Linux migrate_type进一步探索
文章接着上回Linux migrate_type初步探索
1、物理页面添加到buddy系统
我们都知道物理内存一开始是由memblock进行分配管理,后面会切换到buddy系统管理。那么接下来我们看一下,memblock管理的物理页面是怎么添加到buddy系统中的。
start_kernel()
-> mm_init()
--> mem_init()
---> memblock_free_all()
----> free_low_memory_core_early()
1.1 free_low_memory_core_early()
static unsigned long __init free_low_memory_core_early(void)
{unsigned long count = 0;phys_addr_t start, end;u64 i;memblock_clear_hotplug(0, -1);// 处理预留内存for_each_reserved_mem_range(i, &start, &end)reserve_bootmem_region(start, end);/** We need to use NUMA_NO_NODE instead of NODE_DATA(0)->node_id* because in some case like Node0 doesn't have RAM installed* low ram will be on Node1*/// 遍历可释放物理内存区域,进行释放for_each_free_mem_range(i, NUMA_NO_NODE, MEMBLOCK_NONE, &start, &end,NULL)count += __free_memory_core(start, end);return count;
}static unsigned long __init __free_memory_core(phys_addr_t start,phys_addr_t end)
{unsigned long start_pfn = PFN_UP(start);unsigned long end_pfn = min_t(unsigned long,PFN_DOWN(end), max_low_pfn);if (start_pfn >= end_pfn)return 0;// 进行页面释放处理__free_pages_memory(start_pfn, end_pfn);return end_pfn - start_pfn;
}
1.2 __free_pages_memory()
static void __init __free_pages_memory(unsigned long start, unsigned long end)
{int order;while (start < end) {/*** 由于buddy系统最大能存放的页面order是MAX_ORDER - 1UL,所以这里要进行限制* __ffs()函数是用来根据start值计算出最合适的order值* __ffs()函数作用是求第start第一个位为1的位置,例如:start = 0x63300,* 说明该地址以0x100对齐,那么__ffs()返回值为8*/order = min(MAX_ORDER - 1UL, __ffs(start));// 如果发现order太大,实际没有那么多物理内存,则不断减小order,直至能包含为止while (start + (1UL << order) > end)order--;// 将页面释放到buddy系统memblock_free_pages(pfn_to_page(start), start, order);start += (1UL << order);}
}
1.3 memblock_free_pages()
void __init memblock_free_pages(struct page *page, unsigned long pfn,unsigned int order)
{if (early_page_uninitialised(pfn))return;// 调用内部接口释放页面__free_pages_core(page, order);
}void __free_pages_core(struct page *page, unsigned int order)
{unsigned int nr_pages = 1 << order;struct page *p = page;unsigned int loop;/** When initializing the memmap, __init_single_page() sets the refcount* of all pages to 1 ("allocated"/"not free"). We have to set the* refcount of all involved pages to 0.*/prefetchw(p);// 遍历当前order页面内所有page,并初始化for (loop = 0; loop < (nr_pages - 1); loop++, p++) {prefetchw(p + 1);// 清楚页面预留标记__ClearPageReserved(p);// 设置页面引用计数为0set_page_count(p, 0);}__ClearPageReserved(p);set_page_count(p, 0);atomic_long_add(nr_pages, &page_zone(page)->managed_pages);/** Bypass PCP and place fresh pages right to the tail, primarily* relevant for memory onlining.*/// 将页面释放到buddy系统中__free_pages_ok(page, order, FPI_TO_TAIL);
}static void __free_pages_ok(struct page *page, unsigned int order,fpi_t fpi_flags)
{unsigned long flags;int migratetype;unsigned long pfn = page_to_pfn(page);if (!free_pages_prepare(page, order, true))return;// 获取页面所在页块的迁移类型migratetype = get_pfnblock_migratetype(page, pfn);local_irq_save(flags);__count_vm_events(PGFREE, 1 << order);// 将页面放置在对应迁移类型对应order的管理链表上free_one_page(page_zone(page), page, pfn, order, migratetype,fpi_flags);local_irq_restore(flags);
}
这里就是物理内存从memblock转移到buddy系统的流程。
2、迁移类型fallback处理逻辑
接下来我们再来看看一个新问题:一开始页块的迁移类型都是MIGRATE_MOVABLE,那对于MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE迁移类型的内存分配应该怎么处理呢?
2.1 原理图
我们都知道Linux内核内存分配接口alloc_pages(),那么我们就跟踪这个接口,看看是如何分配出MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE迁移类型的内存。
alloc_pages()
-> alloc_pages_node()
--> __alloc_pages_node()
---> __alloc_pages()
----> __alloc_pages_nodemask()
我们接下来仔细研究一下__alloc_pages_nodemask()实现:
2.2 __alloc_pages_nodemask()
/** This is the 'heart' of the zoned buddy allocator.*/
struct page *
__alloc_pages_nodemask(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order, int preferred_nid,nodemask_t *nodemask)
{struct page *page;// 第一次分配时,我们会从zone的low水线以上分配内存unsigned int alloc_flags = ALLOC_WMARK_LOW;gfp_t alloc_mask; /* The gfp_t that was actually used for allocation */struct alloc_context ac = { };/** There are several places where we assume that the order value is sane* so bail out early if the request is out of bound.*/// 如果order>=11时,buddy系统无法分配出内存,因此直接返回错误if (unlikely(order >= MAX_ORDER)) {WARN_ON_ONCE(!(gfp_mask & __GFP_NOWARN));return NULL;}gfp_mask &= gfp_allowed_mask;alloc_mask = gfp_mask;// 这里是根据gfp设置分配标识,以及确定优先从哪个zone里进行内存分配if (!prepare_alloc_pages(gfp_mask, order, preferred_nid, nodemask, &ac, &alloc_mask, &alloc_flags))return NULL;/** Forbid the first pass from falling back to types that fragment* memory until all local zones are considered.*/alloc_flags |= alloc_flags_nofragment(ac.preferred_zoneref->zone, gfp_mask);// 内存分配快速路径,我们今天只需要跟踪该函数实现就好了/* First allocation attempt */page = get_page_from_freelist(alloc_mask, order, alloc_flags, &ac);if (likely(page))goto out;/** Apply scoped allocation constraints. This is mainly about GFP_NOFS* resp. GFP_NOIO which has to be inherited for all allocation requests* from a particular context which has been marked by* memalloc_no{fs,io}_{save,restore}.*/alloc_mask = current_gfp_context(gfp_mask);ac.spread_dirty_pages = false;/** Restore the original nodemask if it was potentially replaced with* &cpuset_current_mems_allowed to optimize the fast-path attempt.*/ac.nodemask = nodemask;// 当快速路径无法分配出内存时,就会调用该函数,走慢速路径内存分配,这里会异步唤醒kswapd线程回收内存等操作page = __alloc_pages_slowpath(alloc_mask, order, &ac);out:if (memcg_kmem_enabled() && (gfp_mask & __GFP_ACCOUNT) && page &&unlikely(__memcg_kmem_charge_page(page, gfp_mask, order) != 0)) {__free_pages(page, order);page = NULL;}trace_mm_page_alloc(page, order, alloc_mask, ac.migratetype);return page;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__alloc_pages_nodemask);
2.3 get_page_from_freelist()
/** get_page_from_freelist goes through the zonelist trying to allocate* a page.*/
static struct page *
get_page_from_freelist(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order, int alloc_flags,const struct alloc_context *ac)
{struct zoneref *z;struct zone *zone;struct pglist_data *last_pgdat_dirty_limit = NULL;bool no_fallback;retry:/** Scan zonelist, looking for a zone with enough free.* See also __cpuset_node_allowed() comment in kernel/cpuset.c.*/no_fallback = alloc_flags & ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;z = ac->preferred_zoneref;// 优先从最优先的zone分配内存,若未分配到,降级到其他可分配内存的zonefor_next_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, ac->highest_zoneidx,ac->nodemask) {struct page *page;unsigned long mark;if (cpusets_enabled() &&(alloc_flags & ALLOC_CPUSET) &&!__cpuset_zone_allowed(zone, gfp_mask))continue;/** When allocating a page cache page for writing, we* want to get it from a node that is within its dirty* limit, such that no single node holds more than its* proportional share of globally allowed dirty pages.* The dirty limits take into account the node's* lowmem reserves and high watermark so that kswapd* should be able to balance it without having to* write pages from its LRU list.** XXX: For now, allow allocations to potentially* exceed the per-node dirty limit in the slowpath* (spread_dirty_pages unset) before going into reclaim,* which is important when on a NUMA setup the allowed* nodes are together not big enough to reach the* global limit. The proper fix for these situations* will require awareness of nodes in the* dirty-throttling and the flusher threads.*/if (ac->spread_dirty_pages) {if (last_pgdat_dirty_limit == zone->zone_pgdat)continue;if (!node_dirty_ok(zone->zone_pgdat)) {last_pgdat_dirty_limit = zone->zone_pgdat;continue;}}if (no_fallback && nr_online_nodes > 1 &&zone != ac->preferred_zoneref->zone) {int local_nid;/** If moving to a remote node, retry but allow* fragmenting fallbacks. Locality is more important* than fragmentation avoidance.*/local_nid = zone_to_nid(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone);if (zone_to_nid(zone) != local_nid) {alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;goto retry;}}mark = wmark_pages(zone, alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK);// 快速水线检查,查看当前zone是否可以分配出所需order大小的页面if (!zone_watermark_fast(zone, order, mark,ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags,gfp_mask)) {int ret;#ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT/** Watermark failed for this zone, but see if we can* grow this zone if it contains deferred pages.*/if (static_branch_unlikely(&deferred_pages)) {if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))goto try_this_zone;}
#endif/* Checked here to keep the fast path fast */BUILD_BUG_ON(ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS < NR_WMARK);if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS)goto try_this_zone;if (node_reclaim_mode == 0 ||!zone_allows_reclaim(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone))continue;// 尝试内存回收ret = node_reclaim(zone->zone_pgdat, gfp_mask, order);switch (ret) {// 返回值为未进行回收扫描,则跳过该zonecase NODE_RECLAIM_NOSCAN:/* did not scan */continue;// 返回值为扫描但不能回收,则跳过该zonecase NODE_RECLAIM_FULL:/* scanned but unreclaimable */continue;default:/* did we reclaim enough */// 已经回收了一部分,检查水线是否满足,满足则使用该zone进行内存分配if (zone_watermark_ok(zone, order, mark,ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags))// 使用该zone进行内存分配goto try_this_zone;continue;}}try_this_zone:// 通过rmqueue从zone的buddy系统中分配页面page = rmqueue(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone, order,gfp_mask, alloc_flags, ac->migratetype);if (page) {// 分配到页面,进行一个处理prep_new_page(page, order, gfp_mask, alloc_flags);/** If this is a high-order atomic allocation then check* if the pageblock should be reserved for the future*/if (unlikely(order && (alloc_flags & ALLOC_HARDER)))reserve_highatomic_pageblock(page, zone, order);// 返回分配到的页面return page;} else {
#ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT/* Try again if zone has deferred pages */if (static_branch_unlikely(&deferred_pages)) {if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))goto try_this_zone;}
#endif}}/** It's possible on a UMA machine to get through all zones that are* fragmented. If avoiding fragmentation, reset and try again.*/if (no_fallback) {alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;goto retry;}return NULL;
}
2.4 rmqueue()
/** Allocate a page from the given zone. Use pcplists for order-0 allocations.*/
static inline
struct page *rmqueue(struct zone *preferred_zone,struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,gfp_t gfp_flags, unsigned int alloc_flags,int migratetype)
{unsigned long flags;struct page *page;// 如果order为0,则从pcplist中分配,这样做是为了加快分配效率,这个在我之前的文章专门讲过,感兴趣的可以自己翻找一下if (likely(order == 0)) {/** MIGRATE_MOVABLE pcplist could have the pages on CMA area and* we need to skip it when CMA area isn't allowed.*/if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CMA) || alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA ||migratetype != MIGRATE_MOVABLE) {page = rmqueue_pcplist(preferred_zone, zone, gfp_flags,migratetype, alloc_flags);goto out;}}/** We most definitely don't want callers attempting to* allocate greater than order-1 page units with __GFP_NOFAIL.*/WARN_ON_ONCE((gfp_flags & __GFP_NOFAIL) && (order > 1));spin_lock_irqsave(&zone->lock, flags);do {page = NULL;/** order-0 request can reach here when the pcplist is skipped* due to non-CMA allocation context. HIGHATOMIC area is* reserved for high-order atomic allocation, so order-0* request should skip it.*/// 如果是中断上下文的内存分配,alloc_flags会带有ALLOC_HARDER标记,会走该分配路径if (order > 0 && alloc_flags & ALLOC_HARDER) {page = __rmqueue_smallest(zone, order, MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC);if (page)trace_mm_page_alloc_zone_locked(page, order, migratetype);}// 一般的内存分配,会走该路径if (!page)page = __rmqueue(zone, order, migratetype, alloc_flags);} while (page && check_new_pages(page, order));spin_unlock(&zone->lock);if (!page)goto failed;__mod_zone_freepage_state(zone, -(1 << order),get_pcppage_migratetype(page));__count_zid_vm_events(PGALLOC, page_zonenum(page), 1 << order);zone_statistics(preferred_zone, zone);local_irq_restore(flags);out:/* Separate test+clear to avoid unnecessary atomics */if (test_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags)) {clear_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags);wakeup_kswapd(zone, 0, 0, zone_idx(zone));}VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(page && bad_range(zone, page), page);return page;failed:local_irq_restore(flags);return NULL;
}
2.5 __rmqueue()
/** Do the hard work of removing an element from the buddy allocator.* Call me with the zone->lock already held.*/
static __always_inline struct page *
__rmqueue(struct zone *zone, unsigned int order, int migratetype,unsigned int alloc_flags)
{struct page *page;#ifdef CONFIG_CMA/** Balance movable allocations between regular and CMA areas by* allocating from CMA when over half of the zone's free memory* is in the CMA area.*/// cma内存分配,这个我们暂时不进行讨论if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA &&zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_CMA_PAGES) >zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_PAGES) / 2) {page = __rmqueue_cma_fallback(zone, order);if (page)return page;}
#endif
retry:// 根据迁移类型从buddy对应迁移链表中分配对应order页面的内存page = __rmqueue_smallest(zone, order, migratetype);if (unlikely(!page)) {if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA)page = __rmqueue_cma_fallback(zone, order);// 未分配到,则转移到fallback流程,我们的迁移类型转换就在这里if (!page && __rmqueue_fallback(zone, order, migratetype,alloc_flags))goto retry;}trace_mm_page_alloc_zone_locked(page, order, migratetype);return page;
}
2.6 __rmqueue_smallest()
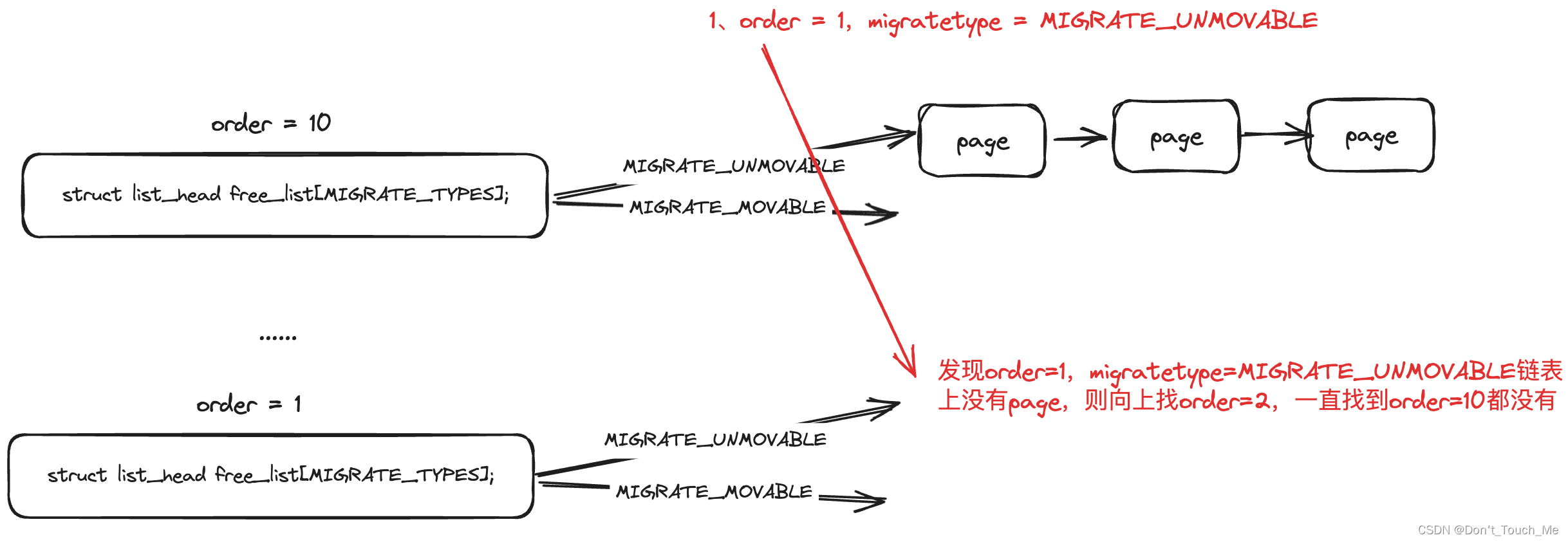
假设我们要分配的页面的迁移类型是MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE,但是一开始所有内存都是MIGRATE_MOVABLE,这样子肯定是分配不出来内存的。
/** Go through the free lists for the given migratetype and remove* the smallest available page from the freelists*/
static __always_inline
struct page *__rmqueue_smallest(struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,int migratetype)
{unsigned int current_order;struct free_area *area;struct page *page;/* Find a page of the appropriate size in the preferred list */// 根据当前请求的order和migratetype进行分配,如果当前order无法满足,则向上找,一直找到最大的MAX_ORDER - 1为止for (current_order = order; current_order < MAX_ORDER; ++current_order) {// 先获取到对应的order数组链表area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);// 以migratetype作为下标,确定存放page的链表page = get_page_from_free_area(area, migratetype);// 如果page没有找到,说明order无法满足分配,则尝试更大的orderif (!page)continue;// 从page链表中删除pagedel_page_from_free_list(page, zone, current_order);// 进行buddy调整expand(zone, page, order, current_order, migratetype);set_pcppage_migratetype(page, migratetype);// 返回已分配到的pagereturn page;}return NULL;
}static inline struct page *get_page_from_free_area(struct free_area *area,int migratetype)
{// 根据迁移类型作为下标return list_first_entry_or_null(&area->free_list[migratetype],struct page, lru);
}
2.7 __rmqueue_fallback() 核心处理
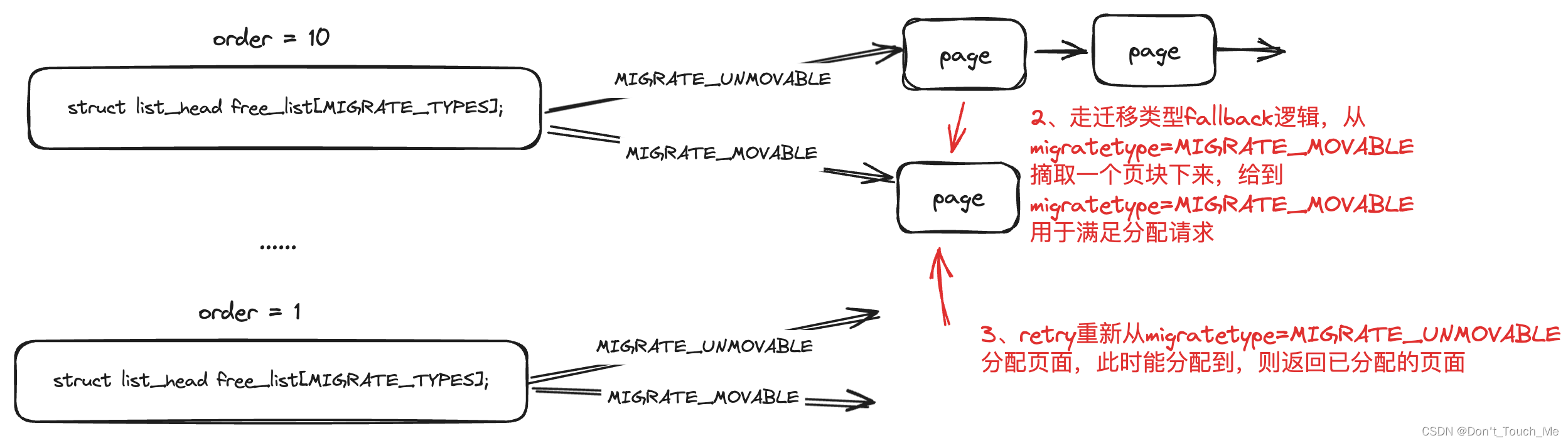
由于我们要分配的页面的迁移类型是MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE,但是一开始所有内存都是MIGRATE_MOVABLE,__rmqueue_smallest()无法分配出来内存,因此会走到__rmqueue_fallback()中进行处理。
/** Try finding a free buddy page on the fallback list and put it on the free* list of requested migratetype, possibly along with other pages from the same* block, depending on fragmentation avoidance heuristics. Returns true if* fallback was found so that __rmqueue_smallest() can grab it.** The use of signed ints for order and current_order is a deliberate* deviation from the rest of this file, to make the for loop* condition simpler.*/
static __always_inline bool
__rmqueue_fallback(struct zone *zone, int order, int start_migratetype,unsigned int alloc_flags)
{struct free_area *area;int current_order;int min_order = order;struct page *page;int fallback_mt;bool can_steal;/** Do not steal pages from freelists belonging to other pageblocks* i.e. orders < pageblock_order. If there are no local zones free,* the zonelists will be reiterated without ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT.*/// 一般的分配外面都会带有这个标记,为了减少页块内部碎片化if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT)min_order = pageblock_order;/** Find the largest available free page in the other list. This roughly* approximates finding the pageblock with the most free pages, which* would be too costly to do exactly.*/// 我们从最大order开始分配,这样对于一个页块只需要改变迁移类型就好,否则会导致一个MIGRATE_MOVABLE迁移类型的页块部分内存用于了MIGRATE_MOVABLE迁移类型的内存分配,导致页块内部碎片化,无法进行回收for (current_order = MAX_ORDER - 1; current_order >= min_order;--current_order) {area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);// 根据迁移类型查找是否可以从别的迁移类型中分配内存fallback_mt = find_suitable_fallback(area, current_order,start_migratetype, false, &can_steal);if (fallback_mt == -1)continue;/** We cannot steal all free pages from the pageblock and the* requested migratetype is movable. In that case it's better to* steal and split the smallest available page instead of the* largest available page, because even if the next movable* allocation falls back into a different pageblock than this* one, it won't cause permanent fragmentation.*/if (!can_steal && start_migratetype == MIGRATE_MOVABLE&& current_order > order)goto find_smallest;// 如果我们可以从别的迁移类型里偷到内存,则进行偷的处理goto do_steal;}return false;find_smallest:for (current_order = order; current_order < MAX_ORDER;current_order++) {area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);fallback_mt = find_suitable_fallback(area, current_order,start_migratetype, false, &can_steal);if (fallback_mt != -1)break;}/** This should not happen - we already found a suitable fallback* when looking for the largest page.*/VM_BUG_ON(current_order == MAX_ORDER);do_steal:// 从可以偷的迁移类型里获取到内存page = get_page_from_free_area(area, fallback_mt);// 这里是将偷到的页块修改为分配请求需要的迁移类型steal_suitable_fallback(zone, page, alloc_flags, start_migratetype,can_steal);trace_mm_page_alloc_extfrag(page, order, current_order,start_migratetype, fallback_mt);return true;}
2.8 find_suitable_fallback()
查找一个合适的fallback迁移类型的页块。
/** Check whether there is a suitable fallback freepage with requested order.* If only_stealable is true, this function returns fallback_mt only if* we can steal other freepages all together. This would help to reduce* fragmentation due to mixed migratetype pages in one pageblock.*/
int find_suitable_fallback(struct free_area *area, unsigned int order,int migratetype, bool only_stealable, bool *can_steal)
{int i;int fallback_mt;if (area->nr_free == 0)return -1;// 先设置为不能偷*can_steal = false;for (i = 0;; i++) {// 从fallbacks数组里遍历fallback_mt = fallbacks[migratetype][i];if (fallback_mt == MIGRATE_TYPES)break;// 如果当前迁移类型没有内存,则换到下一个迁移类型if (free_area_empty(area, fallback_mt))continue;// 如果有内存,查看是否可以偷if (can_steal_fallback(order, migratetype))// 如果可以偷到话,设置为可偷*can_steal = true;if (!only_stealable)return fallback_mt;if (*can_steal)// 在能偷的前提下,将可偷的迁移类型返回return fallback_mt;}return -1;
}/** This array describes the order lists are fallen back to when* the free lists for the desirable migrate type are depleted*/
static int fallbacks[MIGRATE_TYPES][3] = {[MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE] = { MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE, MIGRATE_MOVABLE, MIGRATE_TYPES },[MIGRATE_MOVABLE] = { MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE, MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE, MIGRATE_TYPES },[MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE] = { MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE, MIGRATE_MOVABLE, MIGRATE_TYPES },
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA[MIGRATE_CMA] = { MIGRATE_TYPES }, /* Never used */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_ISOLATION[MIGRATE_ISOLATE] = { MIGRATE_TYPES }, /* Never used */
#endif
};
fallbacks是不同迁移类型内存不足时,可从哪个迁移类型中进行fallback操作,对于MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE迁移类型不足时,可以先MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE迁移类型中偷内存,如果MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE也没有内存的话,会进一步fallback到MIGRATE_MOVABLE迁移类型。因此对于我们一开始需要MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE类型的页面没有时,最终会fallback到MIGRATE_MOVABLE。
/** When we are falling back to another migratetype during allocation, try to* steal extra free pages from the same pageblocks to satisfy further* allocations, instead of polluting multiple pageblocks.** If we are stealing a relatively large buddy page, it is likely there will* be more free pages in the pageblock, so try to steal them all. For* reclaimable and unmovable allocations, we steal regardless of page size,* as fragmentation caused by those allocations polluting movable pageblocks* is worse than movable allocations stealing from unmovable and reclaimable* pageblocks.*/
static bool can_steal_fallback(unsigned int order, int start_mt)
{/** Leaving this order check is intended, although there is* relaxed order check in next check. The reason is that* we can actually steal whole pageblock if this condition met,* but, below check doesn't guarantee it and that is just heuristic* so could be changed anytime.*/// 如果我们偷的是一整个页块的大小,是允许的if (order >= pageblock_order)return true;if (order >= pageblock_order / 2 ||start_mt == MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE ||start_mt == MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE ||page_group_by_mobility_disabled)return true;return false;
}
can_steal_fallback()函数用来检查当前order大小页面是否可以从fallback的迁移类型中偷取,当我们偷取的内存是一整个页块时,页面偷取是可以的。
2.9 steal_suitable_fallback()
/** This function implements actual steal behaviour. If order is large enough,* we can steal whole pageblock. If not, we first move freepages in this* pageblock to our migratetype and determine how many already-allocated pages* are there in the pageblock with a compatible migratetype. If at least half* of pages are free or compatible, we can change migratetype of the pageblock* itself, so pages freed in the future will be put on the correct free list.*/
static void steal_suitable_fallback(struct zone *zone, struct page *page,unsigned int alloc_flags, int start_type, bool whole_block)
{unsigned int current_order = buddy_order(page);int free_pages, movable_pages, alike_pages;int old_block_type;// 获取当前page的迁移类型old_block_type = get_pageblock_migratetype(page);/** This can happen due to races and we want to prevent broken* highatomic accounting.*/if (is_migrate_highatomic(old_block_type))goto single_page;/* Take ownership for orders >= pageblock_order */// 如果我们是偷的一整个页块的话,进入该函数处理if (current_order >= pageblock_order) {// 修改当前page的所在页块的迁移类型,也就是从MIGRATE_MOVABLE变为MIGRATE_UNMOVABLEchange_pageblock_range(page, current_order, start_type);goto single_page;}/** Boost watermarks to increase reclaim pressure to reduce the* likelihood of future fallbacks. Wake kswapd now as the node* may be balanced overall and kswapd will not wake naturally.*/boost_watermark(zone);if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_KSWAPD)set_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags);/* We are not allowed to try stealing from the whole block */if (!whole_block)goto single_page;free_pages = move_freepages_block(zone, page, start_type,&movable_pages);/** Determine how many pages are compatible with our allocation.* For movable allocation, it's the number of movable pages which* we just obtained. For other types it's a bit more tricky.*/if (start_type == MIGRATE_MOVABLE) {alike_pages = movable_pages;} else {/** If we are falling back a RECLAIMABLE or UNMOVABLE allocation* to MOVABLE pageblock, consider all non-movable pages as* compatible. If it's UNMOVABLE falling back to RECLAIMABLE or* vice versa, be conservative since we can't distinguish the* exact migratetype of non-movable pages.*/if (old_block_type == MIGRATE_MOVABLE)alike_pages = pageblock_nr_pages- (free_pages + movable_pages);elsealike_pages = 0;}/* moving whole block can fail due to zone boundary conditions */if (!free_pages)goto single_page;/** If a sufficient number of pages in the block are either free or of* comparable migratability as our allocation, claim the whole block.*/if (free_pages + alike_pages >= (1 << (pageblock_order-1)) ||page_group_by_mobility_disabled)set_pageblock_migratetype(page, start_type);return;single_page:// 并将页面迁移到对应的新的迁移类型所在的链表中move_to_free_list(page, zone, current_order, start_type);
}static void change_pageblock_range(struct page *pageblock_page,int start_order, int migratetype)
{int nr_pageblocks = 1 << (start_order - pageblock_order);while (nr_pageblocks--) {// 设置迁移类型set_pageblock_migratetype(pageblock_page, migratetype);pageblock_page += pageblock_nr_pages;}
}
将从fallback的迁移类型中获取到页面,并将页面放置到所需求的迁移类型后,会重新retry进行内存分配。
好了,这里对于migrate_type进一步探索就到这里了,感谢各位读者浏览!!!
预知后续如何,请看下个博文的分析。
相关文章:

Linux migrate_type进一步探索
文章接着上回Linux migrate_type初步探索 1、物理页面添加到buddy系统 我们都知道物理内存一开始是由memblock进行分配管理,后面会切换到buddy系统管理。那么接下来我们看一下,memblock管理的物理页面是怎么添加到buddy系统中的。 start_kernel() -&g…...

强化学习:时序差分法【Temporal Difference Methods】
强化学习笔记 主要基于b站西湖大学赵世钰老师的【强化学习的数学原理】课程,个人觉得赵老师的课件深入浅出,很适合入门. 第一章 强化学习基本概念 第二章 贝尔曼方程 第三章 贝尔曼最优方程 第四章 值迭代和策略迭代 第五章 强化学习实例分析:GridWorld…...
数据结构-二叉树-二叉搜索树
一、概念 二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者具有以下性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不为空,则左树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值。 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值。 它…...

Linux 磁盘管理命令df du dd
文章目录 3.Linux 磁盘管理命令3.1 df:显示报告文件系统磁盘使用信息案例练习 3.2 du:显示目录或者文件所占的磁盘空间案例练习 3.3 dd:磁盘操作案例练习 3.Linux 磁盘管理命令 3.1 df:显示报告文件系统磁盘使用信息 作用&#x…...

Leetcode 3138. Minimum Length of Anagram Concatenation
Leetcode 3138. Minimum Length of Anagram Concatenation 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3138. Minimum Length of Anagram Concatenation 1. 解题思路 这一题的话我们首先统计出来所有的字母出现的频率。 然后,我们只需要从头开始重新计数一下&…...
IT廉连看——UniApp——样式绑定
IT廉连看——UniApp——样式绑定 一、样式绑定 两种添加样式的方法: 1、第一种写法 写一个class属性,然后将css样式写在style中。 2、第二种写法 直接把style写在class后面 添加一些效果:字体大小 查看效果 证明这样添加样式是没有问题的…...

垃圾的flinkcdc
在 MySQL 中,创建表时使用反引号 将表名或字段名括起来的作用是: 保留字和关键字: 使用反引号可以避免使用MySQL的保留字和关键字作为表名或字段名时产生的冲突。比如,你可以创建一个名为 select 或 order 的表: sqlCopy Code C…...

关于视频号小店,常见问题解答,开店做店各方面详解
大家好,我是电商笨笨熊 视频号小店作为今年风口,一个新推出的项目,凭借着自身流量加用户群体的优势吸引了不少的电商玩家。 但对于很多玩家来说,视频号小店完全是一个新的项目、新的领域,因此也会存在很多的疑问&…...
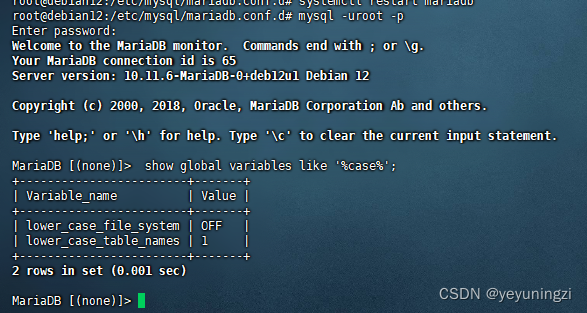
Debian mariadb 10.11设定表名 大小写不敏感方法
目录 问题表现:应用中查询 表提示 表不存在 处理步骤: 1、查询表名大小写敏感情况: show global variables like %case%; 2、修改mariadb 配置设置大小写 不敏感 mysql 配置大小写不敏感 mariadb 10.11设置表名大小写不敏感 /etc/mysq…...
常用六大加密软件排行榜|好用加密文件软件分享
为了保障数据安全,越来越多的企业开始使用文件加密软件。哪款加密软件适合企业哪些办公场景呢? 今天就给大家推荐一下文件加密软件排行榜的前六名: 1.域智盾 这款软件专为企业和政府机构设计,提供全面的文件保护解决方案。 点…...

百川2模型解读
简介 Baichuan 2是多语言大模型,目前开源了70亿和130亿参数规模的模型。在公开基准如MMLU、CMMLU、GSM8K和HumanEval上的评测,Baichuan 2达到或超过了其他同类开源模型,并在医学和法律等垂直领域表现优异。此外,官方还发布所有预…...
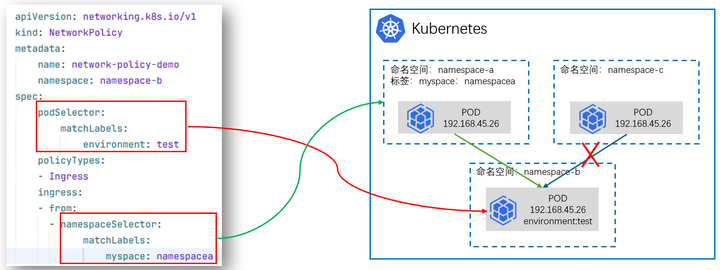
云原生专栏丨基于K8s集群网络策略的应用访问控制技术
在当今云计算时代,Kubernetes已经成为容器编排的事实标准,它为容器化应用提供了强大的自动化部署、扩展和管理能力。在Kubernetes集群中,网络策略(Network Policy)作为对Pod间通信进行控制的关键功能,对保障应用安全和隔离性起到了…...

MySQL 优化 - index_merge 导致查询偶发变慢
文章目录 前言问题描述原因分析总结 前言 今天遇到了一个有意思的问题,线上数据库 CPU 出现了偶发的抖动。定位到原因是一条查询语句偶发变慢造成的,随后通过调整表中的索引解决。 问题描述 下方是脱敏后的 SQL 语句: select oss_path f…...

SpringBoot自动连接数据库的解决方案
在一次学习设计模式的时候,沿用一个旧的boot项目,想着简单,就把数据库给关掉了,结果报错 Consider the following: If you want an embedded database (H2, HSQL or Derby), please put it on the classpath. 没有数据库的需…...

Docker-10 Docker Compose
一、前言 通过前面几篇文章的学习,我们可以通过Dockerfile文件让用户很方便的定义一个单独的应用容器。然而,在日常工作中,经常会碰到需要多个容器相互配合来完成某项任务的情况,或者开发一个Web应用,除了Web服务容器本身,还需要数据库服务容器、缓存容器,甚至还包括负…...

new mars3d.control.MapSplit({实现点击卷帘两侧添加不同图层弹出不同的popup
new mars3d.control.MapSplit({实现点击卷帘两侧添加不同图层弹出不同的popup效果: 左侧: 右侧: 说明:mars3d的3.7.12以上版本才支持该效果。 示例链接: 功能示例(Vue版) | Mars3D三维可视化平台 | 火星科技 相关代…...

数据库中虚拟表和临时表的区别?
虚拟表(Virtual Table)和临时表(Temporary Table)在数据库系统中都用于处理暂时性的数据存储需求,但它们的概念和用途有所不同: 虚拟表(通常是视图View): 虚拟表&#…...

Node.js -- mongoose
文章目录 1. 介绍2. mongoose 连接数据库3. 插入文件4. 字段类型5. 字段值验证6. 文档处理6.1 删除文档6.2 更新文档6.3 读取文档 7. 条件控制8. 个性化读取9. 代码模块化 1. 介绍 Mongoose是一个对象文档模型库,官网http://www.mongoosejs.net/ 方便使用代码操作mo…...
保持亮灯:监控工具如何确保 DevOps 中的高可用性
在快速发展的 DevOps 领域,保持高可用性 (HA) 至关重要。消费者期望应用程序具有全天候响应能力和可访问性。销售损失、客户愤怒和声誉受损都是停机的后果。为了使 DevOps 团队能够在问题升级为中断之前主动检测、排除故障并解决问题,监控工具成为这种情…...
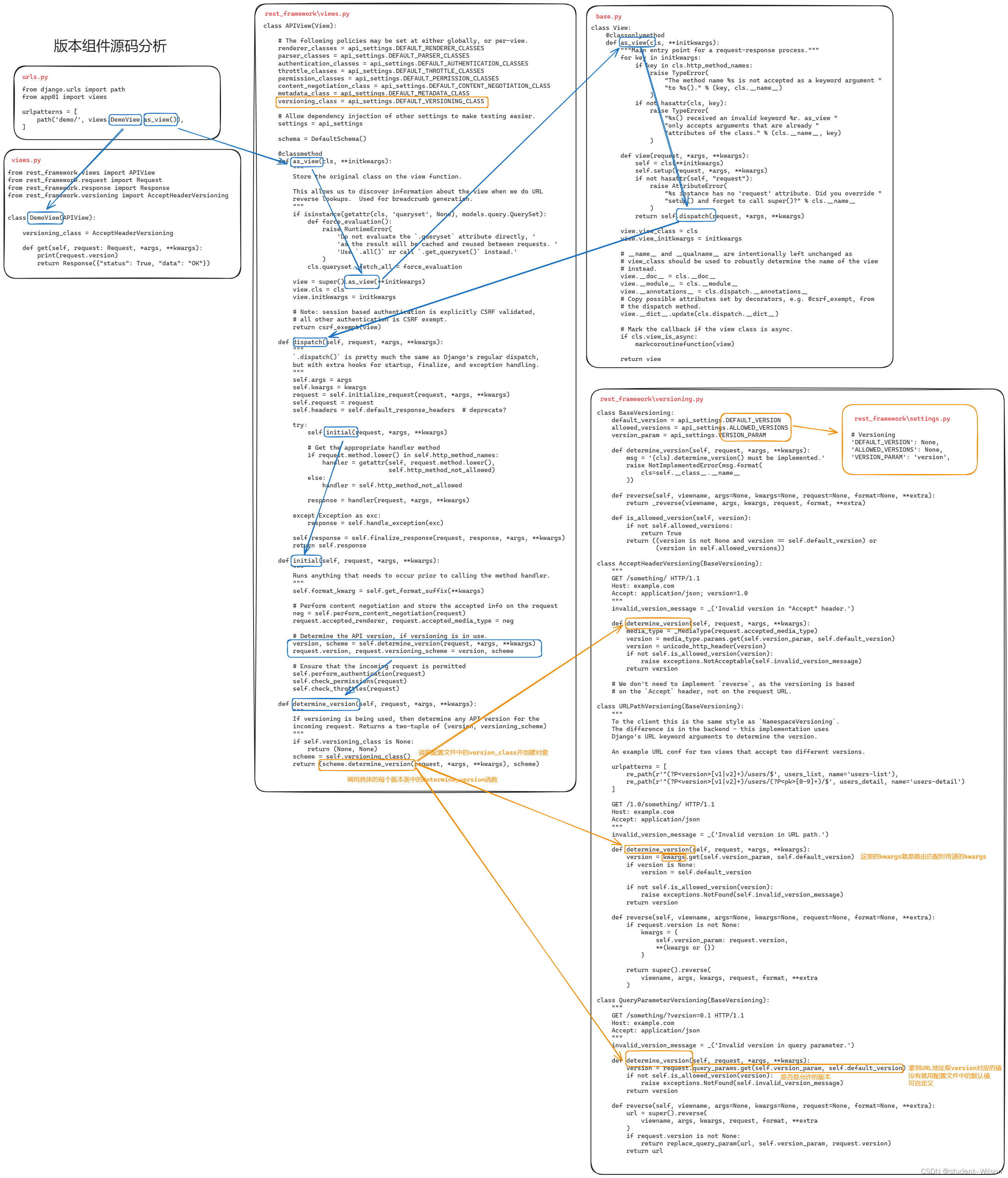
DRF版本组件源码分析
DRF版本组件源码分析 在restful规范中要去,后端的API中需要体现版本。 3.6.1 GET参数传递版本 from rest_framework.versioning import QueryParameterVersioning单视图应用 多视图应用 # settings.pyREST_FRAMEWORK {"VERSION_PARAM": "versi…...

K8S认证|CKS题库+答案| 11. AppArmor
目录 11. AppArmor 免费获取并激活 CKA_v1.31_模拟系统 题目 开始操作: 1)、切换集群 2)、切换节点 3)、切换到 apparmor 的目录 4)、执行 apparmor 策略模块 5)、修改 pod 文件 6)、…...
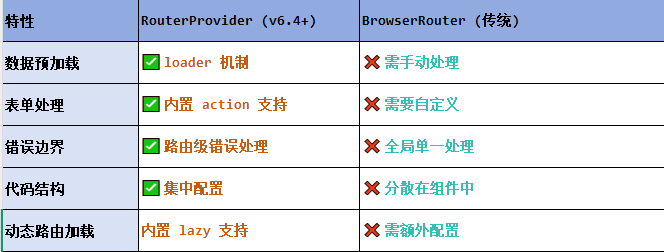
React第五十七节 Router中RouterProvider使用详解及注意事项
前言 在 React Router v6.4 中,RouterProvider 是一个核心组件,用于提供基于数据路由(data routers)的新型路由方案。 它替代了传统的 <BrowserRouter>,支持更强大的数据加载和操作功能(如 loader 和…...
以下是对华为 HarmonyOS NETX 5属性动画(ArkTS)文档的结构化整理,通过层级标题、表格和代码块提升可读性:
一、属性动画概述NETX 作用:实现组件通用属性的渐变过渡效果,提升用户体验。支持属性:width、height、backgroundColor、opacity、scale、rotate、translate等。注意事项: 布局类属性(如宽高)变化时&#…...
练习(含atoi的模拟实现,自定义类型等练习)
一、结构体大小的计算及位段 (结构体大小计算及位段 详解请看:自定义类型:结构体进阶-CSDN博客) 1.在32位系统环境,编译选项为4字节对齐,那么sizeof(A)和sizeof(B)是多少? #pragma pack(4)st…...
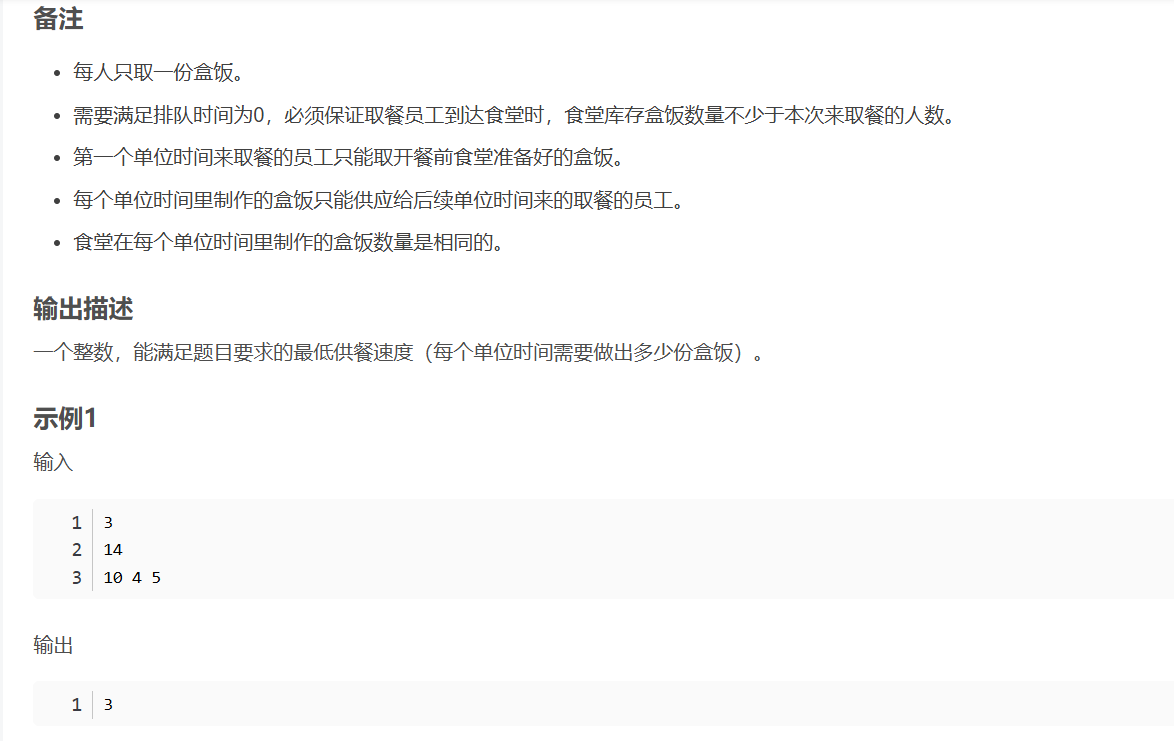
华为OD机试-食堂供餐-二分法
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner;public class DemoTest3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in new Scanner(System.in);// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 caseint a in.nextIn…...
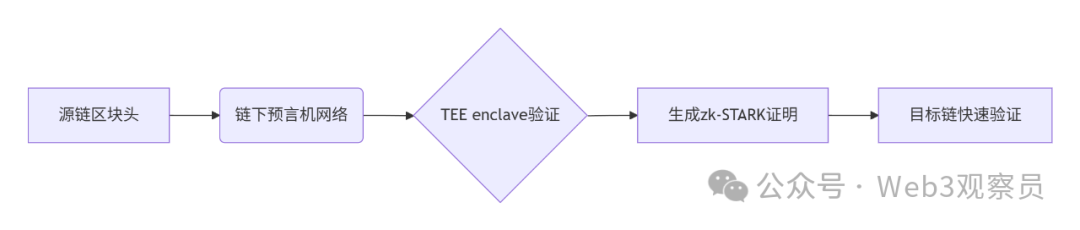
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案 ——构建下一代区块链互联网的技术基石 一、跨链架构的核心范式演进 1. 分层协议栈:模块化解耦设计 现代跨链系统采用分层协议栈实现灵活扩展(H2Cross架构): 适配层…...

聊一聊接口测试的意义有哪些?
目录 一、隔离性 & 早期测试 二、保障系统集成质量 三、验证业务逻辑的核心层 四、提升测试效率与覆盖度 五、系统稳定性的守护者 六、驱动团队协作与契约管理 七、性能与扩展性的前置评估 八、持续交付的核心支撑 接口测试的意义可以从四个维度展开,首…...

Java面试专项一-准备篇
一、企业简历筛选规则 一般企业的简历筛选流程:首先由HR先筛选一部分简历后,在将简历给到对应的项目负责人后再进行下一步的操作。 HR如何筛选简历 例如:Boss直聘(招聘方平台) 直接按照条件进行筛选 例如:…...

全面解析各类VPN技术:GRE、IPsec、L2TP、SSL与MPLS VPN对比
目录 引言 VPN技术概述 GRE VPN 3.1 GRE封装结构 3.2 GRE的应用场景 GRE over IPsec 4.1 GRE over IPsec封装结构 4.2 为什么使用GRE over IPsec? IPsec VPN 5.1 IPsec传输模式(Transport Mode) 5.2 IPsec隧道模式(Tunne…...
中关于正整数输入的校验规则)
Element Plus 表单(el-form)中关于正整数输入的校验规则
目录 1 单个正整数输入1.1 模板1.2 校验规则 2 两个正整数输入(联动)2.1 模板2.2 校验规则2.3 CSS 1 单个正整数输入 1.1 模板 <el-formref"formRef":model"formData":rules"formRules"label-width"150px"…...
