LINUX系统CFS调度模型实现思考和仿真
关于LINUX资源调度
计算机系统中,管理资源的方式一般有两种方法,分别是时间分割和空间分割,可以通过分割硬件的相似性,让软件以一致的逻辑执行,CPU运行特点是在时刻点A和时刻B运行机制是一样的,不同的只是执行现场,可以看作是在时间上有对称性的一种资源,比较适合的管理方法就是分割时间。而对于内存这种资源,不同时刻点的数据是不可预期的,在时间尺度上没有相似性,但是在空间尺度上,A区和B区的晶体管作用基本上是一样的,只是空间范围的起始不同,就比较适合使用空间分割管理。
所以,在操作系统实现中,对于CPU分割时间的管理方式就是任务调度,而对于内存这种进行空间管理的手段就是BUDDY系统。
CPU是否能在空间维度上管理呢?或者内存是否可以在时间维度上进行管理呢?应该是可以的,比如CPU的多核和SMT/SMP设计,就是物理上配置了多组处理器或者流水线资源,实现空间维度的扩展。所以,运行LINUX系统的当代处理器,既支持时分,也支持空分管理,统统属于调度范畴。
那么内存在时间维度上管理的例子呢?或许LINUX系统中的内存交换机制可以看作内存在时间管理上的一个实现,为了在有限的内存提供尽量多的运行进程带宽,LINUX支持在内存紧张的时刻,将匿名页面交换到外部磁盘上,在需要的时候在再交换回来,实现对物理内存页面的分时复用。所以同CPU管理一样,LINUX系统对物理内存的管理也同时支持时分和空分。
CFS调度和优先级队列调度的区别
LINUX内核同时支持CFS调度和优先级队列调度,CFS调度算法用在选择SCHED_NORMAL策略的进程上,而内核支持的SCHED_RR实时调度策略则采用优先级队列的方式调度下一个要运行的进程。
至于这两种调度策略在内核中的区别,个人理解主要体现在对“优先级”的理解上。对于优先级队列这种方式来说,优先级的高低是选择下一个运行进程的唯一标准,在占有CPU这件事情上,高优先级的进程具有绝对的优先权,所以只要有高优先级的进程存在,低优先级进程永远没有执行的机会,所以会有线程饥饿情况的发生。
CFS调度策略对“优先级”的理解则不同,对于CFS调度策略来说,优先级只是代表进程在时间这个资源池中占据的“比重”或者“份数”,而并不是一种绝对的优先权。所以即便就绪队列中存在优先级很低的线程,但是仍然能够有一定的“比重”获取CPU。
所以,对于优先级队列来说,它的调度策略为:
对于CFS调度算法来说,它的调度策略是选择距离执行到“预期比重”进度最慢的任务。需要有一种指标来衡量这种进度,同样的执行时间,进度增量和权重成反比,权重越大,进度增量应该越慢。
假设有两个进程的权重为W1,W2, W1 < W2, 选择W1作为其他任务的对照基准:
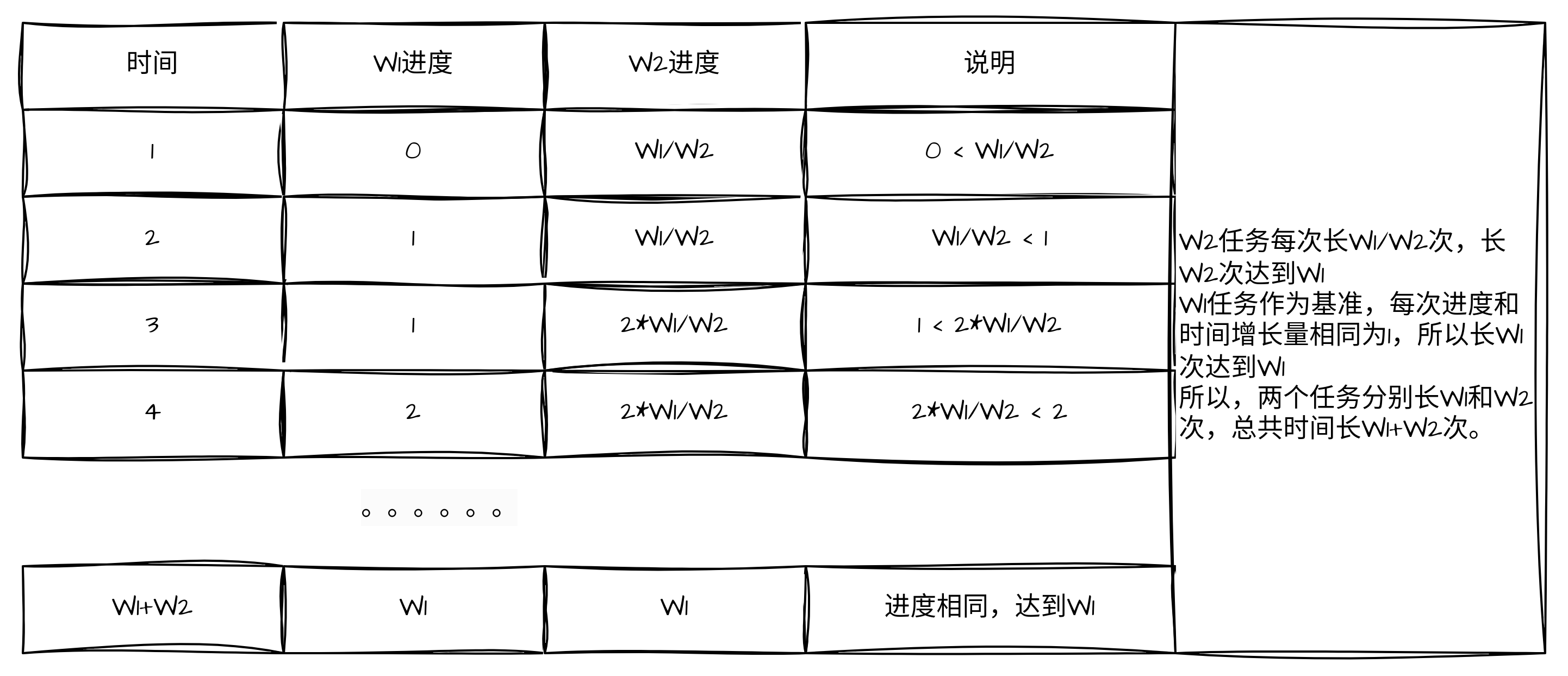
以两个权重分别为2和5的线程举例,按照CFS调度,其调度过程中进度变化如下表所示,进度最终得到相同。
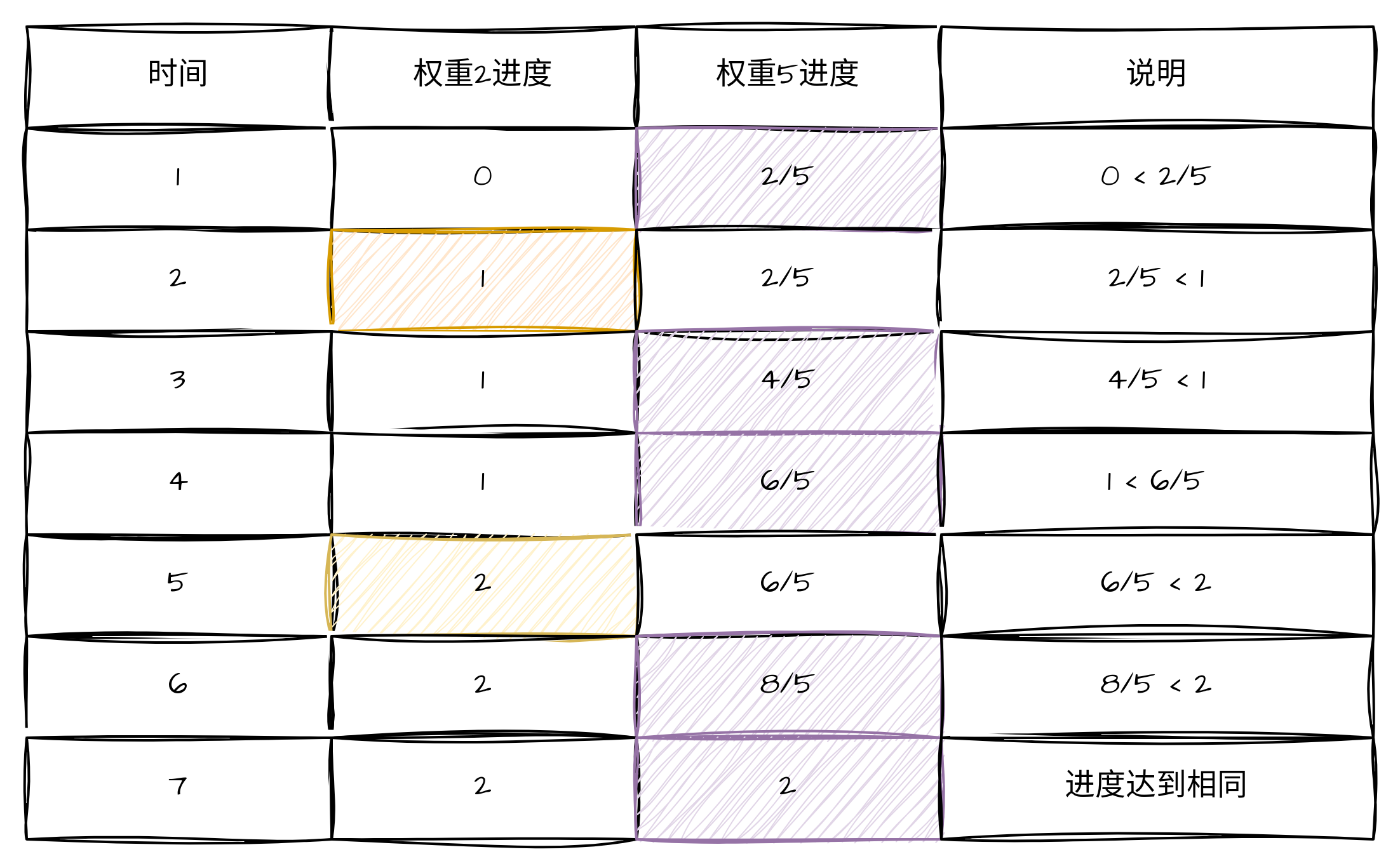
所以,CFS调度算法保证的是,在持续调度的过程中,所有任务的执行进度和参照任务保持一致,其中参照任务是任意指定的,一般选择被大多数线程使用的任务权重作为参考基准,这样在计算过程中,比例引子为1,时间增量和进度增量相同,便于计算。
在LINUX内核调度器中,有一个专有名字表示进度指标,叫做虚拟时间。观察上表可以看到对于高优先级进程,由于其权重较大,因此它的虚拟时间是按照比例缩小的,也就是说,基准权重的时间和正常时间流逝相同,权重大于基准始终的任务,其时间流逝会变慢,CFS调度器会有限选择虚拟时间最慢的线程进行调度,所以高权重的任务才有更多的运行机会。对于权重低于基准权重的低优先级任务来说,前时间流逝会比正常的时间更快,这样,它只要执行较少的时间就可以满足对进度的要求,这样,在一个完整的调度周期内(队列中所有进程都得到一次调度的时间,比如上表中的W1+W2),每个任务都有执行的机会,进入尽量在调度周期结束后对齐虚拟时间。
之所以说是尽量,是因为内核中的调度点并不一定恰好在被权重整除的整数单位上,在一个DELTA TIME中,总会以有进程比预期多执行一会儿,获得了较多的虚拟时间增量,而其它进程少执行了一些。这就需要在下一个调度周期内进行补偿和奖励那些少运行的线程。因为调度周期是有限的,而CFS调度能够保证每个调度周期内每个任务都有机会执行,误差只会在不对齐的调度时刻出现,所以任务的虚拟时间总体上不会相差太大,CFS调度是一个不断追求公平的动态的过程,它实现了程序上的公平,并通过动态纠偏保证了结果的公平。
下面是参考内核CFS调度算法实现的算法模型仿真程序,分别使用红黑数和链表两种方式管理任务队列,支持动态添加任务:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <float.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#include "rbtree.h"#define CFS_USE_RB_TREE
// A CFS Scheduler CModel.
#define DBG(fmt, ...) do { printf("%s line %d, "fmt, __func__, __LINE__, ##__VA_ARGS__); } while (0)
#define assert(expr) \if (!(expr)) { \printf("Assertion failed! %s,%s,%s,line=%d\n",\#expr,__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \while(1); \}static pthread_mutex_t cfs_mutex;
double min_vruntime = 0.0f;
void update_min_vruntime(double vruntime)
{min_vruntime = vruntime;
}
/** Nice levels are multiplicative, with a gentle 10% change for every* nice level changed. I.e. when a CPU-bound task goes from nice 0 to* nice 1, it will get ~10% less CPU time than another CPU-bound task* that remained on nice 0.** The "10% effect" is relative and cumulative: from _any_ nice level,* if you go up 1 level, it's -10% CPU usage, if you go down 1 level* it's +10% CPU usage. (to achieve that we use a multiplier of 1.25.* If a task goes up by ~10% and another task goes down by ~10% then* the relative distance between them is ~25%.)*/
const double sched_prio_to_weight[40] = {
#if 1/* -20 */ 88761, 71755, 56483, 46273, 36291,/* -15 */ 29154, 23254, 18705, 14949, 11916,/* -10 */ 9548, 7620, 6100, 4904, 3906,/* -5 */ 3121, 2501, 1991, 1586, 1277,/* 0 */ 1024, 820, 655, 526, 423,/* 5 */ 335, 272, 215, 172, 137,/* 10 */ 110, 87, 70, 56, 45,/* 15 */ 36, 29, 23, 18, 15,
#else/* -20 */ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,/* -15 */ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,/* -10 */ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,/* -5 */ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,/* 0 */ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,/* 5 */ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,/* 10 */ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,/* 15 */ 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,
#endif
};typedef struct sched_entity {struct rb_node node;int prio;int pid;double weight;double vruntime;double realtime;int ctx_switch;int on_rq;
} sched_entity_t;struct rb_root cfs_root_tree = RB_ROOT;
int sched_period(void)
{return rand() % 10 + 1;
}#define MAX_ENTRY 80
//#define SCHED_PERIOD 100
#define SCHED_PERIOD sched_period()
static sched_entity_t *tasks;// https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/673572911
// in linux kernel, cfs_rq->load used for statistic the total
// weight in rq, refer update_load_add / update_load_sub.
double caculate_total_weight(void)
{double total = 0.0;
#if 1struct rb_node *node;sched_entity_t *task;for (node = rb_first(&cfs_root_tree); node; node = rb_next(node)) {task = rb_entry(node, sched_entity_t, node);total += task->weight;}
#elseint i;for (i = 0; i < MAX_ENTRY; i ++) {total += tasks[i].weight;}
#endifreturn total;
}double caculate_realtime(int task)
{double real = 0.0;real = SCHED_PERIOD * tasks[task].weight / caculate_total_weight();//printf("%s line %d, real %f.\n", __func__, __LINE__, real);return real;
}double caculate_vruntime(sched_entity_t *task, int deltatime)
{double vruntime = 0.0;vruntime = deltatime * sched_prio_to_weight[20] / task->weight ;//printf("%s line %d, vruntime %f.\n", __func__, __LINE__, vruntime);return vruntime;
}#define MAX_TICKS_TEST 100000000UL
double vruntime_total(unsigned long worldtime)
{return worldtime * sched_prio_to_weight[20] / caculate_total_weight();
}double realtime_total(sched_entity_t *task, unsigned long worldtime)
{
#if 1return worldtime * task->weight / caculate_total_weight();
#elsereturn vruntime_total(worldtime) * task->weight / sched_prio_to_weight[20];
#endif
}static int compare_prio(sched_entity_t *task1, sched_entity_t *task2)
{
#if 0if (task1->vruntime < task2->vruntime) {// task1 prior than task2.return -1;} else if (task1->vruntime > task2->vruntime) {// task2 prior than task1.return 1;} else {if (task1->weight > task2->weight) {return -1;} else {// task2 prior than task1.return 1;}}
#elsedouble res = (task1->vruntime == task2->vruntime) ? task1->weight - task2->weight : task2->vruntime - task1->vruntime;return res > 0.0f ? -1 : 1;
#endif
}static int cfs_rq_delete(struct rb_root *root, sched_entity_t *task)
{rb_erase(&task->node, root);return !RB_EMPTY_ROOT(root);
}static int cfs_rq_insert(struct rb_root *root, sched_entity_t *task)
{int ret;struct rb_node **tmp = &(root->rb_node), *parent = NULL;/* Figure out where to put new node */while (*tmp) {sched_entity_t *this = rb_entry(*tmp, sched_entity_t, node);parent = *tmp;ret = compare_prio(task, this);if (ret < 0)tmp = &((*tmp)->rb_left);else if (ret > 0)tmp = &((*tmp)->rb_right);elsereturn -1;}/* Add new node and rebalance tree. */rb_link_node(&task->node, parent, tmp);rb_insert_color(&task->node, root);return 0;
}static void cfs_rq_destroy(struct rb_root *root)
{struct rb_node *node, *next;sched_entity_t *task;node = rb_first(root);while (node) {next = rb_next(node);task = rb_entry(node, sched_entity_t, node);rb_erase(node, root);node = next;}if (!RB_EMPTY_ROOT(root)) {printf("%s line %d, rb is not empty.\n", __func__, __LINE__);}return;
}void print_rbtree(struct rb_root *tree)
{struct rb_node *node;sched_entity_t *task;for (node = rb_first(tree); node; node = rb_next(node)) {task = rb_entry(node, sched_entity_t, node);printf("%s line %d, task(%d) prio %d,weight %f vruntime %f, on rq %d.\n",__func__, __LINE__, task->pid, task->prio, task->weight, task->vruntime, task->on_rq);}return;
}void init_cfs_rbtree(void)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < MAX_ENTRY; i ++) {tasks[i].on_rq = 1;cfs_rq_insert(&cfs_root_tree, &tasks[i]);}print_rbtree(&cfs_root_tree);return;
}#ifdef CFS_USE_RB_TREE
// O(logn) scheduler base on rbtree.
sched_entity_t *schedule(void)
{struct rb_node *node;sched_entity_t *task;node = rb_first(&cfs_root_tree);task = rb_entry(node, sched_entity_t, node);return task;
}#else
// A O(n) linear scheuler impl.
sched_entity_t *schedule(void)
{int i;int taskid = -1;double minruntime = DBL_MAX;// schedule policy:// 1.first find the task with the minum vruntime.// 2.if multiple task the the same minum vruntime, then// select the weighter one.for (i = 0; i < MAX_ENTRY; i ++) {if (minruntime > tasks[i].vruntime) {minruntime = tasks[i].vruntime;taskid = i;} else if (minruntime == tasks[i].vruntime) {if (tasks[i].weight > tasks[taskid].weight) {taskid = i;}}}return &tasks[taskid];
}
#endifdouble list_task_info(unsigned long worldtime)
{double total = 0.0;printf("==================================================================================================================================================================\n");
#if 1struct rb_node *node;sched_entity_t *task;for (node = rb_first(&cfs_root_tree); node; node = rb_next(node)) {task = rb_entry(node, sched_entity_t, node);total += task->realtime;printf("task(pid%d) vuntime %f, realtime %f, prio %d, weight %f, switches %d, ideal real time %f.\n",task->pid, task->vruntime, task->realtime, task->prio, task->weight, task->ctx_switch,realtime_total(task, worldtime));}
#elseint i;for (i = 0; i < MAX_ENTRY; i ++) {double ratio = 0.0;if (i > 0) {ratio = (tasks[i - 1].realtime - tasks[i].realtime) / tasks[i].realtime;}total += tasks[i].realtime;printf("task %d(pid%d) vuntime %f, realtime %f, prio %d, weight %f, incretio %f, switches %d, ideal real time %f.\n",i, tasks[i].pid, tasks[i].vruntime, tasks[i].realtime, tasks[i].prio, tasks[i].weight, ratio * 100, tasks[i].ctx_switch,realtime_total(&tasks[i], worldtime));}
#endifdouble staticis(void);printf("fangcha %f.\n", staticis());printf("==================================================================================================================================================================\n");return total;
}static void *fork_thread(void *arg)
{sched_entity_t *task;unsigned long *pworldtime = (unsigned long *)arg;static unsigned int pid = MAX_ENTRY;int i;while (1) {task = malloc(sizeof(sched_entity_t));memset(task, 0x00, sizeof(sched_entity_t));i = rand() % 40;pthread_mutex_lock(&cfs_mutex);task->prio = -20 + i;task->weight = sched_prio_to_weight[i];//task->vruntime = vruntime_total(*pworldtime) +1.5f;task->vruntime = min_vruntime + 1.5f;task->realtime = 0;task->ctx_switch = 0;task->pid = pid ++;task->on_rq = 0;cfs_rq_insert(&cfs_root_tree, task);task->on_rq = 1;pthread_mutex_unlock(&cfs_mutex);sleep(1);}return NULL;
}static void *exit_thread(void *arg)
{unsigned long *pwordtime = (unsigned long *)arg;while (1) {sleep(1);}return NULL;
}double staticis(void)
{double statics = 0.0f;double average = 0.0f;double total = 0.0f;int count = 0;struct rb_node *node;sched_entity_t *task;for (node = rb_first(&cfs_root_tree); node; node = rb_next(node)) {task = rb_entry(node, sched_entity_t, node);total += task->vruntime;count ++;}average = total / count;for (node = rb_first(&cfs_root_tree); node; node = rb_next(node)) {task = rb_entry(node, sched_entity_t, node);statics += (average - task->vruntime) * (average - task->vruntime);}return sqrt(statics / count);
}
int main(void)
{int i;unsigned long ticks;double total = 0.0;unsigned long worldtime = 0;pthread_t t1, t2;pthread_mutex_init(&cfs_mutex, NULL);tasks = malloc(sizeof(sched_entity_t) * MAX_ENTRY);memset(tasks, 0x00, sizeof(sched_entity_t) * MAX_ENTRY);if (!tasks) {printf("%s line %d, fatal errro, alloc failure.\n",__func__, __LINE__);return -1;}srand((unsigned int)time(0));for (i = 0; i < MAX_ENTRY; i ++) {tasks[i].prio = -20 + i % 40;tasks[i].weight = sched_prio_to_weight[i % 40];tasks[i].vruntime = 0;tasks[i].realtime = 0;tasks[i].ctx_switch = 0;tasks[i].pid = i;tasks[i].on_rq = 0;}#ifdef CFS_USE_RB_TREEinit_cfs_rbtree();
#endif// should be first.printf("%s line %d, first schedule select %ld.\n", __func__, __LINE__, schedule() - tasks);pthread_create(&t1, NULL, fork_thread, &worldtime);pthread_create(&t2, NULL, exit_thread, &worldtime);for (ticks = 0; /* ticks < MAX_TICKS_TEST */ 1; ticks ++) {double deltatime, vruntime;sched_entity_t *task;pthread_mutex_lock(&cfs_mutex);task = schedule();#ifdef CFS_USE_RB_TREEcfs_rq_delete(&cfs_root_tree, task);task->on_rq = 0;#endifdeltatime = SCHED_PERIOD;vruntime = caculate_vruntime(task, deltatime);task->vruntime += vruntime;task->realtime += deltatime;task->ctx_switch ++;worldtime += deltatime;update_min_vruntime(task->vruntime);#ifdef CFS_USE_RB_TREE// USE dequeue and enqueue to trigger the reorder of cfs rbtree ready queue.// this also the same in linux kernel, refer put_prev_entity(enqueue) and set_next_task(dequeue)// the only differenct is in linux kenrel the on_rq still keep no matter put_prev_entity/set_next_entity// involation.cfs_rq_insert(&cfs_root_tree, task);task->on_rq = 1;
#endifif (ticks % 1000 == 0) {list_task_info(worldtime);}pthread_mutex_unlock(&cfs_mutex);}pthread_mutex_lock(&cfs_mutex);total = list_task_info(worldtime);assert(total == worldtime);printf("vruntime %f.\n", vruntime_total(worldtime));pthread_mutex_unlock(&cfs_mutex);pthread_join(t1, NULL);pthread_join(t2, NULL);#ifdef CFS_USE_RB_TREEprint_rbtree(&cfs_root_tree);cfs_rq_destroy(&cfs_root_tree);
#endiffree(tasks);return 0;
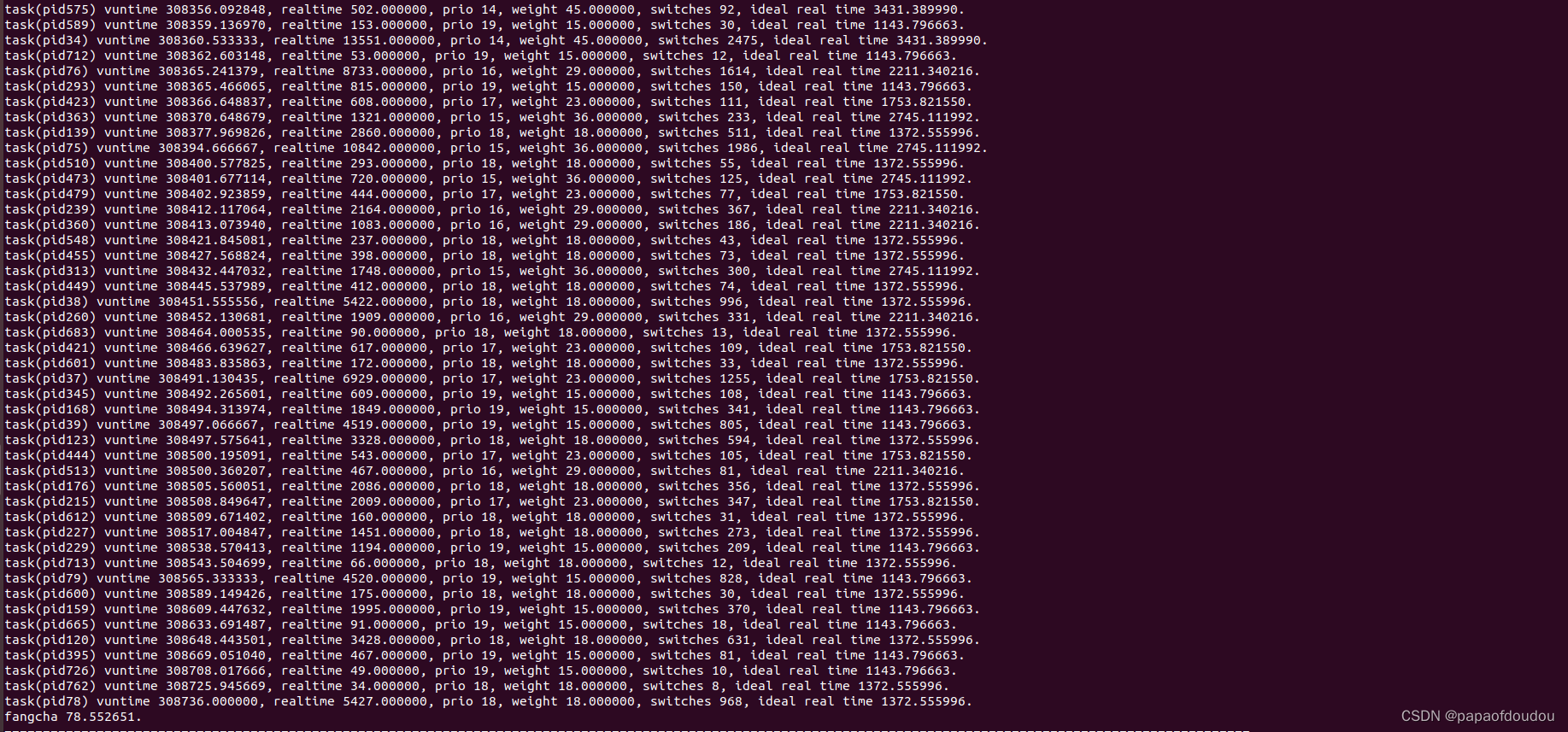
}仿真结果,按照CFS算法调度大约1000个进程,VRUNTIME的方差始终控制在70左右,下面截图中显示所有进程的VRUNTIME集中在[308177.014345,308736.000000],对照方差,VRUNTIME表示的所有任务的执行进度是非常集中的,说明CFS的调度策略确实照顾到了所有优先级的进程,使大家的执行进度基本保持在一个动态的一致范围之内。
参考文章
(五)Linux进程调度-CFS调度器
吐血整理 | 肝翻 Linux 进程调度所有知识点
结束
相关文章:

LINUX系统CFS调度模型实现思考和仿真
关于LINUX资源调度 计算机系统中,管理资源的方式一般有两种方法,分别是时间分割和空间分割,可以通过分割硬件的相似性,让软件以一致的逻辑执行,CPU运行特点是在时刻点A和时刻B运行机制是一样的,不同的只是…...
兑换码生成算法
兑换码生成算法 兑换码生成算法1.兑换码的需求2.算法分析2.重兑校验算法3.防刷校验算法 3.算法实现 兑换码生成算法 兑换码生成通常涉及在特定场景下为用户提供特定产品或服务的权益或礼品,典型的应用场景包括优惠券、礼品卡、会员权益等。 1.兑换码的需求 要求如…...

Vue框架介绍简介
Vue.js,通常简称为Vue,是一个用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架。它发布于2014年2月,由Evan You设计并开发。Vue被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用,这使得开发者可以根据项目的需求灵活地使用Vue。无论是构建简单的轻量级应用,…...

的C++奇迹之旅:值和引用的本质效率与性能比较
文章目录 请添加图片描述 [TOC](文章目录) 📝引用# 🌠引用概念**引用**不是新定义一个变量,而是给**已存在变量取了一个别名**,编译器不会为引用变量开辟内存空间,它和它引用的变量共用同一块内存空间。>定义&#…...
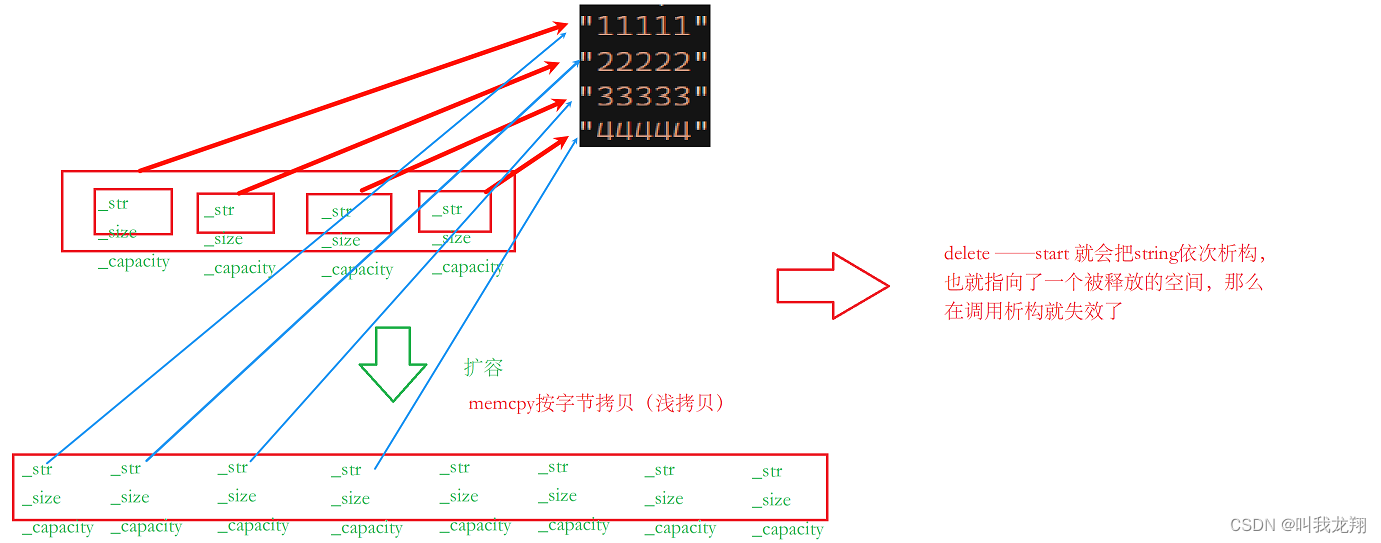
【C++】vector问题解决(非法的间接寻址,迭代器失效 , memcpy拷贝问题)
送给大家一句话: 世界在旋转,我们跌跌撞撞前进,这就够了 —— 阿贝尔 加缪 vector问题解决 1 前言2 迭代器区间拷贝3 迭代器失效问题4 memcpy拷贝问题 1 前言 我们之前实现了手搓vector,但是当时依然有些问题没有解决ÿ…...

风控系统之普通规则条件,使用LiteFlow实现
个人博客:无奈何杨(wnhyang) 个人语雀:wnhyang 共享语雀:在线知识共享 Github:wnhyang - Overview 提要 参考:智能风控筑基手册:全面了解风控决策引擎 前面有可配置输入参数的接…...

在一套Dockerfile中完成编译和运行环境部署
大纲 解释型语言编译环境解释环境编译型语言编译环境运行环境 方法编译环境安装系统安装编译依赖下载代码特殊处理(可以忽略)编译准备(可以忽略)编译打包依赖(编译结果) 运行环境安装操作系统安装运行时依赖…...

ubuntu系统里克隆github代码到本地,提示fatal: unable to connect to github.com的解决方案
打开命令行终端生成一个新的SSH密钥对。如果你还没有SSH密钥或者想创建一个新的,可以使用以下命令: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_emailexample.com"当系统提示你“Enter a file in which to save the key”,时,…...

常见docker使用命令
#搭建镜像 “”" sudo docker build -t es_refresh:V1.20230303 . “”" #启动容器 “”" docker run -d --namepara_classify -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime -v /data/chenhw/multi_label_classification:/edb2vec -p 8066:8066 --gpus ‘“device0”’…...
Ubuntu系统中设置中文输入法的教程
1、Ubuntu介绍: (https://cn.ubuntu.com/) (Ubuntu | 全球领先的用于个人电脑、平板及手机的操作系统) Ubuntu是一款基于Debian的开源Linux操作系统,由英国Canonical公司赞助支持的全球性社区共同开发。U…...
练习14 Web [极客大挑战 2019]Upload
phtml格式绕过,burp修改content-type绕过,常见的文件上传存放目录名 题目就叫upload,打开靶机 直接上传一个图片格式的一句话木马,返回如下: 提交练习5和9中的两种可以执行图片格式php代码的文件,修改con…...
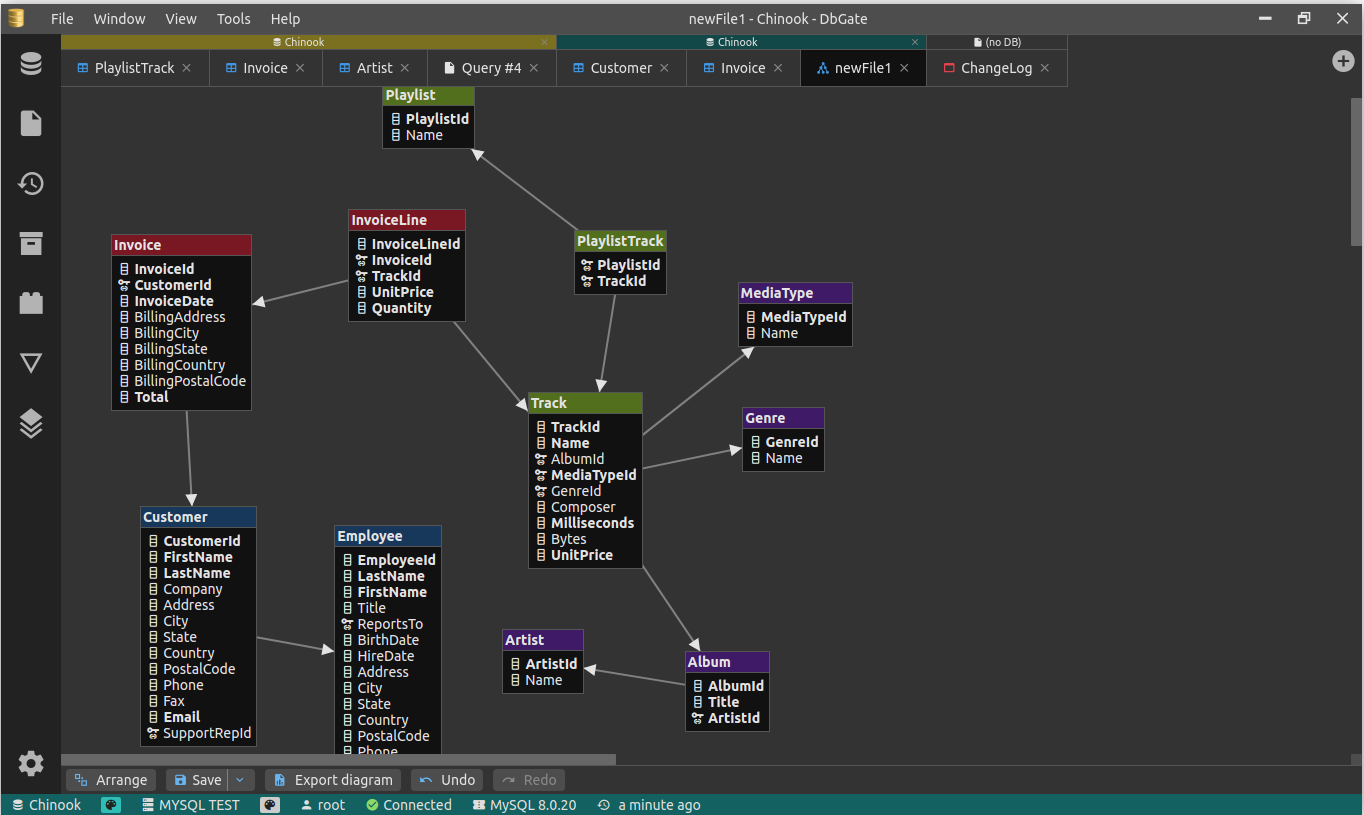
3.6k star, 免费开源跨平台的数据库管理工具 dbgate
3.6k star, 免费开源跨平台的数据库管理工具 dbgate 分类 开源分享 项目名: dbgate -- 免费开源跨平台的数据库管理工具 Github 开源地址: GitHub - dbgate/dbgate: Database manager for MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, MongoDB, SQLite and others. Runs under…...

2024.3.2力扣每日一题——受限条件下可到达节点的数目
2024.3.2 题目来源我的题解方法一 深度优先搜索方法二 并查集 题目来源 力扣每日一题;题序:2368 我的题解 方法一 深度优先搜索 使用深度优先搜索实现,在搜索过程中根据restricted进行截停。 时间复杂度:O(n) 空间复杂度&#…...
在云端遇见雨云:一位服务器寻觅者的指南
引言:寻觅一座云端归宿 当我踏入数字世界的边缘,带着对网络的探索与期待,我迫切需要一座安全可靠的数字栖息地。云计算技术正如一场魔法般的变革,而在这片广袤的云端中,雨云就像是一位友善的向导,引领我穿越…...
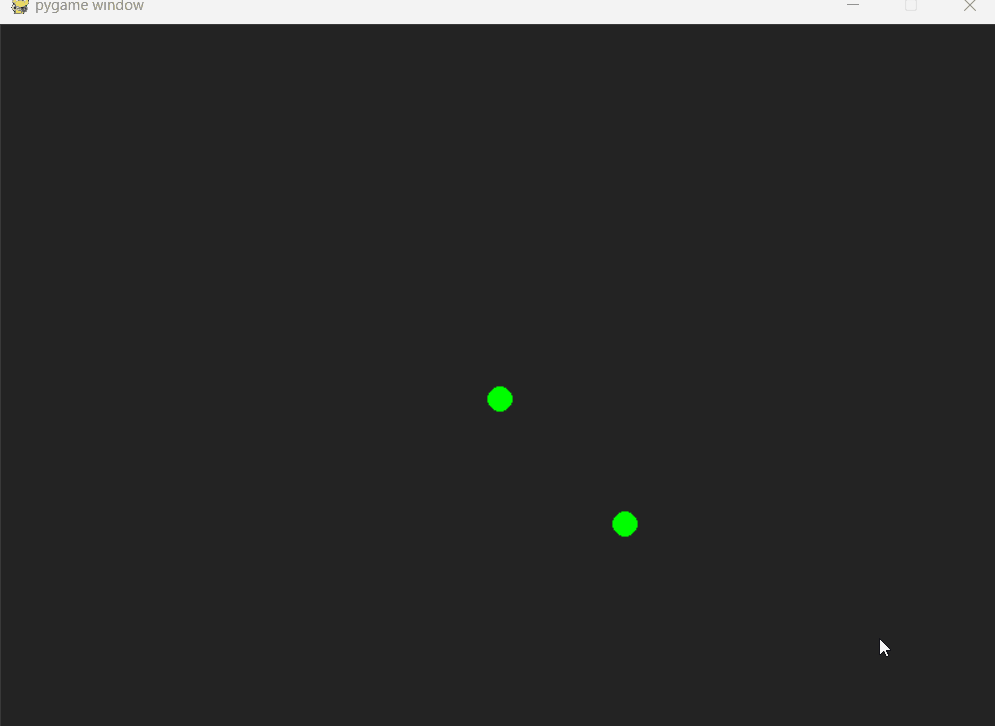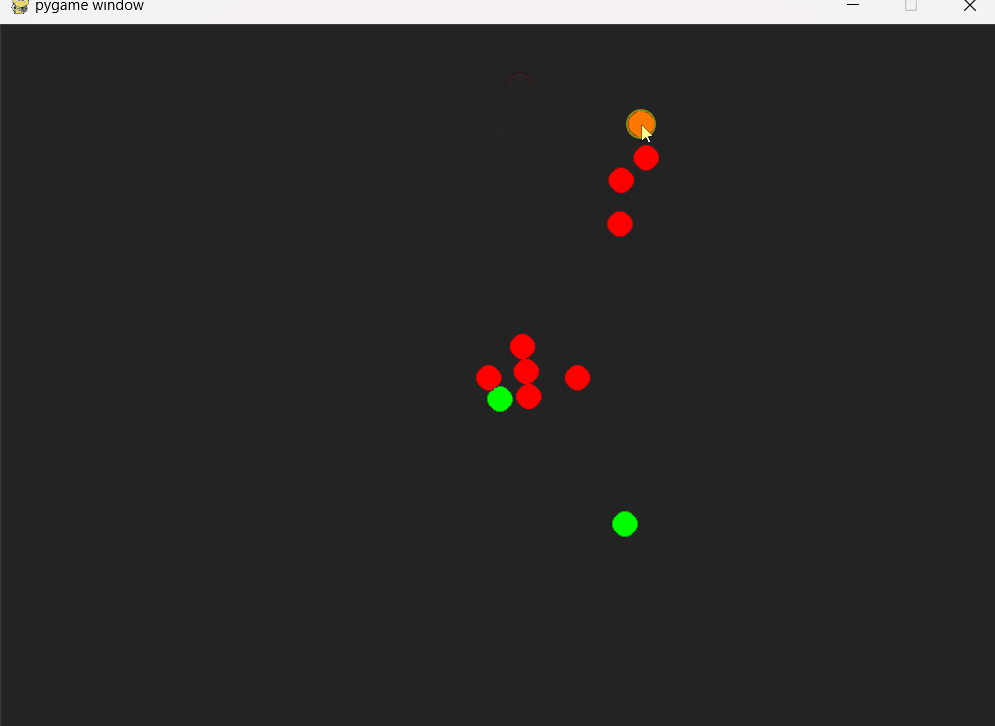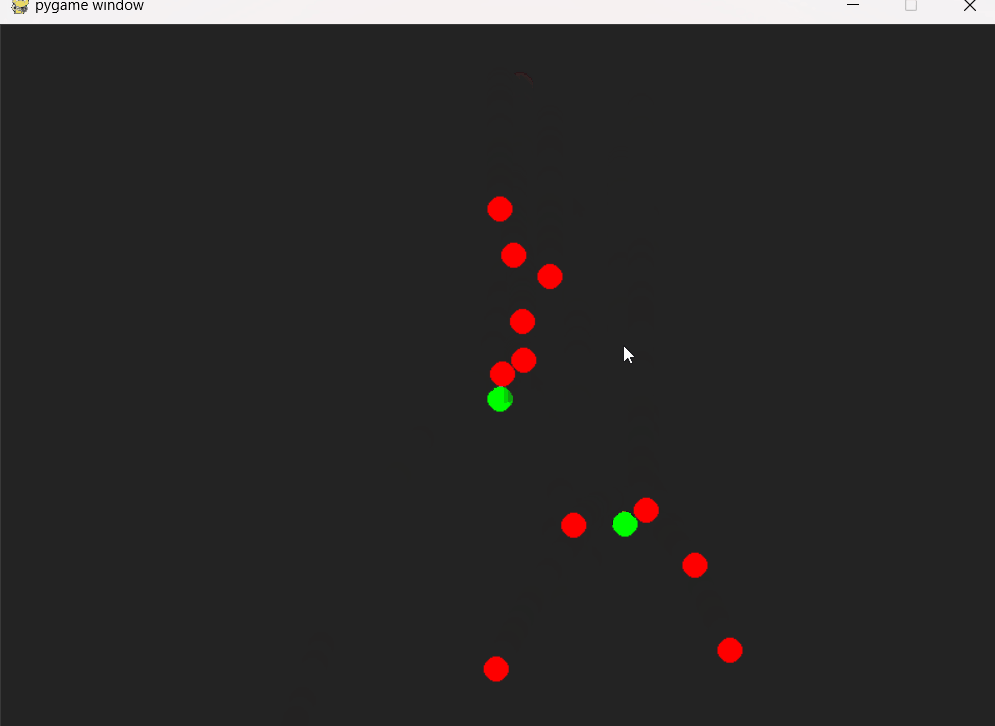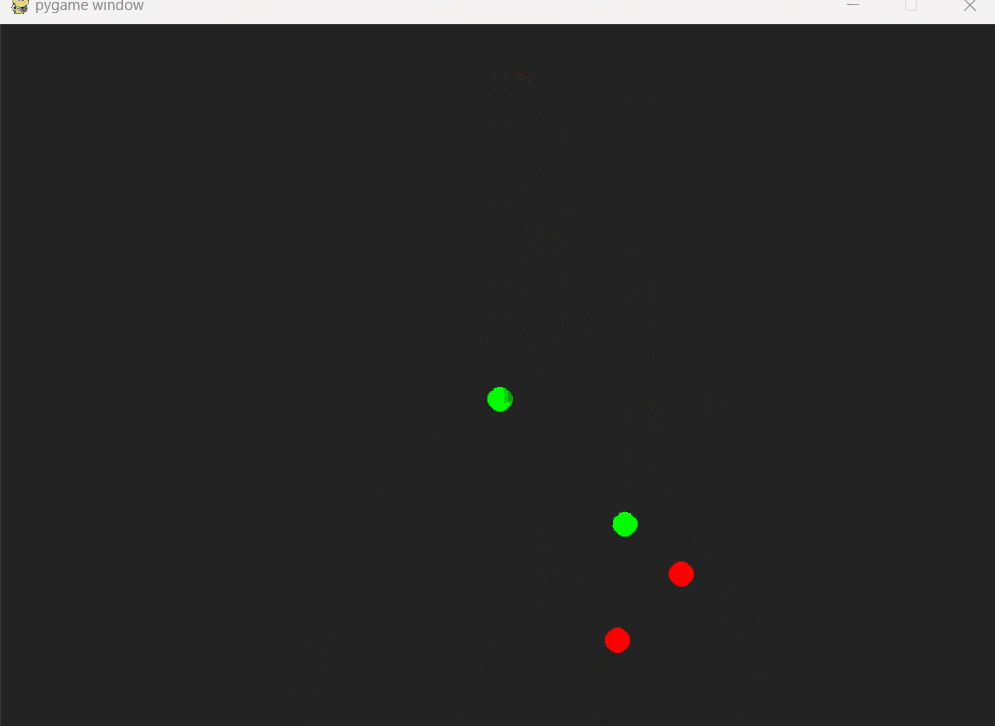
Pygame基础10-物理模拟
PyMunk PyMunk是一个模拟物理的库。 注意,PyMunk只是进行物理模拟,不包含可视化的功能。如果需要可视化,可使用pygame等库。 可用pip安装pymunk pip install pymunk pymunk中的概念: space: 物理空间。 包含gravity 模…...

蓝桥杯 --- 日期问题模板
目录 1.如何判断闰年 2.如何遍历当前年份的每一天 3.如果想要输出某一年某一天到某一年某一天之间一共有多少天。 4.精确到具体周几到周几的问题分析 5.如何直接通过一层for循环枚举年月日 习题: 蓝桥杯竞赛特别喜欢考日期问题,今天给大家分享一下…...

Java 处理Mysql获取树形的数据
Mysql数据: 代码如下: Entity: Data Accessors(chain true) public class Region {private BigInteger id;//名称private String name;//父idprivate BigInteger parentId;private List<Region> children;private Integer createTim…...

前端三剑客 —— CSS ( 坐标问题 、定位问题和图片居中 )
前期内容回顾: 1.常见样式 text-shadow x轴 y轴 阴影的模糊程度 阴影的颜色 box-shadow border-radio 实现圆角 margin 内边距 padding 外边距 background 2.特殊样式 媒体查询:media 自定义字体:font-face { font-family:自定义名称&#…...

向量数据库 | AI时代的航道灯塔
向量数据库 | AI时代的航道灯塔 什么是向量检索服务拍照搜商品 你使用过向量数据库吗?使用体验?为什么向量数据库能借由大模型引起众多关注向量数据库在当前AI热潮中是昙花一现,还是未来AI时代的航道灯塔? 今天的话题主要是讨论向…...

Linux中的conntrack命令深入解析
在Linux网络管理和监控领域,conntrack命令是一个强大的工具,它提供了对netfilter连接跟踪系统的直接访问🔍。这篇文章将深入探讨conntrack的由来、底层原理、参数意义,以及其常见用法,并对返回结果的每个字段进行详细解…...

conda相比python好处
Conda 作为 Python 的环境和包管理工具,相比原生 Python 生态(如 pip 虚拟环境)有许多独特优势,尤其在多项目管理、依赖处理和跨平台兼容性等方面表现更优。以下是 Conda 的核心好处: 一、一站式环境管理:…...

基于大模型的 UI 自动化系统
基于大模型的 UI 自动化系统 下面是一个完整的 Python 系统,利用大模型实现智能 UI 自动化,结合计算机视觉和自然语言处理技术,实现"看屏操作"的能力。 系统架构设计 #mermaid-svg-2gn2GRvh5WCP2ktF {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-…...

TDengine 快速体验(Docker 镜像方式)
简介 TDengine 可以通过安装包、Docker 镜像 及云服务快速体验 TDengine 的功能,本节首先介绍如何通过 Docker 快速体验 TDengine,然后介绍如何在 Docker 环境下体验 TDengine 的写入和查询功能。如果你不熟悉 Docker,请使用 安装包的方式快…...

Java - Mysql数据类型对应
Mysql数据类型java数据类型备注整型INT/INTEGERint / java.lang.Integer–BIGINTlong/java.lang.Long–––浮点型FLOATfloat/java.lang.FloatDOUBLEdouble/java.lang.Double–DECIMAL/NUMERICjava.math.BigDecimal字符串型CHARjava.lang.String固定长度字符串VARCHARjava.lang…...

将对透视变换后的图像使用Otsu进行阈值化,来分离黑色和白色像素。这句话中的Otsu是什么意思?
Otsu 是一种自动阈值化方法,用于将图像分割为前景和背景。它通过最小化图像的类内方差或等价地最大化类间方差来选择最佳阈值。这种方法特别适用于图像的二值化处理,能够自动确定一个阈值,将图像中的像素分为黑色和白色两类。 Otsu 方法的原…...
Mac软件卸载指南,简单易懂!
刚和Adobe分手,它却总在Library里给你写"回忆录"?卸载的Final Cut Pro像电子幽灵般阴魂不散?总是会有残留文件,别慌!这份Mac软件卸载指南,将用最硬核的方式教你"数字分手术"࿰…...

Android15默认授权浮窗权限
我们经常有那种需求,客户需要定制的apk集成在ROM中,并且默认授予其【显示在其他应用的上层】权限,也就是我们常说的浮窗权限,那么我们就可以通过以下方法在wms、ams等系统服务的systemReady()方法中调用即可实现预置应用默认授权浮…...
:邮件营销与用户参与度的关键指标优化指南)
精益数据分析(97/126):邮件营销与用户参与度的关键指标优化指南
精益数据分析(97/126):邮件营销与用户参与度的关键指标优化指南 在数字化营销时代,邮件列表效度、用户参与度和网站性能等指标往往决定着创业公司的增长成败。今天,我们将深入解析邮件打开率、网站可用性、页面参与时…...

LOOI机器人的技术实现解析:从手势识别到边缘检测
LOOI机器人作为一款创新的AI硬件产品,通过将智能手机转变为具有情感交互能力的桌面机器人,展示了前沿AI技术与传统硬件设计的完美结合。作为AI与玩具领域的专家,我将全面解析LOOI的技术实现架构,特别是其手势识别、物体识别和环境…...

实战三:开发网页端界面完成黑白视频转为彩色视频
一、需求描述 设计一个简单的视频上色应用,用户可以通过网页界面上传黑白视频,系统会自动将其转换为彩色视频。整个过程对用户来说非常简单直观,不需要了解技术细节。 效果图 二、实现思路 总体思路: 用户通过Gradio界面上…...
