影响因素分析
Elasticsearch,作为当今最流行的开源搜索和分析引擎,以其分布式、可扩展和高可用的特性赢得了广大开发者的青睐。在Elasticsearch的分布式架构中,集群的稳健性和高可用性很大程度上依赖于其Master节点的选举机制。本文将深入剖析Elasticsearc…...

Leetcode : 215. 数组中的第 K 个最大元素
给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。 请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。 你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。 思路:最开始排序算法&…...

node express实现Excel文档转json文件
有些场景我们需要将Excel文档中的内容抽取出来生成别的文件,作为一个前端,服务框架最应该熟悉的就是node了,以下是基于多语言转换实现代码,看明白原理自己改一改就能用了 1.安装node环境 2.创建一个文件夹,文件夹中创建…...
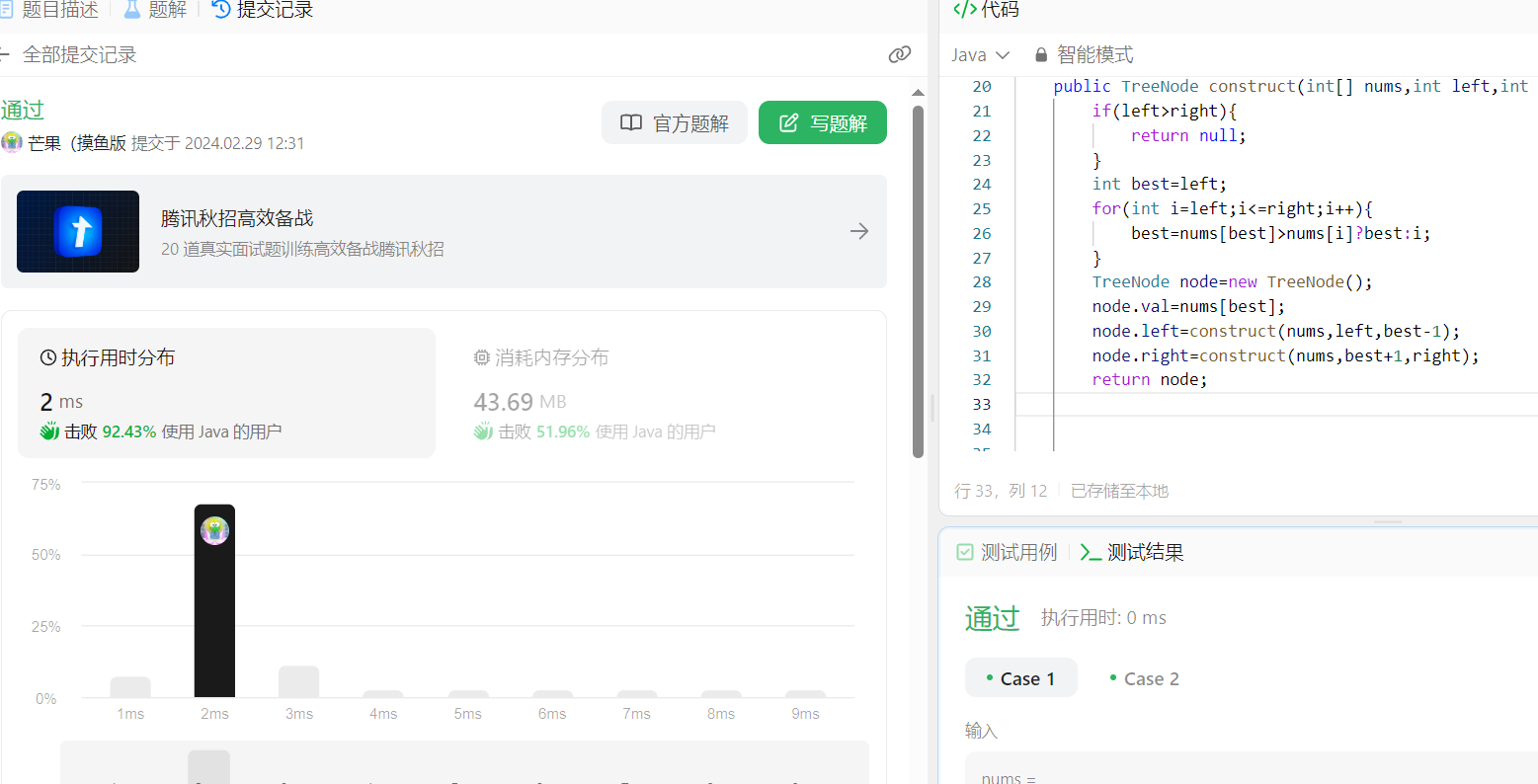
【算法分析与设计】最大二叉树
📝个人主页:五敷有你 🔥系列专栏:算法分析与设计 ⛺️稳中求进,晒太阳 题目 给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建: 创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最…...
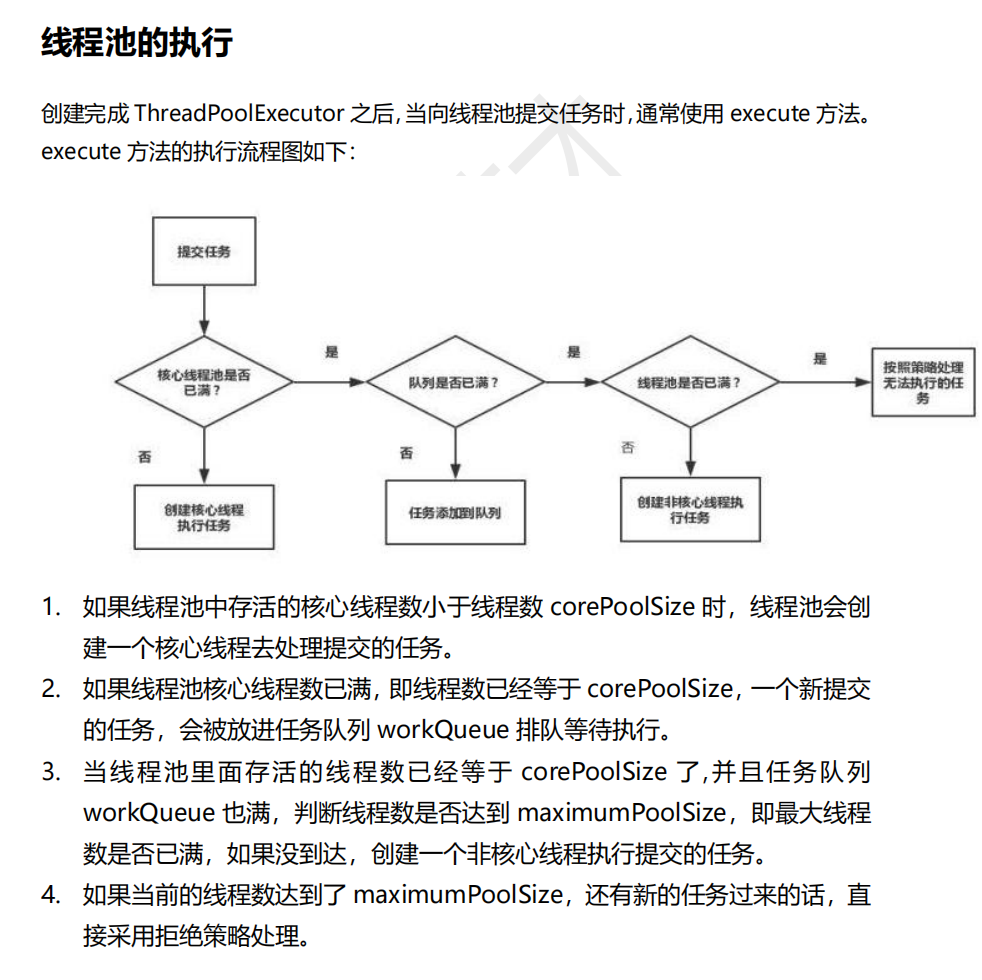
面试问答总结之并发编程
文章目录 🐒个人主页🏅JavaEE系列专栏📖前言:🎀多线程的优点、缺点🐕并发编程的核心问题 :不可见性、乱序性、非原子性🪀不可见性🪀乱序性🪀非原子性…...
使用VSCode开发Django指南
使用VSCode开发Django指南 一、概述 Django 是一个高级 Python 框架,专为快速、安全和可扩展的 Web 开发而设计。Django 包含对 URL 路由、页面模板和数据处理的丰富支持。 本文将创建一个简单的 Django 应用,其中包含三个使用通用基本模板的页面。在此…...

前端倒计时误差!
提示:记录工作中遇到的需求及解决办法 文章目录 前言一、误差从何而来?二、五大解决方案1. 动态校准法(基础版)2. Web Worker 计时3. 服务器时间同步4. Performance API 高精度计时5. 页面可见性API优化三、生产环境最佳实践四、终极解决方案架构前言 前几天听说公司某个项…...

Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B深度解析:多语言语义检索的轻量级利器
第一章 引言:语义表示的新时代挑战与Qwen3的破局之路 1.1 文本嵌入的核心价值与技术演进 在人工智能领域,文本嵌入技术如同连接自然语言与机器理解的“神经突触”——它将人类语言转化为计算机可计算的语义向量,支撑着搜索引擎、推荐系统、…...
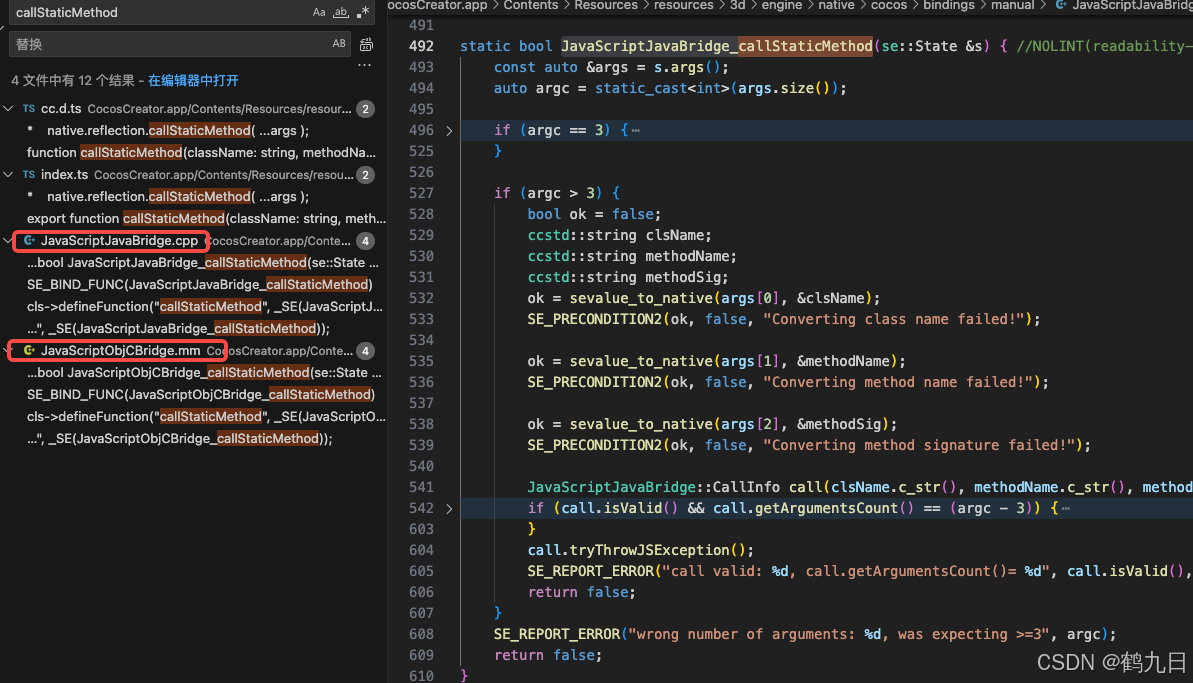
CocosCreator 之 JavaScript/TypeScript和Java的相互交互
引擎版本: 3.8.1 语言: JavaScript/TypeScript、C、Java 环境:Window 参考:Java原生反射机制 您好,我是鹤九日! 回顾 在上篇文章中:CocosCreator Android项目接入UnityAds 广告SDK。 我们简单讲…...

关于 WASM:1. WASM 基础原理
一、WASM 简介 1.1 WebAssembly 是什么? WebAssembly(WASM) 是一种能在现代浏览器中高效运行的二进制指令格式,它不是传统的编程语言,而是一种 低级字节码格式,可由高级语言(如 C、C、Rust&am…...
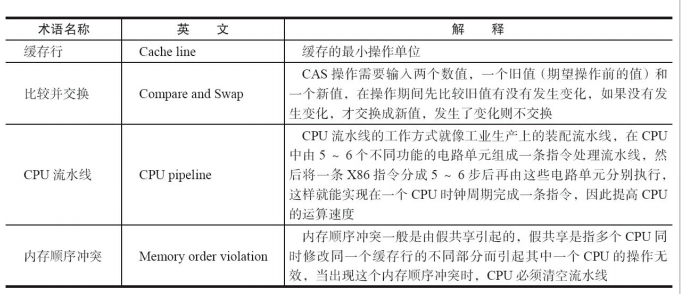
JUC笔记(上)-复习 涉及死锁 volatile synchronized CAS 原子操作
一、上下文切换 即使单核CPU也可以进行多线程执行代码,CPU会给每个线程分配CPU时间片来实现这个机制。时间片非常短,所以CPU会不断地切换线程执行,从而让我们感觉多个线程是同时执行的。时间片一般是十几毫秒(ms)。通过时间片分配算法执行。…...
k8s业务程序联调工具-KtConnect
概述 原理 工具作用是建立了一个从本地到集群的单向VPN,根据VPN原理,打通两个内网必然需要借助一个公共中继节点,ktconnect工具巧妙的利用k8s原生的portforward能力,简化了建立连接的过程,apiserver间接起到了中继节…...
)
安卓基础(aar)
重新设置java21的环境,临时设置 $env:JAVA_HOME "D:\Android Studio\jbr" 查看当前环境变量 JAVA_HOME 的值 echo $env:JAVA_HOME 构建ARR文件 ./gradlew :private-lib:assembleRelease 目录是这样的: MyApp/ ├── app/ …...

Python 包管理器 uv 介绍
Python 包管理器 uv 全面介绍 uv 是由 Astral(热门工具 Ruff 的开发者)推出的下一代高性能 Python 包管理器和构建工具,用 Rust 编写。它旨在解决传统工具(如 pip、virtualenv、pip-tools)的性能瓶颈,同时…...

【SSH疑难排查】轻松解决新版OpenSSH连接旧服务器的“no matching...“系列算法协商失败问题
【SSH疑难排查】轻松解决新版OpenSSH连接旧服务器的"no matching..."系列算法协商失败问题 摘要: 近期,在使用较新版本的OpenSSH客户端连接老旧SSH服务器时,会遇到 "no matching key exchange method found", "n…...
