PostgreSQL中In, Exists在SQL查询中到底有无区别
前言
SQL查询当中,In和Exists子查询到底有无区别?记得很多年以前,确实是有相关的使用戒条的,或者说存在一些使用的惯用法。试图完全抹开两者的区别,就有点过了。
两者的主要区别:
从目的上讲,IN和EXISTS都是SQL中用于子查询的操作符。
IN操作符是用来检查一个值是否在一组值中。例如SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Country IN ('Germany', 'France', 'UK')
EXISTS操作符是用来检查一个子查询是否至少返回一个记录。例如:SELECT * FROM Products WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM OrderDetails WHERE Products.ProductID = OrderDetails.ProductID)
基本的区别还有:
1. 语义上的区别:IN关键字用来查询在某个列表中的数据,EXISTS关键字用来查询是否存在子查询返回的数据。
2. 性能上的区别:在数据量大时,或者进行全表扫描的时候,EXISTS的性能通常优于IN。因为EXISTS只要找到一个满足条件的就不再继续查询,而IN需要查询所有可能的结果。
3. 返回结果的差异:IN只能操作单个字段,EXISTS可以操作多个字段。
使用原则,主要有以下几点:
1. 当子查询返回的结果集非常大的时候,建议使用EXISTS,因为对于EXISTS来说,只要存在就会停止查询,效率更高。
2. 当子查询返回的结果集非常小,主查询的结果集非常大或是需要在结果集内进行查询时优先考虑IN。
3. 当需要比较的是多个字段而非单个字段时,应使用EXISTS。
4. 避免在子查询中使用排序操作,因为无论是IN还是EXISTS都会忽略排序,数据库还为此额外消耗资源。
上边是从ChatGPT里头摘出来的。但是对于PG而言,中间的一些结论未必正确。首先,PG是支持多列进行IN筛选的。下边我们通过简单的例子进行验证。
实例
1、关于多列在IN中是否支持?
create table a(id int primary key, col2 int);
insert into a values(1, 1);
select * from a where id in (1, 2);
select * from a where (id, col2) in (select 1, 1) -- 4
-- select * from a where (id, col2) in (1, 2) -- 5 // 这个语句是不对,不是想象中的那样
如果你拿上边的SQL语句去各DB中去试,大多数DBMS是不支持第4个语句的语法的。比如你在SQLServer2022中,会报如下的错误:
Msg 4145 Level 15 State 1 Line 4
An expression of non-boolean type specified in a context where a condition is expected, near ','.
Sybase ASE那就更不支持了。
MySQL和PostgreSQL是支持的。甚至SQLite也是不支持的。报的错:**Query Error:** Error: SQLITE_ERROR: near ";": syntax error
Oracle号称宇宙最强,看起来是下边这个样子,同样不支持:
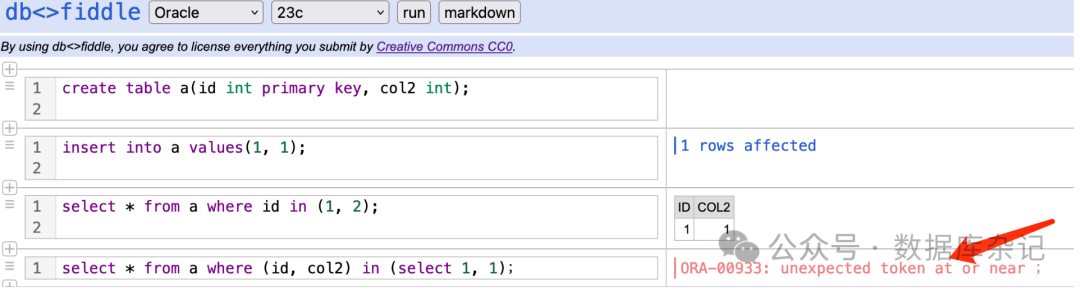
它提示的错,也是比较的含糊。
我们来看看相对强大的PostgreSQL对于多列的支持:
postgres=# select * from a where (id, col2) in (select 1,1);id | col2
----+------1 | 1
(1 row)
postgres=# select * from a where (id, col2) in (1, 2);
ERROR: operator does not exist: record = integer
LINE 1: select * from a where (id, col2) in (1, 2);^
HINT: No operator matches the given name and argument types. You might need to add explicit type casts.
Time: 0.397 ms
既然PG支持,放心大胆的使用就行了。
2、NULL值的处理
这个应该是共性问题。假设表 c (id int, col2 int) , d(id int, col2 int), 其结构如下:
create table c(id int primary key, col2 int);
create table d(id int primary key, col2 int);
insert into c values(1, 1), (2, null);
insert into d values(1, 1), (3, null);
我们看看IN和exists两种操作的区别:
postgres=# select * from c where col2 in (select col2 from d);id | col2
----+------1 | 1
(1 row)Time: 0.702 ms
postgres=# select * from c where col2 not in (select col2 from d);id | col2
----+------
(0 rows)
针对NULL值, IN和NOT IN都是false
postgres=# select * from c where exists (select col2 from d where d.col2 = c.col2);id | col2
----+------1 | 1
(1 row)Time: 0.706 ms
postgres=# select * from c where not exists (select col2 from d where d.col2 = c.col2);id | col2
----+------2 |
(1 row)
Exists 子句好理解,= 操作不适用于NULL, 所以NULL值关联的行被排除。但是not exists就不一样了,它会把NULL值相关行给算在内。实际上就是一个存在性的判断。把前边符合存在条件的那些行给排除了就是最后结果。
3、主表子表的应用原则
3.1、子查询返回值比较少的情形
-- 往 a 表插入500010条记录
\timing
postgres=# insert into a select n, 99000 * random() from generate_series(1, 500000) as n;
INSERT 0 500000
Time: 1023.998 ms (00:01.024)
postgres=# insert into a select n, 99001 + 10 * random() from generate_series(500001, 500010) as n;
INSERT 0 10
Time: 1.796 ms-- 往 b 表 插入 50000条记录
postgres=# insert into b select n, 100000 + 99000 * random() from generate_series(1, 49990) as n;
INSERT 0 49990
Time: 196.378 ms
postgres=# insert into b select n, 99001 + (n-49990) from generate_series(49991, 50000) as n;
INSERT 0 10
Time: 1.402 ms-- 创建合达的索引
postgres=# create index idx_col2_a on a(col2);
CREATE INDEX
Time: 412.309 ms
postgres=# create index idx_col2_b on b(col2);
ERROR: relation "idx_col2_b" already exists
Time: 0.589 ms这里a为500010条记录,b表仅为5000条记录。它们在col2上进行存在性选择。我们看看效果:
-- 子查询建立在b表上:
ostgres=# select * from a where col2 in (select col2 from b);id | col2
--------+-------500001 | 99006500002 | 99006500003 | 99007500004 | 99003500005 | 99004500006 | 99004500008 | 99007500009 | 99010500010 | 99009
(9 rows)Time: 119.565 mspostgres=# select * from a where exists (select col2 from b where b.col2 = a.col2);id | col2
--------+-------500001 | 99006500002 | 99006500003 | 99007500004 | 99003500005 | 99004500006 | 99004500008 | 99007500009 | 99010500010 | 99009
(9 rows)Time: 91.205 ms-- 子表在a上:
postgres=# select * from b where col2 in (select col2 from a);id | col2
-------+-------49992 | 9900349993 | 9900449995 | 9900649996 | 9900749998 | 9900949999 | 99010
(6 rows)Time: 41.531 ms
postgres=# select * from b where exists (select col2 from a where a.col2 = b.col2);id | col2
-------+-------49992 | 9900349993 | 9900449995 | 9900649996 | 9900749998 | 9900949999 | 99010
(6 rows)Time: 73.370 ms
实际上多查几次,你会发现,两者时间上差不多。
而比较查询计划,你也看到用到的几乎是同一个查询计划。这就是在pg中的表现。
看看Not IN, Not Exists:
-- 主表为a
postgres=# select count(*) from a where col2 not in (select col2 from b where a.col2 = b.col2);count
--------500001
(1 row)Time: 484.076 ms
postgres=# select count(*) from a where not exists (select col2 from b where a.col2=b.col2);count
--------500001
(1 row)Time: 108.899 ms-- 主表为b
postgres=# select count(*) from b where col2 not in (select col2 from a where a.col2 = b.col2);count
-------49994
(1 row)Time: 50.395 ms
postgres=# select count(*) from b where not exists (select col2 from a where a.col2 = b.col2);count
-------49994
(1 row)Time: 182.841 ms
从上边的结果来看,基本上区别也不是很明显。这是在子查询的结果集比较小的情况下:只有9个值。如果子查询的结果非常大,有可能得到的结论就不太一样。
不失一般性,采用上边列出的使用原则没有什么坏处。
3.2、子查询返回结果比较多的情形
接上边,把a, b清空,换上公共值比较多的情形,看看是啥效果?
truncate a, b;postgres=# insert into a select n, 10000* random() from generate_series(1, 500000) as n;
INSERT 0 500000
postgres=# insert into b select n, 10000* random() from generate_series(1, 50000) as n;
INSERT 0 50000\timing on-- a 用作主查询
-- 使用 IN
postgres=# explain (analyze, costs) select count(*) from a where a.col2 in (select col2 from b);QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Finalize Aggregate (cost=11894.74..11894.75 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=197.636..197.688 rows=1 loops=1)-> Gather (cost=11894.63..11894.74 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=195.523..197.678 rows=2 loops=1)Workers Planned: 1Workers Launched: 1-> Partial Aggregate (cost=10894.63..10894.64 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=183.432..183.436 rows=1 loops=2)-> Hash Join (cost=1065.25..10178.45 rows=286469 width=0) (actual time=22.662..144.762 rows=248460 loops=2)Hash Cond: (a.col2 = b.col2)-> Parallel Seq Scan on a (cost=0.00..5154.18 rows=294118 width=4) (actual time=0.008..16.545 rows=250000 loops=2)-> Hash (cost=944.00..944.00 rows=9700 width=4) (actual time=22.585..22.587 rows=9939 loops=2)Buckets: 16384 Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 478kB-> HashAggregate (cost=847.00..944.00 rows=9700 width=4) (actual time=20.098..21.235 rows=9939 loops=2)Group Key: b.col2Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 913kBWorker 0: Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 913kB-> Seq Scan on b (cost=0.00..722.00 rows=50000 width=4) (actual time=0.013..11.360 rows=50000 loops=2)Planning Time: 0.268 msExecution Time: 197.841 ms
(17 rows)Time: 198.537 ms-- 使用EXISTS
postgres=# explain (analyze, costs) select count(*) from a where exists (select * from b where a.col2 = b.col2);QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Finalize Aggregate (cost=11894.74..11894.75 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=192.080..192.130 rows=1 loops=1)-> Gather (cost=11894.63..11894.74 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=189.941..192.118 rows=2 loops=1)Workers Planned: 1Workers Launched: 1-> Partial Aggregate (cost=10894.63..10894.64 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=177.449..177.452 rows=1 loops=2)-> Hash Join (cost=1065.25..10178.45 rows=286469 width=0) (actual time=21.696..148.908 rows=248460 loops=2)Hash Cond: (a.col2 = b.col2)-> Parallel Seq Scan on a (cost=0.00..5154.18 rows=294118 width=4) (actual time=0.010..38.817 rows=250000 loops=2)-> Hash (cost=944.00..944.00 rows=9700 width=4) (actual time=21.598..21.600 rows=9939 loops=2)Buckets: 16384 Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 478kB-> HashAggregate (cost=847.00..944.00 rows=9700 width=4) (actual time=19.178..20.280 rows=9939 loops=2)Group Key: b.col2Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 913kBWorker 0: Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 913kB-> Seq Scan on b (cost=0.00..722.00 rows=50000 width=4) (actual time=0.015..11.202 rows=50000 loops=2)Planning Time: 0.330 msExecution Time: 192.297 ms
(17 rows)Time: 193.106 ms两者差不多。-- 再看NOT IN
postgres=# explain (analyze, costs) select count(*) from a where a.col2 not in (select col2 from b);QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Finalize Aggregate (cost=8104.23..8104.24 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=154.519..154.575 rows=1 loops=1)-> Gather (cost=8104.12..8104.23 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=152.256..154.562 rows=2 loops=1)Workers Planned: 1Workers Launched: 1-> Partial Aggregate (cost=7104.12..7104.13 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=139.397..139.398 rows=1 loops=2)-> Parallel Seq Scan on a (cost=847.00..6736.47 rows=147059 width=0) (actual time=21.763..139.242 rows=1540 loops=2)Filter: (NOT (hashed SubPlan 1))Rows Removed by Filter: 248460SubPlan 1-> Seq Scan on b (cost=0.00..722.00 rows=50000 width=4) (actual time=0.023..11.494 rows=50000 loops=2)Planning Time: 0.187 msExecution Time: 154.649 ms
(12 rows)Time: 155.277 mspostgres=# explain (analyze, costs) select count(*) from a where not exists (select * from b where b.col2 = a.col2);QUERY PLAN -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------Finalize Aggregate (cost=9686.56..9686.57 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=143.476..144.009 rows=1 loops=1)-> Gather (cost=9686.44..9686.55 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=143.468..144.001 rows=2 loops=1)Workers Planned: 1Workers Launched: 1-> Partial Aggregate (cost=8686.44..8686.45 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=130.231..130.235 rows=1 loops=2)-> Parallel Hash Anti Join (cost=1268.06..8667.32 rows=7649 width=0) (actual time=6.437..130.089 rows=1540 loops=2)Hash Cond: (a.col2 = b.col2)-> Parallel Seq Scan on a (cost=0.00..5154.18 rows=294118 width=4) (actual time=0.008..34.314 rows=250000 loops=2)-> Parallel Hash (cost=900.41..900.41 rows=29412 width=4) (actual time=5.975..5.976 rows=25000 loops=2)Buckets: 65536 Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 2496kB-> Parallel Index Only Scan using idx_col2_b on b (cost=0.29..900.41 rows=29412 width=4) (actual time=0.022..4.175 rows=50000
loops=1)Heap Fetches: 0Planning Time: 0.351 msExecution Time: 144.057 ms
(14 rows)Time: 144.851 msa 作主查询时,没看到有特别大的区别。
再看看如果b用作主表时的情况:
postgres=# select count(*) from b where b.col2 in (select col2 from a);count
-------50000
(1 row)Time: 122.761 ms
postgres=# select count(*) from b where exists (select * from a where a.col2 = b.col2);count
-------50000
(1 row)Time: 102.271 mspostgres=# select count(*) from b where b.col2 not in (select col2 from a);count
-------0
(1 row)Time: 46994.345 ms (00:46.994)ostgres=# select count(*) from b where not exists (select * from a where a.col2=b.col2);count
-------0
(1 row)Time: 169.132 ms-- 取两者的查询计划看下:
postgres=# explain (analyze, costs) select count(*) from b where b.col2 not in (select col2 from a);QUERY PLAN -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------Finalize Aggregate (cost=189957893.17..189957893.18 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=75657.828..75657.991 rows=1 loops=1)-> Gather (cost=189957893.05..189957893.16 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=75127.117..75657.979 rows=2 loops=1)Workers Planned: 1Workers Launched: 1-> Partial Aggregate (cost=189956893.05..189956893.06 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=75379.382..75379.384 rows=1 loops=2)-> Parallel Index Only Scan using idx_col2_b on b (cost=0.29..189956856.29 rows=14706 width=0) (actual time=75379.372..75379.373 rows=0 lo
ops=2)Filter: (NOT (SubPlan 1))Rows Removed by Filter: 25000Heap Fetches: 0SubPlan 1-> Materialize (cost=0.00..11667.00 rows=500000 width=4) (actual time=0.002..1.906 rows=10013 loops=50000)-> Seq Scan on a (cost=0.00..7213.00 rows=500000 width=4) (actual time=0.004..1.645 rows=9965 loops=15953)Planning Time: 0.244 msExecution Time: 75658.697 ms
(14 rows)Time: 75659.529 ms (01:15.660)postgres=# explain (analyze, costs) select count(*) from b where not exists (select * from a where a.col2=b.col2);QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Aggregate (cost=13479.75..13479.76 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=188.005..191.547 rows=1 loops=1)-> Gather (cost=10979.94..13479.75 rows=1 width=0) (actual time=187.996..191.537 rows=0 loops=1)Workers Planned: 1Workers Launched: 1-> Parallel Hash Anti Join (cost=9979.94..12479.65 rows=1 width=0) (actual time=174.642..174.646 rows=0 loops=2)Hash Cond: (b.col2 = a.col2)-> Parallel Index Only Scan using idx_col2_b on b (cost=0.29..900.41 rows=29412 width=4) (actual time=0.035..2.130 rows=25000 loops=2)Heap Fetches: 0-> Parallel Hash (cost=5154.18..5154.18 rows=294118 width=4) (actual time=125.958..125.959 rows=250000 loops=2)Buckets: 131072 Batches: 8 Memory Usage: 3552kB-> Parallel Seq Scan on a (cost=0.00..5154.18 rows=294118 width=4) (actual time=0.016..67.203 rows=250000 loops=2)Planning Time: 0.488 msExecution Time: 191.611 ms
(13 rows)Time: 192.691 ms
我们会发现,在使用not in时,将大表大结果集放到子查询里头,它花了差不多46秒的时间。这显然是不被推荐的。而not exists则显得相对稳定。
基于此,我仍然认为上边推荐的使用原则还是值得遵守的。
4、奇葩的现象
有时候,会出现在“手误”的情况下:
create table d (id int primary key, col2 int);
create table e (id int primary key, col3 int);
insert into d values(1, 1), (3, null);
insert into e values(1, 1);postgres=# select * from d where col2 in (select col2 from e);id | col2
----+------1 | 1
(1 row)Time: 0.512 ms
postgres=# select * from d where col2 not in (select col2 from e);id | col2
----+------
(0 rows)postgres=# select * from d where exists (select col2 from e);id | col2
----+------1 | 13 |
(2 rows)ostgres=# select * from d where exists (select col2 from e where e.col2 = d.col2);
ERROR: column e.col2 does not exist
LINE 1: ...t * from d where exists (select col2 from e where e.col2 = d...^
HINT: Perhaps you meant to reference the column "e.col3" or the column "d.col2".
Time: 0.402 ms
你会发现,在加了where条件之后,它才会去校验是否真有那个列。
总结:
子查询涉及到NULL值时,需要小心注意NOT IN, NOT exists。实际使用的时候,估然需要结合查询计划以及子查询的结果集大小来进行综合判断。个人认为,要尽量慎用NOT IN。PG是支持IN的多字段子查询的。这个用起来也是很方便的。跨数据库移植时,那还是考虑使用exists的能用形式为宜。
相关文章:

PostgreSQL中In, Exists在SQL查询中到底有无区别
前言 SQL查询当中,In和Exists子查询到底有无区别?记得很多年以前,确实是有相关的使用戒条的,或者说存在一些使用的惯用法。试图完全抹开两者的区别,就有点过了。 两者的主要区别: 从目的上讲,…...

Netty Review - 探究Netty服务端主程序无异常退出的背后机制
文章目录 概述故障场景尝试改进问题分析铺垫: Daemon线程Netty服务端启动源码分析逻辑分析 如何避免Netty服务端意外退出最佳实践 概述 在使用Netty进行服务端程序开发时,初学者可能会遇到各种问题,其中之一就是服务端意外退出的问题。这种问…...
【兔子机器人】修改GO电机id(软件方法、硬件方法)
一、硬件方法 利用上位机直接修改GO电机的id号: 打开调试助手,点击“调试”,查询电机,修改id号,即可。 但先将四个GO电机连接线拔掉,不然会将连接的电机一并修改。 利用24V电源给GO电机供电。 二、软件方…...

Spring MVC | Spring MVC 的“核心类” 和 “注解”
目录: Spring MVC 的“核心类” 和 “注解” :1.DispatcherServlet (前端控制器)2.Controller 注解3.RequestMapping 注解3.1 RequestMapping 注解的 “使用”标注在 “方法” 上标注在 “类” 上 3.2 RequestMapping 注解的 “属性” 4.组合注解4.1 请求处理方法的…...
Python 创建PPT
本篇为如何使用Python来创建ppt文件。 创建PPT 安装必要的库 命令如下: pip install python-pptx 安装过程: 创建ppt文件 在当前目录下创建一个test的ppt文件。其中包含两页,分别使用了不同的布局。 第一页设置了标题和内容。第二页只设…...
【工具】Git的24种常用命令
相关链接 传送门:>>>【工具】Git的介绍与安装<< 1.Git配置邮箱和用户 第一次使用Git软件,需要告诉Git软件你的名称和邮箱,否则无法将文件纳入到版本库中进行版本管理。 原因:多人协作时,不同的用户可…...
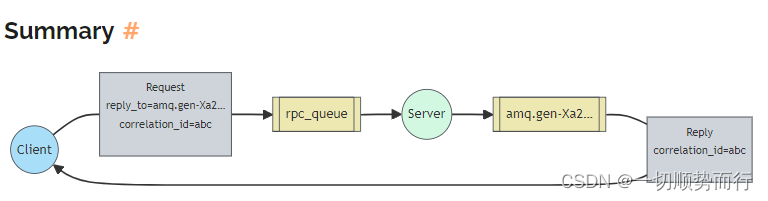
rabbitmq 基本总结
rabbitmq 的基本概念 vhost、broker、producer、 consumer、 exchange、 queue、 routing key rabbitmq 常用的队列类型,工作队列(简单队列),pub/sub, routing key, topic 模式 <dependency><groupId>com.rabbitmq&l…...

7、Copmose自定义颜色和主题切换
Copmose自定义颜色和主题切换 一起颜色的设置的都是在res/values/colors里面去做颜色, 但是当使用compose的时候,抛弃了使用了ui.theme底下的Color.kt和Theme.kt 但是默认使用的是MaterialTheme主题,里面的颜色字段不能定义,因此…...

js-判断变量是否定义
if (typeof myVar undefined) {// myVar (未定义) 或 (已定义但未初始化) } else {// myVar (已定义和已初始化) } 参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/redFeather/p/17662966.html...
视频远程监控平台EasyCVR集成后播放只有一帧画面的原因排查与解决
智慧安防视频监控平台EasyCVR能在复杂的网络环境中(专网、局域网、广域网、VPN、公网等)将前端海量的设备进行统一集中接入与视频汇聚管理,平台可支持的接入协议包括:国标GB28181、RTSP/Onvif、RTMP,以及厂家的私有协议…...

Pulsar 社区周报 | No.2024.03.08 Pulsar-Spark Connector 助力实时计算
关于 Apache Pulsar Apache Pulsar 是 Apache 软件基金会顶级项目,是下一代云原生分布式消息流平台,集消息、存储、轻量化函数式计算为一体,采用计算与存储分离架构设计,支持多租户、持久化存储、多机房跨区域数据复制,…...

Redis--线程模型详解
Redis线程模型 Redis内部使用的文件事件处理器(基于Reactor模式开发的)file event handler是单线程的,所以Redis线程模型才叫单线程模型,它采用IO多路复用机制同时监听多个socket,当被监听的socket准备好执行accep、r…...

[备赛笔记]——5G大唐杯(5G考试等级考考试基础试题)
个人名片: 🦁作者简介:学生 🐯个人主页:妄北y 🐧个人QQ:2061314755 🐻个人邮箱:2061314755qq.com 🦉个人WeChat:Vir2021GKBS 🐼本文由…...

【解读】OWASP 大语言模型(LLM)安全测评基准V1.0
大语言模型(LLM,Large Language Model)是指参数量巨大、能够处理海量数据的模型, 此类模型通常具有大规模的参数,使得它们能够处理更复杂的问题,并学习更广泛的知识。自2022 年以来,LLM技术在得到了广泛的应…...
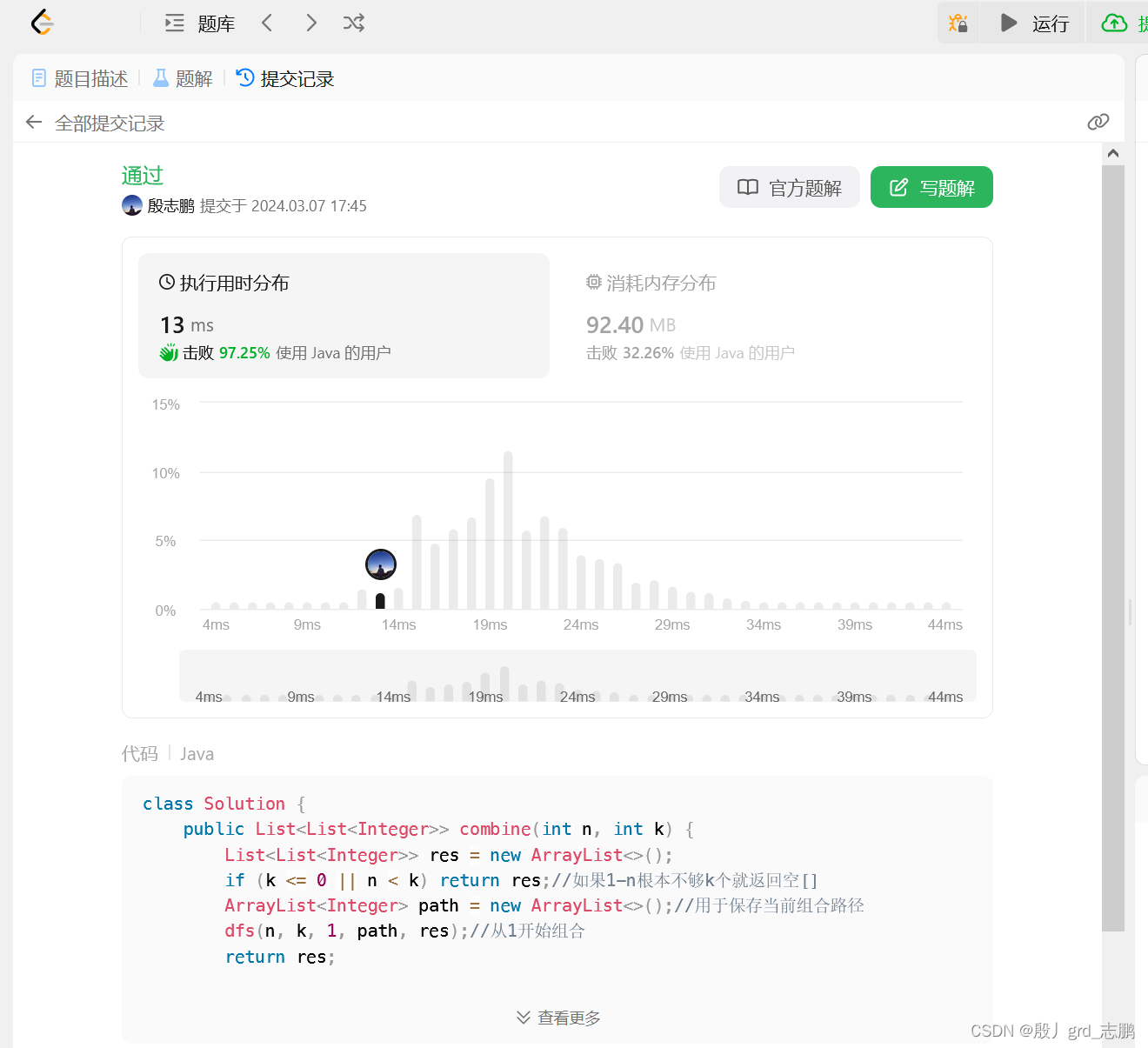
java数据结构与算法刷题-----LeetCode77. 组合
java数据结构与算法刷题目录(剑指Offer、LeetCode、ACM)-----主目录-----持续更新(进不去说明我没写完):https://blog.csdn.net/grd_java/article/details/123063846 文章目录 1. 递归实现 解题思路 这种题只能暴力求解,枚举所有可…...
)
网络安全运营的工作内容(附资料下载)
【推荐】最新网络安全运营方案和实践合集(共80多份).zip 网络安全运营的工作内容是一个多层次、多维度的体系,涵盖了多个关键领域以确保网络环境的稳定和安全。以下是一些主要的工作内容: 安全策略制定与实施: 制定网…...
)
华为OD面试分享13(2024年)
华为OD面经 二战失败选手,双非一本部门目标院校,数学与应用数学专业,无相关工作经验也没有什么拿得出手的项目。3月中旬开始重新学java(大学里有学过一个学期的java,很水)。期间经常通宵肝,学习框架、刷leedcode,可能是因为数学专业出身,数据结构和算法这一块学起来并…...

Android14之解决报错:No module named sepolgen(一百九十二)
简介: CSDN博客专家,专注Android/Linux系统,分享多mic语音方案、音视频、编解码等技术,与大家一起成长! 优质专栏:Audio工程师进阶系列【原创干货持续更新中……】🚀 优质专栏:多媒…...

数电学习笔记——逻辑函数的代数法化简
目录 逻辑函数的化简原则 与或逻辑的化简 1、吸收律(1) ( ABABA) 2、吸收律(2)(3)( AABA;AABAB) 3、多余项定律( ABACBCABAC) 4、拆项法 5、添项法 逻辑函数的化简原则 (1)逻辑函数所用的门最少 (2)各个门的输入端要少 (3)逻辑电路所用的级数要少 (4)逻辑…...
react实战——react旅游网
慕课网react实战 搭建项目问题1.按照官网在index.tsx中引入antd出错?2.typescript中如何使用react-router3.react-router3.1 V63.2 V53.3V6实现私有路由 4.函数式组件接收props参数时定义数据接口?5.使用TypeScript开发react项目:6.要使一个组…...

STM32+rt-thread判断是否联网
一、根据NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP位判断 static bool is_conncected(void) {struct netdev *dev RT_NULL;dev netdev_get_first_by_flags(NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP);if (dev RT_NULL){printf("wait netdev internet up...");return false;}else{printf("loc…...

STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解
STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解 前言如何确定定时器挂载在哪条时钟线上配置及使用方法参数配置PrescalerCounter ModeCounter Periodauto-reload preloadTrigger Event Selection 中断配置生成的代码及使用方法初始化代码基本定时器触发DCA或者ADC的代码讲解中断代码定时启动…...
-----深度优先搜索(DFS)实现)
c++ 面试题(1)-----深度优先搜索(DFS)实现
操作系统:ubuntu22.04 IDE:Visual Studio Code 编程语言:C11 题目描述 地上有一个 m 行 n 列的方格,从坐标 [0,0] 起始。一个机器人可以从某一格移动到上下左右四个格子,但不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 k 的格子。 例…...

IoT/HCIP实验-3/LiteOS操作系统内核实验(任务、内存、信号量、CMSIS..)
文章目录 概述HelloWorld 工程C/C配置编译器主配置Makefile脚本烧录器主配置运行结果程序调用栈 任务管理实验实验结果osal 系统适配层osal_task_create 其他实验实验源码内存管理实验互斥锁实验信号量实验 CMISIS接口实验还是得JlINKCMSIS 简介LiteOS->CMSIS任务间消息交互…...

Swagger和OpenApi的前世今生
Swagger与OpenAPI的关系演进是API标准化进程中的重要篇章,二者共同塑造了现代RESTful API的开发范式。 本期就扒一扒其技术演进的关键节点与核心逻辑: 🔄 一、起源与初创期:Swagger的诞生(2010-2014) 核心…...
提供了哪些便利?)
现有的 Redis 分布式锁库(如 Redisson)提供了哪些便利?
现有的 Redis 分布式锁库(如 Redisson)相比于开发者自己基于 Redis 命令(如 SETNX, EXPIRE, DEL)手动实现分布式锁,提供了巨大的便利性和健壮性。主要体现在以下几个方面: 原子性保证 (Atomicity)ÿ…...

【Android】Android 开发 ADB 常用指令
查看当前连接的设备 adb devices 连接设备 adb connect 设备IP 断开已连接的设备 adb disconnect 设备IP 安装应用 adb install 安装包的路径 卸载应用 adb uninstall 应用包名 查看已安装的应用包名 adb shell pm list packages 查看已安装的第三方应用包名 adb shell pm list…...

LOOI机器人的技术实现解析:从手势识别到边缘检测
LOOI机器人作为一款创新的AI硬件产品,通过将智能手机转变为具有情感交互能力的桌面机器人,展示了前沿AI技术与传统硬件设计的完美结合。作为AI与玩具领域的专家,我将全面解析LOOI的技术实现架构,特别是其手势识别、物体识别和环境…...

算术操作符与类型转换:从基础到精通
目录 前言:从基础到实践——探索运算符与类型转换的奥秘 算术操作符超级详解 算术操作符:、-、*、/、% 赋值操作符:和复合赋值 单⽬操作符:、--、、- 前言:从基础到实践——探索运算符与类型转换的奥秘 在先前的文…...
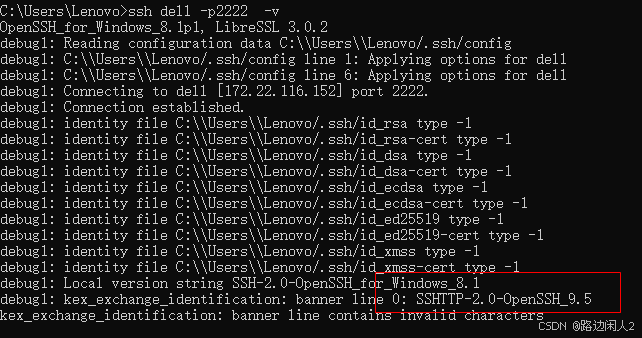
sshd代码修改banner
sshd服务连接之后会收到字符串: SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_9.5 容易被hacker识别此服务为sshd服务。 是否可以通过修改此banner达到让人无法识别此服务的目的呢? 不能。因为这是写的SSH的协议中的。 也就是协议规定了banner必须这么写。 SSH- 开头,…...
