LVGL V8 代码细读——极致的链表使用
极致的链表的使用
- 序章碎碎念
- 从redis源码里掏出来的adlist
- 极致的精简的list.h
- lvgl对链表的巧思lv_ll
- 尾记
序章碎碎念
对于链表,大家应该都不陌生。学过数据结构的,都知道它作为链式储存的基础,重要性不言而喻。
由于本人自动化专业,实际上不学数据结构。在大四众人考研的考研,找工作的找工作的情况下。本人在学校开始了蹭课之旅。在一场和大二学弟们同堂听课的过程中,这里也第一次遇见本次的主题——链表。
早期学习链表的时候,实际上对malloc和free是几乎没有理解的。老师在讲解的时候,就轻描淡写的一带而过,这里如果心里没有对它有初步的认识,很容易搞不清楚情况。
这里在序言中,我就简单的对基础比较差的读者介绍一下这两位后续常用的东西——malloc和free。
// 这是包含我们需要使用的malloc和free函数的头文件
#include <stdlib.h> // 这里是主角之一,malloc
// 首先,malloc本身不是单词,是memory allocation缩写
// 从功能上,malloc会在运行时动态申请内存大小为size字节的内存,然后返回给你这段内存的首地址
// 额外要注意的是,malloc申请的内存只能通过free释放
// 如果申请失败(内存不足等)则返回NULL
void* malloc(size_t size) // 这里是另一位主角,free
// free比较简单,它会通过指针释放掉之前申请的内存
// 那么有问题,如果值传入指针,free函数如何知道自己释放多大内存?
// 这个实际上在malloc的时候,会多申请一块出来用于存放大小信息,一边free的时候能够访问
// 有兴趣的可以探究一下这个问题
void free(void* ptr)| 数组 | malloc+free |
|---|---|
| 声明时申请内存,超过使用域则由系统自动回收(主打一个省心) | 自己申请,自己释放(主打一个自由) |
| 编译初期固定大小(除c99标准下可变数组) | 编译过程中可以通过变量动态申请大小 |
| 随便申请释放,无所畏惧 | 小内存频繁申请释放会产生内存碎片 |
| 不怕产生内存泄漏 | 当内存未释放,但是未有任何指针引用它的时候,会产生内存泄漏 |
| 局部变量出作用域就被释放,有时候会导致野指针 | 内存申请后就算出函数也不会消失,必须等待你释放 |
既然讲到这里,其实基本认为读者已经对指针有所了解了。如果再往下科普,这个话题就越说越跑偏了。
回到这个话题来,初学者的链表之旅会较为容易。更多的精力可能会放到研究链表如何增删改查。学到的也是以简单的单向链表为主:
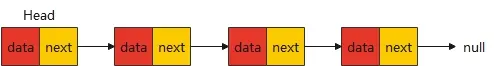
在学习的时候,咱们看到最多的链表也是形如下面的结构体:
struct Node {int data; // 数据struct Node* next; // 指向下一个节点的指针
};
然后每次都是手撸创建、销毁、增删改查。对于新手的我们来说,很难做到封装成模块使用。
于是乎,漫长的时间里,我几乎都不想用这玩意。手撸一套太麻烦了。我开始寻找有无能复用的链表模块。
从redis源码里掏出来的adlist
某个偶然的机会,我从一篇文章里看到了C语言写的数据库 redis 中的一个数据结构。正式咱们后续要说的主角:adlist。我于是乎去翻阅源码,抽丝剥茧。最终总结如下:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "adlist.h"/* Create a new list. The created list can be freed with* listRelease(), but private value of every node need to be freed* by the user before to call listRelease(), or by setting a free method using* listSetFreeMethod.** On error, NULL is returned. Otherwise the pointer to the new list. */
list *listCreate(void)
{struct list *list;if ((list = malloc(sizeof(*list))) == NULL)return NULL;list->head = list->tail = NULL;list->len = 0;list->dup = NULL;list->free = NULL;list->match = NULL;return list;
}/* Remove all the elements from the list without destroying the list itself. */
void listEmpty(list *list)
{unsigned long len;listNode *current, *next;current = list->head;len = list->len;while (len--){next = current->next;if (list->free)list->free(current->value);free(current);current = next;}list->head = list->tail = NULL;list->len = 0;
}/* Free the whole list.** This function can't fail. */
void listRelease(list *list)
{listEmpty(list);free(list);
}/* Add a new node to the list, to head, containing the specified 'value'* pointer as value.** On error, NULL is returned and no operation is performed (i.e. the* list remains unaltered).* On success the 'list' pointer you pass to the function is returned. */
list *listAddNodeHead(list *list, void *value)
{listNode *node;if ((node = malloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)return NULL;node->value = value;if (list->len == 0){list->head = list->tail = node;node->prev = node->next = NULL;}else{node->prev = NULL;node->next = list->head;list->head->prev = node;list->head = node;}list->len++;return list;
}/* Add a new node to the list, to tail, containing the specified 'value'* pointer as value.** On error, NULL is returned and no operation is performed (i.e. the* list remains unaltered).* On success the 'list' pointer you pass to the function is returned. */
list *listAddNodeTail(list *list, void *value)
{listNode *node;if ((node = malloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)return NULL;node->value = value;if (list->len == 0){list->head = list->tail = node;node->prev = node->next = NULL;}else{node->prev = list->tail;node->next = NULL;list->tail->next = node;list->tail = node;}list->len++;return list;
}list *listInsertNode(list *list, listNode *old_node, void *value, int after)
{listNode *node;if ((node = malloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)return NULL;node->value = value;if (after){node->prev = old_node;node->next = old_node->next;if (list->tail == old_node){list->tail = node;}}else{node->next = old_node;node->prev = old_node->prev;if (list->head == old_node){list->head = node;}}if (node->prev != NULL){node->prev->next = node;}if (node->next != NULL){node->next->prev = node;}list->len++;return list;
}/* Remove the specified node from the specified list.* It's up to the caller to free the private value of the node.** This function can't fail. */
void listDelNode(list *list, listNode *node)
{if (node->prev)node->prev->next = node->next;elselist->head = node->next;if (node->next)node->next->prev = node->prev;elselist->tail = node->prev;if (list->free)list->free(node->value);free(node);list->len--;
}/* Returns a list iterator 'iter'. After the initialization every* call to listNext() will return the next element of the list.** This function can't fail. */
listIter *listGetIterator(list *list, int direction)
{listIter *iter;if ((iter = malloc(sizeof(*iter))) == NULL)return NULL;if (direction == AL_START_HEAD)iter->next = list->head;elseiter->next = list->tail;iter->direction = direction;return iter;
}/* Release the iterator memory */
void listReleaseIterator(listIter *iter)
{free(iter);
}/* Create an iterator in the list private iterator structure */
void listRewind(list *list, listIter *li)
{li->next = list->head;li->direction = AL_START_HEAD;
}void listRewindTail(list *list, listIter *li)
{li->next = list->tail;li->direction = AL_START_TAIL;
}/* Return the next element of an iterator.* It's valid to remove the currently returned element using* listDelNode(), but not to remove other elements.** The function returns a pointer to the next element of the list,* or NULL if there are no more elements, so the classical usage* pattern is:** iter = listGetIterator(list,<direction>);* while ((node = listNext(iter)) != NULL) {* doSomethingWith(listNodeValue(node));* }** */
listNode *listNext(listIter *iter)
{listNode *current = iter->next;if (current != NULL){if (iter->direction == AL_START_HEAD)iter->next = current->next;elseiter->next = current->prev;}return current;
}/* Duplicate the whole list. On out of memory NULL is returned.* On success a copy of the original list is returned.** The 'Dup' method set with listSetDupMethod() function is used* to copy the node value. Otherwise the same pointer value of* the original node is used as value of the copied node.** The original list both on success or error is never modified. */
list *listDup(list *orig)
{list *copy;listIter iter;listNode *node;if ((copy = listCreate()) == NULL)return NULL;copy->dup = orig->dup;copy->free = orig->free;copy->match = orig->match;listRewind(orig, &iter);while ((node = listNext(&iter)) != NULL){void *value;if (copy->dup){value = copy->dup(node->value);if (value == NULL){listRelease(copy);return NULL;}}else{value = node->value;}if (listAddNodeTail(copy, value) == NULL){/* Free value if dup succeed but listAddNodeTail failed. */if (copy->free)copy->free(value);listRelease(copy);return NULL;}}return copy;
}/* Search the list for a node matching a given key.* The match is performed using the 'match' method* set with listSetMatchMethod(). If no 'match' method* is set, the 'value' pointer of every node is directly* compared with the 'key' pointer.** On success the first matching node pointer is returned* (search starts from head). If no matching node exists* NULL is returned. */
listNode *listSearchKey(list *list, void *key)
{listIter iter;listNode *node;listRewind(list, &iter);while ((node = listNext(&iter)) != NULL){if (list->match){if (list->match(node->value, key)){return node;}}else{if (key == node->value){return node;}}}return NULL;
}/* Return the element at the specified zero-based index* where 0 is the head, 1 is the element next to head* and so on. Negative integers are used in order to count* from the tail, -1 is the last element, -2 the penultimate* and so on. If the index is out of range NULL is returned. */
listNode *listIndex(list *list, long index)
{listNode *n;if (index < 0){index = (-index) - 1;n = list->tail;while (index-- && n)n = n->prev;}else{n = list->head;while (index-- && n)n = n->next;}return n;
}/* Rotate the list removing the tail node and inserting it to the head. */
void listRotateTailToHead(list *list)
{if (listLength(list) <= 1)return;/* Detach current tail */listNode *tail = list->tail;list->tail = tail->prev;list->tail->next = NULL;/* Move it as head */list->head->prev = tail;tail->prev = NULL;tail->next = list->head;list->head = tail;
}/* Rotate the list removing the head node and inserting it to the tail. */
void listRotateHeadToTail(list *list)
{if (listLength(list) <= 1)return;listNode *head = list->head;/* Detach current head */list->head = head->next;list->head->prev = NULL;/* Move it as tail */list->tail->next = head;head->next = NULL;head->prev = list->tail;list->tail = head;
}/* Add all the elements of the list 'o' at the end of the* list 'l'. The list 'other' remains empty but otherwise valid. */
void listJoin(list *l, list *o)
{if (o->len == 0)return;o->head->prev = l->tail;if (l->tail)l->tail->next = o->head;elsel->head = o->head;l->tail = o->tail;l->len += o->len;/* Setup other as an empty list. */o->head = o->tail = NULL;o->len = 0;
}
#ifndef __ADLIST_H__
#define __ADLIST_H__/* Node, List, and Iterator are the only data structures used currently. */typedef struct listNode
{struct listNode *prev;struct listNode *next;void *value;
} listNode;typedef struct listIter
{listNode *next;int direction;
} listIter;typedef struct list
{listNode *head;listNode *tail;void *(*dup)(void *ptr);void (*free)(void *ptr);int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);unsigned long len;
} list;/* Functions implemented as macros */
#define listLength(l) ((l)->len)
#define listFirst(l) ((l)->head)
#define listLast(l) ((l)->tail)
#define listPrevNode(n) ((n)->prev)
#define listNextNode(n) ((n)->next)
#define listNodeValue(n) ((n)->value)#define listSetDupMethod(l, m) ((l)->dup = (m))
#define listSetFreeMethod(l, m) ((l)->free = (m))
#define listSetMatchMethod(l, m) ((l)->match = (m))#define listGetDupMethod(l) ((l)->dup)
#define listGetFreeMethod(l) ((l)->free)
#define listGetMatchMethod(l) ((l)->match)/* Prototypes */
list *listCreate(void);
void listRelease(list *list);
void listEmpty(list *list);
list *listAddNodeHead(list *list, void *value);
list *listAddNodeTail(list *list, void *value);
list *listInsertNode(list *list, listNode *old_node, void *value, int after);
void listDelNode(list *list, listNode *node);
listIter *listGetIterator(list *list, int direction);
listNode *listNext(listIter *iter);
void listReleaseIterator(listIter *iter);
list *listDup(list *orig);
listNode *listSearchKey(list *list, void *key);
listNode *listIndex(list *list, long index);
void listRewind(list *list, listIter *li);
void listRewindTail(list *list, listIter *li);
void listRotateTailToHead(list *list);
void listRotateHeadToTail(list *list);
void listJoin(list *l, list *o);/* Directions for iterators */
#define AL_START_HEAD 0
#define AL_START_TAIL 1#endif /* __ADLIST_H__ */
在原代码的基础上修改的不多,删掉了一些依赖,替换成了malloc之类的。这部分大家可以自己复制到自己的adlist.c adlist.h文件中,然后引入到自己的工程里面,就能够尝试去使用了。
这里给出一个,本人自己写的简单的使用例程:
#include "adlist.h"
#include <stdio.h>/*** @brief 简单的遍历打印链表* * @param l 链表对象*/
void print_list(list *l)
{printf("list len: %d\n", listLength(l));listIter *iter = listGetIterator(l, AL_START_HEAD); // 创建迭代器// 使用迭代器进行迭代for (listNode *node = listNext(iter);node != NULL;node = listNext(iter)) {if (node != NULL) {printf("list value:%d\n", *(int *)listNodeValue(node));}}listReleaseIterator(iter); // 结束后销毁迭代器
}int main(void)
{list *list1 = listCreate(); // 创建链表对象// 这里最好是malloc或者全局变量// 不然出函数就会被回收,导致链表保存的指针为野指针int value1 = 1; int value2 = 2;// 添加数据到链表尾部listAddNodeTail(list1, &value1); listAddNodeTail(list1, &value2);print_list(list1);return 0;
}
redis里面的adlist我认为是功能最全,代码可读性最好的链表,使用起来也最友好的链表了。代码不需要注释也能明白它用法。所以这里也不多做笔墨去分析它了。
极致的精简的list.h
而后的时间,与朋友交流的时候发现,他们更多的使用linux内核链表。
#ifndef __LIST_H__
#define __LIST_H__#ifndef offsetof
#define offsetof(type,member) __builtin_offsetof(type,member)
#endifstruct list_head {struct list_head *next, *prev;
};typedef struct list_head list_t;/*** container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure* @ptr: the pointer to the member.* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.* @member: the name of the member within the struct.**/#ifndef container_of
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
#endif/** Simple doubly linked list implementation.** Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when* manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as* sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can* generate better code by using them directly rather than* using the generic single-entry routines.*/
//static define
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }#define LIST_HEAD(name) \struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)//动态初始化
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{list->next = list;list->prev = list;
}/** Insert a new_node entry between two known consecutive entries.** This is only for internal list manipulation where we know* the prev/next entries already!*/
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new_node,struct list_head *prev,struct list_head *next)
{next->prev = new_node;new_node->next = next;new_node->prev = prev;prev->next = new_node;
}/*** list_add - add a new_node entry* @new_node: new_node entry to be added* @head: list head to add it after** Insert a new_node entry after the specified head.* This is good for implementing stacks.*/
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new_node, struct list_head *head)
{__list_add(new_node, head, head->next);
}/*** list_add_tail - add a new_node entry* @new_node: new_node entry to be added* @head: list head to add it before** Insert a new_node entry before the specified head.* This is useful for implementing queues.*/
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new_node, struct list_head *head)
{__list_add(new_node, head->prev, head);
}/** Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries* point to each other.** This is only for internal list manipulation where we know* the prev/next entries already!*/
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{next->prev = prev;prev->next = next;
}/*** list_del - deletes entry from list.* @entry: the element to delete from the list.* Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is* in an undefined state.*/
static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry)
{__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
}static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);//entry->next = LIST_POISON1;//entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}/*** list_replace - replace old entry by new_node one* @old : the element to be replaced* @new_node : the new_node element to insert** If @old was empty, it will be overwritten.*/
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,struct list_head *new_node)
{new_node->next = old->next;new_node->next->prev = new_node;new_node->prev = old->prev;new_node->prev->next = new_node;
}static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,struct list_head *new_node)
{list_replace(old, new_node);INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}/*** list_del_init - deletes entry from list and reinitialize it.* @entry: the element to delete from the list.*/
static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{__list_del_entry(entry);INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}/*** list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head* @list: the entry to move* @head: the head that will precede our entry*/
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{__list_del_entry(list);list_add(list, head);
}/*** list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail* @list: the entry to move* @head: the head that will follow our entry*/
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{__list_del_entry(list);list_add_tail(list, head);
}/*** list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head* @list: the entry to test* @head: the head of the list*/
static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,const struct list_head *head)
{return list->next == head;
}/*** list_empty - tests whether a list is empty* @head: the list to test.*/
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{return head->next == head;
}/*** list_empty_careful - tests whether a list is empty and not being modified* @head: the list to test** Description:* tests whether a list is empty _and_ checks that no other CPU might be* in the process of modifying either member (next or prev)** NOTE: using list_empty_careful() without synchronization* can only be safe if the only activity that can happen* to the list entry is list_del_init(). Eg. it cannot be used* if another CPU could re-list_add() it.*/
static inline int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head)
{struct list_head *next = head->next;return (next == head) && (next == head->prev);
}/*** list_rotate_left - rotate the list to the left* @head: the head of the list*/
static inline void list_rotate_left(struct list_head *head)
{struct list_head *first;if (!list_empty(head)) {first = head->next;list_move_tail(first, head);}
}/*** list_is_singular - tests whether a list has just one entry.* @head: the list to test.*/
static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head)
{return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
}static inline void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{struct list_head *new_node_first = entry->next;list->next = head->next;list->next->prev = list;list->prev = entry;entry->next = list;head->next = new_node_first;new_node_first->prev = head;
}/*** list_cut_position - cut a list into two* @list: a new_node list to add all removed entries* @head: a list with entries* @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself* and if so we won't cut the list** This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and* including @entry, from @head to @list. You should* pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list* should be an empty list or a list you do not care about* losing its data.**/
static inline void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{if (list_empty(head)) {return;}if (list_is_singular(head) &&(head->next != entry && head != entry)) {return;}if (entry == head) {INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);} else {__list_cut_position(list, head, entry);}
}static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list,struct list_head *prev,struct list_head *next)
{struct list_head *first = list->next;struct list_head *last = list->prev;first->prev = prev;prev->next = first;last->next = next;next->prev = last;
}/*** list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks* @list: the new_node list to add.* @head: the place to add it in the first list.*/
static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{if (!list_empty(list)) {__list_splice(list, head, head->next);}
}/*** list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue* @list: the new_node list to add.* @head: the place to add it in the first list.*/
static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{if (!list_empty(list)) {__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);}
}/*** list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.* @list: the new_node list to add.* @head: the place to add it in the first list.** The list at @list is reinitialised*/
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{if (!list_empty(list)) {__list_splice(list, head, head->next);INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);}
}/*** list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list* @list: the new_node list to add.* @head: the place to add it in the first list.** Each of the lists is a queue.* The list at @list is reinitialised*/
static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{if (!list_empty(list)) {__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);}
}/*** list_entry - get the struct for this entry* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \container_of(ptr, type, member)/*** list_first_entry - get the first element from a list* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Note, that list is expected to be not empty.*/
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)/*** list_for_each - iterate over a list* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.*/
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)/*** __list_for_each - iterate over a list* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.** This variant doesn't differ from list_for_each() any more.* We don't do prefetching in either case.*/
#define __list_for_each(pos, head) \for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)/*** list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.*/
#define list_for_each_prev(pos, head) \for (pos = (head)->prev; pos != (head); pos = pos->prev)/*** list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.*/
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \pos = n, n = pos->next)/*** list_for_each_prev_safe - iterate over a list backwards safe against removal of list entry* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.*/
#define list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, head) \for (pos = (head)->prev, n = pos->prev; \pos != (head); \pos = n, n = pos->prev)/*** list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type.* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_prepare_entry - prepare a pos entry for use in list_for_each_entry_continue()* @pos: the type * to use as a start point* @head: the head of the list* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Prepares a pos entry for use as a start point in list_for_each_entry_continue().*/
#define list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member) \((pos) ? : list_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_continue - continue iteration over list of given type* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Continue to iterate over list of given type, continuing after* the current position.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse - iterate backwards from the given point* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Start to iterate over list of given type backwards, continuing after* the current position.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse(pos, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_from - iterate over list of given type from the current point* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Iterate over list of given type, continuing from current position.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member) \for (; &pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member), \n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_safe_continue - continue list iteration safe against removal* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Iterate over list of given type, continuing after current point,* safe against removal of list entry.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member), \n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_safe_from - iterate over list from current point safe against removal* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Iterate over list of given type from current point, safe against* removal of list entry.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member) \for (n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse - iterate backwards over list safe against removal* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Iterate backwards over list of given type, safe against removal* of list entry.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member), \n = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.prev, typeof(*n), member))/*** list_safe_reset_next - reset a stale list_for_each_entry_safe loop* @pos: the loop cursor used in the list_for_each_entry_safe loop* @n: temporary storage used in list_for_each_entry_safe* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** list_safe_reset_next is not safe to use in general if the list may be* modified concurrently (eg. the lock is dropped in the loop body). An* exception to this is if the cursor element (pos) is pinned in the list,* and list_safe_reset_next is called after re-taking the lock and before* completing the current iteration of the loop body.*/
#define list_safe_reset_next(pos, n, member) \n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member)#endif /* __LIST_H__*/这个链表更加极致,整体就只有一个头文件。代码不是宏就是内联函数。理论上不使用它,它开销是0。这样的做法导致它的开销极低,但是它使用起来不是很方便。代码的可读性也比较差。但是效率就很高
#include "list.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>typedef struct _student_t {char name[20];int age;list_t list;
} student_t;void student_reg(list_t* student_list, const char *name, int age)
{student_t *student = (student_t *)malloc(sizeof(student_t));student->age = age;strncpy(student->name, name, sizeof(student->name));list_add_tail(&student->list, student_list);
}void main(void)
{list_t student_list = LIST_HEAD_INIT(student_list);student_reg(&student_list, "Alice", 20);student_reg(&student_list, "Bob", 22);student_t *entry, *_entry;list_for_each_entry(entry, &student_list, list) {printf("Name: %s, Age: %d\n", entry->name, entry->age);}list_for_each_entry_safe(entry, _entry, &student_list, list) {list_del(&entry->list); // 从链表中删除节点free(entry);}
}如果说adlist的做法,是认为万物都可以看成指针,包到adlist的void *value;中去。那么,list.h的做法则是讲自己打包,包到任何的数据类型里面去。遍历链表后,可以通过它的container_of找到每个包含了链表节点的结构体的头。从而实现链表的功能。它本身还不涉及任何内存分配和释放,也不依赖任何头文件。真的做到了0依赖,0动态内存分配。对于这种特别底层的东西做到这样的程度是尤为厉害的。这也使得我不得不“捏着鼻子”用。
lvgl对链表的巧思lv_ll
终于到了咱们的主角,lvgl的源码
这次我们先从我写的例子入手,再看源码。逐步分析它:
#include "lv_ll.h"#include <stdio.h>int main()
{// 链表头的创建lv_ll_t list;// 初始化,并设置了链表的value的大小lv_ll_init(&list, sizeof(int));// 插入链表的时候顺带申请了空间(一次malloc)int* a = (int*)lv_ll_ins_tail(&list);int* b = (int*)lv_ll_ins_tail(&list);// 设置数据*a = 1;*b = 2;// 开始遍历链表吗,并打印值for (int* list_node = (int*)lv_ll_get_head(&list); list_node != NULL; list_node = lv_ll_get_next(&list, list_node)){printf("num:%d\n", *list_node);}return 0;
}根着我的注释,大家应该了解了如何使用链表去存储变量。
咱们把adlist list 和 lv_ll拉到一起,做个对比
| 对比内容 | adlist | list | lv_ll |
|---|---|---|---|
| 链表本身 | 创建时分配内存 | 外部传入(用静态动态用户选择) | 创建时分配 |
| 链表数据 | 用户创建传入指针 | 用户创建 | 和链表一起创建 |
实际上list所有内容都是由外部传入,它本身是仅仅关注链表的操作内容。这种方式优点就在于无论使用静态(数组)还是动态(malloc)内存都是可以用户自定义的。
在adlist的时候, 链表的内存使用了malloc。不用再用户端角度考虑传入了,但是void* value还是需要传入。如果这里是局部变量的指针就会导致出现野指针的危险,使用时应当注意。
lv_ll则非同寻常的做法,在初始化的时候会固定好你每个节点的value大小。让我们来看看它链表头是啥样的:
/** Dummy type to make handling easier*/
typedef uint8_t lv_ll_node_t;/** Description of a linked list*/
typedef struct {uint32_t n_size;lv_ll_node_t * head;lv_ll_node_t * tail;
} lv_ll_t;
这里链表头里面有保存每个节点的大小倒是不惊讶。但是这个uint8_t *类型的头尾节点着实和我们之前接触到的链表有所不同。我们继续看看它初始化在做什么:
void lv_ll_init(lv_ll_t *ll_p, uint32_t node_size)
{ll_p->head = NULL;ll_p->tail = NULL;
#ifdef LV_ARCH_64/*Round the size up to 8*/node_size = (node_size + 7) & (~0x7);
#else/*Round the size up to 4*/node_size = (node_size + 3) & (~0x3);
#endifll_p->n_size = node_size;
}
从初始化开始我们来对比一下三者不同的点:
list的结构, 无论是头还是节点,都只用同一个数据结构list_t。遍历的时候判断结尾也是判断下一个是否等于头,是双向循环链表:
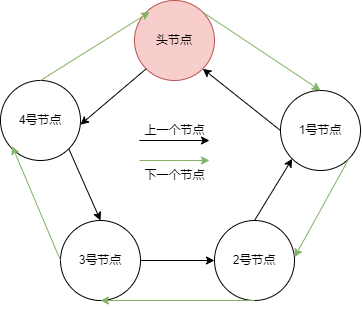
adlist则是有它专属的头list,和节点listNode两种对象
节点本质上是双向链表,遍历到next为NULL的时候结束遍历

从初始化上来看,我们的主角应该也是adlist这样的,所以初始化是NULL。计算node_size 这里是根据架构进行字节对齐(不足32bit或者64bit的算32bit或64bit)。这样不会出现内存对齐的意外。
接下来看看lv_ll_ins_tail的源码:
/*** Add a new tail to a linked list* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return pointer to the new tail*/
void *lv_ll_ins_tail(lv_ll_t *ll_p)
{lv_ll_node_t *n_new;n_new = malloc(ll_p->n_size + LL_NODE_META_SIZE);if (n_new != NULL) {node_set_next(ll_p, n_new, NULL); /*No next after the new tail*/node_set_prev(ll_p, n_new, ll_p->tail); /*The prev. before new is the old tail*/if (ll_p->tail != NULL) { /*If there is old tail then the new comes after it*/node_set_next(ll_p, ll_p->tail, n_new);}ll_p->tail = n_new; /*Set the new tail in the dsc.*/if (ll_p->head == NULL) { /*If there is no head (1. node) set the head too*/ll_p->head = n_new;}}return n_new;
}
这里就是一个技巧点。之前说了lvgl的链表不仅仅将链表使用malloc申请好了,也将你value使用malloc申请好了。这里的节点数据结构实际上是隐藏的,本质上是一个uint8_t的next一个uint8_t类型的prev。所以这里malloc的大小是之前设置好的vlaue的size大小加上"元节点"大小。
#define LL_NODE_META_SIZE (sizeof(lv_ll_node_t *) + sizeof(lv_ll_node_t *))
这里一大块数据被分成了数据区域和next和prev指针,三个结构体元素,且不用结构体。这里实际上没解决一个问题。为啥用uint8_t类型去指向下一个或者上一个节点内存的区域,而不是void。这个比较好理解,首先要了解的是,不同类型的指针本质都是一个指针大小的vlaue,不过里面存放的位置不同罢了。如果value相同(指向同一片内存)。类型不同会导致偏移一个单位后的偏移字节不相同。比如,针对uint32_t类型+1则会偏移四个字节,而uint8_t +1则会偏移一个字节。所以,这里在设计的时候不会对这个指针取值,所以uint8_t设计是为了方便做偏移计算。
很明显一开始声明的n_new是lv_ll_node_t 。但是返回值确实void类型的,其中涉及一个隐式类型转换。也就是说用户拿到手里还是void*类型。
那实际上lvgl的链表本质上和adlist很相似。不过加入了自己的一些小特色。
文章尾部附上lvgl中的lv_ll源码(魔改后无其它依赖)
/*** @file lv_ll.c* Handle linked lists.* The nodes are dynamically allocated by the 'lv_mem' module,*//********************** INCLUDES*********************/
#include "lv_ll.h"
#include <stdlib.h>/********************** DEFINES*********************/
#define LL_NODE_META_SIZE (sizeof(lv_ll_node_t *) + sizeof(lv_ll_node_t *))
#define LL_PREV_P_OFFSET(ll_p) (ll_p->n_size)
#define LL_NEXT_P_OFFSET(ll_p) (ll_p->n_size + sizeof(lv_ll_node_t *))/*********************** TYPEDEFS**********************//*********************** STATIC PROTOTYPES**********************/
static void node_set_prev(lv_ll_t *ll_p, lv_ll_node_t *act, lv_ll_node_t *prev);
static void node_set_next(lv_ll_t *ll_p, lv_ll_node_t *act, lv_ll_node_t *next);/*********************** STATIC VARIABLES**********************//*********************** MACROS**********************//*********************** GLOBAL FUNCTIONS**********************//*** Initialize linked list* @param ll_p pointer to lv_ll_t variable* @param node_size the size of 1 node in bytes*/
void lv_ll_init(lv_ll_t *ll_p, uint32_t node_size)
{ll_p->head = NULL;ll_p->tail = NULL;
#ifdef LV_ARCH_64/*Round the size up to 8*/node_size = (node_size + 7) & (~0x7);
#else/*Round the size up to 4*/node_size = (node_size + 3) & (~0x3);
#endifll_p->n_size = node_size;
}/*** Add a new head to a linked list* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return pointer to the new head*/
void *lv_ll_ins_head(lv_ll_t *ll_p)
{lv_ll_node_t *n_new;n_new = malloc(ll_p->n_size + LL_NODE_META_SIZE);if (n_new != NULL) {node_set_prev(ll_p, n_new, NULL); /*No prev. before the new head*/node_set_next(ll_p, n_new, ll_p->head); /*After new comes the old head*/if (ll_p->head != NULL) { /*If there is old head then before it goes the new*/node_set_prev(ll_p, ll_p->head, n_new);}ll_p->head = n_new; /*Set the new head in the dsc.*/if (ll_p->tail == NULL) { /*If there is no tail (1. node) set the tail too*/ll_p->tail = n_new;}}return n_new;
}/*** Insert a new node in front of the n_act node* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @param n_act pointer a node* @return pointer to the new node*/
void *lv_ll_ins_prev(lv_ll_t *ll_p, void *n_act)
{lv_ll_node_t *n_new;if (NULL == ll_p || NULL == n_act) {return NULL;}if (lv_ll_get_head(ll_p) == n_act) {n_new = lv_ll_ins_head(ll_p);if (n_new == NULL) {return NULL;}} else {n_new = malloc(ll_p->n_size + LL_NODE_META_SIZE);if (n_new == NULL) {return NULL;}lv_ll_node_t *n_prev;n_prev = lv_ll_get_prev(ll_p, n_act);node_set_next(ll_p, n_prev, n_new);node_set_prev(ll_p, n_new, n_prev);node_set_prev(ll_p, n_act, n_new);node_set_next(ll_p, n_new, n_act);}return n_new;
}/*** Add a new tail to a linked list* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return pointer to the new tail*/
void *lv_ll_ins_tail(lv_ll_t *ll_p)
{lv_ll_node_t *n_new;n_new = malloc(ll_p->n_size + LL_NODE_META_SIZE);if (n_new != NULL) {node_set_next(ll_p, n_new, NULL); /*No next after the new tail*/node_set_prev(ll_p, n_new, ll_p->tail); /*The prev. before new is the old tail*/if (ll_p->tail != NULL) { /*If there is old tail then the new comes after it*/node_set_next(ll_p, ll_p->tail, n_new);}ll_p->tail = n_new; /*Set the new tail in the dsc.*/if (ll_p->head == NULL) { /*If there is no head (1. node) set the head too*/ll_p->head = n_new;}}return n_new;
}/*** Remove the node 'node_p' from 'll_p' linked list.* It does not free the memory of node.* @param ll_p pointer to the linked list of 'node_p'* @param node_p pointer to node in 'll_p' linked list*/
void lv_ll_remove(lv_ll_t *ll_p, void *node_p)
{if (ll_p == NULL) {return;}if (lv_ll_get_head(ll_p) == node_p) {/*The new head will be the node after 'n_act'*/ll_p->head = lv_ll_get_next(ll_p, node_p);if (ll_p->head == NULL) {ll_p->tail = NULL;} else {node_set_prev(ll_p, ll_p->head, NULL);}} else if (lv_ll_get_tail(ll_p) == node_p) {/*The new tail will be the node before 'n_act'*/ll_p->tail = lv_ll_get_prev(ll_p, node_p);if (ll_p->tail == NULL) {ll_p->head = NULL;} else {node_set_next(ll_p, ll_p->tail, NULL);}} else {lv_ll_node_t *n_prev = lv_ll_get_prev(ll_p, node_p);lv_ll_node_t *n_next = lv_ll_get_next(ll_p, node_p);node_set_next(ll_p, n_prev, n_next);node_set_prev(ll_p, n_next, n_prev);}
}/*** Remove and free all elements from a linked list. The list remain valid but become empty.* @param ll_p pointer to linked list*/
void lv_ll_clear(lv_ll_t *ll_p)
{void *i;void *i_next;i = lv_ll_get_head(ll_p);i_next = NULL;while (i != NULL) {i_next = lv_ll_get_next(ll_p, i);lv_ll_remove(ll_p, i);free(i);i = i_next;}
}/*** Move a node to a new linked list* @param ll_ori_p pointer to the original (old) linked list* @param ll_new_p pointer to the new linked list* @param node pointer to a node* @param head true: be the head in the new list* false be the tail in the new list*/
void lv_ll_chg_list(lv_ll_t *ll_ori_p, lv_ll_t *ll_new_p, void *node, bool head)
{lv_ll_remove(ll_ori_p, node);if (head) {/*Set node as head*/node_set_prev(ll_new_p, node, NULL);node_set_next(ll_new_p, node, ll_new_p->head);if (ll_new_p->head != NULL) { /*If there is old head then before it goes the new*/node_set_prev(ll_new_p, ll_new_p->head, node);}ll_new_p->head = node; /*Set the new head in the dsc.*/if (ll_new_p->tail == NULL) { /*If there is no tail (first node) set the tail too*/ll_new_p->tail = node;}} else {/*Set node as tail*/node_set_prev(ll_new_p, node, ll_new_p->tail);node_set_next(ll_new_p, node, NULL);if (ll_new_p->tail != NULL) { /*If there is old tail then after it goes the new*/node_set_next(ll_new_p, ll_new_p->tail, node);}ll_new_p->tail = node; /*Set the new tail in the dsc.*/if (ll_new_p->head == NULL) { /*If there is no head (first node) set the head too*/ll_new_p->head = node;}}
}/*** Return with head node of the linked list* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return pointer to the head of 'll_p'*/
void *lv_ll_get_head(const lv_ll_t *ll_p)
{if (ll_p == NULL) {return NULL;}return ll_p->head;
}/*** Return with tail node of the linked list* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return pointer to the tail of 'll_p'*/
void *lv_ll_get_tail(const lv_ll_t *ll_p)
{if (ll_p == NULL) {return NULL;}return ll_p->tail;
}/*** Return with the pointer of the next node after 'n_act'* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @param n_act pointer a node* @return pointer to the next node*/
void *lv_ll_get_next(const lv_ll_t *ll_p, const void *n_act)
{/*Pointer to the next node is stored in the end of this node.*Go there and return the address found there*/const lv_ll_node_t *n_act_d = n_act;n_act_d += LL_NEXT_P_OFFSET(ll_p);return *((lv_ll_node_t **)n_act_d);
}/*** Return with the pointer of the previous node before 'n_act'* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @param n_act pointer a node* @return pointer to the previous node*/
void *lv_ll_get_prev(const lv_ll_t *ll_p, const void *n_act)
{/*Pointer to the prev. node is stored in the end of this node.*Go there and return the address found there*/const lv_ll_node_t *n_act_d = n_act;n_act_d += LL_PREV_P_OFFSET(ll_p);return *((lv_ll_node_t **)n_act_d);
}/*** Return the length of the linked list.* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return length of the linked list*/
uint32_t lv_ll_get_len(const lv_ll_t *ll_p)
{uint32_t len = 0;void *node;for (node = lv_ll_get_head(ll_p); node != NULL; node = lv_ll_get_next(ll_p, node)) {len++;}return len;
}/*** Move a node before an other node in the same linked list* @param ll_p pointer to a linked list* @param n_act pointer to node to move* @param n_after pointer to a node which should be after `n_act`*/
void lv_ll_move_before(lv_ll_t *ll_p, void *n_act, void *n_after)
{if (n_act == n_after) {return; /*Can't move before itself*/}void *n_before;if (n_after != NULL) {n_before = lv_ll_get_prev(ll_p, n_after);} else {n_before = lv_ll_get_tail(ll_p); /*if `n_after` is NULL `n_act` should be the new tail*/}if (n_act == n_before) {return; /*Already before `n_after`*/}/*It's much easier to remove from the list and add again*/lv_ll_remove(ll_p, n_act);/*Add again by setting the prev. and next nodes*/node_set_next(ll_p, n_before, n_act);node_set_prev(ll_p, n_act, n_before);node_set_prev(ll_p, n_after, n_act);node_set_next(ll_p, n_act, n_after);/*If `n_act` was moved before NULL then it become the new tail*/if (n_after == NULL) {ll_p->tail = n_act;}/*If `n_act` was moved before `NULL` then it's the new head*/if (n_before == NULL) {ll_p->head = n_act;}
}/*** Check if a linked list is empty* @param ll_p pointer to a linked list* @return true: the linked list is empty; false: not empty*/
bool lv_ll_is_empty(lv_ll_t *ll_p)
{if (ll_p == NULL) {return true;}if (ll_p->head == NULL && ll_p->tail == NULL) {return true;}return false;
}/*********************** STATIC FUNCTIONS**********************//*** Set the previous node pointer of a node* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @param act pointer to a node which prev. node pointer should be set* @param prev pointer to a node which should be the previous node before 'act'*/
static void node_set_prev(lv_ll_t *ll_p, lv_ll_node_t *act, lv_ll_node_t *prev)
{if (act == NULL) {return; /*Can't set the prev node of `NULL`*/}uint8_t *act8 = (uint8_t *)act;act8 += LL_PREV_P_OFFSET(ll_p);lv_ll_node_t **act_node_p = (lv_ll_node_t **) act8;lv_ll_node_t **prev_node_p = (lv_ll_node_t **) &prev;*act_node_p = *prev_node_p;
}/*** Set the 'next node pointer' of a node* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @param act pointer to a node which next node pointer should be set* @param next pointer to a node which should be the next node before 'act'*/
static void node_set_next(lv_ll_t *ll_p, lv_ll_node_t *act, lv_ll_node_t *next)
{if (act == NULL) {return; /*Can't set the next node of `NULL`*/}uint8_t *act8 = (uint8_t *)act;act8 += LL_NEXT_P_OFFSET(ll_p);lv_ll_node_t **act_node_p = (lv_ll_node_t **) act8;lv_ll_node_t **next_node_p = (lv_ll_node_t **) &next;*act_node_p = *next_node_p;
}/*** @file lv_ll.h* Handle linked lists. The nodes are dynamically allocated by the 'lv_mem' module.*/#ifndef LV_LL_H
#define LV_LL_H#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif/********************** INCLUDES*********************/
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdbool.h>/********************** DEFINES*********************//*********************** TYPEDEFS**********************//** Dummy type to make handling easier*/
typedef uint8_t lv_ll_node_t;/** Description of a linked list*/
typedef struct {uint32_t n_size;lv_ll_node_t * head;lv_ll_node_t * tail;
} lv_ll_t;/*********************** GLOBAL PROTOTYPES**********************//*** Initialize linked list* @param ll_p pointer to lv_ll_t variable* @param node_size the size of 1 node in bytes*/
void lv_ll_init(lv_ll_t * ll_p, uint32_t node_size);/*** Add a new head to a linked list* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return pointer to the new head*/
void * lv_ll_ins_head(lv_ll_t * ll_p);/*** Insert a new node in front of the n_act node* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @param n_act pointer a node* @return pointer to the new node*/
void * lv_ll_ins_prev(lv_ll_t * ll_p, void * n_act);/*** Add a new tail to a linked list* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return pointer to the new tail*/
void * lv_ll_ins_tail(lv_ll_t * ll_p);/*** Remove the node 'node_p' from 'll_p' linked list.* It does not free the memory of node.* @param ll_p pointer to the linked list of 'node_p'* @param node_p pointer to node in 'll_p' linked list*/
void lv_ll_remove(lv_ll_t * ll_p, void * node_p);/*** Remove and free all elements from a linked list. The list remain valid but become empty.* @param ll_p pointer to linked list*/
void lv_ll_clear(lv_ll_t * ll_p);/*** Move a node to a new linked list* @param ll_ori_p pointer to the original (old) linked list* @param ll_new_p pointer to the new linked list* @param node pointer to a node* @param head true: be the head in the new list* false be the tail in the new list*/
void lv_ll_chg_list(lv_ll_t * ll_ori_p, lv_ll_t * ll_new_p, void * node, bool head);/*** Return with head node of the linked list* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return pointer to the head of 'll_p'*/
void * lv_ll_get_head(const lv_ll_t * ll_p);/*** Return with tail node of the linked list* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return pointer to the tail of 'll_p'*/
void * lv_ll_get_tail(const lv_ll_t * ll_p);/*** Return with the pointer of the next node after 'n_act'* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @param n_act pointer a node* @return pointer to the next node*/
void * lv_ll_get_next(const lv_ll_t * ll_p, const void * n_act);/*** Return with the pointer of the previous node after 'n_act'* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @param n_act pointer a node* @return pointer to the previous node*/
void * lv_ll_get_prev(const lv_ll_t * ll_p, const void * n_act);/*** Return the length of the linked list.* @param ll_p pointer to linked list* @return length of the linked list*/
uint32_t lv_ll_get_len(const lv_ll_t * ll_p);/*** TODO* @param ll_p* @param n1_p* @param n2_p
void lv_ll_swap(lv_ll_t * ll_p, void * n1_p, void * n2_p);*//*** Move a node before an other node in the same linked list* @param ll_p pointer to a linked list* @param n_act pointer to node to move* @param n_after pointer to a node which should be after `n_act`*/
void lv_ll_move_before(lv_ll_t * ll_p, void * n_act, void * n_after);/*** Check if a linked list is empty* @param ll_p pointer to a linked list* @return true: the linked list is empty; false: not empty*/
bool lv_ll_is_empty(lv_ll_t * ll_p);/*********************** MACROS**********************/#define lv_LL_READ(list, i) for(i = lv_ll_get_head(list); i != NULL; i = lv_ll_get_next(list, i))#define lv_LL_READ_BACK(list, i) for(i = lv_ll_get_tail(list); i != NULL; i = lv_ll_get_prev(list, i))#ifdef __cplusplus
} /*extern "C"*/
#endif#endif尾记
大家喜欢哪一种链表呢?还是说大家有更方便的链表?评论区欢迎您的讨论
相关文章:

LVGL V8 代码细读——极致的链表使用
极致的链表的使用 序章碎碎念从redis源码里掏出来的adlist极致的精简的list.hlvgl对链表的巧思lv_ll尾记 序章碎碎念 对于链表,大家应该都不陌生。学过数据结构的,都知道它作为链式储存的基础,重要性不言而喻。 由于本人自动化专业ÿ…...
蓝桥杯第十二届c++大学B组详解
目录 1.空间 2.直线 3.路径 4.卡片 5.货物摆放 6.时间显示 7.砝码称重 8.杨辉三角 9.双向排序 10.括号序列 1.空间 题目解析:1Byte 8bit 1kb 1024B 1MB 1024kb; 先将256MB变成Byte 256 * 1024 * 1024; 再将32位 变成Byte就是 32 / 8 4;…...

Tubi 十岁啦!
Tubi 今年十岁了,这十年不可思议,充满奇迹! 从硅谷一个名不见经传的创业小作坊,转变成为四分之一美国电视家庭提供免费流媒体服务的北美领先的平台; 从费尽心力终于签下第一笔内容合作协议,到现在与 450 …...

Qt C++ 实现文件监视源码
以下是使用Qt C++实现文件监视的一个简单示例代码: #include <QCoreApplication> #include <QFileSystemWatcher> #include <QDebug>int main(int argc, char *argv[...
蓝桥杯第十一届c++大学B组详解
目录 1.字符串排序 2.门牌制作 3.即约分数 4.蛇型填数 5.跑步锻炼 6.七段码 7.成绩统计 8.回文日期 9.字串分值和 10.平面切分 1.字符串排序 题目解析:这个题目真没搞懂。有会的大佬教我一下谢谢。 2.门牌制作 题目解析:出过超级多这类题目&am…...

大模型日报2024-04-10
大模型日报 2024-04-10 大模型资讯 微软研究者提出通过可视化思维提升大型语言模型的空间推理能力 摘要: 微软研究者近日提出了一种新方法,旨在通过可视化思维来增强大型语言模型(LLMs)的空间推理能力。尽管LLMs在语言理解和推理任务方面表现…...

redis修改协议改了,有哪些替代品?
Redis 是一款广泛使用的开源内存数据结构存储,它支持多种数据结构,如字符串、哈希表、列表、集合、有序集合等。然而,由于 Redis 最近更改了其开源许可证,一些用户和开发者可能正在寻找替代品。以下是一些 Redis 的替代品…...

《QT实用小工具·十六》IP地址输入框控件
1、概述 源码放在文章末尾 该项目为IP地址输入框控件,主要包含如下功能: 可设置IP地址,自动填入框。 可清空IP地址。 支持按下小圆点自动切换。 支持退格键自动切换。 支持IP地址过滤。 可设置背景色、边框颜色、边框圆角角度。 下面…...
windows 系统下 mysql 数据库的下载与安装(包括升级安装)
windows 系统下 mysql 数据库的下载与安装(包括升级安装) 一、mysql 介绍: MySQL 是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典 MySQL AB 公司开发,属于 Oracle 旗下产品。 MySQL 是最流行的关系型数据库管理系统之一…...

Redis Stack十部曲之三:理解Redis Stack中的数据类型
文章目录 前言String字符串作为计数器限制 List限制列表阻塞列表自动创建和删除聚合类型键限制 Set限制 Hash限制 Sorted Set范围操作字典操作更新分数 JSON路径限制 BitMapBitfieldProbabilisticHyperLogLogBloom filterCuckoo filtert-digestTop-KCount-min sketchConfigurat…...
OneForAll安装使用
OneForAll简介 OneForAll是一款功能强大的子域收集工具 原项目地址:GitHub - shmilylty/OneForAll: OneForAll是一款功能强大的子域收集工具 gitee项目地址:OneForAll: OneForAll是一款功能强大的子域收集工具 # 安装Python Windows系统安装python参…...

【现代C++】线程支持库
现代C(C11及其之后的版本)引入了标准的线程支持库,使得多线程编程变得更加简单和可移植。这个库提供了线程管理、互斥量、条件变量和其他同步原语。 1. std::thread - 基本线程 std::thread允许创建执行特定任务的线程。 #include <ios…...
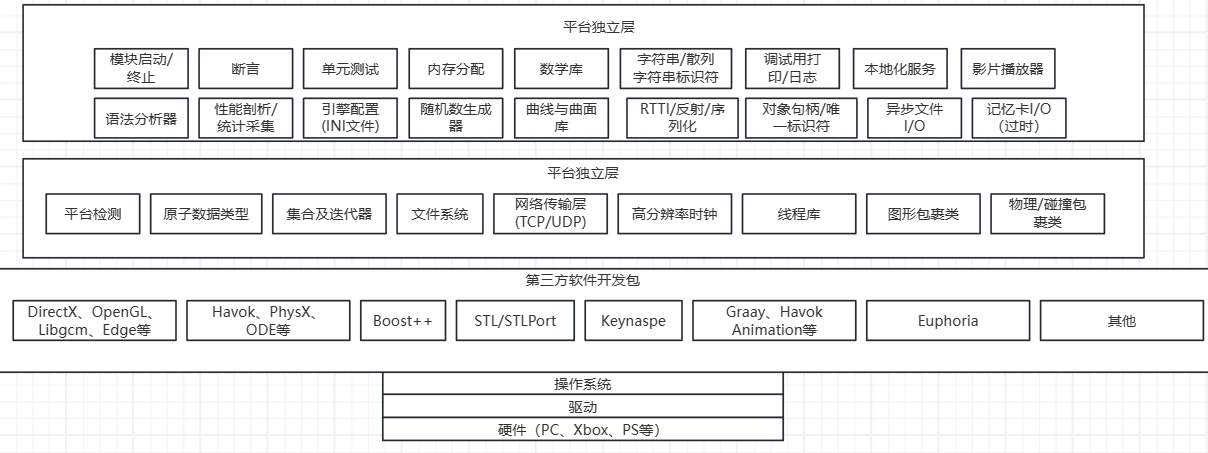
游戏引擎架构01__引擎架构图
根据游戏引擎架构预设的引擎架构来构建运行时引擎架构 ...

[Java、Android面试]_15_Android为什么使用Binder?
Android为什么使用Binder?用 Linux原有的IPC不行吗? 本人今年参加了很多面试,也有幸拿到了一些大厂的offer,整理了众多面试资料,后续还会分享众多面试资料。 整理成了面试系列,由于时间有限,每天…...

Python+Selenium+Unittest 之Unittest3(TestSuite()和TextTestRunner())
目录 1:addTest() 2、addTests() 3:discover() 上一篇说了Unittest的一个基本的执行顺序,那如果我们想要调整用例的执行先后顺序的话,可以用TestSuite()和TextTestRunner()了,可以这么理解,比如一个班级…...
3D桌面端可视化引擎HOOPS Visualize如何实现3D应用快速开发?
HOOPS Visualize是一个开发平台,可实现高性能、跨平台3D工程应用程序的快速开发。一些主要功能包括: 高性能、以工程为中心的可视化,使用高度优化的OpenGL或DirectX驱动程序来充分利用可用的图形硬件线程安全的C和C#接口,内部利用…...
)
Vue探索之Vue2.x源码分析(二)
一.Virtual Dom 虚拟DOM是一种轻量级的抽象,它允许我们在Javascript中创建、更新和删除DOM元素。它是React等现代Javascript框架的核心概念之一。 Vue的虚拟dom是一种抽象层的概念,它使得Vue可以高效地更新Dom。虚拟Dom是通过Javascript对象来表示DOM结…...

人工智能分类算法概述
文章目录 人工智能主要分类算法决策树随机森林逻辑回归K-均值 总结 人工智能主要分类算法 人工智能分类算法是用于将数据划分为不同类别的算法。这些算法通过学习数据的特征和模式,将输入数据映射到相应的类别。分类算法在人工智能中具有广泛的应用,如图…...

理解 Golang 变量在内存分配中的规则
为什么有些变量在堆中分配、有些却在栈中分配? 我们先看来栈和堆的特点: 简单总结就是: 栈:函数局部变量,小数据 堆:大的局部变量,函数内部产生逃逸的变量,动态分配的数据&#x…...
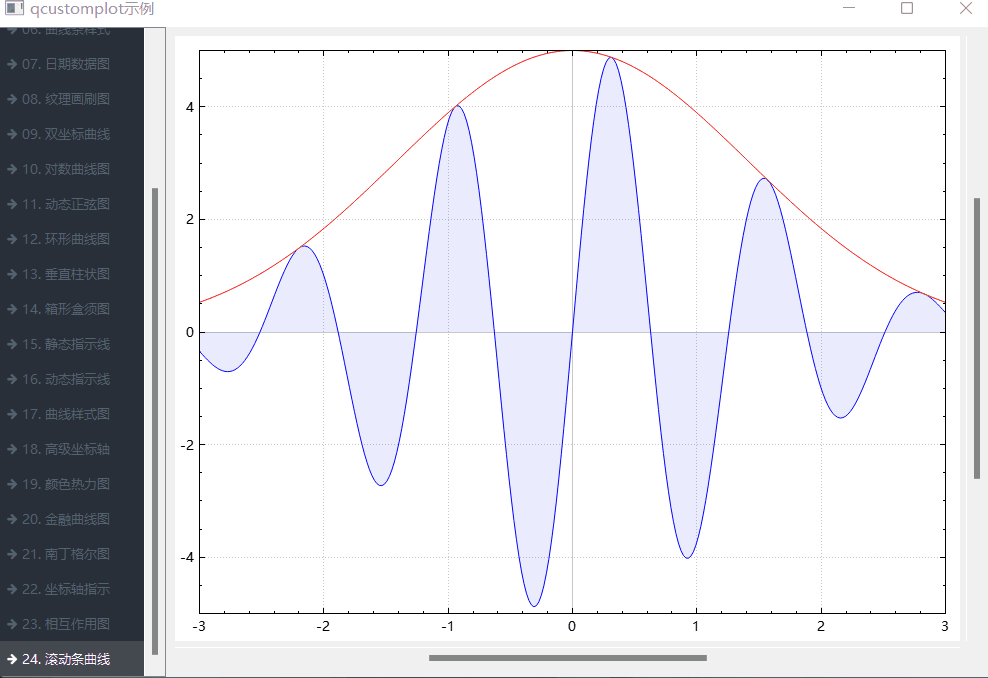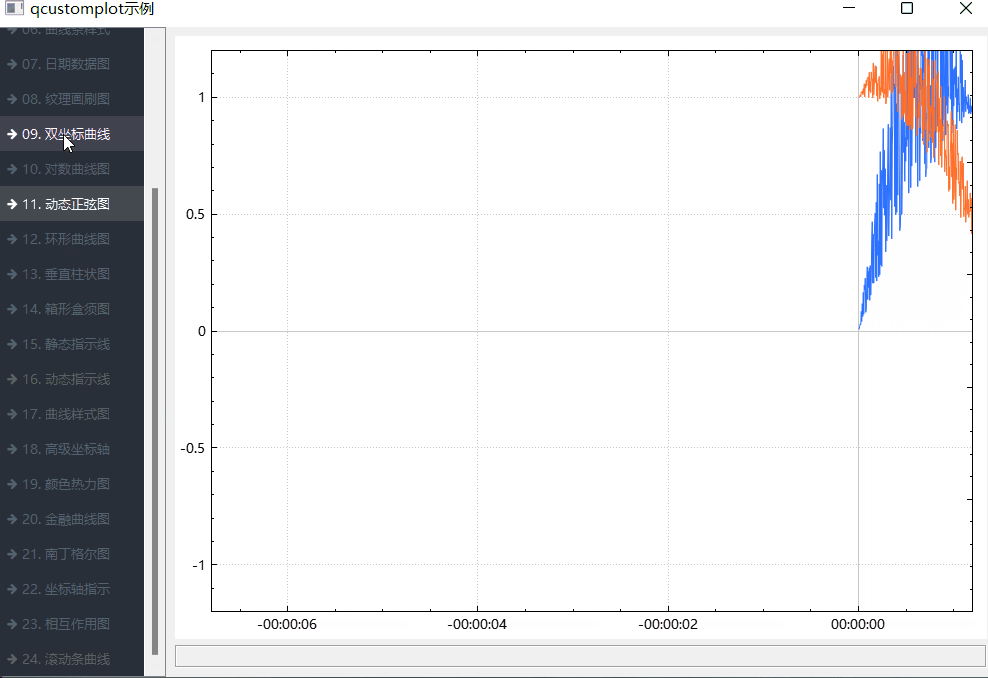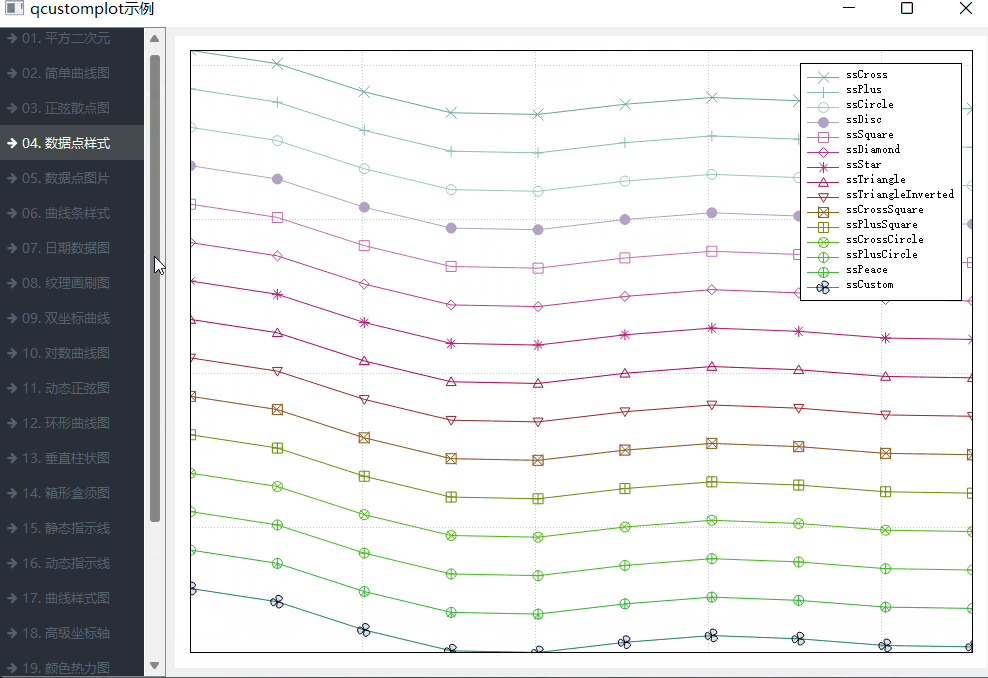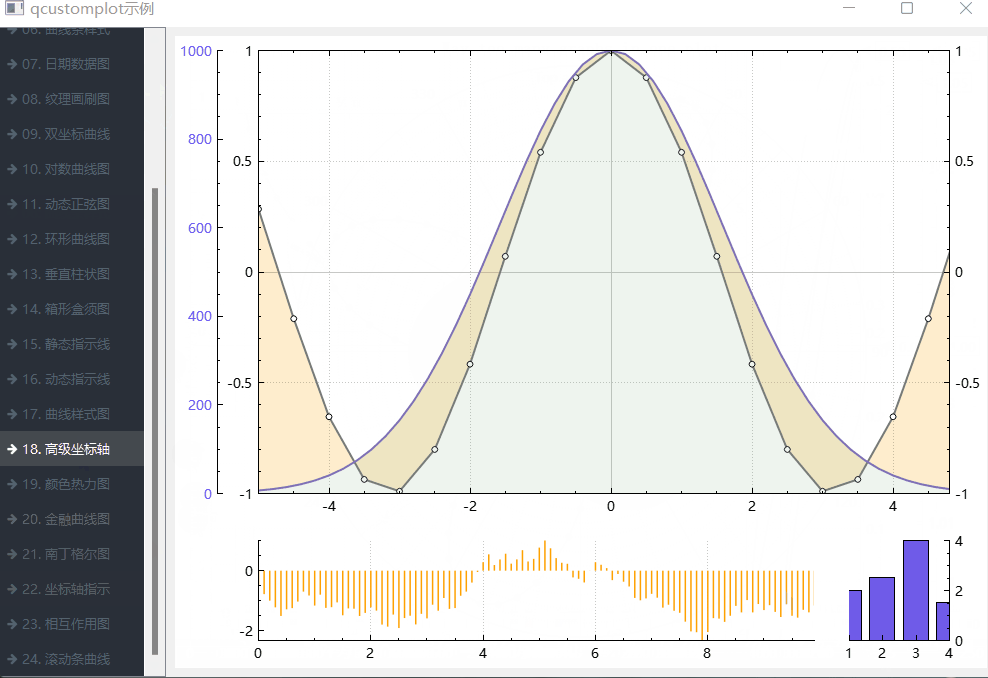
《QT实用小工具·二十四》各种数学和数据的坐标演示图
1、概述 源码放在文章末尾 该项目实现了各种数学和数据的坐标演示图,下面是demo演示: 项目部分代码如下: #ifndef FRMMAIN_H #define FRMMAIN_H#include <QWidget> class QAbstractButton;namespace Ui { class frmMain; }class fr…...

Vim 调用外部命令学习笔记
Vim 外部命令集成完全指南 文章目录 Vim 外部命令集成完全指南核心概念理解命令语法解析语法对比 常用外部命令详解文本排序与去重文本筛选与搜索高级 grep 搜索技巧文本替换与编辑字符处理高级文本处理编程语言处理其他实用命令 范围操作示例指定行范围处理复合命令示例 实用技…...
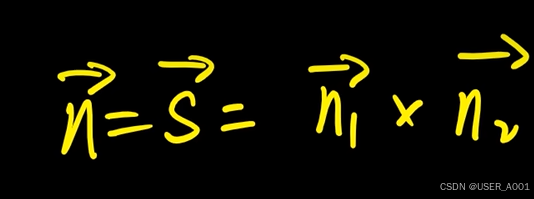
高等数学(下)题型笔记(八)空间解析几何与向量代数
目录 0 前言 1 向量的点乘 1.1 基本公式 1.2 例题 2 向量的叉乘 2.1 基础知识 2.2 例题 3 空间平面方程 3.1 基础知识 3.2 例题 4 空间直线方程 4.1 基础知识 4.2 例题 5 旋转曲面及其方程 5.1 基础知识 5.2 例题 6 空间曲面的法线与切平面 6.1 基础知识 6.2…...
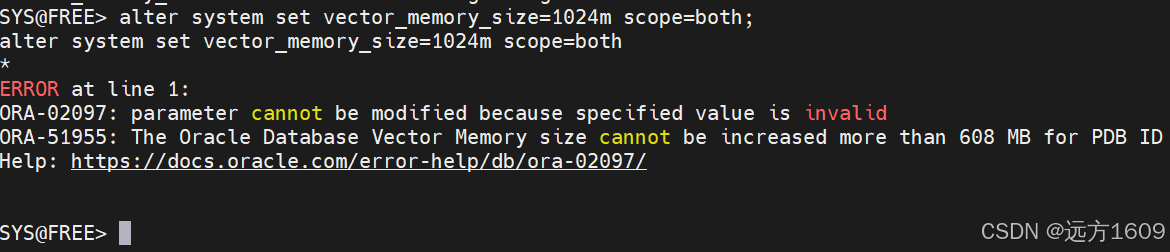
10-Oracle 23 ai Vector Search 概述和参数
一、Oracle AI Vector Search 概述 企业和个人都在尝试各种AI,使用客户端或是内部自己搭建集成大模型的终端,加速与大型语言模型(LLM)的结合,同时使用检索增强生成(Retrieval Augmented Generation &#…...
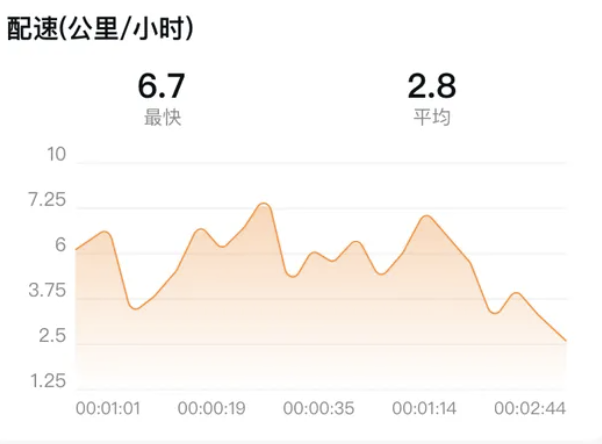
HarmonyOS运动开发:如何用mpchart绘制运动配速图表
##鸿蒙核心技术##运动开发##Sensor Service Kit(传感器服务)# 前言 在运动类应用中,运动数据的可视化是提升用户体验的重要环节。通过直观的图表展示运动过程中的关键数据,如配速、距离、卡路里消耗等,用户可以更清晰…...
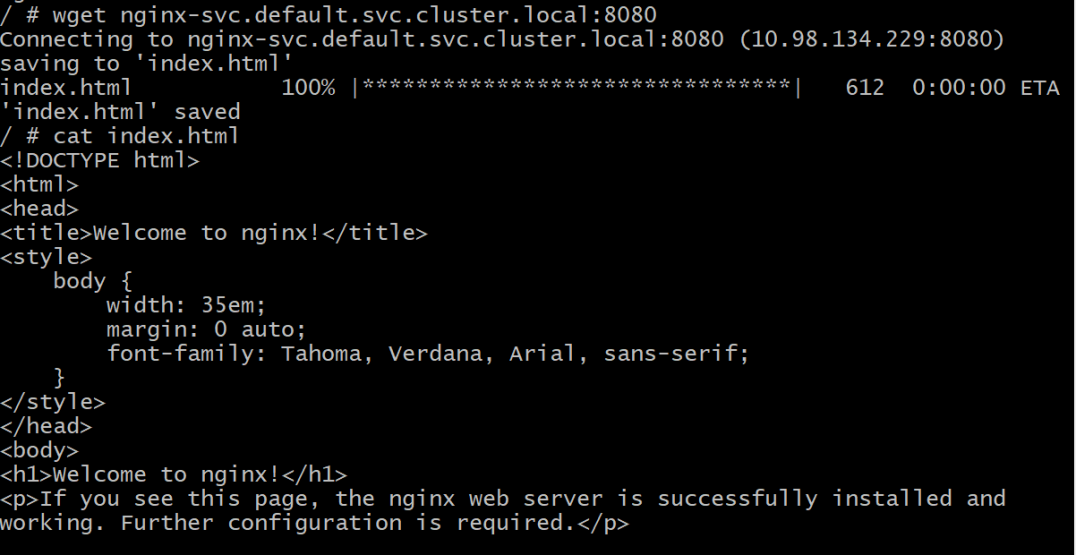
初探Service服务发现机制
1.Service简介 Service是将运行在一组Pod上的应用程序发布为网络服务的抽象方法。 主要功能:服务发现和负载均衡。 Service类型的包括ClusterIP类型、NodePort类型、LoadBalancer类型、ExternalName类型 2.Endpoints简介 Endpoints是一种Kubernetes资源…...

【JavaSE】多线程基础学习笔记
多线程基础 -线程相关概念 程序(Program) 是为完成特定任务、用某种语言编写的一组指令的集合简单的说:就是我们写的代码 进程 进程是指运行中的程序,比如我们使用QQ,就启动了一个进程,操作系统就会为该进程分配内存…...

Webpack性能优化:构建速度与体积优化策略
一、构建速度优化 1、升级Webpack和Node.js 优化效果:Webpack 4比Webpack 3构建时间降低60%-98%。原因: V8引擎优化(for of替代forEach、Map/Set替代Object)。默认使用更快的md4哈希算法。AST直接从Loa…...
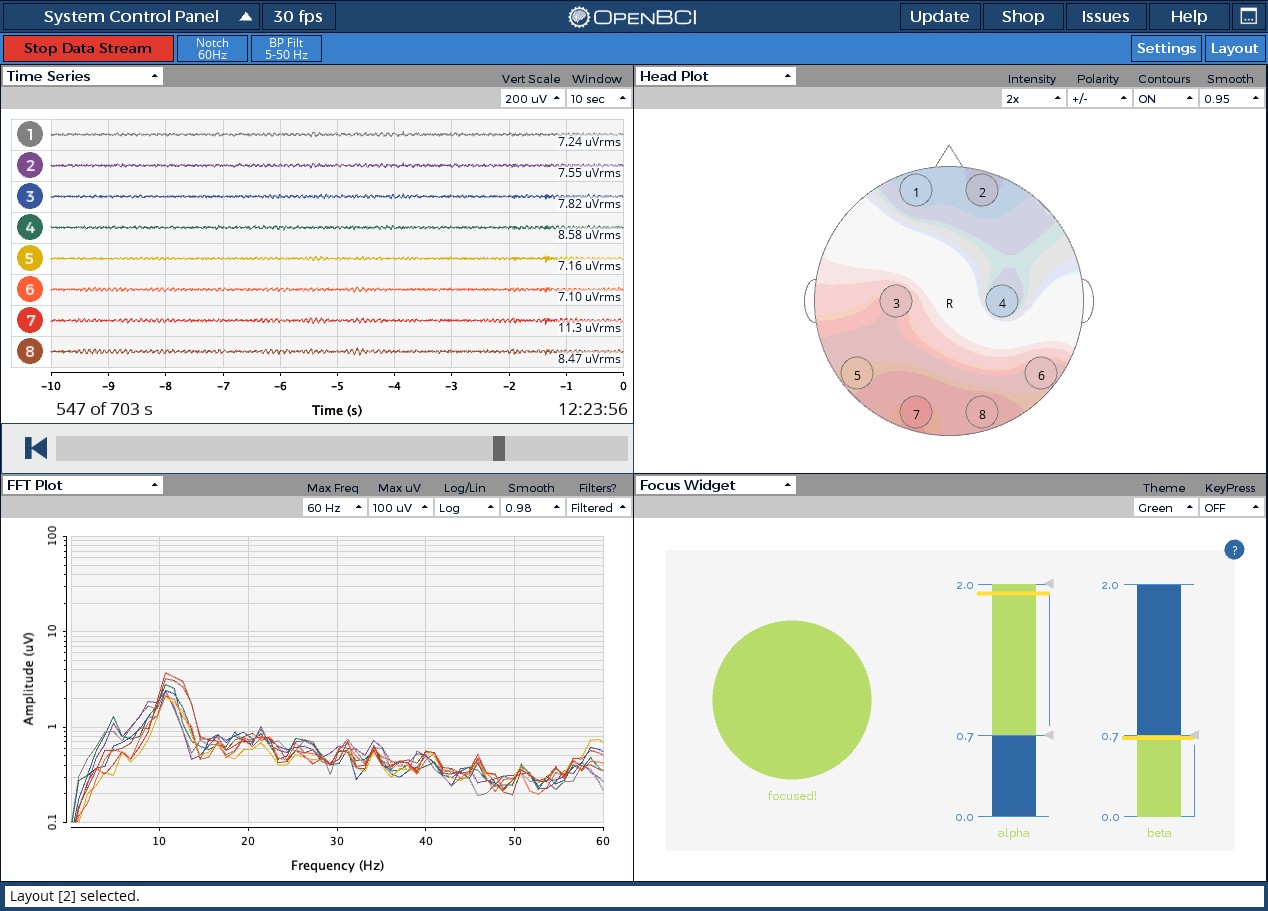
脑机新手指南(七):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(上)
一、OpenBCI_GUI 项目概述 (一)项目背景与目标 OpenBCI 是一个开源的脑电信号采集硬件平台,其配套的 OpenBCI_GUI 则是专为该硬件设计的图形化界面工具。对于研究人员、开发者和学生而言,首次接触 OpenBCI 设备时,往…...

wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像
wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像https://www.cnblogs.com/haodafeng/p/10431387.html 如果你在寻找能够快速在image控件刷新大图像(比如分辨率3000*3000的图像)的办法,尤其是想把内存中的裸数据(只有图像的数据,不包…...
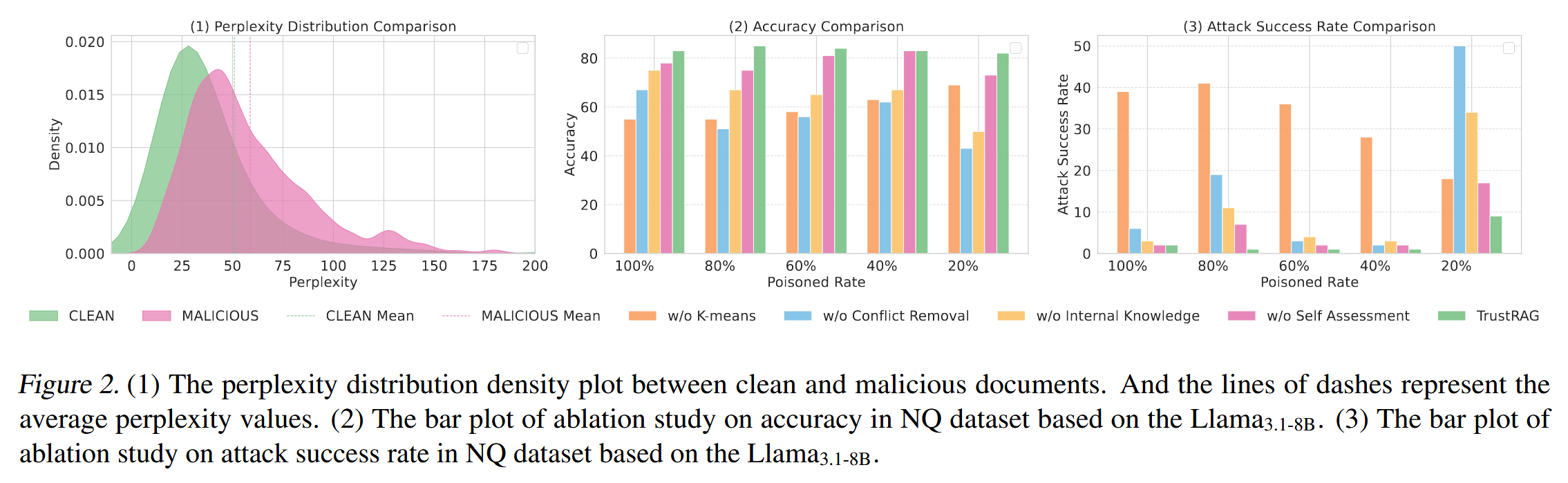
[论文阅读]TrustRAG: Enhancing Robustness and Trustworthiness in RAG
TrustRAG: Enhancing Robustness and Trustworthiness in RAG [2501.00879] TrustRAG: Enhancing Robustness and Trustworthiness in Retrieval-Augmented Generation 代码:HuichiZhou/TrustRAG: Code for "TrustRAG: Enhancing Robustness and Trustworthin…...
