人像抠图HumanSeg——基于大规模电话会议视频数据集的连接感知人像分割
前言
人像抠图将图像中的人物与背景进行像素级别的区分的技术。通过人像分割,可以实现诸如背景虚化、弹幕穿人等各种有趣的功能,为视频通话和影音观看提供更加优质和丰富的体验。由于广泛部署到Web、手机和边缘设备,肖像分割在兼顾分割精度的前提下,需要具有极快的推理速度。
PP-HumanSeg v2人像分割方案是一项重要的突破,采用了深度学习技术,以96.63%的mIoU精度和仅15.86ms的推理耗时,在人像分割领域刷新了SOTA指标。该方案不仅支持商业应用,而且可零成本、开箱即用。
相比于之前的版本,PP-HumanSeg v2在推理速度和精度上都有显著提升,肖像分割模型推理速度提升45.5%,mIoU精度提升3.03%。通用人像分割模型推理速度提升5.7%,mIoU精度提升6.5%。
网络结构
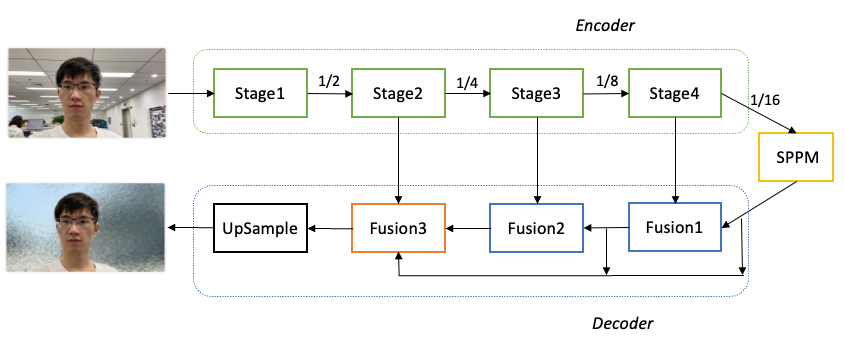
PaddleSeg整体结构如下图所示。具体优化过程如下:
-
骨干网络选择: 为了降低模型的算量要求,选择了MobileNetV3作为骨干网络,用于提取多层特征。
-
参数量优化: 对MobileNetV3进行参数量优化。分析发现MobileNetV3的参数主要集中在最后一个Stage,在不影响分割精度的前提下,保留了MobileNetV3的前四个Stage,成功减少了68.6%的参数量。
-
全局上下文信息汇集: 对于16倍下采样特征图,使用了SPPM(Spatial Pyramid Pooling Module)模块来汇集全局上下文信息,以提高模型对背景和环境的理解能力。
-
特征融合: 使用三个Fusion模块来不断融合深层语义特征和浅层细节特征。这些Fusion模块的作用是将不同层次的特征图进行融合,以获取更加丰富和准确的语义信息。
-
分割结果输出: 最后一个Fusion模块再次汇集不同层次的特征图,并将最终的分割结果输出。
通过以上优化措施,PaddleSeg的肖像分割模型在保证分割精度的情况下,大幅减少了参数量,提高了模型的轻量化程度,并且通过全局上下文信息的汇集和特征融合,进一步提升了模型的语义理解能力和分割效果。
针对肖像分割任务,数据量不足是影响分割精度的一个重要因素。为了解决这一问题,PaddleSeg开源了PP-HumanSeg-14K数据集,其中包含14000张室内场景半身人像的图片,从一定程度上缓解了数据不足的问题。为了进一步提高模型的分割精度和泛化能力,采用了迁移学习的方法。具体来说,首先在大规模的通用人像分割数据集上进行预训练,然后再针对PP-HumanSeg-14K数据集进行微调。
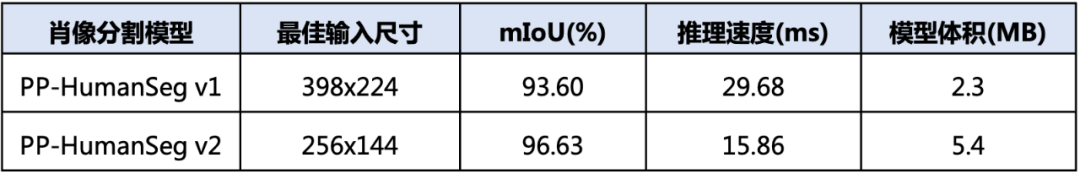
在调整模型的深度和宽度以平衡分割精度和推理速度方面,模型的输入尺寸也是一个需要重视的变量。针对手机和电脑端常见的拍摄尺寸为1028x720的情况,PP-HumanSeg v1肖像分割模型建议将图片缩放为398x224进行预测。为了进一步追求极致的推理速度,PP-HumanSeg v2肖像分割模型将最佳输入尺寸进一步缩小为256x144,从而将推理速度提升了52%(相比输入尺寸398x224)。虽然较小的输入尺寸会减少输入信息量,但由于PP-HumanSeg v2模型具有更强的学习能力,最终也能获得不错的分割效果。
综合考虑上述改进,与PP-HumanSeg v1相比,PP-HumanSeg v2肖像分割模型在推理速度(手机端)提升了45.5%,mIoU精度提升了3.03%,同时具有更佳的可视化效果。此外,该模型还支持手机拍摄的横屏和竖屏输入图像,针对室内场景可以开箱即用,为用户提供了更加便捷和高效的人像分割解决方案。
通用人像分割模型
针对通用人像分割任务,我们在PaddleSeg平台上使用了领先的模型,在大规模数据集上进行了训练,并发布了两个型号的PP-HumanSeg v2通用人像分割模型。
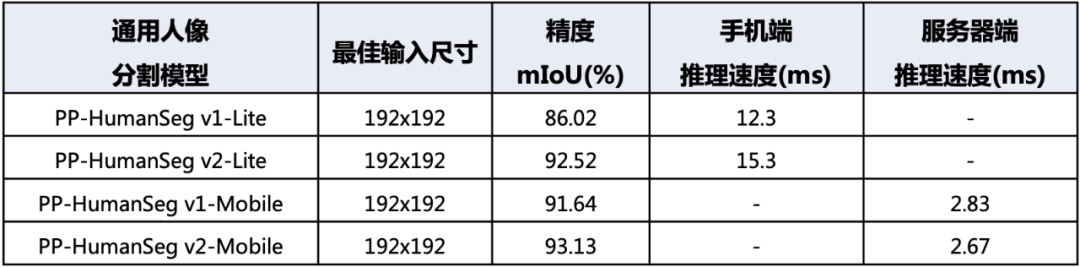
首先是PP-HumanSeg v2-Lite通用人像分割模型,它采用了类似于肖像分割模型的结构,并且特别适合在手机端的ARM CPU上进行部署。相比PP-HumanSeg v1-Lite模型,PP-HumanSeg v2-Lite在精度上提升了6.5%的mIoU。这个模型可以有效地应用于移动端的人像分割场景,提供更高质量的分割效果。
其次是PP-HumanSeg v2-Mobile通用人像分割模型,它采用了PaddleSeg自研的PP-LiteSeg模型结构,更适合在服务器端的GPU上进行部署。相比PP-HumanSeg v1-Mobile模型,PP-HumanSeg v2-Mobile在精度上提升了1.49%的mIoU,同时推理速度也提升了5.7%。这个模型适用于对分割精度和推理速度都有要求的场景,为用户提供了更高效和准确的人像分割解决方案。
由于通用人像分割任务的场景变化很大,我们建议用户在实际应用中评估PP-HumanSeg通用人像分割模型的精度。如果模型符合业务要求,用户可以直接使用。如果需要进一步优化,用户也可以基于PP-HumanSeg通用人像分割模型进行定制化优化,以获得更好的效果。
模型部署
PP-HumanSeg 分割模型提供了最终模型和二次训练以其部署的功能代码。使用提供的肖像分割和通用人像分割配置文件,用户只需准备好数据即可开始训练。该模型支持在多种硬件上进行应用部署,包括NVIDIA GPU、X86 CPU、ARM CPU以及浏览器Web。
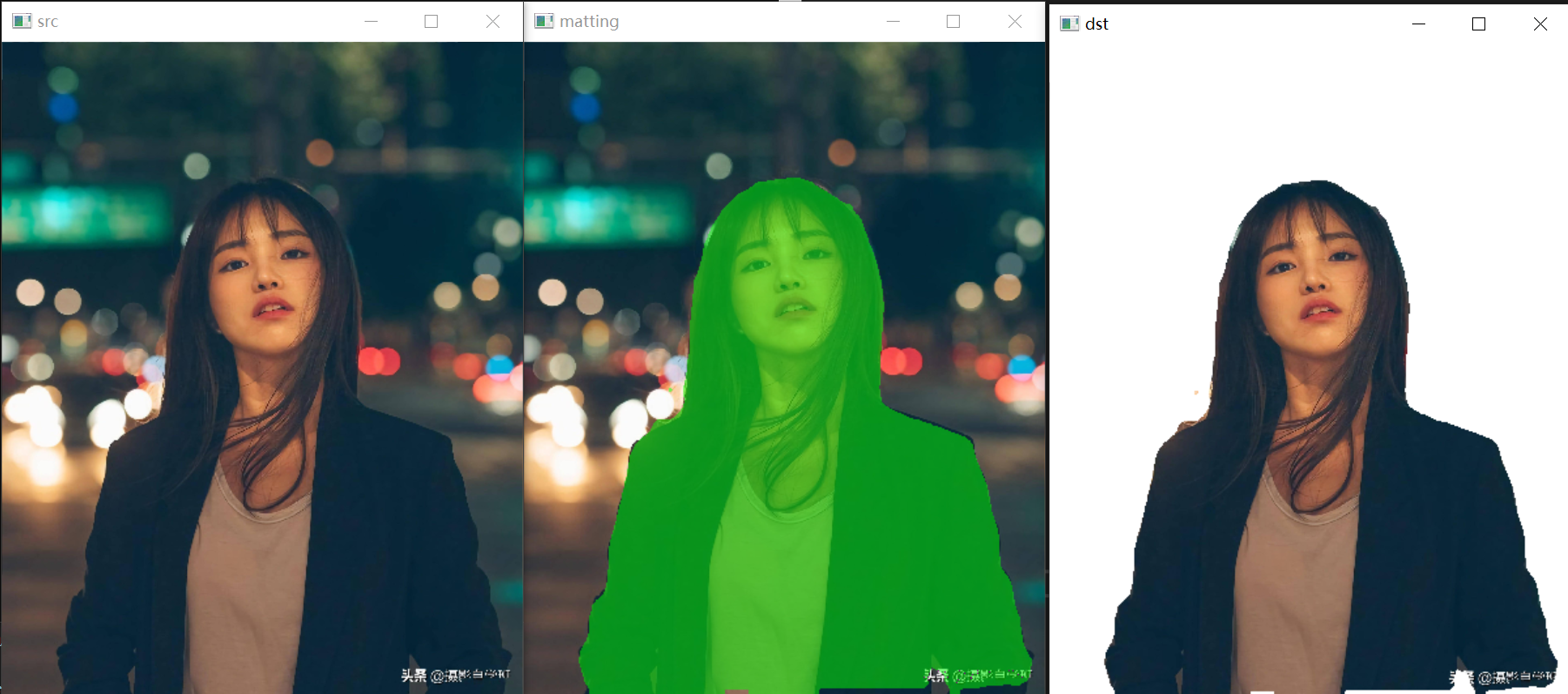
另外,还对模型预测结果进行了形态学后处理操作,以过滤掉背景干扰,保留人像主体。具体流程如下图所示:原始预测图像中每个像素的数值表示其为前景的概率。首先,使用阈值操作来过滤掉概率较小的像素,然后通过腐蚀和膨胀操作来消除细小的噪点。腐蚀操作的核尺寸小于膨胀操作,然后将掩码图像应用于原始预测结果上,得到最终的预测结果。通过形态学后处理,可以有效地提升人像分割的可视化效果,从而使分割结果更加清晰和准确。
C++ onnxruntime推理:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
//#include <cuda_provider_factory.h> ///使用cuda加速
#include <onnxruntime_cxx_api.h>class pphuman_seg
{
public:pphuman_seg(std::string model_path);void inference(cv::Mat &cv_src, std::vector<cv::Mat>& cv_dsts);
private:void preprocess(cv::Mat &cv_src);int inpWidth;int inpHeight;std::vector<float> input_image_;const float conf_threshold = 0.5;Ort::Env env = Ort::Env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_ERROR, "pphuman");Ort::Session *ort_session = nullptr;Ort::SessionOptions sessionOptions = Ort::SessionOptions();std::vector<char*> input_names;std::vector<char*> output_names;std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> input_node_dims; // >=1 outputsstd::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> output_node_dims; // >=1 outputs
};pphuman_seg::pphuman_seg(std::string model_path)
{std::wstring widestr = std::wstring(model_path.begin(), model_path.end()); //windows写法//OrtStatus* status = OrtSessionOptionsAppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(sessionOptions, 0); //使用cuda加速sessionOptions.SetGraphOptimizationLevel(ORT_ENABLE_BASIC);ort_session = new Ort::Session(env, widestr.c_str(), sessionOptions); //windows写法//ort_session = new Session(env, model_path.c_str(), sessionOptions); //linux写法size_t numInputNodes = ort_session->GetInputCount();size_t numOutputNodes = ort_session->GetOutputCount();Ort::AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator;for (int i = 0; i < numInputNodes; i++){input_names.push_back(ort_session->GetInputName(i, allocator));Ort::TypeInfo input_type_info = ort_session->GetInputTypeInfo(i);auto input_tensor_info = input_type_info.GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo();auto input_dims = input_tensor_info.GetShape();input_node_dims.push_back(input_dims);}for (int i = 0; i < numOutputNodes; i++){output_names.push_back(ort_session->GetOutputName(i, allocator));Ort::TypeInfo output_type_info = ort_session->GetOutputTypeInfo(i);auto output_tensor_info = output_type_info.GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo();auto output_dims = output_tensor_info.GetShape();output_node_dims.push_back(output_dims);}this->inpHeight = input_node_dims[0][2];this->inpWidth = input_node_dims[0][3];
}void pphuman_seg::preprocess(cv::Mat &cv_src)
{cv::Mat dstimg;resize(cv_src, dstimg, cv::Size(this->inpWidth, this->inpHeight), cv::INTER_LINEAR);int row = dstimg.rows;int col = dstimg.cols;this->input_image_.resize(row * col * dstimg.channels());for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++){for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){for (int j = 0; j < col; j++){float pix = dstimg.ptr<uchar>(i)[j * 3 + c];this->input_image_[c * row * col + i * col + j] = (pix / 255.0 - 0.5) / 0.5;}}}
}void pphuman_seg::inference(cv::Mat &cv_src,std::vector<cv::Mat> &cv_dsts)
{this->preprocess(cv_src);std::array<int64_t, 4> input_shape_{1, 3, this->inpHeight, this->inpWidth};auto allocator_info = Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeCPU);Ort::Value input_tensor_ = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(allocator_info, input_image_.data(),input_image_.size(), input_shape_.data(), input_shape_.size());std::vector<Ort::Value> ort_outputs = ort_session->Run(Ort::RunOptions{ nullptr }, input_names.data(),&input_tensor_, 1, output_names.data(), output_names.size()); // 开始推理// post process. Ort::Value &mask_pred = ort_outputs.at(0);const int out_h = this->output_node_dims[0][1];const int out_w = this->output_node_dims[0][2];float *mask_ptr = mask_pred.GetTensorMutableData<float>();cv::Mat segmentation_map;cv::Mat mask_out(out_h, out_w, CV_32FC2, mask_ptr);cv::resize(mask_out, segmentation_map, cv::Size(cv_src.cols, cv_src.rows));cv::Mat cv_dst = cv_src.clone();for (int h = 0; h < cv_src.rows; h++){for (int w = 0; w < cv_src.cols; w++){float pix = segmentation_map.ptr<float>(h)[w * 2 + 1];if (pix > this->conf_threshold){float b = (float)cv_dst.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[0];cv_dst.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[0] = uchar(b * 0.5 + 1);float g = (float)cv_dst.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[1] + 255.0;cv_dst.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[1] = uchar(g * 0.5 + 1);float r = (float)cv_dst.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[2];cv_dst.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[2] = uchar(r * 0.5 + 1);}}}cv_dsts.push_back(cv_dst);cv::Mat cv_matting = cv_src.clone();for (int h = 0; h < cv_src.rows; h++){for (int w = 0; w < cv_src.cols; w++){float pix = segmentation_map.ptr<float>(h)[w * 2 + 1];if (pix > this->conf_threshold){cv_matting.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[0] = (float)cv_src.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[0];cv_matting.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[1] = (float)cv_src.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[1];cv_matting.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[2] = (float)cv_src.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[2];}else{cv_matting.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[0] = 255;cv_matting.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[1] = 255;cv_matting.at<cv::Vec3b>(h, w)[2] = 255;}}}cv_dsts.push_back(cv_matting);
}void show_img(std::string name, const cv::Mat& img)
{cv::namedWindow(name, 0);int max_rows = 500;int max_cols = 600;if (img.rows >= img.cols && img.rows > max_rows) {cv::resizeWindow(name, cv::Size(img.cols * max_rows / img.rows, max_rows));}else if (img.cols >= img.rows && img.cols > max_cols) {cv::resizeWindow(name, cv::Size(max_cols, img.rows * max_cols / img.cols));}cv::imshow(name, img);
}cv::Mat replaceBG(const cv::Mat cv_src, cv::Mat& alpha, std::vector<int>& bg_color)
{int width = cv_src.cols;int height = cv_src.rows;cv::Mat cv_matting = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(width, height), CV_8UC3);float* alpha_data = (float*)alpha.data;for (int i = 0; i < height; i++){for (int j = 0; j < width; j++){float alpha_ = alpha_data[i * width + j];cv_matting.at < cv::Vec3b>(i, j)[0] = cv_src.at < cv::Vec3b>(i, j)[0] * alpha_ + (1 - alpha_) * bg_color[0];cv_matting.at < cv::Vec3b>(i, j)[1] = cv_src.at < cv::Vec3b>(i, j)[1] * alpha_ + (1 - alpha_) * bg_color[1];cv_matting.at < cv::Vec3b>(i, j)[2] = cv_src.at < cv::Vec3b>(i, j)[2] * alpha_ + (1 - alpha_) * bg_color[2];}}return cv_matting;
}int main()
{pphuman_seg pp_net("model_float32.onnx");std::string path = "images";std::vector<std::string> filenames;cv::glob(path, filenames, false);for (auto file_name : filenames){cv::Mat cv_src = cv::imread(file_name);std::vector<cv::Mat> cv_dsts;pp_net.inference(cv_src,cv_dsts);show_img("src", cv_src);show_img("matting", cv_dsts[0]);show_img("dst", cv_dsts[1]);cv::waitKey(0);}
}
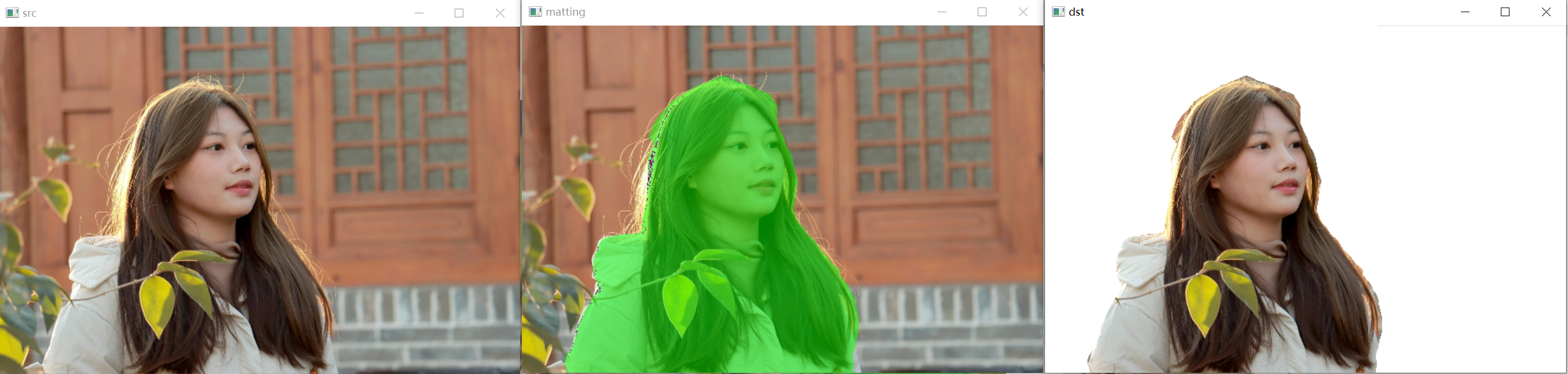


python onnxruntimer推理:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import copy
import argparse
import cv2
import numpy as np
import onnxruntimeclass pphumanseg:def __init__(self, conf_thres=0.5):self.conf_threshold = conf_thres# Initialize modelself.onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession("model_float32.onnx")self.input_name = self.onnx_session.get_inputs()[0].nameself.output_name = self.onnx_session.get_outputs()[0].nameself.input_shape = self.onnx_session.get_inputs()[0].shapeself.input_height = self.input_shape[2]self.input_width = self.input_shape[3]self.mean = np.array([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], dtype=np.float32).reshape(1,1,3)self.std = np.array([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], dtype=np.float32).reshape(1,1,3)def prepare_input(self, image):input_image = cv2.resize(image, dsize=(self.input_width, self.input_height))input_image = (input_image.astype(np.float32) / 255.0 - self.mean) / self.stdinput_image = input_image.transpose(2, 0, 1)input_image = np.expand_dims(input_image, axis=0)return input_imagedef detect(self, image):input_image = self.prepare_input(image)# Perform inference on the imageresult = self.onnx_session.run([self.output_name], {self.input_name: input_image})# Post process:squeezesegmentation_map = result[0]segmentation_map = np.squeeze(segmentation_map)image_width, image_height = image.shape[1], image.shape[0]dst_image = copy.deepcopy(image)segmentation_map = cv2.resize(segmentation_map,dsize=(image_width, image_height),interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR,)# color listcolor_image_list = []# ID 0:BackGroundbg_image = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=np.uint8)bg_image[:] = (0, 0, 0)color_image_list.append(bg_image)# ID 1:Humanbg_image = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=np.uint8)bg_image[:] = (0, 255, 0)color_image_list.append(bg_image)# Overlay segmentation mapmasks = segmentation_map.transpose(2, 0, 1)for index, mask in enumerate(masks):# Threshold check by scoremask = np.where(mask > self.conf_threshold, 0, 1)# Overlaymask = np.stack((mask,) * 3, axis=-1).astype('uint8')mask_image = np.where(mask, dst_image, color_image_list[index])dst_image = cv2.addWeighted(dst_image, 0.5, mask_image, 0.5, 1.0)return dst_imageif __name__ == '__main__':parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()parser.add_argument('--imgpath', type=str, default='images/person.jpg', help="image path")parser.add_argument('--confThreshold', default=0.5, type=float, help='class confidence')parser.add_argument('--use_video', type=int, default=1, help="if use video")args = parser.parse_args()segmentor = pphumanseg(conf_thres=args.confThreshold)if args.use_video != 1:srcimg = cv2.imread(args.imgpath)# Detect Objectsdstimg = segmentor.detect(srcimg)winName = 'pphumanseg in ONNXRuntime'cv2.namedWindow(winName, 0)cv2.imshow(winName, dstimg)cv2.waitKey(0)cv2.destroyAllWindows()else:cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if not ret:breakdstimg = segmentor.detect(frame)key = cv2.waitKey(1)if key == 27: # ESCbreakcv2.imshow('pphumanseg Demo', dstimg)cap.release()cv2.destroyAllWindows()相关文章:

人像抠图HumanSeg——基于大规模电话会议视频数据集的连接感知人像分割
前言 人像抠图将图像中的人物与背景进行像素级别的区分的技术。通过人像分割,可以实现诸如背景虚化、弹幕穿人等各种有趣的功能,为视频通话和影音观看提供更加优质和丰富的体验。由于广泛部署到Web、手机和边缘设备,肖像分割在兼顾分割精度的…...
Qt 项目使用visual studio 进行开发调试
https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemNameTheQtCompany.QtVisualStudioTools2015 https://devblogs.microsoft.com/cppblog/bring-your-existing-qt-projects-to-visual-studio/ 正常Qt开发中,使用Qt Creator 进行windows下MSVC编译器的调试是一件挺麻…...

Kotlin 中的惰性集合
1 通过序列提高效率 首先看以下代码: val list listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) list.filter { it > 2 }.map { it * 2 }上面的写法很简单,在处理集合时,类似于上面的操作能帮我们解决大部分的问题。但是,当 list 中的元素非常多的时…...

2024年React初学者入门路线指南
在这篇文章中,我们一步一步探索了如何从零基础开始学习React,并逐渐成长为一名初级开发者。通过理解基础概念、实践构建静态和动态项目,最终发展到创建复杂的应用程序并加入到个人作品集中,您现在已经准备好迈向React开发者的职业…...

【Java基础】了解Java安全体系JCA,使用BouncyCastle的ED25519算法生成密钥对、数据签名
文章目录 一.Java安全体系结构二.JCA和JCE三.CSP(加密服务提供程序)与Engine类1.CSP2.Engine类如何使用引擎类 四.查看当前JDK支持的算法服务提供商(Provider)五.BouncyCastle是什么六.如何使用BouncyCastle?七.bouncycastle实现ED25519工具类 一.Java安全体系结构 …...

SQL Server创建存储过程
使用以下语句创建一个存储过程: CREATE PROCEDURE [schema_name.]procedure_nameparameter1 datatype,parameter2 datatype,... AS BEGIN-- 存储过程的逻辑代码-- 可以包含SQL语句、控制流语句、变量声明等-- 示例:查询表中的数据SELECT column1, colum…...
GraphPad Prism 10:一站式数据分析解决方案
GraphPad Prism 10是一款功能强大的数据分析和可视化软件,广泛应用于生命科学研究、医学、生物、化学等多个领域。以下是对其详细功能的介绍: 首先,GraphPad Prism 10具有出色的数据可视化功能。它支持各种类型的图表和图形,包括…...
前端基础篇-深入了解 Ajax 、Axios
🔥博客主页: 【小扳_-CSDN博客】 ❤感谢大家点赞👍收藏⭐评论✍ 文章目录 1.0 Ajax 概述 2.0 Axios 概述 3.0 综合案例 1.0 Ajax 概述 通过 Ajax 可以给服务器发送请求,并获取服务器响应的数据。异步交互是指,可以在不…...

是德科技keysight N1912A双通道功率计
181/2461/8938产品概述: Keysight(原Agilent) N1912A P系列双通道功率计可提供峰值、峰均比、平均功率、上升时间、下降时间、最大功率值、最小功率值以及宽带信号的统计数据。 Keysight(原Agilent) N1912A P系列双通道功率计, 可提供峰值、峰均比、平均功率、上升…...
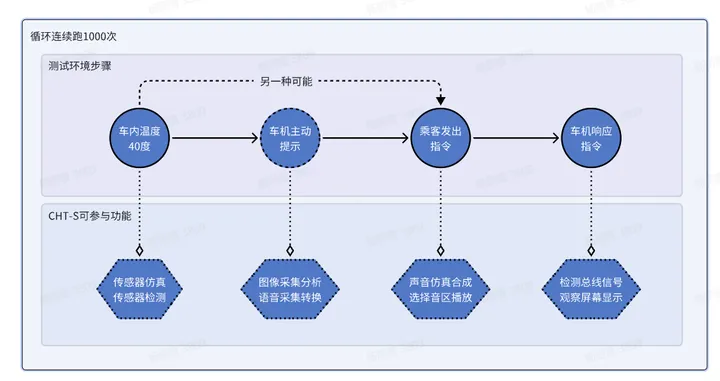
怿星科技Neptune CHT-S测试系统,让智能座舱测试更加高效便捷
随着汽车“智能化”浪潮的推进,汽车的智能化水平正在持续刷新行业认知。在这股智能化潮流中,智能座舱作为客户体验最为直观的部分,其重要性不言而喻。倘若座舱设备出现死机、黑屏、卡顿等现象,都将对客户的使用体验产生非常大的影…...
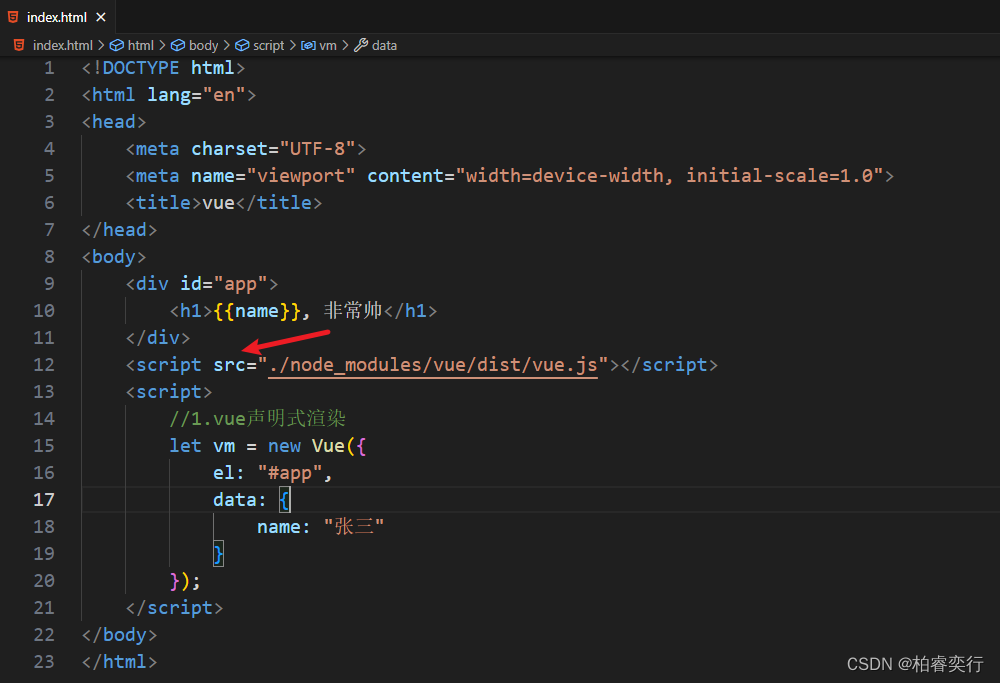
Vscode初建Vue时几个需要注意的问题
首先放图 注意点1.打开文件夹时,可以是VUE2 或者其他,但不能是VUE,会报错 注意点2.终端输入命令“npm init -y" npm init -y -y 的含义:yes的意思,在init的时候省去了敲回车的步骤,生成的默认的packag…...
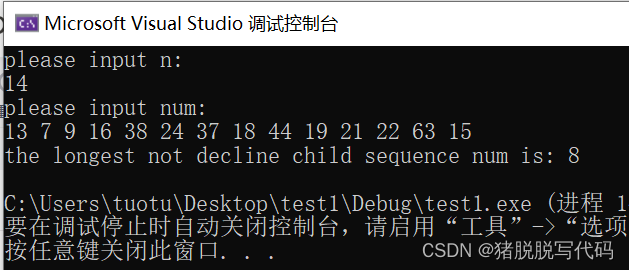
最长不下降子序列
问题描述: 统计一个数组中的最长不下降子序列。 示例: 输入:14 输入:13 7 9 16 38 24 37 18 44 19 21 22 63 15 输出:8(其中是7 9 16 18 19 21 22 63) 方法:借鉴B站UP主T_zhao…...
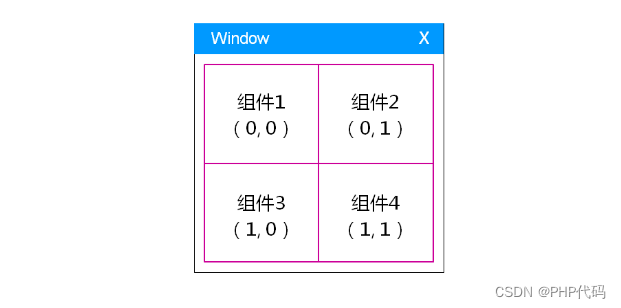
QT gridlayout 循环设置组件,表格也通用 已解决
在需求中。经常遇到,表格 展示需求。 几乎都是json格式的。 // 列表配置文件QJsonArray listJsonArray getCfgJsonData("details_tab_table_config.json");if (listJsonArray.isEmpty()){return;}ui->gridWidget->setMaximumSize(QSize(310, 180)…...
后端前行Vue之路(一):初识Vue
1.Vue是什么 Vue (读音 /vjuː/,类似于 view) 是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架。与其它大型框架不同的是,Vue 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。Vue 的核心库只关注视图层,不仅易于上手,还便于与第三方库或既有项目整合。另一方…...

C#、.NET版本、Visual Studio版本对应关系及Visual Studio老版本离线包下载地址
0、写这篇文章的目的 由于电脑的环境不同,对于一个老电脑找到一个适配的vscode环境十分不易。总结一下C#、.NET、Visual Studio版本的对应关系,及各个版本Visual Studio的下载地址供大家参考 1、C#、.NET版本、Visual Studio版本对应关系如下 2、Visua…...
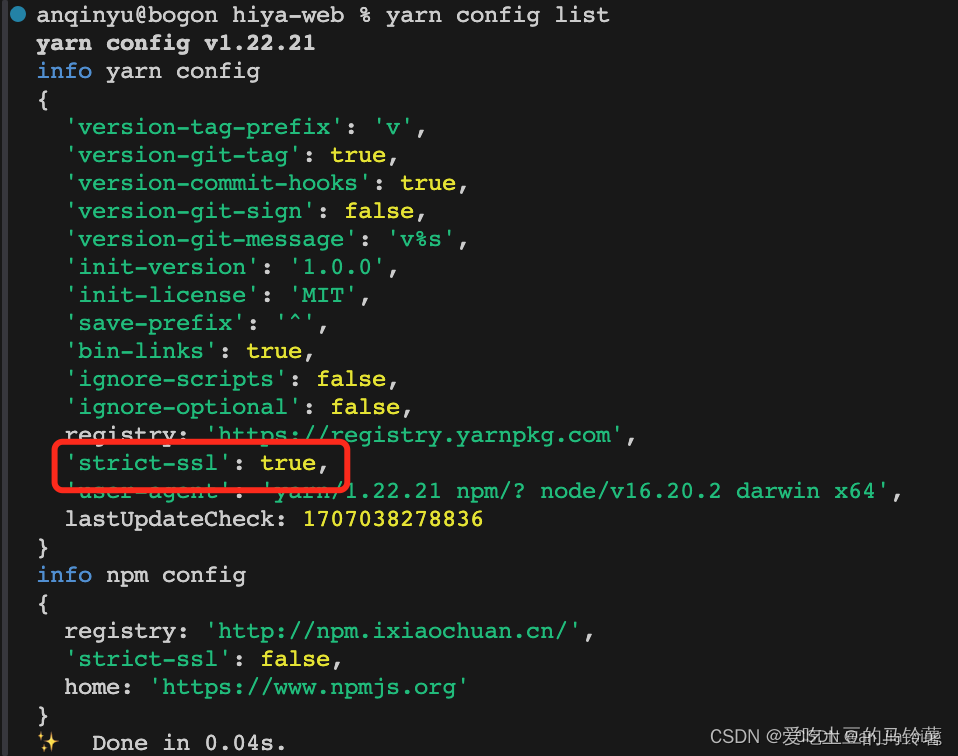
yarn安装包时报错error Error: certificate has expired
安装教程: 配置镜像地址: npm config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com//镜像:https://developer.aliyun.com/mirror/NPM 安装yarn: npm install --global yarn查看版本: yarn --version卸载ÿ…...
手机可以格式化存储卡吗?格式化以后出现什么情况
随着智能手机的普及,存储卡(如SD卡、MicroSD卡等)已成为手机存储扩展的重要工具。然而,在使用过程中,我们有时可能会遇到需要格式化存储卡的情况。那么,手机能否直接格式化存储卡呢?格式化后存储…...
亚马逊AWS展示高效纠错的全新量子比特!
亚马逊网络服务公司(AWS)在量子计算的纠错技术领域取得了显著成就,极大地简化了量子系统的复杂性和资源需求。他们的研究人员通过采用“双轨擦除”量子比特(dual-rail erasure qubit)技术,有效地克服了量子…...

FEX-Emu在Debian/Ubuntu系统使用
FEX-Emu在Debian/Ubuntu系统使用 1. Debootstrap子系统安装(可选)2. Debian/Ubuntu依赖包安装3. 获取FEX-Emu源码并编译4. 根文件系统RootFS安装5. 基于 FEX-Emu 运行应用 1. Debootstrap子系统安装(可选) sudo apt-get install …...

docker 不同架构镜像融合问题解决
1、背景 docker 作为目前容器的标准之一,但是对于多种架构的平台的混合编译支撑不是很好。因此衍生了镜像融合,分别将多种不同的架构构建好,然后将镜像进行融合上传。拉取镜像的会根据当前系统的架构拉取不同的镜像,也可以通过 -…...

C++_核心编程_多态案例二-制作饮品
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;/*制作饮品的大致流程为:煮水 - 冲泡 - 倒入杯中 - 加入辅料 利用多态技术实现本案例,提供抽象制作饮品基类,提供子类制作咖啡和茶叶*//*基类*/ class AbstractDr…...
8k长序列建模,蛋白质语言模型Prot42仅利用目标蛋白序列即可生成高亲和力结合剂
蛋白质结合剂(如抗体、抑制肽)在疾病诊断、成像分析及靶向药物递送等关键场景中发挥着不可替代的作用。传统上,高特异性蛋白质结合剂的开发高度依赖噬菌体展示、定向进化等实验技术,但这类方法普遍面临资源消耗巨大、研发周期冗长…...

前端导出带有合并单元格的列表
// 导出async function exportExcel(fileName "共识调整.xlsx") {// 所有数据const exportData await getAllMainData();// 表头内容let fitstTitleList [];const secondTitleList [];allColumns.value.forEach(column > {if (!column.children) {fitstTitleL…...
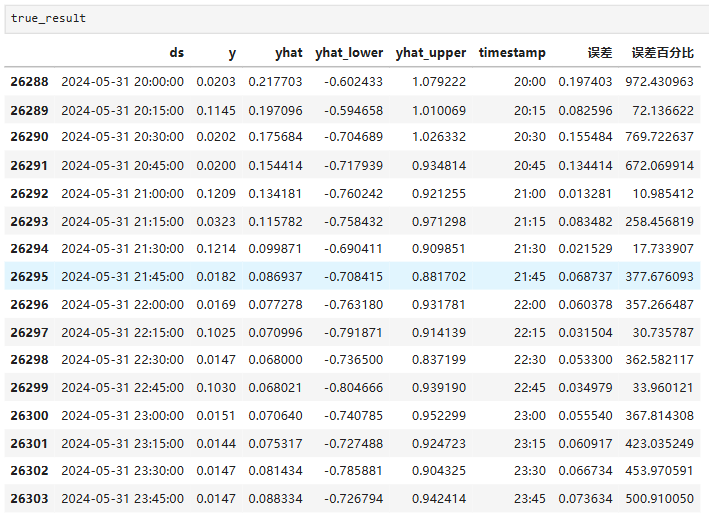
Python实现prophet 理论及参数优化
文章目录 Prophet理论及模型参数介绍Python代码完整实现prophet 添加外部数据进行模型优化 之前初步学习prophet的时候,写过一篇简单实现,后期随着对该模型的深入研究,本次记录涉及到prophet 的公式以及参数调优,从公式可以更直观…...

AI编程--插件对比分析:CodeRider、GitHub Copilot及其他
AI编程插件对比分析:CodeRider、GitHub Copilot及其他 随着人工智能技术的快速发展,AI编程插件已成为提升开发者生产力的重要工具。CodeRider和GitHub Copilot作为市场上的领先者,分别以其独特的特性和生态系统吸引了大量开发者。本文将从功…...

CSS设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整
width: fit-content 是 CSS 中的一个属性值,用于设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整,确保宽度刚好容纳内容而不会超出。 效果对比 默认情况(width: auto): 块级元素(如 <div>)会占满父容器…...

uniapp 字符包含的相关方法
在uniapp中,如果你想检查一个字符串是否包含另一个子字符串,你可以使用JavaScript中的includes()方法或者indexOf()方法。这两种方法都可以达到目的,但它们在处理方式和返回值上有所不同。 使用includes()方法 includes()方法用于判断一个字…...

探索Selenium:自动化测试的神奇钥匙
目录 一、Selenium 是什么1.1 定义与概念1.2 发展历程1.3 功能概述 二、Selenium 工作原理剖析2.1 架构组成2.2 工作流程2.3 通信机制 三、Selenium 的优势3.1 跨浏览器与平台支持3.2 丰富的语言支持3.3 强大的社区支持 四、Selenium 的应用场景4.1 Web 应用自动化测试4.2 数据…...
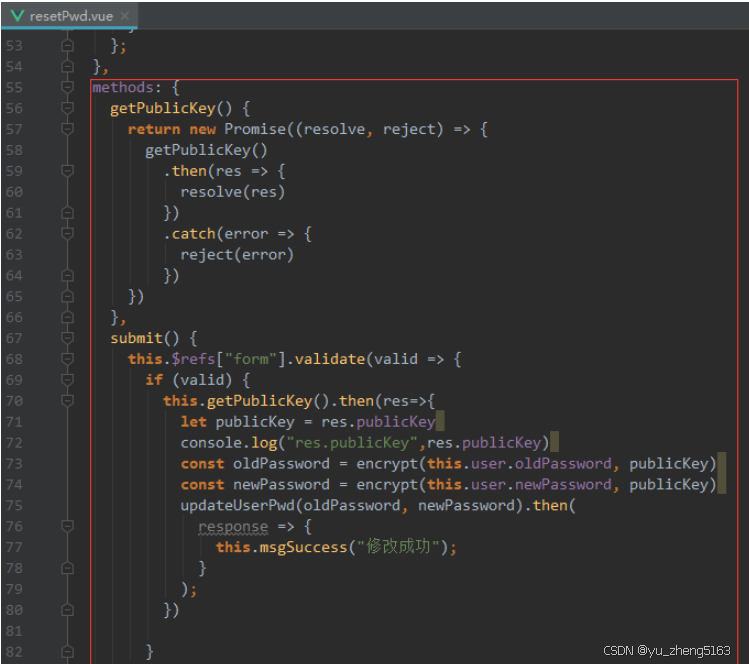
若依登录用户名和密码加密
/*** 获取公钥:前端用来密码加密* return*/GetMapping("/getPublicKey")public RSAUtil.RSAKeyPair getPublicKey() {return RSAUtil.rsaKeyPair();}新建RSAUti.Java package com.ruoyi.common.utils;import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64; im…...
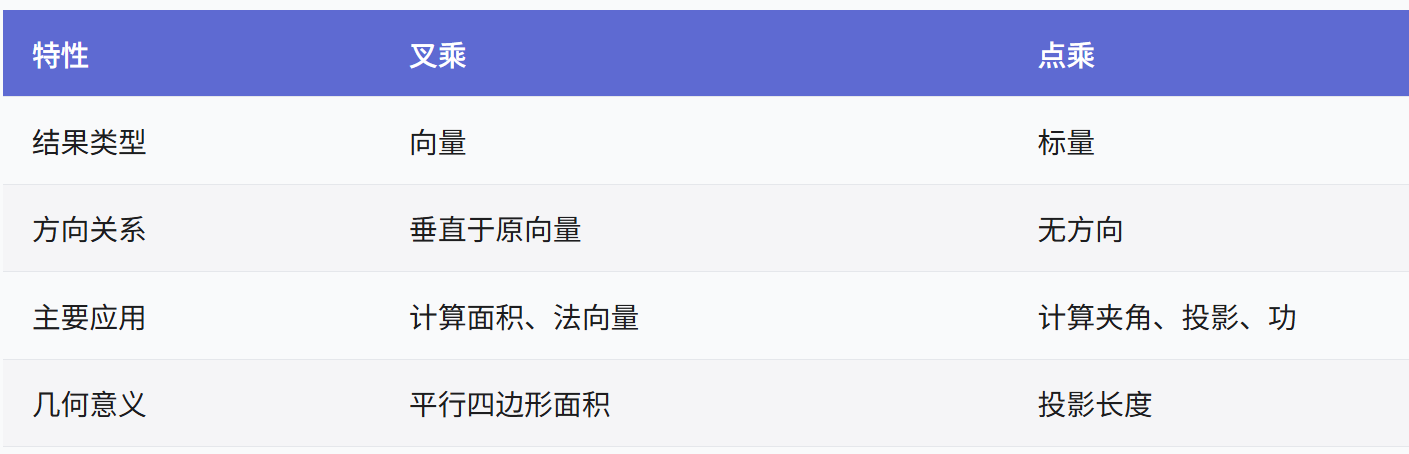
向量几何的二元性:叉乘模长与内积投影的深层联系
在数学与物理的空间世界中,向量运算构成了理解几何结构的基石。叉乘(外积)与点积(内积)作为向量代数的两大支柱,表面上呈现出截然不同的几何意义与代数形式,却在深层次上揭示了向量间相互作用的…...
